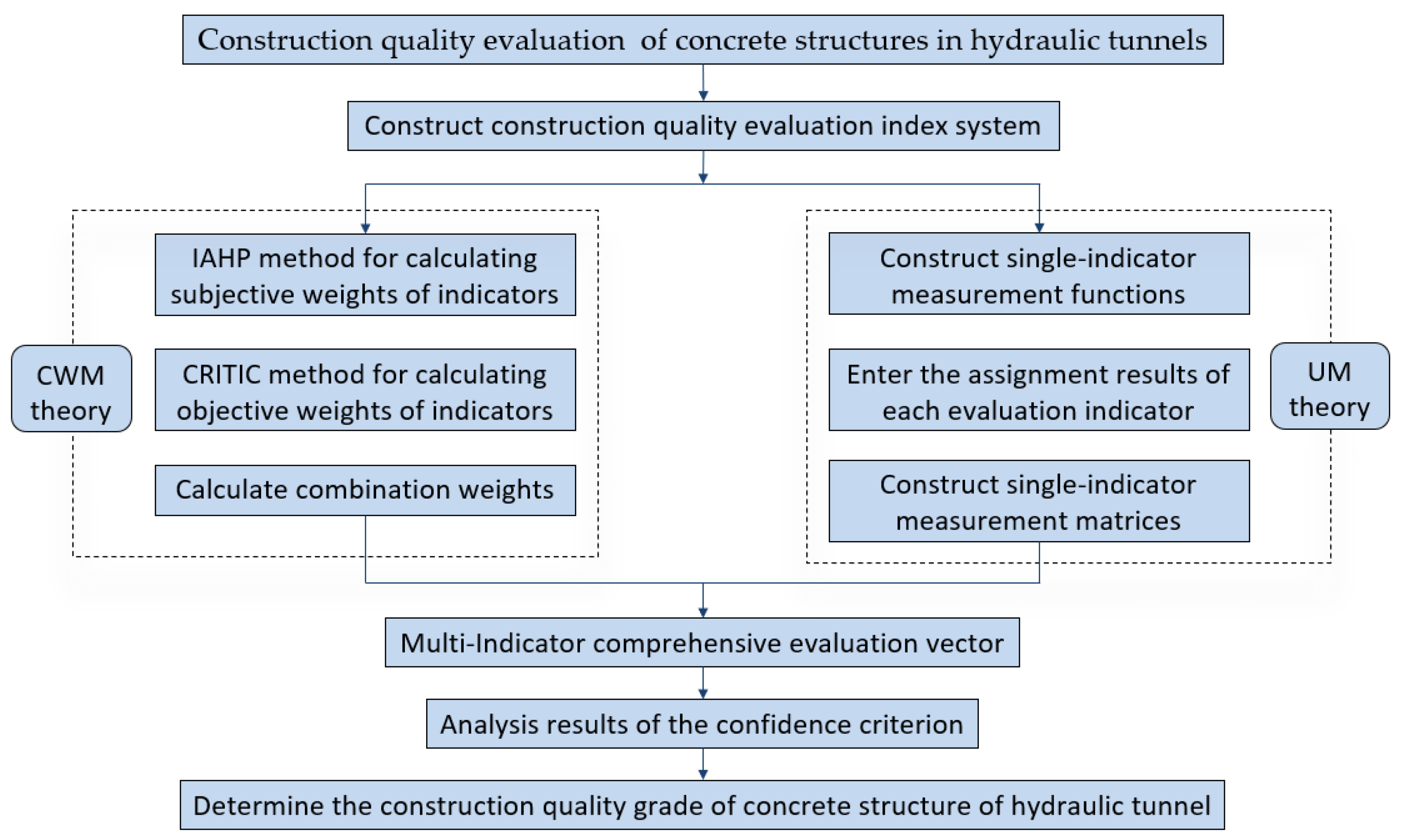
In order to verify the rationality and scientificity of the method, a hydraulic tunnel is applied in this paper. According to the characteristics and general construction procedures of concrete structure in hydraulic tunnel, it can be divided into six main stages: construction survey, tunnel excavation, support construction, anti-drainage construction, secondary lining concrete construction and tunnel grouting.
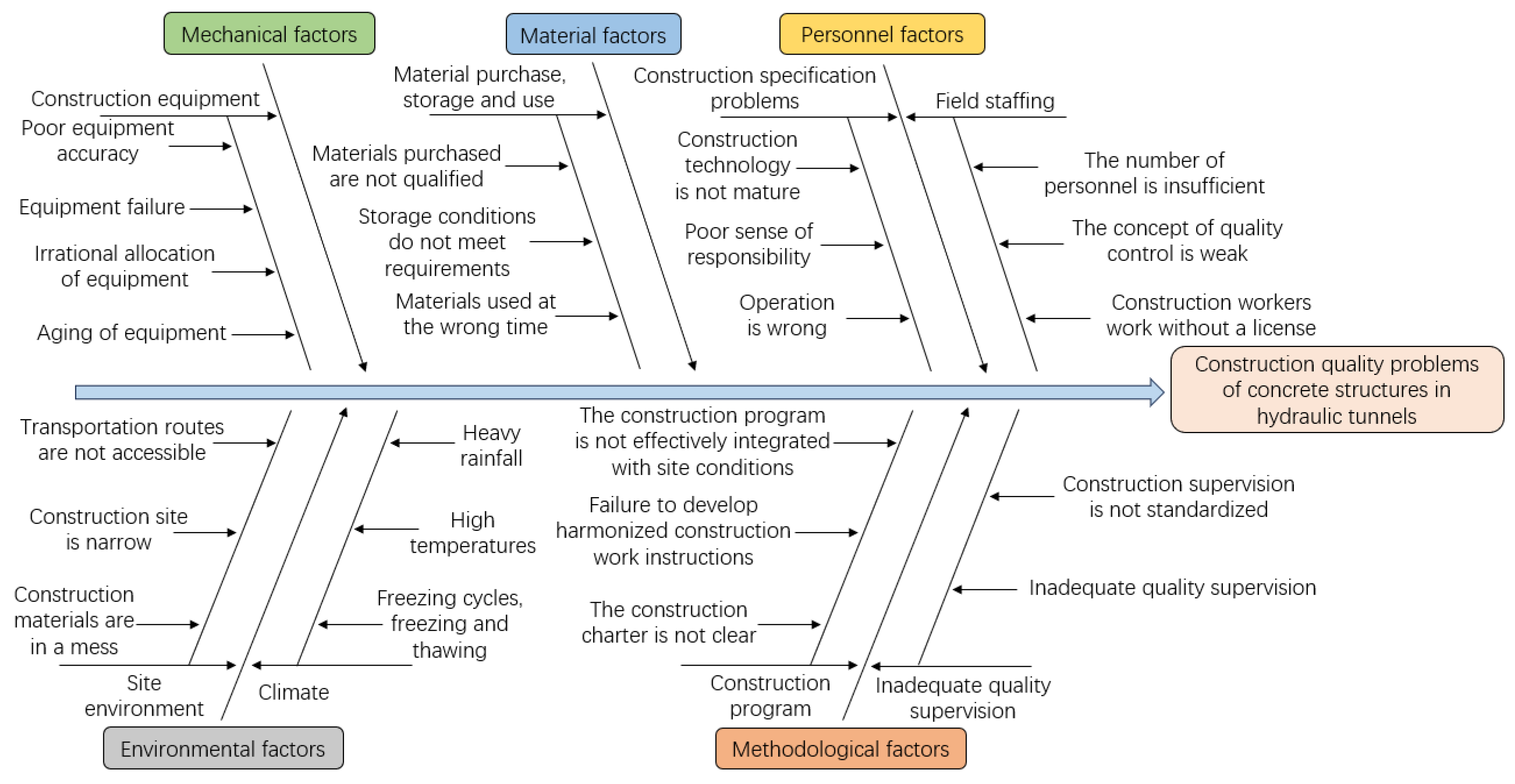
4.1. Reasons affecting construction quality
The construction process of concrete structure in hydraulic tunnels is complex, and there are more uncertainty factors affecting its construction quality, which can be basically summarized as five aspects of personnel, materials, machinery, methods and environment according to the quality management theory. Therefore, according to the actual situation of the project and the existing literature, this paper adopts the fishbone diagram method [
21] to carry out a hierarchical analysis from the aspects of people, materials, machines, methods and environment to summarize the reasons affecting the construction quality.
(1) In the process of construction measurement, due to the unskilled surveyors and the unfavorable influence of the environmental factors such as heavy rain, gale, high temperature, etc., it will cause the quality problems such as horizontal penetration error, vertical penetration error and marking the wrong direction of digging.
(2) In the process of tunnel excavation, due to the unskilled tunneling operators and the low level of construction site management and monitoring, there will be quality problems such as uneven excavation surface, groundwater seepage caused by excavation, and tunnel over-excavation and under-excavation.
(3) In the process of support construction, due to the low business level of the constructor and poor inspection and management, it caused problems such as collapsed holes, deviation of the position and direction of anchor holes, low stability of steel arches, insufficient thickness of sprayed concrete, and lagging of the sprayed concrete construction surface.
(4) In the process of anti-drainage construction, the performance and laying of waterproof materials are not qualified due to non-timely testing; improper treatment of construction joint and deformation joint due to insufficient construction technology level; the drainage system is unreasonable due to lack of scientific planning.
(5) In the process of secondary lining concrete construction, the performance of concrete materials and mixing ratios do not meet the design requirements due to the lack of timely testing; insufficient maintenance of concrete, low strength of concrete demolding, and inadequate concrete pouring and vibration due to the low level of construction management and poor construction environment, and other quality problems. In addition, the quality of secondary lining concrete construction will also be affected by factors such as non-standardized concrete pouring, failure to clean the surface of the formwork in time, insufficient reinforcement of the formwork, and incomplete assembly.
(6) In the process of tunnel grouting, due to the unskilled construction personnel, it is impossible to strictly control the key parameters such as hole diameter, hole position, verticality, etc., resulting in irrational disposal of the drilled holes; due to the lack of advance hydrogeological and engineering geological exploration, it is not possible to effectively predict the ambient temperature of the construction area, which results in the grouting temperature being too large or too small; due to the irregularities in the grouting test, resulting in too high or too low a grouting pressure being selected. low.
In summary, the fishbone diagram of the quality problems of concrete structure construction of hydraulic tunnels is shown in
Figure 2.
4.4. Construction quality evaluation process of concrete structures in hydraulic tunnels
This paper takes a concrete structure of a hydraulic tunnel as an example to carry out construction quality evaluation research. Indicator grading and grading standards are shown in
Table 4.In order to ensure the validity and accuracy of the evaluation results, this paper assigns values to the construction quality indicators by inviting five experts in different aspects, including design units, construction units, construction units, supervisory units and scientific research institutes, with the score range of [0,100], and the better the quality control of the indicators is, the larger the score is. The results of the assigned values are shown in
Table 5.
4.4.1. IAHP method to determine the subjective weight
(1) According to
Table 1, the evaluation indexes of the construction quality of hydraulic tunnels are compared two by two to quantify their relative importance, and the judgment matrix of the evaluation indexes is established as shown below:
The judgment matrix of the construction quality index layer of hydraulic tunnels is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the construction measurement indicator layer is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the tunnel excavation index layer is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the support construction indicator layer is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the anti-drainage construction indicator layer is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the secondary lining concrete construction index layer is as follows:
The judgment matrix of the tunnel grouting index layer is as follows:
(2) According to equations (2) to (7), the subjective weight value of each indicator is calculated, see
Table 6.
4.4.2. CRITIC method to determine the objective weight
According to the assignment results of quality indicators in
Table 5, it is standardized through equation (8) to obtain a standardized matrix. Then, according to equations (9) ~ (13), the variability, conflict, information content and weight values of evaluation indicators can be calculated by writing MATLAB code in turn, as shown in
Table 7.
4.4.3. Calculate combination weights
(1) Rationality analysis of combined weights
According to the subjective and objective weights calculated by the above IAHP method and CRITIC method, the weights are sorted, as shown in
Table 8.
The consistency coefficient can be calculated from equation (14) as , the calculation shows that the weights calculated by IAHP method and CRITIC method satisfy the consistency requirements and can be combined and assigned.
(2) Calculate combination weights
Finally, the MIE principle is utilized to eliminate the subjective and objective weight bias, and by substituting the calculation results into equation (16), the final combined weight calculation results can be obtained, as shown in
Table 9.
4.4.4. Construct uncertain measure function and matrix of single index
In the process of using unascertained measure theory to evaluate construction quality, it is necessary to construct uncertain measure function and matrix of single index scientifically and reasonably.
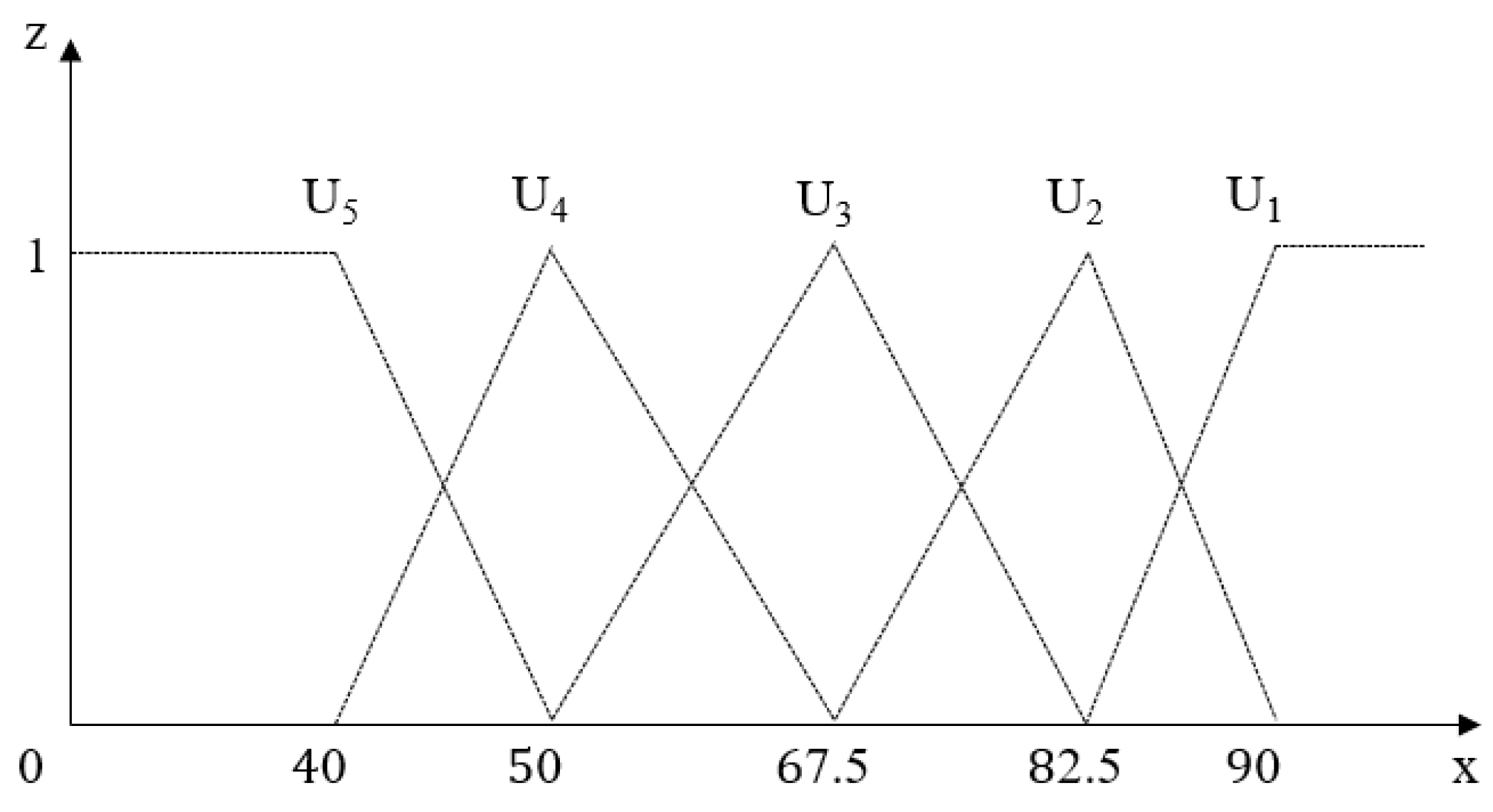
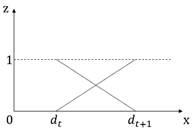
The evaluation level space must conform to a certain order, that is or , where represents the th evaluation level, and its corresponding grading standard is represented as , then conforms to or . Assuming that the measured value of the indicator at belongs to level , when the measured value changes from to , its state value at level gradually changes from 1 to 0, and its state value at level gradually changes from 0 to 1.
The change trend of the evaluation index value can be expressed by the uncertain measure function. The common forms of the uncertain measure function are mainly four types: straight line, parabola, exponential curve and sinusoidal curve type [
24], of which the more widely used is the straight line type, and its corresponding graph and function expression are shown in
Table 10.
Based on the classification standard of tunnel construction quality in
Table 4 and the graph and expression of unascertained measure function in
Table 10, the unascertained measure function and graph of index can be determined as follows:
Figure 3.
Measure function graph.
Figure 3.
Measure function graph.
Based on the evaluation results of quality evaluation indicators in
Table 5, the expected value of five experts' scores for each indicator is taken as the measurement value, as shown in
Table 11, and it is put into the unascertained measure function, and the unascertained measure matrix of single indicator can be calculated as follows:
4.4.5. Calculate multi-index unascertained measure vector
According to the combined weights of the evaluation indicators in
Table 9 and the unascertained measure matrix of the single index mentioned above, the multi-index unascertained measure vector of the construction quality of hydraulic tunnel can be calculated by equation (21):
Construction measurement:
Tunnel excavation:
Support construction:
Anti-drainage construction:
Secondary lining concrete construction:
Tunnel grouting:
Total weight value:
4.4.6. Construction quality evaluation of concrete structures in hydraulic tunnels
According to the multi-indicator unconfirmed measurement vector of hydraulic tunnel construction quality in section 4.4.5, set the confidence level
, and the quality evaluation results of each stage and the whole in the tunnel construction process can be obtained from equation (22), which is shown in
Table 12.
4.5. Comparative study
In order to illustrate the science and rationality of the method, this paper adopts the matter-element extension theory to evaluate the construction quality of hydraulic tunnels, which is used as a comparative study with the above. No further explanation about the matter-element extension theory is given, and specific reference can be made to the literature [
25,
26], and the focus here is on the calculation of the correlation function value of the matter-element grade of hydraulic tunnels to be evaluated.
(1) Correlation of evaluation indicators
The correlation of the construction quality level
t of the hydraulic tunnel to be evaluated is shown in equation (23):
Where, is the th construction quality evaluation index; is the magnitude range of the th index divided by the evaluation grade ; is the magnitude range of the th index divided under each level; is the interval length.
(2) Determine the construction quality evaluation grade of hydraulic tunnel
By combining the weights of the indicators and the value of the correlation function, the comprehensive correlation of the evaluation object can be calculated, see equation (26), if
, the evaluation object
belongs to level
.
Where, is the comprehensive correlation degree of with respect to grade ; take the objective weight value of CRITIC method.
According to the grading standards of each evaluation index in Chapter 4.3, the classical domain and node domain of the construction quality evaluation index of hydraulic tunnel can be determined, as shown in
Table 13.
Based on the expected value of each evaluation indicators in table 11, the correlation degree matrix of the evaluation indicators of hydraulic tunnel construction quality can be obtained from equations (23) to (25):
The weight value of each secondary index calculated by CRITIC method is as follows:
(0.2937, 0.2196, 0.1930,0.2937); (0.2603, 0.2405, 0.2088, 0.2904); (0.3903, 0.3303,0.2794); (0.3475,0.2852,0.3674);
(0.2383, 0.2275, 0.3172, 0.2169); (0.2850,0.3569,0.3580).
According to equation (26), the comprehensive correlation degree of the evaluation level t for the construction quality of the hydraulic tunnel can be calculated as:
Construction measurement:
Tunnel excavation:
Support construction:
Anti-drainage construction:
Secondary lining concrete construction:
Tunnel grouting:
The weight values of the primary indicators calculated by CRITIC method are: (0.1723, 0.1890, 0.1818, 0.1377, 0.2043, 0.1150). According to equation (26), the comprehensive correlation degree of the target layer for the hydraulic tunnel construction quality with respect to the evaluation level can be calculated as:
Overall Construction:
According to the principle of maximum affiliation, the construction quality evaluation grade of the hydraulic tunnel can be determined, as shown in
Table 14.
Comparative analysis of the evaluation results of section 4.4 and section 4.5 shows that the results of both are consistent. And this paper adopts IAHP method and CRITIC method to calculate the subjective and objective weights of the evaluation indexes respectively, which avoids the one-sidedness of the weight calculation, and gives comprehensive consideration to the subjective intention of the decision maker and the objective attributes of the data itself, and the evaluation results are more scientific and reasonable. In summary, the evaluation index system and evaluation model of concrete structure construction quality of hydraulic tunnels established in this paper are scientific and reasonable.