Submitted:
28 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To introduce an efficient n-shifted piecewise sigmoid channel and spatial 3D attention module to improve the network’s learning and generalization capability while reducing the inherent sigmoid vanishing gradient problem.
- To demonstrate that the proposed attention module can just be plugged into existing models and boost their performance.
- To validate that performance is greatly improved in the deep point sets Hough voting process using the SUNRGB-D dataset by inserting the proposed lightweight attention module.
2. Related Works
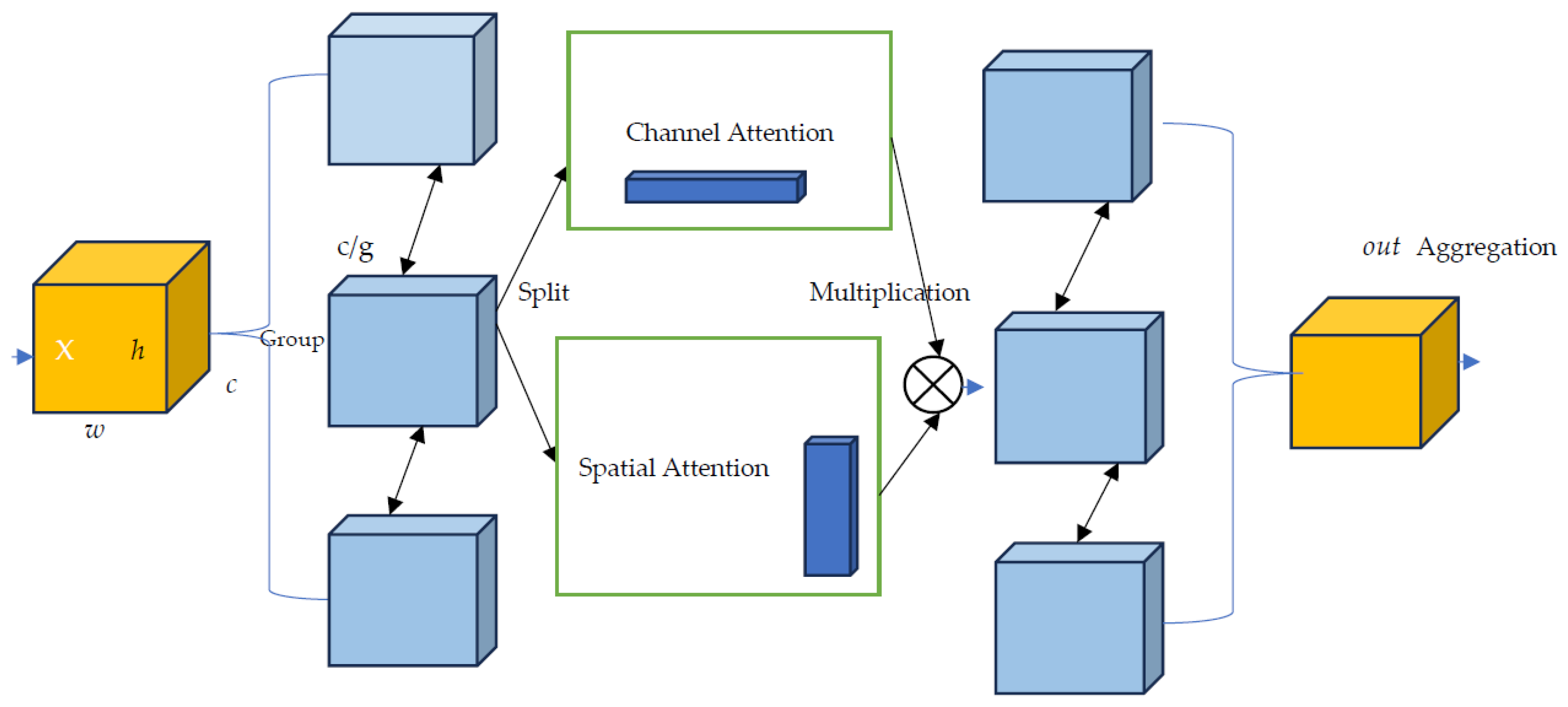
3. The Proposed n-Sigmoid Channel Spatial Attention
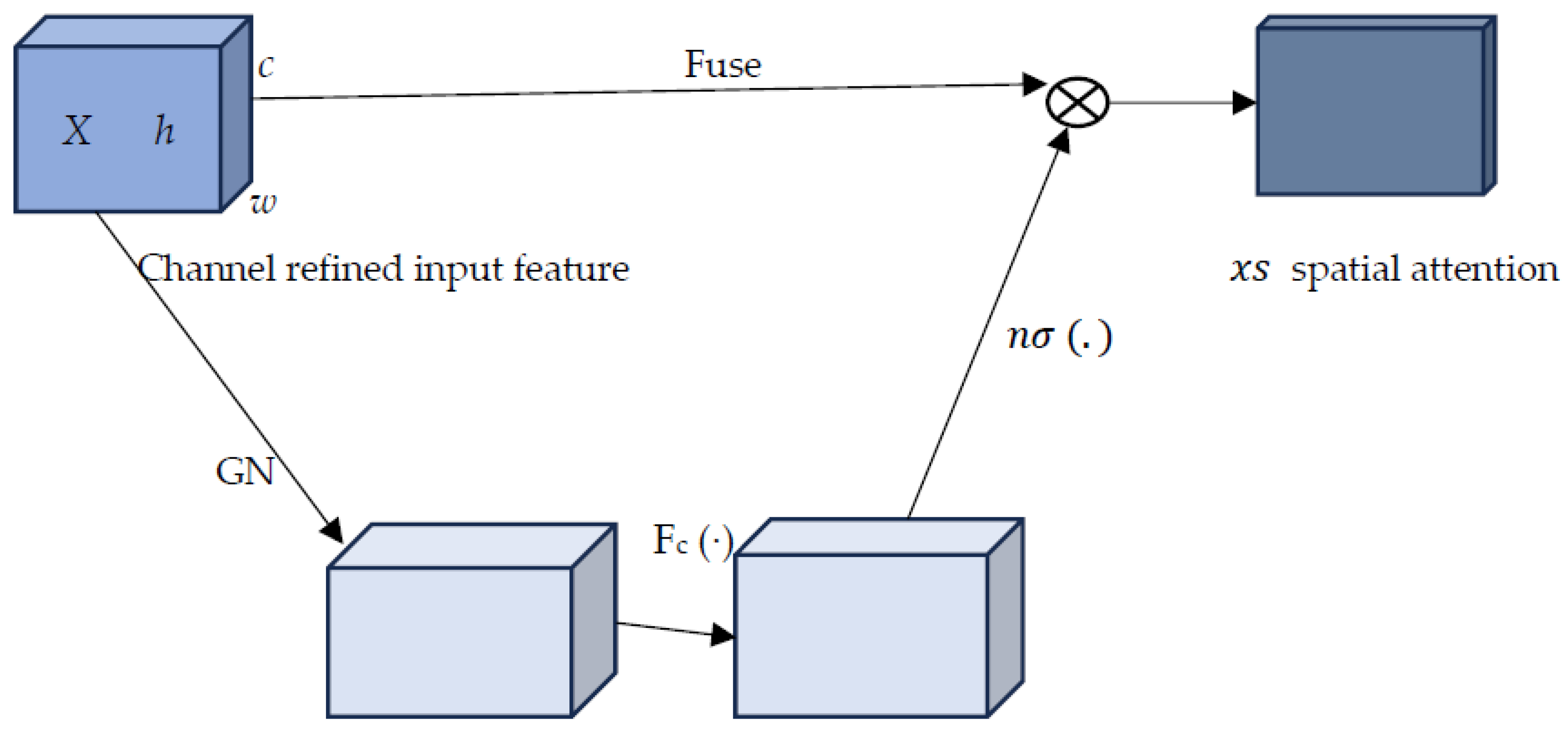
3.1. 3D n-Sigmoid Channel and Spatial Attention Mechanism
-
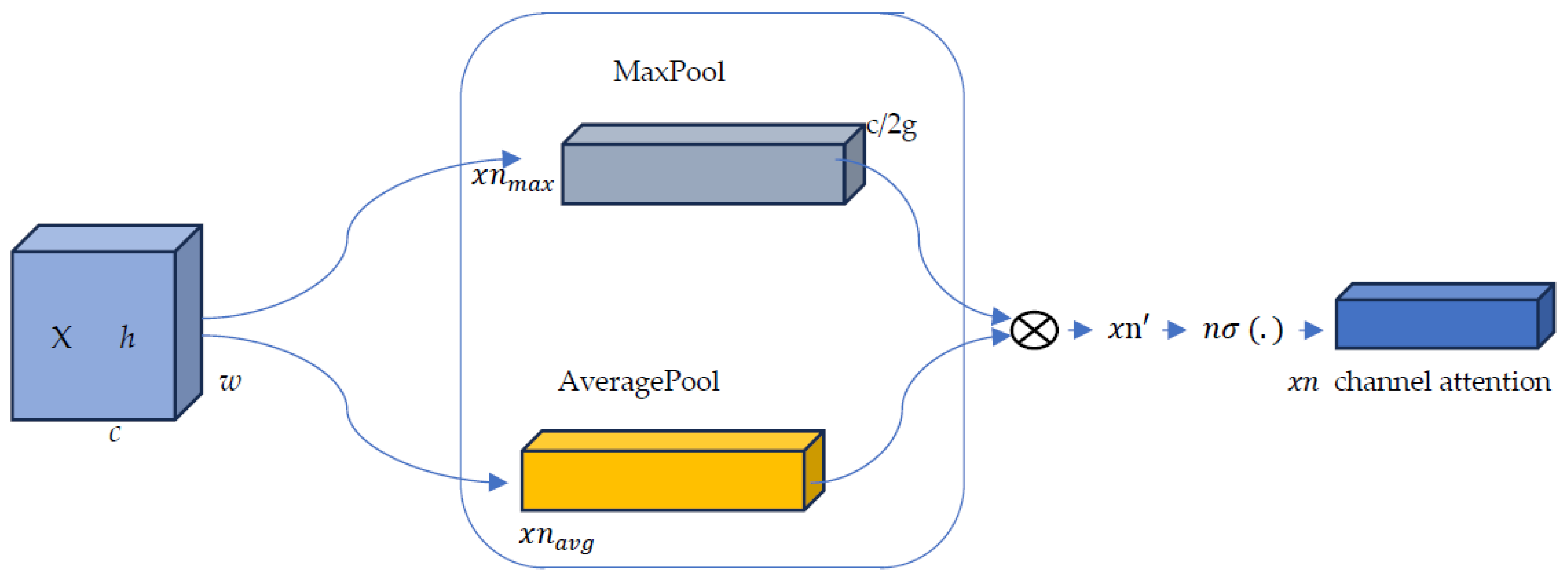
Average Pooling Branch:
- Average pooling operation
- n-shifted sigmoid activation:where is the n-shifted activation function
-
Max Pooling Branch:
- Max pooling operation:
- n-shifted sigmoid activation:where is the n-shifted activation function
- Combination of Average and Max Pooling: Several attention mechanisms normally use either average pooling or max pooling to aggregate channel-wise data. Merging both average and max pooling allows the model to capture various aspects of the feature maps, thereby enhancing the capacity to attend to relevant features.
- Multiplying Channel and Spatial: While addition is a common operation for combining attention mechanisms, multiplying channel and spatial attentions together can provide a totally different type of data regarding the scene in question. Multiplication will lay emphasis on regions where both channel and spatial attentions are important, thus focusing more on salient features.
- The use of n-shifted sigmoid activation as a gating mechanism in the attention module.
- The flexibility that permits the model to learn various types of interactions between spatial and channel attentions. Furthermore, the exploitation of trainable parameters from both max and average pooling as well as from channel and spatial attention, empowers the model to adaptively learn.
3.2. 3D n-Sigmoid CSA Module Integrated in the Point Cloud Learning Using Hough Voting
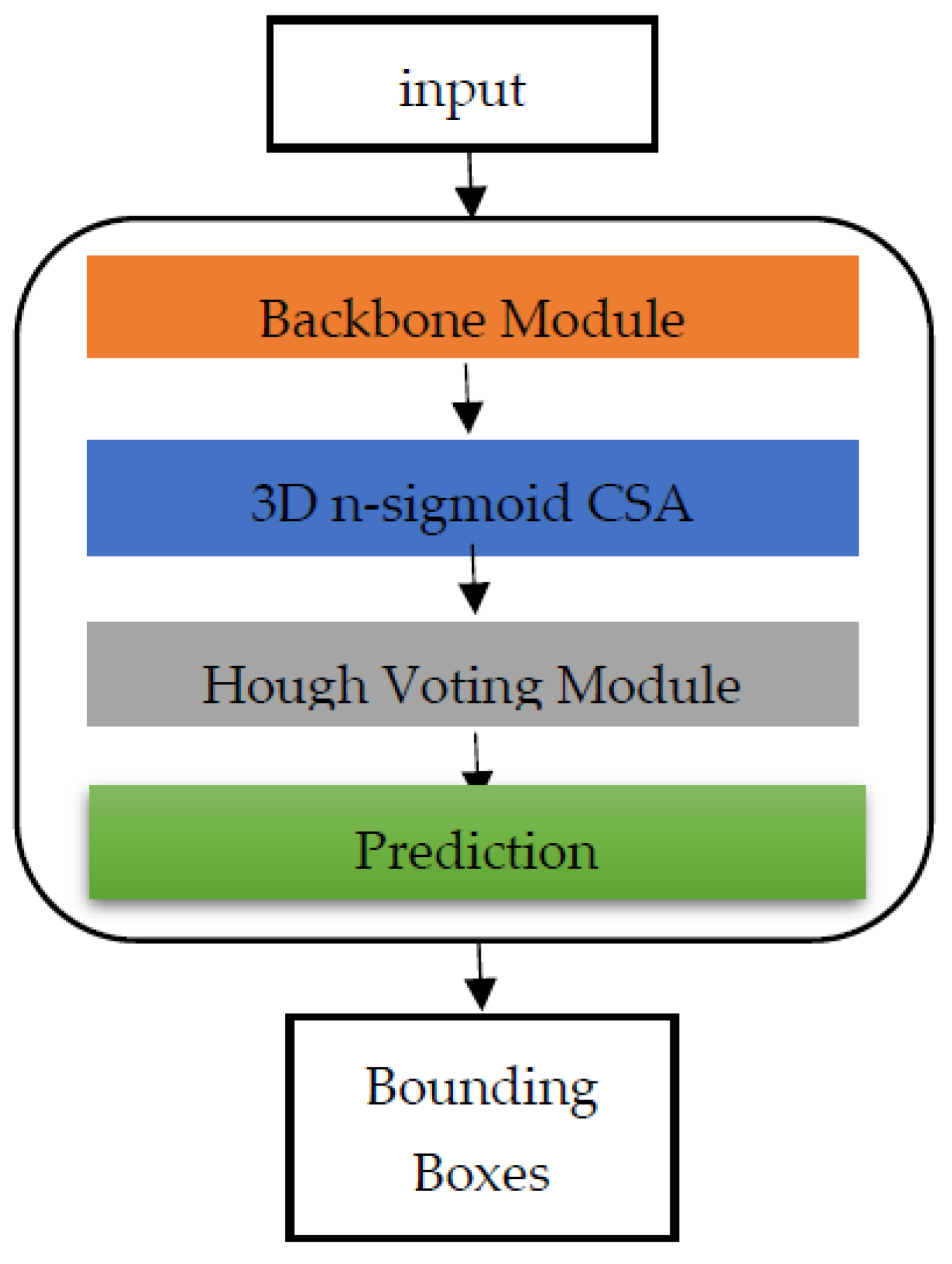
4. Implementation Details
5. Experiments
5.1. 3D n-Sigmoid CSA Module Integrated in the Point Cloud Learning Using Hough Voting
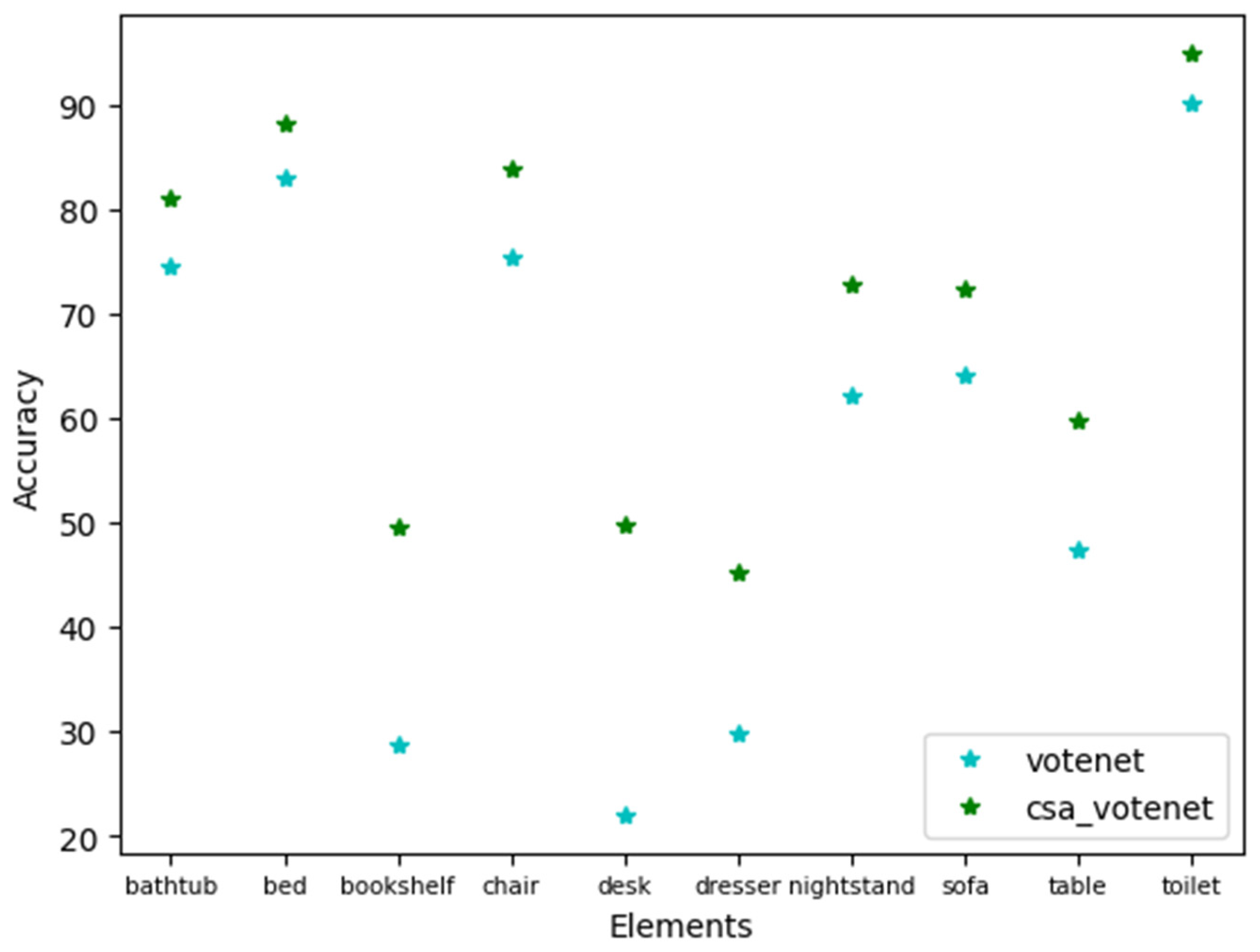
| Methods | Input | Bathtub | bed | Book shelf |
chair | desk | dresser | night- stand |
sofa | table | toilet | mAP |
| DSS [33] COG [34] 2D-driven [35] F-PointNet [36] VoteNet [12] MLCVNet [37] DeMF [38] CSA-VoteNet (ours) |
GEO + RGB GEO + RGB GEO + RGB GEO + RGB GEO only GEO only GEO + RGB GEO only |
44.2 58.3 43.5 43.5 74.4 79.2 79.5 80.9 |
78.8 63.7 64.5 81.1 83.0 83.0 87.0 88.1 |
11.9 31.8 31.4 33.3 28.8 31.9 44.1 49.6 |
61.2 62.2 48.3 64.2 75.3 75.8 80.7 83.8 |
20.5 45.2 27.9 24.7 22.0 26.5 33.8 49.7 |
6.4 15.5 25.9 32.0 29.8 31.3 46.4 45.2 |
15.4 27.4 41.9 58.1 62.2 61.5 66.3 72.8 |
53.5 51.0 50.4 61.1 64.0 66.3 72.5 72.4 |
50.3 51.3 37.0 51.1 47.3 50.4 52.8 59.8 |
78.9 70.1 80.4 90.9 90.1 89.1 92.7 94.9 |
42.1 47.6 45.1 54.0 57.5 59.8 65.6 69.72 |
5.2. 3D n-Sigmoid CSA Module Integrated in the Point
5.3. Discussion
5.4. Model Complexity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, J; Zhu, R.; Chen, B.; Xu, H. and Zhu, X. Channel and Spatial Attention Fusion Module for Detection. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Fu, J. Liu, H. Tian, Y. Li, Y. Bao, Z. Fang and H. Lu. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. 2019. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 3146 –3154.
- Wang, J., Mo, W., Wu, Y., Xu, X., Li, Y., Ye, J. and Lai, X. 2022. Combined Channel Attention and Spatial Attention Module Network for Chinese Herbal Slices Automated Recognition; Publisher: Sec. Brain Imaging Methods, volume 16. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M; Fang, W; Ma, X; Xu, W; Xiong, N. and Ding, Y. 2021. Channel Pruning Guided by Spatial and Channel Attention for DNNs in Intelligent Edge Computing. arXiv:2011.03891v2.
- Zhu, Z; Xu, M; Bai, S; Huang, T. and Bai, X. 2019. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. CoRR. Vol. abs/1908.07678.
- Zhu, Y; Liang, Y; Tang, K; and Ouchi, K. 2022. SC-NET: Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanism for Enhancement in Face Recognition. 5th International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), New York, NY, USA, pp. 166-172. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q; Wu, B; Zhu, P; Li, P; Zuo, W. and Hu, Q. 2020. Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 11531–11539, IEEE.
- Li, X; Hu, X; and Yang, J. 2019. Spatial group wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks. CoRR. Vol.abs/1905.09646.
- Ma, N; Zhang, X; Zheng, H; and Sun, J. 2018. Shufflenet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In Computer Vision- ECCV 2018- 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, September 8-14, 2018, Proceedings, Part XIV, 2018, pp. 122–138.
- Zhang, X; Zhou, X; Lin, M; and Sun, J. 2018. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18-22, 2018. 2018, pp. 6848–6856, IEEE Computer Society.
- Zhang, Q; Yang, Y. 2021. SA-Net: Shuffle Attention For Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv:2102.00240v1.
- Qi, C. R.; Litany, O.; He K. and Guibas. L. 2019. Deep Hough Voting for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds. In IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), pp. 9276-9285. [CrossRef]
- A. Fernández, J. Umpiérrez, and J. R. Alonso. 2023. Generalized Hough transform for 3D object recognition and visualization in integral imaging. In J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 40, C37-C45. [CrossRef]
- Qi, C. R.; Yi, L.; Su, H. and Guibas. L. J. 2017. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on pointsets in a metric space. arXiv:1706.02413.
- Song, S; Lichtenberg, S.P.; and Xiao, J. 2015. Sunrgb-d: A rgb-d scene understanding benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 567–576.
- Chappa, R. T. N. V. S.; and El-Sharkawy, M. 2020. Squeeze-and-Excitation SqueezeNext: An Efficient DNN for Hardware Deployment. In 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), 0691–0697. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xie, C.; Fei, Y.; Tao, H. 2021. Attention Mechanisms in CNN-Based Single Image Super-Resolution: A Brief Review and a New Perspective. Electronics, 10, 1187. [CrossRef]
- Woo, S; Park, J; Lee, J; and Kweon, I.S. 2018. CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2018 -15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, Proceedings, Part VII, pp. 3–19.
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N; Parmar, N; Uszkoreit, J; Jones, L.; Gomez, V; Kaiser, L; Polosukhin, L. 2023. Attention Is All You Need. [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X.; Wang, J. 2023. Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning. Appl. Sci., 13, 7916. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Feng, F.; Tingting, H. 2022. FNNS: An Effective Feedforward Neural Network Scheme with Random Weights for Processing Large-Scale Datasets. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12478. [CrossRef]
- Mulindwa, D.B., Du, S. 2023. “An n-Sigmoid Activation Function to Improve the Squeeze-and-Excitation for 2D and 3D Deep Networks. In Electronics, 12, 911. [CrossRef]
- Rane, C; Tyagi, K; and Manry, M. 2023. Optimizing Performance of feedforward and convolutional neural networks through dynamic activation functions. arXiv:2308.05724v1.
- Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Jin, W.; Meng, X. 2023. “Deep-Learning-Based Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation: A Survey”. Electronics, , 3642. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; Wu, C. and Xu, C. 2022. “A lightweight multi-dimension dynamic convolutional network for real-time semantic segmentation”, Front Neurorobot. 16:1075520. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; and He, K. 2018. Group normalization. In ComputerVision-ECCV2018-15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, Proceedings, Part XIII, pp. 3–19.
- Liu, D.; Han, G.; Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. 2022. A Discriminative Spectral-Spatial-Semantic Feature Network Based on Shuffle and Frequency Attention Mechanisms for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens., 14, 2678. [CrossRef]
- 28. Guo, M; Xu, T.; Liu, J. et al. 2022. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey”. Computational Visual Media. [CrossRef]
- Tliba, M.; Chetouani, A.; Valenzise, G. and F. Dufaux. 2023. Quality Evaluation of Point Clouds: A Novel No-Reference Approach Using Transformer-Based Architecture. arXiv:2303.08634v1.
- Kong, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Jin, X.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, X. 2022. A Spatial Feature-Enhanced Attention Neural Network with High-Order Pooling Representation for Application in Pest and Disease Recognition. Agriculture, 12, 500. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Anwar, S.; and Barnes, N. 2021. Geometric back projection network for point cloud classification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia.
- Zhao, H. ; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P. and Koltun, V. 2020. Point transformer. arXiv:2012.09164.
- Songand, S. and Xiao, J. 2016. Deep sliding shapes for amodal 3dobject detection in rgb-d images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 808-816.
- Ren, Z.; and Sudderth, E. B. 2016. Three-dimensional object detection and layout prediction using clouds of oriented gradients. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1525–1533.
- Lahoud, J.; and Ghanem, B. 2017. 2d-driven 3d object detection in rgb-d images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 4622–4630.
- Qi, C. R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H. and Guibas. L. J. 2018. Frustum pointnets for 3d object detection from rgbd data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 918–927.
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wei, M.; Long, K. and Wang, J. 2022. Multi-feature Fusion VoteNet for 3D Object Detection. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 18, 1, Article 6, 17 pages. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. 2022. Boosting 3D Object Detection via Object-Focused Image Fusion. arXiv:2207.10589.
- Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; and Tu, Z. 2018. Attentional shape contextnet for point cloud recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 4606–4615.
- Feng, M.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Gilani, S. Z.; and Mian, A.. 2020. Point attention network for semantic segmentation of 3d point clouds. Pattern Recognition, 107:107446. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Cai, J.; Liu, Z.; Mu, T.; Martin, R. R.; and Hu, S. 2021. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Computational Visual Media, 7: pages 187–199. [CrossRef]
- Qi, C. R.; Chen, X.; Litany, O; Guibas. L. J. 2020. ImVoteNet: Boosting 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds with Image Votes. arXiv:2001.10692.
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, B.; Yang, H.; and Huang, Q. 2020. H3dnet: 3dobject detection using hybrid geometric primitives. In IEEE/CVF European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 311-329.
- Li, J.; and Feng, J. 2020. Local grid rendering networks for 3D object detection in point clouds. arXiv:2007.02099.
- Chen, J.; Lei, B.; Song, Q.; Ying, H.; Chen, D. Z.; and Wu, J. 2020. A hierarchical graph network for 3D object detection on point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 392-401.
- Dai, A.; Chang, A. X.; Savva, M.; Halber, M.; Funkhouser, T.; and Nießner, M. 2017. ScanNet: Richly annotated 3D reconstructions of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5828–5839.
- Du, H.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; and Vasconcelos, N. 2020. SPOT: Selective point cloud voting for better proposal in point cloud object detection. In ECCV: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, Proceedings, Part XI, Pages 230–247. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Lai, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, D.; Wei, M.; and Wang, J. 2021. VENet: Voting Enhancement Network for 3D Object Detection. ICCV 2021.
- Wang, H.; Ding, L.; Dong, S.; Shi, S.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. 2022. CAGroup3D: Class-Aware Grouping for 3D Object Detection on Point Clouds. arXiv:2210.04264.
- Rukhovich, D.; Vorontsova, A.; Konushin. A. 2022. TR3D: Towards Real-Time Indoor 3D Object Detection. Conference: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Qi, Z.; Shi, W.; and Ma, K. 2023. Point-GCC: Universal Self-supervised 3D Scene Pre-training via Geometry-Color Contrast. arXiv:2305.19623v2.
- Hou, J.; Dai, A.; Nießner, M. 2019. 3D-SIS: 3D Semantic Instance Segmentation of RGB-D Scans. arXiv:1812.07003.
| n-sigmoid Channel and Spatial Attention VoteNet | Other related Networks |
| Enhanced feature refinement Improved attention focus More robust predictions Higher detection accuracy |
Standard feature extraction Traditional attention Moderate detection accuracy Decent object localization and limited refinement |
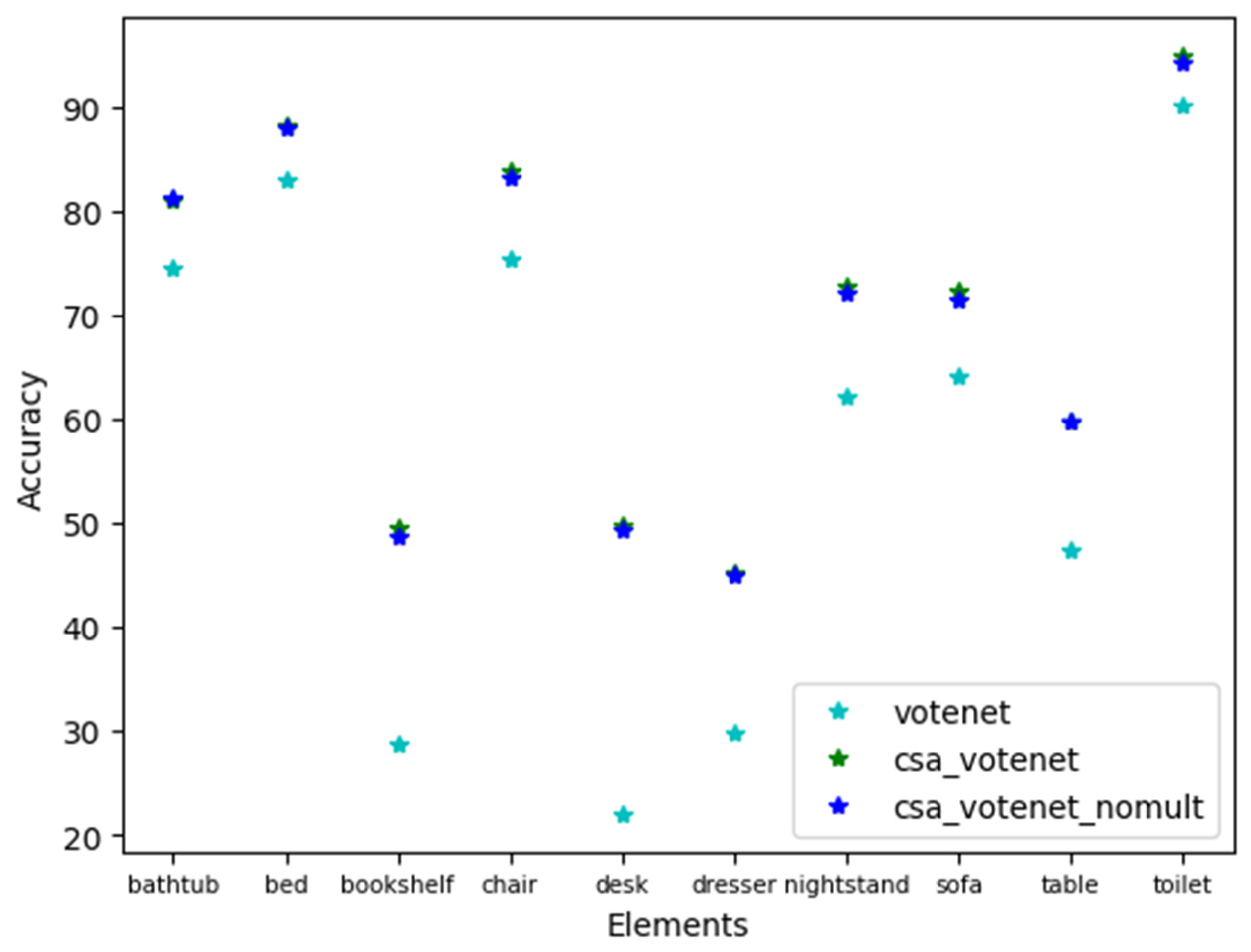
| A: The results of Average Precision on SUNRGBD [15] dataset of SA_VoteNet compared to other attention mechanisms. (IoU threshold = 0.25) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Methods | bed | table | sofa | chair | toilet | desk | dresser | night-stand | book-shelf | bath-tub | mAP | ||||||||||
| VoteNet [12] A-SCN [39] Point-attention [40] CAA [31] Point-transformer [32] Offset-attention [41] CSA-VoteNet (ours) |
83.3 81.8 84.4 83.7 83.9 82.8 88.1 |
49.8 48.9 49.0 50.2 50.4 49.8 59.8 |
64.1 63.8 61.9 63.4 63.7 60.5 72.4 |
74.1 74.0 73.8 74.9 75.2 73.0 83.8 |
89.3 88.3 87.4 89.7 86.6 86.5 94.9 |
23.8 24.5 25.7 25.7 26.3 23.6 49.7 |
26.4 26.7 24.6 30.6 28.1 27.1 45.2 |
60.7 57.5 56.0 64.7 62.5 56.5 72.8 |
30.9 24.9 28.2 27.5 35.8 25.6 49.6 |
72.8 65.4 73.1 77.6 72.2 71.2 80.9 |
57.7 55.6 56.4 58.8 58.5 55.7 69.72 |
||||||||||
| B: The results of Recall on SUN RGB-D [15] dataset of SA-VoteNet compared to other attention mechanisms. (IoU threshold = 0.25) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Methods | bed | table | sofa | chair | toilet | desk | dresser | night-stand | book-shelf | bath-tub | AR | ||||||||||
| VoteNet [12] A-SCN [39] Point-attention [40] CAA [31] Point-transformer [32] Offset-attention [41] CSA-VoteNet (ours) |
95.2 94.1 94.8 94.1 93.4 94.1 95.5 |
85.5 83.3 83.6 84.7 84.5 83.5 82.9 |
89.5 88.4 88.9 89.7 89.4 87.8 91.6 |
86.7 87.3 86.3 86.8 86.1 86.1 87.3 |
97.4 96.7 95.4 97.4 94.7 97.4 97.6 |
78.8 78.8 78.7 79.3 77.4 78.9 77.6 |
81.0 77.3 78.2 80.6 80.6 78.2 83.2 |
87.8 85.4 88.2 89.8 89.4 88.2 88.4 |
68.6 67.6 62.5 65.9 71.9 64.9 73.2 |
90.4 80.8 86.5 90.4 90.4 86.5 91.0 |
86.1 84.0 84.3 85.9 85.8 84.6 86.8 |
||||||||||
| Methods | mAP @ 0.25 | mAP @ 0.5 |
|
Methods without attention H3DNet [43] LGR-Net [44] HGNet [45] SPOT [46] Feng [47] MLCVNey [37] VENet [46] DeMF [38] CAGroup3D [49] TR3D+FF [50] Point-GCC+TR3D+FF [52] Methods with attention VoteNet [12] ImVoteNet 40] CSA-VoteNet (Ours) |
60.0 62.2 61.6 60.4 59.2 59.2 62.5 65.6 66.8 69.4 69.7 57.7 - 69.72 |
39.0 - - 36.3 - - 39.2 45.4 50.2 53.4 54.0 41.3 43.4 54.17 |
| Methods | mAP @ 0.25 | mAP @ 0.5 |
| VoteNet without attention n-sigmoid CSA VoteNet with both avg and max pooling n-sigmoid CSA VoteNet with max pooling only n-sigmoid CSA VoteNet with avg pooling only |
57.7 69.72 69.11 68.84 |
41.3 54.17 53.67 53.22 |
| Methods | mAP @ 0.25 | mAP @ 0.5 |
| VoteNet without attention n-shifted sigmoid CSA VoteNet traditional sigmoid CSA VoteNet p-sigmoid CSA VoteNet |
57.7 69.72 69.21 69.32 |
41.3 54.17 53.96 53.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





