Submitted:
28 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
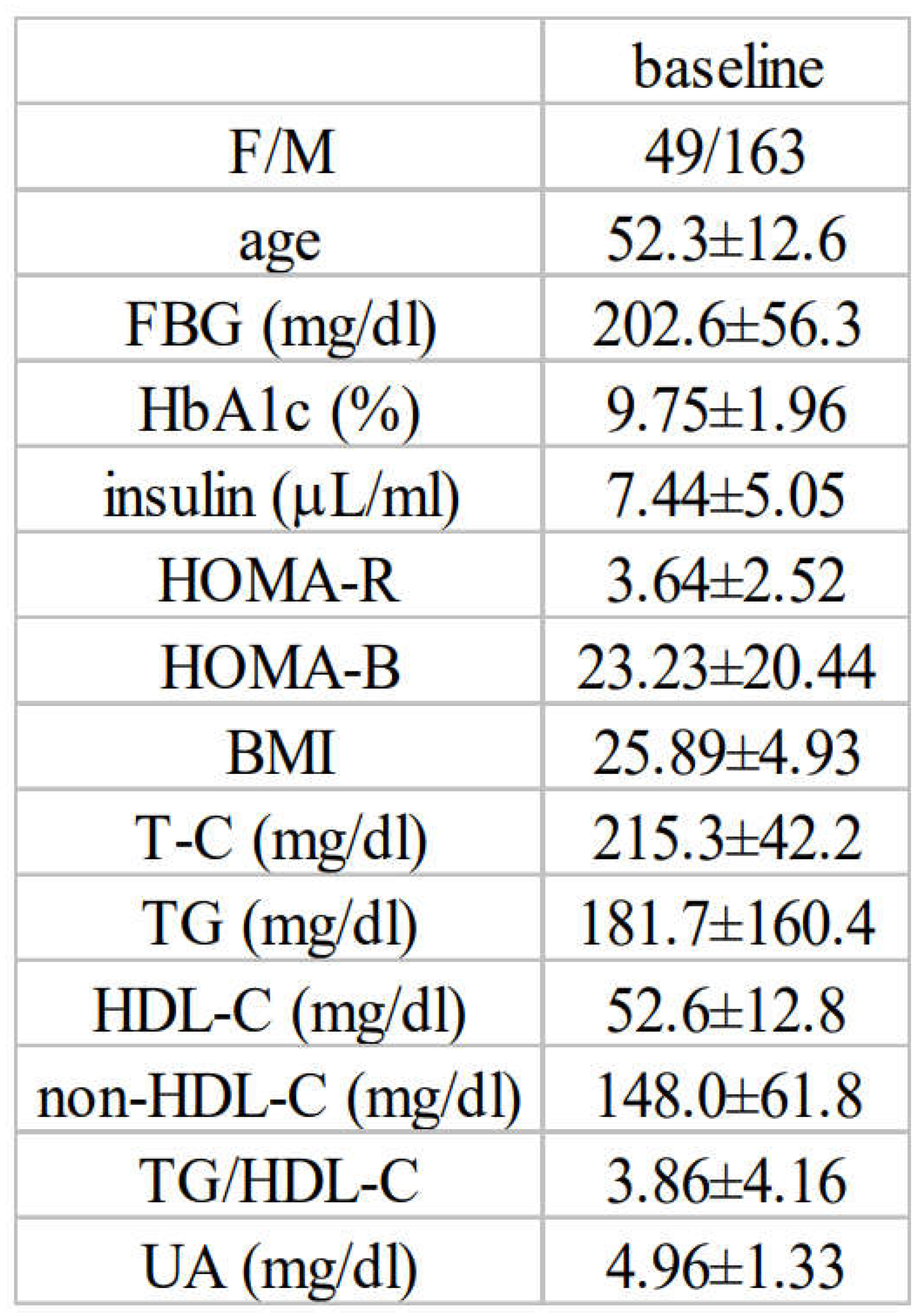
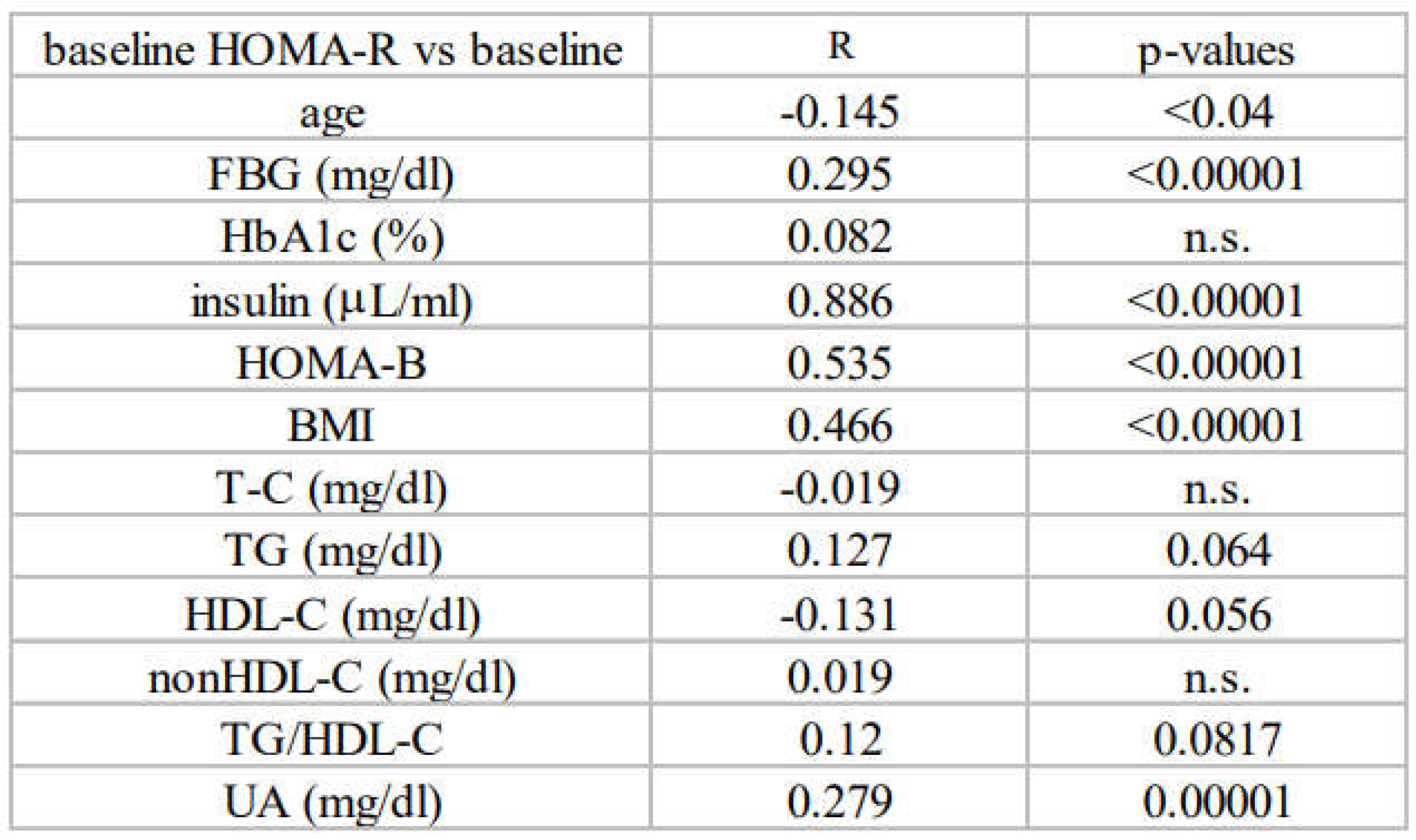
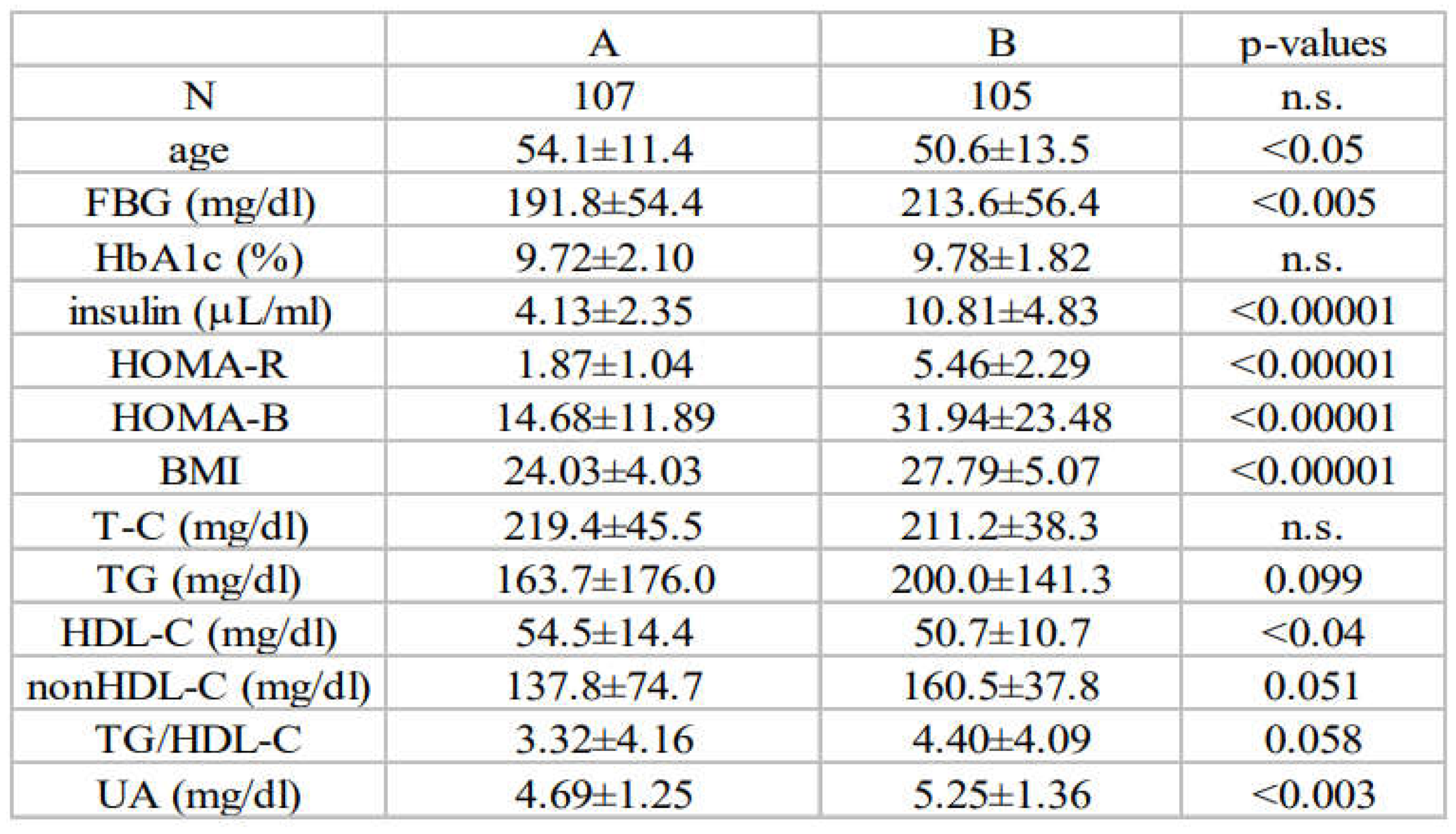
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Associations between Insulin Resistance and Diabetic Parameters in Newly Diagnosed, Treatment-Naïve Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes at Baseline (All Subjects)
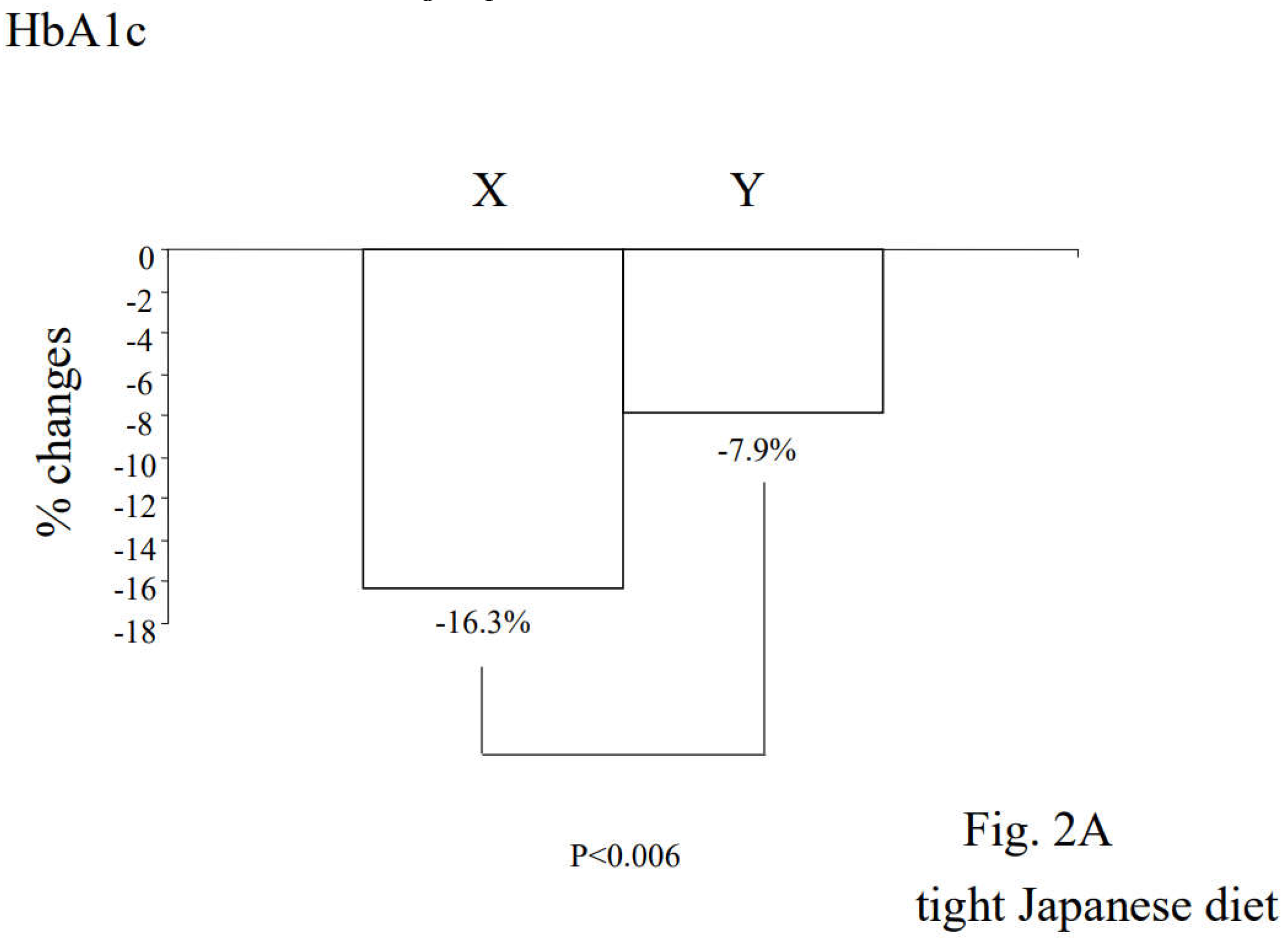
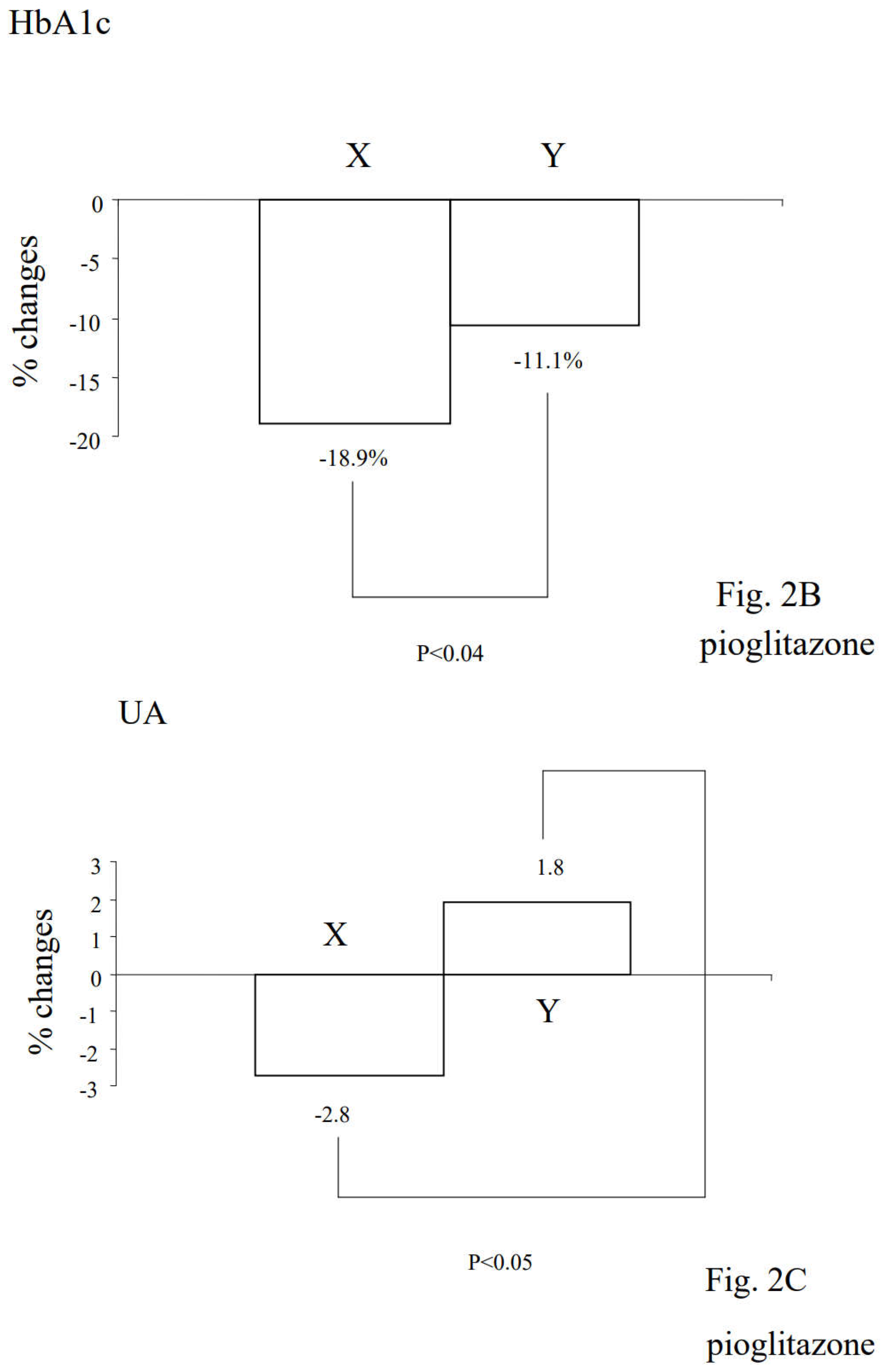
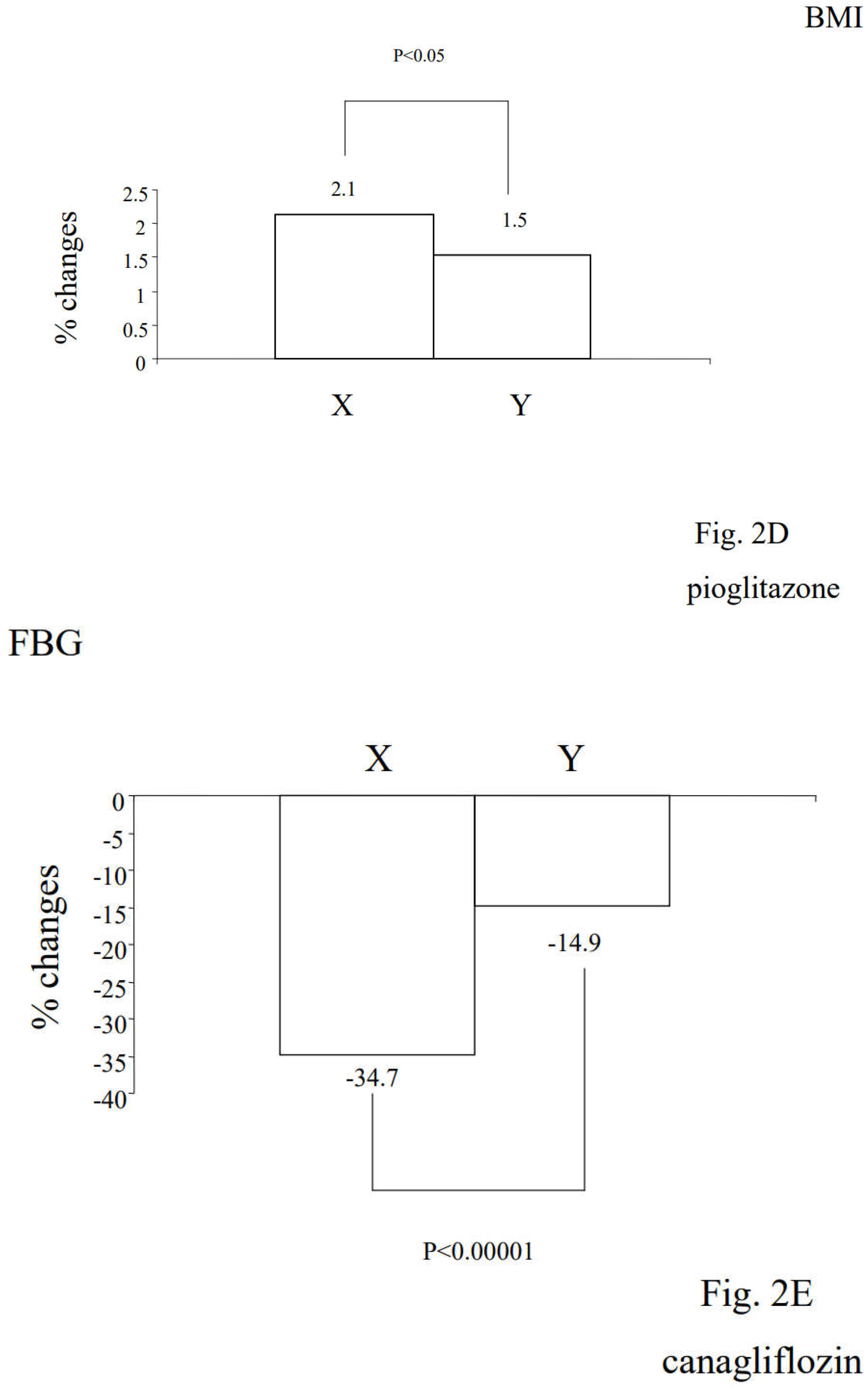
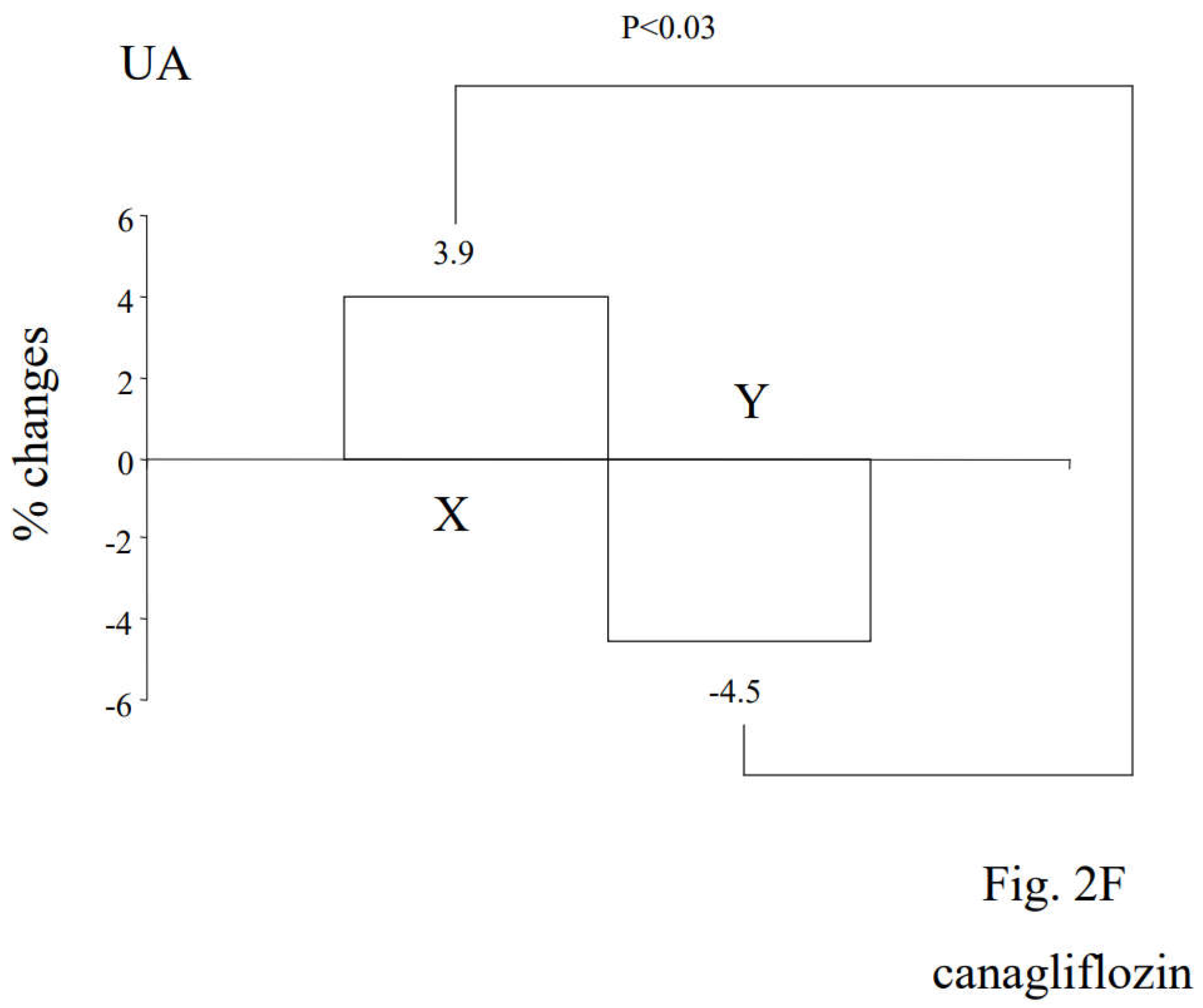
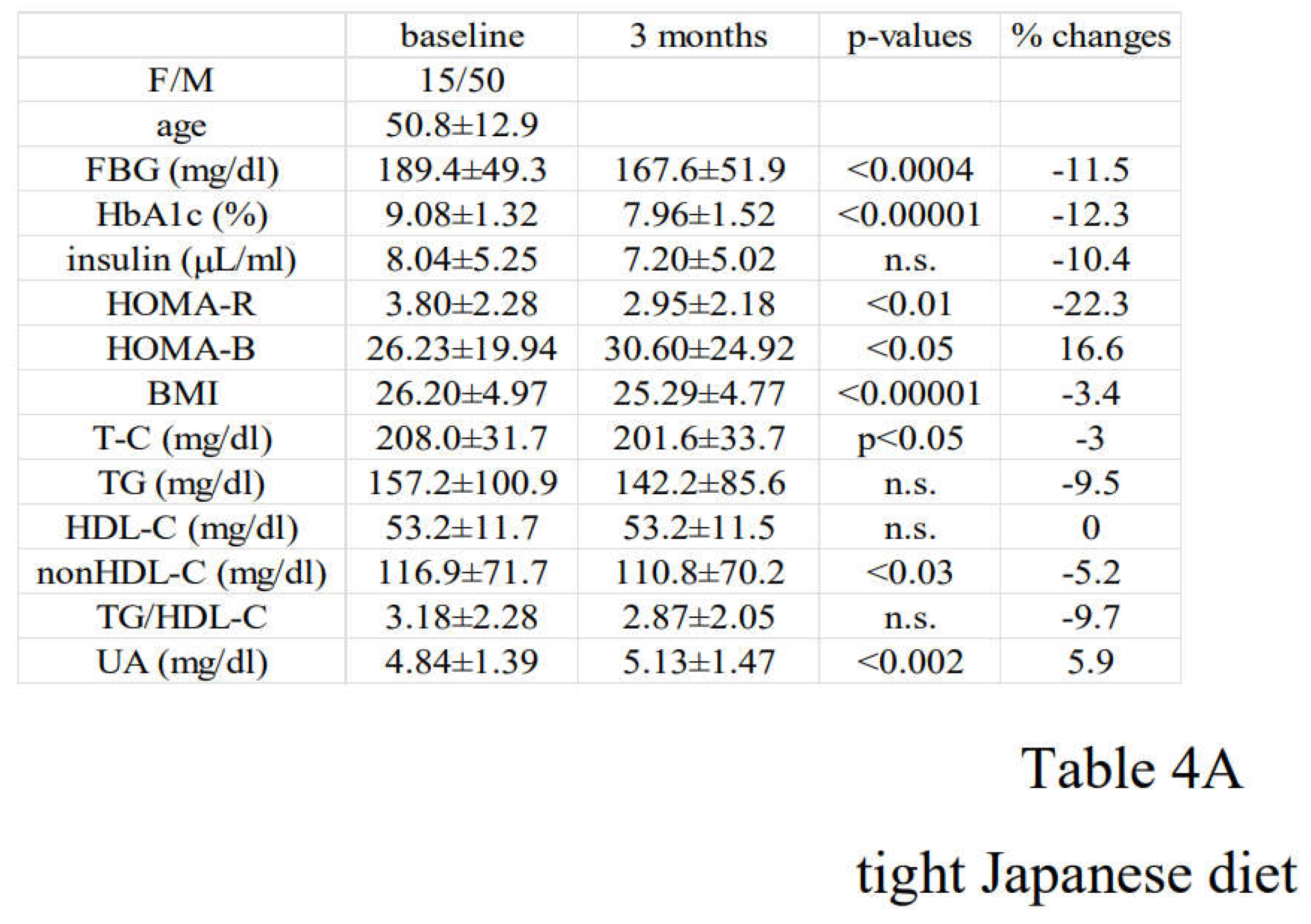
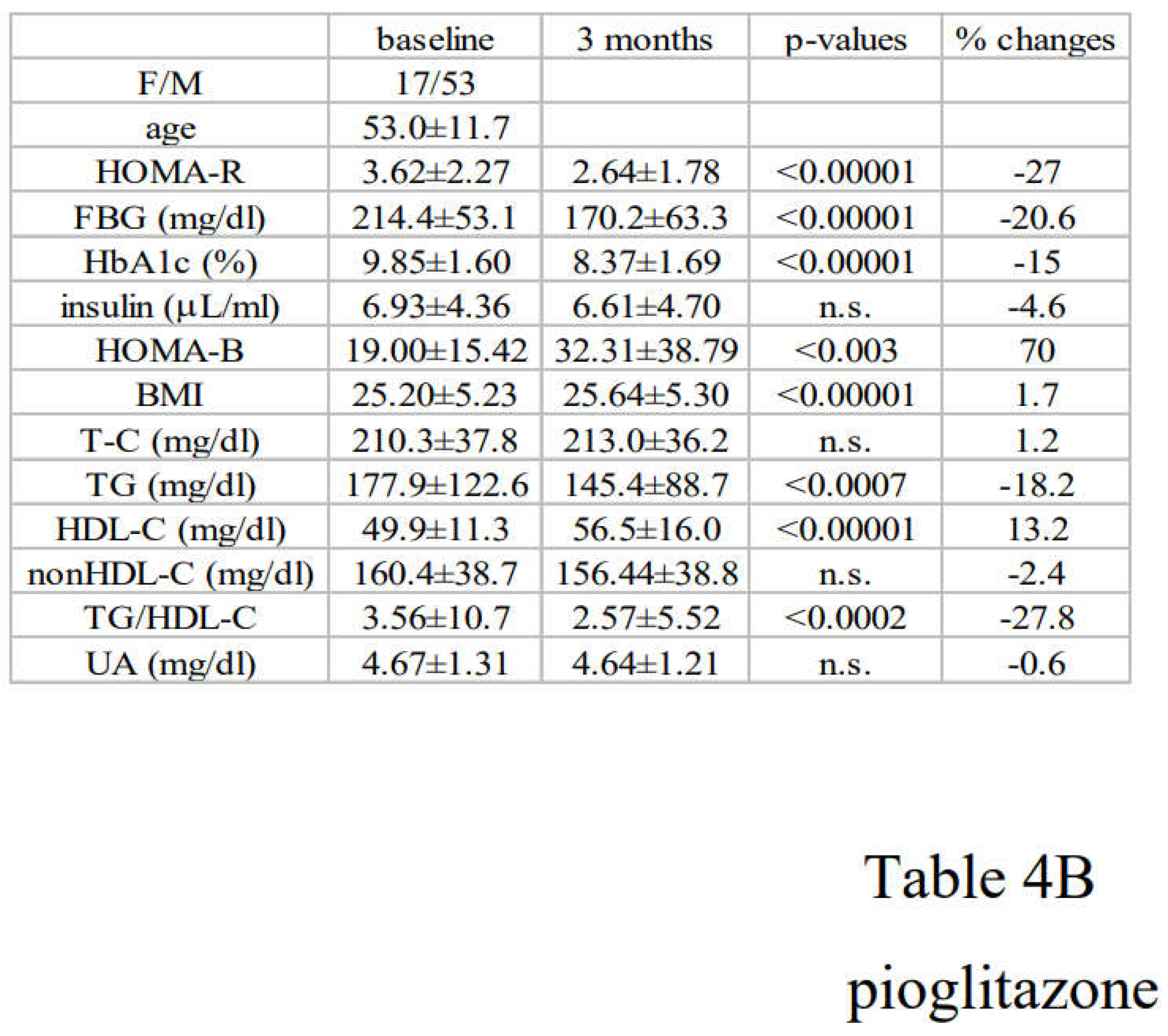
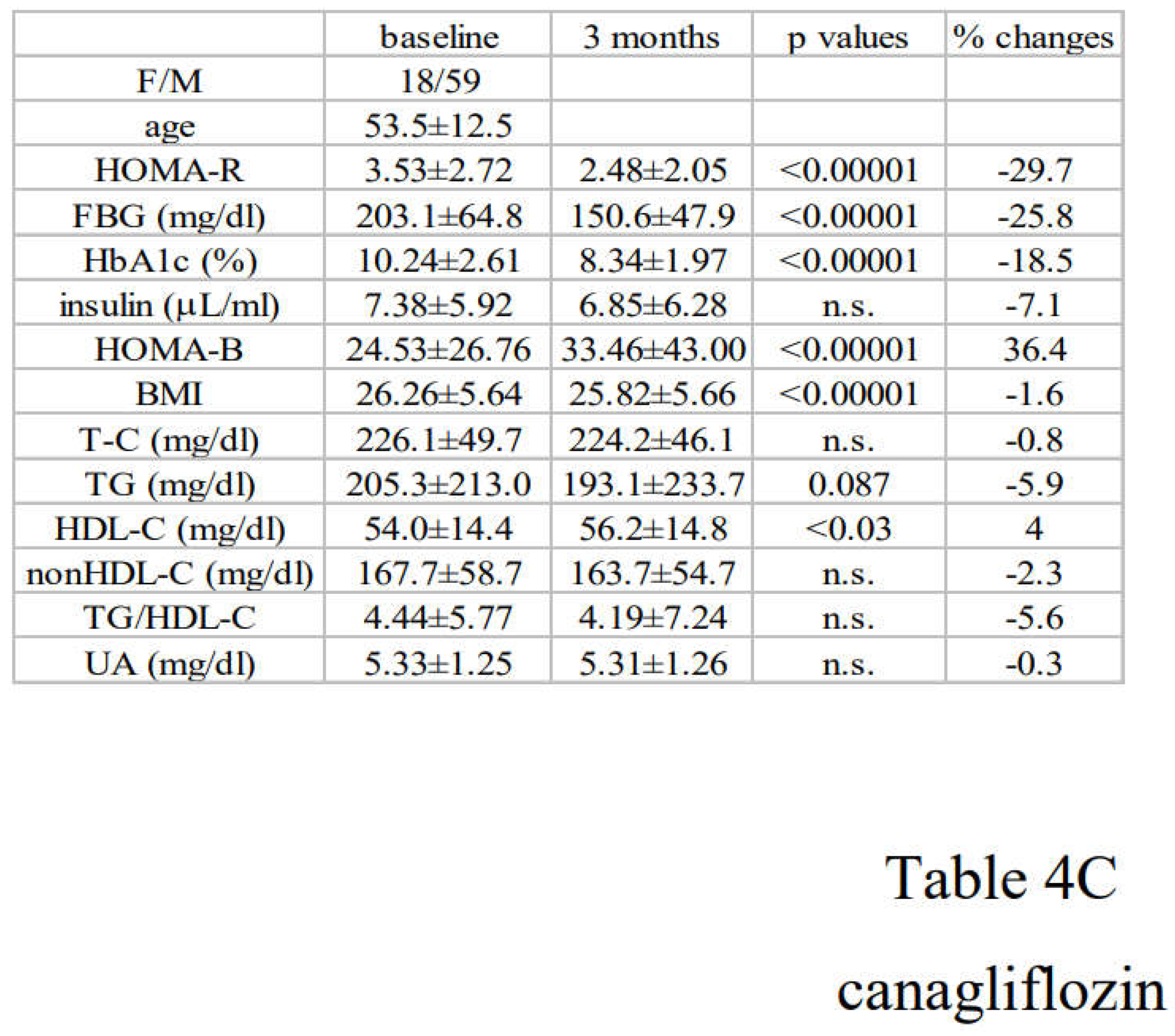
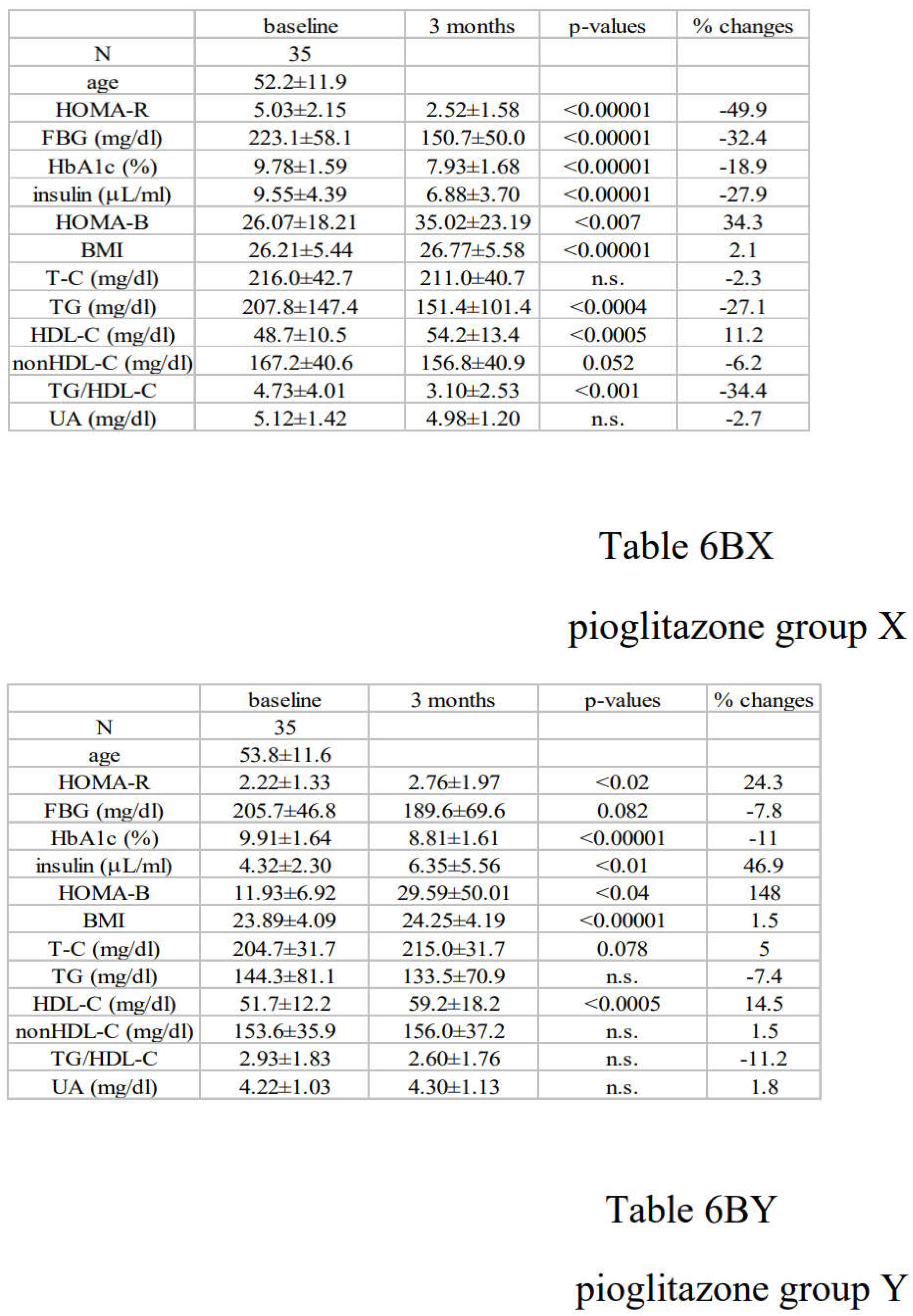
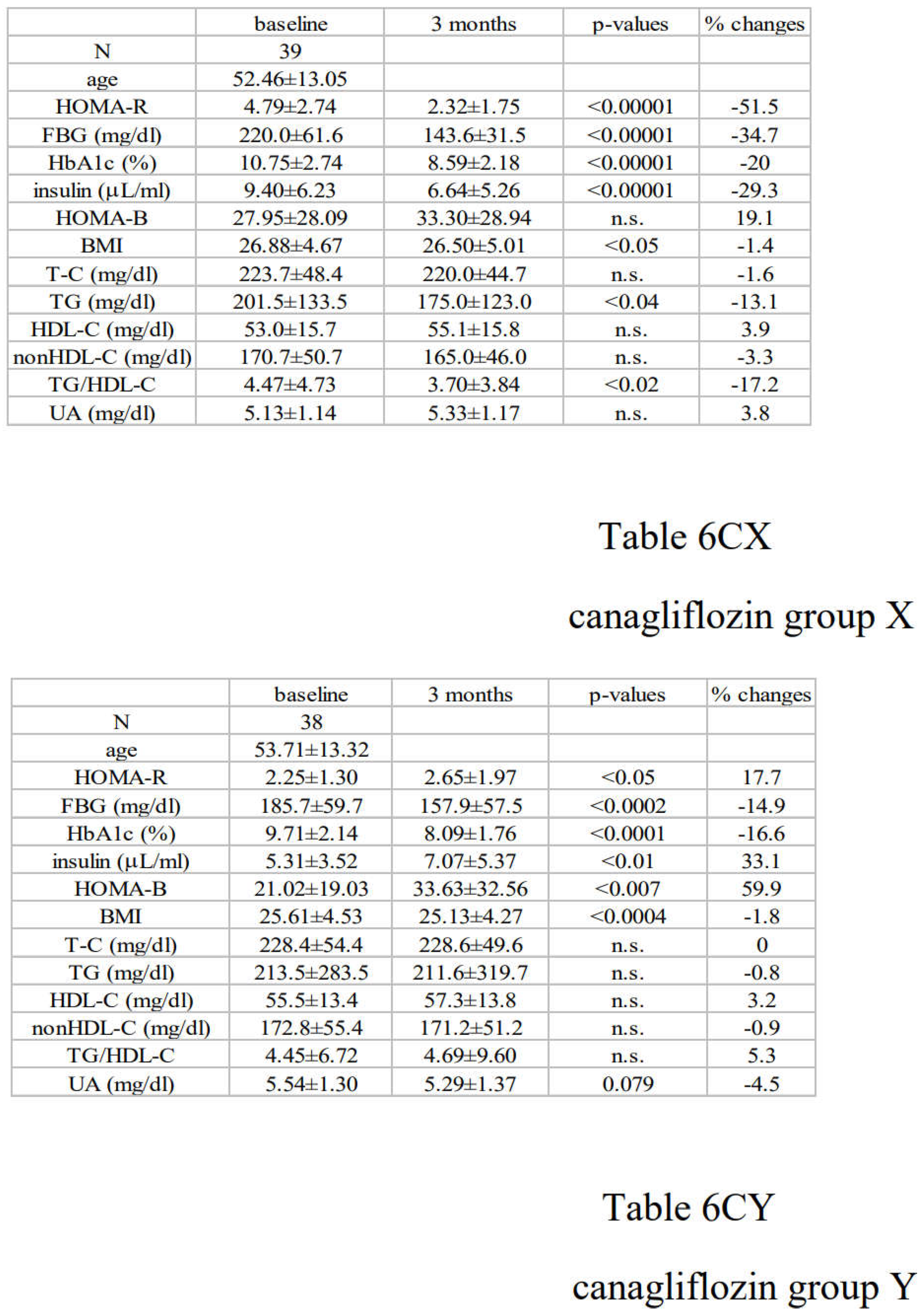
3.2. Alterations in Diabetic Parameters Following Very Low Calorie (Tight) Japanese Diet, Pioglitazone, or Canagliflozin Monotherapy in Treatment-Naïve Subjects with T2DM
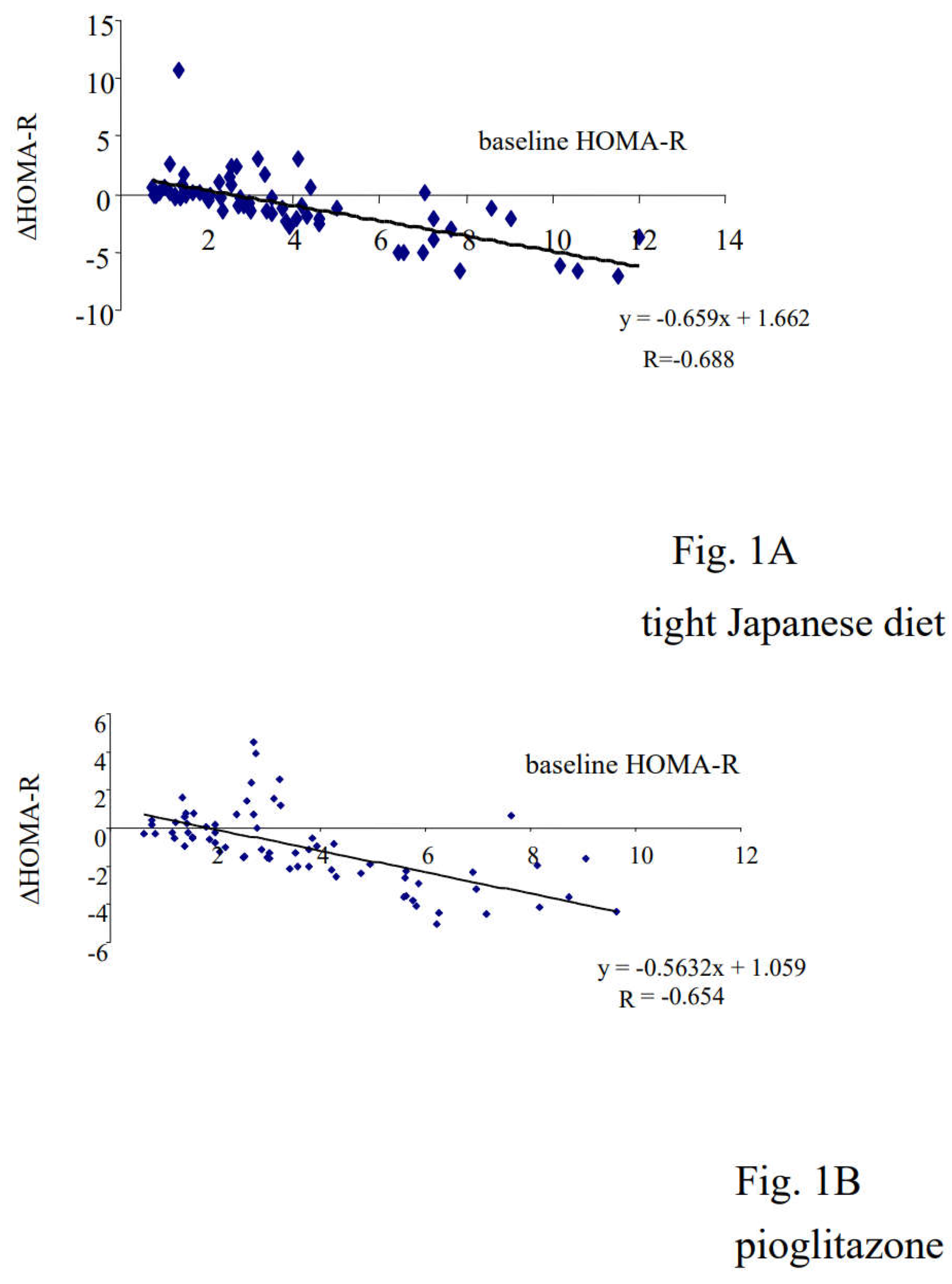
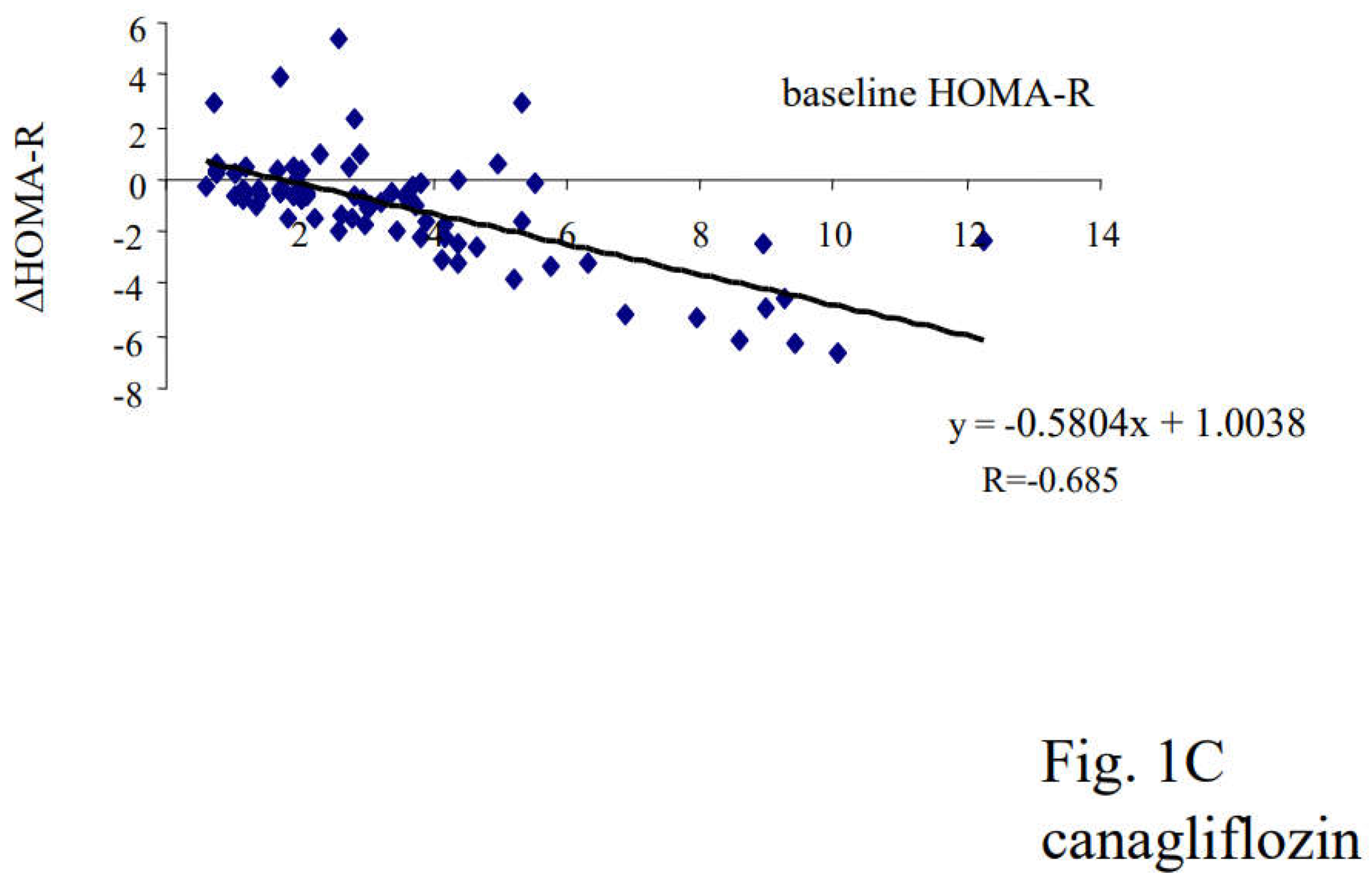
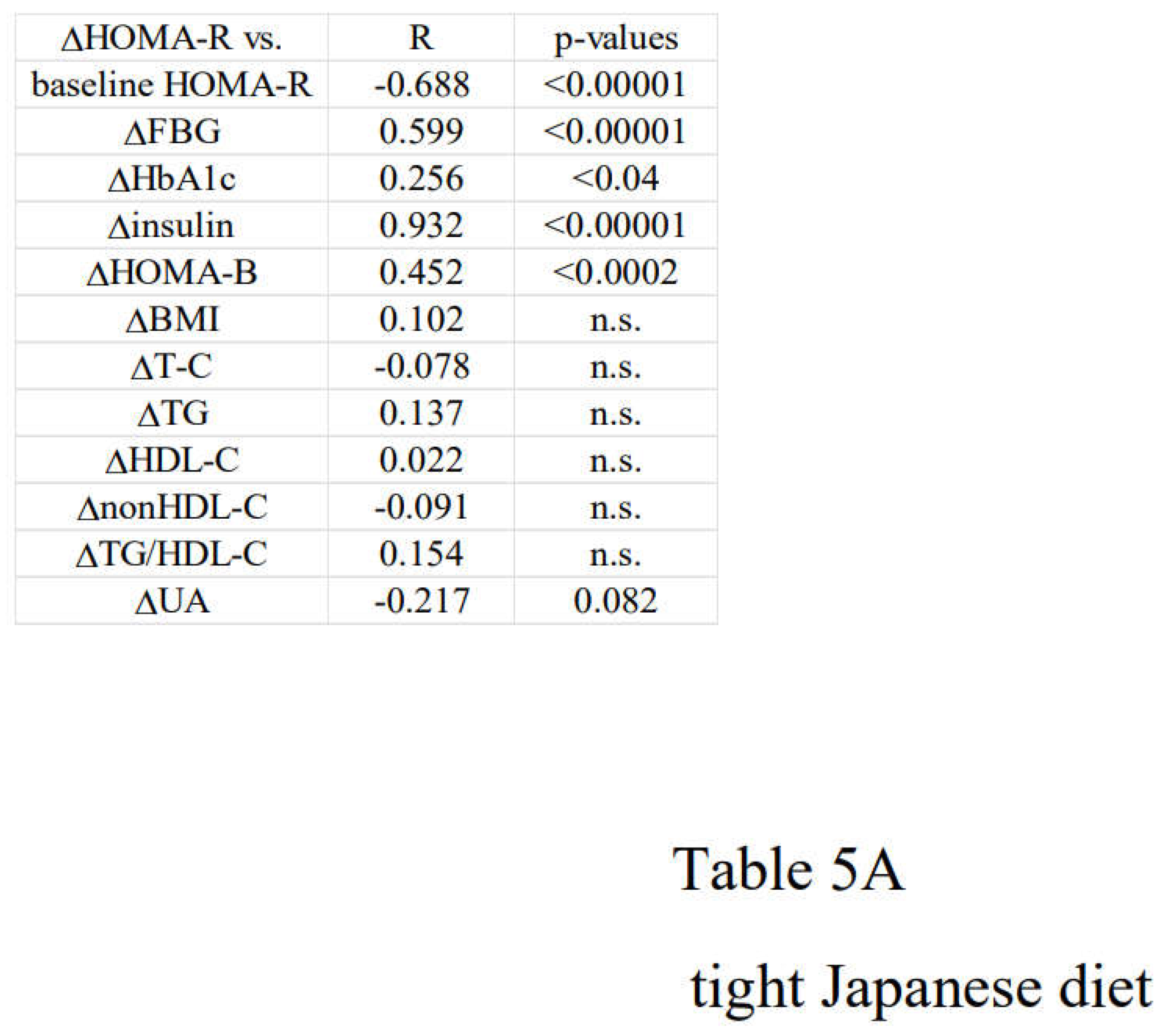
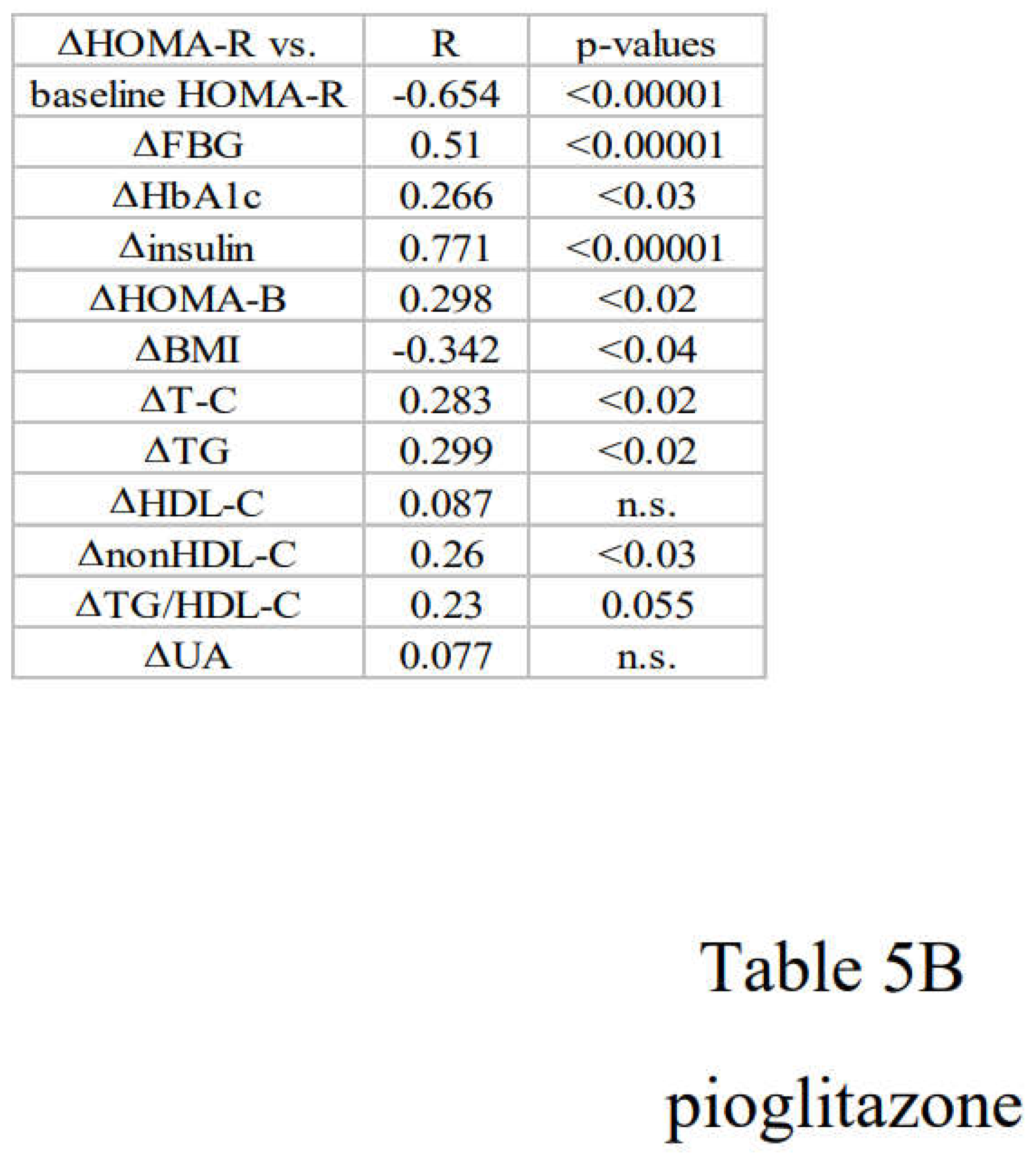
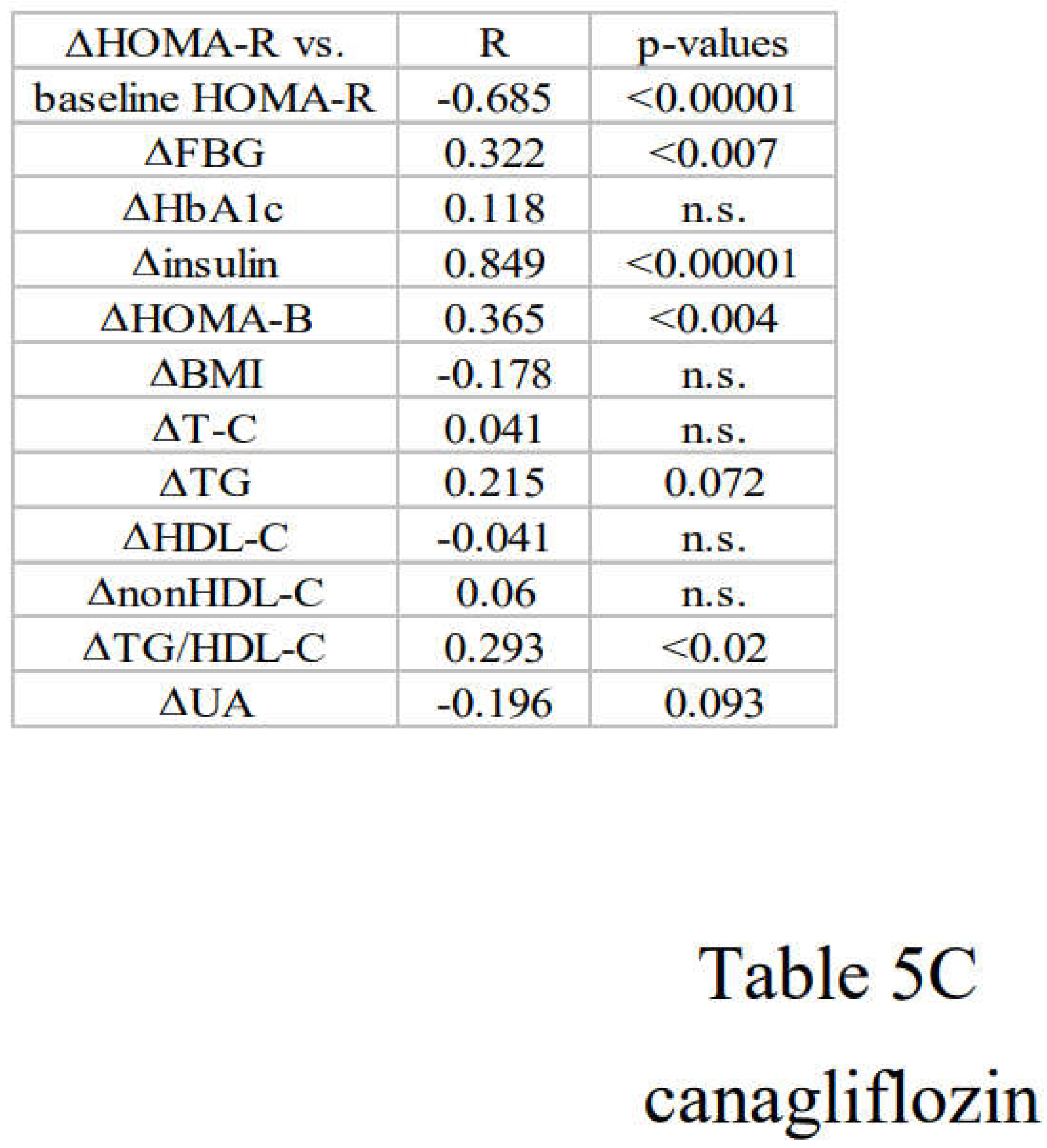
3.3. Correlation between Changes in Insulin Resistance and Diabetic Parameters with Very Low Calorie (Tight) Japanese Diet, Pioglitazone or Canagliflozin
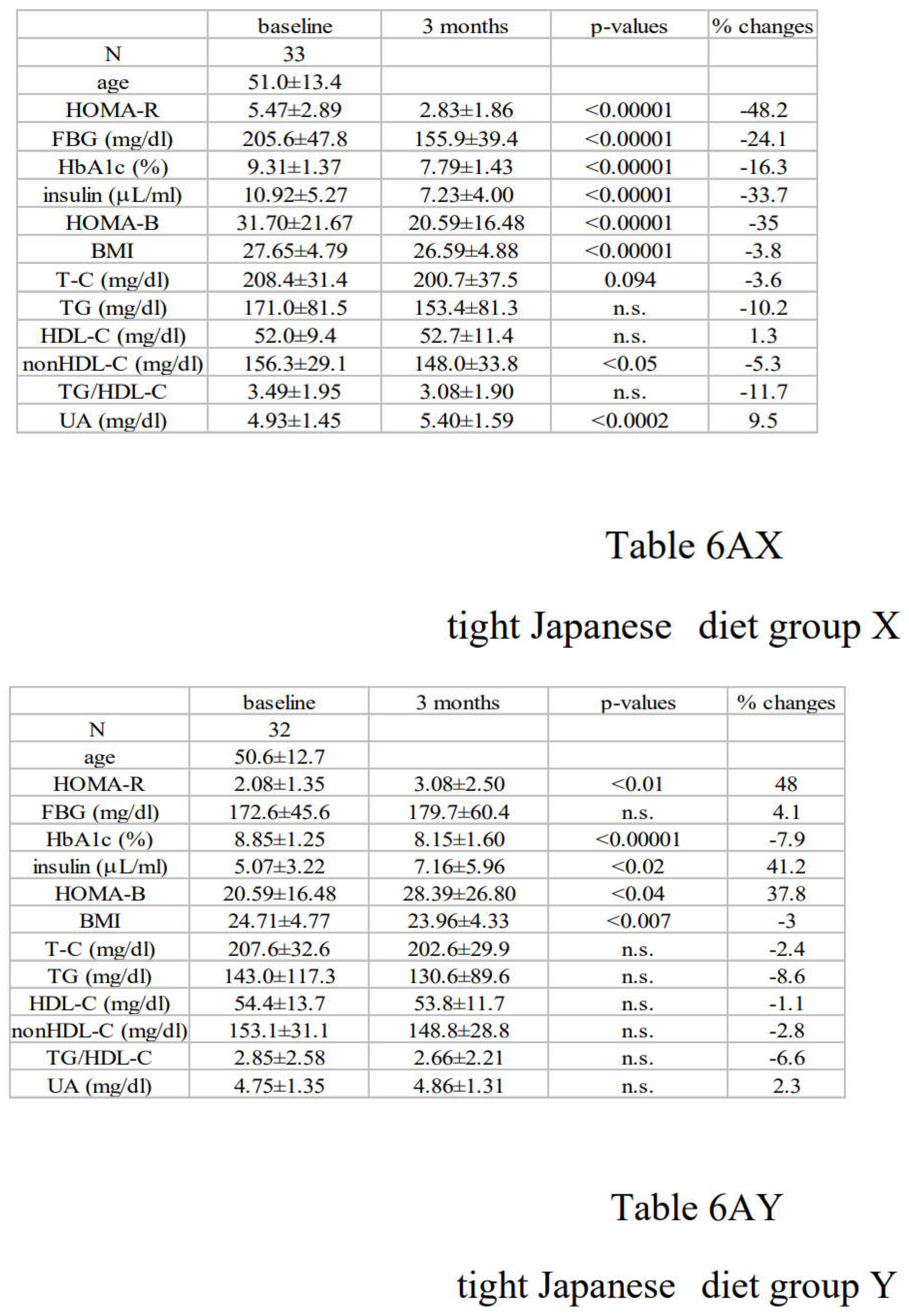
3.4. Differential Regulations of Diabetic Parameters in Two Groups with Distinct Changes in Insulin Resistance
4. Discussions
4.1. Characteristics of Diabetic Parameters in Newly Diagnosed, Drug-Naïve Japanese Patients with T2DM
4.2. Link between Changes in Insulin Resistance and Diabetic Parameters
4.3. Limitations of this Study
5. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| T2DM: type 2 diabetes |
| SGLT-2: sodium-glucose co-transporter |
| BMI: body mass index |
| FBG: fasting blood glucose |
| HOMA-R: homeostasis model assessment-R |
| HOMA-B: homeostasis model assessment-B |
| T-C: total cholesterol |
| TG: triglyceride |
| HDL-C: high density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| UA: uric acid |
Author Contributions Statement
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991 (3):173-194. [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz HE. Insulin resistance: definition and consequences. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109 Suppl 2:S135-148. [CrossRef]
- Cerf ME. Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013;4:37. [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz HE. Thiazolidinediones: the Forgotten Diabetes Medications. Curr Diab Rep. 2019 ;19(12):151. [CrossRef]
- Scheen AJ, Paquot N. Metabolic effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors beyond increased glucosuria: A review of the clinical evidence. Diabetes Metab. 2014 ;40(6 Suppl 1):S4-S11. [CrossRef]
- Kutoh E. Differential regulations of lipid profiles between Japanese responders and nonresponders treated with pioglitazone. Postgrad Med. 2011 ;123(1):45-52. [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo RA, Inzucchi S, Abdul-Ghani M, Nissen SE. Pioglitazone: The forgotten, cost-effective cardioprotective drug for type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019 ;16(2):133-143. [CrossRef]
- Kutoh E, Kuto AN, Ozawa E, Kurihara R, Akiyama M. Regulation of Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance and Diabetic Parameters in Drug Naïve Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Canagliflozin Monotherapy. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2023 ;73(5):279-288. [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli A. Measuring and estimating insulin resistance in clinical and research settings. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022 ;30(8):1549-1563. [CrossRef]
- Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985 ;28(7):412-419.
- Sakamoto N, Koh N. [Very low calorie diet therapy of patients with diabetes mellitus]. Nihon Rinsho. 1990 Dec;48 Suppl:894-8. Japanese. PMID: 2086969.
- Sakata T. A very-low-calorie conventional Japanese diet: its implications for prevention of obesity. Obes Res. 1995 ;3 Suppl 2:233s-239s. [CrossRef]
- Kutoh E, Ukai Y. Alogliptin as an initial therapy in patients with newly diagnosed, drug naïve type 2 diabetes: a randomized, control trial. Endocrine. 2012 ;41(3):435-441. [CrossRef]
- Amrhein V, Korner-Nievergelt F, Roth T. The earth is flat (p > 0.05): significance thresholds and the crisis of unreplicable research. PeerJ. 2017;5:e3544. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi A, Tohidi M, Derakhshan A, Hasheminia M, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Cut-off points of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and fasting serum insulin to identify future type 2 diabetes: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Acta Diabetol. 2015 ;52(5):905-915. [CrossRef]
- Reaven GM. Importance of identifying the overweight patient who will benefit the most by losing weight. Ann Intern Med. 2003 ;138(5):420-323. [CrossRef]
- Apovian CM, Okemah J, O’Neil PM. Body Weight Considerations in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Adv Ther. 2019 ;36(1):44-58. [CrossRef]
- Yokoh H, Kobayashi K, Sato Y, Takemoto M, Uchida D, Kanatsuka A, Kuribayashi N, Terano T, Hashimoto N, Sakurai K, Hanaoka H, Ishikawa K, Onishi S, Yokote K. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin compared with alpha-glucosidase inhibitor in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin or pioglitazone alone (Study for an Ultimate Combination Therapy to Control Diabetes with Sitagliptin-1): A multicenter, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority trial. J Diabetes Investig. 2015 ;6(2):182-191.
- Kutoh E, Kuto AN, Wada A, Hayashi J, Kurihara R. Sitagliptin as an Initial Therapy and Differential Regulations of Metabolic Parameters Depending on its Glycemic Response in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2021 ;71(3):157-165. [CrossRef]
- Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Miki H, Tamemoto H, Yamauchi T, Komeda K, Satoh S, Nakano R, Ishii C, Sugiyama T, Eto K, Tsubamoto Y, Okuno A, Murakami K, Sekihara H, Hasegawa G, Naito M, Toyoshima Y, Tanaka S, Shiota K, Kitamura T, Fujita T, Ezaki O, Aizawa S, Kadowaki T, et al. PPAR gamma mediates high-fat diet-induced adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance. Mol Cell. 1999 Oct;4(4):597-609. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80210-5. PMID: 10549291. [CrossRef]
- Hirano T. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018 ;25(9):771-782. [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt S, Miskin B, Glazer NB, Prince MJ, Robertson KE; Pioglitazone 026 Study Group. The impact of pioglitazone on glycemic control and atherogenic dyslipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Coron Artery Dis. 2001 ;12(5):413-423. [CrossRef]
- Premji R, Nylen ES, Naser N, Gandhi S, Burman KD, Sen S. Lipid Profile Changes Associated with SGLT-2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Agonists in Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2022 ;20(6):321-328. [CrossRef]
- Tassone EJ, Cimellaro A, Perticone M, Hribal ML, Sciacqua A, Andreozzi F, Sesti G, Perticone F. Uric Acid Impairs Insulin Signaling by Promoting Enpp1 Binding to Insulin Receptor in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 ;9:98. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Y, Hu Y, Huang T, Zhang Y, Li Z, Luo C, Luo Y, Yuan H, Hisatome I, Yamamoto T, Cheng J. High uric acid directly inhibits insulin signalling and induces insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 ;447(4):707-714. [CrossRef]
- Wasada T, Katsumori K, Saeki A, Iwatani M. Hyperuricemia and insulin resistance. Nihon Rinsho. 1996 ;54(12):3293-3296.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





