Submitted:
27 May 2024
Posted:
27 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
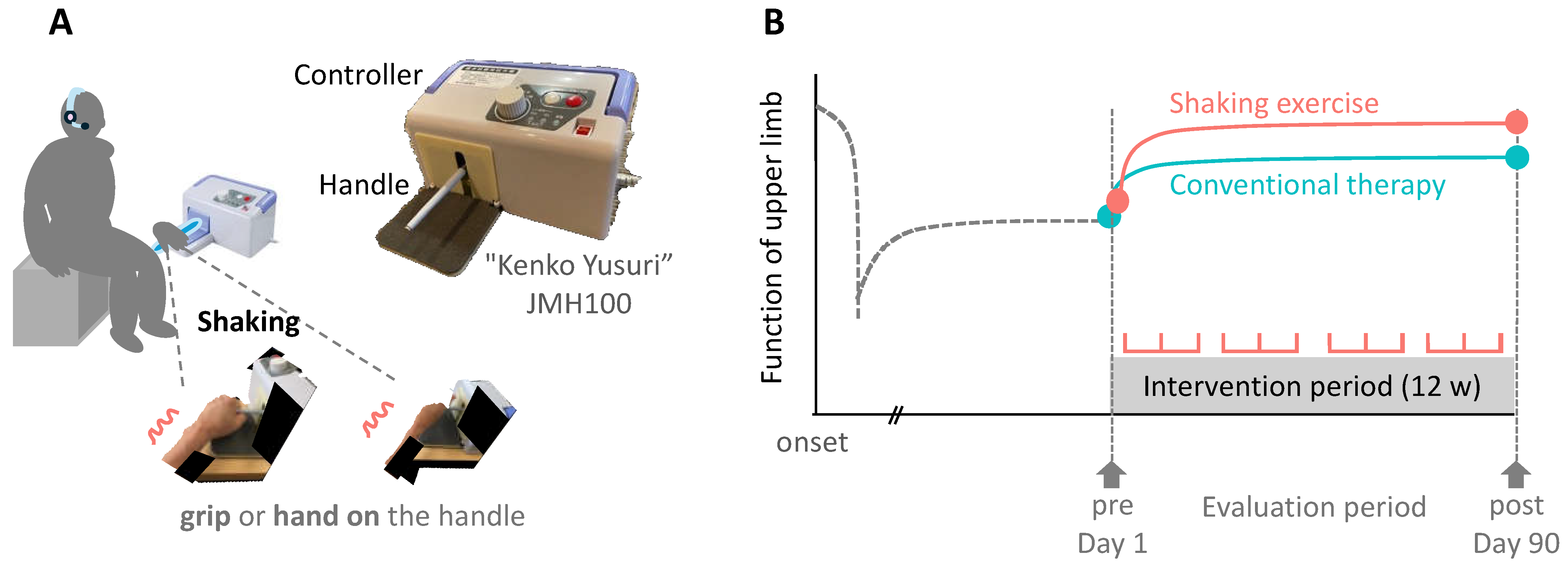
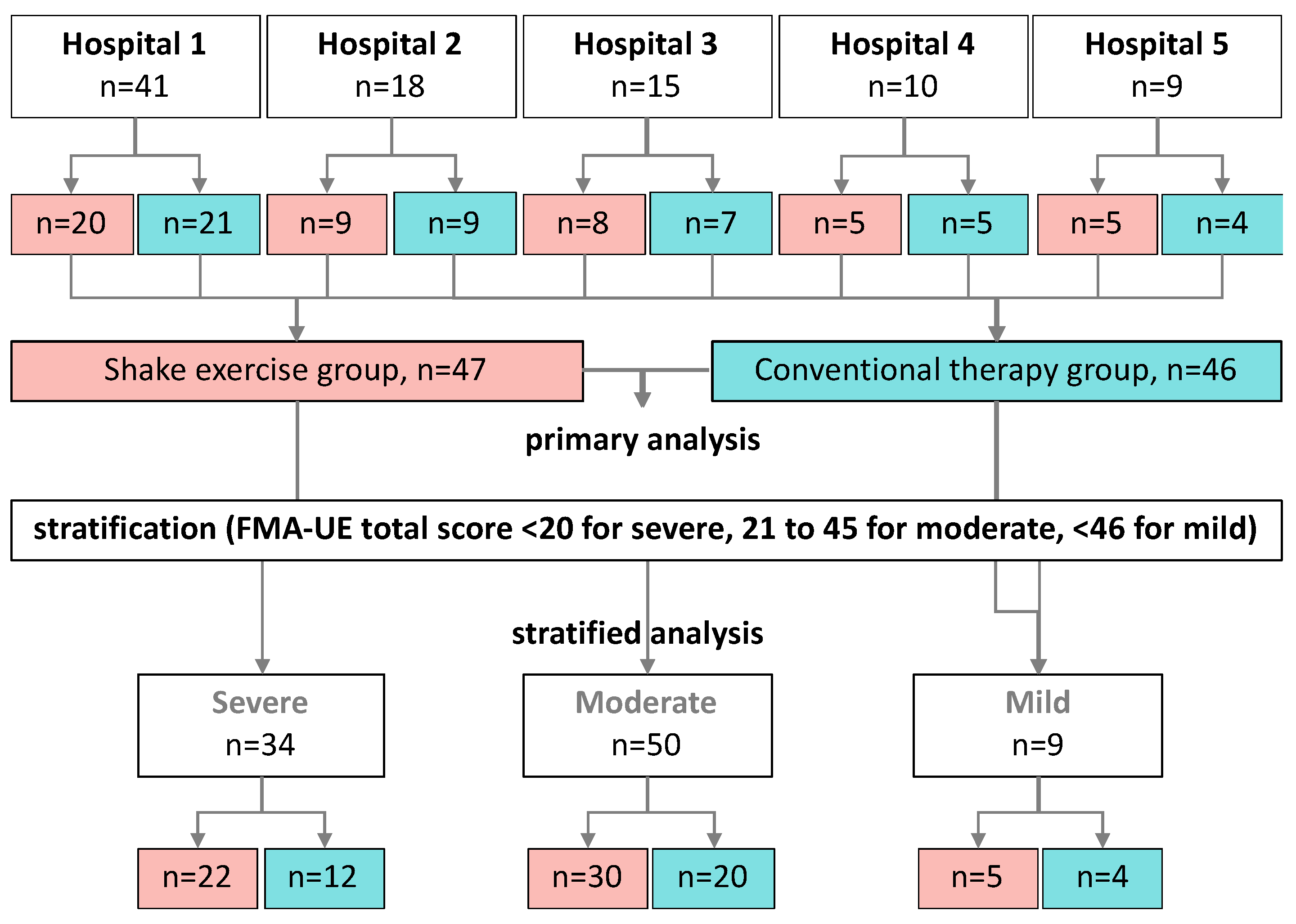
2. Materials and Methods
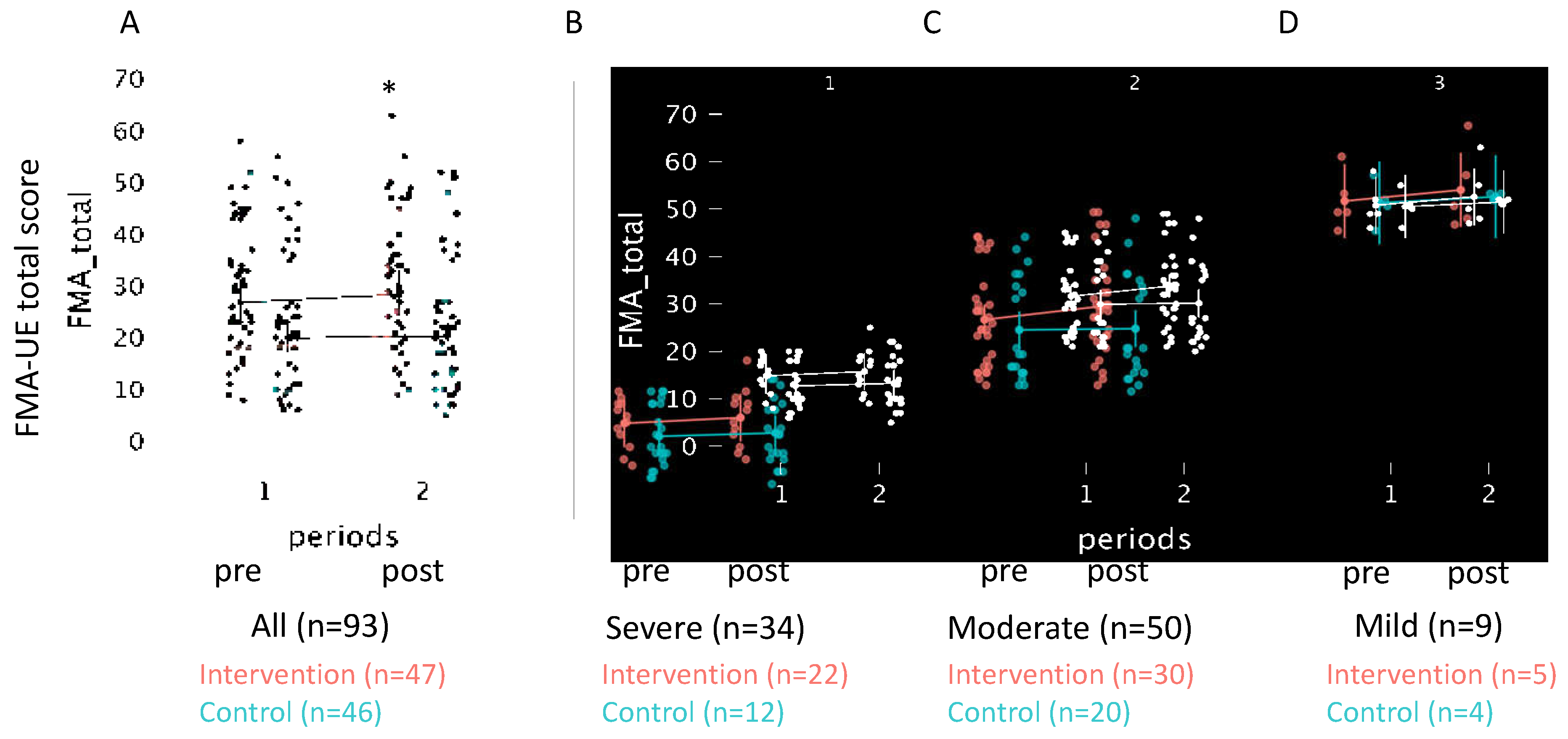
3. Results
- eq 1. Control, Pre-intervention:
- eq 2. Control, Post-intervention:
- eq 3. Intervention, Pre-treatment:
- eq 4. Intervention, Post-treatment:
- To estimate the improvement from pre- to post- in the control group:
- From pre- to post- in the intervention group:
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Intervention group (n=39) | Control group (n=39) | Between-group | Mean change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary endpoints (n=78) | Pre-test | Post-test | Pre-test | Post-test | p-value | Intervention group | Control group |
| (95% CI) | |||||||
| MAS (shoulder flexion) | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 2] | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 0.574 | 0 [1, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (shoulder extension) | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 0.59 | 0 [0, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (Elbow flexion) | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 0.215 | 0 [-1, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (Elbow extension) | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 1] ‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 0.297 | 0 [-1, 0] | 0 [, 1, 0] |
| MAS (Wrist flexion) | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 2] | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 0.367 | 0 [-1, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (Wrist extension) | 1 [1, 2]‡ | 1 [1, 1]‡ | 1 [1, 2] | 1 [1, 1] ‡ | 0.57 | 0 [-1, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (Finger flexion) | 1 [0, 2]‡ | 1 [0, 2] | 1 [0, 1] ‡ | 1 [0, 1] ‡ | 0.64 | 0 [-1, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| MAS (Finger extension) | 0 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 1 [0, 1]‡ | 0.461 | 0 [0, 0] | 0 [0, 0] |
| Sholder flexion active ROM | 102.50±32.39+ | 102.78±35.65 | 80.00±46.73 | 81.03±47.69 | 0.808◊ (-5.33, 6.83) |
0.28±10.07 | 1.03±15.06 |
| Sholder flexion passive ROM | 138.47±23.11 | 140.28±22.86 | 131.76±29.56 | 134.12±29.04 | 0.796 (-3.71, 4.81) |
1.81±10.36 | 2.35±7.10 |
| Sholder extension active ROM | 32.08±15.92 | 37.50±13.91 | 30.88±15.54 | 32.21±25.14 | 0.019 (-12.39, -1.09)† |
5.42±14.31 | -1.32±8.47 |
| Sholder extension passive ROM | 49.58±11.97 | 51.06±11.54 | 45.15±11.38 | 43.82±11.68 | 0.162 (-6.78, 1.19) |
1.47±9.67 | -1.32±6.66 |
| Sholder abduction active ROM | 88.19±38.29+ | 88.89±36.80 | 65.29±33.93 | 65.15±35.52 | 0.819 (-8.19, 6.51) |
0.69±16.13 | -0.15±14.59 |
| Sholder abduction passive ROM | 122.50±35.73 | 124.86±35.89 | 113.68±37.42 | 112.06±40.99 | 0.381 (-12.86, 4.90) |
2.36±14.42 | -1.62±22.22 |
| Sholder adduction active ROM | 7.36±20.86 | 7.50±20.79 | 3.09±12.67 | 3.09±12.43 | 0.937 (-3.65, 3.37) |
0.14±8.58 | 0.00±5.77 |
| Sholder adduction passive ROM | 10.56±20.24 | 10.28±19.82 | 7.24±12.06 | 7.21±13.15 | 0.885 (-3.20, 3.70) |
-0.28±8.10 | -0.03±6.16 |
| Elbow flexion active ROM | 111.33±21.52 | 109.03±29.71 | 102.50±23.07 | 104.56±21.30 | 0.366 (-5.37, 14.09) |
-2.31±26.06 | 2.06±11.69 |
| Elbow flexion passive ROM | 135.14±8.49 | 136.25±8.14 | 132.21±16.34 | 131.47±15.45 | 0.197 (-4.66, 0.97) |
1.11±6.29 | -0.74±6.29 |
| Elbow extension active ROM | -22.78±22.57 | -20.69±21.22 | -24.71±25.88 | -25.29±27.33 | 0.281 (-7.60, 2.26) |
2.08±11.17 | -0.59±9.36 |
| Elbow extension passive ROM | -5.69±12.14 | -5.28±12.07 | -5.15±12.94 | -5.29±13.14 | 0.647 (-3.05, 1.92) |
0.42±6.48 | -0.15±3.37 |
| Wrist flexion active ROM | 23.33±28.23 | 16.67±27.95 | 16.18±30.00 | 17.65±29.47 | 0.026 (0.94, 15.34)† |
-6.67±17.81 | 1.47±11.52 |
| Wrist flexion passive ROM | 68.47±13.46 | 66.94±14.80 | 70.44±13.62 | 72.06±12.86 | 0.106 (-0.70, 7.00) |
-1.53±8.69 | 1.62±7.36 |
| Wrist extension active ROM | 13.47±38.24 | 23.33±28.88 | 7.65±30.83 | 9.41±28.81 | 0.14 (-19.05, 2.86) |
9.86±28.55 | 1.76±14.87 |
| Wrist extension passive ROM | 58.33±21.18 | 60.14±23.25 | 60.15±18.47 | 63.53±15.15 | 0.522 (-3.33, 6.49) |
1.81±10.77 | 3.38±9.75 |
| Pain VAS | 3.17±3.04 | 2.56±2.50* | 2.65±2.84 | 2.79±3.05 | 0.03 (-1.44, 0.07)† |
-0.61±1.59 | 0.15±1.26 |
| The pre-test was performed before the intervention, and the post-test was performed after 12 weeks. The Mann–Whitney U test was performed for MAS. Significantly differences were found *within groups and †between groups. ‡in the pre-test comparisons between the intervention and control groups, a significant difference was observed (p<0.05). The significance level was set at p<0.05 for differences between the two groups. CI; confidence interval, SD; standard deviation, 1Q and 3Q 25th–75th percentile values, MAS; modified Ashworth scale, ROM; range of motion | |||||||
References
- Patient survey 2020 (Classification of diseases). Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/10syoubyo/dl/r02syobyo.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Langhorne, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Kwakkel, G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 2011, 377, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.L.; Winstein, C.J.; Miller, J.P.; Taub, E.; Uswatte, G.; Morris, D.; Giuliani, C.; Light, K.E.; Nichols-Larsen, D.; EXCITE Investigators. Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3 to 9 months after stroke: The EXCITE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2006, 296, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Veerbeek, J.M.; van Wegen, E.E.H.; Wolf, S.L. Constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Jørgensen, H.S.; Raaschou, H.O.; Olsen, T.S. Recovery of upper extremity function in stroke patients: The Copenhagen Stroke Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1994, 75, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstam, A.; Sjödin, A.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Participation and autonomy five years after stroke: A longitudinal observational study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Nakayama, H.; Raaschou, H.O.; Vive-Larsen, J.; Støier, M.; Olsen, T.S. Outcome and time course of recovery in stroke. Part I: Outcome. The Copenhagen stroke study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1995, 76, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, G.E.; Bandari, D.S.; Bavikatte, G.; Jost, W.H.; McCusker, E.; Largent, J.; Zuzek, A.; Esquenazi, A. High clinician- and patient-reported satisfaction with individualized onabotulinumtoxinA treatment for spasticity across several etiologies from the Aspire study. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, G.E.; Jost, W.H.; Bavikatte, G.; Bandari, D.S.; Tang, S.F.T.; Munin, M.C.; Largent, J.; Adams, A.M.; Zuzek, A.; Esquenazi, A. Individualized onabotulinumtoxinA treatment for upper limb spasticity resulted in high clinician- and patient-reported satisfaction: Long-term observational results from the Aspire study. PM R 2020, 12, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mierlo, M.L.; van Heugten, C.M.; Post, M.W.M.; Hajós, T.R.S.; Kappelle, L.J.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A. Quality of life during the first two years post stroke: The Restore4Stroke cohort study. Cerebrovasc Dis 2016, 41, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treger, I.; Shames, J.; Giaquinto, S.; Ring, H. Return to work in stroke patients. Disabil Rehabil 2007, 29, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.B.; Wissel, J.; Borg, J.; Ertzgaard, P.; Herrmann, C.; Kulkarni, J.; Lindgren, K.; Reuter, I.; Sakel, M.; Säterö, P.; et al. Functional goal achievement in post-stroke spasticity patients: The Botox(r) Economic Spasticity Trial (BEST). J Rehabil Med 2014, 46, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Wissel, J.; Fheodoroff, K.; Munin, M.C.; Patel, A.T.; Althaus, M.; Comes, G.; Dekundy, A.; Pulte, I.; Scheschonka, A.; et al. Improvement in quality-of-life-related outcomes following treatment with incobotulinumtoxinA in adults with limb spasticity: A pooled analysis. Toxins (Basel) 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Niimi, M.; Yamada, N.; Shimamoto, Y.; Masuda, G.; Hara, H.; Abo, M. Prognosis prediction of the effect of botulinum toxin therapy and intensive rehabilitation on the upper arm function in post-stroke patients using hierarchical cluster analysis. Disabil Rehabil 2022, 44, 6815–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunnerhagen, K.S.; Francisco, G.E. Enhancing patient-provider communication for long-term post-stroke spasticity management. Acta Neurol Scand 2013, 128, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmcrantz, S.; Holmqvist, L.W.; Sommerfeld, D.K. Long-term health states relevant to young persons with stroke living in the community in southern Stockholm – a study of self-rated disability and predicting factors. Disabil Rehabil 2012, 34, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo, M.; Kakuda, W.; Momosaki, R.; Harashima, H.; Kojima, M.; Watanabe, S.; Sato, T.; Yokoi, A.; Umemori, T.; Sasanuma, J. Randomized, multicenter, comparative study of NEURO versus CIMT in poststroke patients with upper limb hemiparesis: The NEURO-VERIFY Study. Int J Stroke 2014, 9, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuda, W.; Abo, M.; Sasanuma, J.; Shimizu, M.; Okamoto, T.; Kimura, C.; Kakita, K.; Hara, H. Combination Protocol of Low-Frequency rTMS and Intensive occupational therapy for post-stroke Upper Limb Hemiparesis: A 6-year Experience of more than 1700 Japanese Patients. Transl Stroke Res 2016, 7, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, M.; Sasaki, N.; Kimura, C.; Hara, T.; Yamada, N.; Abo, M. Sleep during low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is associated with functional improvement in upper limb hemiparesis after stroke. Acta Neurol Belg 2019, 119, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, D.; Hamaguchi, T.; Murata, K.; Ito, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Abo, M. Upper limb function recovery by combined repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and occupational therapy in patients with chronic stroke according to paralysis severity. Brain Sci 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cuesta, F.J.; González-Zamorano, Y.; Arroyo-Ferrer, A.; Moreno-Verdú, M.; Romero-Muñoz, J.P. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of primary motor cortex for stroke upper limb motor sequelae rehabilitation: A systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2023, 52, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almhdawi, K.A.; Mathiowetz, V.G.; White, M.; delMas, R.C. Efficacy of occupational therapy task-oriented approach in upper extremity post-stroke rehabilitation. Occup Ther Int 2016, 23, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.; Weingarden, H.; Weiss, R.; Yacoby, A.; Reif, S.; Malka, R.; Shiller, D.A.; Zeilig, G. Self-training to improve UE function at the chronic stage post-stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil 2017, 39, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudo, R.J. Recovery after brain injury: Mechanisms and principles. Front Hum Neurosci 2013, 7, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.H.; Corbett, D. Plasticity during stroke recovery: From synapse to behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Koyama, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Takahira, N.; Takaso, M. Impact of jiggling exercise as conservative treatment for hip osteoarthritis: A report of two cases. Case Rep Orthop 2020, 2020, 2804193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizuka, H.; Sato, T.; Murakami, J.; Mitsutake, T.; Hiromatsu, M. Short-term changes in radiographic joint space width after jiggling exercise as conservative treatment for hip osteoarthritis: A retrospective case series of nine patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Danells, C.J.; Black, S.E. The fugl-Meyer assessment of motor recovery after stroke: A critical review of its measurement properties. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2002, 16, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijikata, N.; Kawakami, M.; Ishii, R.; Tsuzuki, K.; Nakamura, T.; Okuyama, K.; Liu, M. Item difficulty of Fugl-Meyer assessment for upper extremity in persons with chronic stroke with moderate-to-severe upper limb impairment. Front Neurol 2020, 11, 577855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchi, Y.; Kyougoku, M.; Takahashi, K.; Okita, Y.; Takebayashi, T. Dimensionality and item-difficulty hierarchy of the Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity among Japanese patients who have experienced stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil 2022, 29, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woytowicz, E.J.; Rietschel, J.C.; Goodman, R.N.; Conroy, S.S.; Sorkin, J.D.; Whitall, J.; McCombe Waller, S. Determining levels of upper extremity movement impairment by applying a cluster analysis to the Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity in chronic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2017, 98, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, C.R.; Zutshi, D.W.; Hrubes, V.; Mason, R.M. Comparison of fixed interval and visual analogue scales for rating chronic pain. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1975, 8, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, M.B.; Daldegan-Bueno, D.; Menezes Oliveira, M.G.; de Souza, A.L. Beyond ANOVA and MANOVA for repeated measures: Advantages of generalized estimated equations and generalized linear mixed models and its use in neuroscience research. Eur J Neurosci 2022, 56, 6089–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, K.S.; Ferris, J.K.; Lohse, K.R.; Borich, M.R.; Borstad, A.; Cassidy, J.M.; Cramer, S.C.; Dukelow, S.P.; Findlater, S.E.; Hawe, R.L.; et al. Observational study of neuroimaging biomarkers of severe upper limb impairment after stroke. Neurology 2022, 99, e402–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; White, I.R.; Carlin, J.B.; Spratt, M.; Royston, P.; Kenward, M.G.; Wood, A.M.; Carpenter, J.R. Multiple imputation for missing data in epidemiological and clinical research: Potential and pitfalls. BMJ 2009, 338, b2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.S.; Cohen, L.G. Mechanisms underlying recovery of motor function after stroke. Arch Neurol 2004, 61, 1844–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Chen, H.; Qin, W.; He, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, K.; Zang, Y.; et al. Dynamic functional reorganization of the motor execution network after stroke. Brain 2010, 133, 1224–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, J.; Wu, X. Effects of whole-body vibration training on lower limb motor function and neural plasticity in patients with stroke: Protocol for a randomised controlled clinical trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasell, R.; Salbach, N.M.; Foley, N.; Mountain, A.; Cameron, J.I.; Jong, A.; Acerra, N.E.; Bastasi, D.; Carter, S.L.; Fung, J.; et al. Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Rehabilitation, Recovery, and Community Participation following Stroke. Part One: Rehabilitation and Recovery Following Stroke; 6th Edition Update 2019. Int J Stroke 2020, 15, 763–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. Differential effect of muscle vibration on intracortical inhibitory circuits in humans. J Physiol 2003, 551, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Butler, K.; Williamon, A.; Cordivari, C.; Lees, A.J.; Rothwell, J.C. Sensorimotor reorganization by proprioceptive training in musician’s dystonia and writer’s cramp. Neurology 2008, 70, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Takebayashi, T.; Hanioka, D.; Okita, Y.; Shimada, S. Comparison of tendon and muscle belly vibratory stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke upper extremity spasticity: A retrospective observational pilot study. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, T.; Chardon, M.K.; Rymer, W.Z.; Suresh, N.L. Stretch reflex excitability in contralateral limbs of stroke survivors is higher than in matched controls. J Neuroeng Rehabil 2019, 16, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmoku, M.; Murata, K.; Taguchi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Sasaki, N.; Abo, M. The effect of 6 treatment with botulinum neurotoxin type A for patients with upper limb hemiparesis after stroke. In Japanes. Tokyo Jikei Medical Journal 2017, 132, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguhi, T.; Abo, M. Recovery of patients with upper limb paralysis due to stroke who underwent intervention using low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with occupational therapy: A retrospective cohort study. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlove, J.; Anantha, V.; Advani, M.; Des Roches, C.; Kiran, S. Comparison of therapy practice at home and in the clinic: A retrospective analysis of the constant therapy platform data set. Front Neurol 2019, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroke, N.C.G.f. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke for the UK and Ireland; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Sohn, M.K.; Shin, Y.I.; Oh, G.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Joo, M.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, J.; Ahn, J.; et al. Revisiting the proportional recovery model in view of the ceiling effect of Fugl-Meyer assessment. Stroke 2021, 52, 3167–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Senoo, A.; Abo, M. Changes in structural neural networks in the recovery process of motor paralysis after stroke. Brain Sci 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.J.; Fulk, G.D.; Boyne, P. Clinically important differences for the upper-extremity Fugl-Meyer Scale in people with minimal to moderate impairment due to chronic stroke. Phys Ther 2012, 92, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| variables | All | Intervention | Control | Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N=93) | (n=47) | (n=46) | χ2 or U | p-value | r or V | |
| Sex (Female/Male) | 50/43 | 26/22 | 24/21 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Age | 59 [53, 68] | 59 [53, 67] | 59 [53, 68] | 1065 | 0.91 | 0.49 |
| Diagnosis (CI/ICH/other) | 33/55/5 | 16/30/2 | 17/25/3 | 0.59 | 0.75 | 0.08 |
| Affected side (L/R) | 46/47 | 27/21 | 19/26 | 1.31 | 0.25 | 0.12 |
| Month from onset | 131 [92, 175] | 136 [98, 177] | 126 [81, 175] | 1487 | 0.36 | 0.56 |
| FMA-UE total score | 24 [18, 30] | 27 [23, 31]* | 20 [17, 23] | 1343 | 0.04 | 0.62 |
| BoNT-A treatments | 14 [10, 18] | 14 [11, 19] | 13 [9, 17] | 1124 | 0.81 | 0.49 |
| BoNT-A dose (Unit) | 250 [200, 350] | 250 [200, 400] | 250 [200, 300] | 1208 | 0.32 | 0.56 |
| Data are presented as median [1st, 3rd quartile]. Chi-square test with Cramer's V for effect size is used to compare the number of patients, diagnosis, and affected side in each group. Month from onset, FMA-UE, BoNT-A are compared with Mann-Whitney U-test. *p<0.05 compared with controls. CI; cerebral infarction, ICH; intra cerebral hemorrhage, FMA-UE; Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity, BoNT-A; Botulinum toxin type A | ||||||
| Variable | β | SD | z | P-value | 95% CI | Model Fit Indices | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMA-UE total | Intercept | 1.48 | 0.55 | 2.67 | 0.01* | (0.39, 2.56) | AIC=789.4 BIC=805.6 REML-based Log-Likelihood=394.8 |
| Intervention | 0.69 | 0.30 | 2.30 | 0.02* | (0.10, 1.27) | ||
| Periods | 1.13 | 0,29 | 3.88 | <0.001* | (0.56, 1.70) | ||
| Baseline | 1.00 | 0.01 | 87.46 | <0.001* | (0.98, 1.02) | ||
| Part A | Intercept | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.18 | 0.86 | (0.94, 1.13) | AIC=423.6 BIC=452.6 REML-based Log-Likelihood=-202.8 |
| Intervention | 0.84 | 0.65 | 1.28 | 0.20 | (0.44, 2.11) | ||
| Periods | 0.33 | 0.29 | 1.12 | 0.26 | (0.25, 0.90) | ||
| Baseline | 0.99 | 0.01 | 67.15 | 000* | (0.96, 1.02) | ||
| Part B | Intercept | 0.22 | 0.10 | 2.26 | 0.02 | (0.03, 0.42) | AIC=230.1 BIC=259.2 REML-based Log-Likelihood=-106.1 |
| Intervention | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.98 | (0.08, 0.08) | ||
| Periods | 0.23 | 0.09 | 2.42 | 0.02* | (0.04, 0.41) | ||
| Baseline | 1.00 | 0.01 | 129.72 | < 0.001* | (0.98, 1.01) | ||
| Part C | Intercept | 0.31 | 0.30 | 1.05 | 0.29 | (0.27, 0.90) | AIC=504.7 BIC=524.1 REML-based Log-Likelihood=−246.4 |
| Intervention | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.86 | 0.39 | (0.45, 1.16) | ||
| Periods | 0.22 | 0.19 | 1.18 | 0.24 | (0.14, 0.58) | ||
| Baseline | 0.37 | 0.26 | 1.41 | 0.16 | (0.88, 0.14) | ||
| Part D | Intercept | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.84 | (0.25, 0.31) | AIC=242.2 BIC=261.5 REML-based Log-Likelihood=115.1 |
| Intervention | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.94 | 0.35 | (0.20, 0.58) | ||
| Periods | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.81 | (0.15, 0.20) | ||
| Baseline | 0.99 | 0.02 | 48.75 | < 0.001* | (0.95, 1.03) | ||
| The model includes data from 186 observations across 93 participants during each period. The intercept represents the predicted FMA_total score for a non-intervention individual at baseline FMA_total of zero. Each coefficient is presented with its respective standard error, z-value, p-value, and 95% confidence interval. The variable 'Intervention' indicates the group, and 'Periods' distinguishes between pre- and post-intervention assessments. 'Baseline' denotes FMA_total score at baseline. Statistical significance is set at *p<0.05. SD; Standard Error, β; estimated coefficient | |||||||
| FMA-UE | Intervention (n=47) | Control (n=46) | U | P-value | (r) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre | post | delta | pre | post | delta | ||||
| Total | 26.8 (23.0, 31.2) |
28.4 (24.4, 33.0) |
1.8 (0.8, 2.8) |
20.0 (17.1, 23.3) |
20.3 (17.4, 23.7) |
0.4 (-0.1, 1.0) |
823 | 0,04* | 0,24 |
| Part A | 21.4 (19.4, 23.5) |
22.6 (20.6, 24.7) |
1.2 (0.6, 1.8) |
17.5 (15.5, 19.6) |
17.9 (15.8, 20.0) |
0.3 (-0.2, 0.9) |
770 | 0,01* | 0,29 |
| Part B | 2.9 (2.1, 3.7) |
3.1 (2.3, 3.9) |
0.2 (-0.2, 0.6) |
1.7 (0.9, 2.4) |
1.9 (1.1, 2.7) |
0.2 (-0.1, 0.6) |
1015 | 0,56 | 0,06 |
| Part C | 4.1 (2.9, 5.2) |
4.2 (3.1, 5.4) |
0.2 (-0.3, 0.6) |
3.5 (2.4, 4.7) |
3.3 (2.2, 4.5) |
-0.2 (-0.5, 0.1) |
977 | 0,37 | 0,10 |
| Part D | 1.3 (0.8, 1.7) |
1.4 (1.0, 1.9) |
0.2 (0.0, 0.4) |
0.8 (0.3, 1.2) |
0.7 (0.3, 1.2) |
0.0 (-0.2, 0.1) |
964 | 0,16 | 0,11 |
| This table presents the results of a Mann–Whitney U test comparing the changes (Δ values) in FMA scores before and after treatment between the control and intervention groups. Δ values are calculated as the difference between post- and pre-intervention scores for each measure. The table includes the median changes along with the first and third quartiles for each group. *P-values <0.05 indicate statistically significant differences between the groups. Effect size (r) is reported to quantify the magnitude of the difference, with values closer to -1 or 1 indicating a stronger effect. Scores are presented as the mean, 95% CI. | |||||||||
| Variable | β | SD | z-Value | P-value | 95% CI | Model Fit Indices | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mild (n=9) | Intercept | 1.56 | 2.73 | -0.57 | 0.57 | (3.78, 6.90) | AIC=71.7 BIC=78.8 REML-based Log-Likelihood=-27.8 |
| Intervention | 0.05 | 0.39 | -0.12 | 0.91 | (0.73, 0.82) | ||
| Periods | 1.44 | 0.73 | 1.98 | 0.04* | (0.02, 2.87) | ||
| Baseline | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.96 | (-0.10, 0.12) | ||
| moderate (n=50) | Intercept | 1.04 | 1.21 | -0.86 | 0.39 | (1.33, 3.42) | AIC=463.5 BIC=479.1 REML-based Log-Likelihood=-225.7 |
| Intervention | 1.03 | 0.48 | 2.14 | 0.03* | (0.09, 1.98) | ||
| Periods | 1.38 | 0.47 | 2.92 | 0.00 | (0.46, 2.31) | ||
| Baseline | 0.97 | 0.03 | 31.84 | < 0.001* | (0.91, 1.03) | ||
| severe (n=34) | Intercept | 0.85 | 0.66 | 1.29 | 0.20 | (0.44, 2.13) | AIC=231.8 BIC=245.1 REML-based Log-Likelihood=-113.9 |
| Intervention | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 0.61 | (0.48, 0.82) | ||
| Periods | 0.68 | 0.30 | 2.25 | 0.02* | (0.09, 1.27) | ||
| Baseline | 1.01 | 0.03 | 29.37 | 0.00* | (0.94, 1.08) | ||
| The model includes data from 186 observations across 93 participants in each period. The intercept represents the predicted FMA_total score for a non-intervention individual at baseline FMA_total of zero. Each coefficient is presented with its respective standard error, z-value, p-value, and 95% confidence interval. The variable 'Intervention' indicates the group, and 'Periods' distinguishes between pre- and post-intervention assessments. 'Baseline' denotes FMA_total score at baseline. Scores are presented as the mean, 95% CI. *p<0.05. SD; Standard Error, β; estimated coefficient | |||||||
| Variables | Intervention group | Control group | ΔControl vs. ΔIntervention |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre | post | delta | pre | post | delta | U | P | r | |||
| modified Ashworth scale | shoulder | flex | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 908 | 0.14 | -0.16 |
| ext | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1028 | 0.62 | -0.05 | ||
| elbow | flex | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1202 | 0.31 | 0.11 | |
| ext | 2 (1, 2) | 2 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 2 (1, 2)* | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 930 | 0.20 | -0.14 | ||
| wrist | flex | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1082 | 1.00 | 0.00 | |
| ext | 2 (1, 2) | 2 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1087 | 0.97 | 0.01 | ||
| finger | flex | 2 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1091 | 0.93 | 0.01 | |
| ext | 0 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) | 1037 | 0.68 | -0.04 | ||
| Active Range of Motion | shoulder | flex | 110 (125, 80) | 110 (125, 88) | 0 (-5, 10) | 83 (110, 43) | 83 (120, 50) | 0 (-5, 9) | 1094 | 0.92 | 0.01 |
| ext | 40 (40, 20) | 40 (50, 30) | 0 (-5, 5) | 35 (40, 25) | 35 (40, 20) | 0 (-5, 5) | 1311 | 0.06 | 0.21 | ||
| abd | 75 (120, 60) |
85 (113, 60) |
5 (0, 10) | 60 (85, 50) | 60 (80, 41) | 0 (-5, 5) | 1187 | 0.41 | 0.10 | ||
| add | 0 (10, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 999 | 0.46 | -0.08 | ||
| elbow | flex | 115 (130, 103) | 115 (130, 100) | 5 (-10, 0) | 100 (114, 76) | 100 (120, 83) | 0 (-5, 5) | 1036 | 0.73 | -0.04 | |
| ext | -15 (-38, 0) | -10 (0, -30) | 5 (0, 10) | -18 (-49, 0) | -15 (-39, -6) | 5 (0, 10) | 1214 | 0.30 | 0.12 | ||
| wrist | flex | 15 (40, 0) | 15 (40, -5) | 0 (-5, 5) | 13 (0, 30) | 18 (-10, 30) | 0 (-5, 5) | 941 | 0.27 | -0.13 | |
| ext | 30 (40, 0) | 30 (45, 5) | 0 (0, 0) | 5 (-28, 35) | 8 (-20, 34) | 0 (-10, 0) | 1141 | 0.64 | 0.06 | ||
| Passive Range of Motion | shoulder | flex | 140 (125, 155) |
140 (120, 160) |
0 (-5, 10) | 138 (120, 160) |
135 (120, 154) |
0 (-5, 9) | 1048 | 0.80 | 0.03 |
| ext | 50 (45, 60) | 50 (48, 58) | 0 (-5, 5) | 50 (41, 50) | 50 (40, 50) | 0 (-5, 0) | 1006 | 0.55 | 0.07 | ||
| abd | 135 (130, 140) |
140 (130, 143) |
0 (0, 5) | 140 (130, 145) |
133 (125, 145) |
0 (-5, 0) | 892 | 0.12 | 0.18 | ||
| add | 0 (-10, 0) | 0 (-5, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (-9, 0) | 0 (-5, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 1054 | 0.81 | 0.03 | ||
| elbow | flex | 120 (95, 150) |
120 (98, 155) |
5 (-10, 10) |
118 (90, 145) | 110 (90, 144) | 0 (-14, 5) | 898 | 0.16 | 0.17 | |
| ext | 0 (0, 13) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 12) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 1187 | 0.27 | -0.10 | ||
| wrist | flex | 70 (60, 80) | 70 (60, 80) | 0 (-8, 5) | 70 (65, 80) | 70 (60, 80) | 0 (0, 5) | 1144 | 0.62 | -0.06 | |
| ext | 60 (45, 70) | 70 (48, 80) | 0 (0, 10) | 68 (50, 75) | 68 (55, 74) | 0 (0, 9) | 1029 | 0.68 | 005 | ||
| Pain VAS | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 6) | 0 (0, 0) | 3 (0, 6) | 2 (0, 5)* | 0 (-1, 0) | 914 | 0.10 | 0.10 | ||
| A Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare changes in MAS and ROM between groups, quantified by calculating the difference (Δ values) between pre- and post-intervention measurements. P-values are presented for the results of comparisons between the shaking exercise and control groups. *p<0.05 for within-group comparisons were performed using a Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Data are presented as medians and 25th–75th percentile values. | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





