Submitted:
23 May 2024
Posted:
24 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
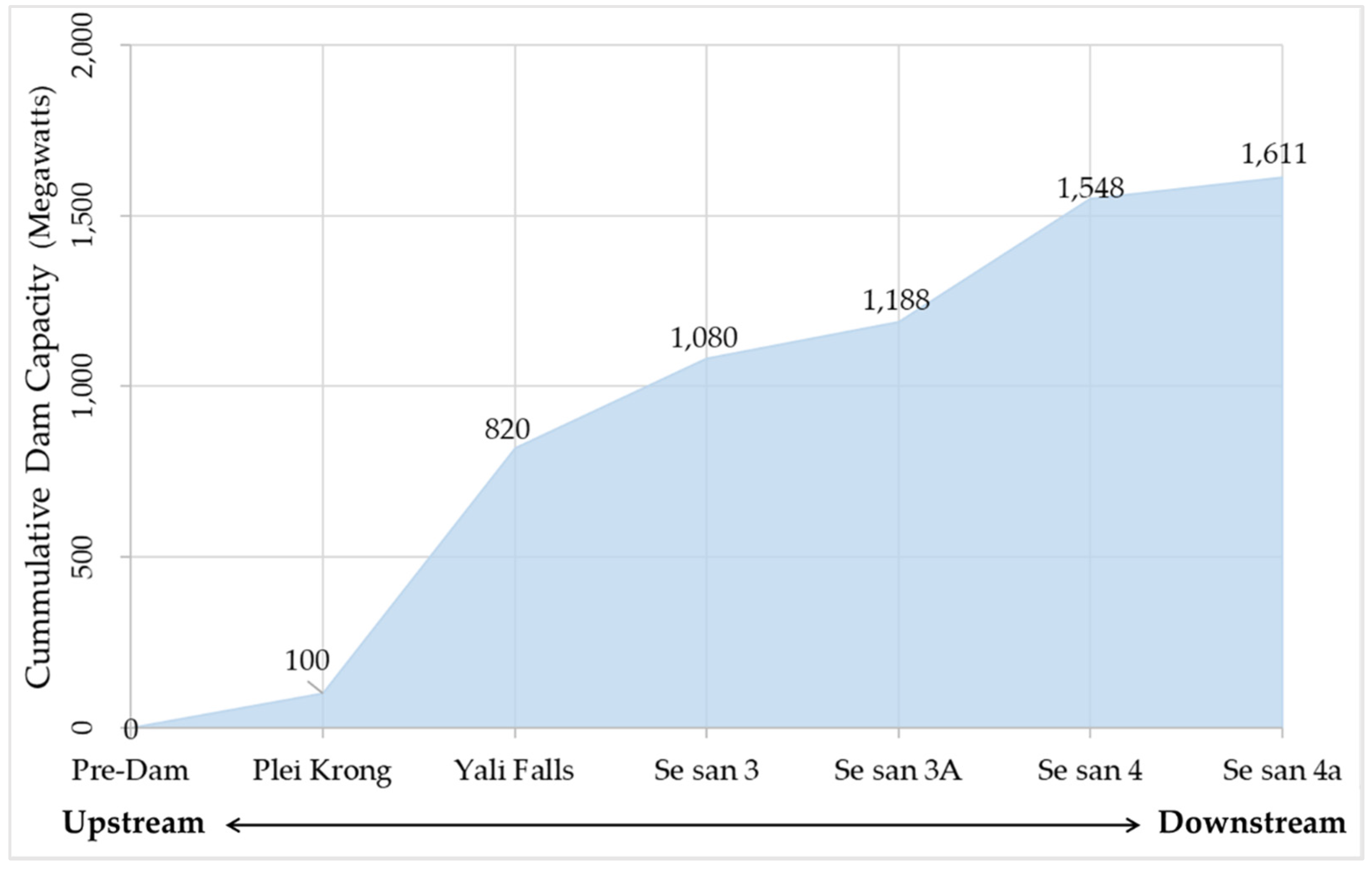
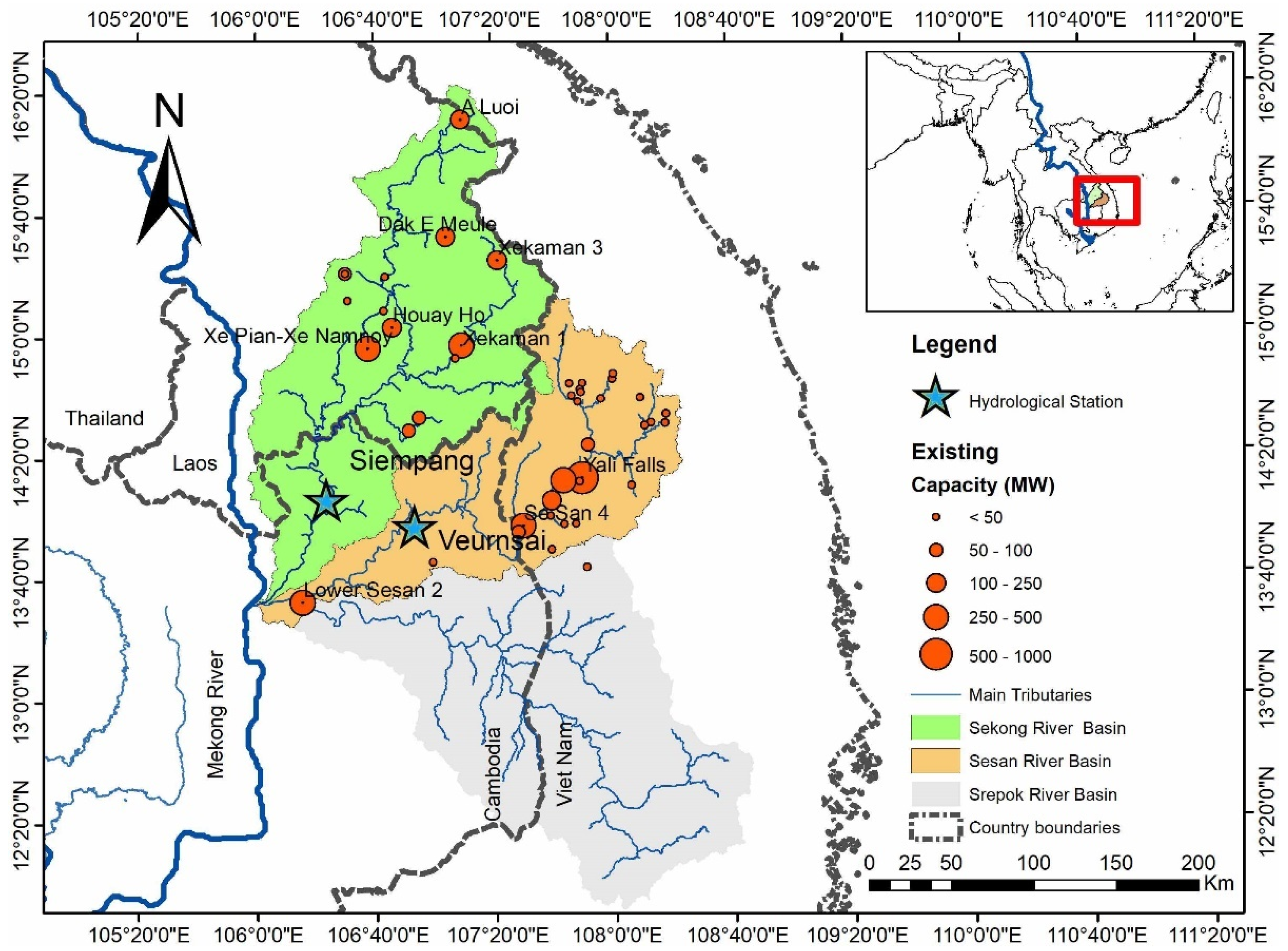
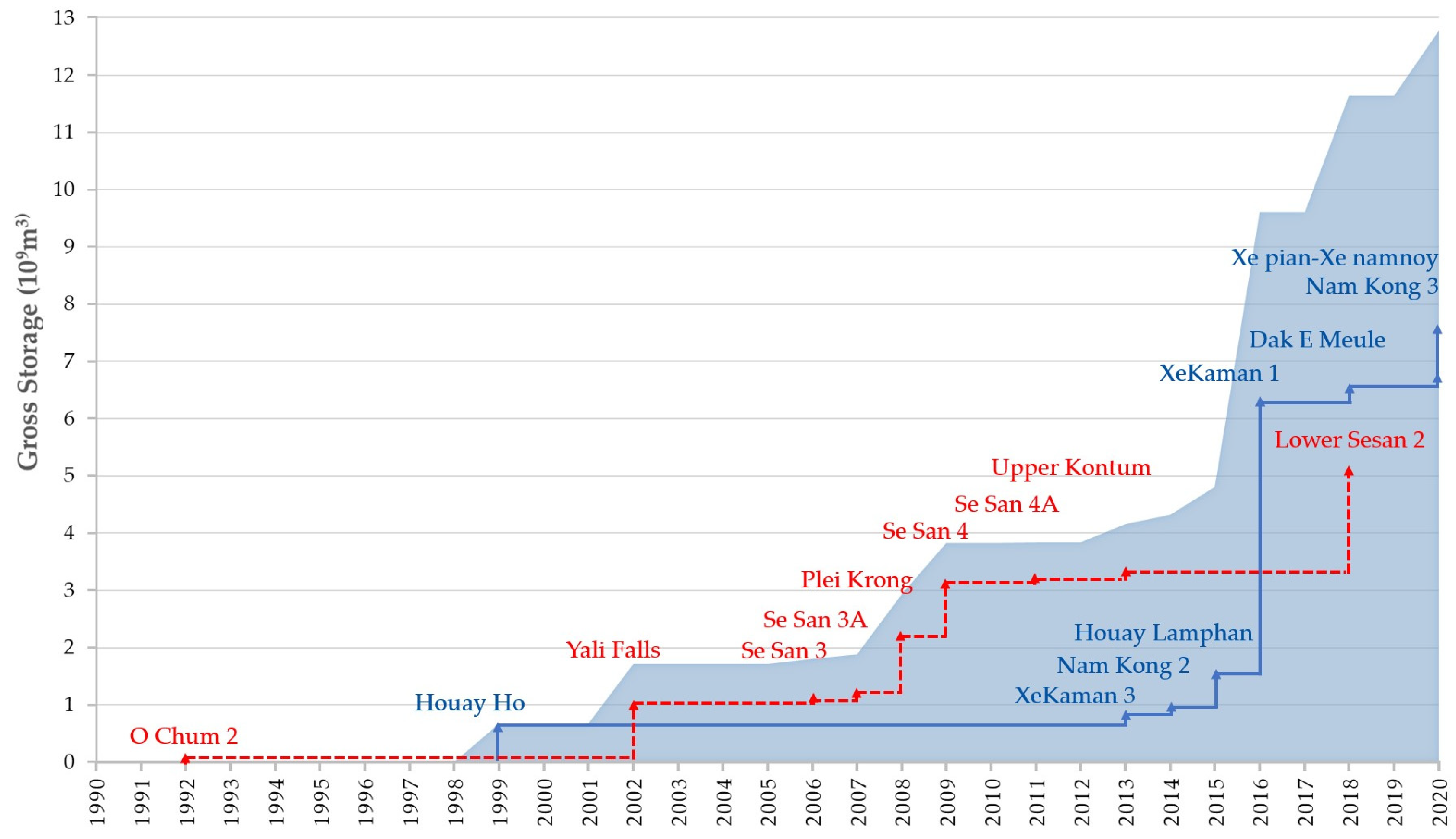
2.1. Study Area
2.2. River Flow Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration and Extreme Flow Events
2.3.2. Hydrologic Alteration Between Periods and Rivers
3. Results
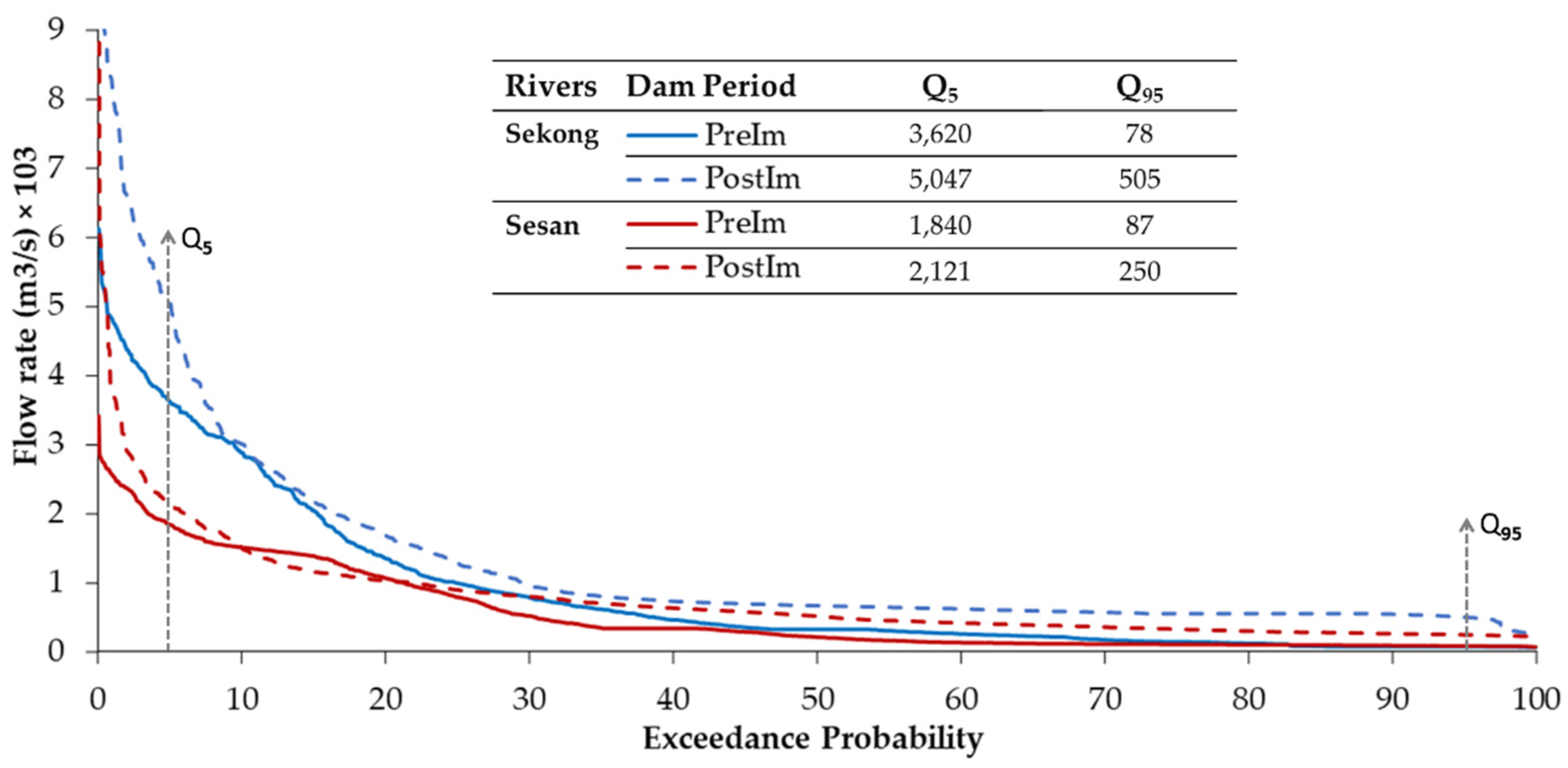
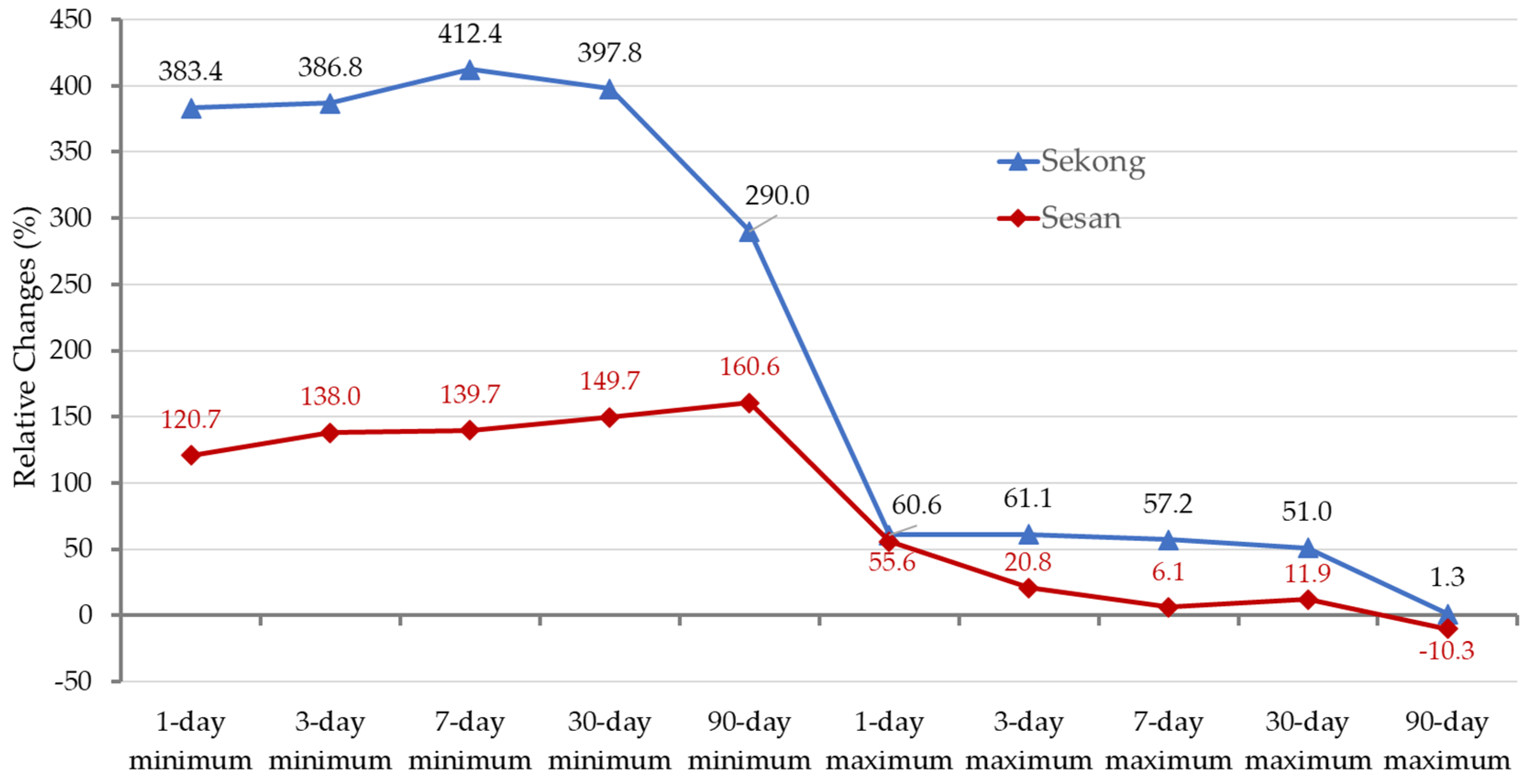
3.1. Changes in Flow Duration Curves and Flow Maxima and Minima
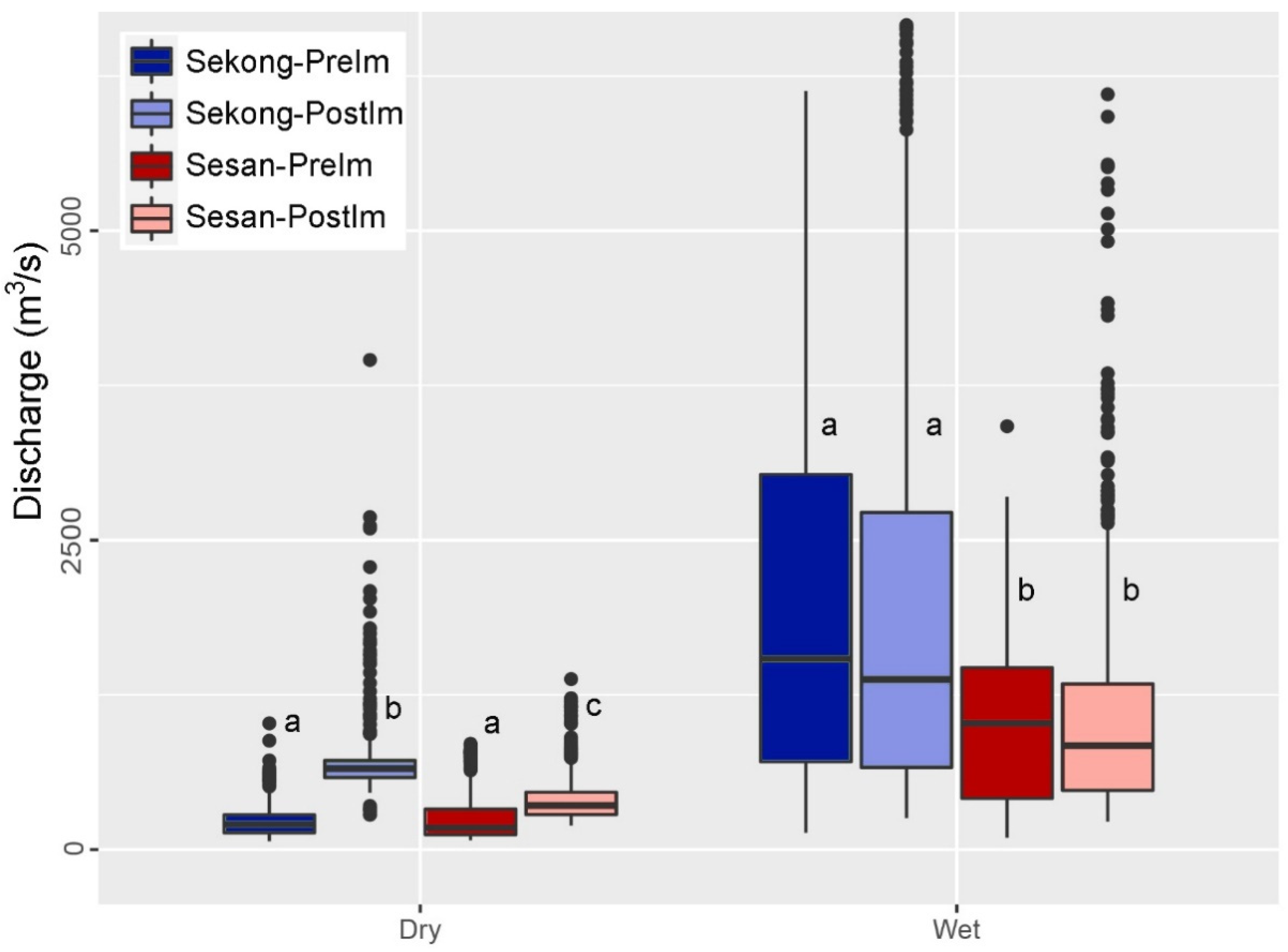
3.2. Hydrologic Alteration between Periods and River Basins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Dry Season | Wet Season | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sekong | Sesan | Sekong | Sesan | |||||
| Pre- | Post- | Pre- | Post- | Pre- | Post- | Pre- | Post- | |
| Mean | 226.5 | 708.3 | 248.1 | 415.0 | 1903.0 | 2085.3 | 1023.2 | 1093.6 |
| Median | 202.0 | 654.0 | 177.0 | 357.4 | 1540.0 | 1374.0 | 1020.0 | 840.7 |
| SD | 132.0 | 304.3 | 172.1 | 194.0 | 1387.3 | 1965.2 | 669.3 | 898.7 |
| Min | 68.0 | 281.0 | 75.0 | 193.3 | 135.0 | 255.0 | 95.0 | 225.2 |
| Max | 1020.0 | 3956.0 | 855.0 | 1377.3 | 6130.0 | 10301.0 | 3420.0 | 6101.5 |
| Range | 952.0 | 3675.0 | 780.0 | 1184.0 | 5995.0 | 10046.0 | 3325.0 | 5876.4 |
References
- Moran, E. F.; Lopez, M. C.; Moore, N.; Müller, N.; Hyndman, D. W. Sustainable hydropower in the 21st century. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, 11891–11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinho, A. A.; Gomes, L. C.; Veríssimo, S.; K. Okada, E., Flood regime, dam regulation and fish in the Upper Paraná River: effects on assemblage attributes, reproduction and recruitment. Reviews in Fish biology and Fisheries 2004, 14, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, F.; Komiyama, E. A challenge to dam improvement for the protection of both salmon and human livelihood in Shiretoko, Japan’s third Natural Heritage Site. Landscape Ecological Engineering 2010, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, R. T. Ecological impacts of dams, water diversions and river management on floodplain wetlands in Australia. Austral Ecology 2000, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R. ; systematics, Environmental effects of dams and impoundments. Annual review of ecology 1977, 8, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T. D.; Cochrane, T. A.; Arias, M. E.; Van, P. D. T.; de Vries, T. T. Hydrological alterations from water infrastructure development in the Mekong floodplains. Hydrological processes 2016, 30, 3824–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J. S.; Lacombe, G.; Arias, M. E.; Dang, T. D.; Piman, T. Hydropower dams of the Mekong River basin: A review of their hydrological impacts. Journal of Hydrology 2019, 568, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, R.; Thomas, R. Destruction of wetlands and waterbird populations by dams and irrigation on the Murrumbidgee River in arid Australia. Environmental management 2004, 34, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Bai, J.; Dong, S. Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water resources management 2009, 23, 1763–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xiang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Hua, W. Effects of cascade reservoir dams on the streamflow and sediment transport in the Wujiang River basin of the Yangtze River, China. Journal Inland Waters 2018, 8, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaver, G.; van Os, B.; Negrel, P.; Petelet-Giraud, E. Influence of hydropower dams on the composition of the suspended and riverbank sediments in the Danube. Journal Environmental Pollution 2007, 148, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukhaphon, A.; Baird, I. G.; Hogan, Z. S. The impacts of hydropower dams in the Mekong River Basin: A review. Water 2021, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.; Dietrich, W.; Trush, W. Downstream ecological effects of dams, a geomorphic perspective. Journal Bioscience 1995, 45, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, G.; Sang, L.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Dai, J.; Yin, D.; Liang, J. Effects of dam construction on biodiversity: A review. Journal of cleaner production 2019, 221, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N. L.; Zimmerman, J. K. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: a literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Journal Freshwater biology 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habit, E.; García, A.; Díaz, G.; Arriagada, P.; Link, O.; Parra, O.; Thoms, M. ; Applications, River science and management issues in Chile: Hydropower development and native fish communities. River Research 2019, 35, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B. D.; Baumgartner, J. V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D. P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conservation biology 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H. K. A review of hydrologic signatures and their applications. Journal Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water 2021, 8, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F. J.; Nislow, K. H. Changes in hydrologic regime by dams. Journal Geomorphology 2005, 71, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, M. E.; Danner, E. M. The drivers of river temperatures below a large dam. Journal Water Resources Research 2020, 56, e2019WR026751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainboth, W. J.; Vidthayanon, C.; Yen, M. D., Fishes of the greater Mekong ecosystem with species list and photographic atlas. 2012.
- Sor, R.; Meas, S.; Wong, K. K.; Min, M.; Segers, H. Diversity of Monogononta rotifer species among standing waterbodies in northern Cambodia. Journal of Limnology.
- Doeurk, B.; Chhorn, S.; Sin, S.; Phauk, S.; Sor, R. Diversity, distribution and habitat associations of aquatic beetles. Cambodian Journal of Natural History 2022, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Chhorn, S.; Chan, B.; Sin, S.; Doeurk, B.; Chhy, T.; Phauk, S.; Sor, R. Diversity, abundance and habitat characteristics. Cambodian Journal of Natural History 2020, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Sor, R.; Boets, P.; Chea, R.; Goethals, P. L.; Lek, S. Spatial organization of macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Lower Mekong Basin. Limnologica 2017, 64, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sor, R.; Ngor, P. B.; Boets, P.; Goethals, P. L.; Lek, S.; Hogan, Z. S.; Park, Y.-S. Patterns of mekong mollusc biodiversity: Identification of emerging threats and importance to management and livelihoods in a region of globally significant biodiversity and endemism. Water 2020, 12, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngor, P. B.; Sor, R.; Prak, L. H.; So, N.; Hogan, Z. S.; Lek, S. In Mollusc fisheries and length–weight relationship in Tonle Sap flood pulse system, Cambodia, Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 2018; EDP Sciences: 2018; p 34.
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S. A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortle, K.; Bamrungrach, P. Fisheries habitat and yield in the Lower Mekong Basin. MRC technical paper 2015, 47, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental consequences of damming the mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A review. Earth-Science Reviews 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciscato, B. R. F.; Udaeta, M. E. M.; Gimenez, A. L. V.; de Almeida Prado Jr, F. A. Strategic decision making based on energy rates and costs from Itaipu's Multinational Energy Agreement Perspective. Energy Strategy Reviews 2022, 44, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sor, R.; Ngor, P. B.; Lek, S.; Chann, K.; Khoeun, R.; Chandra, S.; Hogan, Z. S.; Null, S. E. Fish biodiversity declines with dam development in the Lower Mekong Basin. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piman, T.; Cochrane, T.; Arias, M.; Green, A.; Dat, N., Assessment of flow changes from hydropower development and operations in Sekong, Sesan and Srepok Rivers of the Mekong Basin. 2013.
- Oeurng, C.; Sok, T. Assessing changes in flow and water quality emerging from hydropower development and operation in the Sesan River Basin of the Lower Mekong Region. Journal of Hydrology 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Van Binh, D.; Kantoush, S. A.; Saber, M.; Mai, N. P.; Maskey, S.; Phong, D. T.; Sumi, T. Long-term alterations of flow regimes of the Mekong River and adaptation strategies for the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 2020, 32, 100742. [Google Scholar]
- Piman, T., Multiple drivers of hydrological alteration in the transboundary Srepok River Basin of the Lower Mekong Region. 2020.
- Zhou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Ma, K. J. H.; Sciences, E. S., Development of a revised method for indicators of hydrologic alteration for analyzing the cumulative impacts of cascading reservoirs on flow regime. 2020, 24, 4091–4107.
- Winton, R. S.; Calamita, E.; Wehrli, B. Reviews and syntheses: Dams, water quality and tropical reservoir stratification. Journal Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piman, T.; Lennaerts, T.; Southalack, P. Assessment of hydrological changes in the lower Mekong Basin from Basin-Wide development scenarios. Journal Hydrological Processes 2013, 27, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, D., Atlas of the 3S Basins. 2015.
- Oeurng, C.; Cochrane, T. A.; Arias, M. E.; Shrestha, B.; Piman, T. Assessment of changes in riverine nitrate in the Sesan, Srepok and Sekong tributaries of the Lower Mekong River Basin. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 2016, 8, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Baumgartner, J.; Wigington, R.; Braun, D. How much water does a river need? Freshwater biology 1997, 37, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B. D.; Baumgartner, J. V.; Braun, D. P.; Powell, J. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regulated Rivers: Research Management: An International Journal Devoted to River Research Management 1998, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. D.; Tao, X.; Xu, C. y.; Chen, X. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration caused by dam construction in the middle and lower Yellow River, China. Hydrological Processes: An International Journal 2008, 22, 3829–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Lewis, Q. W.; Wu, J.; Huang, F. A framework to assess the cumulative impacts of dams on hydrological regime: A case study of the Yangtze River. Hydrological Processes 2017, 31, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conservancy, N., Indicators of hydrologic alteration. Version 7. User’s manual. The Nature Conservancy 2007.
- Tian, J.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, T. Influence of Three Gorges Dam on downstream low flow. Water 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, A.; Bart, R. Synthetic monthly flow duration curves for the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Water SA 2012, 38, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abimbola, O. P.; Wenninger, J.; Venneker, R.; Mittelstet, A. R. The assessment of water resources in ungauged catchments in Rwanda. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 2017, 13, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission (MRC), Hydrological Impacts of the Lancang Hydropower Cascade on Downstream Extreme Events. Mekong River Commission Secretariat: Vientiane, Laos 2019.
- Liu, K.-T.; Tseng, K.-H.; Shum, C. K.; Liu, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Shang, K., Assessment of the Impact of Reservoirs in the Upper Mekong River Using Satellite Radar Altimetry and Remote Sensing Imageries. 2016, 8, (5), 367.
- Do, P.; Tian, F.; Zhu, T.; Zohidov, B.; Ni, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exploring synergies in the water-food-energy nexus by using an integrated hydro-economic optimization model for the Lancang-Mekong River basin. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 728, 137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IHA Statistics Group | Regime Characteristics | Streamflow parameter used in this study |
|---|---|---|
| Magnitude and duration of annual extreme water conditions | Magnitude, duration | Annual minima 1-day means Annual maxima 1-day means Annual minima 3-day means |
| Annual maxima 3-day means | ||
| Annual minima 7-day means | ||
| Annual maxima 7-day means | ||
| Annual minima 30-day means | ||
| Annual maxima 30-day means | ||
| Annual minima 90-day means | ||
| Annual maxima 90-day means |
| Pre- vs Post-Impact Comparison | Basin Comparison |
|---|---|
| (1) Dry-season Sekong River Pre- vs Post-Hydropower Impact | (5) Sekong vs Sesan |
| (2) Dry-season Sesan River Pre- vs Post-Hydropower Impact | |
| (3) Wet-season Sekong River Pre- vs Post- Hydropower Impact | (6) Sekong vs Sesan |
| (4) Wet-season Sesan River Pre- vs Post- Hydropower Impact |
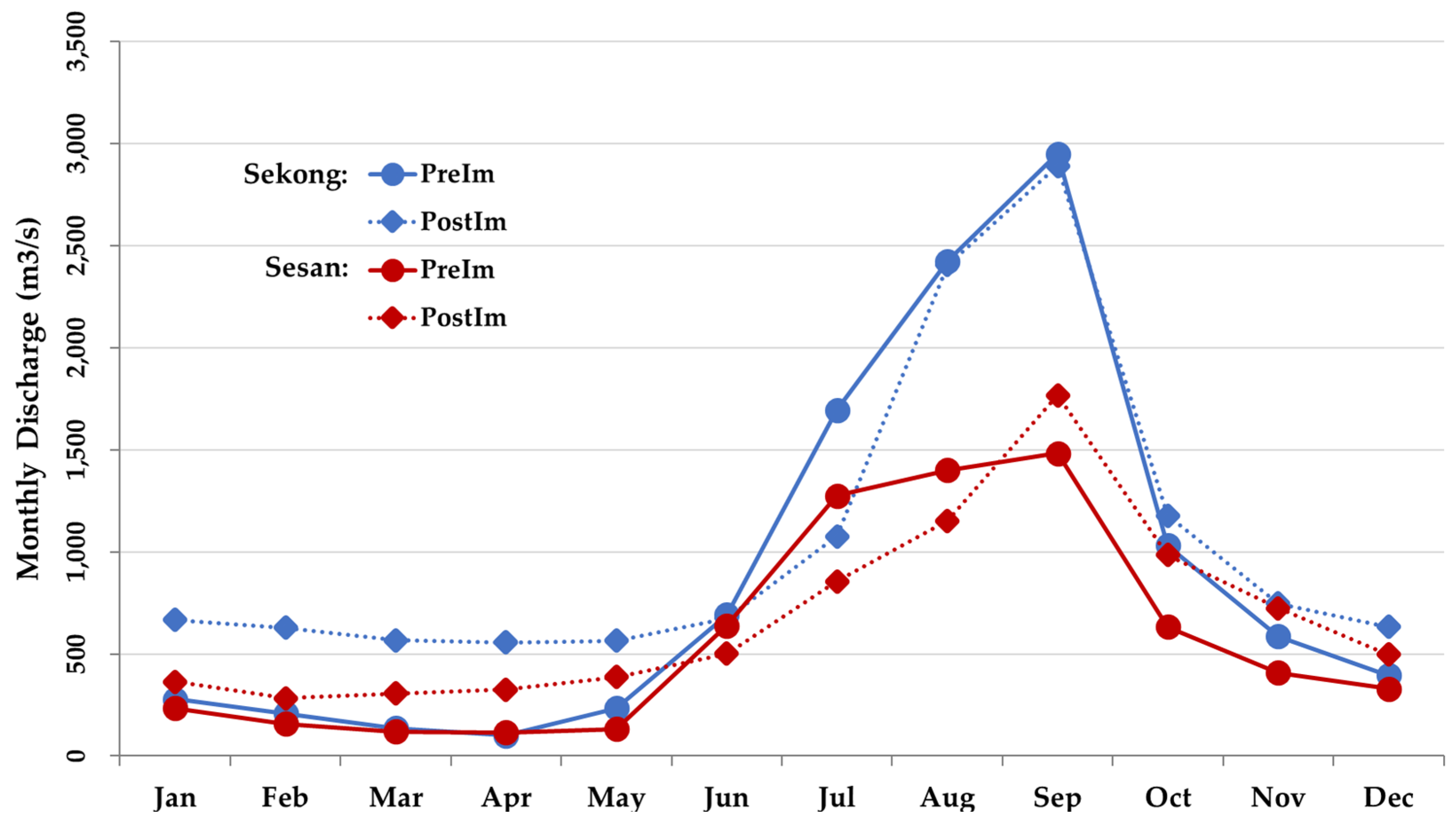
| Month | Sekong | Sesan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre- (m3/s) | Post- (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) |
Degree of Change | Pre- (m3/s) | Post- (m3/s) | Relative Change (%) |
Degree of Change | ||
| Nov | 586 | 747 | 27 | Low | 408 | 723 | 77 | High | |
| Dec | 396 | 632 | 60 | Medium | 330 | 496 | 50 | Medium | |
| Jan | 278 | 667 | 140 | High | 234 | 364 | 55 | Medium | |
| Feb | 209 | 627 | 200 | High | 157 | 284 | 81 | High | |
| Mar | 136 | 567 | 315 | High | 119 | 305 | 156 | High | |
| Apr | 100 | 557 | 457 | High | 116 | 326 | 181 | High | |
|
Dry Season Mean ±SD |
284 ±182 |
633 ±70 |
200 ±163 |
High |
227 ±120 |
416 ±168 |
100 ±55 |
High | |
| May | 234 | 565 | 142 | High | 133 | 387 | 191 | High | |
| Jun | 692 | 675 | -3 | Low | 640 | 501 | -21 | Low | |
| Jul | 1,695 | 1,075 | -37 | Medium | 1,275 | 855 | -33 | Low | |
| Aug | 2,425 | 2,406 | -1 | Low | 1,400 | 1,151 | -18 | Low | |
| Sep | 2,950 | 2,891 | -2 | Low | 1,482 | 1,766 | 19 | Low | |
| Oct | 1,032 | 1,178 | 14 | Low | 633 | 986 | 56 | Medium | |
|
Wet Season Mean ±SD |
1,505±1,046 |
1,465 ±958 |
18.8 ±63 |
Low |
927 ±539 |
941 ±497 |
32 ±84 |
Low | |
|
Annual Mean ±SD |
894±958 |
1,049 ±780 |
109 ±151 |
High |
557 ±522 |
679 ±447 |
66 ±77 |
High | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





