Submitted:
24 May 2024
Posted:
24 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- A new eye tracking dataset entirely based on real event camera footage is established and manually annotated. The dataset contains a total of 365 screened event point sequences with labels, covering various scenarios like different eyes, lighting conditions, and eye movement trajectories.
- A novel eye tracking algorithm combining SNN with event camera is designed, better suited to handle the asynchronous incremental output of event camera than ANN, increasing stability while maintaining accuracy.
- The proposed solution is validated on the custom dataset, achieving a maximum time resolution of approximately 0.081ms and increasing results in tracking accuracy compared to ANNs.
2. Methods
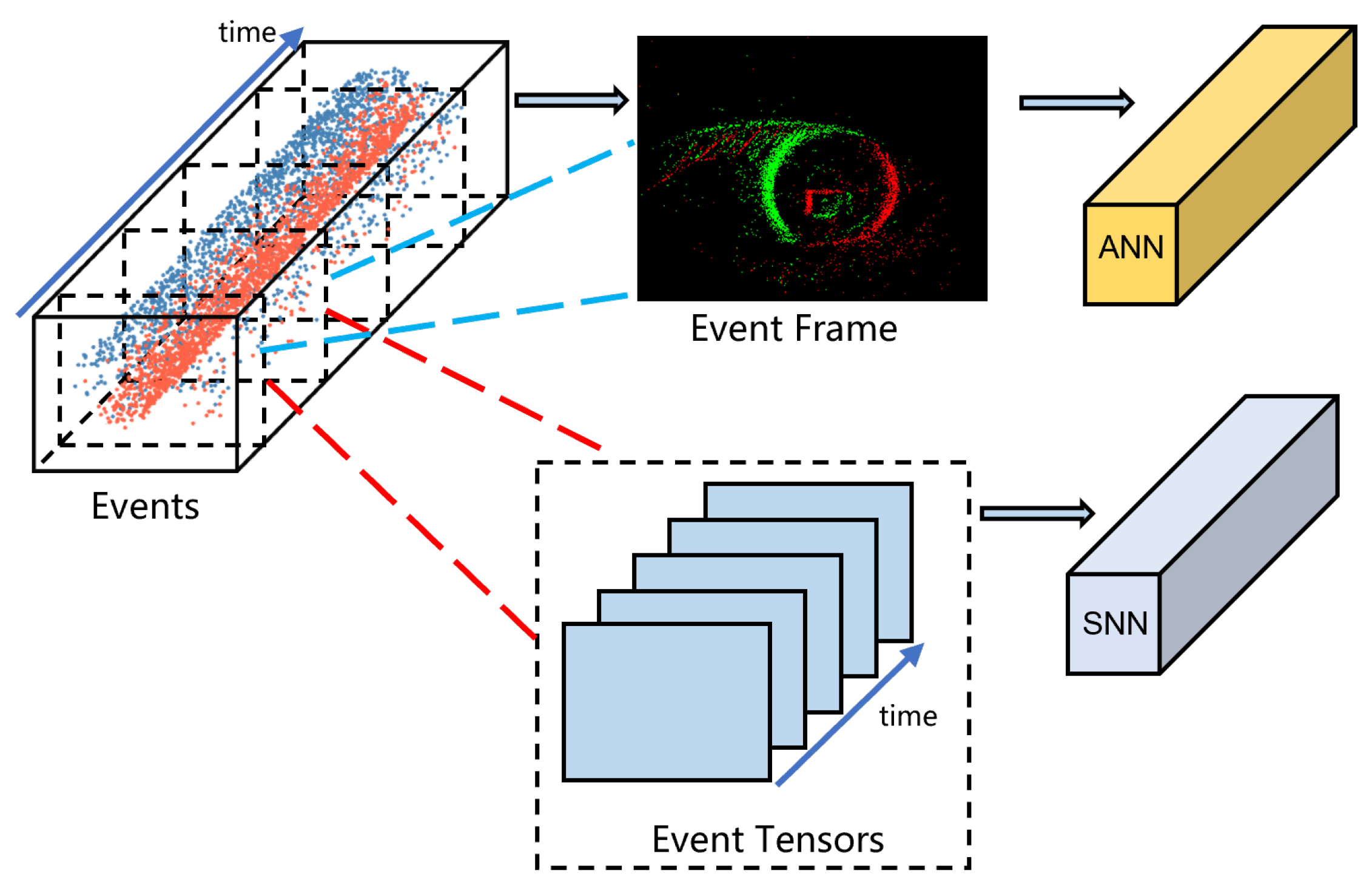
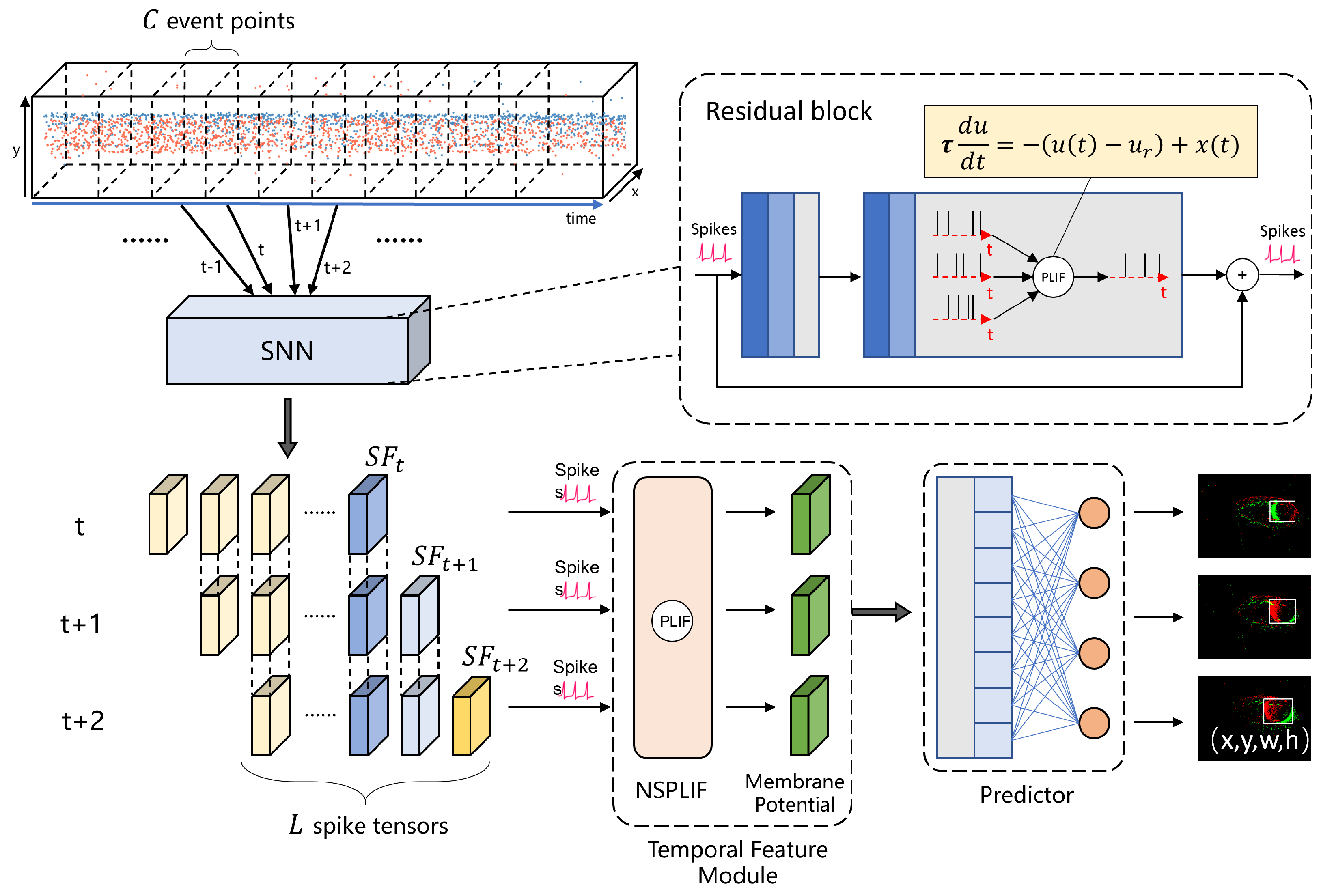
2.1. Event Data Representation
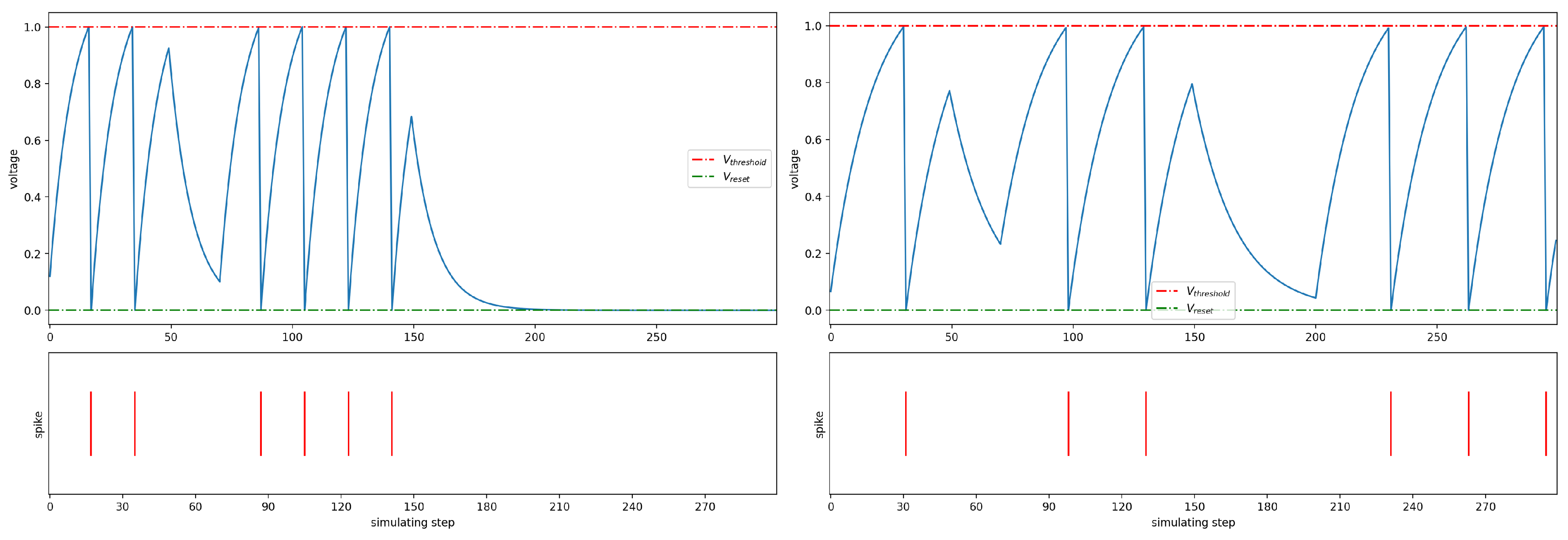
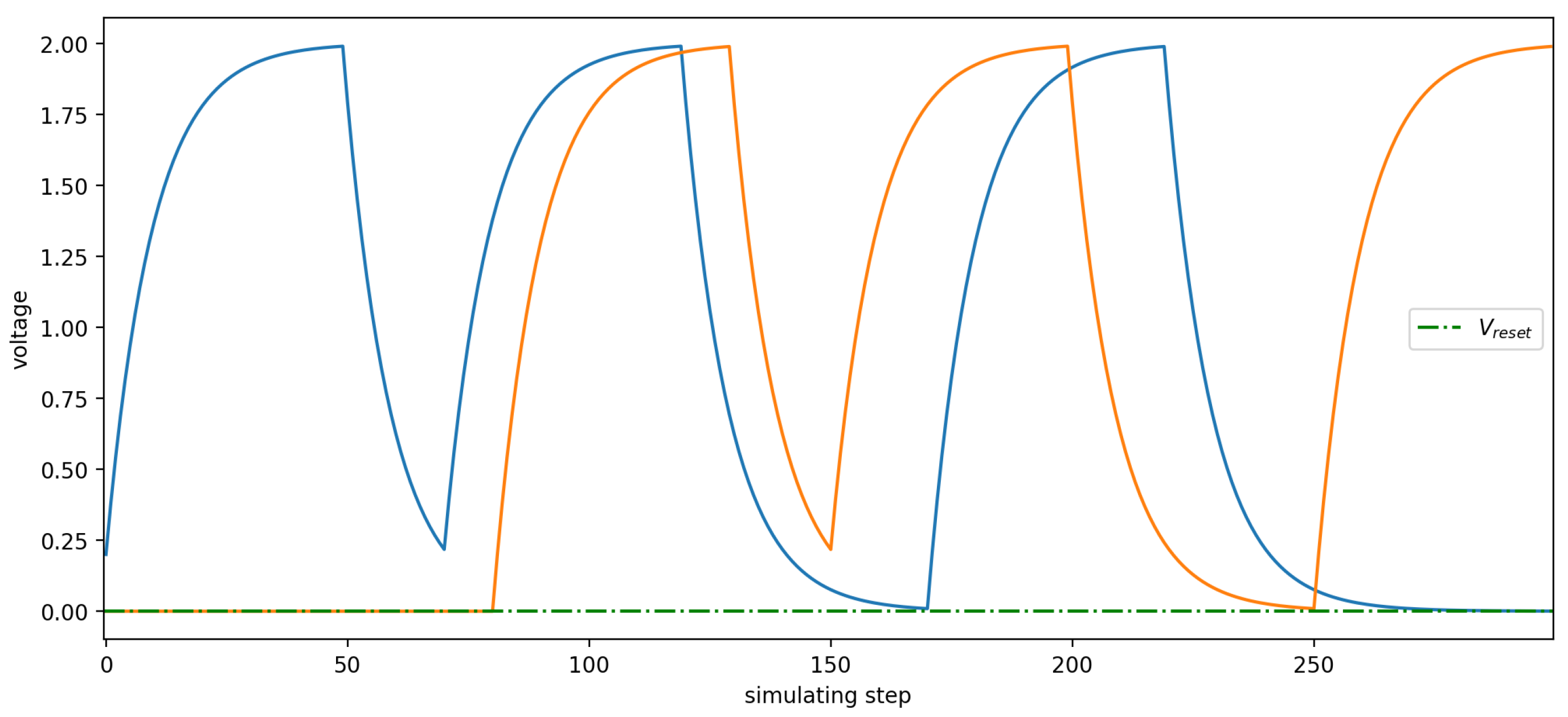
2.2. Eye Tracking Based on Spiking Neuron Network
3. Dataset
3.1. Device Setup
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Labeling
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Training Setup
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
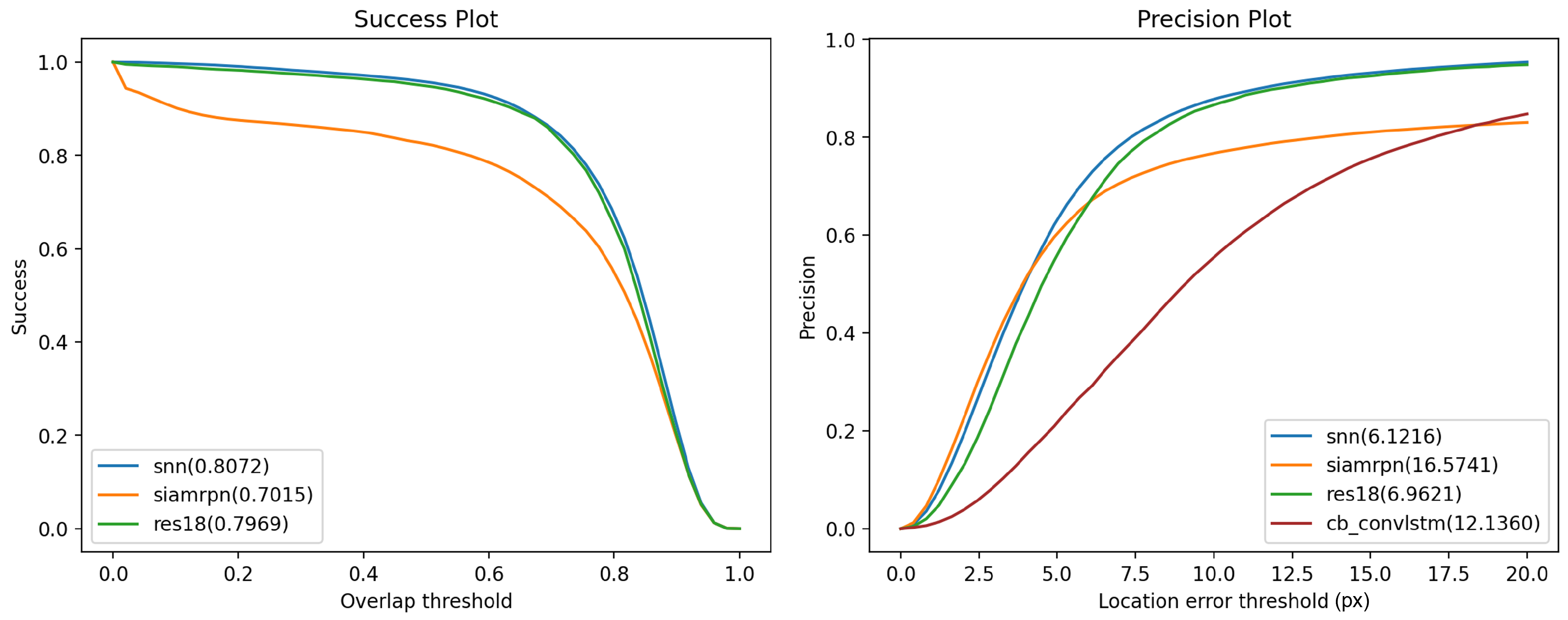
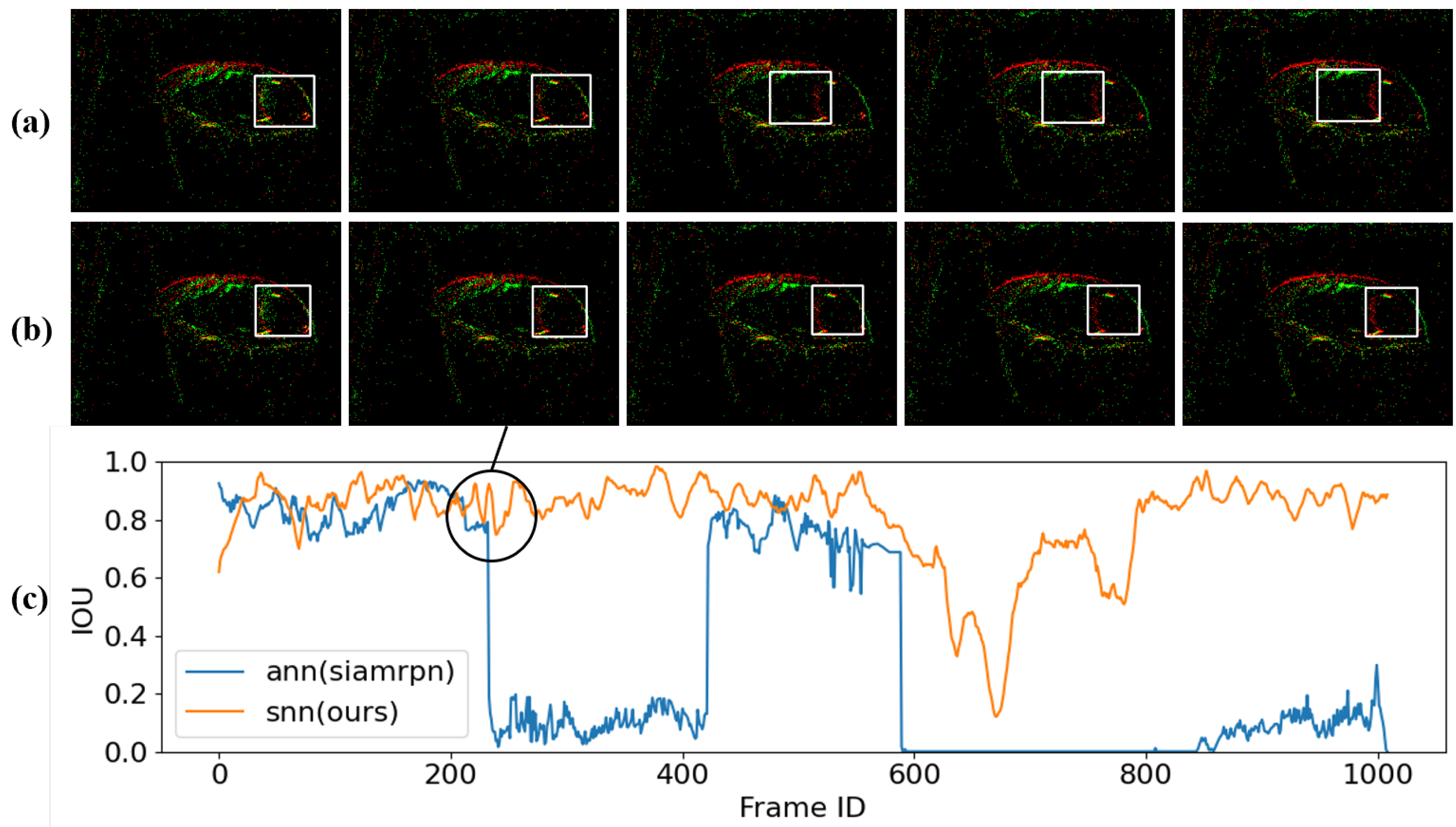
4.3. Performance
| Network | Average IoU↑ | Average PE↓ |
|---|---|---|
| SiamRPN | 0.7015 | 16.5741 |
| CB-ConvLSTM [9] | - | 12.1360 |
| ResNet18 | 0.7969 | 6.9621 |
| SNN(ours) | 0.8072 | 6.1216 |
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poletti B, Solca F, Carelli L, et al. Association of Clinically Evident Eye Movement Abnormalities With Motor and Cognitive Features in Patients With Motor Neuron Disorders. Neurology, 2021, 97, e1835–e1846. [Google Scholar]
- Diao Y, Geng M, Fu Y, et al. A combination of P300 and eye movement data improves the accuracy of auxiliary diagnoses of depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 2022, 297, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covers M L V, De Jongh A, Huntjens R J C, et al. Early intervention with eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy to reduce the severity of post-traumatic stress symptoms in recent rape victims: a randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 2021, 12, 1943188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhanom I B, MacNeilage P, Folmer E. Eye Tracking in Virtual Reality: a Broad Review of Applications and Challenges. Virtual Reality, 2023, 27, 1481–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li N, Bhat A, Raychowdhury A. E-Track: Eye Tracking with Event Camera for Extended Reality (XR) Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), 2023; pp. 1-5.
- Plopski A, Hirzle T, Norouzi N, et al. The Eye in Extended Reality: A Survey on Gaze Interaction and Eye Tracking in Head-worn Extended Reality. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55, 53:1–53:39. [Google Scholar]
- Google Research. MediaPipe Iris: Real-time iris tracking and depth estimation. Retrieved from https://research.google/blog/mediapipe-iris-real-time-iris-tracking-depth-estimation/.
- Qiu H, Li Z, Yang Y, Xin C, and Bian G. Real-Time Iris Tracking Using Deep Regression Networks for Robotic Ophthalmic Surgery. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 50648–50658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Q, Wang Z, Liu S C, et al. 3ET: Efficient Event-based Eye Tracking using a Change-Based ConvLSTM Network. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao G, Yang Y, Liu J, et al. EV-Eye: Rethinking High-frequency Eye Tracking through the Lenses of Event Cameras. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2023, 36, 62169–62182. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos A N, Martel J N P, Kohli A P, et al. Event-Based Near-Eye Gaze Tracking Beyond 10,000 Hz. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2021, 27, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffregen T, Daraei H, Robinson C, et al. Event-Based Kilohertz Eye Tracking using Coded Differential Lighting. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, IEEE, 2022; pp. 3937-3945.
- Kagemoto T, Takemura K. Event-Based Pupil Tracking Using Bright and Dark Pupil Effect. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New York, NY, USA, Association for Computing Machinery, 2023; pp. 1-3.
- Feng Y, Goulding-Hotta N, Khan A, et al. Real-Time Gaze Tracking with Event-Driven Eye Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), 2022; pp. 399-408.
- SHI X, Chen Z, Wang H, et al. Convolutional LSTM Network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems: Vol. 28, Curran Associates, Inc., 2015.
- Maass, W. Networks of spiking neurons: The third generation of neural network models. Neural Networks, 1997, 10, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao Y, Chen Y, Khosla D. Spiking Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Energy-Efficient Object Recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 113, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neftci E O, Mostafa H, Zenke F. Surrogate Gradient Learning in Spiking Neural Networks: Bringing the Power of Gradient-Based Optimization to Spiking Neural Networks. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee J H, Delbruck T, Pfeiffer M. Training Deep Spiking Neural Networks Using Backpropagation. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2016, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y, Yu Z, Wang S, et al. Spike-Based Motion Estimation for Object Tracking Through Bio-Inspired Unsupervised Learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji M, Wang Z, Yan R, et al. SCTN: Event-based object tracking with energy-efficient deep convolutional spiking neural networks. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2023, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y, Xu M, Yuan C, et al. SiamSNN: Siamese Spiking Neural Networks for Energy-Efficient Object Tracking. In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2021, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021; pp. 182-194.
- Yang Z, Wu Y, Wang G, et al. DashNet: A Hybrid Artificial and Spiking Neural Network for High-speed Object Tracking. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hagenaars J, Paredes-Valles F, de Croon G. Self-Supervised Learning of Event-Based Optical Flow with Spiking Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems: Vol. 34, Curran Associates, Inc., 2021; pp. 7167-7179.
- Zhu L, Wang X, Chang Y, et al. Event-based Video Reconstruction via Potential-assisted Spiking Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, IEEE, 2022; pp. 3584-3594.
- Zhang J, Dong B, Zhang H, et al. Spiking Transformers for Event-based Single Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, IEEE, 2022; pp. 8791-8800.
- Hu Y, Liu S C, Delbruck T. v2e: From Video Frames to Realistic DVS Events. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, 2021; pp. 1312-1321.
- Gehrig D, Gehrig M, Hidalgo-Carrio J, et al. Video to Events: Recycling Video Datasets for Event Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, IEEE, 2020; pp. 3583-3592.
- Rebecq H, Gehrig D, Scaramuzza D. ESIM: an Open Event Camera Simulator. In Proceedings of The 2nd Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, 2018; pp. 969-982.
- Fang W, Yu Z, Chen Y, et al. Deep Residual Learning in Spiking Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems: Vol. 34, Curran Associates, Inc., 2021; pp. 21056-21069.
- Fang W, Yu Z, Chen Y, et al. Incorporating Learnable Membrane Time Constant to Enhance Learning of Spiking Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, IEEE, 2021; pp. 2641-2651.
- Brunel N, Latham P E. Firing Rate of the Noisy Quadratic Integrate-and-Fire Neuron. Neural Computation, 2003, 15, 2281–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu Y, Wang Z, Li Z, Yuan Y, and Yu G. SiamFC++: Towards Robust and Accurate Visual Tracking with Target Estimation Guidelines. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 34, no. 0707 (2020): 12549–12556.
- Fang W, Chen Y, Ding J, et al. SpikingJelly: An open-source machine learning infrastructure platform for spike-based intelligence. Science Advances, 2023, 9, eadi1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MMTracking Contributors. MMTracking: OpenMMLab video perception toolbox and benchmark. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking, 2020.
- Li B, Yan J, Wu W, et al. High Performance Visual Tracking with Siamese Region Proposal Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, IEEE, 2018; pp. 8971-8980.
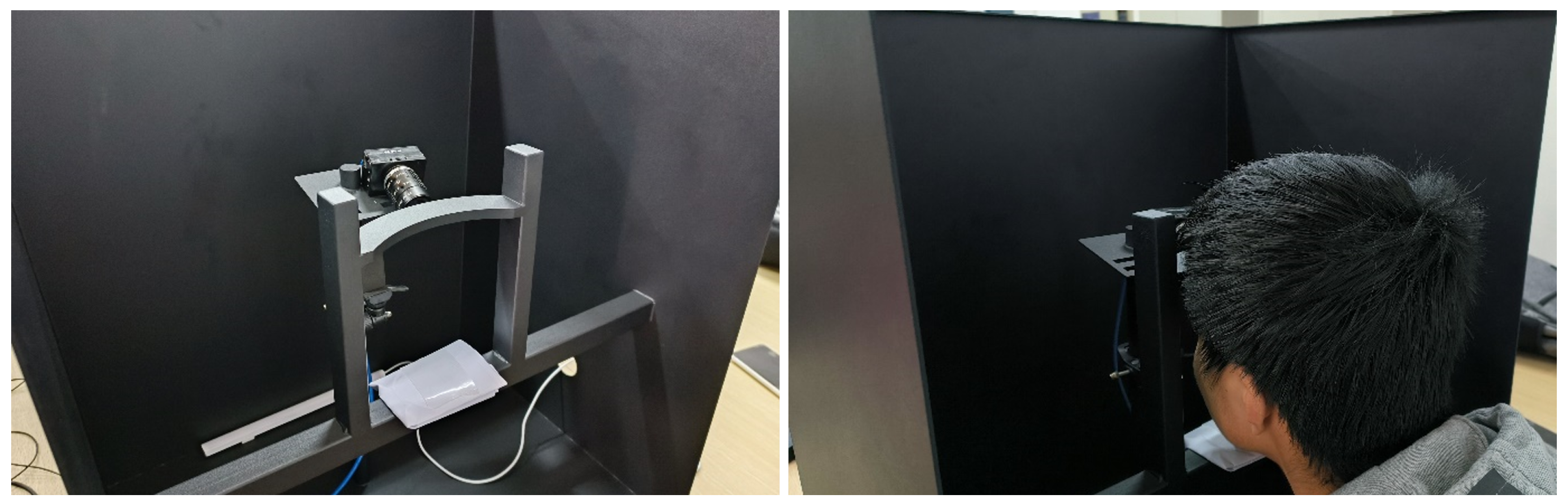


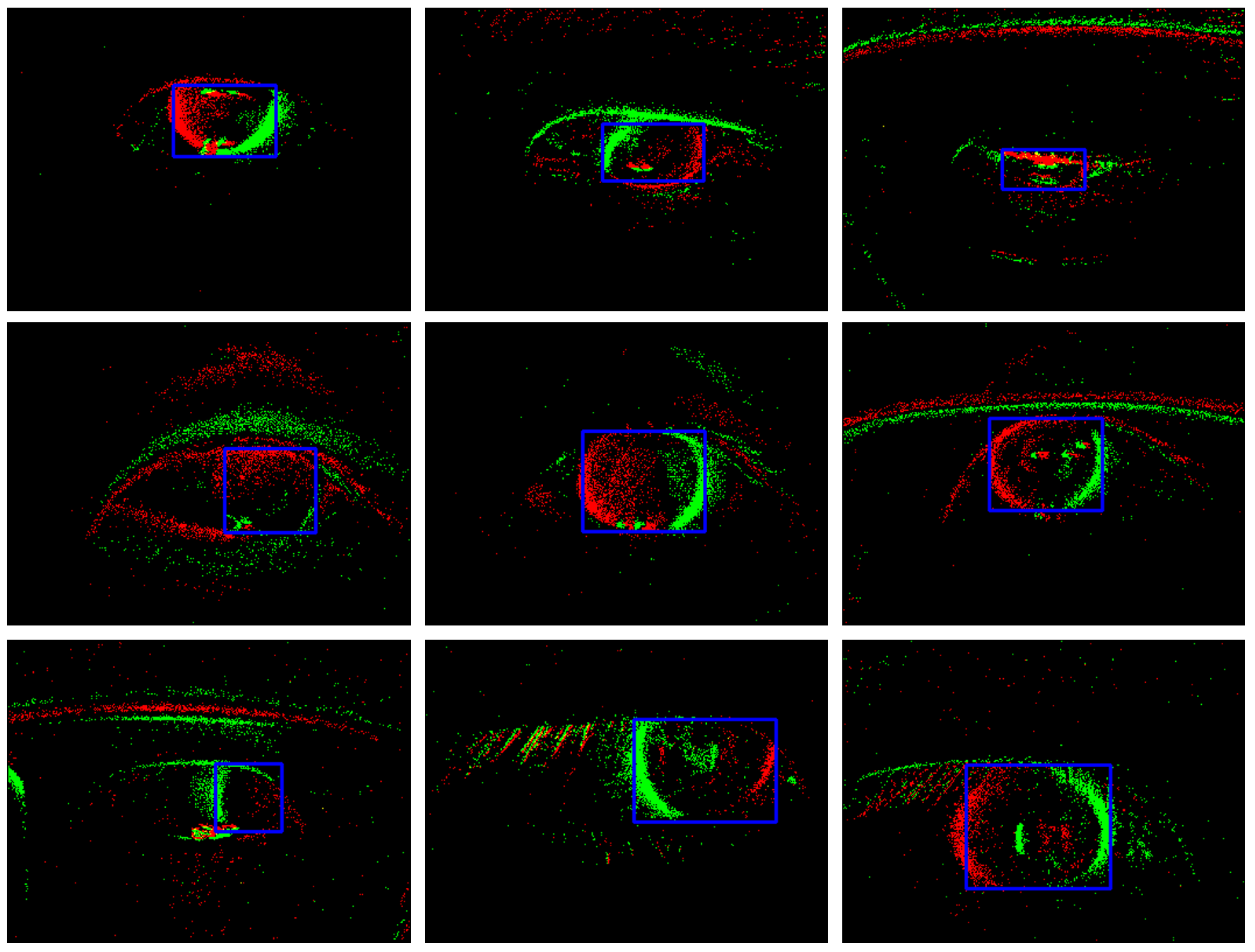
| Condition | Number |
|---|---|
| wearing glasses | 22 |
| low light | 29 |
| natural light | 48 |
| internal light | 26 |
| zero value percentage | Average IoU (without zero value) | Average IoU |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 0.7996 | 0.7676 |
| 30% | 0.7915 | 0.6838 |
| 40% | 0.7892 | 0.6406 |
| Temporal Feature Module | C/L | Average IoU↑ | Average PE↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSPLIF | 4000/1 | 0.6546 | 12.6459 |
| 2000/2 | 0.7727 | 7.9599 | |
| 1000/4 | 0.7980 | 6.7475 | |
| 800/5 | 0.7992 | 6.5223 | |
| 500/8 | 0.8072 | 6.1216 | |
| 400/10 | 0.7893 | 7.5871 | |
| 250/16 | 0.7739 | 7.7990 | |
| Spiking Rate | 4000/1 | 0.7095 | 10.7267 |
| 2000/2 | 0.7121 | 10.2529 | |
| 1000/4 | 0.7382 | 9.0034 | |
| 800/5 | 0.7197 | 10.1972 | |
| 500/8 | 0.7595 | 8.2062 | |
| 400/10 | 0.7512 | 9.1113 | |
| 250/16 | 0.7348 | 9.2386 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





