Submitted:
16 May 2024
Posted:
17 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Rabies Diagnosis
2.3. Antigenic Characterization
2.4. Viral RNA Extraction
2.5. RT-PCR and Sequencing
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Geographic Data
2.8. Regression Analysis
3. Results
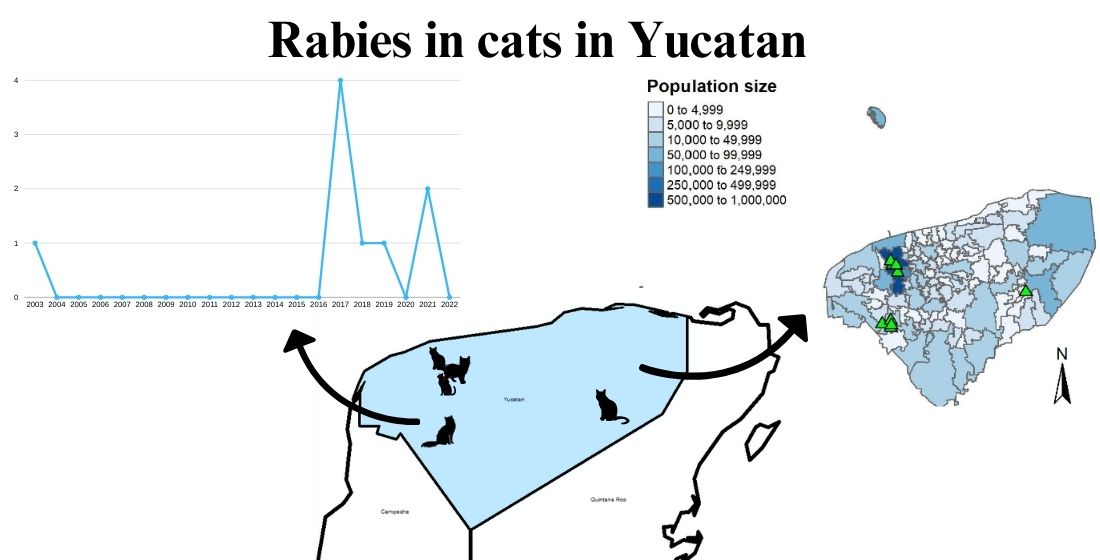
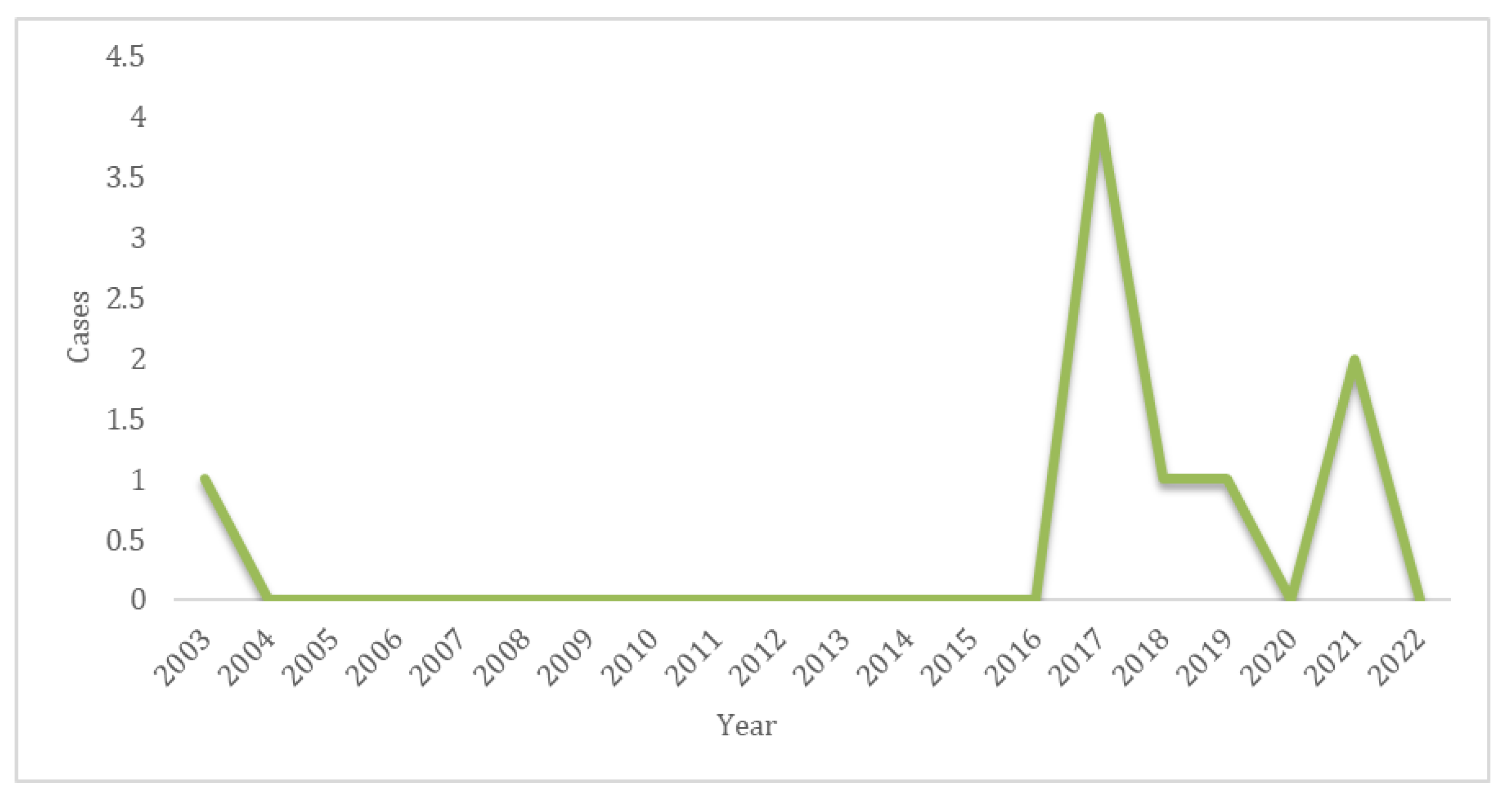
3.1. Rabies Diagnoses
3.2. Antigenic Characterization
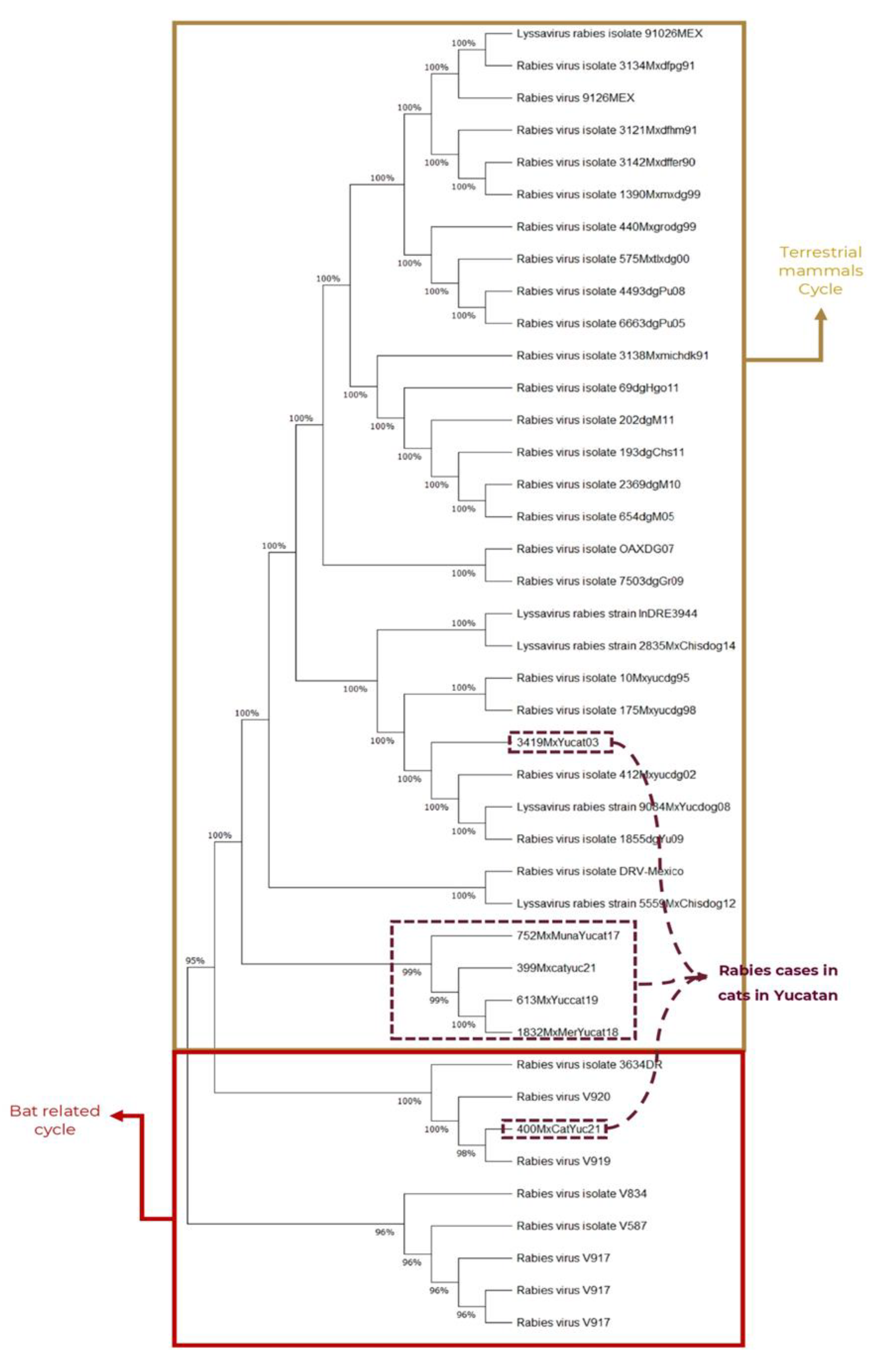
3.3. Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis
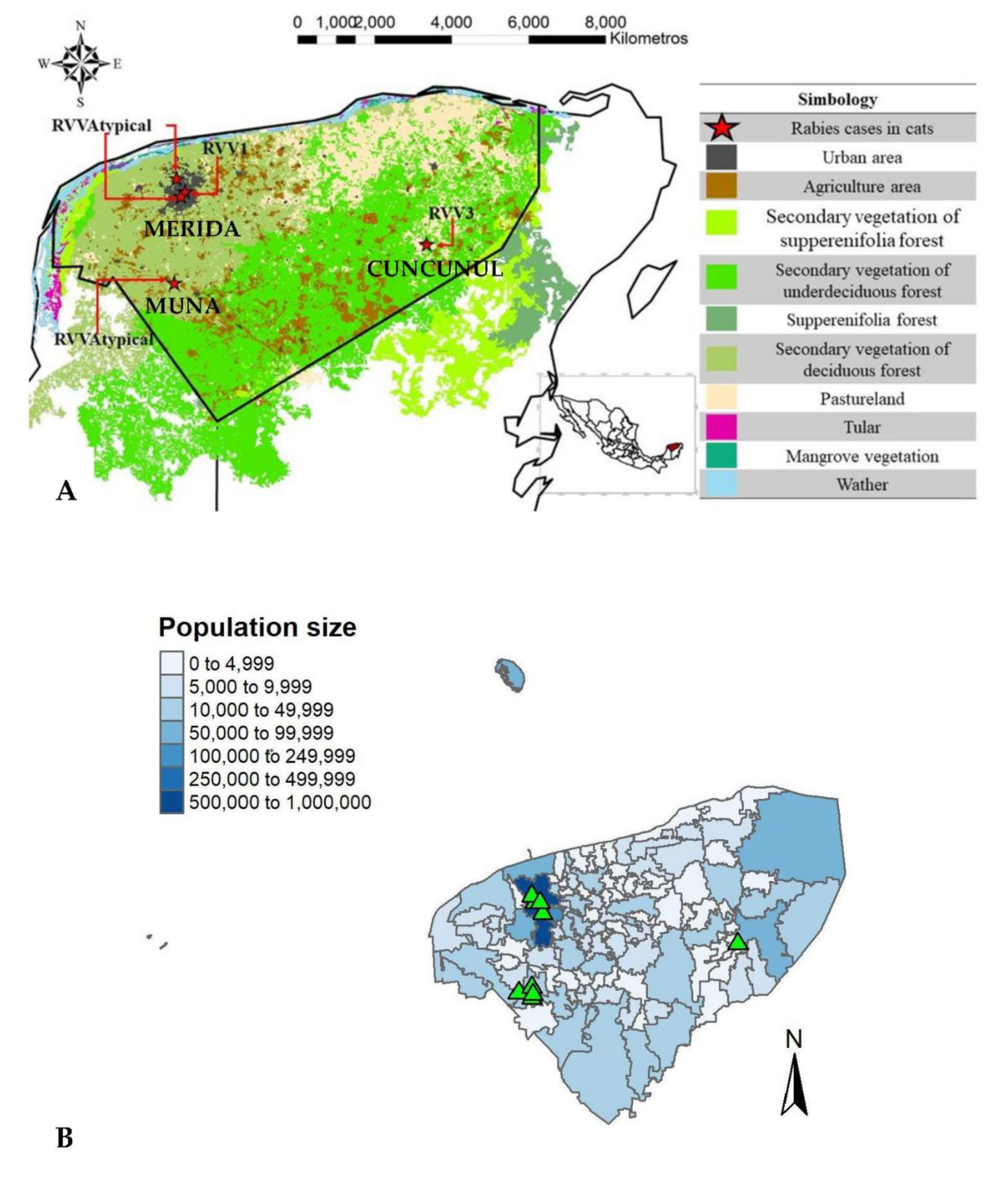
3.4. Geographical Data
3.4.1 Spatial Distribution of Cat Rabies Cases
3.5. Risk Factors for Feline Rabies Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franka, R., Smith, T.G.; Dyer, J.L.; Wu, X.; Niezgoda M.; Rupprecht C.E. Current and future tools for global canine rabies elimination Antiviral Res. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.M.; Gilbert, A.; Slate, D.; Chipman, R; Singh, A.; Cassie, W., et al. Right place, wrong species: a 20-year review of rabies virus cross species transmission among terrestrial mammals in the United States. PLoS One. 2014, 9(10):e107539. [CrossRef]
- Marston D.A, Banyard A.C., McElhinney, L.M., Freuling, C.M., Finke, S., de Lamballerie X, et al. The lyssavirus host-specificity conundrum-rabies virus-the exception not the rule. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 28:68–73.
- Bonnaud, E.M.; Troupin, C.; Dacheux, L.; Holmes, E.; Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Tanguy, M.; et al. Comparison of intra- and inter-host genetic diversity in rabies virus during experimental cross-species transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15(6):e1007799. [CrossRef]
- Mollentze, N.; Streicker, D.G.; Murcia, P.R.; Hampson, K.; Biek, R. Virulence Mismatches in Index Hosts Shape the Outcomes of Cross-Species Transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28859–28866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquot, M., Wallace, M.A, Streicker, D.G., Biek, R. Geographic Range Overlap Rather than Phylogenetic Distance Explains Rabies Virus Transmission among Closely Related Bat Species. Viruses. 2022, 14(11):2399. [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.A. and Bateman, P.W. Novel predation opportunities in anthropogenic landscapes. Anim. Behav. 2018, 138: 145–55. [CrossRef]
- Guiden, P.W., Bartel, S.L., Byer, N.W., Shipley, A.A., Orrock, J.L. Predator-Prey Interactions in the Anthropocene: Reconciling Multiple Aspects of Novelty. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34(7):616-627. [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht C.E. 2023. Rabies in animals in: MSD Veterinary Manual. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. https://www.msdvetmanual.com/nervous-system/rabies/rabies-in-animals?query=Rabies%20in%20animals accessed January 24 ,2024.
- Grobbelaar, A.A.; Blumberg, L.H.; Dermaux-Msimang, V.; Le Roux, C.A.; Moolla, N.; Paweska, J.T., et al. Human rabies associated with domestic cat exposures in South Africa, 1983-2018. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2020, 91:e1–4. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.; Staudacher, C.; Martins, C.M.; Ullmann, L.S.; Ferreira, F.; Araujo, J.P.J, et al. Bat rabies surveillance and risk factors for rabies spillover in an urban area of Southern Brazil. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14:173. [CrossRef]
- Brunt, S.; Solomon, H.; Brown, K.; Davis, A. Feline and Canine Rabies in New York State, USA. Viruses 2021, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, D.J.; Cove, M.V.; McShea, W.J.; Decker, S.; Flockhart, D.T.T.; Moore, S.M. and Gallo, T. Spatial and temporal overlap of domestic cats (Felis catus) and native urban wildlife. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10:1048585. [CrossRef]
- SIRVERA Regional Information System for Epidemiological Surveillance of Rabies 2024. https://sirvera.panaftosa.org.br/ accessed January 24, 2024.
- Ellis, R. and Ellis C. Dog and cat bites. Am. Fam. Physician. 2014, 90(4): 239-243.
- Rupprecht C.E. 2022. Rabies in cats. MSD Veterinary Manual. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. https://www.msdvetmanual.com/cat-owners/brain,-spinal-cord,-and-nerve-disorders-of-cats/rabies-in-cats. Accessed: January 24, 2024.
- INEGI https://www.inegi.org.mx/ Accesed January 24, 2024.
- Secretaría de Salud, 285. México alcanza 15 años sin registro de casos de rabia humana transmitida por perro. gob.mx. https://www.gob.mx/salud/prensa/285-mexico-alcanza-15-anos-sin-registro-de-casos-de-rabia-humana-transmitida-por-perro Accesed on January 24, 2024.
- SNMF, National Forest Monitoring System DEFORESTACIÓN. 2022. Accesed: January 20, 2024, de https://snmf.cnf.gob.mx/deforestacion/.
- CONAFOR, National Forestry Commission Deforestación bruta a nivel estatal en el periodo 2001 al 2021. (2022). https://tableros_snmf.cnf.gob.mx/deforestacion_estatal Accesed: January 20, 2024.
- Chiappy C, Gama L. Modifications and fragmentation of tropical geocomplexes of the Yucatan Peninsula. Universidad y Ciencia Num Esp I. 2004, 17–25.
- Daszak, P., Cunningham, A.A., Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife--threats to biodiversity and human health. Science. 2000, 21;287(5452):443-9. Erratum in: Science 2000, 10;287(5459):1756. [CrossRef]
- OHHLEP, One Health High-Level Expert Panel Adisasmito WB, Almuhairi S, Behravesh CB, Bilivogui P, Bukachi SA, et al. One Health: A new definition for a sustainable and healthy future. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18(6): e1010537. [CrossRef]
- Dean, D.J.; Abelseth, M.K.; Atanasiu, W. The fluorescent antibody test. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies; Meslin, F.-X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.;World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 88–95.
- Smith, J.S. Rabies virus epitopic variation: use in ecologic studies. Adv. Virus Res. 1989, 36, 215–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Seidel, H.D.; Warner, C.K. Epidemiologic and historical relationships among 87 rabies virus isolates as determined by limited sequence analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 166, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.M.; Papo, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Smith, J.S. Antigenic analysis of rabies-virus isolates from Latin America and the Caribbean. J. Vet. Intern. Med., Series B. 1994, 41(1-10), 153-160. [CrossRef]
- McQuiston, J.H.; Yager, P.A.; Smith, J.S.; Rupprecht, C.E. Epidemiologic characteristics of rabies virus variants in dogs and cats in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 1939–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markotter, W.; Kuzmin, I.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Randles, J.; Sabeta, C.T.; Wandeler, A.I.; Nel, L.H. Isolation of Lagos bat virus from water mongoose. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Yolken, R.H.; Morgan, D.R. Manual of Clinical Microbiology (6th ed). Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids. Symp. 1999, Ser. 41:95-98.
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215(3), 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar. S., Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35:1547-1549. [CrossRef]
- CONEVAL 2020 .National Council for the Evaluation of Social Development Policy. https://www.coneval.org.mx/Medicion/IRS/Paginas/Indice_Rezago_Social_2020. aspx Accesed on April 29, 2024.
- SEMARNAT Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources 2024 https://apps1.semarnat.gob.mx:8443/dgeia/informe18/tema/cap3.html Accesed on April 23, 2024.
- Bautista, F., Frausto, O., Ihl, T., Aguilar Y. An update soil map of The Yucatan State, Mexico: Geomorphopedological approach and WRB. Ecosist. y Rec.Agro. 2015. 2(6):303-315.
- CONABIO 2024. National Commission for the Knowledge and Use of Biodiversity. www.conabio.gob.mx Accesed on May 14, 2024.
- Cunningham, A.A., Daszak, P., Wood, J.L.N. One Health, emerging infectious diseases and wildlife: two decades of progress? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2017, 372:20160167. [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.C.; Genaro, G. Comportamento exploratòrio em gatos domésticos (Felis silvestris catus Linnaeus, 1758): uma revisão. Archit. Vet. Sci. 2010, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyd, K. A. T.; Hernandez, S. M.; Carroll, J. P.; Abernathy, K.J.; Marshall, G. J. Quantifying free-roaming domestic cat predation using animal-borne video cameras. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 160, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberg, O. Food Habits and Prey Impact by Feral and House-Based Domestic Cats in a Rural Area in Southern Sweden. J. Mammal.1984, 65(3):424-432.
- Molsher, R.; Newsome, A.; Dickman, C.R. Feeding ecology and population dynamics of the feral cat in relation to the availability of prey in central-eastern New SouthWales. Wildl.Res. 1999, 26, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillotto, L.; Serangeli, M.T.; Russo, D. Curiosity killed the bat: Domestic cats as bat predators. Mamm. Biol. 2013, 78, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.N. and Leppanen C. The threat of invasive species to bats: a review. Mamm. Rev. 2017, 47 (4): 277-290. [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S., Browne, M., Boudjelas, S., De Poorter, M. 2004. 100 of the World’s worst invasive alien species. A selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) a specialist group of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the World Conservation Union (IUCN).
- Loss, Scott R. Will, Tom, Marra, Peter P. The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States. Nat. Comm. 2013, 4(1). [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.S., Glen, A.S., Nimmo, D.G., Ritchie, E.G., Dickman, C.R. Invasive predators and global biodiversity loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2016, 113(40):11261-11265. [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J. S., & Temple, S. A. Rural Residents’ Free-Ranging Domestic Cats: A Survey. Wildl. Soc. B. 1993, 21(4), 381–390. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3783408.
- Lepczyk, C.A.; Mertig, A.G.; Liu, J. Landowners and cat predation across rural to- urban landscapes. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 115, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M., Mcdonald, R.A, and Harris, S. Predation of wildlife by domestic cats Felis catus in Great Britain. Mammal. Review 2003, 33(2)0305-1838. [CrossRef]
- Natoli, E. Spacing pattern in a colony of urban stray cats (Felis catus L.) in the historic center of Rome. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1985, 14, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves F, Galetti M, Streicker DG. Management of vampire bats and rabies: a precaution for rewilding projects in the neotropics. Perspec.t Ecol. Conserv. 2021;19:37–42. [CrossRef]
- Schneider MC, Aron J, Santos-Burgoa C, Uieda W, Ruiz-Velazco S. Common vampire bat attacks on humans in a village of the Amazon region of Brazil. Cad. Saude Publ. 2001, 17:1531–1536. [CrossRef]
- Schneider MC, Romijn PC, Uieda W, Tamayo H, da Silva DF, Belotto A, da Silva JB, Leanes LF. Rabies transmitted by vampire bats to humans: an emerging zoonotic disease in Latin America? Rev Panam Salud Publ. 2009, 25:260–269. [CrossRef]
- Delpietro HA, Lord RD, Russo RG, Gury-Dhomen F. Observations of sylvatic rabies in northern Argentina during outbreaks of paralytic cattle rabies transmitted by vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus) J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45:1169–1173. [CrossRef]
- Favoretto SR, Carrieri ML, Cunha EMS, Aguiar EAC, Silva LHQ, Sodré MM, Souza MCAM, Kotait I. Antigenic typing of Brazilian rabies virus samples isolated from animals and humans, 1989–2000. Rev. Inst. Med. Tro.p Sao Paulo. 2002, 44:91–95. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi Y, Sato G, Shoji Y, Sato T, Itou T, Cunha EMS, Samara SI, Carvalho AAB, Nociti DP, Ito FH, Sakai T. Molecular epidemiological analysis of bat rabies viruses in Brazil. J. Vet Med Sci. 2005, 67:647–652. [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ayala, F.; Aréchiga-Ceballos, N.; Ortiz-Alcántara, J.M.; González-Durán, E.; Pérez-Agüeros, S.I.; Méndez-Tenorio, A.; Torres-Longoria, B.; López-Martínez, I.; Hernández-Rivas, L.; Díaz-Quiñonez, J.A.; Ramírez-González, J.E. Molecular characterization of atypical antigenic variants of canine rabies virus reveals its reintroduction by wildlife vectors in southeastern Mexico. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162(12):3629-3637. [CrossRef]
- Puebla-Rodríguez, P.; Almazán-Marín, C.; Garcés-Ayala, F.; Rendón-Franco, E.; Chávez-López., S.; Gómez-Sierra, M.; Sandoval-Borja, A.; Martínez-Solís, D.; Escamilla-Ríos, B.; Sauri-González, I.; Alonzo-Góngora, A.; López-Martínez, I.; Aréchiga-Ceballos, N. Rabies virus in white-nosed coatis (Nasua narica) in Mexico: What do we know so far?.Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10:1090222. [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.; Lennox, G.D.; Ferreira, J;, Berenguer, E.; Lees, A.C.; Nally, R.M.; Thomson, J.R.; de Ferraz, S.F.B.; Louzada, J.; Oliveira, V.H.; Parry, L.; de Castro, R.; Solar, R.; Vieira, I.C.G.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Begotti, R.A.; Braga, R.F.; Cardoso, T.M.; de Oliveira, R.C, Souza, C.M. Jr.; Moura, N.G.; Nunes, S.S.; Siqueira, J.V.; Pardini, R.; Silveira, J.M.; Vaz-de-Mello, F.Z.; Veiga, .RC.S.; Venturieri, A.; Gardner, T.A. Anthropogenic disturbance in tropical forests can double, biodiversity loss from deforestation. Nature. 2016, 535:144–147. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Klein, G. K, Siebert, S.; Lightman, D.; Ramankutty, N. Anthropogenic transformation of the biomes, 1700 to 2000. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19:589–606. [CrossRef]
- Grantham, H.S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T.D.; Jones, K.R.; Beyer, H.L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J.C.; Robinson, J.G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H.M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P.R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P;, Goldman, E., Goetz, S., Hansen, A., Hofsvang, E., Jantz, P., Jupiter, S., Kang, A., Langhamme,r P., Laurance, W.F., Lieberman, S., Linkie, M., Malhi, Y., Maxwell, S., Mendez, M., Mittermeier, R., Murray, N.J., Possingham, H., Radachowsky, J., Saatchi, S., Samper, C., Silverman, J., Shapiro, A., Strassburg, B., Stevens, T., Stokes, E., Taylor, R., Tear, T., Tizard, R., Venter, O., Visconti, P., Wang, S., Watson, J.E.M. Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11:5978. [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, J.; Ahnström, J.; Weibull, A.C. The effects of organicagriculture on biodiversity and abundance: a meta-analysis. J .Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42:261–269. [CrossRef]
- Bellard, C.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Leadley, P.; Thuiller, W.; Courchamp, F. Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15:365–377. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A., Mooers, A.O. Terrestrial vertebrate biodiversity loss under future global land use change scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10:2764. [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U., Adair, E.C., Cardinale, B.J., Byrnes, J.E., Hungate, B.A., Matulich, K.L., Gonzalez, A., Duffy, J.E., Gamfeldt, L., O’Connor, M.I. A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature. 2012, 486(7401):105-8. [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.A.; Sampaio, G.; Borma, L.S.; Castilla-Rubio, J.C.; Silva, J.S.; Cardoso, M. Land-use and climate change risks in the Amazon and the need of a novel sustainable development paradigm. Proc. Natl .Acad. Sci. USA. 2016, 113:10759–10768. [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Baldi, G.; Hirota, M., Syktus, J.; McAlpine, C. Land use and land cover change impacts on the regional climate of non-Amazonian South America: a review. Glob. Planet. Change. 2015, 128:103–119. [CrossRef]
- Mshelbwala, P.P.J., Soares Magalhães, R., Weese, J.S., Ahmed, N.O., Rupprecht, C.E., Clark, N.J. Modelling modifiable factors associated with the probability of human rabies deaths among self-reported victims of dog bites in Abuja, Nigeria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023 21;17(2):e0011147. [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L., Waller, L.A., Russell, C.A., Childs, J.E., Real, L.A. Assessing the role of long-distance translocation and spatial heterogeneity in the raccoon rabies epidemic in Connecticut. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 71(3-4):225-40. [CrossRef]
- Borremans, B., Faust, C., Manlove, K.R., Sokolow, S.H., Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Cross-species pathogen spillover across ecosystem boundaries: mechanisms and theory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol Sci. 2019, 374(1782):20180344. [CrossRef]
- de Lima, J.S., Mori, E., Kmetiuk, L.B., Biondo, L.M., Brandão, P.E., Biondo, A.W., Maiorka, P.C. Cat rabies in Brazil: a growing One Health concern. Front. Public. Health. 2023, 11:1210203. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiao, H.; Yang, W.; Dellicour, S.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J.; Huang, Z.X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. The Impact of Anthropogenic and Environmental Factors on Human Rabies Cases in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Orozco, P.; Bá Stida-Gonzá Lez, F.; Cruz, L.; Villatoro, J.; Espinoza, E.; Zárate-Segura, P.B.; Recuenco, S.; Díaz, S.S.; Esquina, M.; De, P.; et al. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Canine Rabies in El Salvador: Violence and Poverty as Social Factors of Canine Rabies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, R.K.; Hanlon, C.A.; Goodin, D.G.; Davis, R.; Moore, M.; Moore, S.; Anderson, G.A. Bayesian Spatiotemporal Pattern and Eco-Climatological Drivers of Striped Skunk Rabies in the North Central Plains. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, D.; Chandran, D.; Subedi, S.; Acharya, K.P. Ecological and Socioeconomic Factors in the Occurrence of Rabies: A Forgotten Scenario. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiden, P.W., Bartel, S.L., Byer, N.W., Shipley, A.A., Orrock, J.L. Predator-Prey Interactions in the Anthropocene: Reconciling Multiple Aspects of Novelty. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34(7):616-627. [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Escobar, L.E. A review of the diet of the common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) in the context of anthropogenic change. Mamm. Bio.l 2023, 103, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, D., Beeching, S.; Cleaveland, S.; Cronin, K.; Hampson, K.; Steenson, R.; Abela-Ridder, B. Rabies and the pandemic: Lessons for One Health. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 116:197–200. [CrossRef]
| # | Case | Year | Municipality | Antigenic RVV |
Sequence Name | GenBank Accesion Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3419 | 2003 | Merida | RVV1 | 3419MxcatYuc03 | PP105582 |
| 2 | 751 | 2017 | Muna | Atypical | 751MxcatYuc17 | PP105583 |
| 3 | 752 | 2017 | Muna | Atypical | 752MxcatYuc17 | PP105584 |
| 4 | 753 | 2017 | Muna | Atypical | 753MxcatYuc17 | PP105585 |
| 5 | 754 | 2017 | Muna | Atypical | 754MxcatYuc17 | PP105586 |
| 6 | 1832 | 2018 | Merida | Atypical | 1832MxcatYuc18 | PP105587 |
| 7 | 613 | 2019 | Merida | Atypical | 613MxcatYuc19 | PP105588 |
| 8 | 399 | 2021 | Merida | Atypical | 399MxcatYuc21 | PP105589 |
| 9 | 400 | 2021 | Cuncunul | RVV3 | 400MxCatYuc21 | PP105590 |
| Factor | Estimate | IRR | p- value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population size | 0. 974 | 2.649 | 0.159 |
| % Land cover change | -0.304 | 0.738 | 0.863 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





