Submitted:
16 May 2024
Posted:
16 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Translation Procedures
Sampling Procedures
Sample Description
Data Collection Procedures and Additional Variables
Statistical Methods
Results
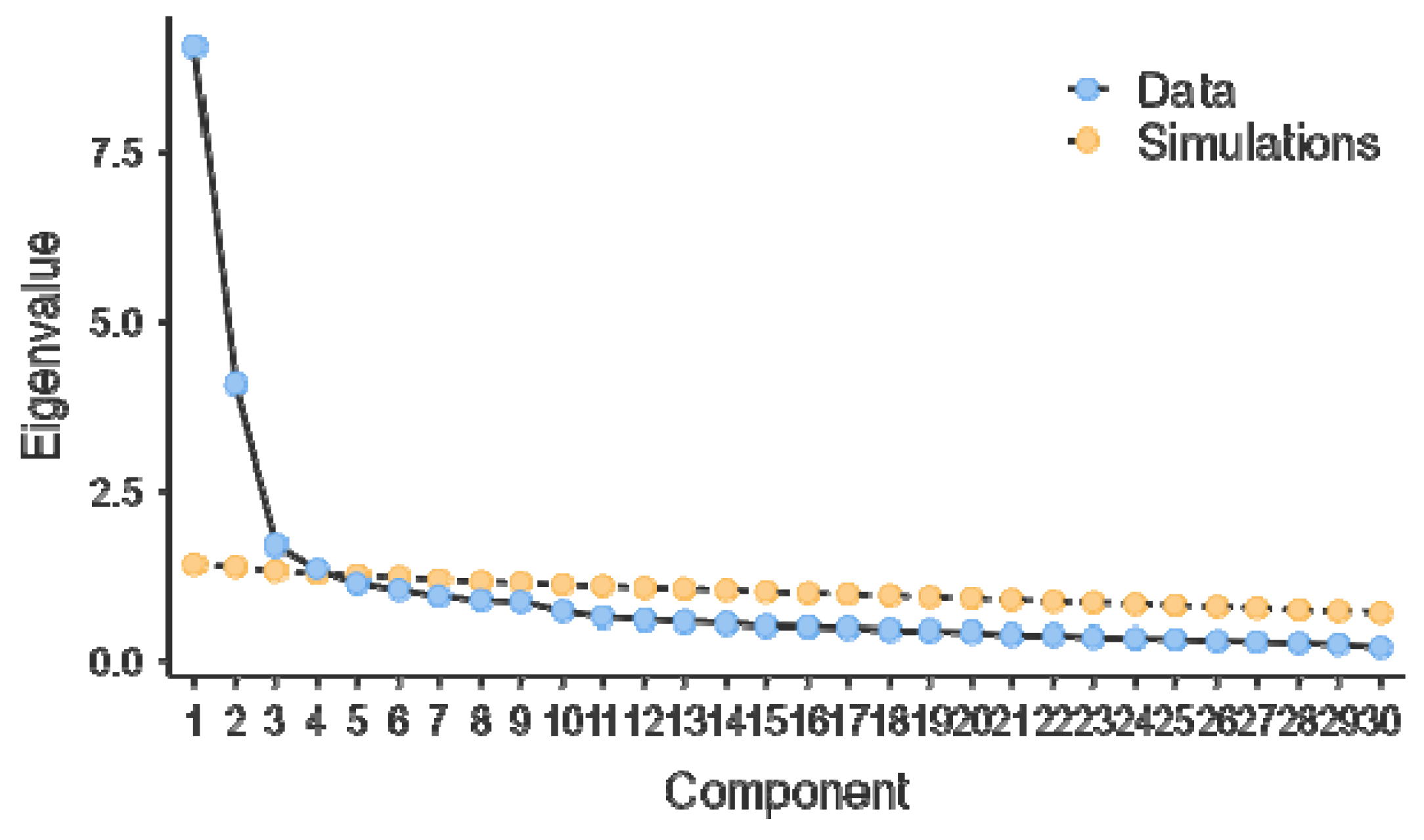
Validity
Discussion
Conclusions
Appendix A
Nursing Attitudes Questionnaire—Italian Version (NAQ-IV)
| Ruolo & professionalità |
| 1. Gli infermieri rappresentano una risorsa per le persone con problemi di salute |
| 2. Essere un infermiere/a richiede intelligenza |
| 3. Il servizio espletato dagli infermieri è importante quanto quello fornito dai medici |
| 4. Gli infermieri integrano gli insegnamenti sanitari nella pratica assistenziale |
| 5. La ricerca scientifica è vitale per la professione infermieristica |
| 6. Gli infermieri sono in grado di operare in modo autonomo |
| 7. Gli infermieri devono avere il diritto di scioperare |
| 8. Gli uomini sono dei bravi infermieri |
| 9. Il lavoro di infermiere è emozionante |
| 10. Gli infermieri integrano i risultati delle ricerche scientifiche nella pratica clinica |
| 11. L' obiettivo più importante della ricerca infermieristica è quello di migliorare l' assistenza al paziente |
| 12. Gli infermieri attribuiscono valore al tempo che trascorrono al letto dei pazienti per prendersi cura di loro |
| 13. Gli infermieri devono avere una laurea per praticare la professione |
| 14. Gli infermieri che hanno conseguito una laurea magistrale danno contributi importanti per la cura dei pazienti |
| Stereotipi |
| 15. Gli infermieri devono indossare una divisa bianca per essere identificati |
| 16. Se gli infermieri trascorressero più tempo a prendersi cura di pazienti e meno all' università tutti ne trarrebbero beneficio |
| 17. Gli infermieri sono ripagati sufficientemente per il loro lavoro dal sapere che stanno aiutando altre persone |
| 18. Gli infermieri eseguono le richieste del medico senza obiezione |
| 19. Molti infermieri che ricercano un avanzamento nella loro attività professionale, in realtà vorrebbero essere piuttosto dei medici |
| 20. Gli infermieri sono adeguatamente pagati per il lavoro che svolgono |
| 21. Uno dei vantaggi di essere un infermiere è quello di sposare un medico |
| Valore & advocacy |
| 22. Gli infermieri sono coloro che sostengono i diritti dei pazienti |
| 23. Gli infermieri tutelano i pazienti all' interno del Sistema Sanitario |
| 24. Gli infermieri partecipano allo sviluppo delle politiche sull' assistenza sanitaria |
| 25. Gli infermieri sono in genere gentili e compassionevoli |
| Motivazione & Soddisfazione |
| 26. Gli infermieri sono politicamente attivi |
| 27. Gli infermieri pronunciano nettamente contro condizioni inadeguate di lavoro |
| 28. Il lavoro di infermiere è una professione rispettata |
| 29. Gli infermieri aggiornano costantemente la loro pratica in relazione alle ultime scoperte sull' assistenza sanitaria |
| 30. Gli infermieri sono soddisfatti del lavoro che svolgono |
References
- Toth, J.C.; Dobratz, M.A.; Boni, M.S. Attitude toward Nursing of Students Earning a Second Degree and Traditional Baccalaureate Students: Are They Different? Nurs. Outlook 1998, 46, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbi, I.; Lupo, R.; Lezzi, A.; Cremonini, V.; Carvello, M.; Caricato, M.; Conte, L.; Antonazzo, M.; Caldararo, C.; Botti, S.; et al. The Social and Professional Image of the Nurse: Results of an Online Snowball Sampling Survey among the General Population in the Post-Pandemic Period. Nurs. reports (Pavia, Italy) 2023, 13, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisch, B.J.; Begeny, S.; Neumann, S. The Image of the Nurse on the Internet. Nurs. Outlook 2007, 55, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauderer, T.M.; Lima, M.A.D. da S. [Nurse’s Image: Review of the Literature]. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2005, 58, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, L. View of Nursing Questionnaire [Mimeograph].; America, W.T.C.U. of, Ed.; 1983.
- Janhonen, S.; Vanhanen, L.; Atwood, J. Developing and Testing a Cognitive Orientation to Nursing Measurement Tool. Nord. J. Nurs. Res. 2000, 20, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhanen, L.; Janhonen, S. Factors Associated with Students’ Orientations to Nursing. J. Adv. Nurs. 2000, 31, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, C.; Grainger, P. Students in the BN Program--Do Their Perceptions Change? Nurse Educ. Today 2009, 29, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainger, P.; Bolan, C. Perceptions of Nursing as a Career Choice of Students in the Baccalaureate Nursing Program. Nurse Educ. Today 2006, 26, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hoeve, Y.; Castelein, S.; Jansen, W.; Jansen, G.; Roodbol, P. Predicting Factors of Positive Orientation and Attitudes towards Nursing: A Quantitative Cross-Sectional Study. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 40, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbi, I.; Cremonini, V.; Artioli, G.; Lenzini, A.; Talenti, I.; Caponnetto, V.; La Cerra, C.; Petrucci, C.; Lancia, L. The Public Perception of Nurses. An Italian Cross-Sectional Study. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbi, I.; Pasquinelli, G.; Cremonini, V.; Fortunato, F.; Gatti, L.; Lepanto, F.; Artioli, G.; Bonacaro, A. Does Student Orientation Improve Nursing Image and Positively Influence the Enrolment of Nursing Students in the University? An Observational Study. Acta Biomed. 2019, 90, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vellis, R. Scale Development; Publications., T.O.S., Ed.; 2003. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ferketich, S. Focus on Psychometrics. Aspects of Item Analysis. Res. Nurs. Health 1991, 14, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomietto, M.; Saiani, L.; Palese, A.; Cunico, L.; Cicolini, G.; Watson, P.; Saarikoski, M. Clinical Learning Environment and Supervision plus Nurse Teacher (CLES+T) Scale: Testing the Psychometric Characteristics of the Italian Version. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2012, 34, B72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbaranelli, C. AnalisideiDati. Tecniche Multivariate per La RicercaPsicologica e Sociale, Milano: LED Bentler, PM and Bonnet, DC (1980). Significance Tests and Goodness of Fit in the Analysis of Covariance Structures. Psychol. Bull. 2003, 88, 588–606. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.W. Missing Data Analysis: Making It Work in the Real World. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2009, 60, 549–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polit, D.; Beck, C. Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice.; Wilkins., P.L.W.&, Ed. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pedhazur, E.; Schmelkin, L. Measurement, Design, and Analysis: An Integrated Approach.; Hillsdale, N.L.E.A., Ed.; 1991.
- Kline, P. An Easy Guide to Factor Analysis; Routledge, L., Ed.; 1994.
- Gorsuch, R. Factor Analysis (2nd Ed.); Hillsdale, N.L.E.A., Ed.; 1983.
- Pett, M.; Lackey, N.; Sullivan, J. Making Sense of Factor Analysis: The Use of Factor Analysis for Instrument Development in Health Care Research; Sage, Ed. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hanks, R.G. The Lived Experience of Nursing Advocacy. Nurs. Ethics 2008, 15, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.; Kelly, B. Bridging the Gap: A Study of General Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Advocacy in Ireland. Nurs. Ethics 2005, 12, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orem, D. Nursing Concepts of Practice. 6th Ed.; Mosby, St. Louis. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.M.; Scott, P.A. Nursing, Advocacy and Public Policy. Nurs. Ethics 2021, 28, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Mao, S.; Chang, R.; Jiang, W. The Influence of Intrinsic Motivation on Pay Satisfaction Among Caregivers in Residential Home for the Elderly in China: The Mediating Role of Job Burnout. J. Nurs. Res. 2020, 28, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NAQ - IV | M±SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | Corrected item to total correlation | Cronbach’s alpha if item deleted | KMO Measure of Sampling Adequacy (MSA) |
| Role & professionalism (α = 0.934; KMO = 0.947) (14 Items) | ||||||
| 5. Nurses act as resource persons for individuals with health problems | 4.24±0.959 | -1.42 | 2.07 | 0.729*** | 0.885 | 0.953 |
| 7. It takes intelligence to be a nurse | 4.13±0.960 | -1.09 | 1.03 | 0.733*** | 0.885 | 0.949 |
| 8. The service given by nurses is as important as that given by physicians | 4.24±0.970 | -1.30 | 1.44 | 0.751*** | 0.884 | 0.948 |
| 10. Nurses integrate health teaching into their practice | 4.01±0.912 | -0.826 | 0.826 | 0.751*** | 0.885 | 0.957 |
| 11. Research is vital to nursing as a profession | 4.04±0.984 | -0.875 | 0.434 | 0.751*** | 0.884 | 0.944 |
| 13. Nurses are capable of independent practice | 3.79±1.13 | -0.655 | -0.265 | 0.631*** | 0.885 | 0.953 |
| 16. Nurses should have a right to strike | 3.99±1.02 | -0.808 | 0.251 | 0.659*** | 0.886 | 0.967 |
| 18. Men make good nurses | 3.46±1.20 | -0.469 | -0.505 | 0.402*** | 0.893 | 0.932 |
| 20. Nursing is exciting | 3.87±1.01 | -0.573 | -0.142 | 0.755*** | 0.884 | 0.957 |
| 21. Nurses incorporate research findings into their clinical practice | 3.80±0.987 | -0.464 | -0.150 | 0.766*** | 0.884 | 0.948 |
| 22. The major goal of nursing research is to improve patient care | 4.04±0.995 | -0.913 | 0.527 | 0.795*** | 0.884 | 0.946 |
| 24. Nurses value time at the bedside caring for patients | 3.70±1.04 | -0.495 | -0.076 | 0.673*** | 0.886 | 0.962 |
| 25. Nurses should have a Baccalaureate degree for entrance into practice | 4.07±1.02 | -0.872 | 0.258 | 0.758*** | 0.884 | 0.946 |
| 26. Nurses with advanced degrees make important contributions to patient care | 3.59±1.08 | -0.483 | -0.136 | 0.552*** | 0.888 | 0.941 |
| Stereotypes (α = 0,865; KMO = 0.865) (7 Items) | ||||||
| 4. Nurses should wear a white uniform in order to be identified | 2.90±1.28 | 0.136 | -0.992 | 0.470*** | 0.898 | 0.874 |
| 9. Everyone would benefit if nurses spent less time in school and more time caring for patients | 3.15±1.33 | 0.009 | -1.09 | 0.568*** | 0.898 | 0.868 |
| 15. Nurses are compensated sufficiently for their work by the knowledge that they are helping people |
3.34±1.24 | -0.174 | -0.879 | 0.664*** | 0.898 | 0.883 |
| 17. Nurses follow the physician’s orders without questions | 3.29±1.20 | 0.061 | -0.814 | 0.682*** | 0.896 | 0.874 |
| 19. Many nurses who seek advanced degrees in nursing would really rather be physicians | 3.46±1.23 | -0.274 | -0.770 | 0.640*** | 0.894 | 0.848 |
| 23. Nurses are adequately paid for the work they do | 3.63±1.22 | -0.403 | -0.752 | 0.730*** | 0.894 | 0.876 |
| 27. One advantage to being a nurse is to marry a physician | 4.09±1.18 | -1.02 | 0.054 | 0.720*** | 0.894 | 0.860 |
| Values & advocacy (α = 0,838; KMO = 0.769) (4 Items) | ||||||
| 1. Nurses are patient’s advocates | 3.87±1.05 | -0.655 | -0.163 | 0.763*** | 0.889 | 0.877 |
| 2. Nurses protect patients in the health care system | 4.02±1.00 | -0.924 | 0.494 | 0.790*** | 0.887 | 0.883 |
| 3. Nurses participate in the development of health care policies | 3.87±1.05 | -0.737 | 0.011 | 0.651*** | 0.889 | 0.940 |
| 6. Nurses in general are kind, compassionate human beings | 3.58±1.02 | -0.531 | 0.103 | 0.497*** | 0.891 | 0.934 |
| Motivation & Satisfaction (α = 0,727; KMO = 0.697) (5 Items) | ||||||
| 12. Nurses are politically active | 3.29±1.09 | -0.302 | -0.180 | 0.486*** | 0.892 | 0.921 |
| 14. Nurses speak out against inadequate working conditions | 3.54±1.05 | -0.266 | -0.262 | 0.475*** | 0.889 | 0.938 |
| 28. Nursing is a respected profession | 2.90±1.20 | 0.087 | -0.732 | 0.412*** | 0.899 | 0.884 |
| 29. Nurses consistently update their practice in relation to current health trends | 3.61±1.04 | -0.291 | -0.370 | 0.469*** | 0.887 | 0.951 |
| 30. Nurses feel good about what they do | 3.19±1.03 | -0.218 | 0.067 | 0.612*** | 0.893 | 0.909 |
| α = 0.893, KMO = 0.930 | ||||||
| EFA | CFA | ||||
| NAQ - IV | r | Estimate | SE | Z | p |
| Role & professionalism | |||||
| 1. Nurses act as resource persons for individuals with health problems | 0.710 | 0.742 | 0.0344 | 21.55 | < .001*** |
| 2. It takes intelligence to be a nurse | 0.752 | 0.734 | 0.0346 | 21.20 | < .001*** |
| 3. The service given by nurses is as important as that given by physicians | 0.752 | 0.763 | 0.0346 | 22.08 | < .001*** |
| 4. Nurses integrate health teaching into their practice | 0.714 | 0.721 | 0.0323 | 22.30 | < .001*** |
| 5. Research is vital to nursing as a profession | 0.688 | 0.773 | 0.0350 | 22.08 | < .001*** |
| 6. Nurses are capable of independent practice | 0.474 | 0.748 | 0.0428 | 17.45 | < .001*** |
| 7. Nurses should have a right to strike | 0.674 | 0.693 | 0.0383 | 18.11 | < .001*** |
| 8. Men make good nurses | 0.471 | 0.476 | 0.0496 | 9.60 | < .001*** |
| 9. Nursing is exciting | 0.716 | 0.792 | 0.0362 | 21.90 | < .001*** |
| 10. Nurses incorporate research findings into their clinical practice | 0.684 | 0.775 | 0.0352 | 21.98 | < .001*** |
| 11. The major goal of nursing research is to improve patient care | 0.792 | 0.814 | 0.0347 | 23.43 | < .001*** |
| 12. Nurses value time at the bedside caring for patients | 0.624 | 0.716 | 0.0391 | 18.32 | < .001*** |
| 13. Nurses should have a Baccalaureate degree for entrance into practice | 0.841 | 0.786 | 0.0366 | 21.49 | < .001*** |
| 14. Nurses with advanced degrees make important contributions to patient care | 0.598 | 0.613 | 0.0427 | 14.36 | < .001*** |
| Stereotypes | |||||
| 15. Nurses should wear a white uniform in order to be identified | 0.633 | 0.643 | 0.0532 | 12.10 | < .001*** |
| 16. Everyone would benefit if nurses spent less time in school and more time caring for patients | 0.620 | 0.792 | 0.0538 | 14.72 | < .001*** |
| 17. Nurses are compensated sufficiently for their work by the knowledge that they are helping people |
0.738 | 0.928 | 0.0468 | 19.83 | < .001*** |
| 18. Nurses follow the physician’s orders without questions | 0.745 | 0.854 | 0.0462 | 18.49 | < .001*** |
| 19. Many nurses who seek advanced degrees in nursing would really rather be physicians | 0.749 | 0.839 | 0.0479 | 17.51 | < .001*** |
| 20. Nurses are adequately paid for the work they do | 0.822 | 0.994 | 0.0440 | 22.60 | < .001*** |
| 21. One advantage to being a nurse is to marry a physician | 0.756 | 0.943 | 0.0432 | 21.84 | < .001*** |
| Values & advocacy | |||||
| 22. Nurses are patient’s advocates | 0.808 | 0.915 | 0.0359 | 25.49 | < .001*** |
| 23. Nurses protect patients in the health care system | 0.785 | 0.912 | 0.0336 | 27.14 | < .001*** |
| 24. Nurses participate in the development of health care policies | 0.695 | 0.744 | 0.0398 | 18.67 | < .001*** |
| 25. Nurses in general are kind, compassionate human beings | 0.558 | 0.557 | 0.0416 | 13.40 | < .001*** |
| Motivation & Satisfaction | |||||
| 26. Nurses are politically active | 0.471 | 0.648 | 0.0456 | 14.21 | < .001*** |
| 27. Nurses speak out against inadequate working conditions | 0.515 | 0.633 | 0.0440 | 14.40 | < .001*** |
| 28. Nursing is a respected profession | 0.676 | 0.622 | 0.0544 | 11.44 | < .001*** |
| 29. Nurses consistently update their practice in relation to current health trends | 0.530 | 0.618 | 0.0442 | 13.96 | < .001*** |
| 30. Nurses feel good about what they do | 0.506 | 0.691 | 0.0426 | 16.24 | < .001*** |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Role & professionalism | 1 | |||
| 2. Stereotypes | 0.239*** | 1 | ||
| 3. Values & advocacy | 0.533*** | -0.143*** | 1 | |
| 4. Motivation & Satisfaction | 0.536*** | -0.237*** | 0.478*** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





