1. Introduction
Gout is characterized by inflammatory arthritis that arises from deposition of urate crystals in joints following persistent hyperuricemia [
1]. This causes recurrent painful flares while increasing the risk of permanent joint damage and disability. Over a prolonged timeframe, elevated serum uric acid (SUA) concentrations have been shown to be a significant risk factor correlating with the development of numerous cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic disorders [
2,
3,
4]. To normalize SUA levels, guidelines from rheumatology associations recommend allopurinol, a purine analog and xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor, as first-line urate-lowering therapy for the management of chronic gout [
5,
6,
7]. In the liver, allopurinol is rapidly and extensively metabolized into the active metabolite oxypurinol, while a minor fraction undergoes conjugation into allopurinol-riboside [
8,
9]. The greater pharmacological potency and half-life of oxypurinol relative to allopurinol (~24hrs vs. ~1.5hr) are responsible for most of the urate-lowering effect by limiting uric acid synthesis through the XO pathway [
9,
10]. Oxypurinol is almost exclusively excreted through the kidney in its unchanged form [
11,
12], thus making renal function an important consideration prior to administration [
5].
Despite the frequent use of allopurinol in the clinic, previous literature has acknowledged the substantial variability in clinical response. General factors have been highlighted, such as the poor treatment adherence that often prevents patients from reaching therapeutic target SUA thresholds [
13,
14,
15]. Recent efforts have also suggested the inclusion of clinical parameters alongside renal function for optimizing current dosing algorithms and account for interindividual differences [
16,
17,
18,
19]. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) specific to allopurinol therapy have historically allowed the discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as risk factors for life-threatening cutaneous reactions [
20,
21,
22], resulting in routine clinical testing being implemented [
23,
24]. They have also been successfully applied to detect genetic risk factors associated with baseline SUA concentration levels and assist in predicting clinical outcomes in gout [
25,
26,
27,
28]. More recently, novel pharmacogenomic (PGx) determinants have been associated to allopurinol clinical response across different populations. Both candidate association studies and GWAS have repeatedly implicated variants located within genes coding for common gut and renal transporters. One example includes
ABCG2 coding for the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) for which urate, allopurinol, and oxypurinol are substrates [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. Interestingly, GWA analyses further revealed a novel SNP in
GREM2 associated with responder rates but not baseline SUA levels, implying that unsuspected genomic regions may harbor PGx elements strictly affecting allopurinol pharmacodynamics instead of physiologic urate transport [
34].
Past PGx investigations on drug concentrations have usually centered around known biological targets. However, the capabilities of GWA methodologies have been demonstrated in cohort studies to detect new PGx elements of drug concentrations with smaller effect sizes beyond well-established transporter and enzymatic pathways [
35,
36]. To our knowledge, this approach has not been performed to investigate variations in allopurinol metabolism. With the resources that institutional biorepositories provide, we sought to utilize similar methods and assess whether randomly collected biobank samples could be leveraged to detect PGx determinants of plasma allopurinol and metabolite concentrations, together with daily dosing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participant Selection
Participants from the previous cross-sectional study were selected from the MHI Biobank’s records. The methods of the MHI Biobank, including patient enrollment and sample storage protocols, have been described in prior works [
37,
38]. Briefly, the biobank consists of biological material and encoded data from patients of the MHI Hospital Cohort who have used the hospital center’s services and provided informed consent for their participation. For this study, selected records and biological samples were retrieved from patients who had enrolled in the MHI Biobank with baseline values taken between May 22nd, 2007, and September 12th, 2018. Samples were acquired from patients randomly with regards to allopurinol intake, concomitant medications, time of day, or food intake. Along with biological sampling, questionnaires were administered to participants concerning personal and family medical history, as well as individual pharmacological, dietary, and psychosocial data, among others. Except for plasma concentrations of allopurinol and its metabolites, all information were collected directly from participants, their medical records, and MHI electronic databases. No prospective recruitment was performed as part of this investigation.
As in our initial cross-sectional study, only self-reported “White” males and females aged ≥18 years were included to minimize confounding risks and population stratification [
39]. Selected participants were treated with allopurinol and needed to have had plasma samples available at the time of their enrolment. Considering the extended half-life for oxypurinol, patients with non-quantifiable concentrations of the metabolite were deemed non-adherent to treatment and excluded from all analyses. We also excluded participants with a history of heart, kidney, or liver transplant since the genotype from the donor and the recipient could differ, thus removing recipient-donor interactions that could mislead inferences on a patient’s metabolic capacity [
40,
41].
2.2. Study Endpoints
The endpoints investigated in the initial study were plasma oxypurinol, allopurinol, and allopurinol-riboside concentrations, as well as patients’ daily allopurinol dosing [
39]. One patient had missing allopurinol dose values and was removed from the final analyses. All concentration levels were measured from blood samples obtained during each participant’s baseline visit.
2.3. Quantification of Oxypurinol, Allopurinol, and Allopurinol-riboside Plasma Concentrations
The quantification of oxypurinol, allopurinol, and allopurinol-riboside was performed from plasma samples collected upon enrolment in the MHI Biobank. All analyses were conducted at the bioanalytical laboratory of the Platform of Biopharmacy at Université de Montréal. Details of the full bioanalytical method have been described previously [
39]. Briefly, oxypurinol, allopurinol, and allopurinol-riboside analyses were carried in a blinded fashion using high-pressure liquid chromatography system coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and based on selective multiple reaction monitoring. Validated quantification ranges were 10-50,000 ng/mL for all analytes. Concentrations below the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ <10 ng/mL) were given a zero value as part of the analyses.
2.4. Genotyping Quality Control and Imputation
The genotyping quality control and imputation methods, as detailed in previous works [
42], were employed in this study. Genome-wide genotyping was performed using 200 ng of genomic DNA at the Beaulieu-Saucier Pharmacogenomics Centre (Montreal, Canada). The Illumina Infinium Global Screening Array v3-MD (Illumina, CA, USA) was utilized following the manufacturer’s instructions. BeadChips were subsequently scanned using the Illumina iScan, with data analysis carried out using the data manifest MHI_GSAMD-24v3-0-EA_20034606_C1.bpm. Plink files were generated with the iaap-clitool (version 1.1.0–80d7e5b). Intensities, B allele frequency and log R ratio were extracted using gtc_convert tool (version 0.1.2). Quality control and genetic data cleanup procedures were performed using PyGenClean (version 1.8.3) [
43] and PLINK (versions 1.07 and 1.9; the latter for the data manipulation steps of the relatedness and ethnicity modules) [
44].
The genotyping experiment involved 184 plates of DNA samples. One control was added per hybridization run, which corresponded to two plates, and chosen from NA06994, NA12717, NA12878, NA18861, and NA19147 that were obtained from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences Human Genetic Cell Repository at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research. The completion rate threshold for genotypes and samples was set to 99%. Cryptic relatedness among samples and sample outliers were identified using the pairwise identity by state matrix and multidimensional scaling, respectively. The first two multidimensional scaling components of each subject were plotted, including the genotypes of HapMap CEU, JPT-CHB, and YRI reference samples. Outliers from the CEU cluster were flagged and removed by k-nearest neighbor with a threshold of 1.9σ in PyGenClean (version 1.8.3). Principal components were computed for the selected study samples to account for population structure [
45]. We excluded nine participants who were not of European ancestry. Genome-wide imputation was carried out with the TOPMed Imputation Server (version 1.5.7) [
46] using Eagle (version 2.4) [
47] for phasing and Minimac4 (version 1.0.2) [
46] for imputation. Gene information was retrieved with Annovar (version 2020-06-07). The rsID numbers were retrieved with Ensembl REST API. Genetic variants from pseudo-autosomal regions were analyzed as autosomal variants, with all positions obtained from build 38. A total of 61,640,018 genetic variants with a quality value (r2) ≥0.6 remained, of which 6,394,414 had a minor allele frequency of ≥5%.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were obtained on the cohort’s demographics, clinical characteristics, and genotype information. For all parameters, means and standard deviations were used for reporting continuous variables, whereas counts with percentages were used for categorical variables. To satisfy normality assumptions, outcomes were log-transformed and the distributions of the residuals were used. Models with transformed outcomes all resulted in more normally distributed measures relative to untransformed datasets.
The GWAS analyses were conducted using the Scalable and Accurate Implementation of GEneralized mixed model (SAIGE) version 0.44.6.5 on the R software (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing) [
48]. This package uses a linear mixed regression framework with individual-level data to analyze large-scale datasets while simultaneously controlling for sample relatedness and case-control imbalances. Sample relatedness was accounted with the use of a genetic relationship matrix for random effects. Phenotype and genotype data were merged for all participants and only those with European ancestry, related or not, were included. Multivariable linear regression modeling was performed for every outcome assessed, with covariable selection made to maximize convergence: plasma oxypurinol concentrations were adjusted using age, sex, weight, daily allopurinol dosage, and ten principal components (PC1-10); plasma allopurinol and allopurinol-ribose concentrations were both adjusted using age, sex, daily allopurinol dosage, and PC1-5; allopurinol dosage was adjusted using age, sex, and PC1-5. Then, as part of exploratory analyses, we used the same regression models to investigate variants from multiple GWAS that were previously associated with SUA concentrations and allopurinol response in large cohorts [
26,
27,
34]. All genetic variants with significance threshold p<10
-4 were compiled into the final GWA results.
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
Overall, the final GWA analysis consisted of 439 participants with quantifiable plasma oxypurinol concentrations, with baseline patient characteristics consistent relative to those from the initial cohort treated with allopurinol (
Table 1) [
39]. Patients were prescribed allopurinol daily doses averaging 194.5 mg ± 77.1 (range 42.9 [100 mg 3 times per week] to 600 mg). As expected, patients presented comorbidities and received various concomitant cardiovascular drugs.
3.2. Genome-Wide Association Analyses: Allopurinol Metabolism and Dosing
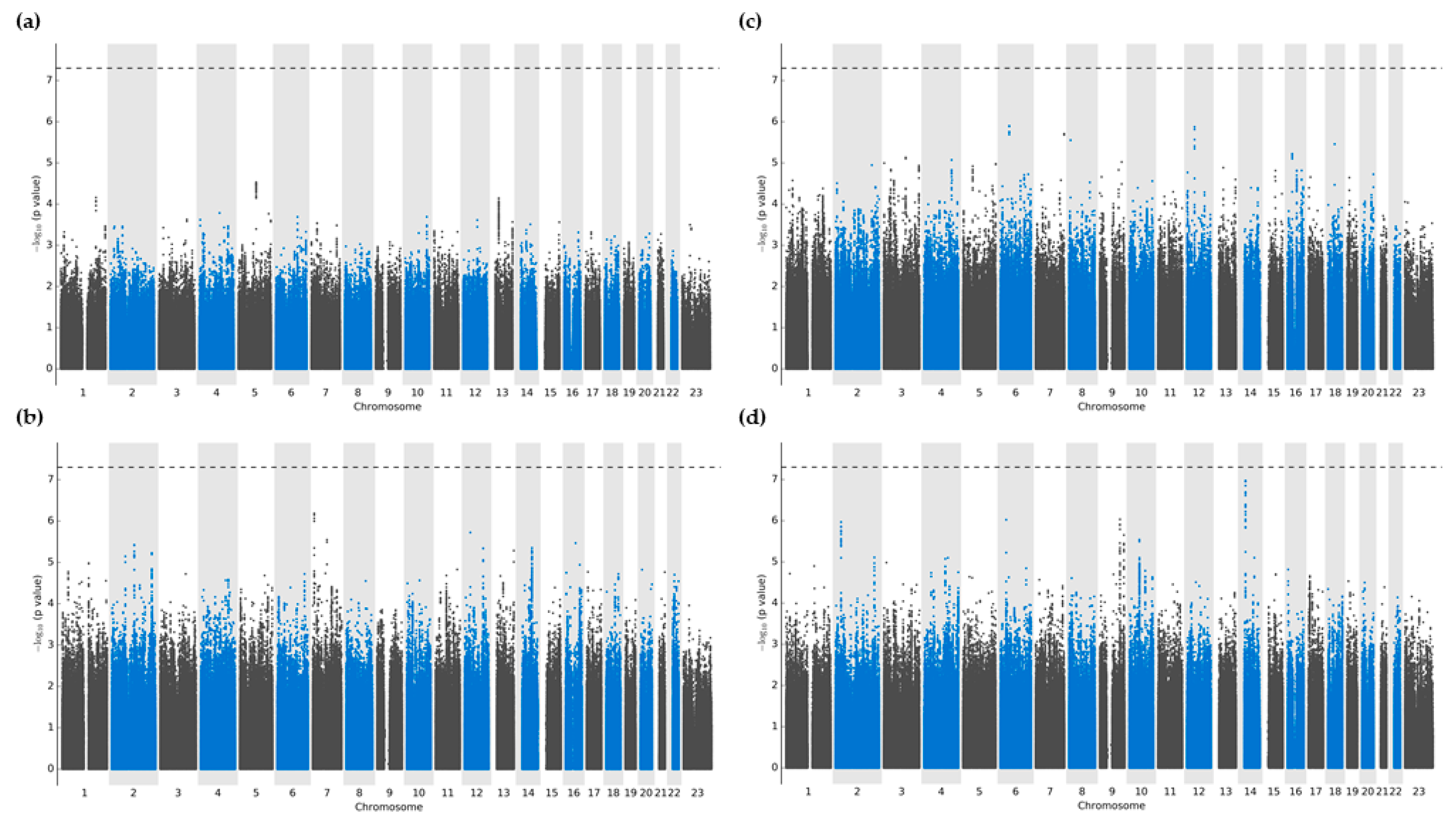
There were no variants that reached significance thresholds for either oxypurinol, allopurinol, or allopurinol-ribose plasma concentrations (
Figure 1A-C). After multivariable regression modeling, variants that showed the strongest associations were located predominantly in intergenic regions, followed by intronic portions of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) (
Supplementary Materials,
Tables S1–S4). More precisely, plasma oxypurinol concentrations had the highest association with the intergenic variant chr5:98238797:G:A closest to
LINC01846 (p=2.9 × 10
-5). Meanwhile, plasma allopurinol and allopurinol-riboside concentrations showed the greatest significance with intergenic variants chr6:49561859:T:C (p=1.3 × 10
-6) and chr7:8405423:G:A with nearest proximity to
C6orf141 and
NXPH1 (p=6.5 × 10
-7), respectively.
Regarding daily allopurinol dosing, the strongest associations were detected within intronic ncRNA regions of the
LINC02588 gene, although none reached the predefined significance thresholds (all
p>2.9 × 10
-7) (
Figure 1d). Additional signals were found in intronic regions of two more loci, namely
HLA-DQB1 (chr6:32663671:A:G; p=9.4 × 10
-7) and
DNAJC25-GNG10 (rs1570303; p=9.2 × 10
-7).
Results for the lookups of previously identified genetic variants of allopurinol response showed no variant reaching statistical significance thresholds from the previously reported genomewide analyses in our cohort (
Supplementary Materials,
Tables S5–S8). This could further underscore the likely role of these SNPs in regulating either physiologic SUA concentrations, gout risk, and allopurinol/oxypurinol pharmacological effect rather than their pharmacokinetic profiles or drug concentrations.
4. Discussion
Allopurinol is a mainstay of gout therapy due to its demonstrated urate-lowering benefits, well-tolerated safety profile, and high affordability [
2,
3,
4,
49,
50]. Studies using candidate gene and genome-wide approaches have revealed numerous SNPs of membrane transporters that may predict clinical response to allopurinol. In this study, we conducted a GWAS to identify PGx determinants on allopurinol concentrations and metabolism. We found no association that reached statistical significance regarding variants that would affect the concentrations levels of allopurinol and its metabolites. The top SNP of our GWA analyses of plasma oxypurinol concentrations was a variant located in an intergenic region near the
LINC01846 gene. A long intergenic ncRNA, there is little information available regarding its biological function. Whether nearby genomic alterations or interactions can impact its role in pharmacokinetics or drug concentrations more broadly, if any, has yet to be elucidated. Allopurinol concentrations had a top SNP closest to the
C6orf141 gene. An open reading frame with higher relative expression in the duodenum and gallbladder, the function of
C6orf141 has not been extensively studied, although cohort data indicates a tumor-suppressor effect in squamous cell oral cancer [
51]. As for plasma allopurinol-riboside concentrations, we also observed intergenic variants that showed near-significance close to
NXPH1. Altogether, even if associations of varying significance have been made in prior GWAS with a wide range of phenotypes for those genes [
52], we failed to demonstrate statistical significance. Their involvement in treatment response variability and pharmacokinetics therefore requires more extensive evidence.
We found suggestive association signals in regions of the long ncRNA transcript
LINC01588 with daily allopurinol dosing. Similar to genetic elements associated to drug concentrations, functional data on this gene is scarce, thus making any plausible biological or pharmacological implication uncertain. However, it is worth noting that additional near-significant associations were also seen with an intronic SNP of the well-characterized
HLA-DQB1 gene. Different from the variant we detected, GWAS results from a meta-analysis also identified a SNP in
HLA-DQB1 with suggestive association to SUA handling [
53]. Though unclear, the impacts from genetic variations could signify that the HLA region may regulate the renal transport of uric acid or other urate-dependant inflammatory mechanisms, therefore impacting gout susceptibility and staying in line with its role in autoimmunity [
54,
55]. Again, further investigations are required to support these findings.
Studies evaluating allopurinol and oxypurinol pharmacokinetics have not been able to consistently identify PGx determinants [
31,
56]. Even recently, a cohort of 300 gout patients was used to predict the impacts of genetic variability from multiple gut and renal urate transporters on oxypurinol metabolism through population pharmacokinetic modeling [
57]. After assessing several known variants, no signal was detected for any of the membrane transporter genotypes when accounting for common clinical variables. As previously emphasized, increasing evidence suggests that allopurinol metabolism is influenced by a combination of factors including oligogenic predictors, clinical and anthropometric variables, SUA regulation, and endogenous markers [
29,
58,
59]. Thus, varied interactions between these parameters could define allopurinol and metabolite pharmacokinetics, as well as its response, with the involvement of pathways that extend beyond those impacting drug concentration levels [
27,
34]. This is illustrated by the recent discovery of unknown mechanisms of action of oxypurinol in gout. GWA analyses followed by joint functional assays were able to validate the uricosuric properties of oxypurinol through direct inhibition of GLUT9-mediated urate reabsorption [
27,
34]. Still, one could assert that the pleiotropic effects of BCRP in gout, and potentially other membrane transporters, would rather arise from a modulation of allopurinol pharmacodynamics and urate reuptake than changes in the drug’s pharmacokinetics, thus justifying the lack of significant metabolic variability across investigations.
4.1. Study Limitations
Our study does contain some limitations, the size of our study population being an important one. Previous observational cohorts with subsequent meta-analyses have been performed for replication of previous observations with
ABCG2 and
GREM2 [
29,
34]. In the future, this could imply that multiple observational cohorts are needed through collaborative efforts in assessing genetic predictors of allopurinol metabolism and concentrations on a genome-wide scale. To this end, our GWAS results have been made publicly available via the PheWeb portal (
https://pheweb.statgen.org/allo-mhi/) which could enable meta-analyses to be carried out, therefore overcoming the limitations of small-scale studies. The composition of our cohort may also limit the interpretation of this study. For example, >26% of participants presented chronic heart failure, a factor known for influencing the clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of drugs [
60]. Although this does not invalidate our results, it is possible that allopurinol and metabolite concentrations could have been affected by unaccounted disease-induced physiological changes. Furthermore, we limited our investigation to participants of European ancestry. As was recently demonstrated, multi-ethnic cohorts have allowed the identification and validation of PGx signals impacting both plasma drug concentrations and metabolic ratios while displaying consistent effects sizes across ancestries [
61]. Therefore, limiting the study to a single ancestry may have hindered the detection of PGx variants impacting allopurinol and metabolite concentrations. Finally, since participants from the MHI Biobank had blood sampling performed without consideration to timing post-dose, adequate quantification of drugs with significantly shorter half-lives may prove to be challenging using a random sampling approach. In our case in which oxypurinol had a longer half-life and was the primary analyte of interest, such limitation did not affect our main objective, but could prevent allopurinol from being reliably quantified across cohorts taking the drug.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the current GWAS did not identify PGx determinants associated to plasma concentration levels of oxypurinol, allopurinol and allopurinol-riboside, and daily allopurinol dosing. These results support the notion that complex gene interactions, non-genomic markers, or multiple PGx elements with modest effect sizes may be identified as collaborative investigations expand to include larger patient cohorts. Ultimately, more definitive PGx signals regarding allopurinol pharmacokinetics and clinical response might be ascertained in future works to predict clinical outcomes in gout patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: GWAS results for oxypurinol concentrations (log) in the ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S2: GWAS results for allopurinol concentrations (log) in the ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S3: GWAS results for allopurinol-riboside concentrations (log) in the ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S4: GWAS results for daily allopurinol dose (log) in the ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S5: AS results of genetic lookups for oxypurinol concentrations (log) using a linear regression with ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S6: GWAS results of genetic lookups for allopurinol concentrations (log) using a linear regression with ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S7: GWAS results of genetic lookups for allopurinol-riboside concentrations (log) using a linear regression with ALLO-MHI biobank participants; Table S8: GWAS results of genetic lookups for daily allopurinol dose (log) using a linear regression with ALLO-MHI biobank participants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M., S.P., and S.D.; methodology, M.M., S.P., E.O., M.-P.D., and S.D.; software, S.P. and L.-P.L.P.; validation, M.M., S.P., E.O., I.S.-J., M.J., M.-P.D., and S.D.; formal analysis, M.M., S.P., E.O., I.S.-J., M.J., D.V., M.-J.G., and S.D.; investigation, M.M., S.P., E.O., I.S.-J., M.J., M.-J.G., and S.D.; resources, G.L., I.M., D.B., and S.D.; data curation, S.P., E.O., L.-P.L.P., D.V., I.M., and D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M., S.P., I.M., and S.D.; writing—review and editing, M.M., S.P., I.S.-J., M.J., I.M., J.-L.R., J.-C.T., M.-P.D., and S.D.; visualization, M.M. and S.P.; supervision, G.L., D.B., M.-P.D., and S.D.; project administration, G.L., D.B., M.-P.D., and S.D.; funding acquisition, G.L., J.-C.T., and S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant number 154862;
https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/193.html), the Montreal Heart Institute Foundation, and the Université de Montréal Beaulieu-Saucier Chair in Pharmacogenomics. M-P.D. holds the Canada Research Chair in precision medicine data analysis.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Scientific and Ethics Committees of the Montreal Heart Institute (protocol code 2109-2485, approved on 2018-11-06). Access to the biobank’s participant data were granted upon ethical and scientific approval of the main project (2018-11-06). Approvals covered the entire biobank cohort and allowed for participant record selection starting from the initial biobank creation date (2007-01-24) up to project approval date. Protocol amendments regarding subsequent genomewide analyses were also approved. Biobank data were accessed for research purposes from the date of initial project approval (2018-11-06) up until all genomewide analyses had been completed (2023-09-26). All data were deidentified and none of the research team members had access to information that could potentially lead to reidentification of individual participants.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
S.D. reports grants outside the submitted work from AstraZeneca, and RMS/Dalcor. M.-P.D. has minor equity interest in Dalcor Pharmaceuticals. M.-P.D. has a patent Methods for Treating or Preventing Cardiovascular Disorders and Lowering Risk of Cardiovascular Events issued to Dalcor Pharmaceuticals, no royalties received; a patent Genetic Markers for Predicting Responsiveness to Therapy with HDL-Raising or HDL Mimicking Agent issued to Dalcor Pharmaceuticals, no royalties received; and a patent Methods for using low dose colchicine after myocardial infarction, assigned to the Montreal Heart Institute. J.-C.T. has received research grants from Amarin, AstraZeneca, Ceapro, DalCor Pharmaceuticals, Esperion, Ionis, Novartis, Pfizer, RegenXBio, and Sanofi; honoraria from AstraZeneca, DalCor Pharmaceuticals, HLS Pharmaceuticals, Pendopharm, and Pfizer; and minor equity interest in DalCor Pharmaceuticals. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Dalbeth, N.; Choi, H.K.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Khanna, P.P.; Matsuo, H.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Stamp, L.K. Gout. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2019, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, T.; Richette, P. Impact of comorbidities on gout and hyperuricaemia: an update on prevalence and treatment options. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Gaffo, A. Gout epidemiology and comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.F.; Grainge, M.J.; Mallen, C.; Zhang, W.; Doherty, M. Comorbidities in patients with gout prior to and following diagnosis: case-control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.D.; Dalbeth, N.; Mikuls, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Guyatt, G.; Abeles, A.M.; Gelber, A.C.; Harrold, L.R.; Khanna, D.; King, C.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2020, 72, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joey, T.; Michael, R.K. Targeting uric acid levels in treating gout. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 671. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, M.; Carr, A.; Cameron, S.; Davenport, G.; Doherty, M.; Forrester, H.; Jenkins, W.; Jordan, K.M.; Mallen, C.D.; McDonald, T.M.; et al. The British Society for Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017, 56, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannangara, D.R.W.; Roberts, D.M.; Furlong, T.J.; Graham, G.G.; Williams, K.M.; Day, R.O. Oxypurinol, allopurinol and allopurinol-1-riboside in plasma following an acute overdose of allopurinol in a patient with advanced chronic kidney disease. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2012, 73, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.O.; Graham, G.G.; Hicks, M.; McLachlan, A.J.; Stocker, S.L.; Williams, K.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Allopurinol and Oxypurinol. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 2007, 46, 623–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnheim, K.; Krivanek, P.; Oberbauer, R. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of allopurinol in elderly and young subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1999, 48, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, H.A. Urinary excretion of purines, pyrimidines and pyrazolopyrimidines in patients treated with allopurinol or oxipurinol. Clin. Chim. Acta 1969, 23, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsutsumi, Z.; Takahashi, S.; Hada, T. Effects of angiotensin II infusion on renal excretion of purine bases and oxypurinol. Metabolism 2002, 51, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Richman, J.; Yang, S.; Bridges, S.L.; Saag, K. Allopurinol adherence and its predictors in gout: a national cohort study in US veterans. The Lancet Rheumatology 2020, 2, e281–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisman, A.; Tomlinson, G.A.; Lipscombe, L.L.; Perkins, B.A.; Hawker, G.A. Allopurinol adherence, persistence and patterns of use in individuals with diabetes and gout: A retrospective, population-based cohort analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.K.; Merriman, T.R.; Barclay, M.L.; Singh, J.A.; Roberts, R.L.; Wright, D.F.; Dalbeth, N. Impaired response or insufficient dosage? Examining the potential causes of “inadequate response” to allopurinol in the treatment of gout. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.K.; Chapman, P.T.; Barclay, M.; Horne, A.; Frampton, C.; Merriman, T.R.; Wright, D.F.B.; Drake, J.; Dalbeth, N. Relationships Between Allopurinol Dose, Oxypurinol Concentration and Urate-Lowering Response-In Search of a Minimum Effective Oxypurinol Concentration. Clin Transl Sci 2020, 13, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.K.; Chapman, P.T.; Barclay, M.; Horne, A.; Frampton, C.; Tan, P.; Drake, J.; Dalbeth, N. The effect of kidney function on the urate lowering effect and safety of increasing allopurinol above doses based on creatinine clearance: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.K.; Chapman, P.T.; Barclay, M.L.; Horne, A.; Frampton, C.; Tan, P.; Drake, J.; Dalbeth, N. How much allopurinol does it take to get to target urate? Comparison of actual dose with creatinine clearance-based dose. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, G.G.; Kannangara, D.R.W.; Stocker, S.L.; Portek, I.; Pile, K.D.; Indraratna, P.L.; Datta, I.; Williams, K.M.; Day, R.O. Understanding the dose–response relationship of allopurinol: predicting the optimal dosage. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2013, 76, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohkin, M.; Kaniwa, N.; Saito, Y.; Sugiyama, E.; Kurose, K.; Nishikawa, J.; Hasegawa, R.; Aihara, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Abe, M.; et al. A whole-genome association study of major determinants for allopurinol-related Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Japanese patients. Pharmacogenomics J 2013, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.I.; Chung, W.H.; Liou, L.B.; Chu, C.C.; Lin, M.; Huang, H.P.; Lin, Y.L.; Lan, J.L.; Yang, L.C.; Hong, H.S.; et al. HLA-B*5801 allele as a genetic marker for severe cutaneous adverse reactions caused by allopurinol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 4134–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarjour, S.; Barrette, M.; Normand, V.; Rouleau, J.L.; Dubé, M.P.; de Denus, S. Genetic markers associated with cutaneous adverse drug reactions to allopurinol: a systematic review. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, T.M.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, K.S.; Yu, K.H.; Chu, C.S.; Huang, C.M.; Wang, C.R.; Weng, C.T.; Yu, C.L.; et al. Use of HLA-B*58:01 genotyping to prevent allopurinol induced severe cutaneous adverse reactions in Taiwan: national prospective cohort study. BMJ 2015, 351, h4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-W.; Preclaro, I.A.C.; Lin, W.-H.; Chung, W.-H. An Updated Review of Genetic Associations With Severe Adverse Drug Reactions: Translation and Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Testing in Clinical Practice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Nakayama, A.; Sakiyama, M.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, A.; Nakamura, T.; Nakashima, H.; Takada, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association study of clinically defined gout identifies multiple risk loci and its association with clinical subtypes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, R.; Tang, S.S.; Chen, M.; Peng, D.F.; Yan, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.Y.; Bao, Y.Q.; et al. Serum uric acid levels are associated with polymorphisms in the SLC2A9, SF1, and GCKR genes in a Chinese population. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köttgen, A.; Albrecht, E.; Teumer, A.; Vitart, V.; Krumsiek, J.; Hundertmark, C.; Pistis, G.; Ruggiero, D.; O’Seaghdha, C.M.; Haller, T.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 18 new loci associated with serum urate concentrations. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolz, M.; Johnson, T.; Sanna, S.; Teumer, A.; Vitart, V.; Perola, M.; Mangino, M.; Albrecht, E.; Wallace, C.; Farrall, M.; et al. Meta-analysis of 28,141 individuals identifies common variants within five new loci that influence uric acid concentrations. PLoS Genet 2009, 5, e1000504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.C.; Roberts, R.L.; Nanavati, P.; Miner, J.N.; Dalbeth, N.; Topless, R.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K. Association between ABCG2 rs2231142 and poor response to allopurinol: replication and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018, 57, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yee, S.; Liang, X.; Hoffmann, T.; Kvale, M.; Banda, Y.; Jorgenson, E.; Schaefer, C.; Risch, N.; Giacomini, K. Genome-wide association study identifies ABCG2 (BCRP) as an allopurinol transporter and a determinant of drug response. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2015, 97, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, B.; Brackman, D.J.; Zou, L.; Garcia-Cremades, M.; Sirota, M.; Savic, R.M.; Giacomini, K.M. Oxypurinol pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers: Influence of BCRP Q141K polymorphism and patient characteristics. Clin Transl Sci 2021, 14, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis-Moffatt, J.E.; Phipps-Green, A.J.; Chapman, B.; Jones, G.T.; van Rij, A.; Gow, P.J.; Harrison, A.A.; Highton, J.; Jones, P.B.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. The renal urate transporter SLC17A1 locus: confirmation of association with gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis-Moffatt, J.E.; Xu, X.; Dalbeth, N.; Merriman, M.E.; Topless, R.; Waddell, C.; Gow, P.J.; Harrison, A.A.; Highton, J.; Jones, P.B.; et al. Role of the urate transporter SLC2A9 gene in susceptibility to gout in New Zealand Māori, Pacific Island, and Caucasian case-control sample sets. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 60, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, D.J.; Yee, S.W.; Enogieru, O.J.; Shaffer, C.; Ranatunga, D.; Denny, J.C.; Wei, W.-Q.; Kamatani, Y.; Kubo, M.; Roden, D.M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association and Functional Studies Reveal Novel Pharmacological Mechanisms for Allopurinol. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2019, 106, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardiñas, A.F.; Nalmpanti, M.; Pocklington, A.J.; Legge, S.E.; Medway, C.; King, A.; Jansen, J.; Helthuis, M.; Zammit, S.; MacCabe, J.; et al. Pharmacogenomic Variants and Drug Interactions Identified Through the Genetic Analysis of Clozapine Metabolism. Am J Psychiatry 2019, 176, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetting, W.S.; Wu, B.; Schladt, D.P.; Guan, W.; van Setten, J.; Keating, B.J.; Iklé, D.; Remmel, R.P.; Dorr, C.R.; Mannon, R.B.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated With Immunosuppressant Pharmacokinetics and Adverse Effects in the DeKAF Genomics Genome-wide Association Studies. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chami, N.; Chen, M.H.; Slater, A.J.; Eicher, J.D.; Evangelou, E.; Tajuddin, S.M.; Love-Gregory, L.; Kacprowski, T.; Schick, U.M.; Nomura, A.; et al. Exome Genotyping Identifies Pleiotropic Variants Associated with Red Blood Cell Traits. Am J Hum Genet 2016, 99, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcot, V.; Brunet, J.; Daneault, C.; Tardif, J.C.; Des Rosiers, C.; Lettre, G. Validation of fatty acid intakes estimated by a food frequency questionnaire using erythrocyte fatty acid profiling in the Montreal Heart Institute Biobank. J Hum Nutr Diet 2015, 28, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, M.-O.; Leclair, G.; Oussaïd, E.; St-Jean, I.; Jutras, M.; Gaulin, M.-J.; Mongrain, I.; Busseuil, D.; Rouleau, J.L.; Tardif, J.-C.; et al. An association study of ABCG2 rs2231142 on the concentrations of allopurinol and its metabolites. Clinical and Translational Science 2022, 15, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nieuwenhuis, L.M.; Keating, B.J.; Festen, E.A.M.; de Meijer, V.E. The Impact of Donor and Recipient Genetic Variation on Outcomes After Solid Organ Transplantation: A Scoping Review and Future Perspectives. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monek, O.; Paintaud, G.; Bechtel, Y.; Miguet, J.P.; Mantion, G.; Bechtel, P.R. Influence of donor and recipient genotypes on CYP2D6 phenotype after liver transplantation: a study of mutations CYP2D6*3 and CYP2D6*4. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1998, 54, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverdière, J.; Meloche, M.; Provost, S.; Leclair, G.; Oussaïd, E.; Jutras, M.; Perreault, L.L.; Valois, D.; Mongrain, I.; Busseuil, D.; et al. Pharmacogenomic markers of metoprolol and α-OH-metoprolol concentrations: a genome-wide association study. Pharmacogenomics 2023, 24, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux Perreault, L.P.; Provost, S.; Legault, M.A.; Barhdadi, A.; Dubé, M.P. pyGenClean: efficient tool for genetic data clean up before association testing. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1704–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, P.R.; Danecek, P.; Palamara, P.F.; Fuchsberger, C.; Y, A.R.; H, K.F.; Schoenherr, S.; Forer, L.; McCarthy, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; et al. Reference-based phasing using the Haplotype Reference Consortium panel. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Nielsen, J.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Dey, R.; Gabrielsen, M.E.; Wolford, B.N.; LeFaive, J.; VandeHaar, P.; Gagliano, S.A.; Gifford, A.; et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2018, 50, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R.; Espinoza, L.R.; Wells, A.F.; MacDonald, P.; Lloyd, E.; Lademacher, C. The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of the hyperuricemia of gout: the CONFIRMS trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarawate, C.A.; Patel, P.A.; Schumacher, H.R.; Yang, W.; Brewer, K.K.; Bakst, A.W. Serum Urate Levels and Gout Flares: Analysis From Managed Care Data. JCR: Journal of Clinical Rheumatology 2006, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Chang, H.S.; Chen, H.C.; You, J.J.; Liou, H.H.; Ting, S.C.; Ger, L.P.; Li, S.C.; Tsai, K.W. Low C6orf141 Expression is Significantly Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güneş, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: knowledgebase and deposition resource. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D977–d985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatochi, M.; Kanai, M.; Nakayama, A.; Hishida, A.; Kawamura, Y.; Ichihara, S.; Akiyama, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Furusyo, N.; Shimizu, S.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel loci associated with serum uric acid levels in Japanese individuals. Commun Biol 2019, 2, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Sim, X.; Go, M.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Gu, D.; Takeuchi, F.; Takahashi, A.; Maeda, S.; Tsunoda, T.; Chen, P.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies multiple loci associated with kidney function-related traits in east Asian populations. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, R.; Cadzow, M.; Markie, D.; Bixley, M.; Phipps-Green, A.; Major, T.J.; Li, C.; Choi, H.K.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; et al. Trans-ancestral dissection of urate- and gout-associated major loci SLC2A9 and ABCG2 reveals primate-specific regulatory effects. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.L.; Wallace, M.C.; Phipps-Green, A.J.; Topless, R.; Drake, J.M.; Tan, P.; Dalbeth, N.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K. ABCG2 loss-of-function polymorphism predicts poor response to allopurinol in patients with gout. Pharmacogenomics J 2017, 17, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishe, H.Z.; Stocker, S.L.; Stamp, L.K.; Dalbeth, N.; Merriman, T.R.; Phipps-Green, A.; Wright, D.F.B. The impact of genetic variability in urate transporters on oxypurinol pharmacokinetics. Clin Transl Sci 2023, 16, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, J.E.; Albrecht, E.; Teumer, A.; Mangino, M.; Kapur, K.; Johnson, T.; Kutalik, Z.; Pirastu, N.; Pistis, G.; Lopez, L.M.; et al. Modulation of Genetic Associations with Serum Urate Levels by Body-Mass-Index in Humans. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0119752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleophas, M.C.; Joosten, L.A.; Stamp, L.K.; Dalbeth, N.; Woodward, O.M.; Merriman, T.R. ABCG2 polymorphisms in gout: insights into disease susceptibility and treatment approaches. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 2017, 10, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Jarmuzewska, E.A. The influence of heart failure on the pharmacokinetics of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular drugs: a critical appraisal of the evidence. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2019, 85, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardiñas, A.F.; Kappel, D.B.; Roberts, M.; Tipple, F.; Shitomi-Jones, L.M.; King, A.; Jansen, J.; Helthuis, M.; Owen, M.J.; O’Donovan, M.C.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics of clozapine in an ancestrally diverse sample: a longitudinal analysis and genome-wide association study using UK clinical monitoring data. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).