1. Introduction
The task of determining the semantic meaning of a word from the context of a sentence is a challenging problem in natural language processing (NLP) that can be difficult for both humans and computers [
1]. The Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) problem is one such challenge that has been the subject of extensive research in the field of NLP. In fact, some researchers believe that the WSD problem is AI-complete [
2]. This means that if a computer could solve this problem, it would be able to solve all other artificial intelligence problems at the same time. However, in this paper the WSD problem is treated as a simple data classification problem, which large neural networks must be able to solve with almost 100 % accuracy if a suitable classification scheme is provided.
Various WSD solutions have been proposed over several decades of research, among which deep neural networks are the most effective [
3]. These solutions model the WSD problem as a classification task, where each class corresponds to a specific concept or synset. Usually, a separate model is trained for each word on a corpus of sentences annotated with that word. However, a neural network-based WSD solution requires a large amount of annotated data, which may not be available for many words. Therefore, knowledge-based methods, which exploit the relations between semantic categories in a knowledge base, offer an alternative way to solve the WSD problem [
4,
5]. These methods infer the most likely sense of a word based on the semantic context.
One of the main assumptions of knowledge-based methods is that the relations between concepts in the knowledge base are accurate and reliable, i.e. they are free of errors. To illustrate that this is not always the case, we take the word ‘
table’ from the semantic dictionary WordNet [
5], which is the primary knowledge base used in this study, and examine its suitability as a formal ontology.
The word ‘table’ has 8 senses, 6 of which are nouns. Only 2 of these noun senses can be considered as ontology classes: ‘table%1:14:00::’ - (a set of data arranged in rows and columns). ‘table%1:06:01::’ - (a piece of furniture having a smooth flat top that is usually supported by one or more vertical legs). The remaining 4 noun senses are not appropriate as ontology classes of the word ‘table’. For instance, ‘table%1:06:02::’ - (a piece of furniture with tableware for a meal laid out on it) is a specific instance of the sense ‘table%1:06:01::’ and can be ignored for many natural language semantic analysis tasks. Another sense: ‘table%1:14:01::’ - (a company of people assembled at a table for a meal or game) is described in WordNet as an abstract entity and it is impossible logically derive from the WordNet knowledge base that it is a collection of physical entities.
Some may contest the assertion that the word "table" possesses only two discernible semantic meanings, thereby raising the query: can a formal methodology be devised for categorizing words into distinct semantic classes? This question becomes even more pertinent when considering the lack of uniformity in existing approaches. Previous works [
6], [
7], [
8] and [
9] demonstrate a significant disparity in how semantic meanings are classified for individual words. This inconsistency poses a challenge for researchers attempting to compare findings across different studies and hinders the development of a unified framework for semantic analysis.
Addressing this query constitutes a focal point of this research paper. The central idea of our proposed formalization revolves around harnessing the capabilities of deep learning models to extract word embedding vectors. It is assumed that these vectors, when subjected to clustering analysis, should correspond closely to the conceptual categories delineated within a formal ontology, given the sufficient training and parameterization of the deep learning model.
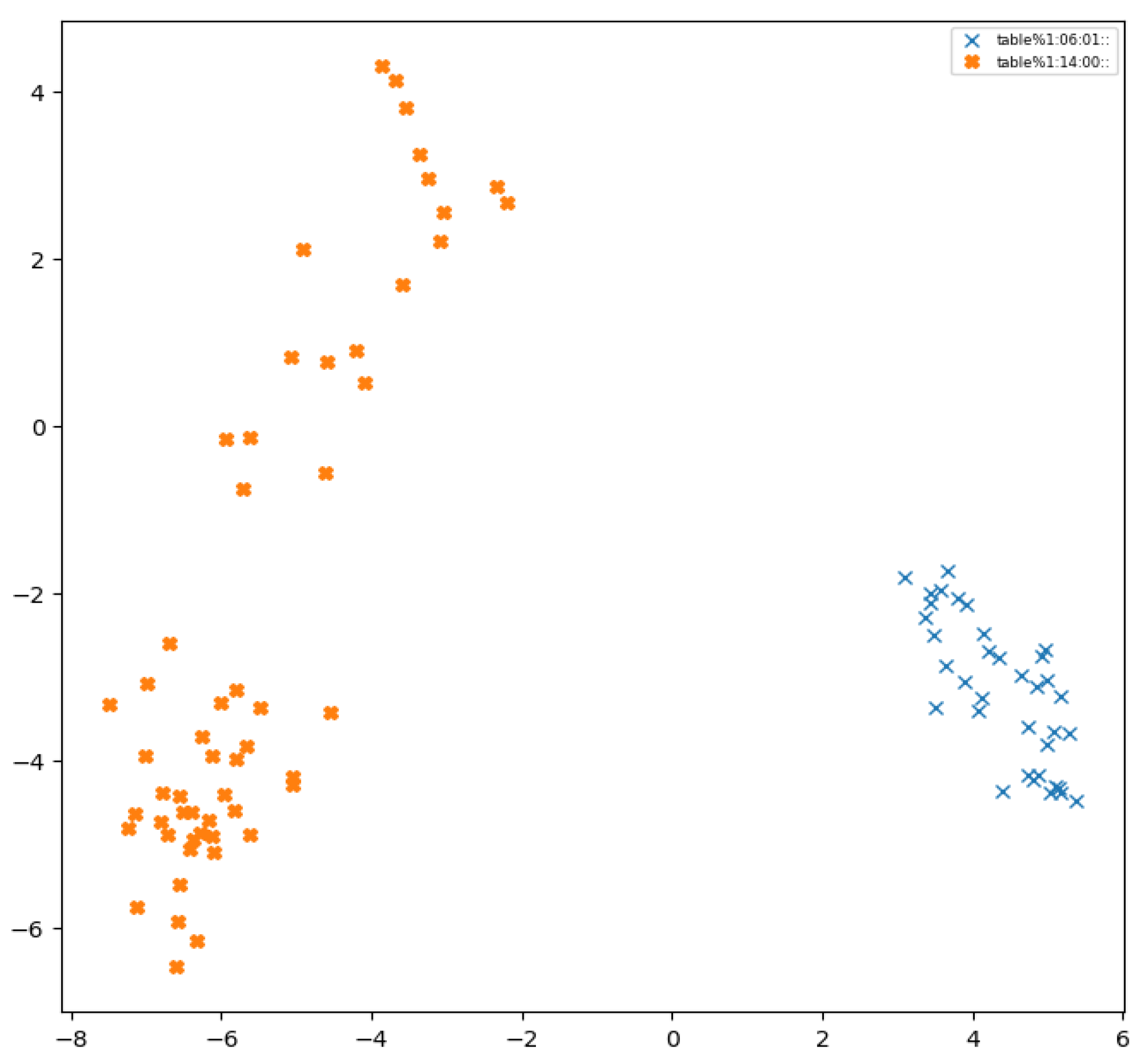
Figure 1 illustrates this premise, depicting the projection of embedded vectors onto the first two principal components derived through principal component analysis (PCA), obtained from the BERT [
10] model after processing sentences containing the term "table." Notably, the visual representation in the figure reveals two distinct clusters discerned by the BERT model. The method presented within this paper facilitated the consolidation of six synsets attributed to the word "table" within WordNet into two coherent categories. Remarkably, the alignment between these two synsets and the delineated clusters in the PCA projection underscores the efficacy of presented approach in aligning semantic categorization with the inherent structure of the deep learning model's representations.
Another important assumption made in WSD tasks is the assumption that human-annotated sentences are the gold standard that is error-free. However, this assumption is fundamentally flawed, as errors can occur not only in programming but also in the process of annotating data. During programming, we can compile and test the program that is to eliminate some errors. Meanwhile, when annotating natural language sentences, we often have no feedback about the quality of the annotations, and as a result, the probability of errors is quite high.
Method presented in this paper abandons these two assumptions and considers that the uncertainty of the WSD problem arises from the following elements of the knowledge base: 1) not having enough annotated sentences, 2) poorly annotated sentences, that is, cases when the person annotating the sentences made a mistake in determining the semantic meaning of the word, and 3) incomplete and erroneously designed knowledge base. By addressing these issues, suggested method is able to achieve high accuracy in solving the WSD task.
In addition to the proposed WSD method, this paper introduces a system that effectively implements it. The system consists of two essential components: the novel WSD system, characterized by its ability to achieve classification accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art systems while maintaining relatively low computational memory consumption. This makes it particularly valuable in natural language tasks that involve the use of embedded word vectors derived from deep neural networks, where computational resources are often limited.
The other component of the system is a debugger tool for the WSD task. The key idea behind this tool is to use embedded vector clusters as the reference standard, allowing the detection of outliers in the embedding space that indicate inconsistent annotations or inaccuracies in the knowledge base design. The motivation for developing this tool came from the system’s error analysis. Interestingly, the analysis showed that many classification errors were due to human annotator mistakes rather than system limitations.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 describes the new WSD system, which has two main advantages over other WSD systems. First, it achieves comparable accuracy while consuming much less computational memory. Second, it is implemented in a Google Colab notebook, which enables easy testing and integration of the system with other NLP frameworks using only a web browser.
Section 3 introduces the system training algorithm, highlighting its reliance on standard machine learning libraries, a unique feature that enhances its accessibility and extensibility.
Section 4 introduces the debug method for the WSD task, a tool for creating semantic dictionaries and ontologies. This WSD debug method not only identifies incorrectly annotated sentences but also lets users to refine and correct these sentences, assessing their impact on model training.
Section 6 presents the results of a comprehensive experiment, encompassing standard datasets for the WSD problem, to evaluate the developed system's accuracy. The paper concludes with a summary and a discussion of future work.
2. WSD framework
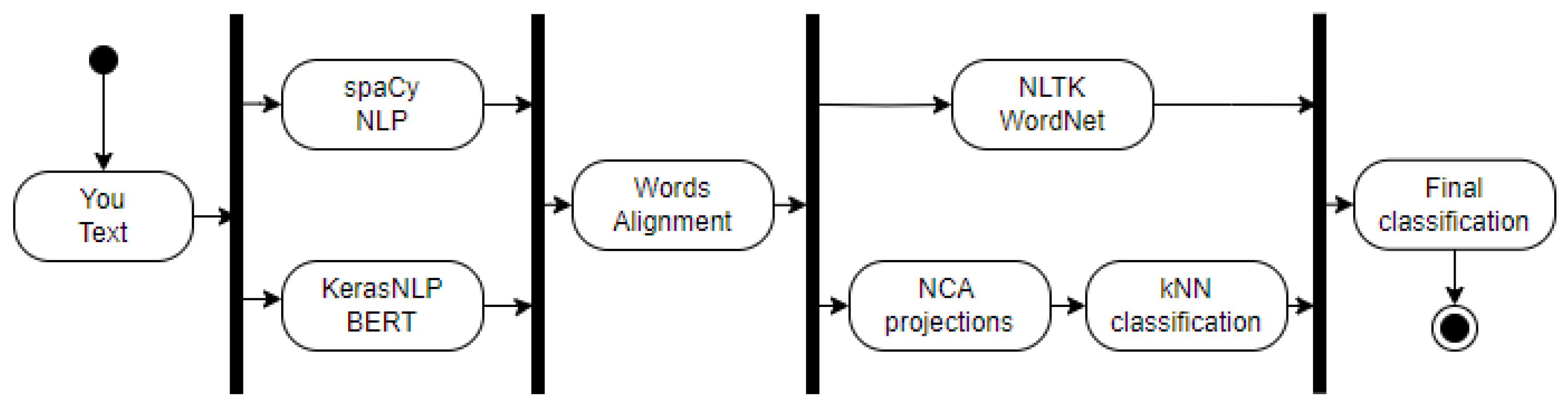
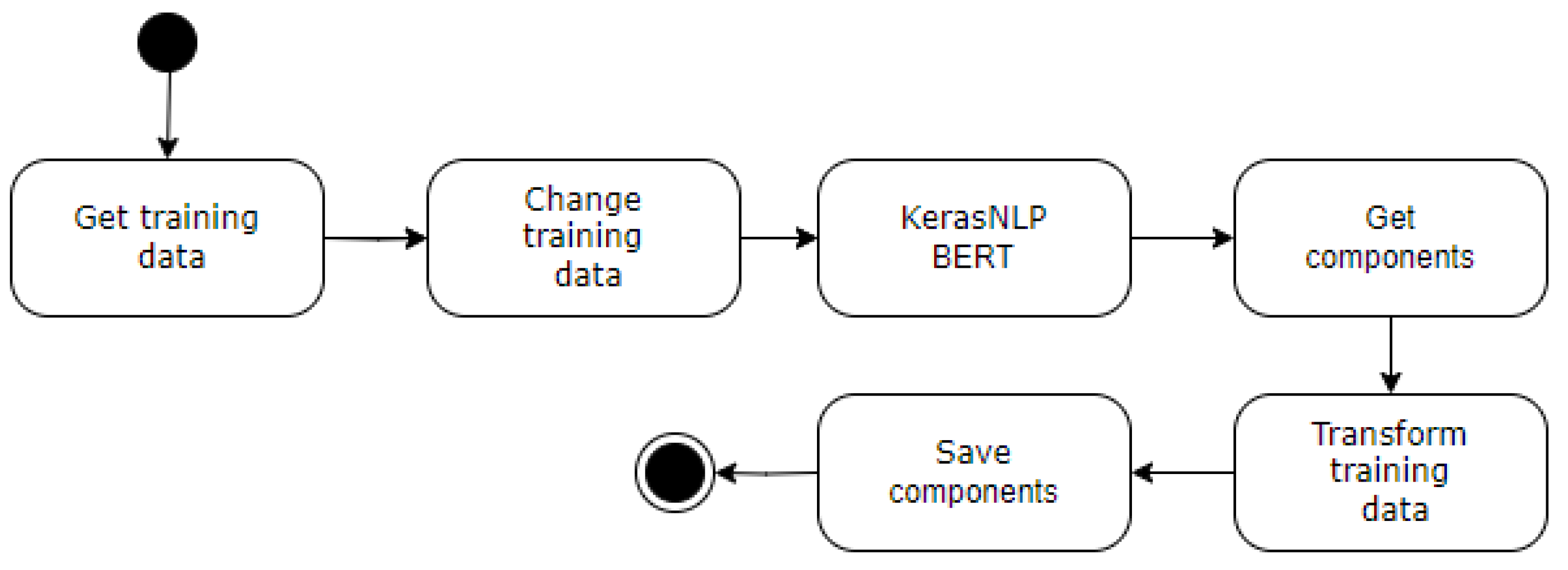
The proposed word sense disambiguation framework sits within a broader natural language processing pipeline (
Figure 2). This minimal representation showcases the system's integration and clarifies its role in addressing the WSD problem. The framework comprises eight key components:
You Text: The initial stage begins by receiving raw text input.
spaCy NLP: This component processes the text, extracting word lemmas and determining grammatical forms through spaCy's NLP models [
11].
KerasNLP BERT: Leveraging the KerasNLP library [
12], the system generates contextual BERT neural network embedding vectors for each word in the sentence.
Words Alignment: Alignment results from both spaCy and KerasNLP models are combined, creating an index that maps corresponding words between the two representations.
NLTK WordNet: Employing NLTK [
13] WordNet synset tags, this module annotates all words in the text. The algorithm selects the most frequent synset for each word.
NCA Projections: The system projects each word into a n dimensional space derived from the training data, capturing essential semantic relationships.
kNN classification: Employing the kNN method for the classification of words potentially having multiple semantic meanings, where their lemma can be described by several WordNet synset values.
Final classification: This model consolidates the information from previous stages, providing the final, refined classification for each word.
Detailed descriptions of the critical components follow, offering a deeper understanding of the WSD framework's inner workings.
spaCy NLP. The core component of the proposed WSD framework is the spaCy NLP library. spaCy offers several functionalities critical to WSD, each addressing a specific aspect of the problem:
Tokenization and Lemmatization. spaCy segments the input text into individual words (tokens) and identifies the lemma (base form) for each token. This is crucial for WSD as the synset classifier operates on lemmas, ensuring consistent representation across different word inflections.
Noun Phrase Chunking. spaCy identifies noun phrases (NPs) within the text. NPs play a twofold role: first, they help pinpoint potential word combinations aligning with distinct synsets in WordNet. Second, chunking facilitates the identification of the head noun within the NP, enabling the selection of the most relevant synset for the entire phrase.
Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging. spaCy assigns grammatical tags (POS tags) to each word, indicating its role within the sentence (e.g., noun, verb, adjective). POS tags are valuable features for the synset classifier, providing additional context alongside the lemma for more accurate WSD.
Dependency Parsing. spaCy can also extract dependency relationships between words in a sentence. While not currently utilized in this WSD framework, dependency information holds promise for future development. Analyzing these relationships could refine word sense disambiguation by considering the syntactic structure of the sentence.
Named entity recognition (NER): NLP libraries often include NER modules that identify pre-defined named entities like people, locations, and organizations. However, NER typically covers a limited range of semantic categories compared to WSD. In spaCy and similar libraries (e.g., Stanford CoreNLP [
14]), NER addresses only a subset of noun phrases. This framework proposes aligning NER categories with their corresponding hypernyms in WordNet, potentially leveraging existing NER functionalities to support WSD. By contrast, the WordNet WSD module independently identifies words and phrases suitable for disambiguation, going beyond the limitations of NER.
Two widely recognized NLP libraries, spaCy and Stanford CoreNLP, were subjected to experimentation. Individual Colab documents were generated for each library, presenting a comprehensive illustration of their potential in addressing the word sense disambiguation problem. The subsequent discussion will center on the spaCy library, with the understanding that the outlined principles are equally applicable to the Stanford CoreNLP library.
KerasNLP BERT. A crucial element of the proposed WSD method is the integration of KerasNLP. This library offers the capability to leverage various pre-trained deep neural network models, enabling further training on fresh data or the extraction of embedded word vectors. In the context of this research, the focus is on showcasing outcomes derived from employing the BERT neural network. BERT's adeptness lies in its capacity to generate embedding vectors for words within a sentence, a process integral to assessing the significance of each word synset. By using BERT's word embedding vectors, we aim to enhance the precision and granularity of disambiguation results, thereby reinforcing the overall efficacy of our WSD approach.
Words Alignment. The integration of spaCy NLP and KerasNLP modules stands as a pivotal aspect of our methodology. These modules operate independently, each generating its own tables of words (or tokens in the case of KerasNLP). However, due to potential disparities between these tables, an additional step is necessary to establish correspondence. This entails creating an index that maps spaCy words to their respective tokens in KerasNLP. The algorithm facilitating this matching process is straightforward and involves the following key steps:
Sequentially scanning the spaCy word table, each word is matched to the beginning of a token from the list generated by BERT tokenizer.
To identify the corresponding beginning of the word (token) from the BERT module, consecutive tokens are successively combined and compared against the given spaCy word. Upon finding a match, the index of the first located BERT token is returned. This iterative process ensures the alignment of spaCy words with their corresponding tokens in KerasNLP, facilitating integration within the WSD framework.
NLTK WordNet. The NLTK WordNet module is a key component of our WSD methodology, as it provides a convenient API for accessing the WordNet dictionary. This module helps us assign synset values to words that either have no sample sentences or have only one synset value. Furthermore, the choice of the NLTK WordNet module was driven by important non-functional requirements that emerged during the project development.
One of these requirements was the compatibility of the WSD system code with the Google Colab environment, especially when using the “Run all” menu option. Among the various approaches to the WSD problem that have been proposed in the last 30 years, only the NLTK WordNet module, along with its WSD Lesk algorithm [
15], fulfilled this requirement. This demonstrates the NLTK WordNet module’s dependability and flexibility, making it an essential element of our WSD framework.
NCA projections. The Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm is a simple yet powerful method for solving the word sense disambiguation problem. It only depends on one parameter, and its accuracy improves as more training data is available. However, KNN faces a significant challenge when applied to the WordNet WSD problem. This challenge stems from the high computational cost of storing and searching the whole dataset in memory to find the synsets for each word in a given sentence. In our approach, we overcome this limitation of KNN by using a technique that projects the embedded word vectors into a lower-dimensional subspace before applying the KNN classifier. The dimensionality of this subspace is dynamically adjusted during the training phase. To choose the best components for this transformation, we use the Neighbourhood Components Analysis (NCA) method [
16], which ensures an efficient and effective solution to the WSD problem within the WordNet framework.
Final classification. The word sense disambiguation problem is often a prerequisite for solving other tasks in natural language processing. The final classification module, which integrates the results of previous steps, is crucial for delivering these results to the specific task that needs WSD resolution. In this project, we have identified some NLP tasks that benefit from the outcomes of WSD. One of them is 3D scene generation, where the WSD results help us make two important decisions: determining whether a noun phrase refers to a physical object that needs to be represented in the 3D scene, and finding out whether the objects in the scene have any movement. Another task is animating works of fiction. Like in 3D scenes, identifying noun phrases that describe relevant objects is essential. Therefore, the algorithm for the Final Classification module consists of the following steps:
Using the spaCy library, we extract noun and verb phrases.
Using spaCy's grammatical relation analysis, we find the main (head) word in each phrase.
Using the WSD module, we select noun phrases where the head word indicates a physical object. We also mark verb phrases where the head word expresses physical body movement.
Only the selected phrases that meet these criteria are used for the final NLP task, which involves phrases related to physical objects and stage movement, thus enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of subsequent NLP operations.
3. Training
The principal objective of this project was to develop a model capable of achieving accuracy comparable to existing models utilizing embedded word vectors, as demonstrated in [
17,
18,
19]. A key innovation pursued from inception was the imperative for the model to significantly reduce computational memory footprint while maintaining such accuracy levels.
Following the successful attainment of predefined targets related to model size and accuracy, an exhaustive investigation was undertaken to dissect the underlying causes of error propagation in the context of word sense disambiguation. Leveraging established datasets [
20,
21,
22,
23], our analysis revealed that certain inaccuracies did not originate from inherent model deficiencies but rather from distinct sources:
Test Dataset Discrepancies: The first source of error was discrepancies within the test datasets themselves. Variability in annotation quality, data distribution, and contextual diversity posed challenges for accurate disambiguation.
Annotation Errors in Training Data: Secondly, we identified annotation errors within the training dataset [
24]. These inaccuracies propagated through the model, affecting its performance during inference. Addressing and rectifying such errors became crucial for enhancing model robustness.
WordNet Synset Limitations: Our investigation highlighted inadequacies within WordNet synset relations and descriptions. While WordNet serves as a valuable lexical resource, it occasionally fails to capture subtle nuances required for comprehensive sense disambiguation. Notably, we observed an overly granular segmentation of certain words into synsets, hindering accurate sense resolution. Therefore, when modifying WordNet synset lists or relations, it is crucial to consider the intended application of natural language processing. In this work, synset merging decisions were guided by the ultimate goal of using NLP to generate 2D and 3D models, as described in [
1]. Over the past five decades, starting with the pioneering SHRDLU system [
25], numerous systems have attempted natural language manipulation of computer graphics objects (see [
26] for a review of 26 such systems). Many of these systems process multiple sentences to identify physical objects within a 3D scene, often leveraging spatial knowledge to resolve ambiguities (e.g., SceneSeeer [
27]). This specific NLP application guided the WSD solution presented in this paper.
Data Scarcity for Specific Words: Another critical constraint emerged—the lack of sufficient data to construct reliable classifiers for specific words. This limitation hindered the model’s ability to generalize effectively across the entire lexicon, particularly for low-frequency or domain-specific terms.
To address the limitations identified in the error analysis, we propose a refined model training process outlined in
Figure 3. This section delves into a detailed breakdown of each component and its contribution to enhanced model performance.
Get training data. This project employed a multi-phased approach to data acquisition, aiming to create a robust and iteratively improvable WSD model.
The initial training data consisted of sentences from the widely used SemCor corpus [
24]. While effective, this dataset's limitations necessitated exploring alternative sources. Here, we detail the exploration of various data augmentation techniques and their impact on model performance.
WordNet Definitions: Initially, we attempted to improve model performance by augmenting data using the existing WordNet synset definitions. However, utilizing the WSD debug method described later, we observed a detrimental effect on accuracy when incorporating certain definitions. Consequently, some definitions were excluded during the iterative improvement process.
Artificially Generated Sentences: We further investigated the inclusion of artificially generated sentences based on WordNet's hypernym and hyponym relations. These sentences were constructed by combining hypernym/hyponym definitions with a phrase indicating the intended meaning. Evaluation revealed this approach to be ineffective, and the generated sentences were not used in further training.
Wikipedia Articles: Given the BERT neural network's pre-training on Wikipedia data, we explored the impact of incorporating additional Wikipedia sentences. This approach proved successful. Adding approximately 10 new sentences per novel synset value demonstrably improved the model's ability to identify those synsets.
FrameNet Sentences: Considering the planned future integration of FrameNet with WordNet, we investigated the inclusion of FrameNet sentences. While a comprehensive FrameNet-WordNet merger falls outside this paper's scope, a subset of FrameNet sentences was incorporated to enhance the model's performance.
Chatbot-Generated Sentences: Finally, we explored the use of chatbots (ChatGPT 3.5, Microsoft Copilot, and Google Gemini) for generating new training data. This method offered a convenient way to obtain novel sentences. However, rigorous human expert evaluation ensured only accurate sentences were added to the training data.
Change training data. Following data acquisition, a process of data replacement ensued, whereby synset tags of certain words were substituted either due to mislabeling within the dataset or as a result of the consolidation of WordNet synsets by the knowledge base manager, thereby creating a new version of WordNet. All requisite transformations were documented in textual format on the GitHub portal, facilitating direct editing through the platform's integrated text editor.
KerasNLP BERT. Subsequently, the KerasNLP library is employed to generate embedding vectors for each word within the sentences. Noteworthy observations during this phase highlighted a limitation of the BERT model pertaining to its sensitivity when encountering words absent from its dictionary. For instance, the word 'Fujimoto' would be tokenized into 'Fuji', 'mo', and 'to', potentially leading to significant deviations in embedded vectors for other words within the sentence. Nevertheless, the selection of the KerasNLP library was predicated upon its adherence to key non-functional requirements, namely stable performance, rapid model loading, and anticipated long-term support.
Get Components. This project explores a novel approach to word sense disambiguation (WSD) by leveraging Neighborhood Component Analysis (NCA) in conjunction with word embedding vectors derived from the BERT neural network. While established methods such as fine-tuning and transfer learning excel at integrating pre-trained networks for new tasks (e.g., sentiment analysis), they are often tailored towards creating new classifiers. Our objective, however, diverges from simply generating a WordNet synset classifier. Instead, we aim to reshape WordNet's structure to better align with the knowledge encoded within BERT. This focus on interactive knowledge restructuring necessitates a WSD method that facilitates the visualization of learned knowledge.
Here, word embedding vectors and their multidimensional projections become the cornerstone of model selection due to their inherent visualizability. Following a comprehensive evaluation of vector design methods offered by scikit-learn, NCA projections were chosen for their demonstrably superior performance in identifying synset values.
We further refined the NCA model by meticulously tuning its meta-parameters. Notably, each word sense is assigned a k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) classifier operating within the n-dimensional NCA component space. Exploration of these parameters (k ranging from 2 to 5, n ranging from 2 to 5) was conducted during model training, with a focus on maximizing classification accuracy. Additionally, a stringent regularization criterion was implemented: each unit increment in a parameter must yield at least a one percent enhancement in model accuracy. This ensures robustness and stability during the training process.
Transform training data. In our model, we employ a systematic approach to project word embedding vectors into the foundational NCA component space. This projection process constitutes the core architecture of our model, which is composed of two principal elements: the NCA component vectors and the training data projections derived from the NCA framework. It is crucial to highlight that both vector types—NCA components and data projections—are precisely rounded to two decimal places. This exacting standard serves a twofold purpose: it optimizes memory resource utilization, facilitating efficient data storage and computational processing; and it ensures uniformity and coherence in the model's representational schema. By adopting this method, we achieve equilibrium between computational efficiency and the fidelity of the model's representations, allowing for smooth integration and deployment across various computational settings.
Save components. A critical stage in the training process involves the development of a dedicated classifier. This independent classifier plays a vital role in refining the model's capacity for accurate word sense disambiguation. Once the training phase is complete, the WSD model is serialized and stored in the JSON format. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a well-established and interoperable data exchange standard that facilitates the efficient storage and transmission of the model's architecture and parameters. This preservation strategy ensures seamless accessibility and enables straightforward dissemination of the model for future research applications.
4. Debugging and Knowledge Base Management System
The WSD model heavily relies on established lexical resources such as WordNet and the SemCor corpus. While these resources have proven valuable for NLP tasks, their lack of recent updates (over a decade) can limit their ability to handle the evolution of language and the emergence of new word senses. This paper proposes a systematic approach to address this limitation. We aim to enhance the quality and coverage of WordNet and SemCor for WSD tasks. This section will focus on debugging and expanding the knowledge base within WordNet, as well as enriching the annotated textual sentences in SemCor. By improving these resources, we aim to increase the adaptability and applicability of WordNet to diverse linguistic contexts and domains.
This paper proposes a multifaceted methodology to address limitations in existing lexical resources like WordNet. The methodology focuses on two key aspects: (1) Debugging the WordNet knowledge base to identify and rectify inconsistencies and inaccuracies in synset descriptions, thereby enhancing their reliability for WSD tasks. (2) Expanding WordNet with new synsets to accommodate the evolving nature of language and ensure its continued relevance for contemporary NLP applications. By improving the quality and coverage of WordNet and similar resources like SemCor, this approach aims to increase the adaptability and applicability of these tools to diverse linguistic contexts and domains.
Figure 4 illustrates a schematic of the proposed WSD debugging methodology, a five-stage process designed to address inconsistencies and inaccuracies in WordNet. The initial stages (1 & 2) focus on data preparation and semantic representation. Stage 1 involves rigorous data selection and pre-processing of training and testing data (including cleaning and augmentation) to ensure data quality and representativeness. Stage 2 leverages the pre-trained "KerasNLP BERT" module to acquire embedded word vectors from the prepared data. This captures rich semantic representations for each word within its context.
Stages 3-5 address knowledge base exploration and refinement. Stage 3 performs cluster analysis on the embedded vectors. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reduces dimensionality and groups words with similar semantic properties, facilitating synset consolidation and revealing potential inconsistencies. Stage 4 utilizes "Projection Analysis" to provide an interactive interface for exploring semantic relationships between synsets. This visual exploration (2D/3D) helps identify and rectify inconsistencies within the synset hierarchy. Finally, Stage 5 involves the evaluation and integration of various WSD candidate models. This rigorous assessment ensures selection of the most effective model for integration, ultimately improving disambiguation performance. Next, we will describe these steps in the WSD debug task in more detail.
Figure 4.
WSD debug method.
Figure 4.
WSD debug method.
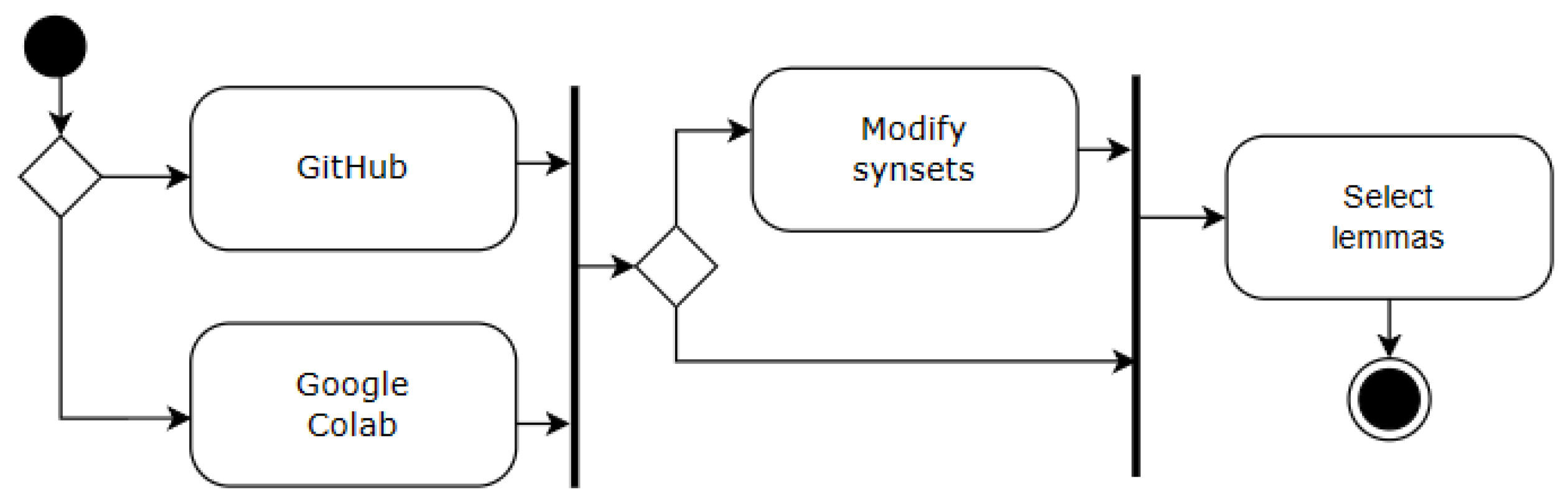
4.1. Select data
This work introduces the "Select Data" process, a flexible framework for evaluating word sense disambiguation model performance through targeted data selection (Figure 4). The process empowers researchers to investigate the influence of both individual words and word group characteristics on model accuracy.
Figure 4.
Select data sub-process.
Figure 4.
Select data sub-process.
The first step involves choosing an appropriate data source. This project employed a curated training and testing dataset publicly available on GitHub (https://github.com/aalgirdas/wordnet_onto). Alternatively, researchers can leverage custom datasets stored locally (e.g., Google Drive) to address specific research questions.
Despite its extensive history, WordNet remains a foundational resource for WSD tasks. However, inaccuracies in corpus annotation and WordNet synset relationships were identified during this project, necessitating modifications for improved semantic representation. The "Modify Synsets" step allows researchers to select either the original WordNet version or implement targeted modifications to synset descriptions and sentence annotations. Importantly, all modifications are meticulously documented and stored on GitHub, enabling transparent and reproducible research.
Finally, the "Target Word Selection" step provides granular control over the analysis. Researchers can choose to investigate a specific lemma, select individual words, or designate a list of lemmas for analysis. This flexibility ensures investigations align precisely with research objectives, facilitating a more refined and targeted approach to WSD model development.
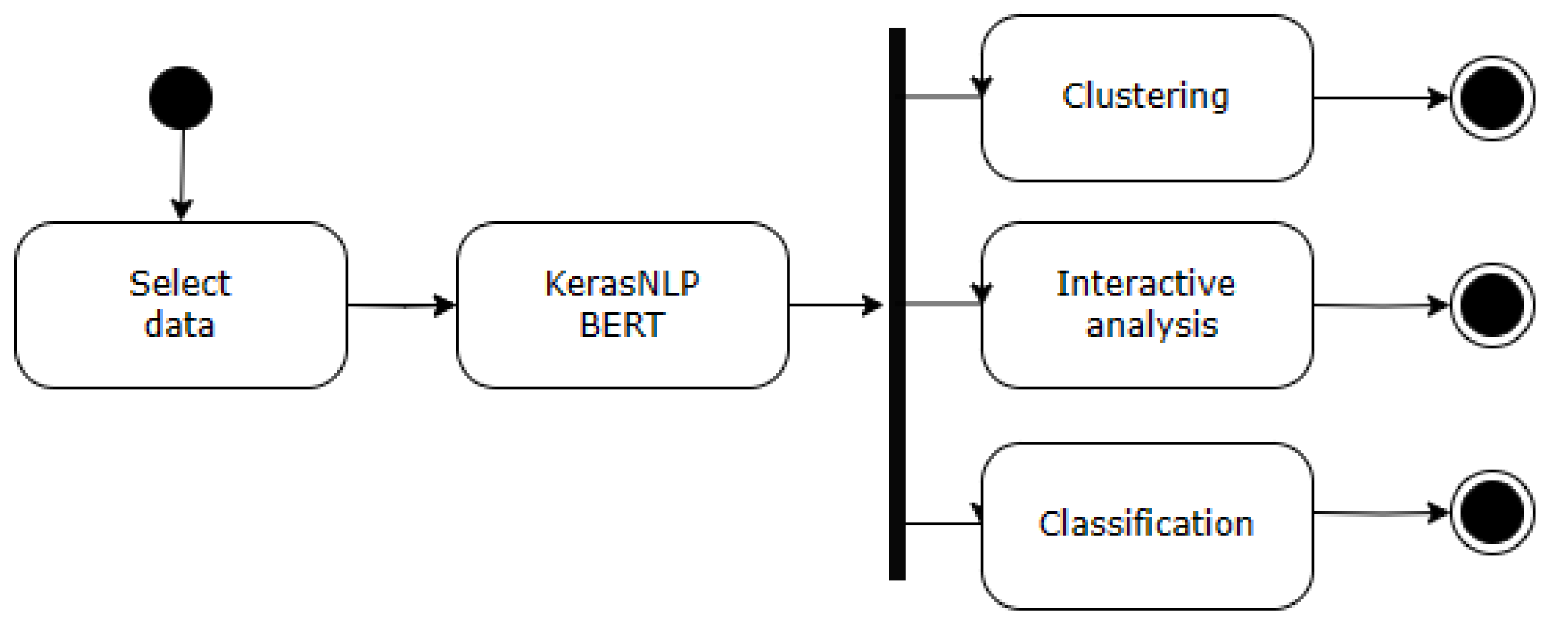
4.2. Clustering
This work hypothesizes that a deep neural network (DNN) trained on comprehensive natural language processing tasks can implicitly capture semantic relationships useful for word sense disambiguation. We propose an approach where embedded vectors learned by such a DNN are clustered, with each cluster potentially representing a distinct sense. By comparing these data-driven clusters with the existing sense inventory of a knowledge base (e.g., WordNet), discrepancies between the two can be identified. These inconsistencies may indicate the need for refinements in either the knowledge base's sense definitions or the DNN architecture and training data.
To facilitate WSD debugging and knowledge base refinement, we propose a clustering-based approach to analyze embedded vectors. This method empowers knowledge engineers to make informed decisions regarding synset merging, deletion, or creation. Two clustering algorithms are considered for this purpose: Principal Component Analysis and Neighborhood Component Analysis. While KMeans is employed for all clustering tasks throughout this project for consistency, future work will explore the potential benefits of utilizing alternative algorithms in the context of WSD debugging to assess their impact on efficacy.
The initial phase of clustering entails determining the optimal number of clusters. The algorithm unfolds through several key steps:
Selection of vector projection method: The clustering algorithm offers flexibility in vector projection methods, including Principal Component Analysis or Neighborhood Component Analysis.
Vector projection: Embedded vectors undergo projection, a crucial preparatory step for subsequent calculations.
-
Cluster determination and evaluation:
- 3.1.
Application of KMeans clustering algorithm: Employing the KMeans algorithm on the projected vectors enables the delineation of clusters and the assignment of each sample to its corresponding cluster.
- 3.2.
Metric calculation: Two pivotal metrics, namely silhouette score and adjusted mutual information score, are computed for each potential cluster configuration, providing quantitative insights into the quality and coherence of resultant clusters.
Optimal cluster selection: The ultimate determination of the ideal number of clusters hinges upon selecting the configuration yielding the highest product of silhouette score and adjusted mutual information score, indicative of optimal clustering performance.
This systematic approach to cluster determination not only ensures robustness and reproducibility but also facilitates informed decision-making for knowledge engineers engaged in WSD debugging tasks. Furthermore, the incorporation of diverse vector design methods and comprehensive evaluation metrics underscores the methodological rigor essential for advancing the field of natural language processing.
4.3. Clasification
In alignment with the objectives of this project, the Classification module within the WSD debugging task shares a fundamental aim with its clustering counterpart: to equip knowledge engineers with actionable insights for merging, deleting, or introducing new sentence examples. To achieve this objective, a submodel named as the "Confusion Matrix" has been designed and implemented. The procedural delineation of this component is outlined as follows:
Data Partitioning: The initial step entails determining the allocation ratio for test and training data. By default, this parameter is set to 0.1, signifying that 10 percent of the total dataset will be randomly earmarked for testing purposes, with the remainder designated for training.
k-Nearest Neighbors Exploration: Subsequently, an experimental phase ensues, leveraging the k-nearest neighbors (KNN) method on the designated test and training datasets.
Iterative Experimentation: This experimentation process is iterated N times, facilitating the accumulation of a broader spectrum of measurements.
Confusion Matrix Computation: Following experimentation, the confusion matrix is computed based on the amassed data. These results are then presented to the knowledge engineer, who assumes the pivotal role of making final determinations concerning potential synset redesigns.
This methodical approach to classification not only serves to enhance the efficacy of the WSD debugging endeavor but also empowers knowledge engineers with actionable insights derived from rigorous experimentation. Moreover, the iterative nature of the experimentation process, coupled with the utilization of established methodologies such as KNN and the computation of the confusion matrix, underscores the methodological robustness essential for advancing the domain of natural language processing.
4.4. Interactive Analysis for Informed Synset Editing
In tandem with the classification and clustering models, an interactive analysis module was developed to facilitate informed decisions regarding synset editing by knowledge engineers. This module leverages dimensionality reduction techniques and visual representations to provide a user-friendly exploration of the underlying semantic relationships within the data.
Visualizing Semantic Clusters: The module offers a 2D scatter plot depicting the projections of word embedding vectors onto the first two principal components (PCs) derived from Principal Component Analysis applied to the training data. Test data projections are overlaid for comparison. Users can interactively select data points or regions on the plot to retrieve the corresponding sentence examples. Additionally, the ability to overlay WordNet lexnames, synset labels, or hypernym labels further aids in comprehending whether specific data clusters align with these semantic categories. This visual exploration empowers knowledge engineers to identify potential synset refinements by uncovering clusters that deviate from expected semantic groupings.
Dimensionality Reduction and Neighborhood Analysis: While PCA provides a valuable 2D visualization for initial analysis, Neighborhood Component Analysis can be employed to assess the information retained in higher dimensions. The NCA projection, presented as another interactive 2D graph, allows users to evaluate the feasibility of disambiguating the target word based on the inherent structure of the data. This visualization can also serve as a valuable tool for identifying potential annotation errors within the training data by highlighting points that deviate significantly from their expected semantic neighbors.
3D Exploration for Enhanced Insights: For a more comprehensive perspective, the system offers the option to explore the data in a 3D scatter plot. Similar to the 2D view, users can select between PCA and NCA for dimensionality reduction, allowing for in-depth examination of potential semantic relationships across multiple dimensions. This interactive 3D environment provides additional opportunities for knowledge engineers to refine their understanding of the data and make informed decisions regarding synset modifications.
Overall, the inclusion of the interactive analysis module empowers knowledge engineers with a comprehensive set of visual tools to analyze semantic relationships within the data [
28], [
29]. This facilitates a more informed approach to synset editing, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of the WSD system.
5. Results
This work initially focused on enriching the SemCor dataset with WordNet gloss descriptions to enhance semantic representation. The core objective was to develop a WSD model with two key properties: 1) significantly reduced memory footprint compared to existing deep learning approaches, ensuring compatibility with resource-constrained environments like Google Colab, and 2) state-of-the-art accuracy on benchmark datasets like SemEval. This goal was achieved through a novel method that leverages Neighborhood Component Analysis (NCA) for dimensionality reduction and incorporates a vector quantization step, where embedded vector values are rounded to a predefined precision (e.g., two decimal places).
Following the initial model development, a detailed error analysis was conducted to investigate the misclassification of a significant number of synsets. This analysis revealed two key issues: (1) the presence of errors in sentence annotations within the training data, and (2) inconsistencies in synset assignments for semantically similar words within WordNet. To address these shortcomings, we developed a WordNet debugging tool specifically designed to identify annotation errors and propose modifications for improved alignment between embedded vector clusters and the WordNet structure. This comprehensive approach not only led to the creation of a novel WSD system but also resulted in the development of an updated WordNet version, ensuring compatibility with the latest iteration. A crucial modification involved the merging of synonymous synsets to maximize the overlap between embedded vector representations and their corresponding WordNet concepts.
To achieve the first project objective of reducing memory footprint while maintaining accuracy, we investigated dimensionality reduction techniques. Notably, the size of the embedded vector base was compressed from 3 gigabytes to 100 megabytes, representing a significant reduction. Interestingly, this compression not only preserved model accuracy but also led to a slight improvement in F1 scores (
Table 1). This unexpected finding suggests the effectiveness of the NCA component model in mitigating data noise during the projection of embedding vectors from a high-dimensional space (1024 dimensions) to a lower-dimensional space (ranging from 2 to 5 dimensions).
Table 1 summarizes the F1 scores achieved by various models using unmodified WordNet synset relationships and SemCor data for training. It excludes chart-bot generated synset examples for consistency with the reference models (Most Frequent Sense (MFS) and BERT1024 1-NN [
1]). Additionally, the evaluation focuses solely on nouns and verbs, aligning with the word forms used in the reference work [
1]. While the BERT-2NCA 1-NN model, employing two fixed NCA components and kNN classification with k=1, exhibited a slightly lower F1 score compared to BERT
1024 1-NN, the BERT-NCA k-NN model achieved a marginally higher F1 score. This improvement stems from its ability to dynamically determine the optimal number of NCA components and the k parameter for each lemma individually. This data-driven approach highlights the efficacy of dynamic parameter tuning in achieving superior performance for semantic classification tasks.
Table 1 clearly demonstrates a significant improvement in noun classification accuracy for the WSD task when employing neural networks like BERT. Compared to the MFS baseline, which assigns the most frequent sense in the SemCor dataset to a word, BERT achieves an approximate 10% improvement in F1 score (
Table 1). This finding highlights the limitations of simple rule-based approaches and the effectiveness of deep learning for WSD.
However, the observed improvement of 10% served as a basis for further exploration. We aimed to redefine the state-of-the-art for WSD by pushing the boundaries of accuracy beyond this initial gain. This work further seeks to transform WordNet into a formal ontology similar to established resources like Cyc [
30] or SUMO [
31,
32]. This led to a two-pronged strategy: (1) enhancing the semantic knowledge base (WordNet) itself, and (2) enriching its training corpus with meticulously annotated sentences. The ultimate objective of this approach was to achieve near-perfect WSD accuracy. We implemented three distinct types of modifications to WordNet during the project:
Synset Refinement: We replaced specific synsets with more contextually appropriate alternatives to improve the accuracy of sense representation.
Pruning: Synsets with negligible semantic value, particularly those limited to niche domains, were removed to streamline the knowledge base.
Lexicon Expansion: Novel synsets were introduced to broaden the scope and capture the evolving nature of language.
It is important to note that the deletions and additions of synsets were primarily undertaken as an experimental investigation, paving the way for future advancements in knowledge base research.
Table 2 details the statistics of these modifications to WordNet.
Within the framework of the WSD task, additional refinements were implemented, including the generation of new sentences and rectification of errors in existing annotations. A detailed breakdown of these modifications is presented in
Table 2. It is crucial to recognize the iterative development process undertaken, similar to that of evolving software ecosystems. Each subsequent version of the WSD system incorporates updates to improve functionality and address new requirements. The statistics provided in
Table 2 reflect the version used for the model classification accuracy reported in
Table 3. This highlights the ongoing effort to continually refine WSD capabilities.
Our work aimed to significantly advance the state-of-the-art in WSD, potentially limiting direct comparisons with previous studies due to the implemented modifications.
Table 3 details the achieved model accuracy, reflecting these adjustments. While exceeding a 90% accuracy threshold, we acknowledge the ongoing pursuit of 100% accuracy. Several factors hindered this goal:
Vocabulary Limitation: The BERT neural network's inherent vocabulary limitation (30,522 words/tokens) can significantly impact WSD outcomes for out-of-vocabulary words.
Incomplete WordNet Modification: Incomplete data supplementation or relation augmentation within WordNet synsets posed a further challenge.
Network Architecture and Training Data: The specific architecture of the neural network and the composition of its training dataset likely contributed to the deviation from perfect accuracy. Exhaustive testing was conducted using all KerasNLP library neural network variants, with BERT chosen for comparability with prior research. However, larger LLM networks might yield superior results, warranting future investigation.
6. Discussion
This work introduces a WSD system emphasizing minimal memory footprint. The system leverages the KerasNLP library and the BERT model for efficient embedded word vector acquisition, promoting computational resource conservation. A key feature is its seamless compatibility with the Google Colab environment, enabling straightforward execution through a single "Run All" command.
Traditional semantic dictionary construction relies on subjective interpretations by knowledge engineers for assigning semantic tags. This paper proposes a novel methodology for formalizing semantic knowledge attribution by correlating it with neural network-derived word embedding vector clusters. Our study demonstrates the effectiveness of this approach in justifying WordNet synset merging where granularity becomes excessive. While initial validation employed a moderate-sized neural network, we anticipate that further exploration with larger language models (LLMs) will produce insightful results in future investigations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.; methodology, A.L.; software, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Laukaitis, A.; Ostašius, E.; Plikynas, D. Deep semantic parsing with upper ontologies. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navigli, R. ; Word sense disambiguation: A survey. ACM computing surveys (CSUR). 2009, 41, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, D.; Jorge, A. Language Modelling Makes Sense: Propagating Representations through WordNet for Full-Coverage Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5682–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.F.; Fillmore, C.J.; Lowe, J.B. The berkeley framenet project. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and 17th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–14 August 1998; Volume 1, pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fellbaum, C. WordNet. In Theory and Applications of Ontology: Computer Applications; Poli, R., Healy, M., Kameas, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.; Savva, M.; Manning, C.D. Learning spatial knowledge for text to 3D scene generation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 26–28 October 2014; pp. 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niles, I.; Pease, A. Towards a standard upper ontology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Formal Ontology in Information Systems, Ogunquit, ME, USA, 17–19 October 2001; pp. 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Laukaitis, A.; Plikynas, D.; Ostasius, E. Sentence Level Alignment of Digitized Books Parallel Corpora. Informatica 2018, 29, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Chen, D.; Martins, A.F.; Schneider, N.; Smith, N.A. Frame-semantic parsing. Comput. Linguist. 2014, 40, 9–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, Y. Natural language processing with Python and spaCy: A practical introduction. No Starch Press. 2020.
- Watson; Matthew; Qian; Chen; Bischof; Jonathan; Chollet; Francois and others. KerasNLP. 2022. https://github.com/keras-team/keras-nlp.
- Bird, S.; Klein, E.; Loper, E. Natural language processing with Python: analyzing text with the natural language toolkit. O'Reilly Media, Inc. 2009.
- Manning, C.D.; Surdeanu, M.; Bauer, J.; Finkel, J.R.; Bethard, S.; McClosky, D. The Stanford CoreNLP natural language processing toolkit. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23–24 June 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, M. Automatic sense disambiguation using machine readable dictionaries: how to tell a pine cone from an ice cream cone. In Proceedings of the 5th annual international conference on Systems documentation. 1986, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, J.; Hinton, G. E.; Roweis, S.; Salakhutdinov, R. R. Neighbourhood components analysis. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2004, 17.
- Moro, A.; Navigli, R. Semeval-2015 task 13: Multilingual all-words sense disambiguation and entity linking. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2015), Denver, CO, USA, 4–5 June 2015; pp. 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Raganato, A.; Camacho-Collados, J.; Navigli, R. Word sense disambiguation: A unified evaluation framework and empirical comparison. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Loureiro, D.; Jorge, A.M.; Camacho-Collados, J. LMMS Reloaded: Transformer-based Sense Embeddings for Disambiguation and Beyond. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, P.; Cotton, S. Senseval-2: Overview. In Proceedings of the SENSEVAL-2 Second International Workshop on Evaluating Word Sense Disambiguation Systems, Toulouse, France, 5–6 July 2001; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, B.; Palmer, M. The English all-words task. In Proceedings of the SENSEVAL-3, Third International Workshop on the Evaluation of Systems for the Semantic Analysis of Text, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, S.; Loper, E.; Dligach, D.; Palmer, M. Semeval-2007 task-17: English lexical sample, srl and all words. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop on Semantic Evaluations (SemEval-2007), Prague, Czech Republic, 23–24 June 2007; pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Navigli, R.; Jurgens, D.; Vannella, D. Semeval-2013 task 12: Multilingual word sense disambiguation. In Proceedings of the Second Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics, Volume 2: Proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2013), Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 14–15 June 2013; pp. 222–231.
- Miller, G.A.; Chodorow, M.; Landes, S.; Leacock, C.; Thomas, R.G. Using a semantic concordance for sense identification. In Proceedings of the Workshop Human Language Technology, Plainsboro, NJ, USA, 8–11 March 1994; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Winograd, T. Understanding natural language. Cogn. Psychol. 1972, 3, 1–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, K.; Lee, W.S. Visualizing natural language descriptions: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.X.; Eric, M.; Savva, M.; Manning, C.D. SceneSeer: 3D scene design with natural language. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.00050. [Google Scholar]
- Doval, Y.; Vilares, J.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C. Towards robust word embeddings for noisy texts. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Bleda, M.J.; Iklódi, E.; Recski, G.; Borbély, G. Towards a Universal Semantic Dictionary. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenat, D.B. CYC: A large-scale investment in knowledge infrastructure. Commun. ACM 1995, 38, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Sutcliffe, G.; Urban, J.; Pease, A. Detecting inconsistencies in large first-order knowledge bases. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automated Deduction, Gothenburg, Sweden, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 310–325. [Google Scholar]
- Pease, A.; Sutcliffe, G.; Siegel, N.; Trac, S. Large theory reasoning with SUMO at CASC. Ai Commun. 2010, 23, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).