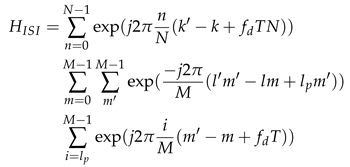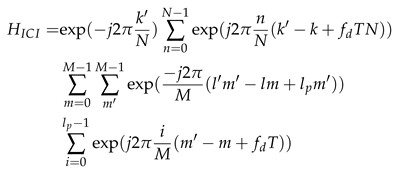Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
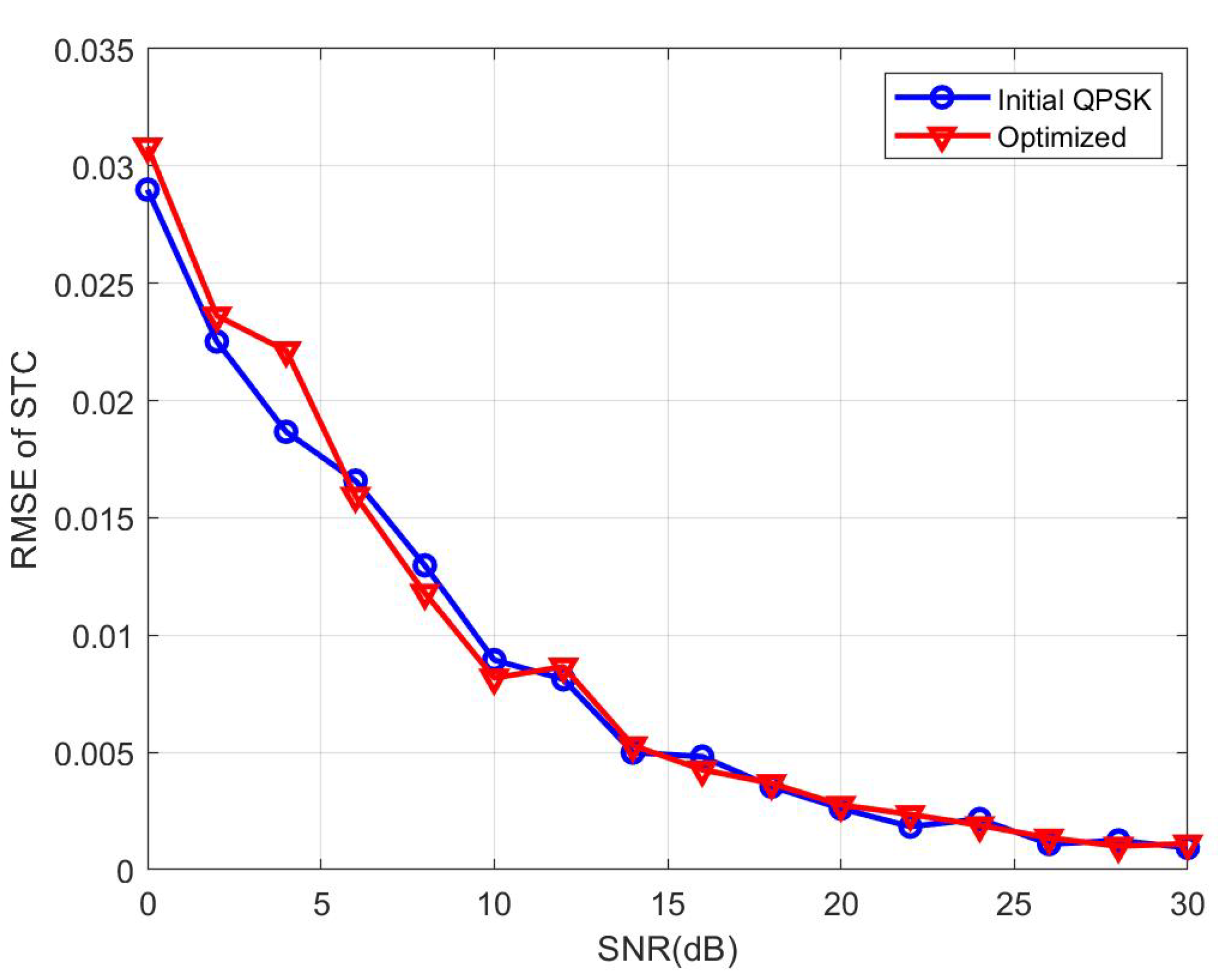
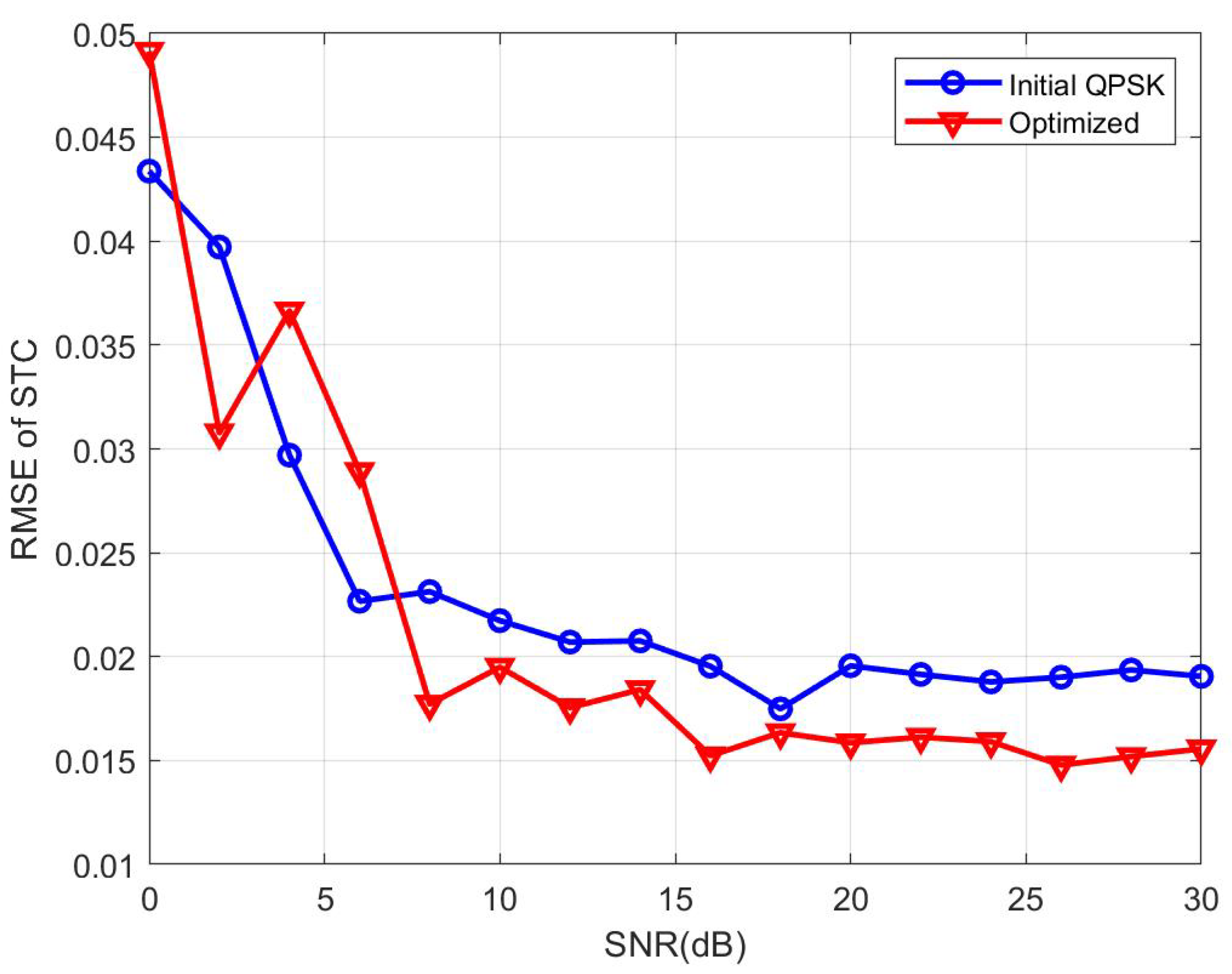
- The framework of ISWSCPTS is proposed. This framework comprises two operational modes: SM and JWM. To enhance sensing capabilities for both SM and JWM, The CP-OTFS matched filter (MF) based target detection and parameters estimation (MF-TDaPE) algorithm is proposed. This algorithm exhibits superior performance to OFDM in high-speed scenarios.
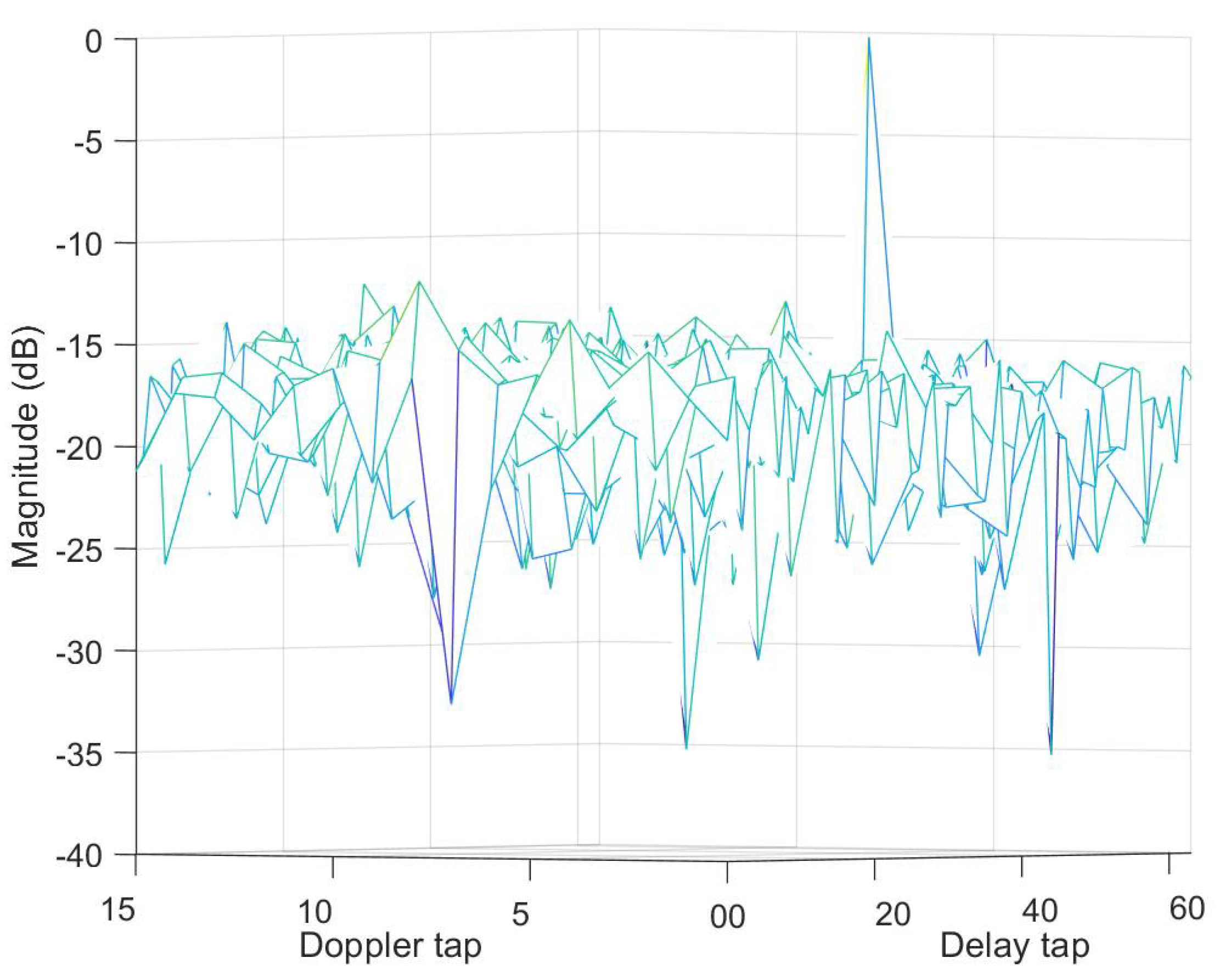
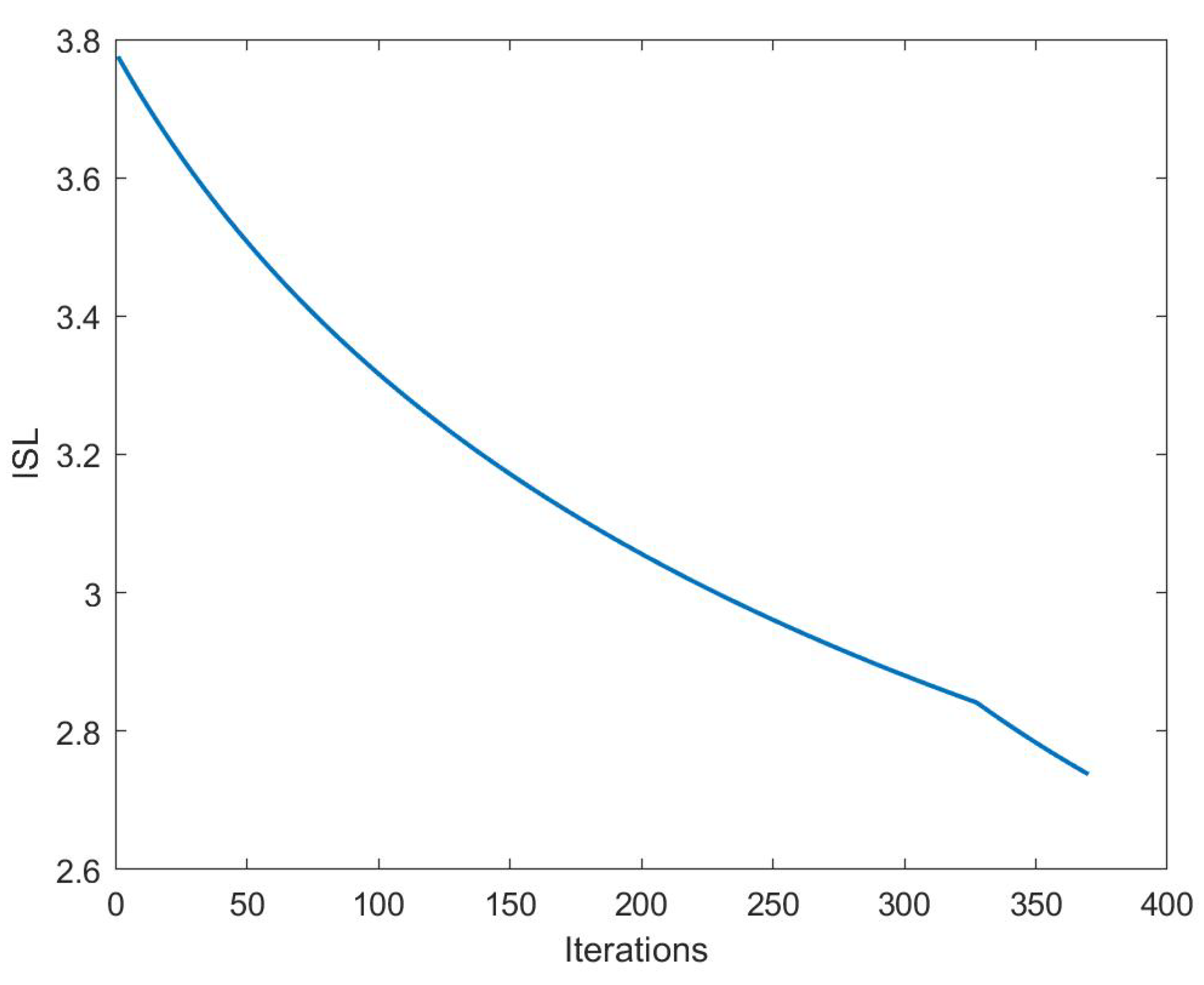
- An CP-OTFS ambiguity function (AF) shaping (AFS) waveform design algorithm is proposed. Firstly, a novel DD domain AF for CP-OTFS is proposed. Subsequently, aiming to minimize the integrated sidelobe level (ISL) of the proposed AF while adhering to the QoS for communication and PT and constant modulus constraints, a non-convex CP-OTFS waveform design optimization problem is formulated. This problem is then solved through an iterative algorithm to obtain waveforms with superior AF characteristics and interference resilience.
- The semidefinite relaxation (SDR) beamforming design (SDR-BD) algorithm tailored for ISWSCPTS is proposed. Initially, a non-convex optimization problem is formulated with sensing QoS as the optimization objective and communication and PT QoS as constraints. Subsequently, the SDR technique is employed to solve this problem. The designed waveform optimizes perceptual capability while ensuring communication and PT performance.
2. Materials and Methods
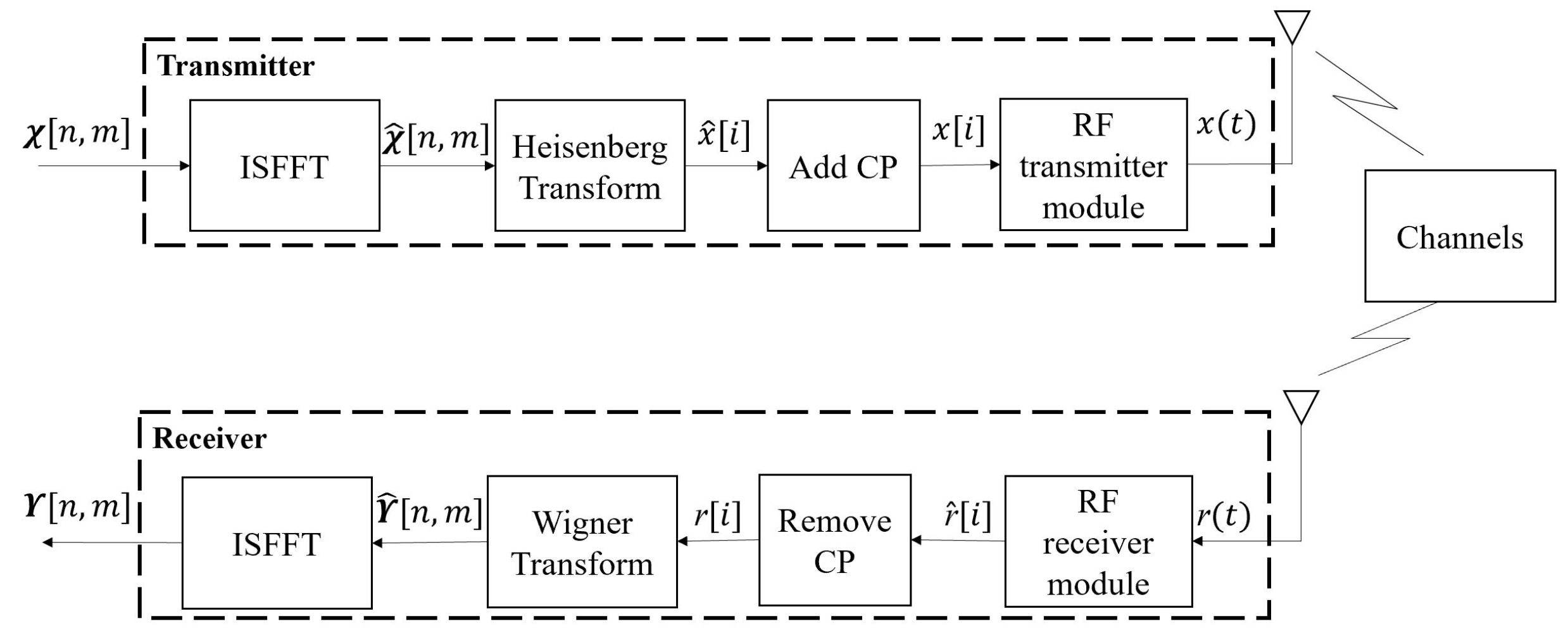
2.1. The CP-OTFS Model
2.1.1. Basic Concepts of CP-OTFS
2.1.2. Input-Output Relationship of CP-OTFS Based ISWSCPTS
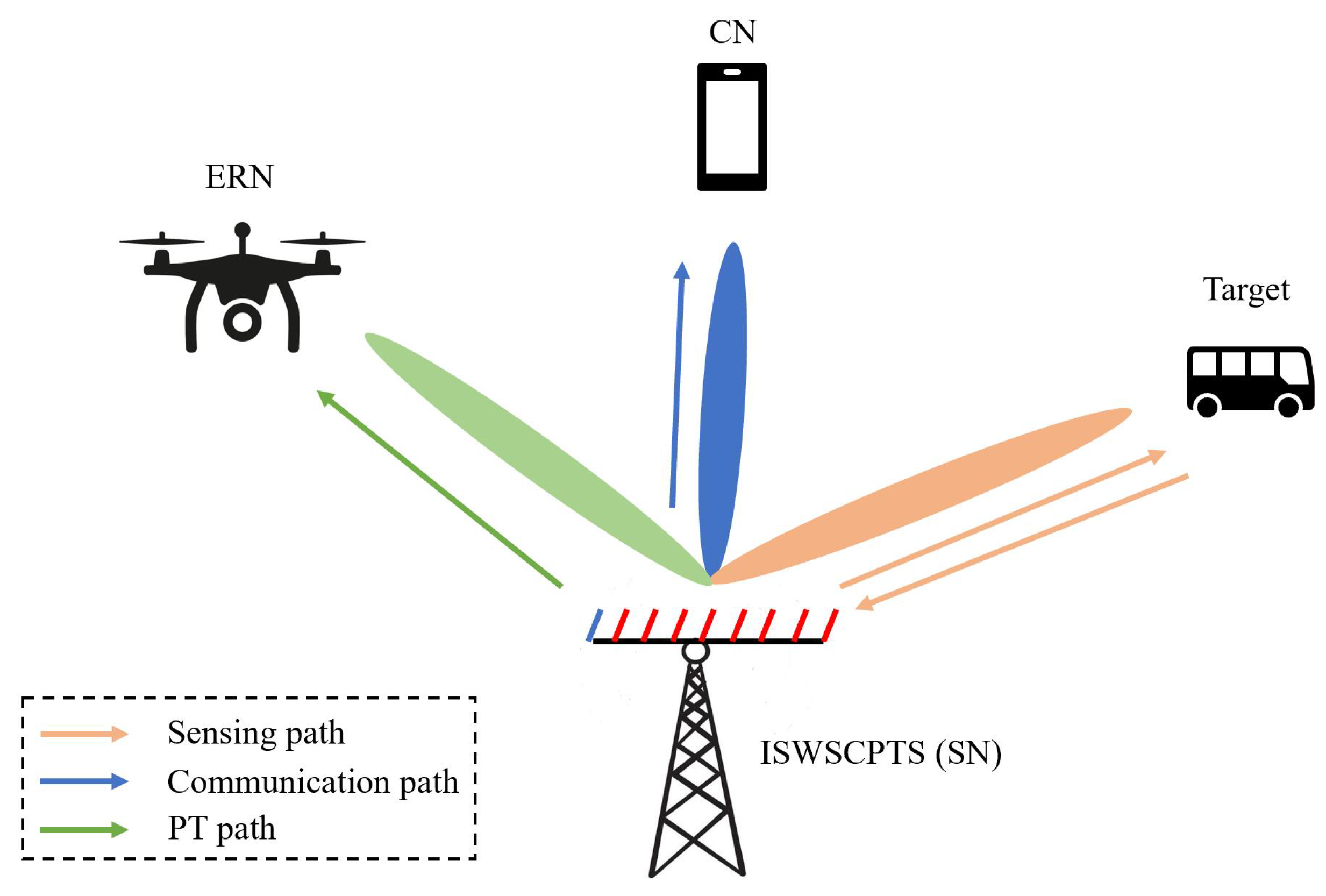
2.2. Framework of CP-OTFS Based ISWSCPTS
2.2.1. The SM of ISWSCPTS
| Algorithm 1: The CP-OTFS MF-DaPE algorithm |
|
Input: ,
Output: , ,
1 Calculate through (31)
2 Find peak index in through CFAR algorithm
3 Calculate through (32)
4 Calculate through (33)
5 Calculate through (34)
6 Return , and .
|
2.2.2. The JWM of ISWSCPTS
| Algorithm 2: CP-OTFS AFS |
|
Input: Initial and stop condition
Output: The optimized waveform
1 Let and
2
3
4
5
6 If , return . Otherwise, return to step 2.
|
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Simulation of CP-OTFS MF-TDaPE
3.2. Simulation of CP-OTFS AFS
3.3. Simulation of SDR-BD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PT | Power Transfer |
| ISACS | Integrated Sensing and Communication System |
| SWIPT | Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer |
| OTFS | Orthogonal Time Frequency Space |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| CP | Cyclic Prefix |
| ISWSCPTS | Integrated Simultaneous Wireless Sensing, Communication, and Power Transfer System |
| MF | Matched Filter |
| AF | Ambiguity Function |
| AFS | AF Shaping |
| MF-TDaPE | MF based Target Detection and Parameters Estimation |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| SDR | Semidefinite Relaxation |
| SDR-BD | SDR Beamforming Design |
| OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| SM | Search Mode |
| JWM | Joint Work Mode |
| ISL | Integrated Sidelobe Level |
| ULA | Uniform Linear Array |
| CN | Communication Node |
| ERN | Energy Receiving Node |
| SN | Sensing Node |
| TF | Time-Frequency |
| DD | Doppler-Delay |
| DDC | DD Channel |
| SFFT | Symplectic Finite Fourier Transform |
| ISFFT | Inverse SFFT |
| TSC | Target Scattering Coefficient |
| CFAR | Constant False Alarm Rate |
| DDC | DD Channel |
| CSI | Channel State Information |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| QPSK | Quadrature Phase Shift Keying |
References
- Hassanien, A.; Amin, M.G.; Aboutanios, E.; Himed, B. Dual-Function Radar Communication Systems: A solution to the spectrum congestion problem. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2019, 36, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.V.; Bhavani Shankar, M.; Koivunen, V.; Ottersten, B.; Vorobyov, S.A. Toward Millimeter-Wave Joint Radar Communications: A Signal Processing Perspective. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2019, 36, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Masouros, C.; Petropulu, A.P.; Griffiths, H.; Hanzo, L. Joint Radar and Communication Design: Applications, State-of-the-Art, and the Road Ahead. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2020, 68, 3834–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Masouros, C.; Xu, J.; Han, T.X.; Eldar, Y.C.; Buzzi, S. Integrated Sensing and Communications: Toward Dual-Functional Wireless Networks for 6G and Beyond. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2022, 40, 1728–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, L.R. Transporting information and energy simultaneously. 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, 2008, pp. 1612–1616. [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Chughtai, O.; Naeem, M.; Ejaz, W. SWIPT-Assisted Energy Efficiency Optimization in 5G/B5G Cooperative IoT Network. Energies 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrawes, A.; Nordin, R.; Abdullah, N.F. Energy-Efficient Downlink for Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access with SWIPT under Constrained Throughput. Energies 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H.; Lee, J.R. Energy-Neutral Operation Based on Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer for Wireless Powered Sensor Networks. Energies 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviteja, P.; Phan, K.T.; Hong, Y.; Viterbo, E. Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) Modulation Based Radar System. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), 2019, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yuan, W.; Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Bharatula, G.; Hadani, R.; Hanzo, L. Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space Modulation: A Promising Next-Generation Waveform. IEEE Wireless Communications 2021, 28, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadani, R.; Rakib, S.; Tsatsanis, M.; Monk, A.; Goldsmith, A.J.; Molisch, A.F.; Calderbank, R. Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Modulation. 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2017, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Raviteja, P.; Phan, K.T.; Hong, Y.; Viterbo, E. Interference Cancellation and Iterative Detection for Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Modulation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 17, 6501–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, L.; Kobayashi, M.; Caire, G.; Colavolpe, G. On the Effectiveness of OTFS for Joint Radar Parameter Estimation and Communication. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2020, 19, 5951–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, L.; Kobayashi, M.; Bissinger, B.; Caire, G. Performance Analysis of Joint Radar and Communication using OFDM and OTFS. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2019, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Han, K.; Han, Z.; Gong, Y. Multi-User Beamforming Design for Integrating Sensing, Communications, and Power Transfer. 2023 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2023, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cui, G.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, L. Cognitive Local Ambiguity Function Shaping With Spectral Coexistence. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 50077–50086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.q.; Ma, W.k.; So, A.M.c.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, S. Semidefinite Relaxation of Quadratic Optimization Problems. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2010, 27, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, C.; Wiesbeck, W. Waveform Design and Signal Processing Aspects for Fusion of Wireless Communications and Radar Sensing. Proceedings of the IEEE 2011, 99, 1236–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
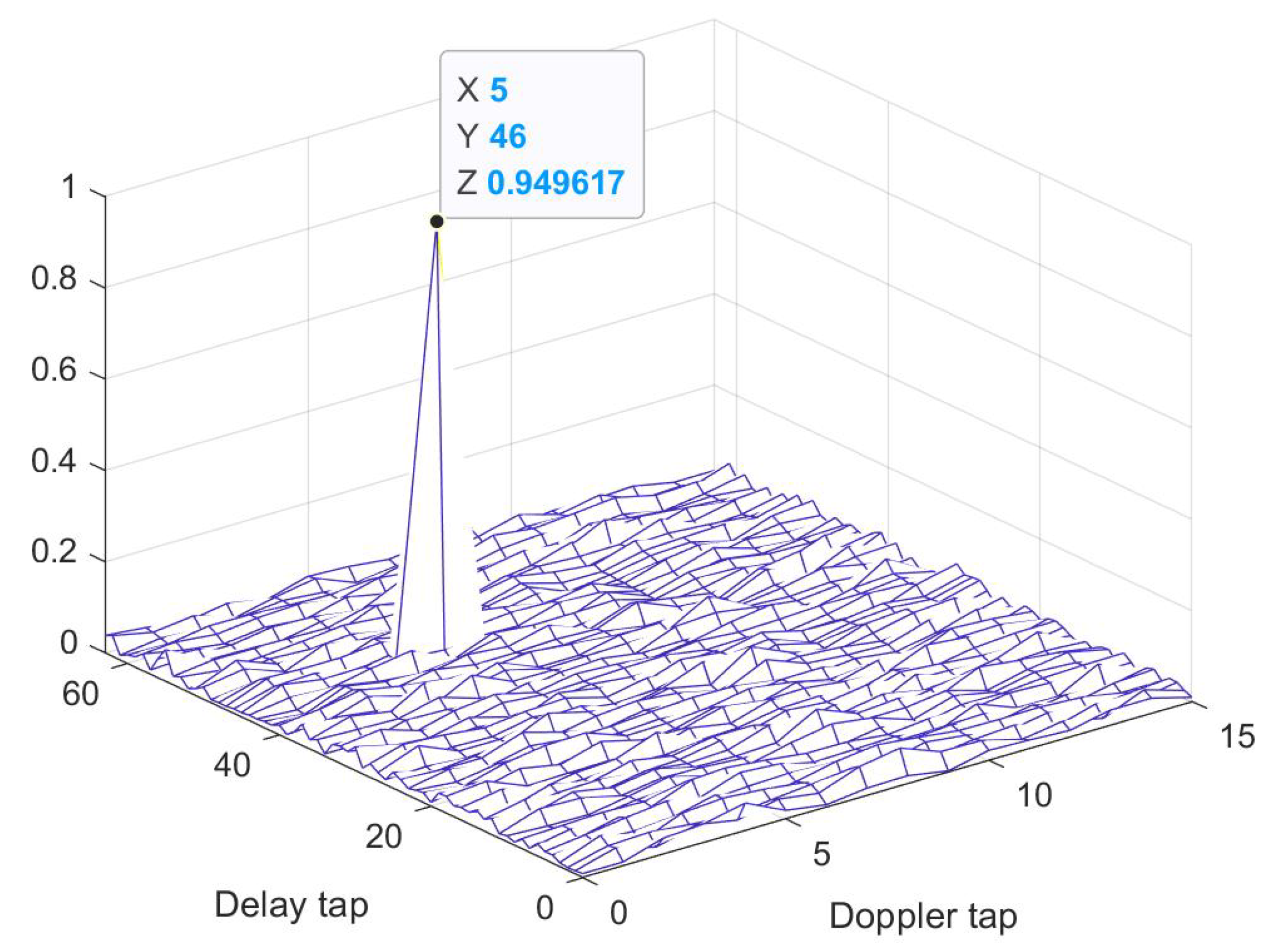
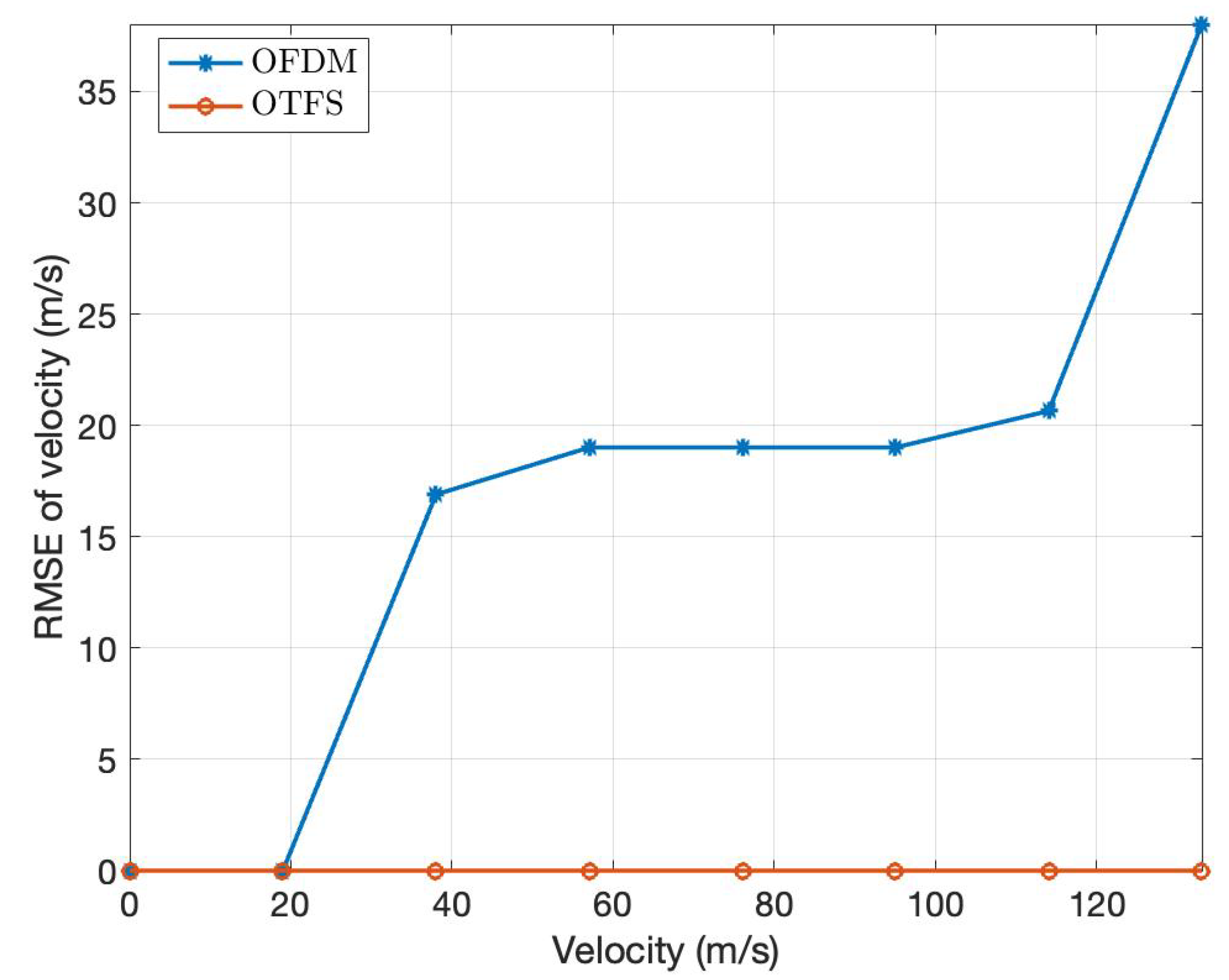
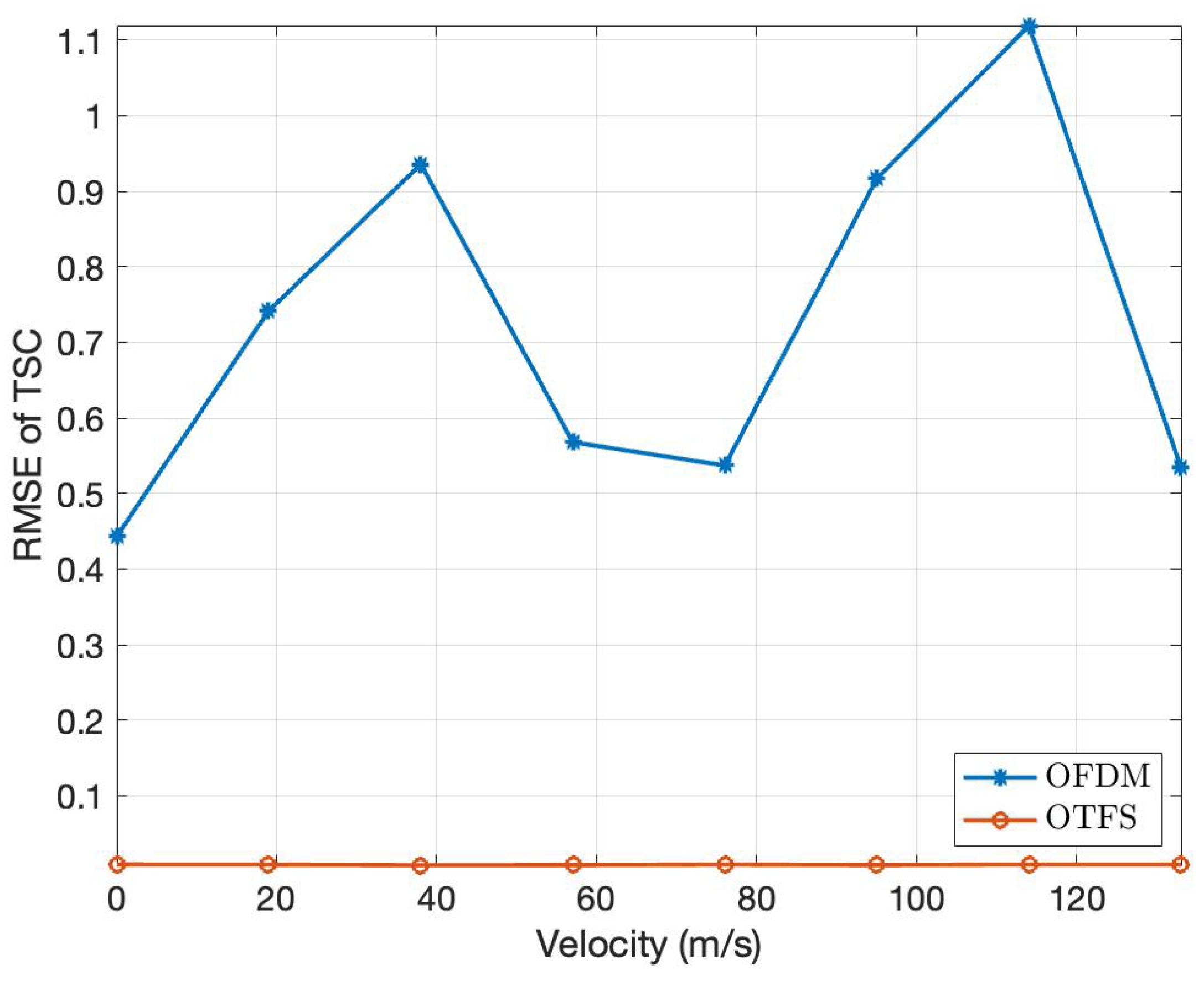
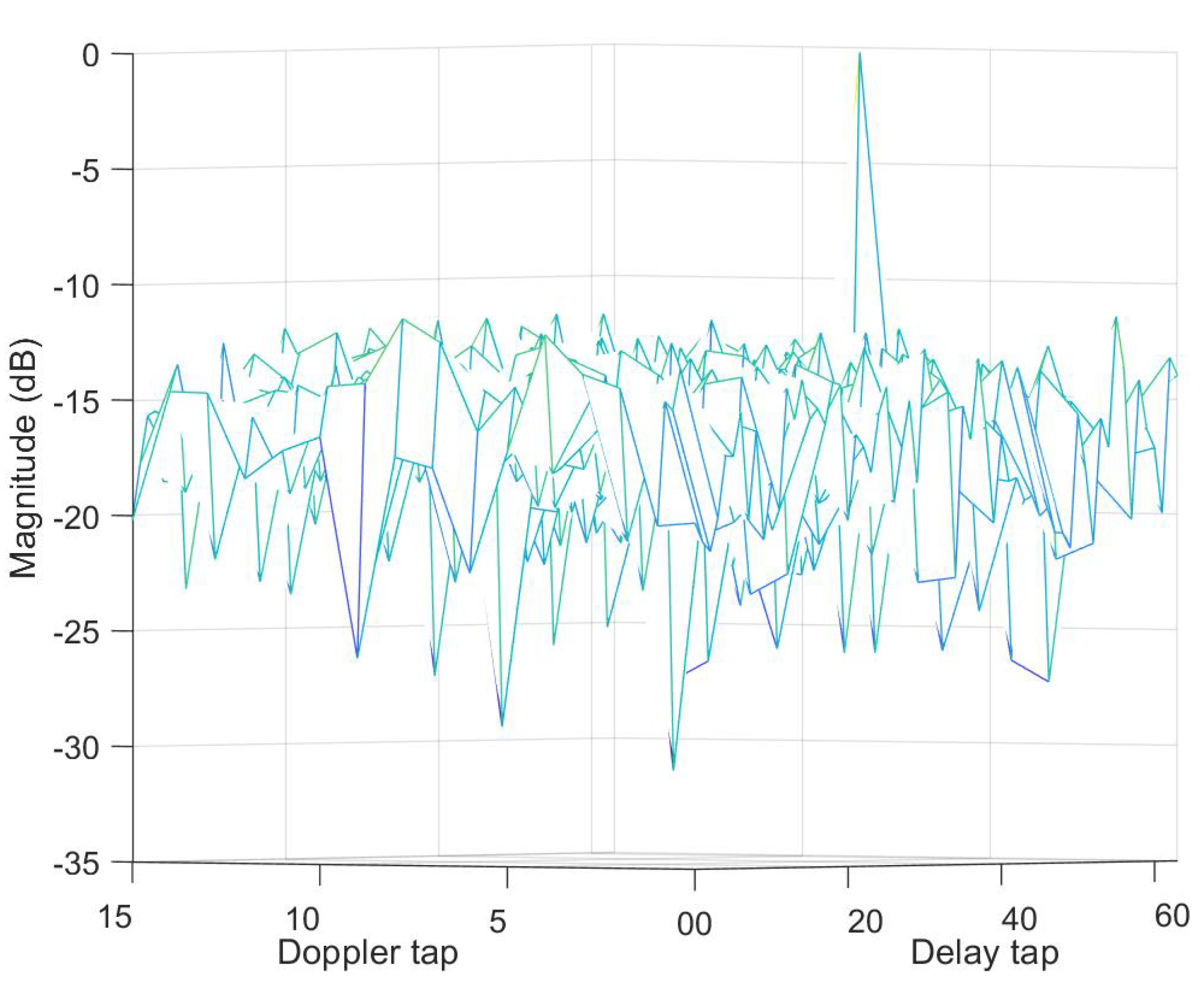
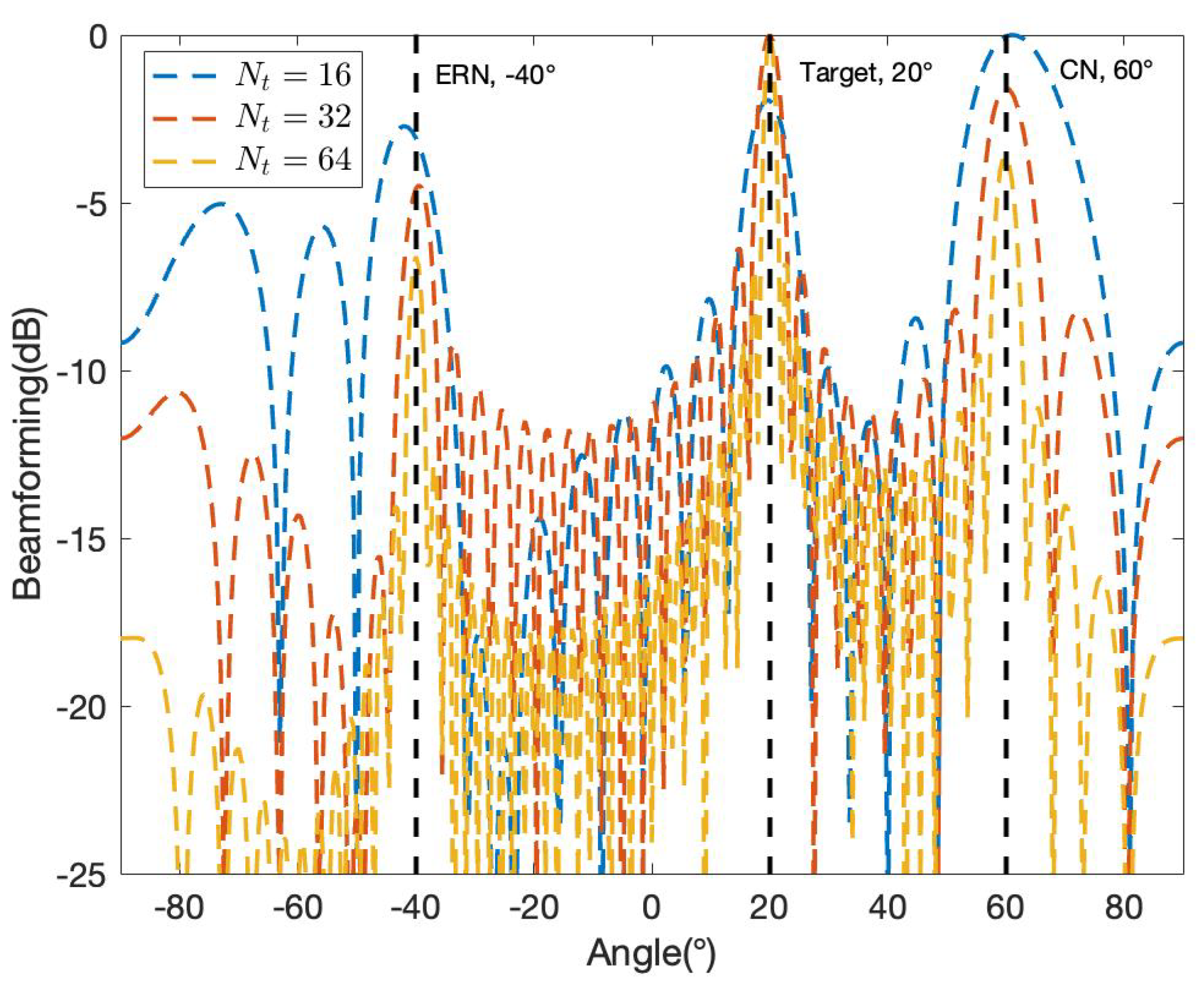
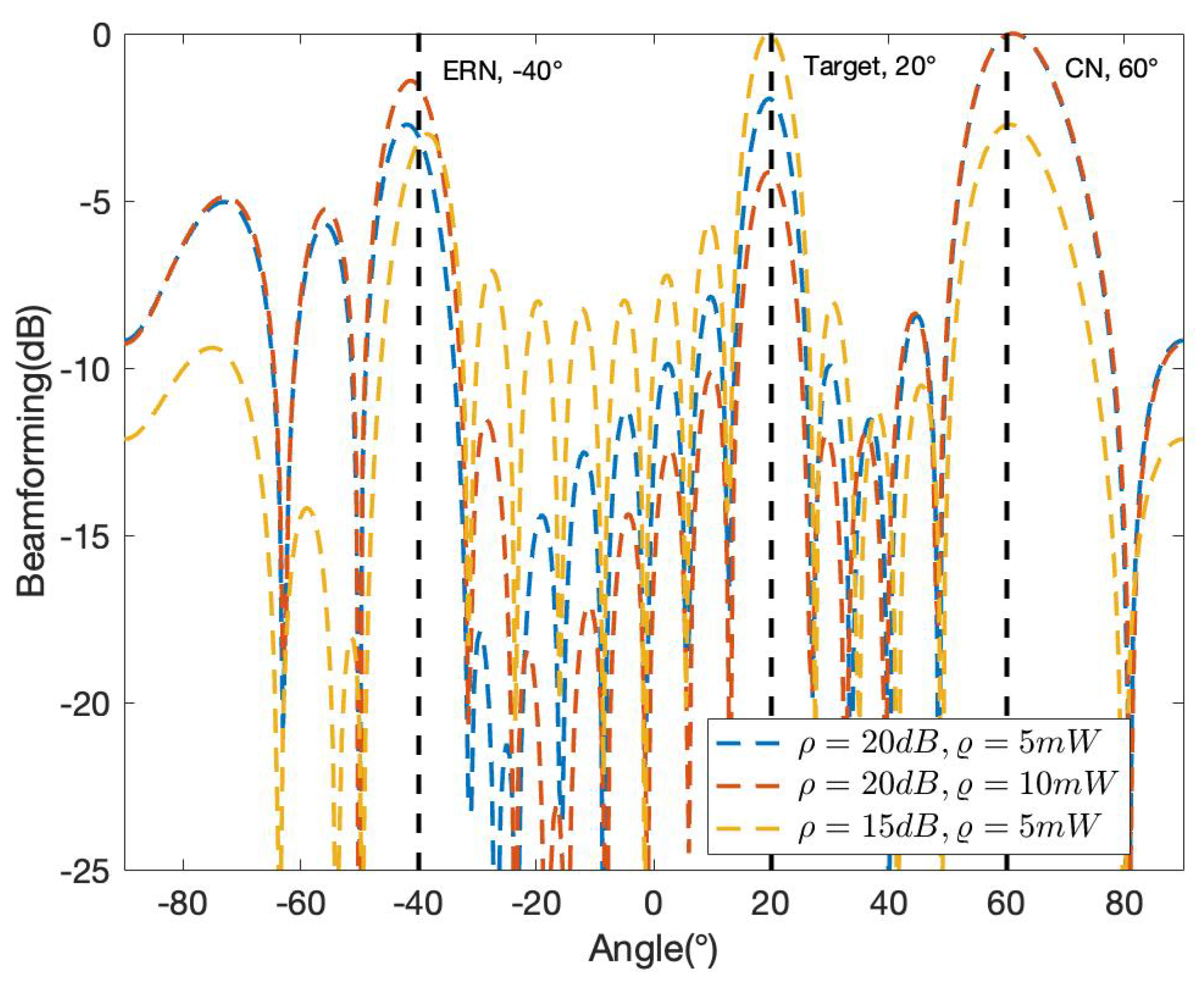
| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 77 GHz | |
| N | Number of Doppler samples | 16 |
| N | Number of delay samples | 64 |
| B | Total bandwidth | 10 MHz |
| Subcarrier spacing | 156.250 kHz | |
| Range resolution | 14.99 m | |
| Velocity resolution | 19.01 m/s | |
| Unambiguous range | 959.336 m | |
| Unambiguous velocity | ±152.086 m/s |
| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitting power | 1 W | |
| Variance of noise in CN | 0 dBm | |
| Variance of noise in SN | 10 dBm | |
| TSC | 0.8247+0.4709i | |
| Communication channel gain | 0.01 | |
| PT channel gain | 0.02 m | |
| Energy harvesting efficiency | 0.1 | |
| SNR required in CN | Configured | |
| Energy requirement in SN | Configured |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).