1. Introduction
In 1973, Lücke described for the first time how a vibratory stimulus of 100 Hz applied by a vibrator on the mastoid process may provoke pathological nystagmus [
1]. In later years, several authors have further elaborated on the significance of this finding, as well as its relationship with the different pathologies affecting the vestibular system [
2]. Thus, nowadays, it is well known that the nystagmus induced by applying an intense vibratory stimulus to the skull (SVIN) mainly at the mastoid [
3], indicates the existence of a functional asymmetry between the right and left side vestibular nuclei, mostly beginning at the level of the labyrinth [
4]. For this, it is considered a test to perform at bedside in patients seen for vertigo, dizziness and other vestibular symptoms. In patients with a unilateral vestibular loss (UVL), a 100-Hz bone-conducted vibration given to either mastoid immediately causes a primarily horizontal nystagmus with fast phases beating away from the affected side. In healthy, asymptomatic people, the identical stimulation has little or no impact, since in the healthy subject the response to vibration would occur bilaterally, simultaneously, causing a nystagmus of the same speed, but in the opposite direction and, therefore, an annulment of this nystagmus [
2,
5]. In those few cases where healthy subjects develop nystagmus upon vibratory stimulation, the nystagmus response tends to be slow and inconsistent [
6]. Moreover, SVIN has also shown to be useful as a predictor of the follow up in patents with recurring vertigo and migraine symptoms, as those who predominantly show SVIN are more prone to develop Ménière’s than those who do not and that otherwise show positional nystagmus and who more frequently develop Vestibular Migraine [
7].
This type of nystagmus has some interesting features. There is no latency: in patients without spontaneous nystagmus (SN) the SVIN appears soon when the stimulus is applied to the skull, and when there is SN, its intensity increases or direction changes immediately too. The intensity of the evoked nystagmus remains similar along the period of stimulation without reducing its intensity or frequency. It also disappears soon when the stimulation ceases and surprisingly whatever the intensity of the response is, there is no reversion nystagmus [
8]. Some of these features would probably change given a prolonged period of stimulation; however, skull vibration is a bothersome type of mechanical testing that has some potential undesirable side effects not being recommended to maintain that stimulus for more than 20-30s. Some of the characteristics, absence of latency, habituation and slow adaptation and the marked coupling to the stimulus, remind very much other type of nystagmus as that induced in the magnetic field [
9].
In common practice this test is performed in complete darkness to avoid for visual fixation [
10] but, there is no data about how much visual fixation affects the often-intense SVIN. Visual fixation suppression of nystagmus is a common phenomenon that points to a peripheral origin of nystagmus, but it can also be seeing in patients with central lesion as in stroke [
11].
To test for vestibular function, the video head impulse test (vHIT) provides fast and accurate information. It has been shown that SVIN intensity correlates with the amount of vestibular deficit obtained in the vHIT [
12,
13]. A similar correlation was also found before when the relative asymmetry between the right and left inner ear function was evaluated with the caloric test [
14].
In this work we were interested in analyzing the amount of reduction of SVIN when visual fixation is allowed during testing: as a primary hypothesis that should be complete or near complete. Given that in unilateral vestibulopathy the intensity of the SVIN depends on the severity of the vestibular damage in a second study we should also analyze the relation between the amount of visual fixation effect and the gain of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
We have included all patients seen for vertigo or dizziness who underwent a complete oto-neurological exam and who during testing showed a positive SVIN. According to the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act (WMO), ethical approval was not required due to the retrospective nature of the study and anonymization of the data. The SVIN examination was performed as part of the regular clinical evaluation of patients with vestibular symptoms.
All patients had normal eye position in primary gaze and, during the cover and cover-uncover test there was no large shift of both eyes; the visual acuity was sufficient as to be able to see the red-light during testing of the effect of visual fixation [
15].
2.2. Nystagmus Evaluation
In all subjects the same video equipment was used for nystagmus registration and analysis: The VisualEyes®525 by Interacosutics A/S (Denmark).
Spontaneous nystagmus (SN). This was registered with the patient seated with gaze ahead, rightward, and leftward and in all of them with and without visual fixation. Time for registration was 30s. SN was characterized by its direction and slow-phase velocity (SPV). The patients here included all showed a complete or marked reduction of SN when visual fixation was allowed.
SVIN. We followed a previously used protocol. The SVIN was evoked in a sitting patient by stimulating both mastoid process for 15 s using a 100 Hz handheld vibrator (VVIB 100; Synapsys, France). Nystagmus evoked upon stimulation was recorded using videonystagmoscopy in the dark. Subjects were instructed to continue looking straight ahead while stimulation. SVIN was considered positive when the same nystagmus was registered placing the vibrator in both the right and left mastoids: no directional dissociation. Nystagmus had to be present during the complete period of stimulation with an abrupt initiation and ending both coupled to the application of the vibrator. To test for visual fixation, the side in which the intensity of nystagmus (as measured by maximum SPV) was higher was the one to test. In this second time of evaluation, SVIN was registered for 10 seconds without visual fixation and 10s with visual fixation: for this, a red dot was presented in front of the left eye which was the eye to measure nystagmus. Thus, we obtained an aSVINwo (in darkness) and aSVINw (with visual fixation) as average SPV without and with visual fixation. Only patients with a aSVINwo>2º/s were considered for the study.
The visual fixation index was calculated as the ratio of slow phase velocities:
In this formula, 0 result indicates a complete reduction or completely absent nystagmus during visual fixation; the higher the score indicates that visual suppression is worst or incomplete.
2.3. Video Head-Impulse Test (vHIT)
It was done using a vHIT system that allows to test all 6 semicircular canals (GN Otometrics, Denmark). For this test the patient wears a pair of lightweight, tightly-fitting goggles on which is mounted a small video camera and a mirror that reflects the image of the patient’s right eye into the camera. The eye is illuminated by a low-level infra-red light-emitting diode. A small sensor on the goggles measures the head movement. Calibration is performed and the procedure of vestibulo-ocular testing is initiated. Horizontal semicircular canals are then tested: the clinician asks the patient to keep staring at an earth-fixed target 1 m. in front, and gives the patient brief, abrupt, head rotations through a small angle (about 10-20 degrees), unpredictably turning to the left or right on each trial. At the end of each head turn, the head-velocity stimulus and eye-velocity response are displayed simultaneously on the screen, together with a graph of the calculated VOR gain (ratio of eye velocity to head velocity) for every head rotation. In a full test, 20 impulses are delivered randomly in each direction. Gain was evaluated as normal or abnormal according to norms by age [
16]. A relative parameter was obtained to measure the gain asymmetry (Gass) between both sides:
In this formula Gh was the highest gain value and Gl the lowest gain value, that in the case of patients with unilateral vestibulopathy (see later) were also the unaffected and affected sides respectively. The result extends from 0 when both gains were similar to 1 when 1 of them is 0.
2.4. Statistics
Quantitative variables were described using the mean and standard deviation, and the range. Qualitative variables were described using the percentage. Hypothesis contrasts were performed between FISVIN groups and the study variables. The Chi-square test with Monte Carlo simulation was chosen when the study variables were categorical. In the case of the age, the Mood's Median test was used, since the distributions were not normally distributed and had different shape and spread. Finally, Spearman's correlation coefficient was used to study correlation between the SVIN and VOR. A p-value of < 0.005 was considered statistically significant.
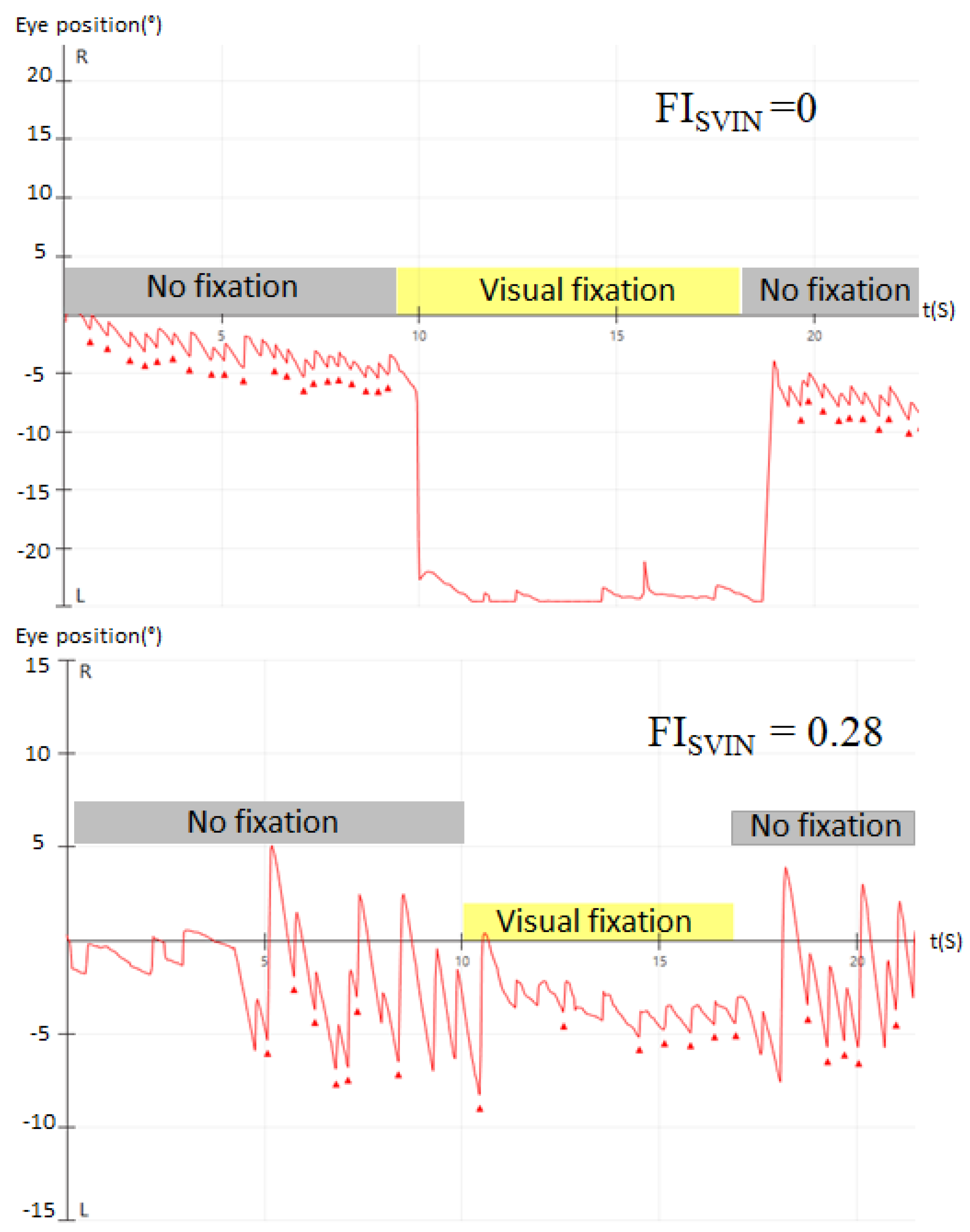
According to the effect of visual fixation on SVIN, the patients were classified into 2 groups: 1) complete visual fixation when the FI
SVIN =0, and, 2) incomplete visual fixation when >0 FI
SVIN <1 (
Figure 1).
3. Results
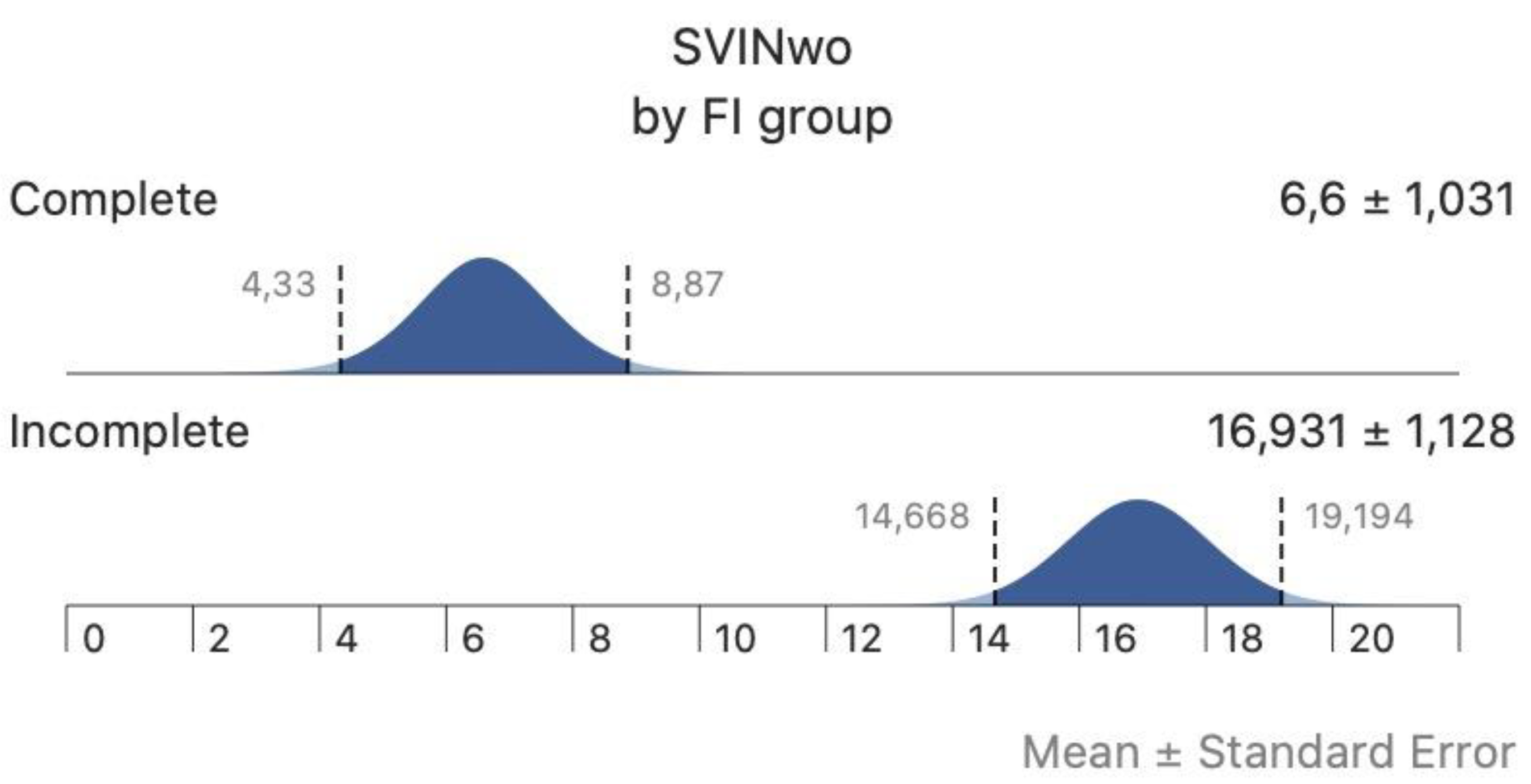
We have included 124 patients who during the period of study showed SVIN at their corresponding vestibular examination. They were 65 (52.5%) females and 59 (47.5%) males. Main diagnostic categories and patients were the following: 51 Ménière’s disease (26 not previously treated, and 25 treated with intratympanic gentamicin), 26 sub-acute vestibular neuritis, 17 Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), 16 recurrent non-positional vertigo and, 14 surgically treated vestibular schwannoma. The right side was affected in 59 (47.58%) patients and the left in 46 (37.10%); no side data was evident in 19 (15.32%). The 65 patients in whom there was a unilateral vestibulopathy (UVL) due to post gentamicin treatment, vestibular neuritis or post-surgical vestibular schwannomas, will be the subject of the second study.
In the complete group of patients SN was found in 31 (25%) and the mSPV (without visual fixation) of SN was 2.6±2.4º/s. The aSPV of SVIN (aSVINwo) was 11.2±8.3º/s and when performed allowing visual fixation, the aSPVw of SVIN (aSVINw) was 3.6±4.5º/s: differences were significantly different. The mean FI
SVIN was 0.27±0.29. The FI
SVIN was 0 in 42 (33.8%) patients and >0 FI
SVIN <1 in 82 (66.2%) patients; in these the mean FI
SVIN was 0.39±0.02. There were no significant differences for age (p=0.656), sex (p=0.268), ear affected (p=0.135), SN (p=1), SN direction (p=0.414), according to amount of FI
SVIN. In
Table 1 we present the data by main diagnoses and gain of the VOR asymmetry.
In patients with no significant UVL, the gain of the VOR for head impulses towards the lowermost side was 0.86±0.23 and to the opposite 0.99±0.02. In the group of patients with UVL the gain of the VOR for head impulses towards the affected side was 0.52±0.02 and towards the unaffected 0.87±0.16. Differences were significant for the mean Gass, aSVINwo and aSVINw between patients in the group without unilateral vestibulopathy and with unilateral vestibulopathy (in the three, Student’s t-test p<0.001). However, the amount of visual fixation was similar in both groups. In
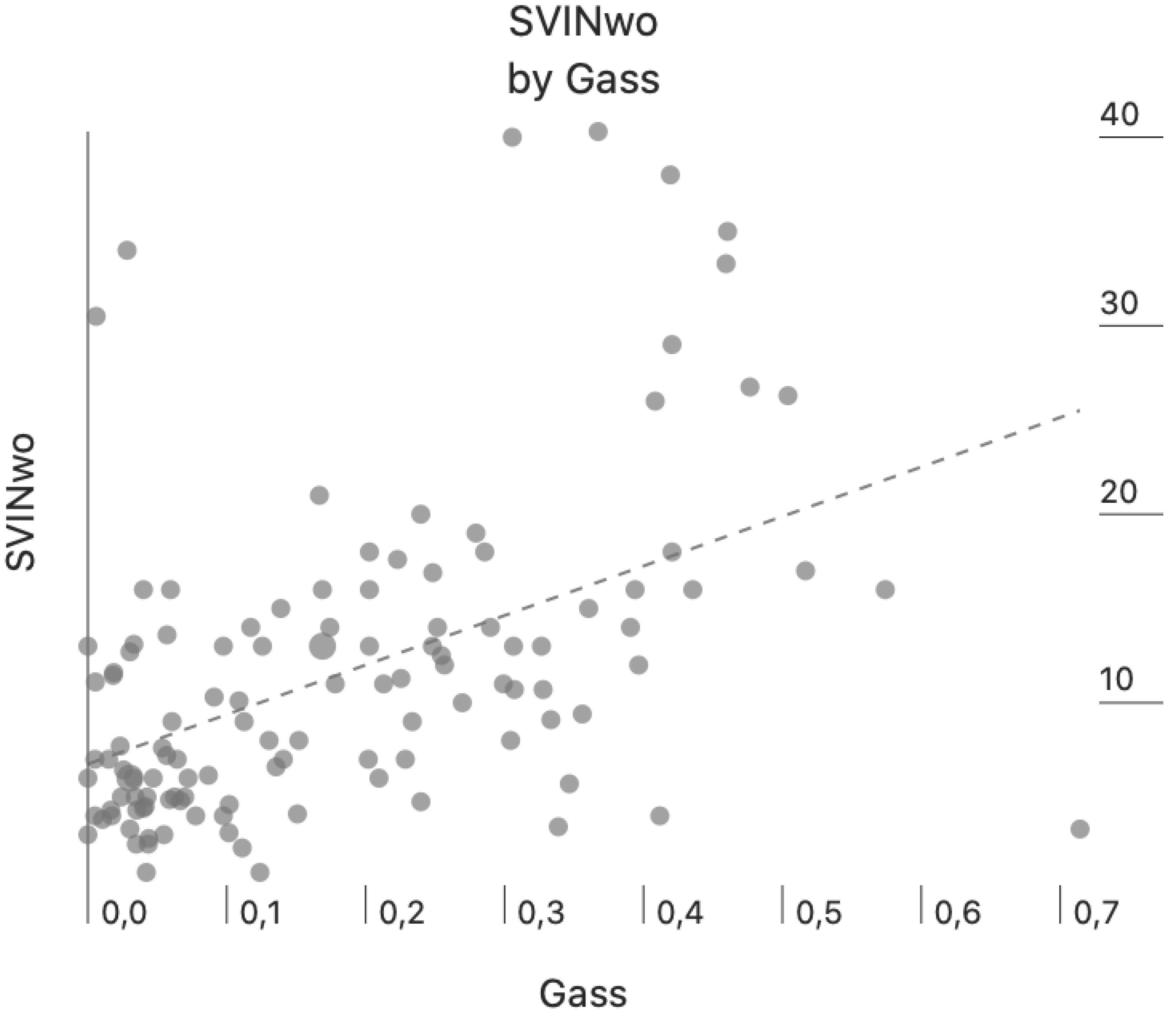
Figure 2 we present the intensity of SVINwo according to the gain asymmetry of the VOR for all the patients in the study (Pearson-Moment correlation, r=0.484, p=<0.001).
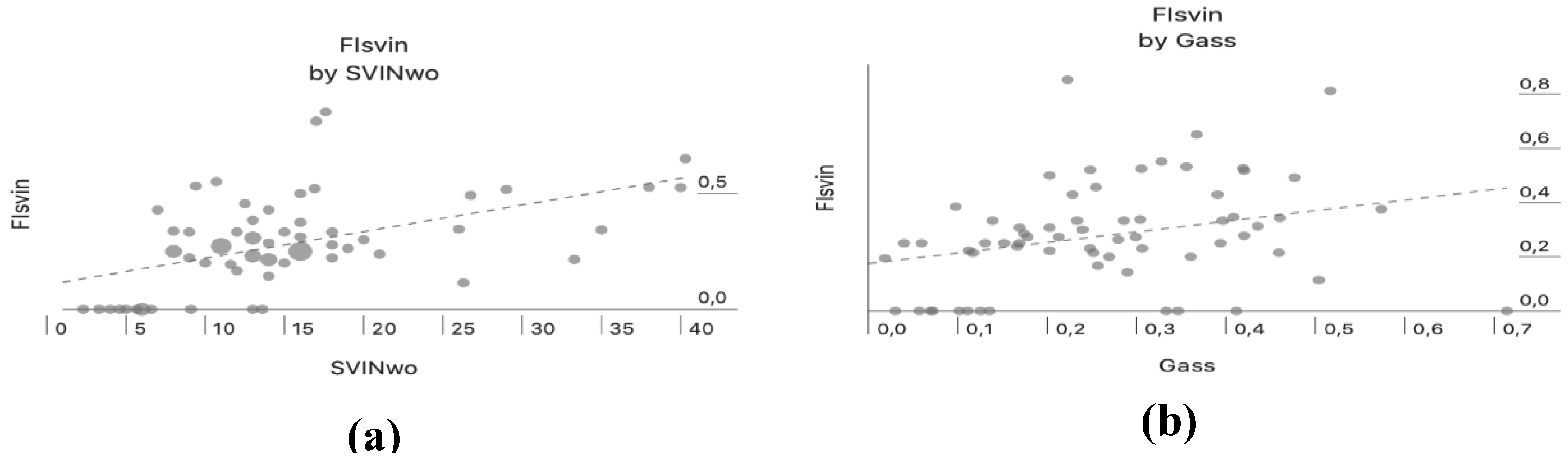
There was a positive correlation between aSVINwo and the FI
SVIN (Pearson correlation, r=0.51, p=<0.001) only in patients with UVL, this indicates that when the intensity of SVIN is high the amount of reduction by vision is lower (
Figure 3a). Both parameters (aSVINwo and FI
SVIN) also showed a positive correlation with Gass (Pearson correlation, r=0.39, p=0.002 and Pearson correlation, r=0.33, p<0.001, respectively) only in patients with UVL (
Figure 3b and
4, respectively). In the group of patients with UVL, the median Gass in patients with a complete visual suppression of SVIN was 0.118 and when incomplete 0.257 and differences were significantly different (U Mann-Whitney test, p=0.041).
4. Discussion
In this work we have shown that SVIN is suppressed by visual fixation. The amount of fixation can be either complete (no nystagmus during testing when allowing visual fixation) or incomplete (there is still some nystagmus during the visual task). We have seen reduction of the intensity of nystagmus in all the patients of our study being the most frequent finding the incomplete. As previous authors have shown the intensity of SVIN (as measured by the aSVINwo) correlates to the degree of asymmetry in the VOR between the right and left vestibules [
4,
12]. In patients with UVL, we have also shown that the amount of reduction of SVIN as measured with the FI
SVIN correlates to both: the asymmetry of gain of the VOR and the intensity of SVIN. When the asymmetry of VOR is higher or the intensity of nystagmus is also higher, then the degree of velocity reduction by visual fixation is lower.
SVIN is another type of triggered nystagmus this case evoked when applying a precise stimulus at both mastoids. It is expected to occur when there is a functional vestibular asymmetry between both sides. In our procedure (100Hz stimulation) both the otoliths and semicircular canals are activated [
17]. This probably explains SVIN in some cases in which the right left VOR asymmetry is very low or even in cases without a specific vestibulopathy. The former are patients with Ménière’s disease and recurrent non-positional vertigo and the later patients with BPPV. Unfortunately, we do not have information in all of them about the functional status of the saccule and utricle who could potentially be also the source of vestibular asymmetry and SVIN [
18]. We have shown here that the amount of reduction of nystagmus when visual fixation is allowed is the same in this group of patients as in those with UVL. This is because it is a central effect [
19] common to other spontaneous or induced nystagmus with [
20] or without [
21] permanent vestibular damage.
The interest in visual fixation effect on SVIN first, rests in that impaired fixation suppression of nystagmus is frequently seen in central lesions and must be part of any nystagmus test evaluation [
22]. This is an effect mediated by different parts of the cerebellum but mainly at the flocculus, paraflocculus, nodulus and uvula, so that when nystagmus is not suppressed by visual fixation, or even increases/appears, it is suspected some degree of damage at that level [
23]. In these cases, there will be also additional signs of oculomotor dysfunction as VOR visual suppression is mediated by smooth-pursuit cancellation.
We found that visual suppression was in some cases complete, and no nystagmus was found when vision was allowed. However, some patients still show some nystagmus even in that situation. When the whole population is considered the amount of visual fixation is very much like that shown in caloric nystagmus and per-rotatory nystagmus in patients with peripheral vestibulopathy and also with the later test in controls: the mean reduction found by authors was 80% [
24]. But, when patients with some response during visual fixation are considered then the mean fixation index falls to 0.4. It will be interesting to analyze if with time and in case of vestibular periphery functional recovery, as occurs in some cases after intratympanic gentamicin [
25] there is some modification of the fixation index.
We have not included patients with central vestibulopathy because of the unusual finding of SVIN [
26] and because the most frequent is vertical [
27]; in this sense the peripheral counterpart in which vertical SVIN is more common are patients with superior semicircular dehiscence for which the best frequency (500Hz) is above the one used in our work (100Hz) and preferentially stimulating the vertex [
28].
The second interest of visual fixation in SVIN rests in the effects of skull vibration in the light or visual fixation condition. It has been shown that both the horizontal and vertical components of nystagmus in patients with non-acute unilateral vestibular loss are abolished (as measured in our work), but there is a torsional shift of the eye of approximately 3º-6º towards the ipsilesional side, no matter the mastoid side stimulated [
29]. The degree of torsion is only related to the amount of vestibular damage when the vibration is on the sternocleidomastoid muscles but not on mastoid. This effect is also seen in normal subjects and explains the modification of visual orientation perception in the roll plane [
30]. We have not evaluated that finding that needs also to be assessed with corresponding fixation index value and otolithic functional evaluation.
In conclusion given that fixation suppression was found in all patients with SVIN in cases of peripheral vestibulopathy it is interesting as a confirmatory bedside test. When quantified by any of the different nystagmography methods the fixation index clearly delineates two populations of patients with or without complete visual reduction of nystagmus. Better measures of vestibular function that implicate visual-vestibular interaction need to be considered.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to this work as follows: Conceptualization –A.B-C. and N.P-F.; methodology, M.B., C.M-R., A.B-C. and N.P-F.; formal analysis, M.A.d.L-A. and P.M.F-M.; investigation, M.B., C.M-R., M.A.d.L-A., P.M.F-M., B.M., A.B-C. and N.P-F.; resources, M.B., C.M-R., A.B-C. and N.P-F.; data curation, M.A.d.L-A. and P.M.F-M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B., C.M-R., M.A.d.L-A., P.M.F-M., B.M. and N.P-F.; writing—review and editing, M.B., M.A.d.L-A., P.M.F-M., A.B-C. and N.P-F.; visualization, M.B. and N.P-F.; supervision, N.P-F. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional review board approval and informed consent from all patients were obtained in June 2018 (RGPD 2016/679).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to their institution for providing research means.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lücke K. Eine Methode zur Provokation eines pathologischen Nystagmus durch Vibrationsreize von 100 Hz [A vibratory stimulus of 100 Hz for provoking pathological nystagmus (author's transl)]. Z Laryngol Rhinol Otol. 1973 Oct;52(10):716-20. German. PMID: 4766429.
- Ulmer, E., Chays, A., & Brémond, G. Nystagmus induit par des vibrations : Physiopathogénie et intérêt en clinique. Annales d’Otolaryngologie et de Chirurgie Cervico-Faciale, 2004,121(2), 95–103. [CrossRef]
- Dumas G, Curthoys IS, Lion A, Perrin P, Schmerber S. The Skull Vibration-Induced Nystagmus Test of Vestibular Function-A Review. Front Neurol. 2017 Mar 9;8:41. [CrossRef]
- Batuecas-Caletrío A, Martínez-Carranza R, García Nuñez GM, Fernández Nava MJ, Sánchez Gómez H, Santacruz Ruiz S, Pérez Guillén V, Pérez-Fernández N. Skull vibration-induced nystagmus in vestibular neuritis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020; 140: 995-1000. [CrossRef]
- Perez N. Vibration induced nystagmus in normal subjects and in patients with dizziness. A videonystagmography study. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2003; 124: 85-90.
- Zamora EG, Araújo PE, Guillén VP, Gamarra MFV, Ferrer VF, Rauch MC, Garrigues HP. Parameters of skull vibration-induced nystagmus in normal subjects. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Aug;275(8):1955-1961. Epub 2018 Jun 1. PMID: 29858923. [CrossRef]
- Teggi R, Familiari M, Gatti O, Bussi M. Vertigo without cochlear symptoms: Vestibular migraine or Menière disease? Neurol Sci. 2021; 42: 5071-6.
- Curthoys, I.S. The Neural Basis of Skull Vibration Induced Nystagmus (SVIN). Audiol. Res. 2021, 11: 557–66. [CrossRef]
- Jareonsettasin P, Otero-Millan J, Ward BK, Roberts DC, Schubert MC, Zee DS. Multiple Time Courses of Vestibular Set-Point Adaptation Revealed by Sustained Magnetic Field Stimulation of the Labyrinth. Curr Biol. 2016; 26: 1359-66. [CrossRef]
- Dumas G, Perrin P, Ouedraogo E, Schmerber S. How to perform the skull vibration induced nystagmus test (SVINT). Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2016; 133: 343–8. [CrossRef]
- Mantokoudis G, Wyss T, Zamaro E, Korda A, Wagner F, Sauter TC, Kerkeni H, Kalla R, Morrison M, Caversaccio MD. Stroke Prediction Based on the Spontaneous Nystagmus Suppression Test in Dizzy Patients: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Neurology. 2021; 97: e42-e51. [CrossRef]
- Díaz MPG, Torres-García L, Zamora EG, Belén Castilla Jiménez A, Pérez Guillén V. Is Skull Vibration-Induced Nystagmus Useful in Vestibular Neuritis Follow Up? Audiol Res. 2022; 12: 126-131.
- Martin-Sanz, E., Esteban-Sánchez, J., González-Márquez, R., Larrán-Jiménez, A., Cuesta, Á., & Batuecas-Caletrio, Á. Vibration-induced nystagmus and head impulse test screening for vestibular schwannoma. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 2021, 141(4), 340–347. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Soper J, Lohse CM, Eggers SDZ, Kaufman KR, McCaslin DL. Agreement between the Skull Vibration-Induced Nystagmus Test and Semicircular Canal and Otolith Asymmetry. J Am Acad Audiol. 2021; 32:283-9. [CrossRef]
- Eggers SDZ, Bisdorff A, von Brevern M, Zee DS, Kim JS, Perez-Fernandez N, Welgampola MS, Della Santina CC, Newman-Toker DE. Classification of vestibular signs and examination techniques: Nystagmus and nystagmus-like movements. J Vestib Res. 2019; 29: 57-87. [CrossRef]
- Matiño-Soler E, Esteller-More E, Martin-Sanchez JC, Martinez-Sanchez JM, Perez-Fernandez N. Normative data on angular vestibulo-ocular responses in the yaw axis measured using the video head impulse test. Otol Neurotol. 2015; 36: 466-71. [CrossRef]
- Sinno S, Schmerber S, Perrin P, Dumas G. Fifty Years of Development of the Skull Vibration-Induced Nystagmus Test. Audiology Research. 2022; 12: 10-12. [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto C, Kawahara T, Yagi M, Murofushi T. Association between vestibular dysfunction and findings of horizontal head-shaking and vibration-induced nystagmus. J Vestib Res. 2020; 30: 319-27. [CrossRef]
- Korda A, Zee DS, Wyss T, Zamaro E, Caversaccio MD, Wagner F, Kalla R, Mantokoudis G. Impaired fixation suppression of horizontal vestibular nystagmus during smooth pursuit: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Eur J Neurol. 2021; 28: 2614-21. [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen TP, Juhola M, Aalto H. Suppression of spontaneous nystagmus during different visual fixation conditions. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 269: 1759-62. [CrossRef]
- Özel HE, Karakuzu AT, Temir H, Alpay M, Özdoğan F, Genç S. Effect of ocular fixation on positional nystagmus in BPPV patients. Int J Audiol. 2023; 62: 644-9. [CrossRef]
- Huh YE, Kim JS. Bedside evaluation of dizzy patients. J Clin Neurol. 2013; 9: 203-13. [CrossRef]
- Kim HA, Yi HA, Lee H. Failure of Fixation Suppression of Spontaneous Nystagmus in Cerebellar Infarction: Frequency, Pattern, and a Possible Structure. Cerebellum. 2016; 15: 182-9. [CrossRef]
- Murai N, Funabiki K, Naito Y, Ito J, Fukuyama H. Validity and limitation of manual rotational test to detect impaired visual-vestibular interaction due to cerebellar disorders. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2005; 32: 23-8. [CrossRef]
- Alonso SM, Ayerve NA, Roca CM, Touma GC, Dios JCDP, Gómez HS, Ruíz SSC, Caletrío ÁB. Use of skull vibration-induced nystagmus in the follow-up of patients with Ménière Disease treated with intratympanic gentamicin. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023; 16: 236-43. [CrossRef]
- Dumas G, Michel J, Lavieille JP, Ouedraogo E. Intérêt sémiologique et essai d'optimisation du stimulus au cours du test vibratoire: Résultats d'une analyse 3D du nystagmus. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2000; 117: 299-312.
- Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim JS. Pearls & Oysters: Vibration-Induced Downbeat Nystagmus: A New Cerebellar Sign Observed in Paraneoplastic Syndrome. Neurology. 2023; 100: 43-6.
- Dumas G, Tan H, Dumas L, Perrin P, Lion A, Schmerber S. Skull vibration induced nystagmus in patients with superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2019; 136: 263-72. [CrossRef]
- Karlberg M, Aw ST, Black RA, Todd MJ, MacDougall HG, Halmagyi GM. Vibration-induced ocular torsion and nystagmus after unilateral vestibular deafferentation. Brain. 2003; 126: 956-64. [CrossRef]
- McKenna GJ, Peng GC, Zee DS. Neck muscle vibration alters visually perceived roll in normals. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2004; 5: 25-31. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).