1. Introduction
Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness mainly characterized by delusions, hallucinations, and cognitive dysfunction [
1]. This invalidating disorder affects millions of people worldwide and nearly 1% of the general Canadian population, giving rise to considerable societal costs [
2,
3,
4]. Auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) (i.e., voices heard in the absence of a speaker) are amongst the most debilitating symptoms associated with schizophrenia and are experienced by most patients [
5,
6]. In fact, AVH have been associated with lower levels of employment and social isolation [
7,
8].
First-line treatment for schizophrenia patients is based on the administration of antipsychotics [
9]. Antipsychotic agents aim to reduce psychotic symptoms [
9]. However, up to a third of schizophrenia patients do not respond adequately to these treatments [
9,
10]. Clozapine is usually the next recommended pharmacological approach, as it is considered the most effective medication for treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients [
11,
12,
13]. Nonetheless, over 50% of these patients will not show clinical improvement following this treatment [
14]. In these cases, psychological interventions can be combined with pharmacological treatments to optimize outcomes [
15]. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the most commonly utilized psychotherapy for the treatment of psychotic symptoms [
16]. CBT has proven to reduce AVH, but its efficacy remains modest for many patients [
17].
To address these limitations, novel therapeutic approaches, such as virtual reality (VR)-based therapies, have been put forth. VR has previously been used in a wide array of therapeutic contexts as it can aid in exposing patients to different stimuli related to their psychopathology and contribute to clinical improvement [
18]. Several studies have explored its efficacy for different mental illnesses including anxiety disorders and psychotic disorders [
18]. Notably, VR-assisted therapies including CBT components have been shown to improve symptoms such as paranoid ideations in patients with schizophrenia disorders [
19,
20]. Moreover, Avatar therapy (AT) is an innovative VR-based psychotherapeutic intervention which specifically targets AVH [
21]. During this intervention, patients communicate with representations of their AVH through a VR interface. Patients are invited to create a computerized visual representation of their most distressful voice and personalize the associated voice [
22]. The therapist animates this representation (i.e., the Avatar) and uses it to communicate with the patient. AT allows patients to interact with their voice in a safe environment and eventually develop a sense of empowerment and control. This approach enables the creation of an experience similar to what patients are faced with when hearing these tormenting voices. Descriptions of the contents of the dialogue with the voices are used by the therapist to recreate realistic interactions with the patient. This helps to explore the patient’s real-life reactions to the voices so that these can be adjusted with the therapist throughout the sessions. Previous trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of AT in reducing the frequency and distress associated with AVH in patients with schizophrenia [
21,
22,
23].
Many aspects of VR, such as sense of presence, have been studied to better understand the role of these components in immersive experiences [
24]. Sense of presence is a multidimensional concept generally defined as the sense of being in a context displayed by a virtual environment [
25]. Several studies have shown that most virtual environments can induce a sense of presence, which could be linked to emotional reactions and learning [
26,
27]. In fact, some studies have found a bidirectional relationship between emotions and sense of presence in a therapeutic context, showing that a higher sense of presence is associated with higher emotional intensity and vice versa [
28].
Moreover, emotions play a crucial role in psychological therapy efficacy [
29,
30]. Hence, dialogue during AT can be very emotionally charged. Emotions such as anger, joy, interest and disgust have been highlighted as being predominant during Avatar-patient interactions [
31]. Since emotional response and learning are key components of AT, it is possible that the feeling of presence may impact clinical outcomes and emotional reactions of patients. Furthermore, some studies have found positive correlations between therapy efficacy for anxiety symptoms and sense of presence [
32,
33]. One study also found that the interaction between reduction of anxiety and sense of presence was a significant predictor of symptom improvements related to AVH in AT [
34]. However, very few other studies have examined the mutual interactions between presence, emotions and AVH outcomes in AT.
This exploratory study is one of the first to investigate the relationship between sense of presence, emotional response and clinical outcomes related to AVH in AT. Based on the previous literature mentioned above, the following was hypothesized: 1. Higher levels of sense of presence would correlate positively with higher emotional response and intensity; 2. Higher levels of presence would correlate positively with a better clinical outcome; 3. Participants with a high clinical improvement would report higher levels of sense of presence than participants with a lesser clinical improvement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
To conduct this investigation, data from previous and ongoing AT randomized clinical trials were used (ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier numbers: NCT03585127, NCT04054778 and NCT03148639). Participants all provided informed written consent. These trials were approved by the “Centre intégré universitaire de santé et de services sociaux de l’Est-de-l’Île-de-Montréal” ethics committee.
To be included in this study, participants had to be 18 years or older and have a diagnosis of treatment-resistant schizophrenia, which was defined as the presence of persistent AVH after adequate trials of two or more antipsychotics (therapeutic doses for a minimum of 6 consecutive weeks). Data from a total of 123 participants was used to conduct this analysis.
2.2. Procedures
Participants had all been enrolled for AT between 2015 and 2023. AT consists of 9 weekly psychotherapeutic sessions including 8 immersive sessions during which participants interact with a virtual representation of their AVH (the Avatar). Participants viewed the Avatar, with a neutral background, through a VR head-mounted display. Each session lasted one hour, with approximately 15 minutes being allotted to the VR immersion. Since the first session does not include an immersion, it was not included in the current analysis. The present dataset included participants who had completed between 2 to 8 immersive AT sessions. However, certain participants had participated in more than one trial and therefore completed more than 8 sessions [
22]. Auditory hallucinations assessments were completed at baseline (around one week before the beginning of AT), post-therapy (around one week after the end of therapy), and follow-up (3 months after the end of AT) by research nurses. Additional details regarding AT can be found in one of the preceding trials [
21]
2.3. Measures
Clinical data was collected during three interviews: baseline, post-therapy and 3-month follow-up. These were led by research nurses or research assistants, all of whom underwent questionnaire-specific training before the beginning of the clinical trials. Sociodemographic data was collected during the baseline evaluation. Moreover, during each evaluation, auditory hallucinations were assessed using the auditory hallucinations subscale of the Psychotic Symptom Rating Scales (PSYRATS—AH) [
35]. The auditory hallucinations subscale comprises 11 Likert-type items. The PSYRATS was demonstrated to be a reliable instrument to measure different aspects associated with auditory hallucinations [
35]. In the present study, the PSYRATS—AH total score, as well as the following subscales were used for statistical analyses: frequency, distress, attribution, and loudness [
36].
The Igroup Presence Questionnaire (IPQ) was used to evaluate sense of presence. This validated questionnaire is composed of 14 items divided into 4 subscales: general presence, spatial presence, involvement, and realism. The items are rated on a 7-point Likert-type scale ranging from 0 (“not at all/fully disagree”) to 6 (“very much/fully agree”). This questionnaire has been previously validated and found to be reliable in different samples [
37]. Participants completed the questionnaire with a research assistant at the end of the first and last immersive sessions, with the exception of 14 participants who completed the IPQ during every immersive session. For the analyses presented in the current paper, a modified version of the IPQ excluding items 3, 11 and 12 was used. Indeed, this change was made due to concerns regarding the participants’ comprehension of certain items. By removing these items, the internal consistency greatly increased; Cronbach’s alpha went from 0.58 to 0.72. This resulted in a total score varying from 6 to 66. Of note, the IPQ was only used during certain trials, therefore less data was acquired with this questionnaire.
Sense of presence was also measured using a graphic rating scale (GRS) ranging from 0 (“not at all”) to 10 (“very strongly”). Participants rated how present they felt with the Avatar during the VR immersion. This question was asked by the therapist at the end of each immersive AT session. This scale was used to mitigate the comprehension concerns raised with the IPQ and include a measure of presence that considers the Avatar.
The emotional response during each therapeutic session was evaluated using a GRS with a rating system ranging from 0 (“not at all”) to 10 (“very strongly”). This scale was utilized to evaluate the following emotions: anxiety, control, anger, fear, serenity, and sadness. Subjects were asked by the therapist to rate how much they felt these emotions during the immersive experience. This questionnaire was completed at the end of each immersive AT session. As sadness was only evaluated in certain trials, fewer responses were collected for this emotion.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
First, the relation between emotional response and sense of presence was explored with a bivariate Spearman correlation because the data did not present a normal distribution [
38]. The GRS scores (sense of presence and emotions) were averaged over all completed immersive AT sessions. IPQ total scores were also averaged over the sessions during which they were completed, thereby providing a representation of the overall sense of presence and emotions experienced throughout AT. The mean scores were used to perform the different correlations. The same procedure was used with the maximum emotion GRS scores for positive emotions (control, serenity), negative emotions (anxiety, anger, fear, sadness) and total emotions. These scores were used as a measure for maximum emotional intensity to evaluate the relation between emotional intensity and sense of presence. A bivariate Spearman correlation was also used to evaluate the association between clinical symptomatology and sense of presence. To perform this test, the variation percentage between baseline and 3-month follow-up PSYRATS—AH total scores as well as IPQ average total scores and average scores for the sense of presence GRS were used. PSYRATS—AH score variations were used as an indicator of severity variation of AVH and were calculated using the following formula: ((baseline PSYRATS—AH score - 3-month follow-up PSYRATS—AH score)/baseline PSYRATS—AH score * 100). Therefore, a negative result of this variable indicated a reduction in the severity of AVH. If the 3-month follow-up visit had not occurred, post-therapy scores were used instead. The use of 3-month follow-up PSYRATS—AH scores was preferred as clinical symptomatology reaches a higher variation during this period [
22]. Out of 65 participants who completed baseline and post-therapy PSYRATS—AH evaluations, 40 participants completed the 3-month follow-up PSYRATS—AH evaluation. To carry out clinical outcome-related analyses, data from participants who completed all AT sessions was used.
Next, the relationship between the main therapeutic outcome and sense of presence was explored. Using the previously calculated variation percentages of PSYRATS—AH total scores, a dichotomic analysis was conducted using a reduction threshold of 20% or more in PSYRATS—AH symptomatology as an indicator of a clinical response. This is a commonly used threshold for the evaluation of treatment response in schizophrenia patients [
39,
40,
41]. Thus, participants were categorized in the responders’ group if they had a PSYRATS—AH score reduction of 20% or more. Otherwise, they were categorized in the non-responders’ group. A Mann-Whitney U test was then used to compare average sense of presence scores (GRS mean scores and IPQ mean scores) between responders and non-responders [
42]. Effect size for this test was estimated with Cohen’s d [
43].
Finally, associations between sense of presence (IPQ mean scores and GRS mean scores) and PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores variation percentages were evaluated using bivariate Spearman correlations (see
Table S1). PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores variation percentages were calculated using the baseline PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores and the 3-month follow-up PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores, or the post-therapy PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores when 3-month follow-up scores were not available. Also, the relationship between mean emotional response scores and average PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores variation percentages was assessed using bivariate Spearman correlations (see
Table S2).
As some data from different questionnaires had not yet been collected for participants from ongoing trials, or had not been collected in previous trials, available measures sometimes varied between statistical tests. Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS 28 [
44]. Correlation coefficients were categorized as weak (±0.1-0.3), moderate (±0.4-0.6), strong (±0.7-0.9), and perfect (±1) [
45]. Effect sizes (Cohen’s d) were categorized as small (0.2-0.5), moderate (0.5-0.8) and large (>0.8) [
46]. P-value significance threshold was set to 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
A total of 123 participants with psychotic disorders were included in this study, and 68.3% of the participants were men. While 78.9% of the sample was diagnosed with schizophrenia, 21.1% of the participants suffered from a schizoaffective disorder. The detailed sample characteristics are presented in
Table 1.
3.2. Sense of Presence and Emotions
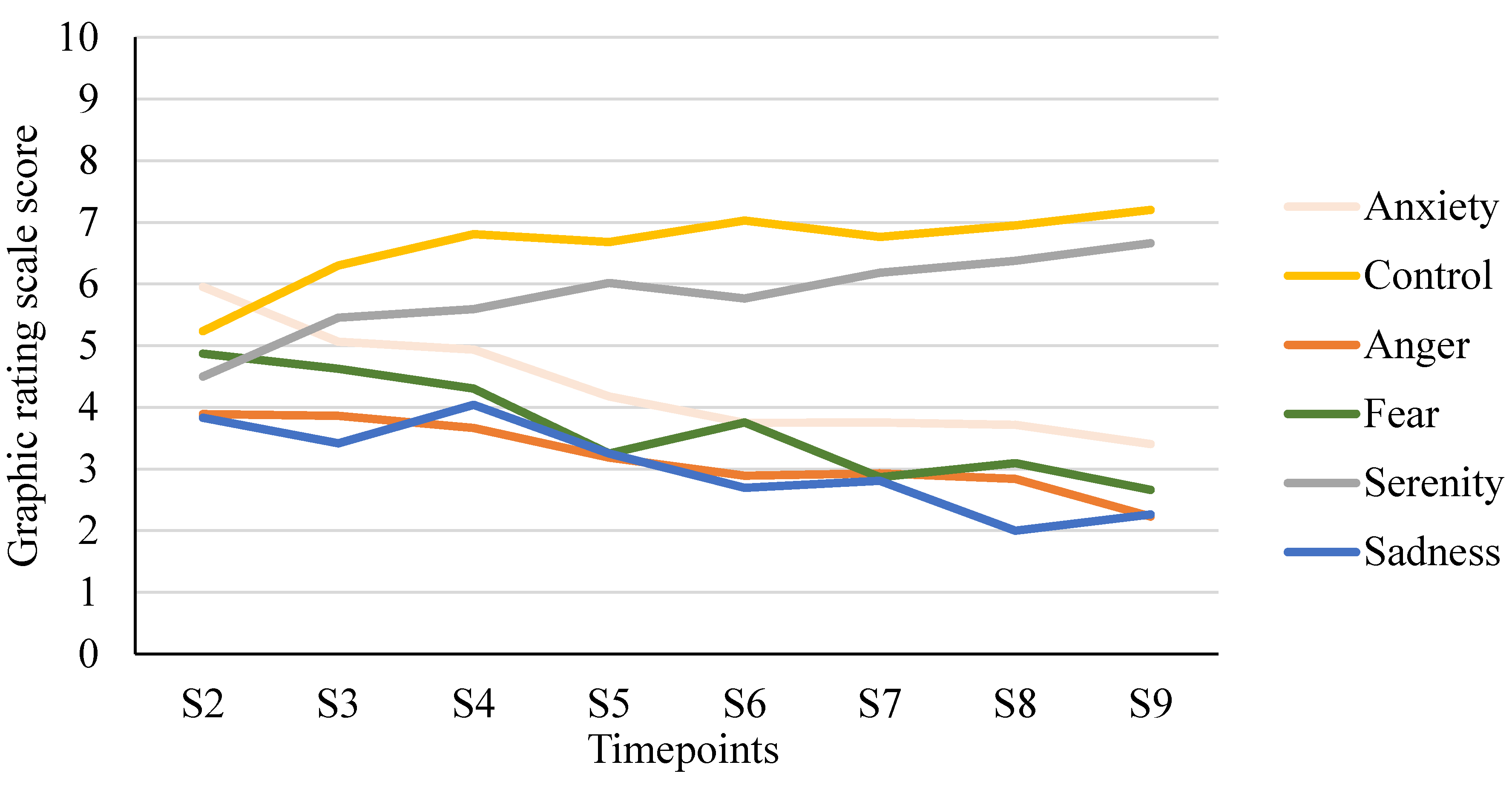
The evolution of emotional response scores throughout the sessions is illustrated in
Figure 1. Emotions related to control and serenity tended to increase throughout the therapy sessions, while feelings of anxiety, fear, anger and sadness tended to decrease.
Regarding the association between the two presence scales, a moderate positive correlation was observed between the GRS mean scores and IPQ mean scores (
rs=0.460, p <0.01). The impact of presence on experienced emotions during AT is detailed in
Table 2. A weak to moderate positive correlation between sense of presence and control (
rs =0.337, p < 0.01), and a weak positive correlation between sense of presence and serenity (
rs =0.242, p < 0.05) were detected with the GRS scores. Also, a weak positive correlation between sense of presence and control (
rs =0.225, p < 0.05) was detected with the IPQ scores. However, no significant correlation was found between presence and serenity with the IPQ scores (
rs =0.113, p = 0.305).
The impact of presence on emotional intensity during AT is presented in
Table 2. With the GRS scores, a weak to moderate positive correlation between sense of presence and positive emotional intensity (
rs =0.337, p < 0.01), and a weak positive correlation between sense of presence and total emotional intensity (
rs =0.242, p < 0.05) were observed. Regarding the IPQ scores, a weak positive correlation was found between sense of presence and total emotional intensity (
rs =0.284, p < 0.01).
3.3. Sense of Presence and Clinical Outcomes
The results regarding the impact of presence on variation percentages in PSYRATS—AH scores were mixed (as shown in
Table 2). In fact, with the GRS scores, sense of presence was weakly to moderately associated with a reduction of auditory hallucinations (
rs =-0.384, p < 0.01). In other words, higher levels of presence were correlated with a reduction of AVH. However, with the IPQ scores, no significant correlation was found between these variables (
rs =-0.257, p=0.15).
Then, mixed results were found concerning sense of presence score differences between responders and non-responders (as shown in
Table 3). The GRS mean scores showed a significant difference between sense of presence scores in the two groups (p=0.047), with a moderate effect size (d=0.543). In fact, with the GRS, participants in the responders’ group had higher sense of presence scores. However, with the IPQ scores, no significant difference between sense of presence scores was detected (p=0.963).
Higher GRS presence scores were associated with a higher decrease in distress PSYRATS—AH subscale scores, and a higher decrease in loudness PSYRATS—AH subscale scores. Greater IPQ scores were also correlated with a greater decrease in loudness PSYRATS—AH subscale scores (see
Table S1). Higher levels of certain negative emotions (anger, anxiety, maximum intensity of negative emotions) were associated with a higher reduction of frequency PSYRATS—AH subscale scores (see
Table S2). No significant correlations were noted between the other PSYRATS—AH subscales (distress, attribution, loudness) and emotions (See
Table S2).
4. Discussion
This study sought to explore the relationships between sense of presence, emotions, and clinical outcomes in AT. Positive associations between sense of presence and control were found. A positive association was also found between sense of presence and serenity. Moreover, positive associations between sense of presence and emotional intensity were also observed. Relative to results for the relationship between therapeutic outcome and sense of presence, the two sense of presence questionnaires (IPQ and GRS) yielded different outcomes. Indeed, higher GRS presence scores were associated with a reduction of AVH and a better clinical outcome. However, no association with overall clinical symptomatology was observed with the IPQ scores.
Regarding the evolution of emotional responses during AT, the results suggest that positive emotions (control, serenity) became more prominent towards the end of AT. Inversely, negative emotions (anger, fear, anxiety, sadness) seemed to decrease as the sessions progressed. Similarly, previous studies have demonstrated that levels of anxiety and fear tend to diminish significantly between the first and last session of AT [
22,
34]. Traditional interventions for psychotic disorders, such as acceptance and commitment therapy, have also shown that feelings of anxiety tend to diminish during the therapeutic process [
47]. Moreover, the noted increase in positive emotions aligns with one of the therapeutic goals of AT, which is to help patients develop a sense of control over the voices they hear and reduce the distressing feelings associated with them. Overall, these results suggest that AT could enhance positive emotions while reducing negative emotions.
In addition, sense of presence, evaluated with the GRS, was positively correlated with positive emotions. Similar results were observed with the IPQ, as the IPQ scores were positively correlated with control. This is congruent with the moderate positive association found between the two scales, which indicates that there is some overlap between the measures of sense of presence reported by the GRS and the IPQ. The results regarding sense of presence and emotional intensity are coherent with these outcomes. In fact, the sense of presence GRS and IPQ scores were both positively associated with emotional intensity for total emotions, which indicates that emotional response intensity is directly associated with levels of sense of presence in AT. Consistent with these results, previous literature has shown that emotions may be a fundamental factor influencing sense of presence [
28,
48]. Additionally, GRS presence scores were positively correlated with emotional intensity for positive emotions, which, combined with the previous results, suggests that sense of presence could be more strongly associated with positive emotions, compared to negative emotions, in AT. Other VR-based therapy studies have mostly explored the relationship between negative emotions and sense of presence, showing that there seems to be a positive association between these two variables [
49]. However, these VR interventions are predominantly targeted towards phobias and mostly involve an approach using exposure therapy [
49]. This may contribute to explaining the disparities with the present findings [
49]. Moreover, as AT progresses, the Avatar tends to act in a more positive and friendly way toward the patient compared to the first sessions during which the Avatar will act in a negative and confrontational manner with the patient [
50]. This is congruent with the previous results showing that positive emotions become more important as the therapy sessions progress. This implies that positive emotions could be a central aspect of the Avatar-patient dynamic, which could explain why associations with sense of presence were mainly observed with positive emotions. Freeman et al. (2005) have previously proposed that the relationship between presence and emotions could be dependent on the stimulus and its significance for the viewer [
51]. Therefore, associations between emotions and sense of presence may vary based on the dynamics involved in the VR intervention. Nevertheless, more studies are needed to further understand the associations between emotions and presence in AT and other VR-based therapies for psychotic disorders.
As for the associations between the sense of presence GRS scores and the PSYRATS—AH score variations, these results suggest that the reduction in severity of AVH is associated with a higher sense of presence. Other VR-based therapy studies show conflicting results regarding correlations between sense of presence and clinical outcomes. Indeed, some studies have shown that presence is significantly associated with therapeutic outcomes in interventions targeting anxiety and phobias [
33,
52]. Although, other anxiety and phobia studies have found no association between these variables [
32]. Further research is needed to better understand the association between presence and clinical outcomes. Furthermore, the sense of presence GRS scores were significantly higher for AT responders compared to non-responders, which is congruent with the association found between the reduction of AVH symptomatology and higher GRS presence scores. However, these results were not observed with the IPQ scores.
Collectively, these results seem to indicate that sense of presence may be a contributing factor to clinical outcomes in AT. Despite some associations with the sense of presence GRS scores and the IPQ scores being similar, it is possible that the differences regarding therapeutic outcomes are attributable to variations in measures between the two scales. In fact, even though a significant positive correlation between the sense of presence GRS scores and the IPQ scores was found, this association remains moderate. The GRS involves a relational measure of presence, as it takes into consideration the Avatar. Conversely, the IPQ mainly evaluates physical presence in the VR environment [
37]. This measure may be complexified with the use of a neutral VR background in AT, as characteristics of VR environments may impact presence. Since AT is a psychological intervention centered on the relationship the patient has with the Avatar, it is possible that the consideration of the relational aspect of presence, with the GRS, may have impacted sense of presence scores. Moreover, the IPQ has not yet been validated in patients suffering from psychotic disorders and may therefore not be adapted for this population.
Though this study provides a new insight into the role of sense of presence and emotions in AT, some limitations should be considered while interpreting the results of this investigation. Firstly, the sense of presence GRS has not been previously validated. To compensate for this limit, the IPQ was also used, which allowed for the comparison of the two scales. Secondly, the number of participants was limited. Thus, a limited statistical power could have led to the underestimation of certain results. Nonetheless, multiple associations were statistically significant. Finally, as this is a correlational study, causal relationships cannot be established between the analyzed variables. It is also important to note that, because this is an exploratory study, these results cannot be generalized, which limits their interpretation. in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study’s main objective was to evaluate the relationship between sense of presence, emotional response, and clinical outcomes in AT. It was found that sense of presence is mainly associated with positive emotions and overall emotional intensity. Additionally, it was observed that greater levels of presence may contribute to the improvement of AVH. Since VR interventions for psychotic disorders are newly emerging, it is important to understand the role sense of presence plays in the effectiveness of such therapies. It is also important to explore the role of emotional responses in VR-based therapies, as emotions are a central part of psychological interventions. Furthermore, adding objective measures of sense of presence and a presence questionnaire centered on the social aspect of presence could help to obtain measures more specific to AT’s therapeutic objectives. However, other studies are needed to verify the reproducibility of these results in AT, but also in other VR-based psychotherapeutic interventions for psychotic disorders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Correlations between the variation percentages of PSYRATS – AH subscales’ scores and sense of presence evaluated with the GRS and the IPQ; Table S2: Correlations between the variation percentages of PSYRATS—AH subscales’ scores and emotions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.P. and M.B.; methodology, M.B.; validation, M.B..; formal analysis, E.A.; resources, A.D., K.P.; data curation, E.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.D., M.B, S.G.; visualization, E.A., S.G., M.B.; supervision, A.D.; project administration, K.P.; funding acquisition, A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Otsuka Canada Pharmaceutical Inc. (OCPI); Le Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé (FRQS); Fondation J.-Louis Lévesque; Fondation Pinel.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the CIUSSS de l’Est-de-l’Île-de-Montréal (CER IPPM 16-17-06; 2017-03-28).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the data are part of an ongoing study. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Dr. Alexandre Dumais.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- McCutcheon RA, Reis Marques T, Howes OD. Schizophrenia—An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020, 77, 201–210. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson FJ, Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Diminic S, Stockings E, Scott JG; et al. Global Epidemiology and Burden of Schizophrenia: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Schizophr Bull. 2018, 44, 1195–1203. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System (CCDSS) [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024-02-13]. Available from: https://health-infobase.canada.ca/ccdss/data-tool/Index.
- Jin H, Mosweu I. The Societal Cost of Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. PharmacoEconomics. 2017, 35, 25–42. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix J, Ma E, Nguyen A, Ortiz Collado MA, Rexhaj S, Favrod J. Safety-seeking behaviours and verbal auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research. 2014, 220, 158–162. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley P, Fernyhough C, Ellison A. Auditory verbal hallucinations as atypical inner speech monitoring, and the potential of neurostimulation as a treatment option. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013;37(10 Pt 2):2794-805. [CrossRef]
- Kråkvik B, Larøi F, Kalhovde AM, Hugdahl K, Kompus K, Salvesen Ø; et al. Prevalence of auditory verbal hallucinations in a general population: A group comparison study. Scand J Psychol. 2015, 56, 508–515. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brederoo SG, de Boer JN, Linszen MMJ, Blom RE, Begemann MJH, Sommer IEC. Social Deafferentation and the Relation Between Loneliness and Hallucinations. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 2023;49(Supplement_1):S25-S32. [CrossRef]
- Lally J, MacCabe JH. Antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia: A review. British Medical Bulletin. 2015, 114, 169–179. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey A, Kalita KN. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia: How far have we traveled? Front Psychiatry. 2022, 13, 994425. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll CU, Rubio JM, Inczedy-Farkas G, Birnbaum ML, Kane JM, Leucht S. Efficacy of 42 Pharmacologic Cotreatment Strategies Added to Antipsychotic Monotherapy in Schizophrenia: Systematic Overview and Quality Appraisal of the Meta-analytic Evidence. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017, 74, 675–684. [CrossRef]
- Buchanan RW, Kreyenbuhl J, Kelly DL, Noel JM, Boggs DL, Fischer BA; et al. The 2009 Schizophrenia PORT Psychopharmacological Treatment Recommendations and Summary Statements. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 2009, 36, 71–93. [CrossRef]
- Hasan A, Falkai P, Wobrock T, Lieberman J, Glenthoj B, Gattaz WF; et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia, Part 1: Update 2012 on the acute treatment of schizophrenia and the management of treatment resistance. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry. 2012, 13, 318–378. [CrossRef]
- Siskind D, Siskind V, Kisely S. Clozapine Response Rates among People with Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Data from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 2017, 62, 772–777. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison AP, Law H, Carter L, Sellers R, Emsley R, Pyle M; et al. Antipsychotic drugs versus cognitive behavioural therapy versus a combination of both in people with psychosis: A randomised controlled pilot and feasibility study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018, 5, 411–423. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bighelli I, Huhn M, Schneider-Thoma J, Krause M, Reitmeir C, Wallis S; et al. Response rates in patients with schizophrenia and positive symptoms receiving cognitive behavioural therapy: A systematic review and single-group meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2018, 18, 380. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhar S, McKenna PJ, Radua J, Fung E, Salvador R, Laws KR. Cognitive–behavioural therapy for the symptoms of schizophrenia: Systematic review and meta-analysis with examination of potential bias. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2014, 204, 20–29. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebe A, Kannen K, Selaskowski B, Mehren A, Thöne A-K, Pramme L; et al. Virtual reality in the diagnostic and therapy for mental disorders: A systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review. 2022, 98, 102213. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraets CNW, Snippe E, van Beilen M, Pot-Kolder RMCA, Wichers M, van der Gaag M; et al. Virtual reality based cognitive behavioral therapy for paranoia: Effects on mental states and the dynamics among them. Schizophrenia Research. 2020, 222, 227–234. [CrossRef]
- Pot-Kolder RMCA, Geraets CNW, Veling W, van Beilen M, Staring ABP, Gijsman HJ; et al. Virtual-reality-based cognitive behavioural therapy versus waiting list control for paranoid ideation and social avoidance in patients with psychotic disorders: A single-blind randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2018, 5, 217–226. [CrossRef]
- Dellazizzo L, Potvin S, Phraxayavong K, Dumais A. One-year randomized trial comparing virtual reality-assisted therapy to cognitive-behavioral therapy for patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. NPJ Schizophr. 2021, 7, 9. [CrossRef]
- du Sert OP, Potvin S, Lipp O, Dellazizzo L, Laurelli M, Breton R; et al. Virtual reality therapy for refractory auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: A pilot clinical trial. Schizophr Res. 2018, 197, 176–181. [CrossRef]
- Craig TK, Rus-Calafell M, Ward T, Leff JP, Huckvale M, Howarth E; et al. AVATAR therapy for auditory verbal hallucinations in people with psychosis: A single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018, 5, 31–40. [CrossRef]
- McCreery MP, Schrader PG, Krach SK, Boone R. A sense of self: The role of presence in virtual environments. Computers in Human Behavior. 2013, 29, 1635–1640. [CrossRef]
- Slater, M. How Colorful Was Your Day? Why Questionnaires Cannot Assess Presence in Virtual Environments. Presence. 2004, 13, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak K, Biocca F. The Effect of the Agency and Anthropomorphism on Users' Sense of Telepresence, Copresence, and Social Presence in Virtual Environments. Presence Teleoperators & Virtual Environments. 2003, 12, 481–494. [CrossRef]
- Ochs C, Sonderegger A. The Interplay Between Presence and Learning. Frontiers in Virtual Reality. 2022;3. [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe R, Fabrizia M. Being There: Understanding the Feeling of Presence in a Synthetic Environment and its Potential for Clinical Change. In: Christiane E, editor. Virtual Reality in Psychological, Medical and Pedagogical Applications. Rijeka: IntechOpen; 2012. p. Ch. 1.
- Abargil M, Tishby O. How therapists' emotion recognition relates to therapy process and outcome. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2022, 29, 1001–1019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, K. Emotion Processing and the Role of Compassion in Psychotherapy from the Perspective of Multiple Selves and the Compassionate Self. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2019, 2019, 7214752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudon A, Lammatteo V, Rodrigues-Coutlée S, Dellazizzo L, Giguère S, Phraxayavong K; et al. Exploration of the role of emotional expression of treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients having followed virtual reality therapy: A content analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2023, 23, 420. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbos E, Rapee RM, Kavakli M. A controlled study of agoraphobia and the independent effect of virtual reality exposure therapy. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 2013, 47, 160–168. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani D, Riva F, Riva G. New Technologies for Relaxation: The Role of Presence. International Journal of Stress Management Copyright. 2007, 14, 260–274. [CrossRef]
- Rus-Calafell M, Ward T, Zhang XC, Edwards CJ, Garety P, Craig T. The Role of Sense of Voice Presence and Anxiety Reduction in AVATAR Therapy. J Clin Med. 2020;9(9). [CrossRef]
- Faragher EB, Haddock G, McCarron J, Tarrier N. Scales to measure dimensions of hallucinations and delusions: The psychotic symptom rating scales (PSYRATS). Psychological Medicine. 1999, 29, 879–889. [CrossRef]
- Woodward TS, Jung K, Hwang H, Yin J, Taylor L, Menon M; et al. Symptom dimensions of the psychotic symptom rating scales in psychosis: A multisite study. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S265-74. [CrossRef]
- Schubert T, Friedmann F, Regenbrecht H. The Experience of Presence: Factor Analytic Insights. Presence. 2001, 10, 266–281. [CrossRef]
- Mishra P, Pandey CM, Singh U, Gupta A, Sahu C, Keshri A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann Card Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, D. Howes, M. R.C.Psych., Ph.D.,, Rob McCutcheon, M.R.C.Psych.,, Ofer Agid, M.D.,, Andrea de Bartolomeis, M.D., Ph.D.,, Nico J.M. van Beveren, M.D., Ph.D.,, Michael L. Birnbaum, M.D.,; et al. Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Treatment Response and Resistance in Psychosis (TRRIP) Working Group Consensus Guidelines on Diagnosis and Terminology. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2017, 174, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang L, Bai A, Tang Z, Liu X, Li Y, Ma J. Incidence and factors associated of early non-response in first-treatment and drug-naïve patients with schizophrenia: A real-world study. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2023;14. [CrossRef]
- Loebel A, Citrome L, Correll CU, Xu J, Cucchiaro J, Kane JM. Treatment of early non-response in patients with schizophrenia: Assessing the efficacy of antipsychotic dose escalation. BMC Psychiatry. 2015, 15, 271. [CrossRef]
- The Mann - Whitney U: A Test for Assessing Whether Two Independent Samples Come from the Same Distribution2007.
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Frontiers in Psychology. 2013;4. [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. Released 2021. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows VA, NY: IBM Corp.
- Akoglu, H. User's guide to correlation coefficients. Turkish Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan GM, Feinn R. Using Effect Size-or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J Grad Med Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spidel A, Lecomte T, Kealy D, Daigneault I. Acceptance and commitment therapy for psychosis and trauma: Improvement in psychiatric symptoms, emotion regulation, and treatment compliance following a brief group intervention. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice. 2018, 91, 248–261. [CrossRef]
- Riches S, Elghany S, Garety P, Rus-Calafell M, Valmaggia L. Factors Affecting Sense of Presence in a Virtual Reality Social Environment: A Qualitative Study. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2019, 22, 288–292. [CrossRef]
- Diemer J, Alpers GW, Peperkorn HM, Shiban Y, Mühlberger A. The impact of perception and presence on emotional reactions: A review of research in virtual reality. Frontiers in Psychology. 2015;6. [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin M, Potvin S, Machalani A, Dellazizzo L, Bourguignon L, Phraxayavong K; et al. The therapeutic processes of avatar therapy: A content analysis of the dialogue between treatment-resistant patients with schizophrenia and their avatar. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy. 2021, 28, 500–518. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman J, Lessiter J, Pugh K, Keogh E. When Presence and emotion are related, and when they are not. 2005.
- Price M, Anderson P. The role of presence in virtual reality exposure therapy. J Anxiety Disord. 2007, 21, 742–751. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).