1. Introduction
As powerplant of the cells, the mitochondria have the essential function and task of maintaining cellular metabolic balance: the provision of energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) play a central role as well as the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their protective antioxidants in order to maintain the redox balance.
A small part of energy is provided by the citrate cycle, in which "all" substances ingested with food are catabolized: fats, carbohydrates and proteins. In the matrix space of the mitochondrion, the citrate cycle is in close proximity to the enzyme complexes of oxidative phosphorylation, to which the reduction equivalents formed here are made available for the exergonic redox reactions. The lion's share of ATP comes from the respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation (36 mol ATP/mol glucose), which is extremely dependent on an optimal oxygen supply due to the high oxygen requirement.
Defects in mitochondrial energy metabolism can lead to a variety of diseases, be they of genetic origin, defects in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or due to the normal aging process, or an accumulation of mitochondrial defects that result in increasing ATP deficiency and an increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
We here focus on diseases that are causally linked to high oxidative stress, overproduction of superoxide radicals and corresponding secondary products, the ROS, and lead to a disturbance of the mitochondrial and cellular redox balance.
Mitochondrial ROS production.
Among the enzyme complexes, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane,
complex IV is mainly responsible for the formation of superoxide radicals ⋅O-O
-. In a healthy, energetically intact system, the heme centers of the cytochrome complexes (Fe
2+Fe
3+ + e
- ) transfer 2 electrons per mole of oxygen, so that O
2 is formally reduced to O
2- or H
2O. In the case of mitochondrial insufficiency, the electron transfer is also deficient, oxygen reduction stops with a one-electron transfer, forming O-O
-, the superoxide radical [
1]. Among the ROS subsequently formed, H
2O
2 and the ⋅OH radicals have a special function: Essential for the defense against infections, H
2O
2 also acts as an important signal and regulatory molecule [
2,
3].
The mitochondria's own antioxidant system -superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD2), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSHox), glutathione reductase (GSred) and others - responsible for maintaining the mitochondrial redox balance, also deals with external oxidative stress, thus forming a cellular ROS sink to a certain extent [
4]. If the antioxidant system is overwhelmed, the redox balance shifts in favor of an overproduction of reactive oxygen species, with ⋅OH radicals ultimately being responsible for the degenerative processes due to their non-specific and high reactivity. Enzymes are blocked, metabolic pathways are slowed down, e.g., the citrate cycle. ATP production decreases and the cell switches its survival strategy to other metabolic pathways, such as anaerobic glycolysis in the cytoplasm (Warburg effect), which leads to neoplastic cells [
5,
6]. Mitochondrial dysfunction can therefore induce a variety of diseases: Cancer, vascular inflammatory processes and associated diseases, age-related diseases or neurodegenerative processes, as summarized in
Table 1.
2. Mitochondriopathies, Preferred Indications for Redox Regulation through Ozone
The low-dose ozone concept with its redox regulatory effect has emerged as a successful complementary treatment strategy in mitochondriopathies linked to high oxidative stress as listed in
Table 2 (without any claim to completeness). We here only refer to diseases based on clinical studies and animal trials as published in peer-reviewed journals. Our focus is on a disturbed and restored redox balance, illustrated by very few typical parameters to demonstrate the common basis: oxidative stress versus the repair effect obtained by redox regulation through ozone.
3. Evaluation and Discussion of the Relevant Data in Redox Regulation for Selected Mitochondriopathies
Our hypothesis that controlled ozone applications interfere into the redox balance of the biological organism, first published1998 [
26] with a preclinical trial in preventing the liver from CCl
4 intoxication, has been verified over the last 2 decades. In ROS-induced mitochondriopathies, low-dose ozone acts as a redox bioregulator: a restoration of the redox balance is verifiable in all preclinical and clinical studies - those in which no redox parameters were available have not been included in this paper. Here we find the basic mechanism of action of systemic ozone applications, which, in addition to the known mechanisms of disinfection in topical ozone application (wound cleansing and wound disinfection), covers all ozone indications: chronic inflammatory diseases, silent inflammation and diseases associated with high oxidative stress: antioxidants as repair and protecting markers increase, stress markers decrease as discussed and summarized in
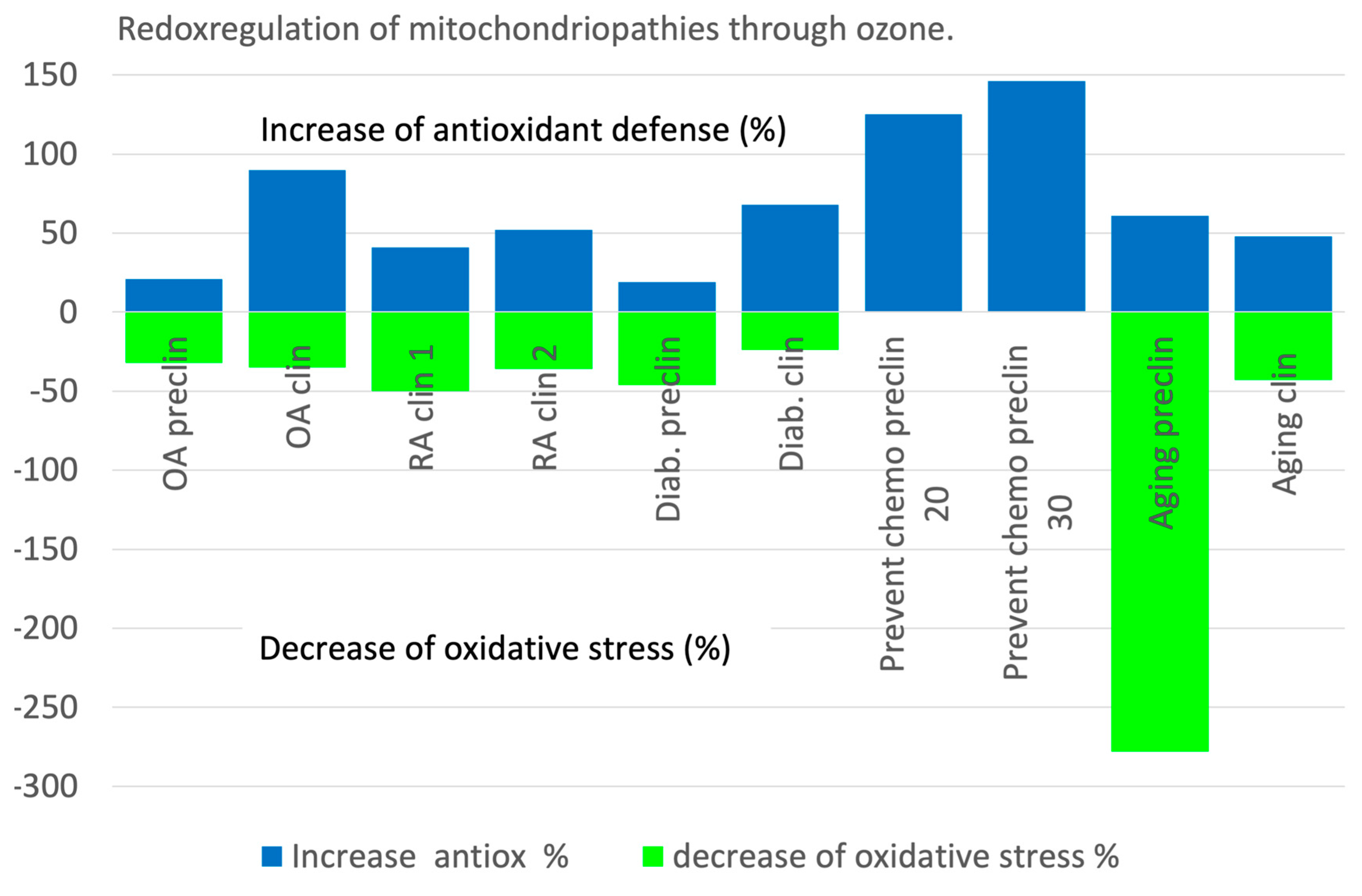
Figure 1.
The repair side of the equilibrium increases by 21 up to 140 % compared with the non-ozone treated groups, the stress markers are simultaneously reduced by at least 24 % to approx. 50 %, in aging process using an animal model even to the extent of 278 %.
Increase of antioxidant defense measured as GSH in % compared to the non-ozone treated controls and decrease of oxidative stress compared to the non-ozone treated controls, expressed as MDA (TH only in diabetes clin.) in %. For details see text.
OA preclin: Osteoarthritis in an animal study; OA clin: Osteoarthritis in a clinical study. RA clin: Rheumatoid arthritis, clinical study, Diab preclin: Animal study with STZ-induced diabetes: Diab clin: Clinical trial in diabetes 2; Prevent chemo preclin: Prevention of kidney damage due to cis platinum intoxication by rectal ozone application with an ozone concentration of 20 g/mL and 30 g/mL. Aging preclin: Animal trial in aging by lifelong regular rectal ozone application; Aging clin: Clinical study in attenuating the aging process.
3.1. Reference Substances.
To verify the regulatory effect of medical ozone in mitochondrial pathologies significant, reliable and reproducible oxidative stress parameters were measured: Malone dialdehyde (MDA), total hydroperoxide (TH)
and corresponding parameters from the group of antioxidants: Superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase GSHox, GSred and others in order to recognize the restoration of the redox balance. As all of these diseases are accompanied by a GSH deficiency (reduced glutathione), it makes particular sense to measure GSH as a follow-up parameter. For each study we here discuss the corresponding reference substances, see also
Table 3.
3.2. Toxicity of Ozone versus Therapeutical Efficacy
Over the last 2 decades a number of preclinical trials confirmed in clinical studies, have revealed the effective, non-toxic concentrations and doses of medical ozone and have allowed us to set up the guidelines for the use of ozone in prevention and therapy [
27] (Viebahn et al.2012).
Ozone concentrations in the range of 10 to 30 /mL (max. 40 /mL) are those preferred for systemic application and the redox bio regulatory effect taking a volume of 50-100 mL in case of extracorporeal blood treatment (Major autohemotherapy MAH) or 200-300 mL in case of rectal insufflation (RI). High concentrations contribute to oxidative stress blocking the regulation. They are administered locally to make use of the germicidal effect of ozone in highly infected wounds. For wound healing, the concentrations have to be reduced drastically to the systemic ones. High concentrations would destroy the freshly formed epithelium, the wounds enlarge and would never heal [
28].
3.3. Evaluation of Mitochondrial Pathologies and the Regulatory Effect of Medical Ozone. Restoration of the Redox Balance
Frequently and successfully applied in private clinics to avoid surgical interventions, preclinical and clinical studies in knee osteoarthritis were not published before 2010. Since then, however, a large number of clinical studies have been carried out. Our aim here is to demonstrate the rationale, namely to regulate the redox balance that has grown out of control, by administering ozone systemically or locally. For this purpose, a few exemplary redox parameters are analyzed in preclinical and clinical studies, see
Table 2.
3.3.1. Osteoarthritis
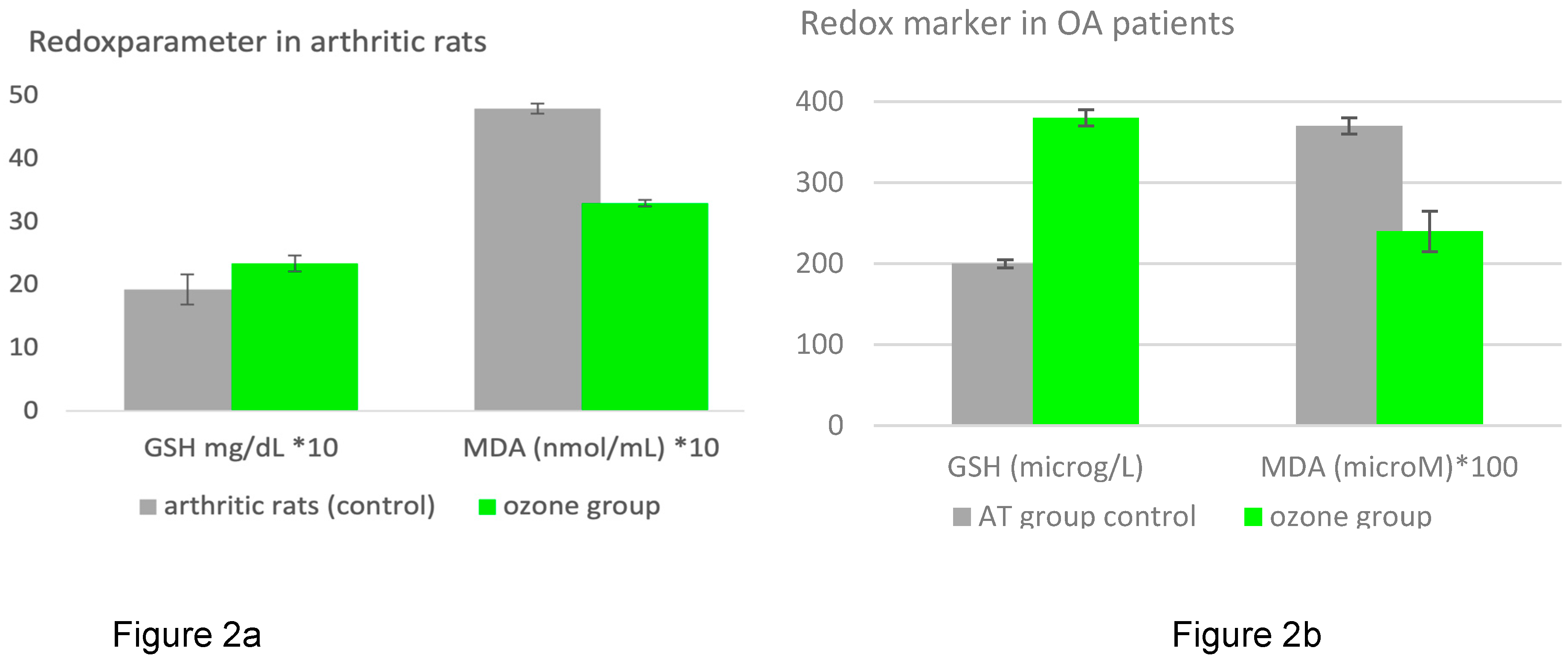
Preclinical trial in an animal model with rats [
12] using only one parameter on the oxidative stress side of the balance, one of the main causes of the disease, and one of the antioxidants on the other side: MDA and GSH, very reliable and reproducible as reference substances representing the effect of ozone. The study was designed for two study arms, firstly a preventive arm in which ozone was administered prior to inducing arthritis in the animals and secondly the therapeutic arm (not shown here): ozone was administered after the arthritis had become manifest for 24 days. The route of ozone administration was exactly the same and -interestingly enough- the results were the same: an increase in antioxidative capacity, here measured as GSH, returned to normal values as well as oxidative stress, here MDA. This means: systemically administered ozone as a preventive (protective) or therapeutic measure is able to restore redox balance in inflammatory diseases, in this case knee arthritis (
Figure 2 a).
Clinical trial, systemic ozone regulates the redox balance in osteoarthritis patients. A beneficial, preconditioning effect of ozone in osteoarthritis patients was revealed in a clinical study involving 40 patients undergoing surgical procedure via arthroscopy (AT). 20 patients received ozone in the form of rectal insufflation before AT (ozone group) and 20 underwent arthroscopy without the preventive ozone measure (AT group). Clinical and biochemical parameters were determined 30 days later (for the whole spectrum, material and methods please see original publication). Here again, we focus on the redox balance and evaluate GSH as antioxidant and MDA as oxidative stress parameter, shown in
Figure 2b. GSH as protective redox biomarker, is upregulated by 85 % through ozone application prior to arthroscopy. MDA as injury redox biomarker decreases accordingly by 35 % corresponding to a restoration of the redox balance [
13].
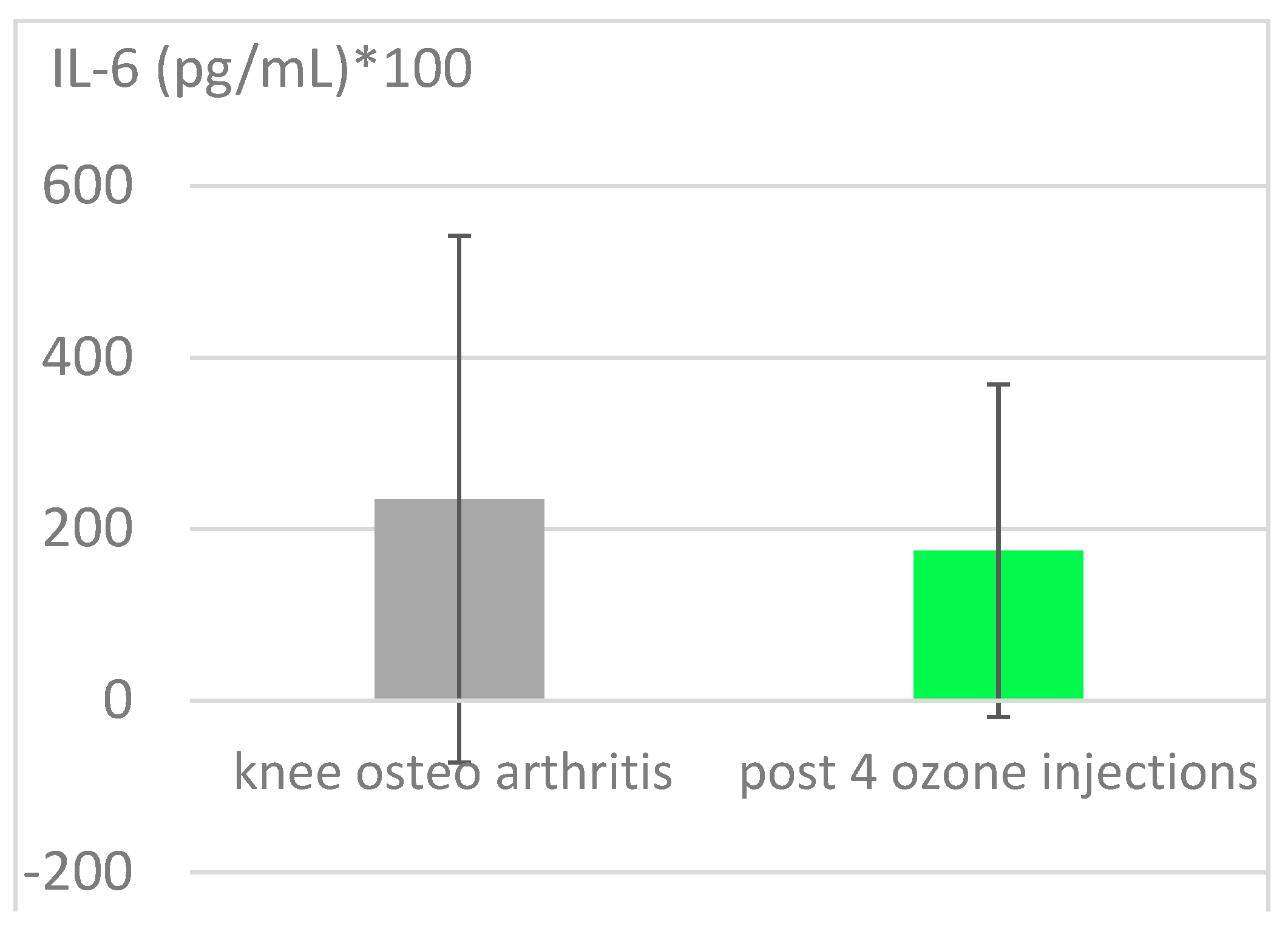
The upregulation of antioxidants and downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF- in inflammatory diseases is well known In this context, a clinical study on knee osteoarthritis [
14] comprising 51 patients (non-diabetic, non-obesity) is taken to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory effect of ozone in knee osteoarthritis as example of high oxidative stress in mitochondrial deficiencies. Elevated IL-6 serves as typical parameter. It is downregulated by 26 % (
Figure 3) simultaneously improving the clinical parameters (not shown here). The ozone mechanism of action involving the nuclear factor NFkB is discussed in section 4 of this article.
3.3.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Torequl Islam et al. 2023 [
29] published a comprehensive overview on the pathogenesis of rheumatoid diseases, the dysregulated redox system and therapeutic strategies including complementary therapies.
Ozone improves cellular redox balance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Here we focus again to the critical parameters GSH and MDA and the restoration of the redox balance to show and underline the basic mechanism of ozone in mitochondriopathies.
60 RA patients received a basic therapy: methotrexate + ibuprofen + folic acid. MTX group (n =30) with basic therapy only and the ozone group (n=30) received the same treatment as the MTX group plus additional ozone. Ozone treatment: 20 rectal insufflations. concentration 25–40 /mL increasing by 5 /mL per week with a volume of 150-200 mL during 4 weeks. As usual in inflammatory processes, the redox balance is regulated through systemically administered ozone at low concentrations and low doses, demonstrated by the characteristic increase in the antioxidant defense, shown in
Figure 4 as an increase in GSH by 41% and a decrease in oxidative stress by 50% as a consequence, here MDA [
15].
A Redox Regulator with Selectivity for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.
Although RA and osteoarthritis are of different origin, both are compared concerning the impact of redox regulation through ozone. RA as an autoimmune disease is usually treated using antirheumatic drugs, such as MTX which involves a risk of liver toxicity. In osteoarthritis patients, the therapy is mostly based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). Combined therapies with ozone at low concentrations has proven its worth in RA as well as in OA [
17].
Rheumatoid arthritis. Controlled clinical study n=40; basic therapy: MTX, Ibuprofen, folic acid. MTX group as control, n=20, basic therapy only. Ozone group, n=20, the same basic therapy and additional ozone application.
Osteoarthritis. Controlled clinical study n=40; basic therapy: NSAID. Control n=20 basic therapy only. Ozone group: basic therapy plus ozone application as described above.
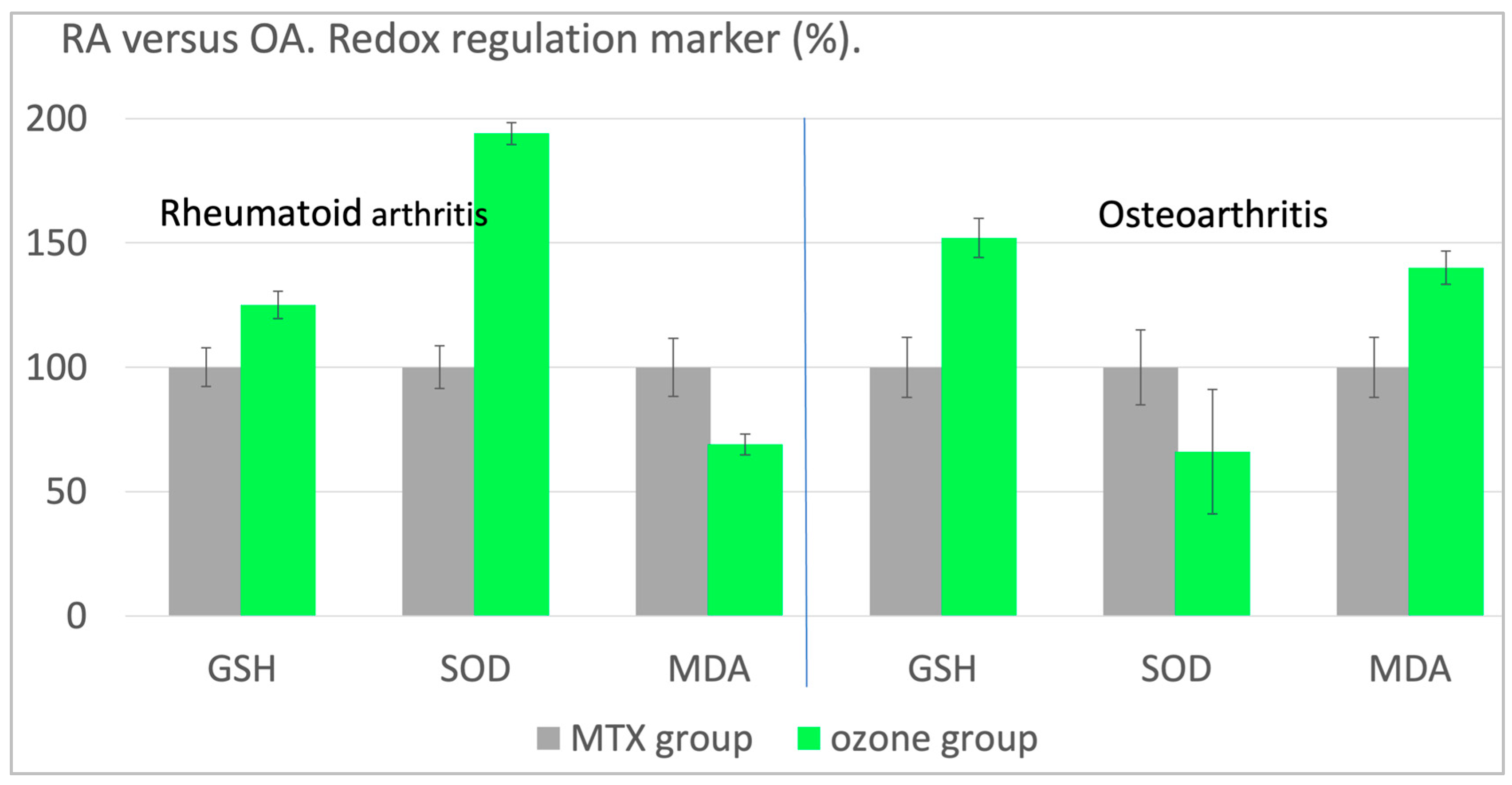
Apart from the clinical parameters, such as pain and disability, the redox balance was also assessed using MDA, TH, GGT as injury markers and GSH, SOD and CAT as antioxidant defense markers. Here we once more discuss GSH and MDA: in the RA patients the antioxidant capacity, measured as GSH, increases by 25% and the oxidative stress -here as MDA- decreases by 31 %. Thus the redox balance is largely restored in rheumatoid arthritis.
In comparison, ozone application is less successful in the osteoarthritis trial. Although GSH increases by 52% (whereby the absolute values are considerably lower compared to RA), oxidative stress also increases. With SOD as a typical antioxidant, the effect is much more pronounced. SOD even decreases by approx. 34 % in OA. superoxide radicals cannot be reduced, which explains the increase of the oxidative stress parameter MDA. Obviously a restoration of the disturbed redox balance cannot be achieved in osteoarthritis (
Figure 5).
2. Osteoarthritis. Controlled clinical study n=40;: NSAID as basic therapy, control n=20 basic therapy only. Ozone group: basic therapy plus rectal ozone application as described above. Antioxidants, here GSH and SOD increasing in RA by 25 % or 94%, respectively. In OA an increase of GSH by 52% although a drastic decrease of SOD was measured, and oxidative stress -here MDA- shows a remarkable rise. Result: RA responds to the systemic ozone application to regulate and torestore the redox balance. Not so in the case of OA, oxidative stress even increases by 40% [
17].
Medical Ozone Effects and Innate Immune Memory. This study in RA patients (n=20) shows the same results as those revealed by León et al. 2016 [
15], even better results after a second cycle of ozone treatment due to the formation of memory cells during or after the first treatment cycle [
16].
3.3.3. Diabetes.
Preclinical study. Ozone treatment regulates oxidative stress in an experimental diabetes model in rats shown in STZ-induced diabetes.
Since diabetes is closely associated with oxidative stress, this first animal model in diabetes with ozone allows us to confirm hypothesis that medical ozone is able to regulate and / or restore the redox balance. Procedure: rectal insufflation with an ozone amount of 1.1 mg/kg rat, 10 treatments in 2 weeks.
Out of 5 animal groups (10 in each group) the diabetic animal group serves as control. Redox regulation is clearly pronounced: GSH increases by 19 % after ozone application, and oxidative stress drops by 46% as presented in
Figure 6a [
18].
Diabetes, clinical study. Therapeutic efficacy of ozone in patients with diabetic foot. In type 2 diabetes, oxidative stress not only plays a key role in the development of the disease, but also to a particular extent in the progression, metabolic disorders, angiopathies and typical concomitant diseases. In this clinical study, 101 patients with diabetic foot were examined and the clinical findings as well as the metabolic results under systemic ozone administration are analyzed. An antibiotic group with systemic antibiotics and conventional wound care serves as control, n=49. 51 patients in the ozone group received 5 ozone treatments per week within 4 weeks in the form of rectal insufflation. taking a volume of 200 mL and an ozone concentration of 50 mL. The healing process improved, plasma glucose decreased. Total hydroperoxides as oxidative stress parameter decreased corresponding to an increase of SOD which could not be seen in MDA. The results are displayed in
Figure 6b [
19].
3.5.4. Oncology. Prevention from Side Effects of Chemotherapy.
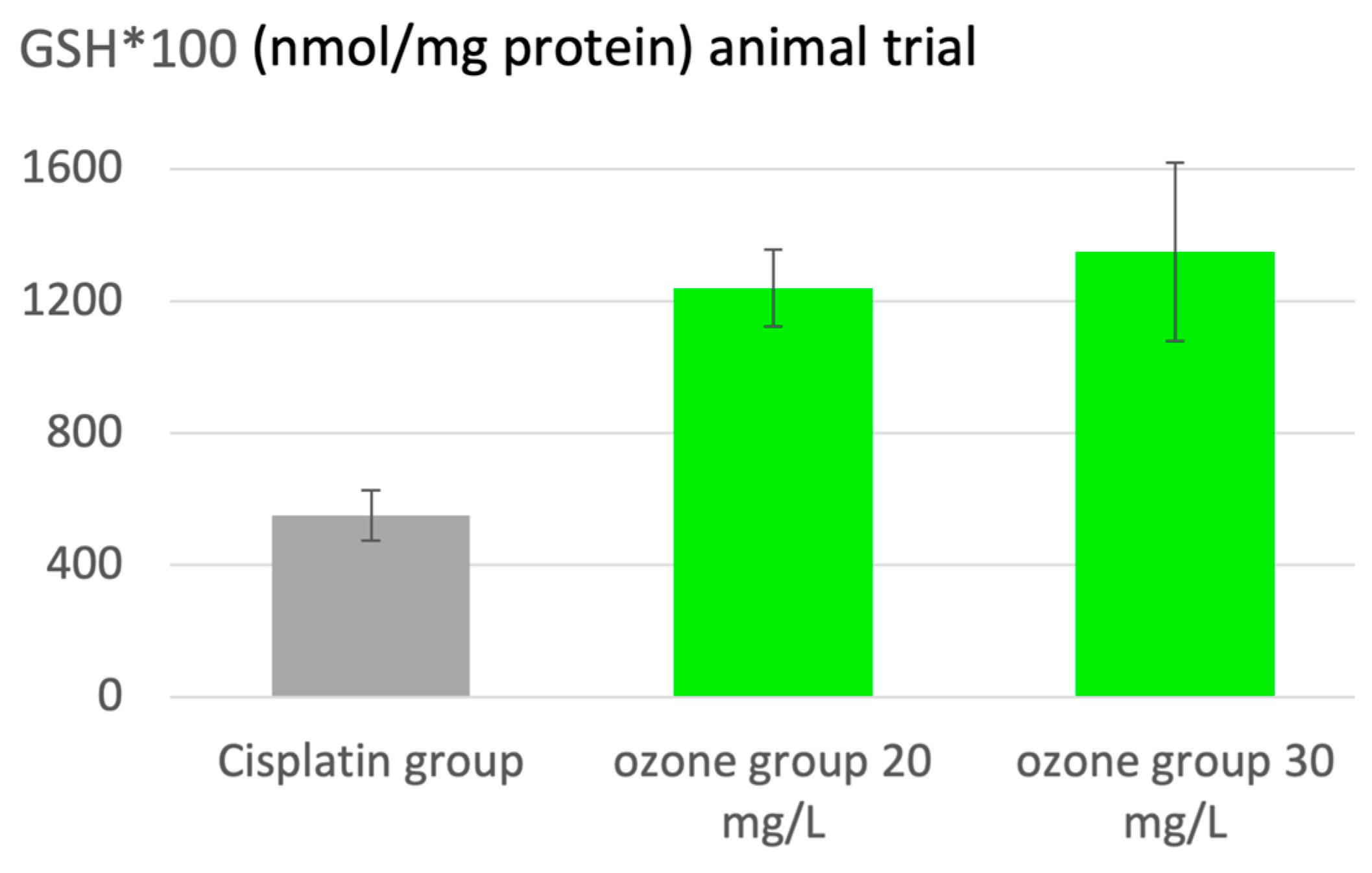
In oncology, ozone can be used as part of a complementary therapeutic system, its major effect is a protective one, the prevention of liver and kidney intoxication from chemotherapeutics, here shown in an animal model with kidney intoxication through cisplatin. Ozone interferes by upregulation of the antioxidants and downregulation of oxidative stress, as shown in
Figure 7 with GSH as sensitive parameter in redox regulation. At low ozone concentrations (20 to 30 /mL) kidney-GSH remains within the healthy range after cisplatin administration, but not at concentrations of 50 /mL or 70 /mL, where ozone itself contributes to toxicity (not shown here). A preclinical trial with 70 rats in 10 groups demonstrates the protective effect; ozone was administered via rectal insufflation, with approximately 7 ml and ozone at 0.7 to 1.0 mg/kg rat corresponding to an ozone concentration of 20 to and 30 /mL: the redox balance remains completely intact [
23].
3.5.5. Aging.
We cannot stop the aging process, but we can influence high oxidative stress as one of its main causes due to mitochondrial aging and dysfunction. Low-dose ozone applications are able to intervene here as redox regulator and offer at least one preventive measure against age-related diseases.
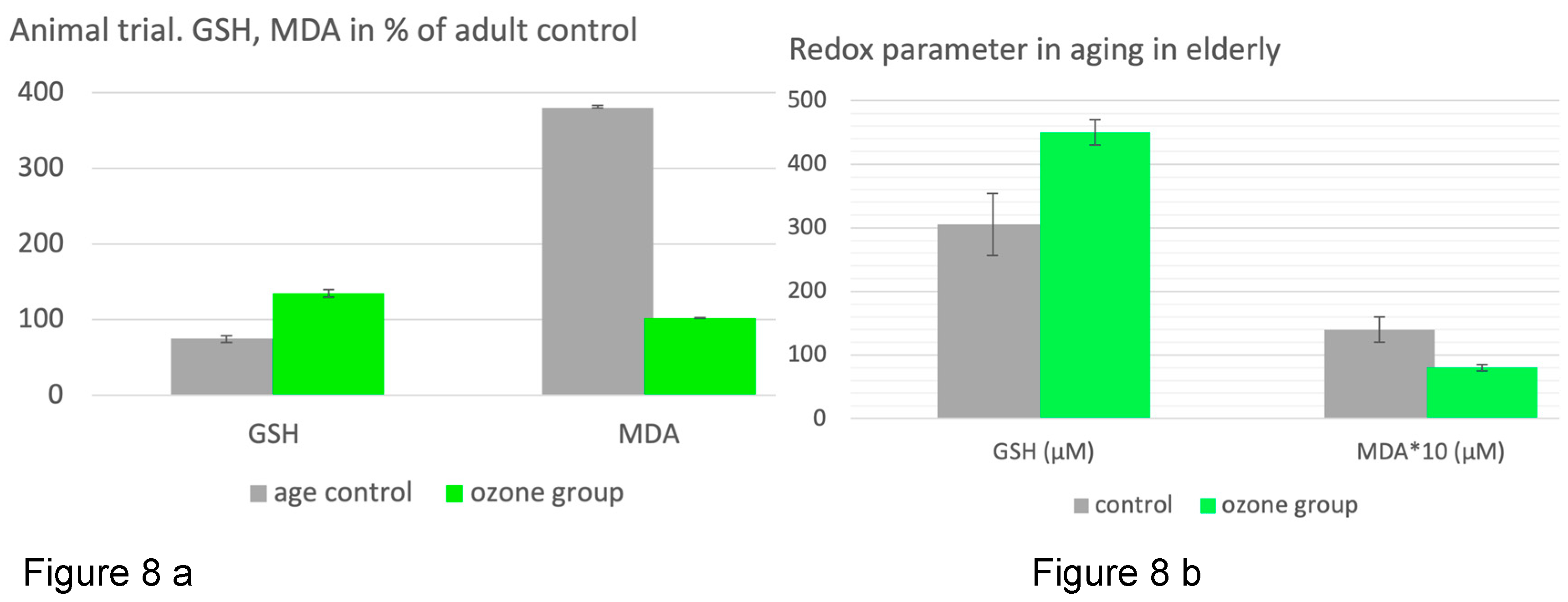
Preclinical trial. Shehata et al. [
30] and Safwat et al. [
24] set up preclinical studies in rats demonstrating a significant regulation of the disturbed redox balance by systemic ozone administration in the form of rectal insufflation. The critical redox parameter GSH and MDA (here measured in the liver) and others underline the restoration of the balance by life-long preventive as well by “therapeutic” (here not shown) treatments in old animals. GSH and MDA are expressed in % of healthy adult animals aged 4 months. GSH antioxidant capacity decreases in aging process by 25 % (p<0.001), oxidative stress increases by 280 %. The redox balance is manifestly disturbed,
Preventive ozone administration was able to increase GSH by 25 % compared with healthy control and 61 % to untreated, normally aging animals (age control). Oxidative stress in the form of MDA increased accordingly: age control, untreated animals to 380 %; ozone group: to 102 %, which is 278 % less than the normally aging animals (
Figure 8a), p<0.001.
Clinical study in elderlies.
Elderly patients at the age of 60 to 75 years with diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis as comorbidities were examined in a controlled, randomized clinical study. All of them received a basic therapy. Control (n=15) received the basic medication only, ozone group (n=15) : basic medication plus ozone treatment. Ozone concept: 20 rectal insufflation over 4 weeks, 5 per week. Concentrations: 20 up to 30 /mL, slowly increasing week by week. A third group with asthma (n=30) is not discussed here.
As Redox parameter we once more use GSH as defense marker and MDA as oxidative stress parameter after 4 weeks of treatment without and with ozone.
Compared within the baseline (start at 450 GSH dropped by 67 % control group after 4 weeks with basic treatment only, whereas GSH showed no change in the ozone group (p<0.05).
Ozone treatment attenuates the aging process, thus preventing from age- related diseases: GSH shows a 48 % higher level after 4 weeks compared with the control group. As a consequence of the upregulation of antioxidants through ozone, the oxidative stress, measured as MDA, is 43 % lower than in the control group without ozone treatment, p<0.05, see
Figure 8b [
25].
3.3.6. Prevention
Preventive, therapeutic measures are always difficult to communicate to patients, but in the wake of pandemics, people tend to be interested in and open to prevention, especially in the case of impending viral infections. This is where the use of medical ozone has proven to be useful [
31], supported by a number of animal models, but also clinical studies, as discussed above. It has been repeatedly shown that the liver as a detoxification organ responds particularly well to ozone, so that intoxications caused by drugs such as MTX [
15], chemotherapeutics [
23] and others can be largely avoided. Preventive administration prior to surgical interventions, for example to avoid reperfusion damage, which is the rule in transplantations appears to be particularly reasonable [
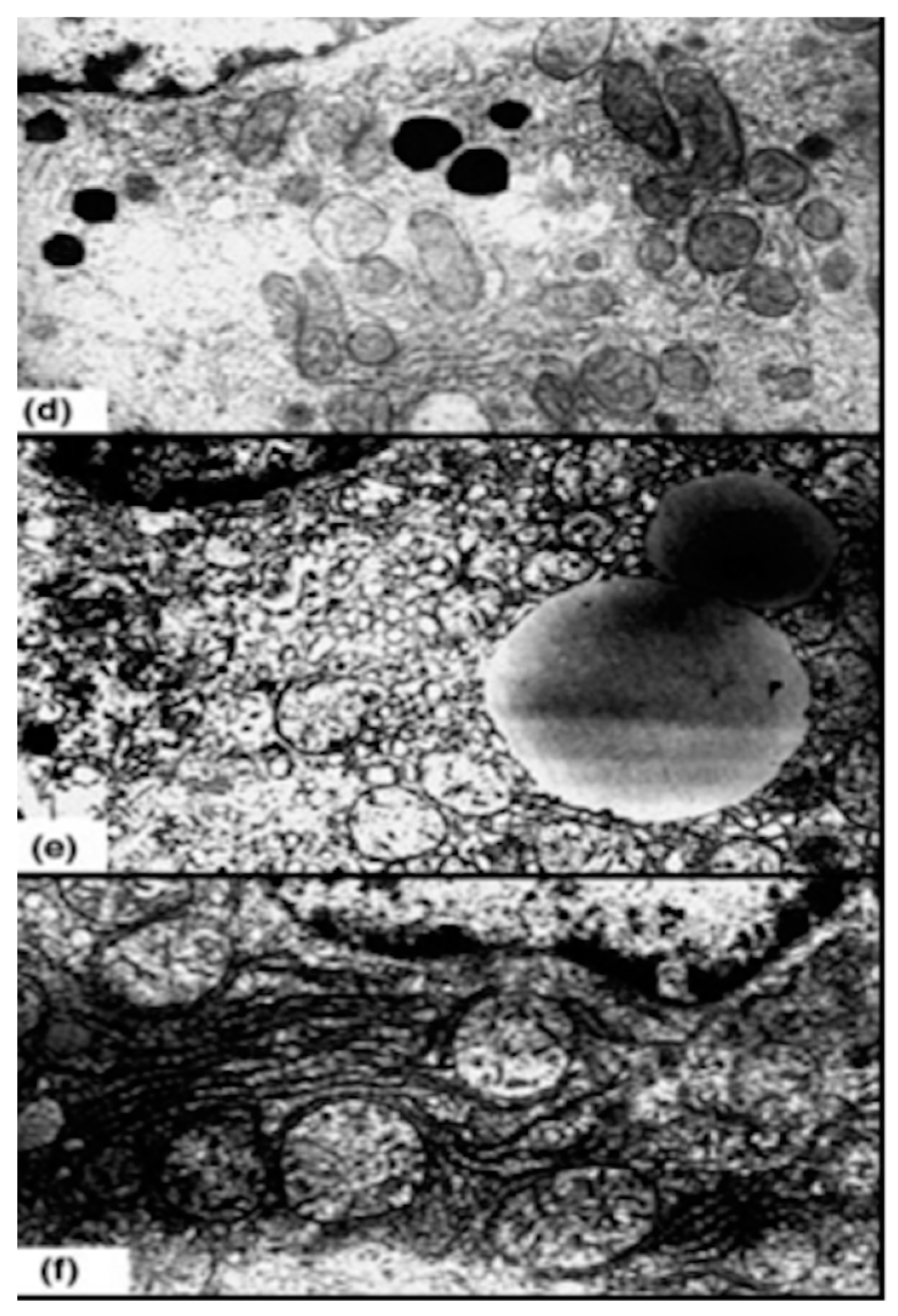
32]. In addition to the restoration of the redox balance (GSH increase, MDA decrease - among other characteristic parameters), electron microscopic examinations show in animal experiments that the integrity of the mitochondria is largely preserved by ozone preconditioning (OP), see
Figure 9: in 9 d, the regular structure of the mitochondria and other organelles in liver tissue can be seen. In 9 e large lipid droplets and moderate reperfusion damage are visible after I/R (90 min ischemia and 90 min reperfusion), while OP causes extensive integrity of the mitochondria (
Figure 9 f)
4. Mechanism of Action
The anti-inflammatory and regulatory mechanism of ozone was described in detail in an earlier paper [
33]and is summarized here in
Figure 9: an excessive production of ROS, mostly as a result of mitochondria deficiency, leads to high oxidative stress, inflammation and a number of ROS- based diseases, such as chronic inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis. cerebral and peripheral angiopathies, metabolic syndrome and diabetes 2, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, neurodegenerative pathologies and others.
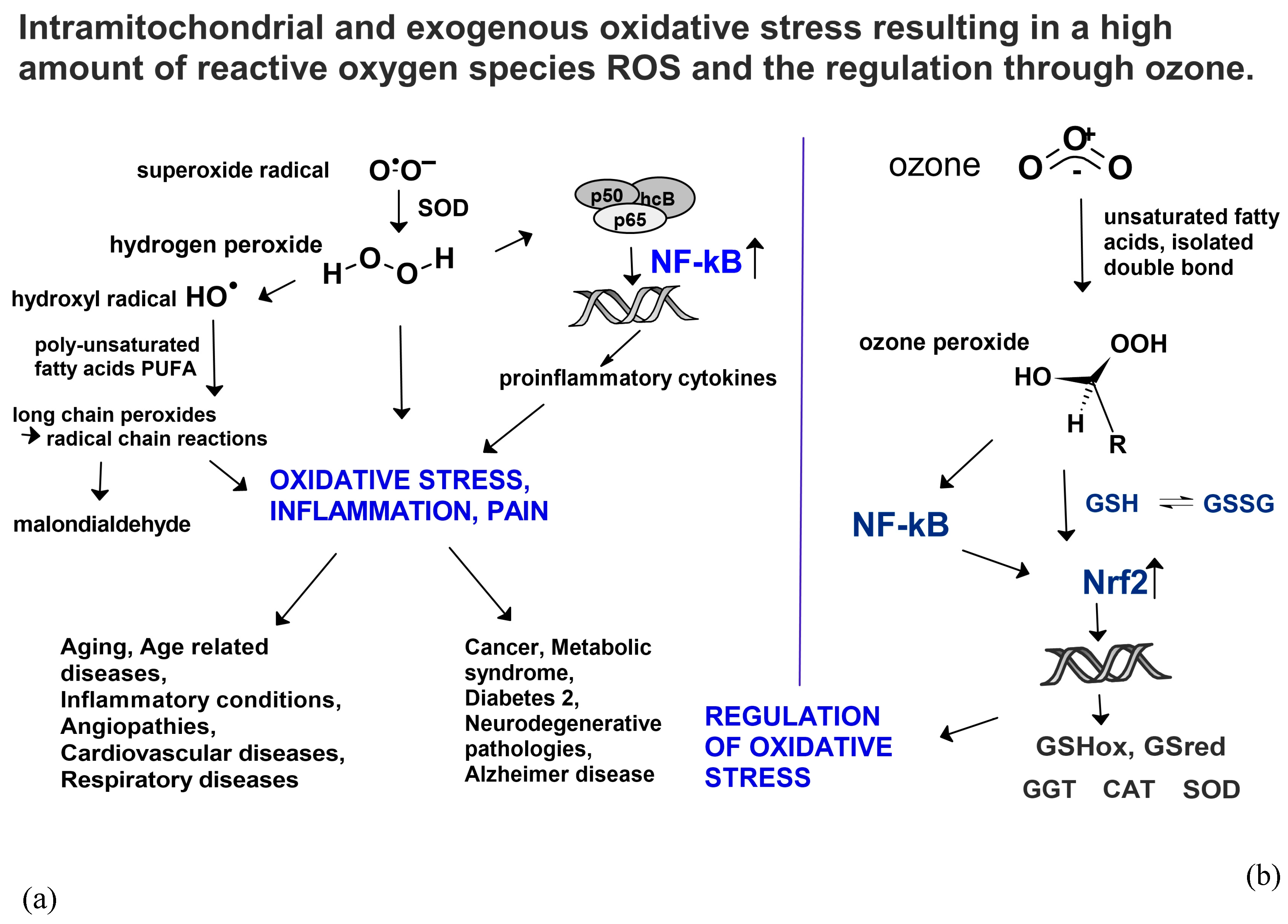
In general ozone or better the second messenger “ozone peroxide” as reaction product interferes via the glutathione balance GSH/GSSG by signal transduction, Nrf2 activation and translocation to the nucleus.
Ozone peroxides at low concentrations and low doses do not contribute to oxidative stress in the entire system as we are dealing with a small and reactive molecule having a short half-life, completely different from the long chain peroxides (
Figure 10 a, b), which are stable and have a fairly long half-life inducing radical chain reactions and contributing to chronic oxidative stress.
Following an activation of NFkB and a cross talk to Nrf2 [
34] antioxidants are upregulated and available to reduce the ROS in order to at least partially restore the unbalanced ROS/antioxidant equilibrium.
Figure 10. Mitochondrial and exogenous oxidative stress and its regulation via ozone. (a) Mitochondrial deficiency with formation of superoxide radicals: one electron transfer to oxygen forming in O-O-, the superoxide radical as starting molecule for ROS production, such as H2O2, ⋅OH radicals, long chain peroxides and others inducing mitochondrial pathologies. (b) “Ozone peroxide” reduced by GSH informing the DNA via NFkB and Nrf2 upregulating the antioxidants in order to restore the unbalanced ROS/antioxidant equilibrium. GSHox: Glutathione peroxidase, GSred: Glutathione reductase; GGT: - glutamyl transferase, CAT: Catalase, SOD: Superoxide dismutase, NFkB and Nrf2: Nuclear factors.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Since medical ozone as redox bioregulator is well established in the international literature, we understand the typical ozone indications much better as well as the integration into a complementary system, either in prevention or therapy. ROS-induced mitochondriopathies are the major part of these indications: The disturbed redox balance is regulated by the low-concentration and low-dose ozone concept. It is time and urgently needed to enable larger clinical trials, as already exist in pain therapy with several thousand patients (among others: [
35,
36]).
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; methodology, R.V.-H.; software, R.V.-H.; validation, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; formal analysis, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; investigation, R.V.-H.and O.S.L.F.; resources, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; data curation, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; writing—originaldraft preparation, R.V.-H.; writing—review and editing, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; visualization, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; supervision, R.V.-H. and O.S.L.F.; project administration, R.V.-H. All authors have readand agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was not funded.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Löffler, Petridis. Biochemie und Pathobiochemie. [Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry]. Springer publisher 2014. Berlin, Heidelberg.
- Sies, H. Oxidative Eustress: On Constant Alert for Redox Homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signaling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020. 21, 363–383. [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, G.; Fasciolo, G.; Venditti, P. Mitochondrial Management of Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Darshi, M.; Sharma, K. The Warburg Effect in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Manjula Seminars in Nephrology 2018, 38, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.; Joven, J.; Cufi, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cuyàs, E.; Vazquez-Martin, A. The Warburg effect version 2.0: Metabolic reprogramming of cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle 2013. 12, 1166–1179. [CrossRef]
- Green,D. R.: Galluzzi,L.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondria and the Autophagy–Inflammation–Cell Death Axis in Organismal Aging. Science 2011, 333, 1109. [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J. S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders —A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanan, R.; Oikawa, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Ohnishi, S., Ma; Pinlaor, S.; Yongvanit, P.; Kawanishi, S.; Murata, M. Oxidative Stress and its Significant Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschoor, M. L. ; Ungard,R. ; Harbottle, A.; Jakupciak, J. P.; Parr R. L.; Singh, G. Mitochondria and Cancer: past, present and future. BioMed Res Int. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, V; Parinandi, N. (edts), Mitochondrial Function in Lung Healtr and Disease. Respiratory Medicine, Humana Press. 2014. ISBN 978-1-4939-0829-5 (eBook) Springer New York, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, London.
- Mawsouf, M.N.; El-Sawalhi, M.M.; Darwish, H.D.; Shaheen, A.A.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Re, L. Effect of ozone therapy on redox status in experimentally induced arthritis. Revista Española de Ozonoterapia 2011, 1, 32–43 https://wwwresearchgatenet/publication/277217462_Effect_of_ozone_therapy_on_redox_status_in_experimentally_induced_arthritis. [Google Scholar]
- Leon Fernandez, O.S.; Oru, G.T.; Vega, J.S.P.; Fernandez, E.G.; Viebahn-Hänsler, R.; Torres-Carballeira, R.; Cabreja, G. L.; Mendez, R.M. Ozone + Arthros¬copy: Improved Redox Status, Function and Surgical Outcome in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients. Int J Innov Surg. 2020, 3, 1011. https://mail.meddocsonline.org/international–journal. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Cuadros, M.E.; Pérez-Moro, O.S.; Albaladejo-Florín, M.J.; Tobar-Izquierdo, M.M.; Magaña-Sánchez, A.; Jiménez-Cuevas, P.; Rodríguez-de-Cía, J. Intra Articular Ozone Modulates Inflammation and has Anabolic Effect on Knee Osteoarthritis. IL-6 and IGF-1 as Pro-Inflammatory and Anabolic Biomarkers. Processes 2022, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, F.O.S.; Viebahn-Haensler, R.; López, C.G.; Serrano, E.I.; Hernández, M.Y.; Delgado, R.L.; Tamargo, S.B.; Takon, O.G.; Polo, V.J.C. Medical ozone increases methotrexate clinical response and improves cellular redox balance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 789, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takon Oru, G.; Viebahn-Haensler, R.; García Fernández, E.; Alvarez Almiñaque, D.; Juan Polo Vega, C.; Tamargo Santos, B.; López Cabreja, G.; Serrano Espinosa, I.; Tabares Nápoles, N.; León Fernández, O.S. Medical Ozone Effects and Innate Immune Memory in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Methotrexate+Ozone After a Second Cycle of Ozone Exposure. Chronic Pain Manag. 2019, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León Fernández, O.S.; Oru, G.T.; Viebahn-Haensler, R.; López Cabreja, G.; Serrano Espinosa, I.; Corrales Vázquez, M.E. Medical Ozone: A Redox Regulator with Selectivity for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalain, S.M.; Martínez, G.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Menendez, S.; Re, L. ; Giuliani, A,; León, O. S. Ozone treatment reduces markers of oxidative and endothelial damage in an experimental diabetes model in rats. Pharmacological Research 2001, 44, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Sanchez, G,; Al-Dalain, S. M.; Menendez, S.; Re, L.; Giuliani, A.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Alvarez, H., JI Fernandez-Montequin, J.L.; Leon, O.S. Therapeutic efficacy of ozone in patients with diabetic foot. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 523, 151–161. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavo, B.; Rodriguez-Esparragon, F.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D. ; Martinez-Sanchez,G. ; of Liontop, P.; Aguiar Bujanda, D.; Fernandez-Perez, L.; Santana-Rodriguez, N. Oxidative Stress by Ozone Therapy in the Prevention and Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity: Review and Prospects. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 588. https://www.mdpi.com/2076–3921/8/12/588. [Google Scholar]
- Clavo, B.; Ruiz, A.; Lloret, M.; López, L.; Suárez, G.; Macías, D.; Rodríguez, V.; Hernández, M.; Martín-Oliva, R.; Quintero, S.; Cuyás, J. ; Francisco Robaina. Adjuvant Ozone therapy in Advanced Head and Neck Tumors: A Comparative Study. Evid Based Complemen Alternat Med. 2004, 1, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavo, B.; Santana-Rodriguez, N.; Llontop, P.; Gutierrez, D.; Ceballos, D.; Mendez, C.; Rovira, G.; Suarez, G.; Rey-Baltar, D.; Garcia-Cabrera, L.; et al. Ozone Therapy in the Management of Persistent Radiation-Induced Rectal Bleeding in Prostate Cancer Patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015, Article ID 480369. [CrossRef]
- Borrego, A.; Zamora, Z.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Romay, C.; Menendez, S.; Hernandez, F.; Montero, T.; Rojas, E. Protection by ozone preconditioning is mediated by the antioxidant system in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2004, 13, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safwat, M.H.; El Sawalhi, M.M.; Mawsouf, M.N.; Shaheen, A.A. ; Ozone ameliorates age related oxidative stress changes in rat liver and kidney: effects of pre- and post-aging administration. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2014, 79, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León Fernández, O. S.; Takon Oru, G.; Viebahn-Hänsler, R.; López Cabreja, G.; Serrano Espinosa, I.; García Fernández, E. Medical ozone arrests oxidative damage progression and regulates vasoactive mediator levels in older patients (60-70 years) with oxidative etiology diseases. Front. Physiol. 2022, . https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2022. 03 November 1029. [Google Scholar]
- Léon, O.S.; Menendéz, S.; Merino, N.; Castillo, R.; Sam, S.; Pérez, L.; Cruz, E.; Bocci, V. Ozone oxidative preconditioning: A protection against cellular damage by free radicals. Mediat. Inflamm. 1998, 7, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viebahn-Haensler, R.; León Fernández, O.S.; Fahmy, Z. Ozone in medicine: The low-dose ozone concept. Guidelines and treatment strategies. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2012, 34, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.M. Mawsouf, M. N.; Viebahn-Hänsler, R. Ozone Therapy in Diabetic Foot and Chronic, Nonhealing Wounds Ozone. Sci. Eng. 2012, 34, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torequl Islam, M.; Sarkar, C.; Hossain, R. , Bhuia, S. M.; Mardare, I.; Kulbayeva, M.; Ydyry, A.; Calina, D.; Habtemariam, S.; Kieliszek, M.; ShariL-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatic diseases and disorders: targeting redox imbalance and oxidative stress Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 164, 114900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, N.I.; Abd-Elgawad, H.M.; Mawsouf, M.N.; Shaheen, A.A. ; The potential role of ozone in ameliorating the age-related biochemical changes in male rat cerebral cortex. Biogerontology 2012, 13, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viebahn-Haensler, R.; León Fernández, O.S. Ozone as Redox Bioregulator in Preventive Medicine: The Molecular and Pharmacological Basis of the Low-Dose Ozone Concept—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamieh, H.H.; Berlanga, J.; Merino, N.M.; Martinez Sanchez, G.; Carmona, A.M.; Menendez Cepero, S.; Giuliani, A. , Re, L. ; Leon, O.S. Role of protein synthesis in the protection conferred by ozone-oxidative-preconditioning in hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion. Transplant International 2005, 18, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viebahn-Haensler, R.; León Fernández, O. Ozone in Medicine. The Low-Dose Ozone Concept. The Redox-Bioregulatory Effect as Prominent Biochemical Mechanism and the Role of Glutathione. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Togi, S.; Togi, M.; Nagashima, S.; Kitay, Y.; Muromoto, R.; Kashiwakura, J.; Miura, T.; Matsuda, T. Implication of NF-kB Activation on Ozone-Induced HO-1 Activation. BPB Reports 2021, 4, 59–63 doiorg/101248/bpbreports42_59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreula, C.F.; Luigi Simonetti, L.; De Santis, F.; Agati, R.; Ricci, R.; Leonardi, M. Minimally Invasive Oxygen-Ozone Therapy for Lumbar Disk Herniation Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24, 996–1000. PMC797 5773.
- Rashid, U.; Rauf, F. ; Hameedullah A,; et al. Ozonucleolysis in Cervical Radiculopathy. Neurol Res Surg. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).