Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
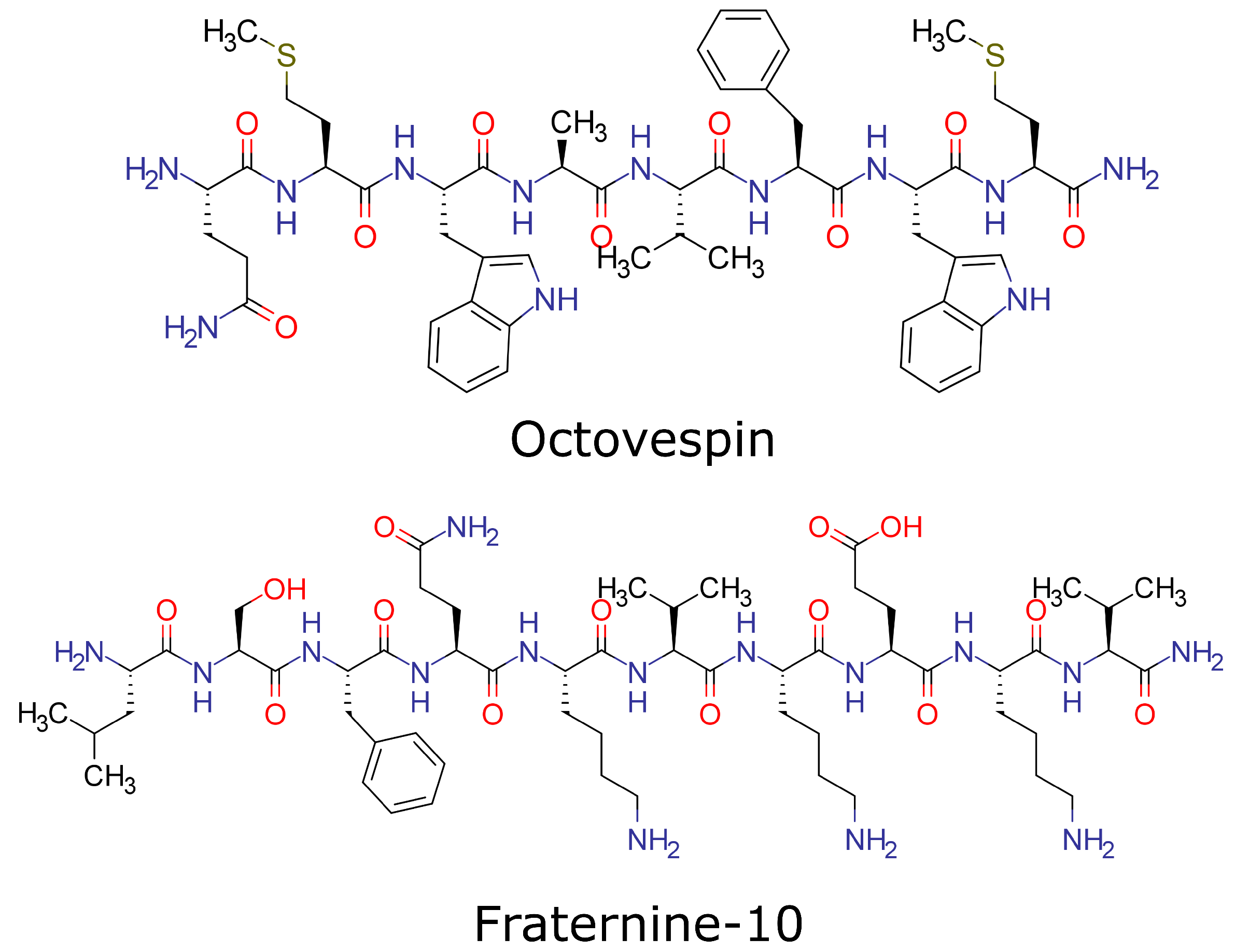
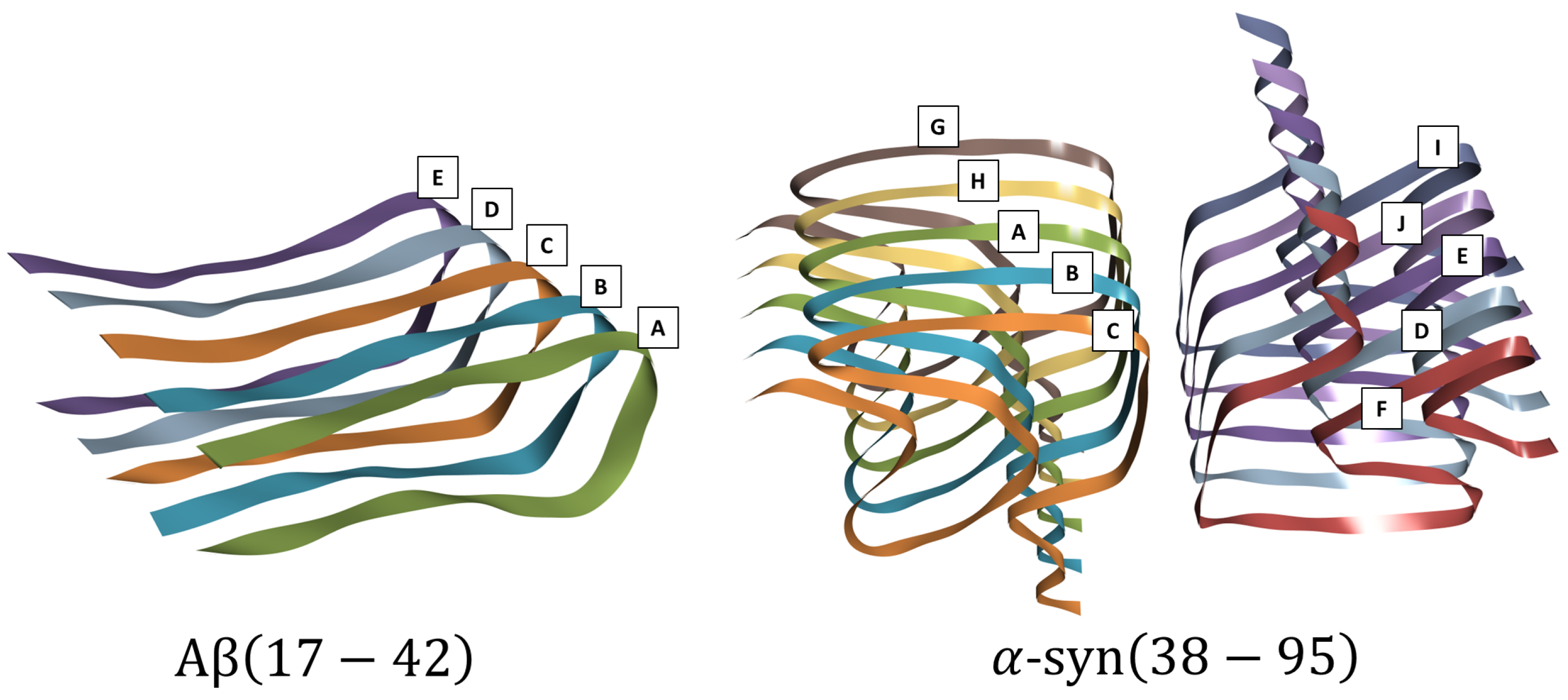
1.1. Target Proteins
2. Methodology
2.1. Computational Details
2.2. Thioflavin T (ThT) Assay
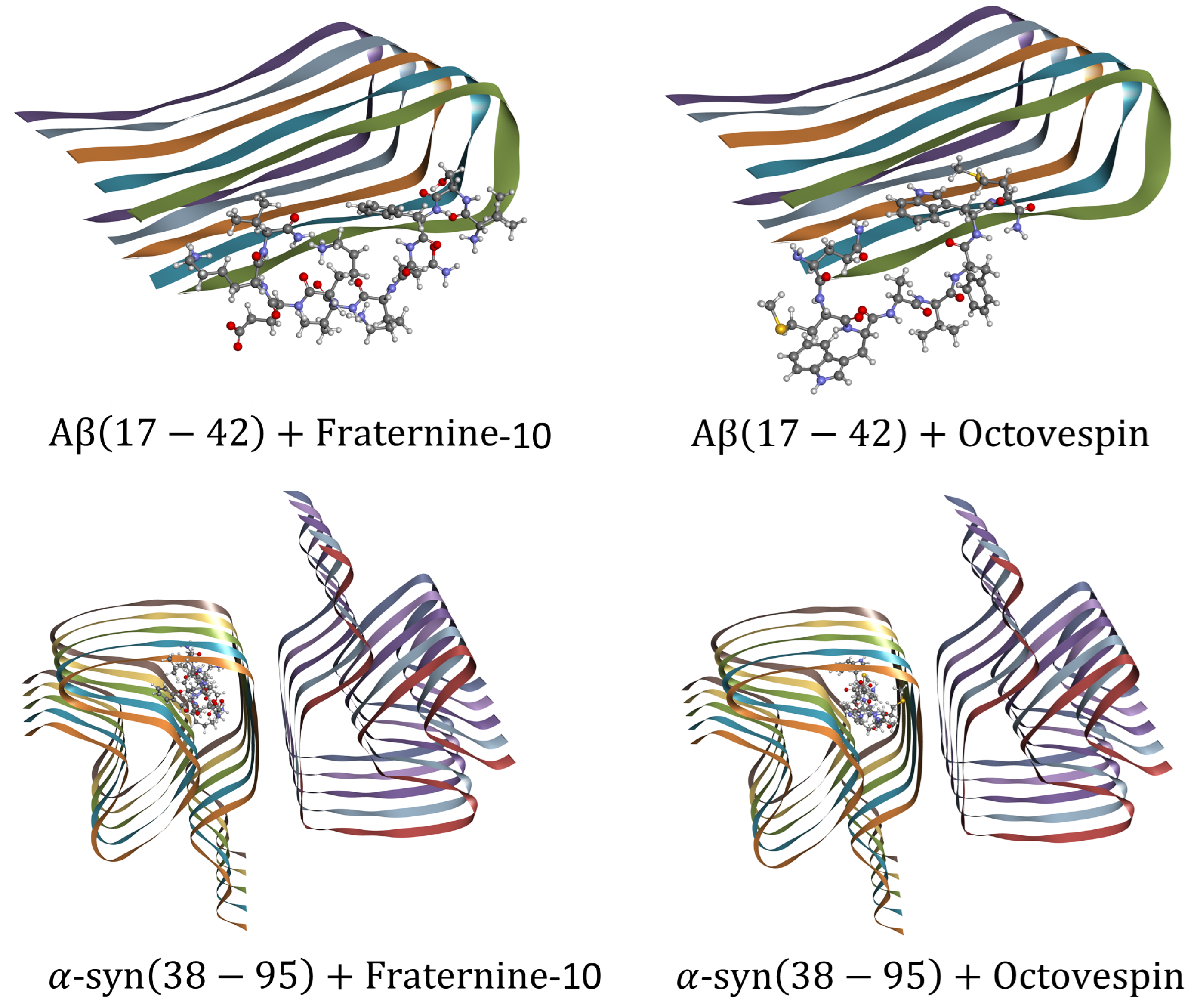
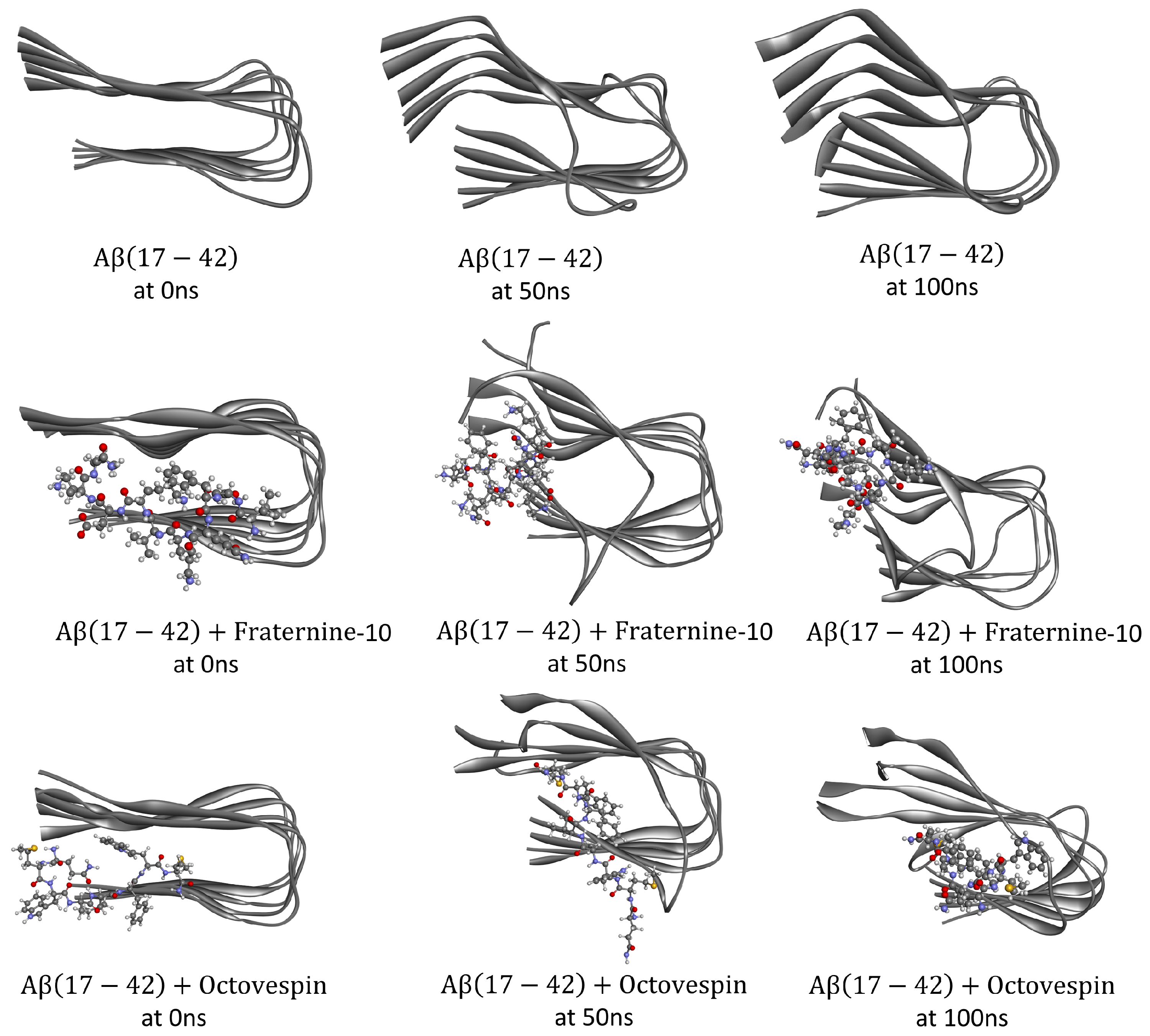
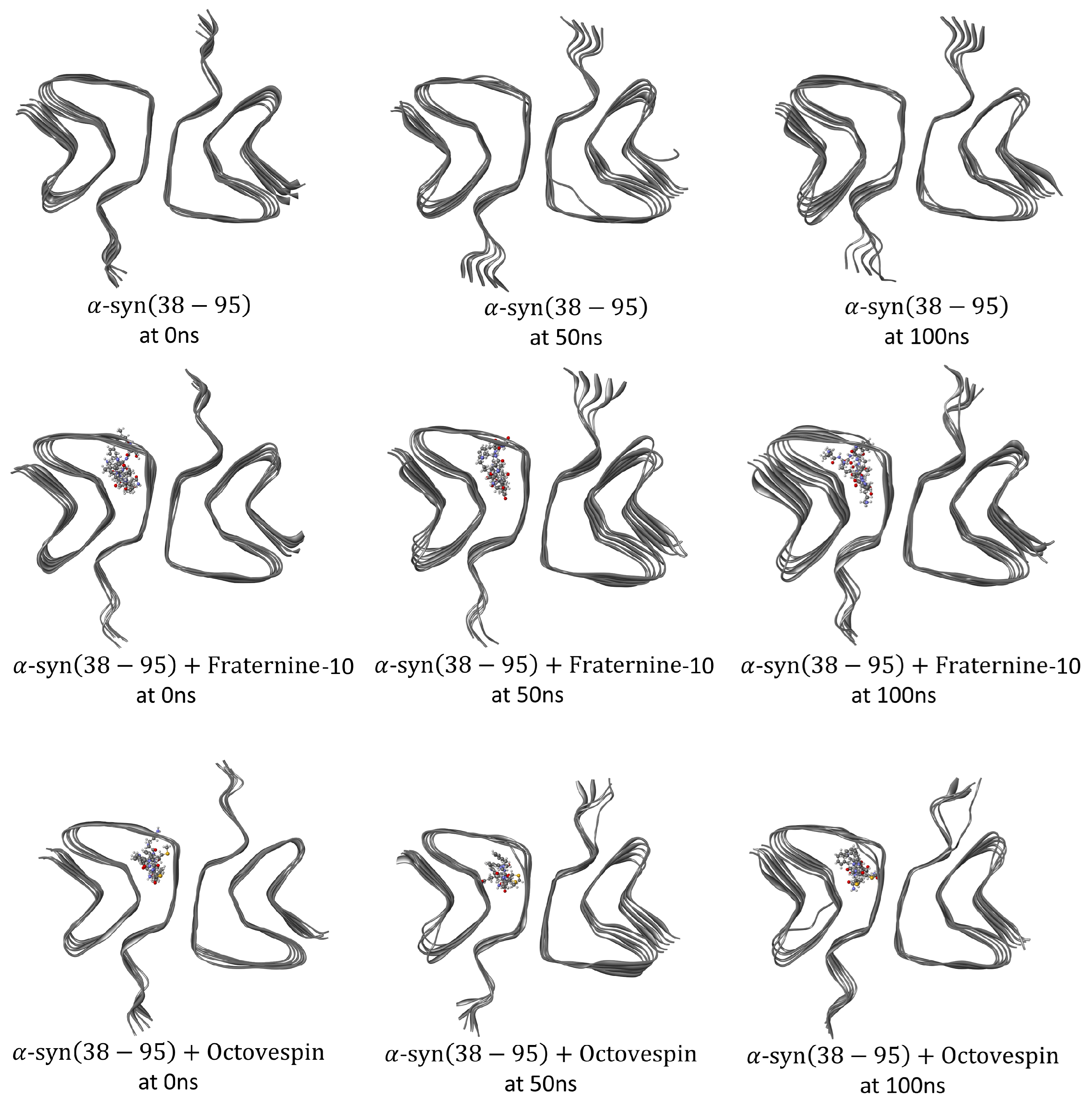
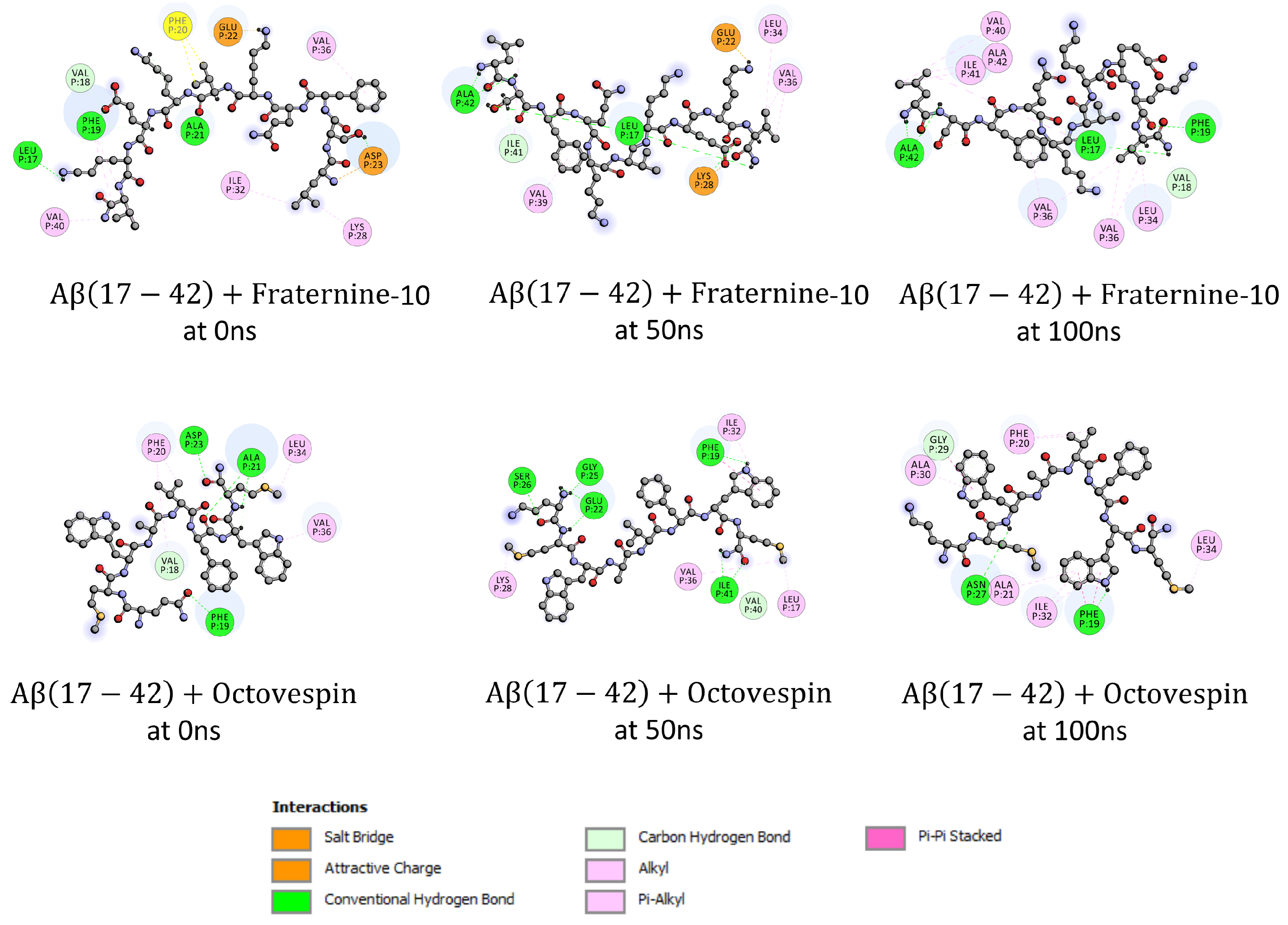
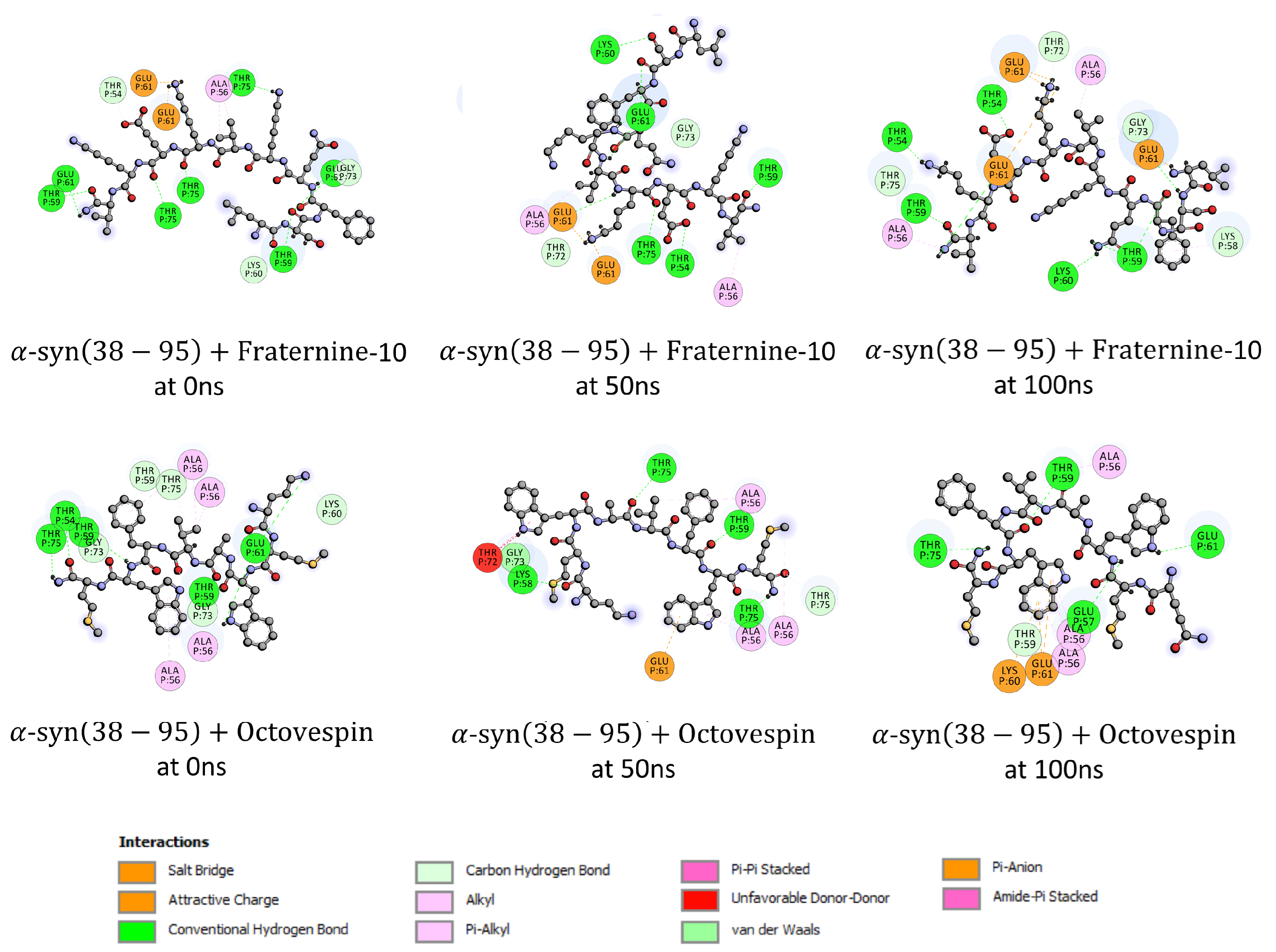
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, S.S.; Khan, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Wasi, U. The Structure and Function of α, β and γ-Secretase as Therapeutic Target Enzymes in the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 2019, 18, 657–667. [Google Scholar]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Choomwattana, S.; Wongchitrat, P.; Phopin, K.; Suwanjang, W.; Malik, A.A.; Vincent, B.; Nantasenamat, C. Multidisciplinary approaches for targeting the secretase protein family as a therapeutic route for Alzheimer’s disease. Medicinal Research Reviews 2019, 39, 1730–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, Y.; Halliday, G.M.; Sue, C.M. PARK genes link mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-synuclein pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2021, 9, 612476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Pajarillo, E.; Nyarko-Danquah, I.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Role of Astrocytes in Parkinson’s Disease Associated with Genetic Mutations and Neurotoxicants. Cells 2023, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouaud, T.; Corbillé, A.G.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; de Lataillade, A.d.G.; Lionnet, A.; Preterre, C.; Damier, P.; Derkinderen, P. Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease: Mitochondria, alpha-synuclein and much more…. Revue Neurologique 2021, 177, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.; Vats, A.; Taneja, V. Toxic species in amyloid disorders: Oligomers or mature fibrils. Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology 2015, 18, 138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, M.K.; Majid, N.; Malik, S.; Alam, P.; Khan, R.H. Amyloid oligomers, protofibrils and fibrils. Macromolecular Protein Complexes II: Structure and Function, 2019; 471–503. [Google Scholar]
- Cascella, R.; Bigi, A.; Cremades, N.; Cecchi, C. Effects of oligomer toxicity, fibril toxicity and fibril spreading in synucleinopathies. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2022, 79, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SÓ, Y.A.d.O. Estudo Teórico de Moléculas Multialvo-dirigidas para o Tratamento da Doença de Alzheimer via Hipótese Metálica. Doutorado, Universidade de Brasília, Distrito Federal, 2022.
- Bajda, M.; Filipek, S. Computational approach for the assessment of inhibitory potency against beta-amyloid aggregation. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2017, 27, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.E.; Takeda, T.; Raman, E.P.; Klimov, D.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Anti-Aggregation Effect of Ibuprofen. Biophysical Journal 2010, 98, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, E.P.; Takeda, T.; Klimov, D.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Ibuprofen Binding to Aβ Peptides. Biophysical Journal 2009, 97, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.B. Novos analógos da Fraternina: avaliação do efeito antiparkinsoniano em modelo murino da Doença de Parkinson e identificação dos alvos farmacológicos. Doutorado, Universidade de Brasília, Distrito Federal, 2018.
- Biolchi, A.M.; de Oliveira, D.G.R.; Amaral, H.d.O.; Campos, G.A.A.; Gonçalves, J.C.; de Souza, A.C.B.; Lima, M.R.; Silva, L.P.; Mortari, M.R. Fraternine, a novel wasp peptide, protects against motor impairments in 6-OHDA model of parkinsonism. Toxins 2020, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, L.C. Avaliação neuroprotetora do peptídeo octovespina, bioinspirado da peçonha de vespa social, em um modelo murino de Alzheimer. Mestrado, Universidade de Brasília, Distrito Federal, 2017.
- Mayer, A.B.; de Oliveira Amaral, H.; de Oliveira, D.G.R.; Campos, G.A.A.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Fernandes, S.C.R.; de Souza, A.C.B.; de Castro, R.J.A.; Bocca, A.L.; Mortari, M.R. New fraternine analogues: Evaluation of the antiparkinsonian effect in the model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropeptides 2024, 103, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.C.; Veras, L.G.; Vaz, G.; de Souza, A.C.B.; Mortari, M.R. Octovespin, a peptide bioinspired by wasp venom, prevents cognitive deficits induced by amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neuropeptides 2022, 93, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lührs, T.; Ritter, C.; Adrian, M.; Riek-Loher, D.; Bohrmann, B.; Döbeli, H.; Schubert, D.; Riek, R. 3D structure of Alzheimer’s amyloid-β (1–42) fibrils. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2005, 102, 17342–17347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. elife 2018, 7, e36402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Rosell, G.; Giorgino, T.; De Fabritiis, G. PlayMolecule ProteinPrepare: a web application for protein preparation for molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2017, 57, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Forli, S. Using AutoDock 4 and AutoDock vina with AutoDockTools: a tutorial. The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Graphics Laboratory 2012, 10550, 1000. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, R.P.; Rohane, S.H. Role of autodock vina in PyRx molecular docking. Asian Journal of Research in Chemistry 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Science 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Science 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studio, D. Dassault systemes BIOVIA, Discovery studio modelling environment, Release 4.5. Accelrys Softw Inc, 2015; 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. Journal of computational chemistry 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Cheng, X.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.J.; Patel, D.S.; Beaven, A.H.; Lee, K.I.; Rui, H.; Park, S.; others. CHARMM-GUI 10 years for biomolecular modeling and simulation. Journal of computational chemistry 2017, 38, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; others. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. The Journal of chemical physics 2020, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoete, V.; Cuendet, M.A.; Grosdidier, A.; Michielin, O. SwissParam: a fast force field generation tool for small organic molecules. Journal of computational chemistry 2011, 32, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E water models at 298 K. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2001, 105, 9954–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. Journal of molecular graphics 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, A.; Barca, A.; Romano, A.; Guerrieri, S.; Storelli, C.; Rinaldi, R.; Verri, T. Anti-aggregating effect of the naturally occurring dipeptide carnosine on aβ1-42 fibril formation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e68159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Só, Y.A.; de Abreu Silva, M.; Kiametis, A.S.; Sette, C.D.; Pereira Junior, M.L.; Ribeiro Júnior, L.A.; Gargano, R. A Multi-target Study of Natural Compounds in Preventing Neurodegenerative Disease Progression: A Computational Modeling Study. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry 2023, 22, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Lou, J.; Mehrazma, B.; Rauk, A.; Beazely, M.; Leonenko, Z. Pseudopeptide amyloid aggregation inhibitors: in silico, single molecule and cell viability studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Barale, S.S.; Kamble, S.A.; Paymal, S.B.; Sonawane, K.D. Molecular insights into the inhibition of early stages of Aβ peptide aggregation and destabilization of Alzheimer’s Aβ protofibril by dipeptide D-Trp-Aib: A molecular modelling approach. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 242, 124880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, L.; Platts, J.A. How Cu(II) binding affects structure and dynamics of α-synuclein revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 2023, 239, 112068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahihi, M.; Gaci, F.; Navizet, I. Identification of new alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis inhibitor using in silico structure-based virtual screening. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling 2021, 108, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohankumar, T.; Chandramohan, V.; Lalithamba, H.S.; Jayaraj, R.L.; Kumaradhas, P.; Sivanandam, M.; Hunday, G.; Vijayakumar, R.; Balakrishnan, R.; Manimaran, D.; others. Design and molecular dynamic investigations of 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone derivatives as potential neuroprotective agents against alpha-synuclein. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




