Submitted:
19 April 2024
Posted:
28 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Automated Wet-Etch Scheduling Problem
2.2. ASP and CASP
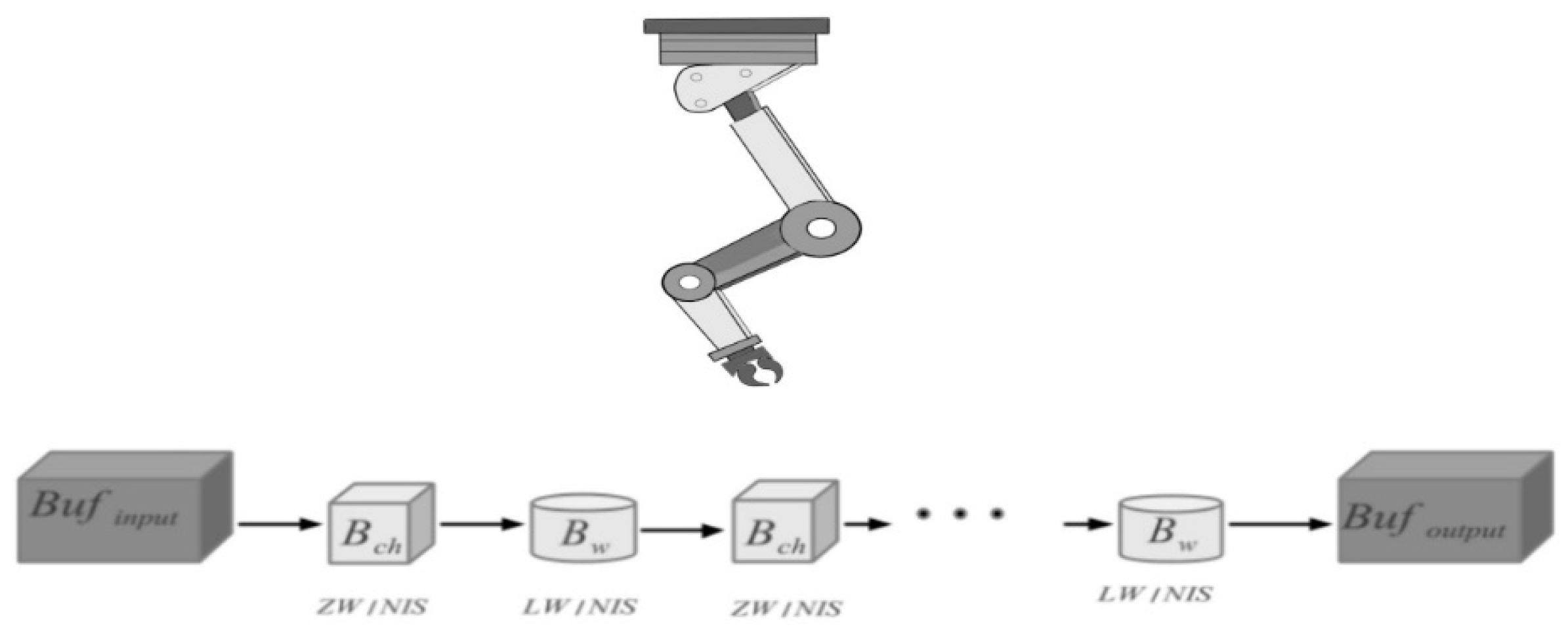
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Production Model
3.2. Problem Definition
3.3. Notations and Nomenclature
- -
- the scheduled start time slot for j processing in bath b
- -
- the scheduled completion time for j processing in bath b
- -
- the bath assigned to job j
- -
- he scheduled start time slot for robot r transfer the job j from bath to bath
- -
- the scheduled completion time slot for robot r finishes the job transfer from bath to bath
- -
- the deadline for finishing processing all the jobs.
3.4. Constraints and Function Definitions
3.5. Encoding the Problem in CASP
4. Results
4.1. Input Data
4.2. Design of the Experiment
4.3. Discussion of the Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Author Contribution
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S., Wan, J., Li, D., Liu, C. (2018). Knowledge reasoning with semantic data for real-time data processing in smart factory. Sensors (Switzerland) 18 (2), pp. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Negri, E., Fumagalli, L., Garetti, M., Tanca, L. (2015). Requirements and languages for the semantic representation of manufacturing systems. Computers in Industry. Vol. 81, pp. 55-66. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R. Y., Xu, X., Klotz, E., Newman, S. T. (2017). Intelligent manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0: A review. Engineering, Vol. 3 (5), pp. 616-630. [CrossRef]
- Crama, Y. J., Klundert. V.D. (1997). Robotic Flowshop Scheduling is Strongly NP- Complete. In Klein Haneveld, W.K. et al. (Eds.): Ten Years LNMB, CWI Tract, Amsterdam, pp. 277-286. https://EconPapers.repec.org/RePEc:unm:umamet:1997010.
- Gelfond, M, and Lifschitz, V. (1988). The stable model semantics for logic programming. In: ICLP 1988, Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Logic Programming, pp.1070-1080, Seattle, Washington, USA. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2408055_The_Stable_Model_Semantics_For_Logic_Programming.
- Gelfond, M. and Lifschitz, V. (1991). Classical negation in logic programs and disjunctive databases, New Generation Computing, 9 (3–4), pp. 365-386. [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, M., Schaub, T. (2012). ASP modulo CSP: The clingcon system. Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, Vol. 12 (4-5), 485-503. [CrossRef]
- Banbara, M., Kaufmann, B., Ostrowski, M., & Schaub, T. (2017) Clingcon: The next generation. Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 17(4), pp. 408-461. [CrossRef]
- Gebser, M., Kaminski, R., Kaufmann, B., & Schaub, T. (2018). Multi-shot asp solving with clingo. Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 19(1), 27-82. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M., Balduccini, M., Gelfond, M., Watson, R. and Barry, M. (2001). A prolog decision support system for the space shuttle. In PADL 2001: Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages, Vol. 1990 of LNCS, Springer, 169-183. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-45241-9_12.
- Ricca, F., Grasso, G., Alviano, M., Manna, M. Lio, V. Liritano, S. and Leone, N. (2012). Team-building with answer set programming in the gioia-tauro seaport, Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 12 (3), pp. 361-381. [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E. (2011). Applications of answer set programming in phylogenetic systematics. In Balduccini M. and Son T.C. (Eds.): Logic Programming, Knowledge Representation, and Nonmonotonic Reasoning: Essays Dedicated to Michael Gelfond on the Occasion of His 65th Birthday, Vol. 6565 of LNCS, pp.415-431 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Gebser, M., Obermeier, P., Schaub, T., Ratsch-Heitmann, M., Runge, M. (2018). Routing Driverless Transport Vehicles in Car Assembly with Answer Set Programming. TPLP, 18(3-4), pp. 520-534. [CrossRef]
- Dodaro, C., Galtat, G., Kamran-Khan, M. Maratea and Porro, I. Operating Room (Re)Scheduling with Bed Management via ASP. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2021. Vol, 22. pp. 220-253. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:233864374.
- Lierler, Y.Y., Susman, B. (2016). Constraint Answer Set Programming versus Satisfiability Modulo Theories, In Proc. of 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), pp. 1181-1187. https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3060785.
- Gebser, M., Ostrowski, M., Schaub, T. (2009). Constraint answer set solving. In Proceedings of International Conference on Logic Programming (ICLP), pp. 235-249. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-02846-5_22.
- Balduccini, M. (2009). Representing constraint satisfaction problems in answer set programming. In Working Notes of the Workshop on Answer Set Programming and Other Computing Paradigms (ASPOCP).
- Gebser, M., Kaminski R., Kaufmann B., Ostrowski M., Schaub T., Thiele S. (2010). A Users Guide to gringo, clasp, clingo, and iclingo. http://potassco.sourceforge.net/labs.html.
- Bhushan, S., & Karimi, I. A. (2003). An MILP approach to automated wet-etch scheduling. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, Vol. 42 (7), pp. 1391-1399. [CrossRef]
- Ahn, G.; Park, M.; Park, Y.J.; Hur, S. Interactive Q-Learning Approach for Pick-and-Place Optimization of the Die Attach Process in the Semiconductor Industry. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4602052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q., Zhou, M., Qiao, Y., Wu, N. (2017) Close-down Process Scheduling of Wafer Residence Time-Constrained Multi-cluster Tools. IEEE International Conference of Robotics and Automation (ICRA).
- Li,P.Q., Ma, H. H. (2017)Integrating Preventive Maintenance Planning and Production Scheduling under Reentrant Job Shop, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 6758417. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qiao, F.; Zhao, F.; Sutherland, J. Dynamic Scheduling of a Semiconductor Production Line Based on a Composite Rule Set. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, H.Y., and S. Rangel. 2017. A Survey of Case Studies in Production Scheduling: Analysis and perspectives. Journal of Computational Science. [CrossRef]
- Mönch, L., Lars, L., Fowler, J.W., Dauzère-Pérès, S., Mason, S.J. and Rose, O. (2011). A Survey of problems, solution techniques, and future challenges in scheduling semiconductor manufacturing operations, Journal of Scheduling, 14 (6), pp. 583-599. [CrossRef]
- García-Mata, C.L., Márquez-Gutiérrez, P.R., Burtseva, L. (2015). Rescheduling in Industrial Environments: Emerging Technologies and Forthcoming Trends. Int. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization Problems and Informatics, Vol. 6(3), pp. 34-48. https://ijcopi.org/index.php/ojs/article/view/50/48.
- Dequeant, K., Vialletele, P., Lemaire, P., Espinouse, M. L. A. (2016). Literature review on variability in semiconductor manufacturing: The next forward leap to Industry 4.0. Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), 2598 – 2609. [CrossRef]
- Khakifirooz, M., Fathi, M., Wu, K. (2019) Development of smart semiconductor manufacturing: Operations research and data science perspectives. In: IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 108419–108430. [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.M.; Méndez, C.A.; Garcia Sánchez, A.; Ortega-Mier, M.; Castro, P.M. General framework for automated manufacturing systems: Multiple hoists scheduling solution. Chemical Engineering Transactions 2013, 32, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J., Che, A., Chu, C. (2015). Dynamic Hoist Scheduling Problem with Multi-capacity Reentrant Machines: A Mixed Integer Programming Approach, Comput. Ind. Eng. Vol. 87, pp. 611-620. [CrossRef]
- Yan, P., Wang, G., Che, A. and Li, Y. (2016) Hybrid discrete differential evolution algorithm for biobjective cyclic hoist scheduling with reentrance, Computers and Operations Research, vol. 76, pp. 155–166.
- Karimi, I.A., Tan, Z.Y.L., Bhushan, S. (2004). An improved formulation for scheduling an automated wet-etch station. Computers and Chemical Engineering 29, 217-224. [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.M., Méndez, C.A. and Castro, P.M. (2011). A novel optimization method to automated wet-etch station scheduling in semiconductor manufacturing systems, Computers and Chemical Engineering, Vol. 28, pp. 883- 888. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K., Salleh, M.N.M., Cheng, S., Shi, Y. (2018). Metaheuristic research: A comprehensive survey. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Geiger, C. D., Kempf, K. G., Uzsoy, R. (1997). A Tabu search approach to scheduling an automated wet etch station. J. Manuf. Syst., Vol. 2, pp. 102-116. [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, S., Karimi I.A. (2004) Heuristic algorithms for scheduling an automated wet-etch station. Comput. Chem. Eng., Vol. 28 (3), pp. 363-379. [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, A., P. Young, and J. Geraghty. (2015) Sequencing Optimisation for Makespan Improvement at Wet-Etch Tools. Computers & Operations Research 53, pp. 261–274.
- Zeballos, L. J., Castro, P. M. and Méndez, C. A. (2011). Integrated constraint programming scheduling approach for automated wet-etch stations in semiconductor manufacturing, Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50 (3), pp. 1705-1715. [CrossRef]
- Novas, J.M. and Henning, G.P. (2010). Reactive scheduling framework based on domain knowledge and constraint programming, Computers and Chemical Engineering, 34 (12), pp. 2129-2148. [CrossRef]
- Hegyháti, M., Ösz, O., Kovács, B. (2015). Combinatorial Approach for Scheduling Automated Wet-etch Stations. 5th International Conference on Recent Achievements in Mechatronics, Automation, Computer Science and Robotics.
- Van Gelder, A., Ross, A. K. and Schlipf, J. S. (1991). The well-founded semantics for general logic programs, Journal of ACM, 38 (3), 620-650. [CrossRef]
- Son, T.C., Pontelli, E. and Le, T. (2014). Two applications of the ASP-prolog system: Decomposable programs and multi-context systems. In PADL 2014: Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Symposium on Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages, (pp.87-103), San Diego, CA, USA. [CrossRef]
- Cabalar, P., Fandinno, J., Schaub, T., and Wanko, P. “On the Semantics of Hybrid ASP Systems Based on Clingo,” Algorithms, vol. 16, no. 4, p. 185, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, R., Oliveras, A., Tinelli, C. (2006). Solving SAT and SAT modulo theories: From an abstract Davis-Putnam- Logemann-Loveland procedure to DPLL(T). Journal of the ACM, Vol. 53 (6), pp. 937-977. [CrossRef]
- Biere, A., Heule, M., Van Mareen, H., y Walsh, T. (2009). Handbook of Satisfiability. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications. IOS Press.
- Michel, R., Hubaux, A., Ganesh, V. and Heymans, P. (2012). An SMT-based approach to automated configuration. In Pascal Fontaine and Amit Goel, editors, Proc. 10th International Workshop on Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT), pp. 107-117. [CrossRef]
- Lierler, Y. Constraint Answer Set Programming: Integrational and Translational (or SMT-based) Approaches. Theory and Practice of Logic 2023, 23, 195–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, A., Geraghty, J., Young, P. (2018) Generalization of EF-based Assignment Strategies for Cycle Time Optimization at Complex Wet Stations. 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC). [CrossRef]
- Röck, H. (1984). The three machine no wait flow shop scheduling problem is NP-complete, Journal of the ACM, Vol. 33, pp. 336-345. [CrossRef]
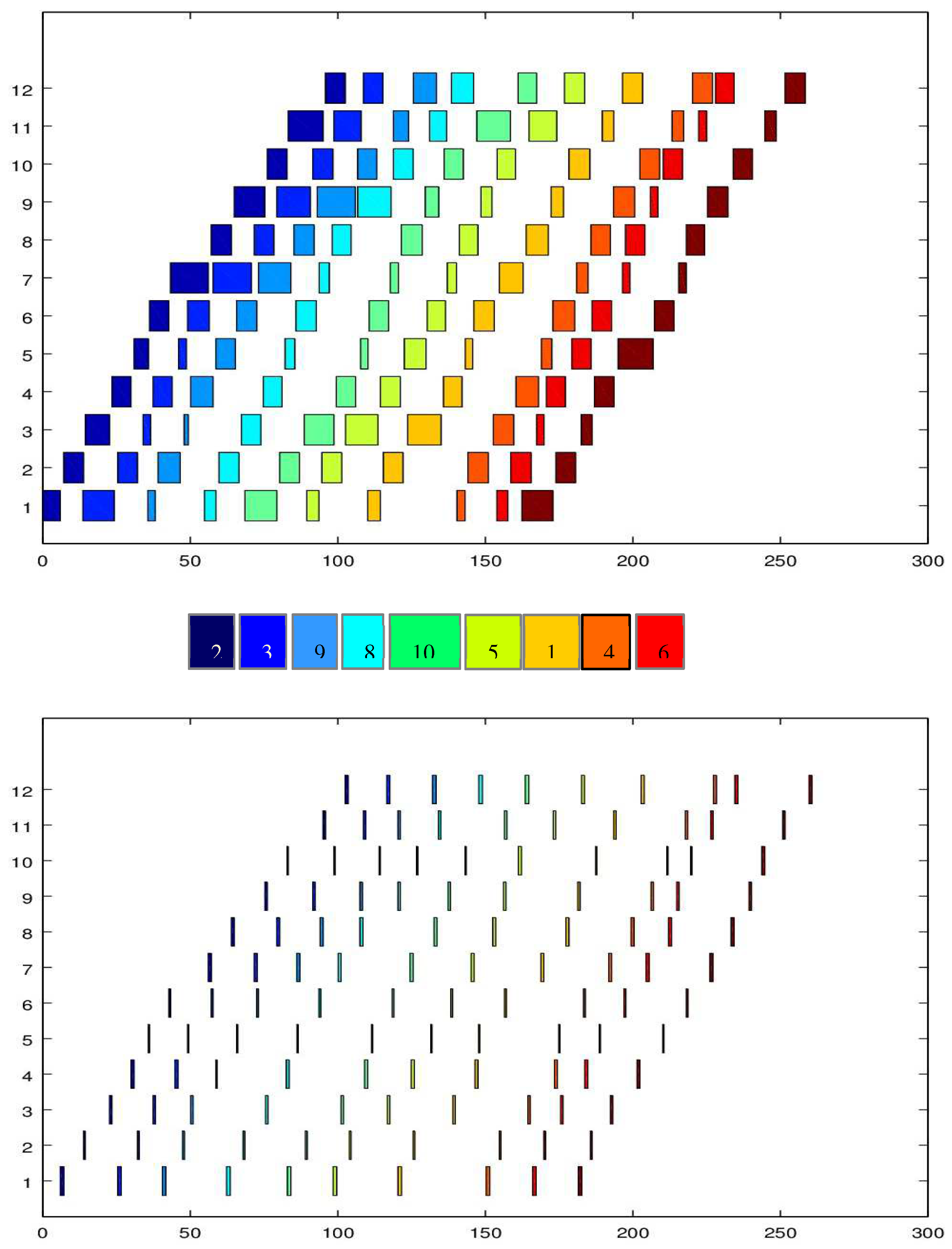
| Job/Bath | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.3 | 6.7 | 11.3 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 6.9 | 8.1 | 7.5 | 4.2 | 7.1 | 3.9 | 6.8 |
| 2 | 5.8 | 6.7 | 8.2 | 6.5 | 4.9 | 6.5 | 12.8 | 6.8 | 10.4 | 6.7 | 11.8 | 6.7 |
| 3 | 10.6 | 6.7 | 2.6 | 6.4 | 2.7 | 7.3 | 13.0 | 6.6 | 11.4 | 6.8 | 9.2 | 6.6 |
| 4 | 2.7 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 7.6 | 3.5 | 7.4 | 3.9 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 6.7 | 3.9 | 6.8 |
| 5 | 4.1 | 6.7 | 11.0 | 6.8 | 7.4 | 6.2 | 3.1 | 6.3 | 3.7 | 6.2 | 9.4 | 6.9 |
| 6 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 2.5 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 6.6 | 2.5 | 6.6 | 2.6 | 6.5 | 2.7 | 6.3 |
| 7 | 10.5 | 6.7 | 3.7 | 6.6 | 11.9 | 6.6 | 2.6 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 3.9 | 6.8 |
| 8 | 3.9 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 3.3 | 6.9 | 3.4 | 6.4 | 11.3 | 6.7 | 5.8 | 7.5 |
| 9 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 1.4 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 11.0 | 6.9 | 12.9 | 6.5 | 5.2 | 7.8 |
| 10 | 10.8 | 6.7 | 10.1 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 6.6 | 2.7 | 7.1 | 4.6 | 6.5 | 11.4 | 6.3 |
| 11 | 8.7 | 6.2 | 4.2 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 4.6 | 6.7 | 8.8 | 6.6 |
| 12 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 2.7 | 6.7 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 2.9 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 6.8 |
| 13 | 9.1 | 6.8 | 2.8 | 6.4 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 10.4 | 6.9 | 8.8 | 6.5 |
| 14 | 2.7 | 6.1 | 11.4 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 10.0 | 6.8 |
| 15 | 2.8 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.3 | 4.2 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 6.6 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 4.3 | 6.9 |
| 16 | 5.7 | 6.9 | 2.8 | 7.1 | 4.7 | 6.1 | 3.9 | 6.9 | 4.4 | 6.4 | 2.7 | 6.3 |
| 17 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 6.4 | 3.4 | 7.2 | 2.9 | 6.7 | 7.8 | 6.4 |
| 18 | 3.9 | 6.8 | 12.1 | 6.8 | 2.7 | 6.3 | 9.3 | 6.2 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 2.6 | 6.8 |
| 19 | 9.7 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 6.4 | 10.9 | 6.9 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 4.6 | 6.6 | 10.1 | 6.3 |
| 20 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 2.9 | 6.5 | 10.4 | 6.9 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 11.5 | 6.6 | 3.7 | 6.2 |
| 21 | 4.7 | 6.6 | 4.9 | 6.9 | 2.6 | 6.8 | 12.7 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.4 |
| 22 | 2.5 | 6.3 | 2.6 | 6.6 | 7.9 | 6.8 | 12.5 | 6.8 | 2.6 | 6.5 | 7.8 | 6.4 |
| 23 | 11.4 | 6.4 | 8.9 | 6.6 | 2.7 | 6.4 | 11.4 | 7.4 | 11.3 | 6.8 | 2.9 | 6.9 |
| 24 | 6.8 | 6.5 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 3.9 | 7.2 | 9.8 | 6.5 | 8.6 | 6.3 | 11.8 | 6.2 |
| 25 | 8.8 | 6.9 | 8.8 | 6.8 | 11.3 | 6.8 | 11.3 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 6.4 |
| Lots | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baths | 1 | 11,1 | 8,47 | 9,19 | 10,8 | 7,4 | 10,8 | 3,48 | 2,51 |
| 2 | 6,68 | 6,35 | 6,35 | 7,12 | 7,05 | 6,76 | 6,67 | 6,23 | |
| 3 | 5,24 | 10,1 | 4,6 | 10,2 | 4,07 | 1,01 | 1,41 | 8 | |
| 4 | 6,92 | 7,02 | 6,71 | 6,83 | 6,58 | 6,37 | 6,46 | 6,23 |
| τ1 | τ2 | τ3 | τ4 | τ5 | τ6 | τ7 | τ8 | τ9 | τ10 | τ11 | τ12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| Problem | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baths | 6 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 12 |
| Jobs | 5 | 15 | 25 | 5 | 15 | 25 | 8 | 8 | 10 |
| Problem P[B x J] |
First Solution | Optimal Solution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| makespan | CPU time | makespan | CPU time | |
| P1 [6 x 5] | 89.6 | 0.090 | 89.6 | 0,09 |
| P2 [6 x 15] | 209.3 | 0.790 | 209,3 | 1,19 |
| P3 [6 x 25] | 316.0 | 1,82 | 286,4 | 5,81 |
| P4 [12 x 5] | 144.1 | 0,26 | 144,1 | 0,28 |
| P5 [12 x 15] | 251.0 | 2,74 | 303,8 | 32,2 |
| P6 [12 x 25] | 397.5 | 8.61 | 417.8 | 8.45 |
| P7 [4 x 8] | 107 | 0,09 | 107 | 0,08 |
| P9 [12 x 10] | 246,6 | 1,08 | 234,7 | 1,43 |
| P:[B x J] | First Solution | Optimal Solution | Approach | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Makespan | CPU time | makespan | CPU time | ||
| P1 [6 x 5] | 218.1 | 0.01 | 82.6 | 0.94 | MILP |
| 92.6 | 0.01 | 82.6 | 2,84 | CP+GVDR | |
| 89.6 | 0.09 | 89.6 | 0,09 | CASP | |
| P2 [6 x 15] | 196.1 | 1687 | 195,2 | 3600 a | MILP |
| 205.4 | 0,14 | 185 | 350 a | CP+GVDR | |
| 209.3 | 0.790 | 209,3 | 1,19 | CASP | |
| P3 [6 x 25] | NS | - | NS | 3600 a | MILP |
| 325,1 | 0,53 | 297,3 | 1346 a | CP+GVDR | |
| 316.0 | 1,82 | 286,4 | 5,81 | CASP | |
| P4 [12 x 5] | 154.4 | 2,38 | 144.1 | (7.39)14.49 | MILP |
| 161.5 | 0,06 | 144.1 | 0.39 a | CP+GVDR | |
| 144.1 | 0,26 | 144,1 | 0,28 | CASP | |
| P5 [12 x 15] | NS | - | NS | 3600 a | MILP |
| 294.0 | 0.76 | 273.2 | 949 s | CP+GVDR | |
| 251.0 | 2,74 | 303,8 | 32,2 | CASP | |
| P6 [12 x 25 ] | NS | - | NS | 3600 a | MILP |
| 497.5 | 17.29 | 443.4 | 493.37 | CP+GVDR | |
| 397.5 | 8.61 | 417.8 | 8.45 | CASP | |
| P7 [4 x 8] | 139.1 | 3.45 | 120.47 | (72.34)152 | MILP |
| 128.20 | 0.05 | 120.47 | 1.40 a | CP+GVDR | |
| 106,3 | 0,08 | 106,2 | 0,1 | CASP | |
| P9 [12 x 10] | 206.30 | 3452 | 206.30 | 3452 a | MILP |
| 232.8 | 0.38 | 199.0 | 3440 a | CP+GVDR | |
| 246.6 | 1.08 | 234.7 | 1.43 | CASP | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





