1. Introduction
The ongoing need for sustainable building solutions has spurred the search for novel materials capable of improving energy efficiency and tackling emerging issues like electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Traditional construction materials like cement, gypsum, concrete, and brick have long been staples in wall construction. However, recent attention has shifted towards developing materials that not only fulfill structural requirements but also exhibit thermal energy storage capabilities [
1]. This focus on thermal energy storage aligns with the wider push to enhance energy efficiency and sustainability in building practices. Moreover, the demand for buildings equipped to counteract the effects of electromagnetic waves has grown more urgent in our increasingly technology-driven surroundings. The rapid evolution of electronic devices has raised concerns about electromagnetic radiation, as it can disrupt device functionality and potentially pose risks to human well-being [
2]. In light of these challenges, integrating advanced materials with diverse properties has emerged as a promising avenue toward achieving multifunctionality in building solutions.
Within this context, the incorporation of phase change materials (PCMs) into building elements such as gypsum and cement boards has garnered considerable interest. This interest stems from their capacity to store and release thermal energy, thereby facilitating effective temperature control within enclosed environments [
1,
3,
4]. The cost-effectiveness and adaptability of PCM products have catalyzed inventive approaches in the construction sector. They are progressively acknowledged for their capacity to improve energy efficiency and regulate thermal conditions within constructed spaces [
1,
5,
6]. The adoption of these materials has undergone extensive examination within the engineering and scientific spheres. This scrutiny is largely attributed to their ability to absorb and release thermal energy throughout phase transitions, presenting an encouraging avenue for improving indoor temperature management [
1]. Nonetheless, the practical implementation of PCMs encounters hurdles stemming from their inherent drawbacks, including low thermal conductivity and the possibility of leakage when in a liquid state during phase transition [
7]. To effectively tackle these obstacles, the adoption of a shape-stabilizing (SS) support matrix has emerged as a highly effective strategy. This matrix serves as a safeguarding enclosure for the PCM, guaranteeing its containment and stability in a molten state, particularly at higher temperatures. As a result, it prevents leakage and reduces corrosion in structural materials [
8]. Carbon-based porous materials, such as carbon-based foam, expanded graphite, graphene oxide, graphene aerogel, and activated carbon, present a promising platform for incorporating functional additives like PCMs. This integration results in enhanced thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding capabilities, offering compelling opportunities for various applications [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
Significant studies in the literature have delved into integrating carbon-based materials with shape-stabilized PCMs into composite cement or gypsum boards [
1,
13].
Chin et al. showed that concrete panels incorporated with paraffin-oil palm kernel shell-activated carbon exhibit increased thermal lag and reduced peak temperature during the phase transition of composite PCM [
14]
. Qian and Li, reported the preparation of cement composites with n-octadecane stabilized on diatomite/carbon matrix [
15]. The heat-storage cement mortar developed has been found to mitigate fluctuations in interior temperature, showcasing significant potential for energy savings and enhanced thermal comfort in the built environment. Chen et al. reported that the incorporation of SAT-urea eutectic salts encapsulated with modified commercial-activated carbon in gypsum, could slowly reduce the thermal conductivity and significantly improved the thermal inertia of the composites [
16]. Finally, in our recently published work [
17], the incorporation of activated carbon/RT18HC on gypsum boards led to composite gypsum boards with enhanced properties on thermal storage and EMI shielding applications, compared to the net gypsum board.
In this study, we present a novel investigation into the advancement of building materials with dual functionalities by incorporating gypsum and cement boards with shape-stabilized organic phase change materials (ssPCM). This ssPCM consists of n-octadecane (OD) stabilized on carbon red-mud foam (CCF). Our previous research has extensively examined the thermal and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding properties of OD@CCF composites, demonstrating their effectiveness in thermal management and EMI reduction in electronic devices [
8]. Our current study focuses on assessing the impact of varying percentages of this additive on the thermal storage capacity and EMI shielding abilities of gypsum and cement boards. We conducted experiments under real-world conditions, simulating realistic weather scenarios using a custom-designed environmental chamber. By integrating n-octadecane encapsulated in carbon red-mud foam into the matrix of these building components, we aim not only to efficiently regulate indoor temperatures but also to enhance structural resilience against electromagnetic interference. This approach offers a comprehensive solution to the dual challenges of energy conservation and electromagnetic shielding in modern architectural designs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The materials used to produce Ceramic Carbon Foam (CCF) and shape stabilized n-octadecane on CCF (OD@CCF) were commercially sourced and are extensively detailed in our previous publication [
8]. The raw materials required for cement production were supplied by Energy Houses (ENHSS, Serres, Greece), a collaborating business partner based in Greece. Gypsum and starch were provided by KNAUF (Amfilochia, Greece), a globally recognized company, to ensure that the final product closely resembled commercial standards.
2.2. Preparation of CCF and OD@CCF Hybrid
Comprehensive details regarding the experimental procedures for preparing these materials can be found in our previously published research [
18]. The CCF matrix was synthesized through the polymeric foam replication technique, utilizing a polyurethane sponge as a template, resin as a carbon source, and red mud as a filler.
2.3. Preparation of Cement Boards
The experimental procedure devised for manufacturing the cement boards received guidance from a Greek collaborative partner, Energy Houses (ENHSS, Serres, Greece), which not only supplied the necessary raw materials but also offered technical insights throughout the production process. In accordance with both company and international standards, the raw materials included cement powder, polypropylene fibers, acrylic polymer emulsion-resin, perlite, water, and composites containing encapsulated n-octadecylamine with foams (OD@CCF) in varying proportions. The cylindrical morphology composites (D=30 mm, h=30 mm) were subsequently fragmented into smaller pieces to facilitate their uniform dispersion within the cement boards. The experimental procedure involved weighing the aforementioned raw materials in specified quantities for each composition (detailed in
Table 1) and then subjecting them to continuous manual stirring for at least fifteen minutes to ensure thorough homogenization. Following this, the mixture was applied to a wooden mold and allowed to dry at room temperature for a minimum of twenty-four hours, resulting in specimens measuring 200 x 200 x 37 mm. The cement board without additives is denoted as CB, while those with composite additions are referred to as CB/OD@CCF-x, where x represents the volume percentage of OD@CCF additive.
2.4. Preparation of Gypsum Boards
To produce the gypsum boards, all solid materials were thoroughly mixed manually until a uniform consistency was achieved. Water was then added while vigorously stirring the mixture. The blending process continued for approximately five minutes before pouring the resulting slurry into a mold, resulting in gypsum boards with dimensions of 200 x 200 x 12.5 mm. The slurry was left undisturbed in the mold for a minimum of 24 hours at room temperature to allow for drying. The specific compositions of the prepared gypsum boards are detailed in
Table 2. The reference gypsum board is denoted as GB, while composite boards are labeled as GB/OD@CCF-x, where ‘x’ represents the volumetric percentage of OD@CCF additive.
2.5. Measurements of Density
The bulk densities (ρ) of the gypsum and cement boards were initially estimated in the original specimens using the formula ρ = m/V, where ‘m’ represents weight, and ‘V’ stands for the volume of the boards. However, to enhance measurement accuracy, a modified Archimedes water displacement method was employed, following a standardized procedure [
19]. This method involved initially measuring the bulk volume and then determining the bulk density for small-sized porous specimens. Before immersion into a cylinder with known dimensions, the samples were sealed with wax. Both density measurement techniques yielded similar ρ-values, showing no significant deviations.
2.6. X-ray Computed Microtomography (Micro-CT)
X-ray computed microtomography (micro-CT) imaging was employed to investigate the internal structure of composites with varying concentrations of additive (10%, 20%, and 30%). Radiographic imaging was carried out on a Bruker SkyScan 1275 (Billerica, MA, USA) scanner, equipped with a distortion-free 3 Mp active flat-panel detector. An accelerating voltage of 60 kV and a current of 60 μA were applied, while a 1 mm thick Al filter was used. The object distance was 20 mm leading to a pixel size of 10 μm. A 360° scan was performed with a 0.20° rotation step corresponding to 25 minutes scan duration. The reconstruction was performed on Bruker’s NRecon – v2.1.0.1 software. While CTan and Dataviewer were used for the image analysis.
2.7. Thermal Properties
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) measurements were performed under N
2 atmosphere using instrument DSC 214 NETZCH Polyma instrument (Selb, Germany). Rate of heating and cooling was 2
oC/min, while temperature ranged from 0
oC to 40
oC and 40
oC to 0
oC respectively. The thermal transport properties of gypsum board specimens, including thermal conductivity (k) and heat capacity (Cp), were assessed using a C-Therm TCi Thermal Conductivity analyzer (Fredericton, Canada). The Modified Transient Plane Source (MTPS) method (ASTM D7984) [
20] was employed, wherein a one-sided thermal sensor applied a low-energy current pulse for 0.8 seconds to the specimen. This ensured that the measurement of thermal conductivity (k) was not influenced by thermal convection. Some of the heat generated was absorbed by the specimens, while the remaining portion was utilized to raise the temperature at the sensor-sample interface. The resulting temperature variation indicated a resistance change in the sensor, leading to a voltage drop. The voltage data were utilized to assess the thermal transport properties of the investigated material. Thermal conductivity (k) and thermal effusivity (e) were measured directly, providing a detailed overview of the heat transfer properties of the sample material. The final values were derived from an average of 5 measurements for the specimen using the polymer test method and pyrex glass as a standard (k=1.143W/m∙K). The heat capacity (Cp) was then calculated using the equation: Cp =e
2/k∙ρ where ρ is the density of each specimen.
2.8. Mechanical Properties
The modulus of rupture, MOR of gypsum boards
(GB, GB/OD@CCF), was determined via three-point bending strength tests (Autograph AGS-H; Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), according to ASTM C293/C293M-16 [
21]. More specifically, the cross-sectional dimensions of each specimen were measured (the accuracy was ± 0.01 mm). Then, the gypsum specimen (200 mm x 50 mm x 12.5 mm) was centered at the gap (the span was 100 mm) between the supporting rods of the test machine. The velocity of the bending load was 2.0 mm/min, and the load until fracture was measured. The flexural strength (σ) was calculated using the equation (1)
where,
W (N) is the fracture load, and
L, W, and h are the span between the supporting rods, the specimen width, and the thickness, respectively. Five specimens from each subgroup (n = 5) were tested.
The mechanical properties of the cement boards
(CB, CB/OD@CCF)were evaluated by measuring the compressive deformation behavior of cubic specimens x=y=z ~50 mm, using the same testing machine. The compressive strength (CS=Load / Area(N/mm
2) of every cement board was conducted according to standard ASTM C109/C109M-20 [
22]. Compressive stress- stain (%) curves were derived from the load- displacement curves, and subsequently compressive strength and modulus of elasticity of the samples were calculated. The results are the average of measurements made on, at least, 5 specimens.
2.9. Thermal Performance Measurements
We utilized a custom-built environmental chamber [
23] for conducting thermal performance measurements. The chamber, illustrated in
Figure S2, was crafted from polystyrene foam panels and had internal dimensions of 1000 mm length, 1000 mm width, and 1000 mm height. An opening in the top section of the side panel accommodated the installation of a fan heater and a portable air conditioner.
Below the main chamber, four smaller chambers were positioned as test rooms, each with internal dimensions of 200 mm length, 200 mm width, and 200 mm height. These test chambers, also constructed from polystyrene foam panels, featured a design with a hollow top side panel to facilitate the placement of test samples.
Temperature measurements were conducted using Type K thermocouples placed at the center of each test room, along with additional thermocouples attached to both the outer and inner surfaces of each test sample. Additionally, a centrally placed thermocouple within the environmental chamber allowed for comprehensive temperature monitoring.
The chamber’s internal temperature was manipulated by the fan heater and portable air conditioner, causing elevation and decrease, respectively, from the top of the chamber. This setup enabled the assessment of thermal reactions in the test samples under varying temperature conditions. Temperature measurements were recorded at intervals of 5 minutes.
2.10. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding Properties
The EMI shielding effectiveness properties were evaluated using a P9372A Keysight Streamline Vector Network Analyzer (Keysight, Santa Rosa, CA, USA) and two sets of microwave standard 15 dB gain waveguides (WR 187 and WR 147, respectively, obtained from Advanced Technical Materials Inc. (ATM), Patchogue, NY, USA) covering a broad C frequency band in the range of 3.2–7.0 GHz (C-band), which is used for long-distance radio telecommunications, such as satellite communications transmissions, Wi-Fi devices, cordless telephones, weather radar systems, etc. In particular, every sample was placed in the middle of each set of waveguides, and its scattering parameters (S-parameters; S11, S12, S22, S21) were recorded.
3. Results and Discussion
In our earlier research research [
18], we extensively examined the structural and physicochemical attributes of both the Carbon-Red mud foam matrix (CCF) and the composite OD@CCF. To summarize, our analysis revealed that CCF possesses a remarkably porous structure, featuring elliptical and spherical pores ranging from 50 to 500 μm. The cell walls exhibit partial graphitization of carbon alongside various oxide phases. Of particular note, the hybrid foam OD@CCF exhibited exceptional efficiency in encapsulating paraffins, with a loading capacity of 48.8 %w.t. of octadecane. In the forthcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the characteristics of gypsum and cement composite boards integrated with OD@CCF additive at different concentrations.
3.1. Density Results and Microtomography Analysis of Composite Boards
Figure 1 and
Figure 2, illustrate the images of both the reference gypsum or cement board (GB or CB) and the GB/OD@CCF or CB/OD@CCF composite boards, respectively.
Table S1 presents the results of density measurements, while
Figure 3 illustrates the plotted data against the percentage content of OD@CCF. For GB/OD@CCF composites. The data in
Figure 3a reveals a slight decrease in gypsum board density with increasing additive content. Specifically, integrating 30% OD@CCF into gypsum boards reduced the density from 0.96 to 0.92 g cm
-3, showing a relatively consistent trend considering the error margins. This decrease aligns with previous findings, where the density of the current shape stabilizer, carbon foam, was measured at 0.54 g cm
-3 [
18], significantly lower than the initial density of the reference gypsum board (0.96 g cm
-3). Incorporating such lightweight additives contributes to the overall density reduction of the composite boards, although they still meet the minimum density requirement of 0.60 g cm
-3, as specified by European regulation UNE-EN 13279-1 for gypsum binders and plasters [
24,
25]. Similar density reduction trends during additive incorporation have been observed in the literature. For instance, in our prior research [
17], adding 30% activated carbon-PCM to gypsum boards led to a density decrease from 0.96 to 0.81 g cm
-3. Additionally, Jameel et al. [
26] noted a density decrease in gypsum boards enhanced with chopped carbon fibers, reaching from 1.258 to 1.098 g cm
-3 for a 0.3% volume fraction.
Conversely, in CB/OD@CCF composites, density increases with rising additive content (
Figure 3b), attributed to the higher density of PCM compared to the components of cement boards. The solid-phase density of the current PCM, raw octadecane, stands at 0.88 g cm
-3 [
27], contrasting with the measured density of the reference cement board at 0.51 g cm
-3. A similar trend was observed by Ye et al. [
28], who reported an increase in cement board density from 0.32 to 0.43 g cm
-3 upon adding 40% w.t. RT28HC stabilized on expanded perlite.
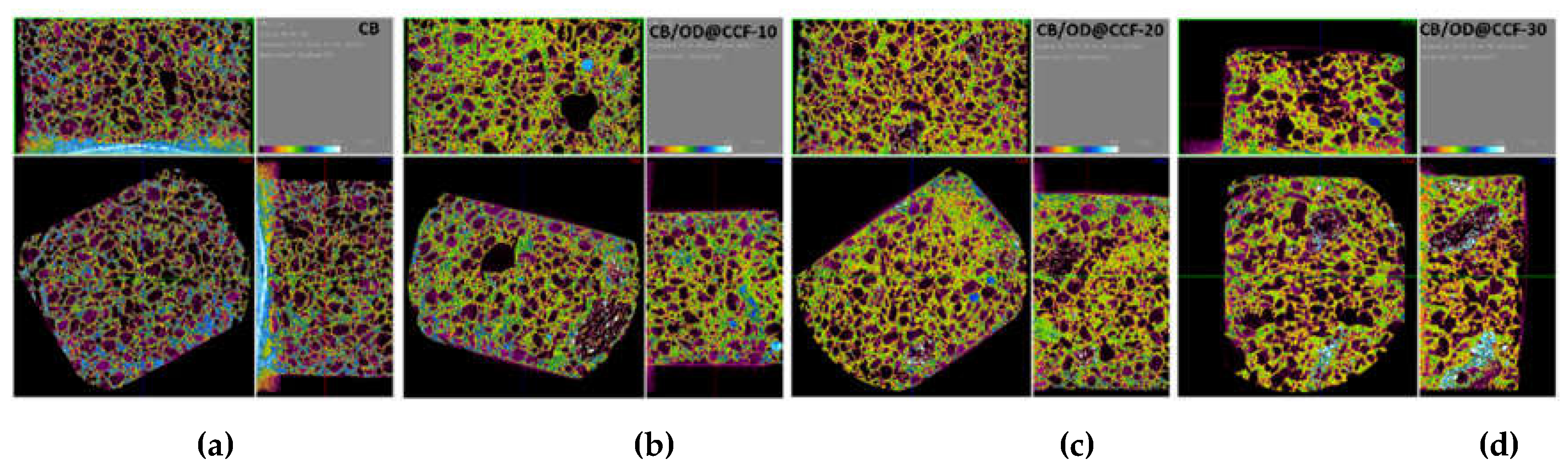
To substantiate the findings and investigate the cement and gypsum structure, X-ray computed microtomography (μCT) was conducted. These results offer crucial insights into the correlation between additive concentration and the microstructural characteristics of the composites. Microscale images (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5) show distinctive features corresponding to varying levels of additive incorporation. The colored scale bar in the images represents different X-ray attenuation values, indicating distinct physical density values of the wall-board components, ranging from lower (black) to higher (white) indices. The black spots in all images signify lower intensity areas (air voids), representing the porous regions of the boards. In the case of the cement boards, the images for CB reference board, predominantly feature black- and purple-colored areas (
Figure 4a). For 10 % additive OD@CCF, the microtomography images (
Figure 4b) display a reduction in black and purple areas, accompanied by the emergence of new yellow and green areas (higher index components). These areas are more intense in the images of composite boards with higher OD@CCF content, 20 and 30 %w.t (
Figure 4c,d, respectively). These latter components likely correspond to OD@CCF particles, indicating their homogeneous integration into the cement board even at the higher loading (30 %). These findings are also, in agreement with the density measurements, where the density of the cement board increases with increment of OD@CCF loading.
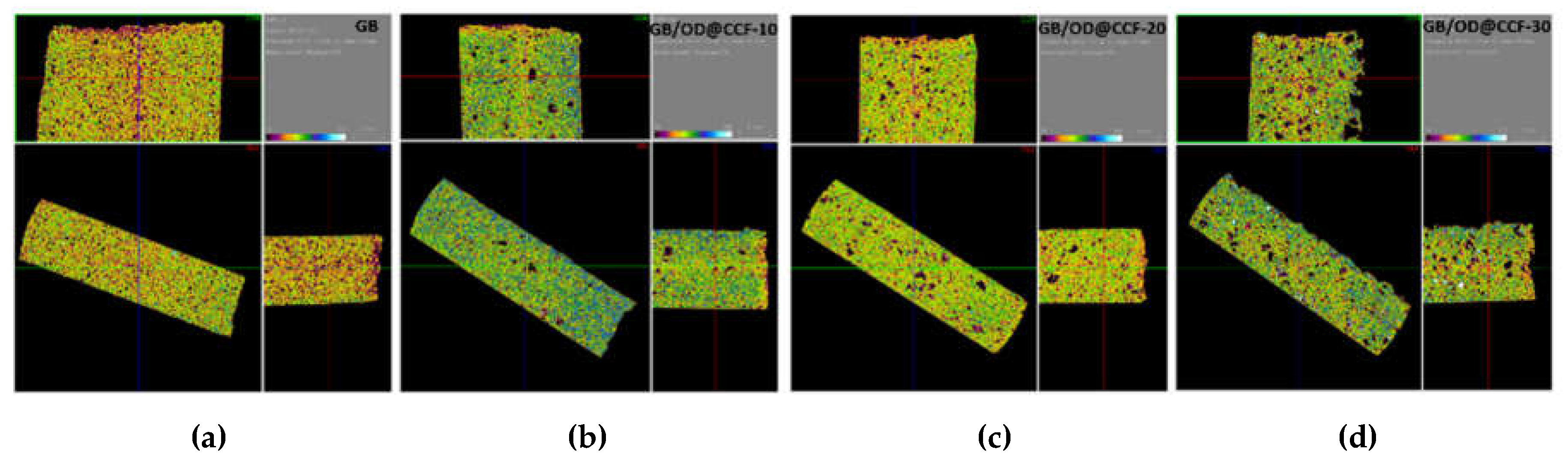
In the case of gypsum boards, the corresponding microtomography images are shown in
Figure 5. The images for GB reference board, predominantly feature yellow- and green- colored areas as well as few purple- and back- colored areas (
Figure 5a). For 10 % additive OD@CCF, the microtomography images (
Figure 5b) display more black- colored areas (lower index components, air voids) accompanied by the emergence of blue (higher index components). After a careful observation of black areas, it is obvious that consists also from purple- colored areas and these components may attributed to OD@CCF particles having lower intensity than gypsum components. Similar features are also shown in the images of composite boards with higher OD@CCF content, 20 and 30 %w.t (
Figure 5c,d, respectively) and OD@CCF particles seems to be homogenously dispersed in gypsum matrix, even at higher loadings (30 %).
3.2. Thermal Properties
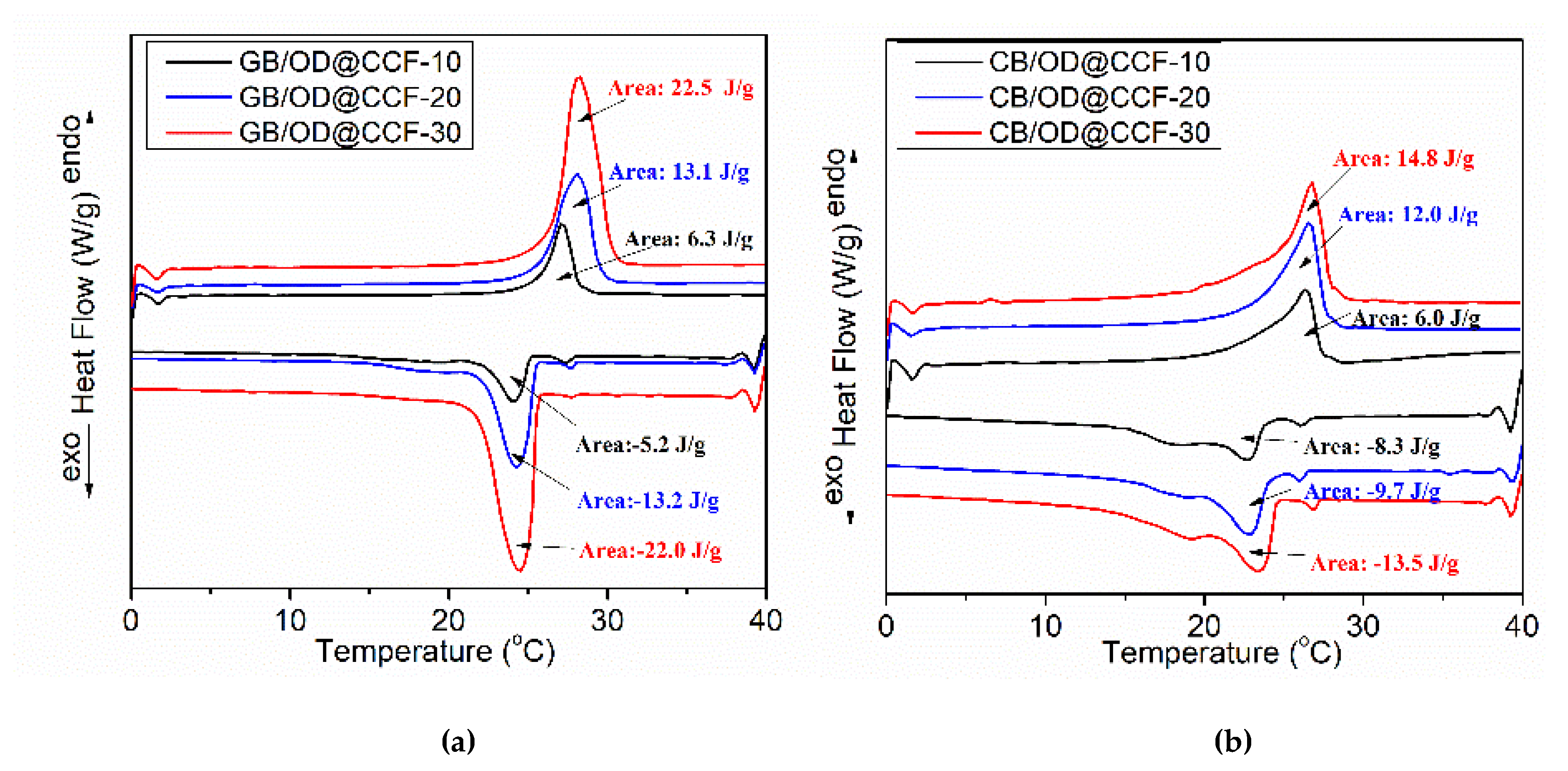
Figure 6 displays the Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) curves for (a) composite gypsum boards GB/OD@CCF and (b) composite cement boards CB/OD@CCF with varying percentages of OD@CCF content. The coresponding curves for pure octadecane are presented in
Figure S1. The melting (Tm) and solidification (Ts) temperatures, along with their corresponding enthalpies (ΔHm and ΔHs), are detailed in
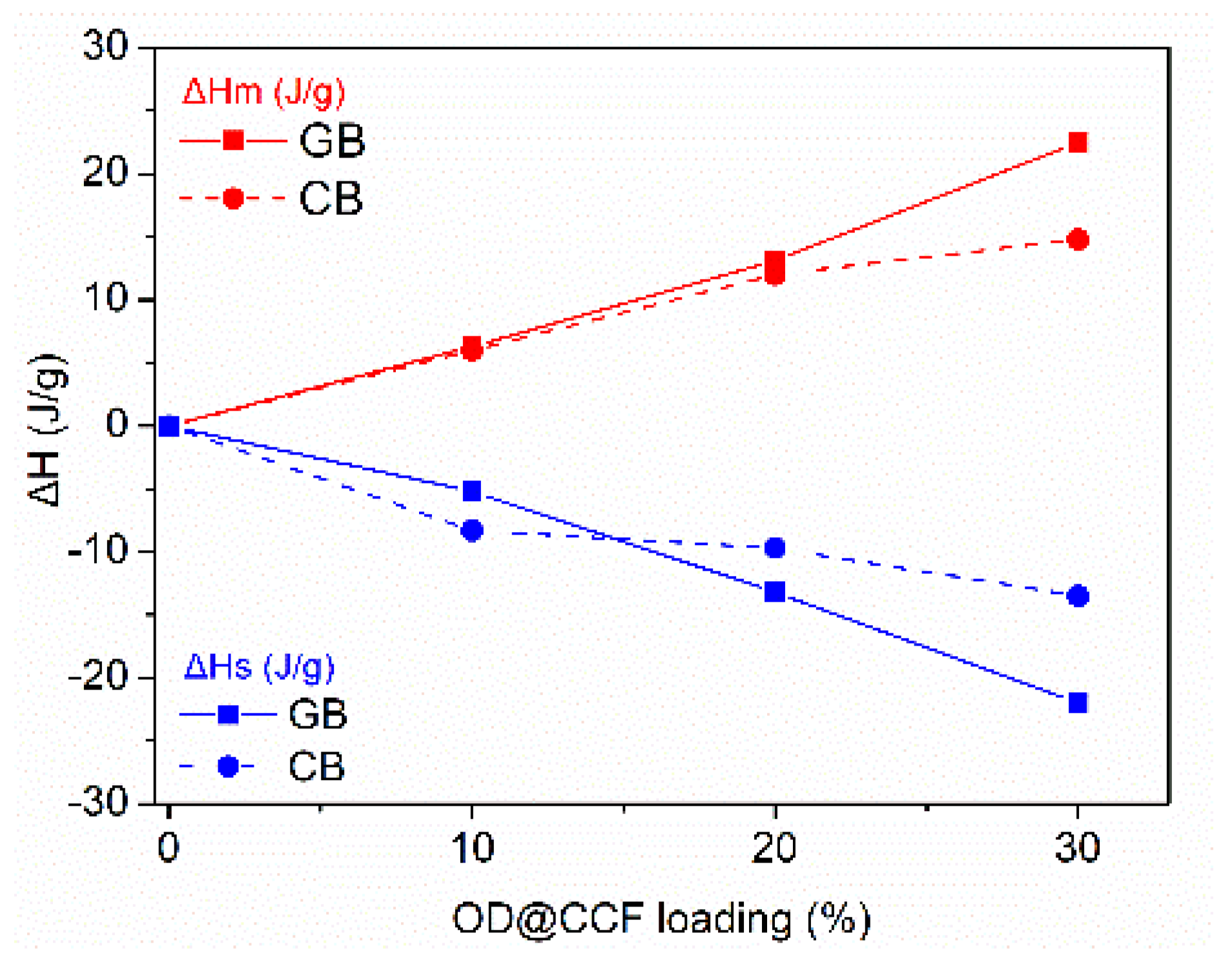
Table S1. The analysis reveals that for both gypsum and cement boards, the melting temperature of octadecane falls within the range of 26.4-28.3°C, while the solidification temperature ranges from 22.7-24.5°C. Additionally, the melting enthalpy increases from the lowest to the highest OD@CCF loading, as anticipated (6.3 J/g to 22.5 J/g for gypsum boards and 6.0 J/g to 14.8 J/g for cement boards). Conversely, the solidification enthalpy decreases from -5.2 J/g to -22.0 J/g for gypsum boards and from -8.3 J/g to -13.5 J/g for cement boards. These findings are plotted in
Figure 7.
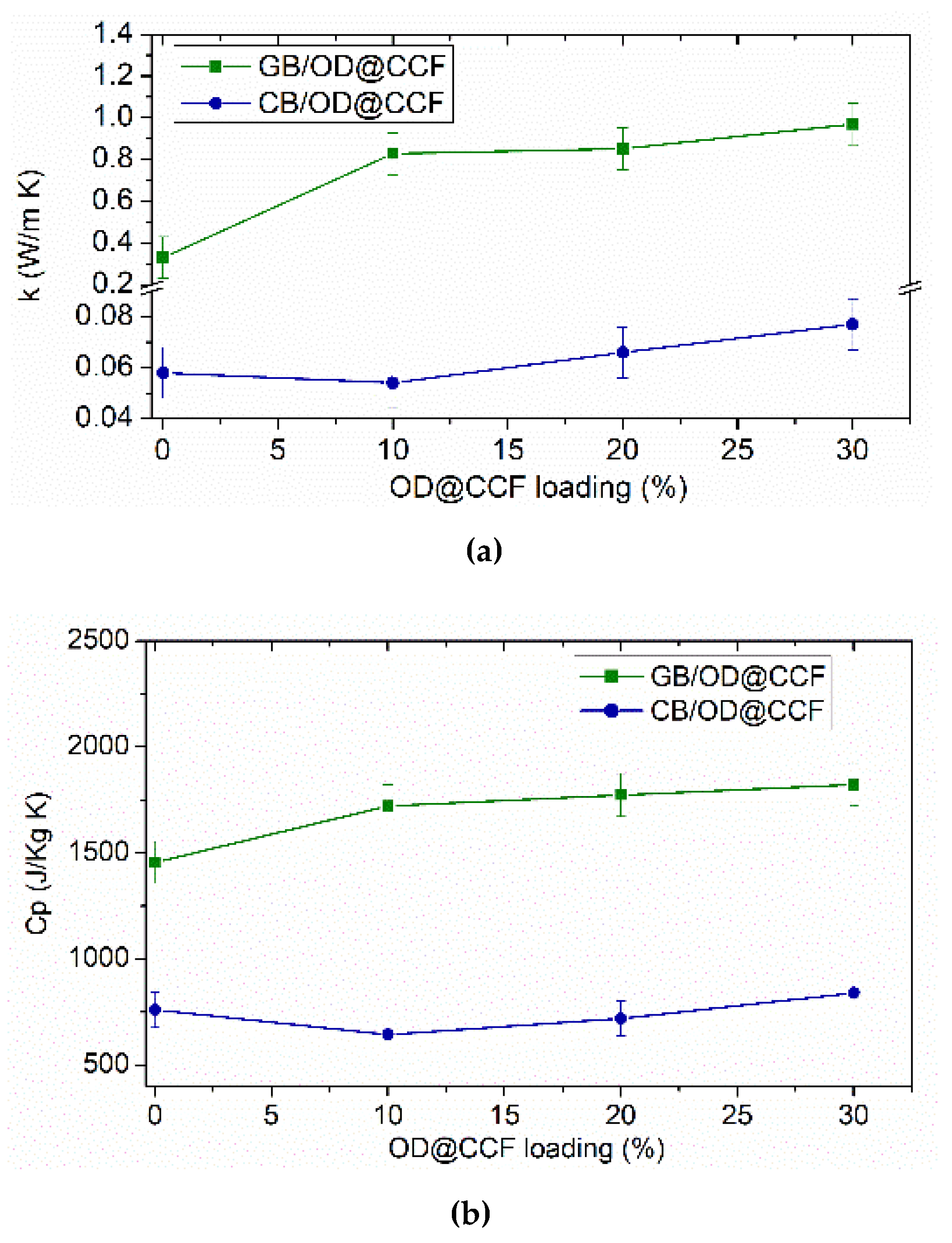
The results from thermal conductivity (k) and specific heat capacity (Cp) measurements for reference gypsum and cement boards and their composites GB/OD@CCF and CB/OD@CCF are presented in
Table S2. Additionally,
Figure 8 illustrates the graphical relationship between thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity as the percentage content of OD@CCF additive increases. The data reveals noticeable variations in these parameters corresponding to the incremental increase in additive content. Specifically, a positive correlation is evident, indicating an improvement in both thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity with higher additive content. This positive correlation is interpreted as the OD@CCF component making a positive contribution to the heat transfer capabilities within the composite gypsum and cement boards. The data suggests that as the percentage of OD@CCF additive increases, there is a concurrent enhancement in both thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity, highlighting the positive influence of the additive on the heat transfer properties of the composite material. This improvement can be attributed to two main factors. Firstly, carbon foam contributes to an overall enhancement in the thermal conductivity of the composites. Secondly, the well-dispersed and inter-connected carbon foam particles within the gypsum or cement matrix create additional channels for heat transfer [
29]. Similar findings are reported in the literature. For instance, in our previous work [
17] the incorporation of activated carbon/RT18HC in gypsum boards increased thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity from 0.33 W/(m·K) and 1455 (J/Kg·K), to 0.53 and 1833 (J/Kg·K), respectively for 30% w.t. additive. Zhang et al. [
30] noticed that diatomite/paraffin incorporation into gypsum boards reinforced with 1% carbon fibers, resulted in increament of thermal conductivity from 0.86 to 0.93 W/(m·K). In addition, according to the same team, expanded Graphite/Paraffin Gypsum-Based Composites with 20% w.t. additive, increased thermal conductivity from 0.742 W/(m·K) to 1.137 W/(m·K) [
31]. Concerning cement composite boards, in our case, the thermal conductivity values are measured in the range of 0.06-0.08 W/(m·K), which are in agreement with the literature for perlite-concrete thermal conductivity properties (0.07-0.08 W/(m·K)) [
32], showing ~33 % increment for 30 % additive. According to previous published works, carbon based nanomaterials can significantly improve cement’s thermal conductivity [
33,
34,
35]. Also, Ye et al. [
28] reported the increment of cement board’s thermal conductivity by adding expanded perlite stabilized RT28HC and specifically for 40 % w.t. additive reached to 0.149 W/(m·K) from 0.11 W/(m·K). Octadecane exhibits 0.2 W/(m·K) [
27], which also can improve in our case, the lower thermal conductivity of perlite-cement boards.
3.3. Mechanical Properties
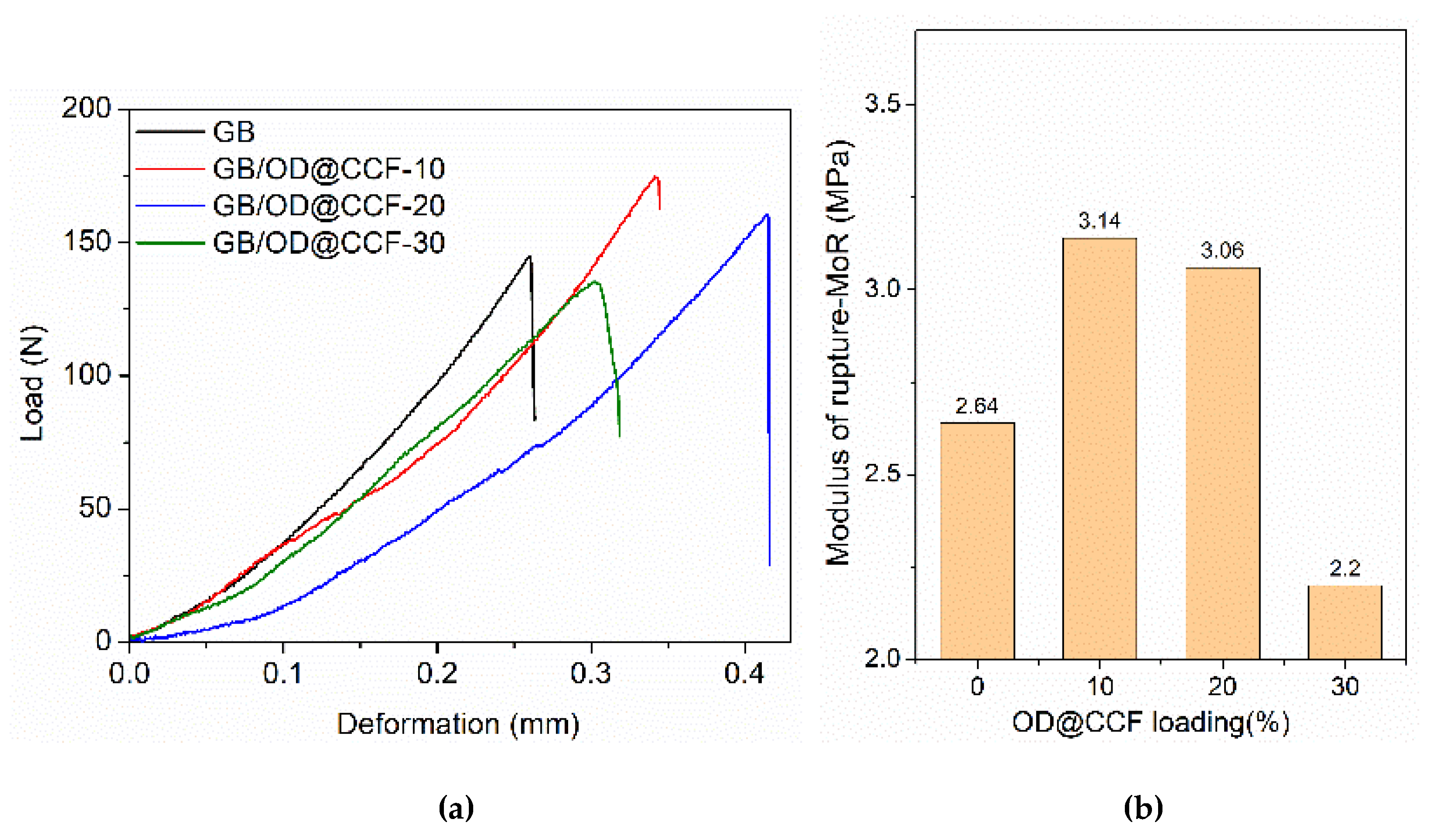
The results of mechanical testing on gypsum and cement boards with varying OD@CCF content are presented in
Figure 9 and
Figure 10, respectively. Analysis of load-deformation data from bending tests on GB/OD@CCF boards (
Figure 9) indicates a clear relationship between additive percentage and composite board mechanical properties. At lower concentrations (up to 20%), a positive correlation is observed, indicating that OD@CCF inclusion enhances material strength likely due to improved intermolecular interactions and reinforcement effects. However, with increasing OD@CCF content, a decline in mechanical strength is evident, possibly due to potential disruption of the gypsum matrix by higher OD@CCF concentrations. As shown in
Figure 9b, the optimal OD@CCF content for gypsum boards is found to be 10%. At this concentration, the modulus of rupture measures at 3.14 MPa, significantly higher than the 2.64 MPa for the reference gypsum board. This suggests that mechanical strength of the composite board peaks at 10% OD@CCF content in bending tests.
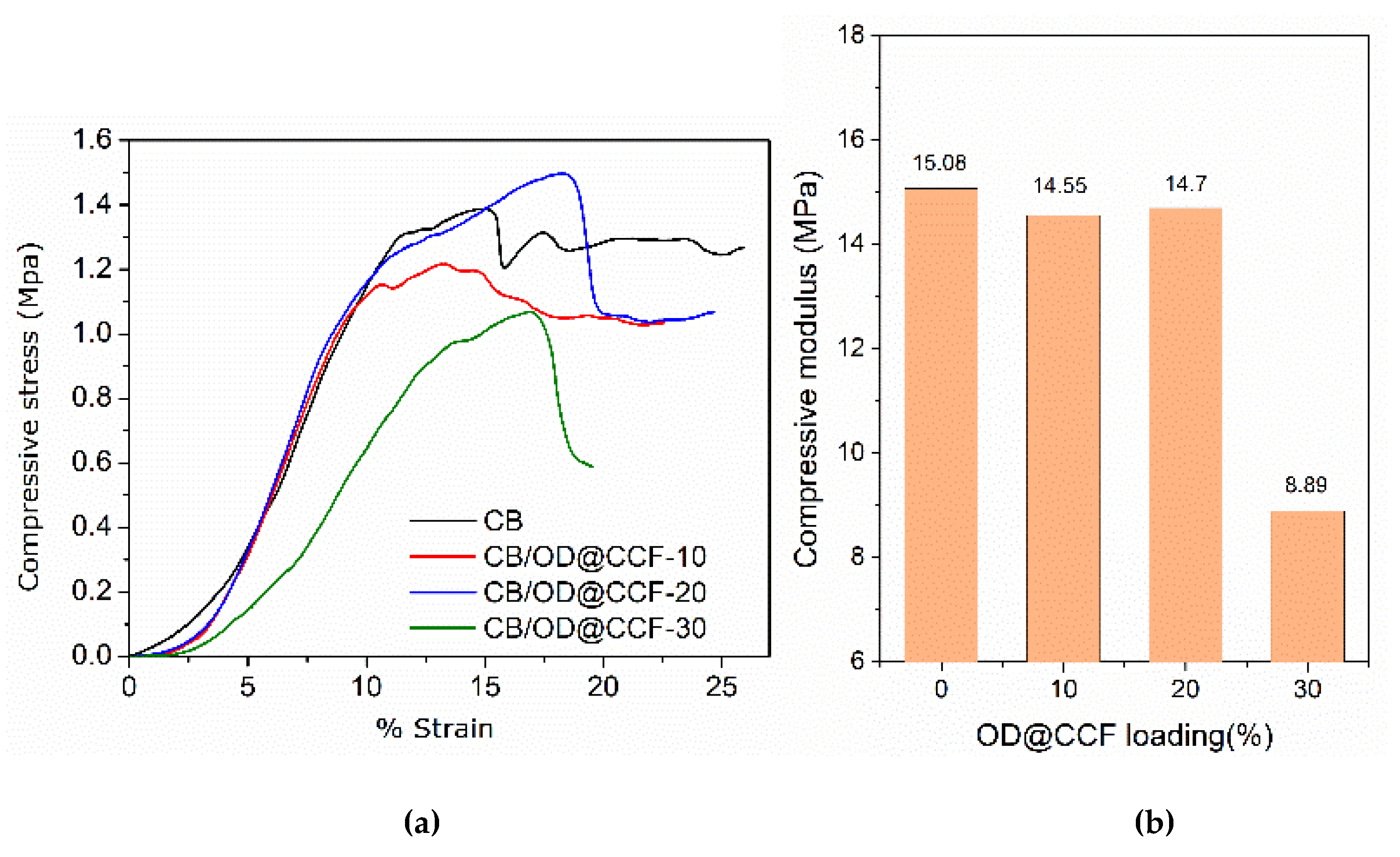
The results of compression tests on cement boards (CB) with varying percentages of OD@CCF additive are presented in
Figure 10. The corresponding parameters from these tests are outlined in
Table S3. A minor reduction in compressive strength is noted with increasing OD@CCF loading, decreasing from 1.09 MPa to 0.96 MPa for 10% and 20% loading, respectively. However, with a higher OD@CCF loading of 30%, this reduction is more pronounced, resulting in a compressive strength of 0.81 MPa.
3.4. EMI Shielding Properties
The performance of the EMI protection of developed samples was assessed from the point of view of the EMI protection (SE) efficiency in the frequency range of 3.2–7.0 GHz.
SET can be expressed as the sum of reflection from the surface (
SER), absorption (
SEA) and multiple-reflection (
SEM) as follows [
36]:
Generally, multiple-reflection at internal interfaces inside the material can be excluded if
SE > 10-15 dB. Thus, we calculated the average
SET as
where
SER, SEA refer to the reflection and absorption SE, respectively.
The higher the
SE the better the shielding. The
SE (also denoted as
SET, with
A,
T,
R indicating the absorption, transmission and reflection, respectively) is usually quantified in terms of the logarithm of the incident power
Pinc over the transmitted power
Ptrn [
37,
38] and thus expressed in decibels (dB).
Figure 11 depicts the S
21 (transmission;
Figure 11a) and the S
11 parameters (reflection;
Figure 11b) of the GB/OD@CCF composite samples for a series of shape stabilized octadecane stabilized in carbon foam OD@CCF concentrations, in the frequency range 3.2-7.0 GHz.
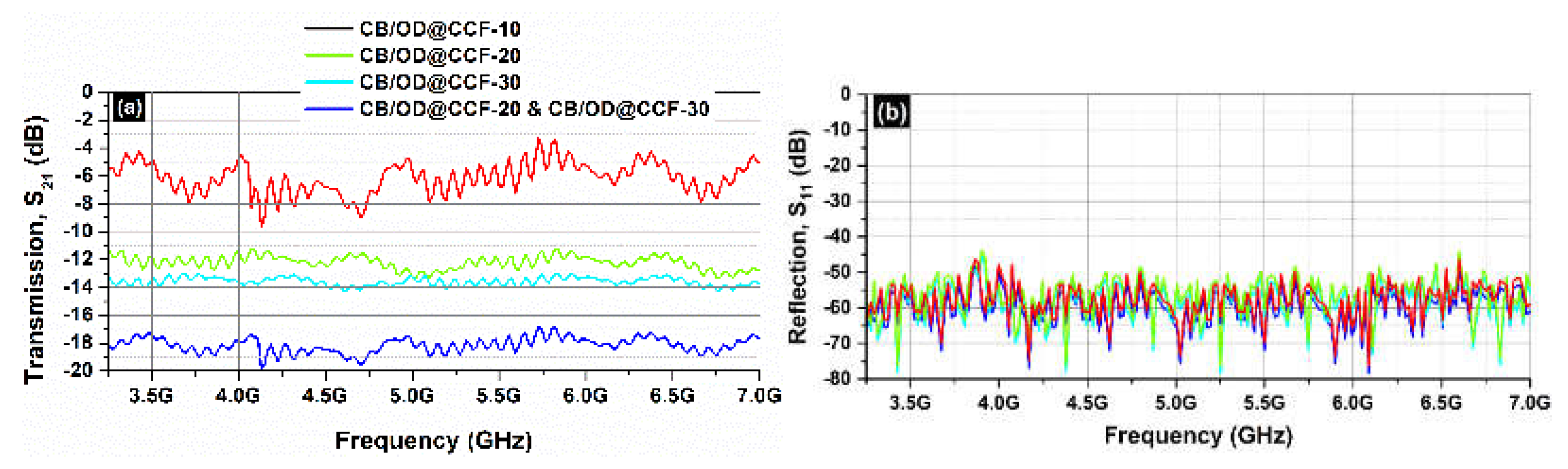
Figure 11b clearly illustrates that the reflection of the samples is almost zero for all the additive concentration from 0.00-30%. As a result, the EMI shielding effect due to reflection (
SER) is also negligible and in all cases the total
SE is simply
SET =
SEA [see equation (4)], in agreement with other research groups working on carbon based composite materials [
39].
Figure 12 depicts the absorption (
Figure 12a) and the total shielding efficiency (
SET) (
Figure 12b) spectra of the GB/OD@CCF composite samples for a series of shape stabilized octadecane stabilized in carbon foam OD@CCF concentrations, in the frequency range 3.2-7.0 GHz.
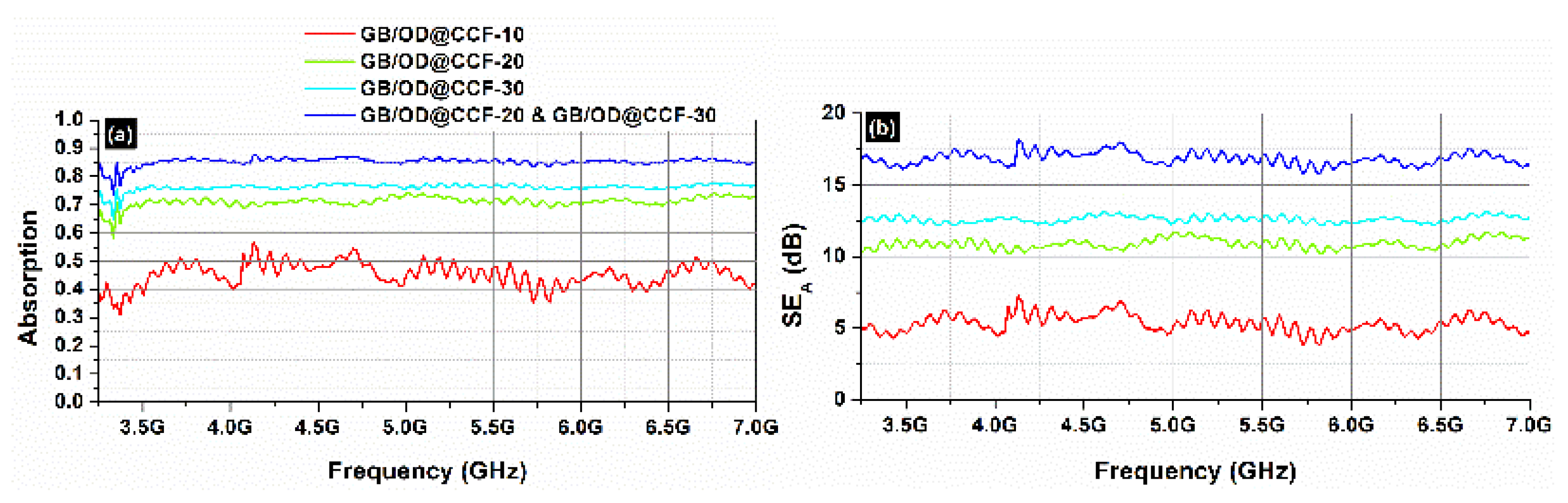
As one can see, the dominant shielding mechanism is absorption, which is also supported by the continuously increasing absorption levels with increasing OD@CCF content in the gypsum board composites.
When the loading amount of OD@CCF was low, the interconnected electrically conductive network was incomplete, and there is a small difference in electrical conductivity between gypsum board samples and air, leading to a large impedance match and a large number of electromagnetic waves transmitted into the samples [
40]. Indeed, as one can easily observe in
Figure 12b, for OD@CCF concentrations up to 10%, the
SEA does not exceed 5-6 dB, while, for 20% up to 30%, the
SEA varies from 10 to 12.5 dB, suggesting the absorption-dominant EMI shielding mechanism of our composite samples, in agreement with the literature [
39].
At this point, it should be noted that, the addition of GB/ OD@CCF-20 with the GB/OD@CCF-30 samples was studied in order to verify higher additives’ concentration could reach a
SET of ~ 15-20 dB which is considered sufficient for EM shielding, e.g., electronic devices, etc. [
41].
Similar samples to those described above were studied, making cement boards that can be used outdoors.
Figure 13 depicts the S
21 (transmission;
Figure 13a) and the S
11 parameters (reflection;
Figure 13b) of the CB/OD@CCF composite samples for a series of shape stabilized octadecane stabilized in carbon foam OD@CCF concentrations, in the frequency range 3.2-7.0 GHz.
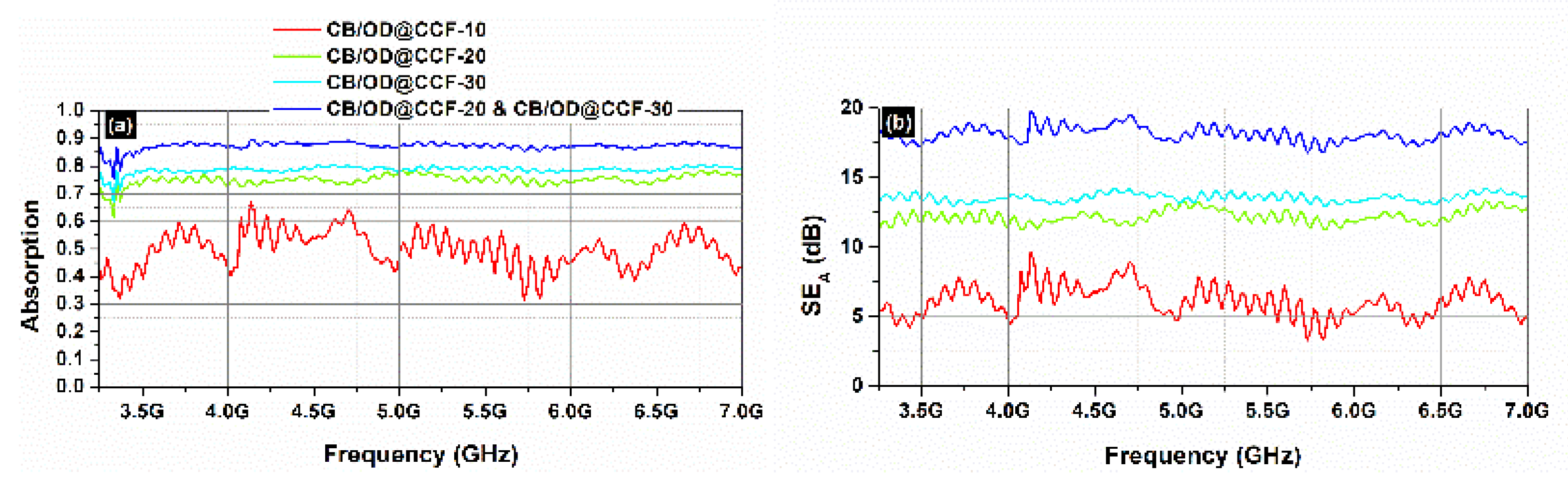
Like previously, the dominant shielding mechanism is absorption, which is also supported by the continuously increasing absorption levels with increasing OD@CCF content in the cement board composites.
Figure 14 depicts the absorption (
Figure 14a) and the total shielding efficiency (
SET) (
Figure 14b) spectra of the CB/OD@CCF composite samples for a series of shape stabilized octadecane stabilized in carbon foam OD@CCF concentrations, in the frequency range 3.2-7.0 GHz.
It is worth noticing that the
SEA levels of the cement board samples are higher that the corresponding ones of the gypsum samples, reaching a value of ~19.5 dB for the combination of CB/OD@CCF-20 with the CB/OD@CCF-30 samples (compared to ~18 dB for GB/OD@CCF-20 & CB/OD@CCF-20. Concrete and cementitious composites in general, are very poor electrical conductors, but still conductors, at least compared to gypsum [
42,
43]; This is actually the reason for their enhanced EMI effect. Moreover, it has been shown that the dry resistance of cement specimens is related to the porosity inside the material and the free-moving ions [
44]. As shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, pore sizes inside the gypsum samples are much smaller, compared to cement boards; As a result some of the big channels available for free ion movement in CB/OD@CCF composite boards (
Figure 4), close in GB/OD@CCF samples, and consequently the mean path of ion movement increases [
45]. In turn, this changes the electrical conductivity of gypsum (compared to cement) boards and increases the resistance, which decreases EMI accordingly.
3.5. Thermal Performance Measurements
To assess the thermal performance of the test samples, the upper environmental chamber underwent an 8h heating phase, followed by an 8h cooling period.
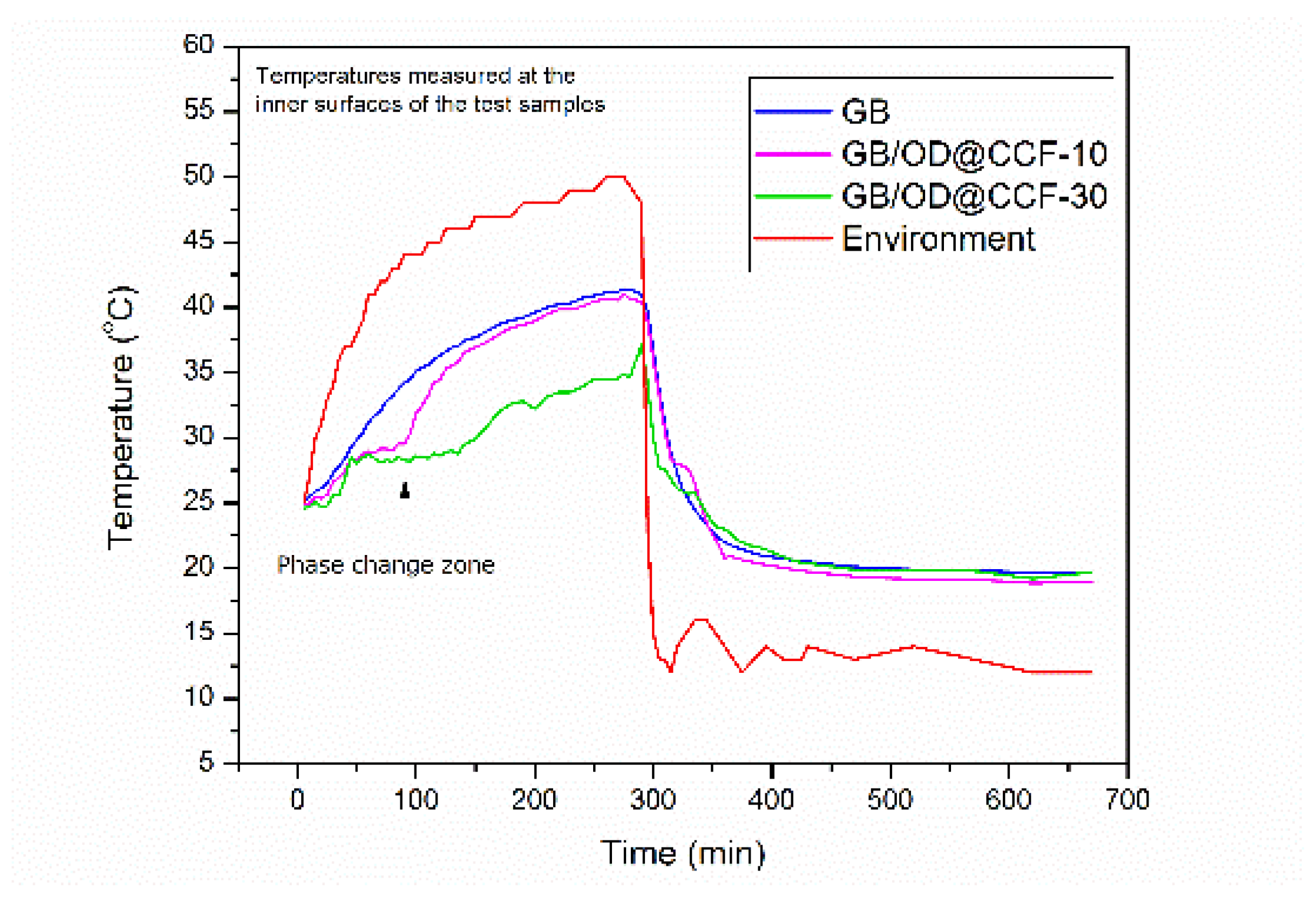
Figure 15 displays the temperature curve of the environmental chamber and the temperature curves measured at the lower surface of the samples, specifically the surface within the testing room of each sample, namely gypsum boards GB/OD@CCF-10, GB/OD@CCF-30, and the reference gypsum board GB.
In the first 45 minutes of heating, the rate of temperature increase (RTI) of the GB/OD@CCF-10 and GB/OD@CCF-30 samples is identical to that of the reference sample. At this point, the temperature is 28°C. After this point, the phenomenon of phase change of the stabilized PCMs begins. The absorption of the required heat for the n-octadecane change from solid to liquid is depicted by the decrease in the RTI of the two samples and the appearance of a “plateau” in their temperature curves (phase change zone). Interestingly, the duration of this plateau in each sample is obviously related to their different paraffin loading. In GB/OD@CCF-10, the phase change zone extends to 90 minutes, while in GB/OD@CCF-30 it extends to 135 minutes. When all the paraffin has become liquid, a brief sharp increase in the RTI of the two samples compared to that of the reference sample is observed, followed by a smoothing of these rates and their equalization with the reference. The difference in the absolute temperatures of the two samples compared to the reference is also noteworthy. GB/OD@CCF-10 has a difference of approximately 2°C, and GB/OD@CCF-30 has a difference of approximately 7°C, highlighting the effect of the loading percentage on the effectiveness of the advanced gypsum board to maintain a lower temperature within a space. The response of the samples to the subsequent sudden cooling of the environmental chamber confirms the positive effect of the higher paraffin content on the properties of the gypsum board. The rate of temperature decrease of the GB/OD@CCF-30 sample is noticeably lower than that of the GB/OD@CCF-10 sample in the phase change zone. Furthermore, the final temperature of GB/OD@CCF-30 is approximately 2°C higher than that of the reference.
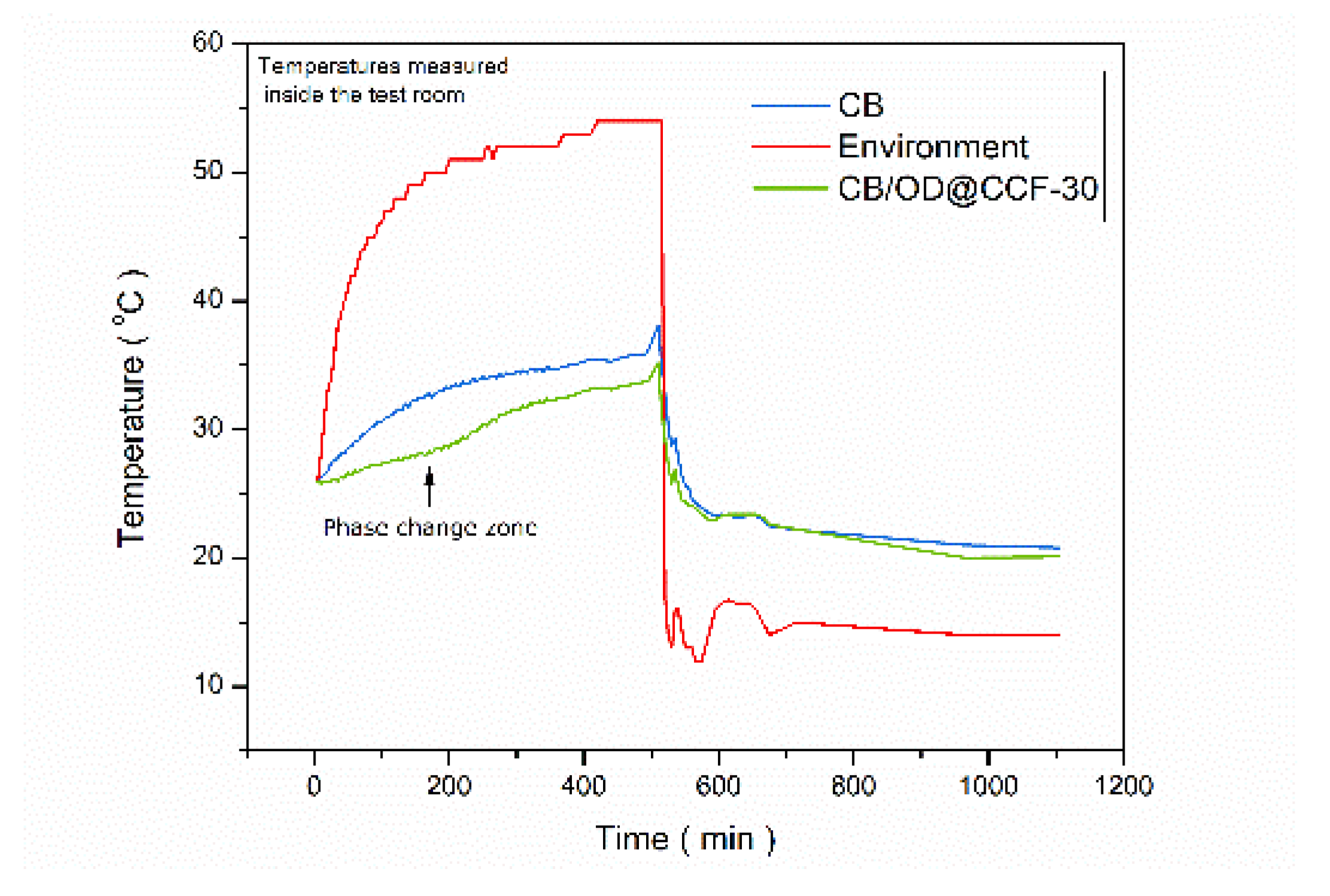
The temperature curves of the indoor spaces of the test rooms are shown in
Figure 16 along with the temperature curve of the environmental chamber. Specifically, the temperature variation is recorded in the environmental chamber and in the test rooms (indoor temperature) of the reference cement board CB, and the cement board CB/OD@CCF-30 respectively.
As the temperature of the environmental chamber increases, a difference in the rate of temperature increase (RTI) is observed between the reference sample CB and the CB/OD@CCF-30 sample. This difference, evident near 28°C, can be attributed to the thermal energy absorbed by the CB/OD@CCF-30 sample for the phase change of the stabilized PCM from solid to liquid. Notably, the phase change zone stabilizes the temperature in the test room around 28°C for approximately 3 hours, unlike the reference cement board CB test room temperature, which steadily rises to around 33°C during the same period. Subsequently, after about 5.5 hours, the RTI in both rooms becomes similar. The absolute temperature difference between the two rooms remains constantly at approximately 2.3°C. It is evident that the cement board with the stabilized n-octadecane has the capability to maintain the room cooler for a longer period compared to the plain reference cement board.
4. Conclusions
To summarize, this research represents a significant step forward in the development of cement and gypsum building boards infused with shape-stabilized n-octadecane within carbon-based foams, aiming to improve energy storage and electromagnetic interference shielding capabilities. Our investigation underscores the critical importance of optimizing the concentration of shape-stabilized n-octadecane in these composite materials. Determining the optimal concentration is pivotal for achieving the desired balance between enhanced energy storage, EMI shielding, and mechanical properties.
Key findings from this study include:
i) Incorporating OD@CCF into gypsum and cement boards enhances thermal energy storage properties, resulting in improved thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity. Notably, temperature differentials of up to 7°C were observed between reference gypsum and composite board inner surfaces, with a 2.3°C improvement in the indoor test room temperature for composite cement boards.
ii) EMI shielding properties also improve with increasing OD@CCF content, with the combination of boards containing 20% and 30% OD@CCF achieving EMI shielding absorption levels of approximately 18 dB and 19.5 dB for gypsum and cement boards, respectively.
iii) Mechanical properties remain largely unaffected with up to 20% OD@CCF additive in both gypsum and cement boards. Particularly for gypsum boards, the modulus of rupture increases by approximately 19% compared to the baseboard. However, mechanical degradation is observed with higher additive loadings.
Overall, these positive results pave the way for practical applications and future innovations in construction materials. They offer a sustainable and technologically advanced solution for enhancing energy storage and EMI shielding in building environments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: Preprints.org, Table S1: The melting and solidification temperatures (Tm and Ts, respectively) and enthalpies (ΔHm and ΔHs, respectively) derived from DSC measurements; Table S2: Thermal conductivity (k), thermal effusivity (e), specific heat capacity (Cp) and density (d) of reference gypsum or cement board and the corresponding composite boards. Table S3: Mechanical properties of CB reference and composite boards derived from compression tests. Compressive strength, Compressive modulus, percentage of compressive strength (ICS) and compressive modulus (ICM) of CB respective values; Figure S1: DSC curves of pure n-octadecane; Figure S2: Pictures from the custom made environmental chamber. a) The chamber during the measurements, b) and c) the internal area of the chamber.
Author Contributions
Supervision, M.A.K. and G.K.; project administration, M.A.K. and G.K.; funding acquisition, M.A.K. and G.K; conceptualization, M.A.K. and G.K.; methodology, M.A.K. and G.K.; investigation, C.G., K.C.V., Z.V., and A.N.; formal analysis, C.G., K.C.V., Z.V., C.E.S., M.A.K. and G.K.; data curation, M.A.K., G.K., Z.V., C.G., K.C.V., M.B., A.N., A.P. and C.E.S.; validation, C.E.S.; resources, M.A.K., G.K., and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B., G.K, and M.A.K.; writing—review and editing, G.K., K.C.V., M.B. and M.A.K.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work co-financed by the project “Advanced Nanostructured Materials for Sustainable Growth: Green Energy Production/Storage, Energy Saving and Environmental Remediation” (TAEDR-0535821) which is implemented under the action “Flagship actions in interdisciplinary scientific fields with a special focus on the productive fabric” (ID 16618), Greece 2.0 – National Recovery and Resilience Fund and funded by European Union NextGenerationEU. Also, the work was co-financed by the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation, under the call RESEARCH—CREATE—INNOVATE (acronym: SEMI-WEB; project code: T2EDK-02073) and it was also supported by proposal number 101092339 (Exploit4InnoMat), under the call: HORIZON-CL4-2022-RESILIENCE-01 (topic: HORIZON-CL4-2022-RESILIENCE-01-20; type of action: HORIZON-IA).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Τhe authors would like to thank the companies, Energy Houses (ENHSS, Serres, Greece) and KNAUF (Amfilochia, Greece) for supplying us with raw materials for the production of cement and gypsum boards respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rashid, F.L.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Dulaimi, A.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Eleiwi, M.A.; Mahood, H.B.; Hashim, A. A Review of Recent Improvements, Developments, Effects, and Challenges on Using Phase-Change Materials in Concrete for Thermal Energy Storage and Release. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, S.M.; Antony, T.; Grohens, Y.; Thomas, S. From Waste to Wealth: A Critical Review on Advanced Materials for EMI Shielding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, A.; Velraj, R.; Seeniraj, R.V. Phase Change Material-Based Building Architecture for Thermal Management in Residential and Commercial Establishments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, K.; Khaled, M.; Faraj, J.; Hachem, F.; Castelain, C. A Review on Phase Change Materials for Thermal Energy Storage in Buildings: Heating and Hybrid Applications. J. Energy Storage 2021, 33, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnæs, S.E.; Jelle, B.P. Phase Change Materials and Products for Building Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review and Future Research Opportunities. Energy Build. 2015, 94, 150–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Joseph, A.; Elsharkawy, M.; Hamada, M.A.; Kandeal, A.W.; Elkadeem, M.R.; Kumar Thakur, A.; Ma, Y.; Eid Moustapha, M.; Rashad, M.; et al. Thermal Energy Storage Using Phase Change Materials in Building Applications: A Review of the Recent Development. Energy Build. 2023, 285, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Li, M.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y. Development of Cost-Effective PCM-Carbon Foam Composites for Thermal Energy Storage. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1696–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioti, C.; Karakassides, A.; Asimakopoulos, G.; Baikousi, M.; Salmas, C.E.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Kenanakis, G.; Karakassides, M.A. Multifunctional Carbon-Based Hybrid Foams for Shape-Stabilization of Phase Change Materials, Thermal Energy Storage, and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Functions. Micro 2022, 2, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Mai, X.; Naik, N.; Pan, D.; Guo, Z.; Shi, Z. Review on the Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of Carbon Based Materials and Their Novel Composites: Recent Progress, Challenges and Prospects. Carbon 2021, 176, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X. Preparation and Characterization of Polyethylene Glycol/Active Carbon Composites as Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadiran, T.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z.; Rusli, R. Shape-Stabilised n-Octadecane/Activated Carbon Nanocomposite Phase Change Material for Thermal Energy Storage. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 55, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Leng, Z.; Lu, G.; Wang, D.; Huo, Y. A Critical Review of Carbon Materials Engineered Electrically Conductive Cement Concrete and Its Potential Applications. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2023, 14, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.K.S.; Shukla, S.K. Enhanced Thermophysical Properties of Organic PCM through Shape Stabilization for Thermal Energy Storage in Buildings: A State of the Art Review. Energy Build. 2021, 236, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.O.; Yang, X.; Paul, S.C.; Susilawati; Wong, L. S.; Kong, S.Y. Development of Thermal Energy Storage Lightweight Concrete Using Paraffin-Oil Palm Kernel Shell-Activated Carbon Composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Li, J. Octadecane/C-Decorated Diatomite Composite Phase Change Material with Enhanced Thermal Conductivity as Aggregate for Developing Structural–Functional Integrated Cement for Thermal Energy Storage. Energy 2018, 142, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiu, S.; Chen, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Modified Activated Carbon-Based Shape Stabilized Eutectic Phase Change Materials for Gypsum Composites Application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioti, C.; Vasilopoulos, K.C.; Baikousi, M.; Salmas, C.E.; Ntaflos, A.; Paipetis, A.S.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Ikram, R.; Agathopoulos, S.; Kenanakis, G.; et al. Enhanced Gypsum Boards with Activated Carbon Composites and Phase Change Materials for Advanced Thermal Energy Storage and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties. Micro 2024, 4, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioti, C.; Karakassides, A.; Asimakopoulos, G.; Baikousi, M.; Salmas, C.E.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Kenanakis, G.; Karakassides, M.A. Multifunctional Carbon-Based Hybrid Foams for Shape-Stabilization of Phase Change Materials, Thermal Energy Storage, and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Functionsmi. Micro 2022, 2, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, U.W.; Etuk, S.E.; Agbasi, O.E. Modified Water Displacement Method and Its Use for Determination of Bulk Density of Porous Materials. J. Renew. Energy Mech. REM 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Measurement of Thermal Effusivity of Fabrics Using a Modified Transient Plane Source (MTPS) Instrument. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d7984-21.html (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam With Center-Point Loading). Available online: https://www.astm.org/c0293_c0293m-16.html (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- ASTM C109/C109M-20. Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-Mm] Cube Specimens) 2020.
- Cui, H.; Tang, W.; Qin, Q.; Xing, F.; Liao, W.; Wen, H. Development of Structural-Functional Integrated Energy Storage Concrete with Innovative Macro-Encapsulated PCM by Hollow Steel Ball. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard EN 13279-1. Gypsum Binders and Gypsum Plasters. Part 1: Definitions and Requirements. 2009. Available From: Available online: https://www.en.une.org/encuentra-tu-norma/busca-tu-norma/norma?c=N0043416 (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- López Pedrajas, D.; Borreguero Simón, A.M.; Sáenz, I.G.; Ramos, F.J.; Rodríguez Romero, J.F.; Carmona Franco, M. Thermoregulating Gypsums by Using Nanoencapsulated Phase Change Material Slurry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 9959–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid Jameel, M.; Al-Asadi, L.S.M.; Abd Hacheem, Z.; AL-Ridha, A.S.D. Effect of Chopped Carbon Fibre (CCF) on Enhancing the Compressive Strength and Density of Gypsum Plaster. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.U.; Park, J.H.; Yun, B.Y.; Yang, S.; Wi, S.; Kim, S. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Artificial Stone Finishing Materials Mixed with PCM Impregnated Lightweight Aggregate and Carbon Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X. Preparation, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Cement Board with Expanded Perlite Based Composite Phase Change Material for Improving Buildings Thermal Behavior. Materials 2015, 8, 7702–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Geng, L.; Fang, Y. Enhancement on Thermal Properties of Paraffin/Calcium Carbonate Phase Change Microcapsules with Carbon Network. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, T.; Tang, W.; Cui, H. Mechanical and Thermo-Physical Performances of Gypsum-Based PCM Composite Materials Reinforced with Carbon Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.; Jin, X.; Lo, T.Y.; Cui, H. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Expanded Graphite/Paraffin Gypsum-Based Composite Material Reinforced by Carbon Fiber. Materials 2018, 11, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, C. Perlite: The Most Sustainable Insulation Solution for Buildings. Available online: https://www.perlite.org/perlite-the-most-sustainable-insulation-solution-for-buildings/ (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Sedaghat, A.; Ram, M.K.; Zayed, A.; Kamal, R.; Shanahan, N. Investigation of Physical Properties of Graphene-Cement Composite for Structural Applications. Open J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 4, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Jiang, L.; Xu, N.; Jin, M.; Jiang, S. Enhancement of Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Graphene/Cement Composite Due to Improved Dispersion of Graphene by Addition of Silica Fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahawi, A.; Öztürk, O.; Emami, F.; Yıldırım, G.; Şahmaran, M. Effect of Mixing Methods on the Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Incorporating Different Carbon-Based Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 104, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Singh, A.P.; Sambyal, P.; Singh, B.P.; Dhawan, S.K.; Choudhary, V. Barium Ferrite Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Effective Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 17, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Saadeh, W.H.; Sundararaj, U. EMI Shielding Effectiveness of Carbon Based Nanostructured Polymeric Materials: A Comparative Study. Carbon 2013, 60, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskadourakis, Z.; Vasilopoulos, K.C.; Economou, E.N.; Soukoulis, C.M.; Kenanakis, G. Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of 3D Printed Polymer Composites. Appl. Phys. Mater. Sci. Process. 2017, 123, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Nie, W.; Wang, P.; Li, C. Roll-to-Roll Layer-by-Layer Assembly Bark-Shaped Carbon Nanotube/Ti3C2Tx MXene Textiles for Wearable Electronics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qiu, H.; Gu, J. Structural Design Strategies of Polymer Matrix Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Gelves, G.A.; Sundararaj, U. Copper Nanowire/Polystyrene Nanocomposites: Lower Percolation Threshold and Higher EMI Shielding. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Liu, S.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, J. Cement Based Electromagnetic Shielding and Absorbing Building Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Ou, J. Electromagnetic Wave Shielding/Absorbing Concrete. In Smart and Multifunctional Concrete Toward Sustainable Infrastructures; Han, B., Zhang, L., Ou, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 313–328; ISBN 978-981-10-4349-9. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, A.; Niklasson, G.A.; Brantervik, K.; Hedberg, B.; Nilsson, L.O. Dielectric Properties of Cement Mortar as a Function of Water Content. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 5897–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasinghe, D.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Effect of Water to Cement Ratio, Fly Ash, and Slag on the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Photos from the (a) reference gypsum board (GB) and GB/OD@CCF composite boards with (b) 10, (c) 20 and (d) 30% OD@CCF additive.
Figure 1.
Photos from the (a) reference gypsum board (GB) and GB/OD@CCF composite boards with (b) 10, (c) 20 and (d) 30% OD@CCF additive.
Figure 2.
Photos from the (a) reference cement board (CB) and CB/OD@CCF composite boards with (b) 10, (c) 20 and (d) 30% OD@CCF additive.
Figure 2.
Photos from the (a) reference cement board (CB) and CB/OD@CCF composite boards with (b) 10, (c) 20 and (d) 30% OD@CCF additive.
Figure 3.
Density variation of (a) GB/OD@CCF and (b) CB/OD@CCF composites as a function of the percentage content of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 3.
Density variation of (a) GB/OD@CCF and (b) CB/OD@CCF composites as a function of the percentage content of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 4.
X-ray computed microtomography (micro CT) images from CB reference board (a) and CB/OD@CCF composite boards with 10% (b), 20% (c) and 30% (d) OD@CCF content.
Figure 4.
X-ray computed microtomography (micro CT) images from CB reference board (a) and CB/OD@CCF composite boards with 10% (b), 20% (c) and 30% (d) OD@CCF content.
Figure 5.
X-ray computed microtomography (micro CT) images from GB reference board (a) and GB/OD@CCF composite boards with 10% (b), 20% (c) and 30% (d) OD@CCF content.
Figure 5.
X-ray computed microtomography (micro CT) images from GB reference board (a) and GB/OD@CCF composite boards with 10% (b), 20% (c) and 30% (d) OD@CCF content.
Figure 6.
DSC curves of (a) GB/OD@CCF and (b) CB/OD@CCF with various % OD@CCF.
Figure 6.
DSC curves of (a) GB/OD@CCF and (b) CB/OD@CCF with various % OD@CCF.
Figure 7.
Variations in ΔHm and ΔHs values of composite boards GB and CB at different percentages of OD@CCF content.
Figure 7.
Variations in ΔHm and ΔHs values of composite boards GB and CB at different percentages of OD@CCF content.
Figure 8.
(a) Thermal conductivity, denoted as ‘k’, and (b) Specific heat capacity, abbreviated as ‘Cp’, for gypsum and cement boards with varying percentages of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 8.
(a) Thermal conductivity, denoted as ‘k’, and (b) Specific heat capacity, abbreviated as ‘Cp’, for gypsum and cement boards with varying percentages of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 9.
Curves representing (a) load-deformation and (b) modulus of rupture extracted from bending tests conducted on gypsum boards with varying loading of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 9.
Curves representing (a) load-deformation and (b) modulus of rupture extracted from bending tests conducted on gypsum boards with varying loading of OD@CCF additive.
Figure 10.
Results from compression tests for cement boards CB with varying % content of OD@CCF additive. (a) Representative stress-strain curves and (b) compressive strength versus OD@CCF content.
Figure 10.
Results from compression tests for cement boards CB with varying % content of OD@CCF additive. (a) Representative stress-strain curves and (b) compressive strength versus OD@CCF content.
Figure 11.
Transmission S21 (a) and reflection S11 (b) coefficients from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different gypsum board samples.
Figure 11.
Transmission S21 (a) and reflection S11 (b) coefficients from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different gypsum board samples.
Figure 12.
Absorption (a) and SEA (b) from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different gypsum board samples.
Figure 12.
Absorption (a) and SEA (b) from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different gypsum board samples.
Figure 13.
Transmission S21 (a) and reflection S11 (b) coefficients from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different cement board samples.
Figure 13.
Transmission S21 (a) and reflection S11 (b) coefficients from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different cement board samples.
Figure 14.
Absorption (a) and SEA (b) from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different cement board samples.
Figure 14.
Absorption (a) and SEA (b) from 3.2 to 7.0 GHz (C-band) for different cement board samples.
Figure 15.
Curves from thermal performance measurements for gypsum board samples with 10 and 30% OD@CCF loadings in comparison with the reference gypsum board GB.
Figure 15.
Curves from thermal performance measurements for gypsum board samples with 10 and 30% OD@CCF loadings in comparison with the reference gypsum board GB.
Figure 16.
Curves from thermal performance measurements for cement board sample with 30% OD@CCF loading in comparison with the reference cement board.
Figure 16.
Curves from thermal performance measurements for cement board sample with 30% OD@CCF loading in comparison with the reference cement board.
Table 1.
Composition of ingredients used in the manufacturing of Cement Boards.
Table 1.
Composition of ingredients used in the manufacturing of Cement Boards.
| Sample |
Cement
(g) |
Water
(g) |
Perlite (ml) |
Polypropylene Fibers (g) |
Resin (ml) |
OD@CCF
(g) |
| CB |
624 |
624 |
2080 |
2.08 |
10.4 |
- |
| CB/OD@CCF-10 |
624 |
624 |
1936 |
2.08 |
10.4 |
144 |
| CB/OD@CCF-20 |
624 |
624 |
1780 |
2.08 |
10.4 |
300 |
| CB/OD@CCF-30 |
624 |
624 |
1648 |
2.08 |
10.4 |
432 |
Table 2.
Composition of ingredients used in the manufacturing of Gypsum Boards.
Table 2.
Composition of ingredients used in the manufacturing of Gypsum Boards.
| Sample |
Gypsum
(g) |
Water
(g) |
Starch
(g) |
OD@CCF
(g) |
| GB |
550 |
448 |
28.5 |
- |
| GB/OD@CCF-10 |
495 |
448 |
28.5 |
55 |
| GB/OD@CCF-20 |
440 |
448 |
28.5 |
110 |
| GB/OD@CCF-30 |
385 |
448 |
28.5 |
165 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).