Submitted:
22 April 2024
Posted:
23 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Working Methodology
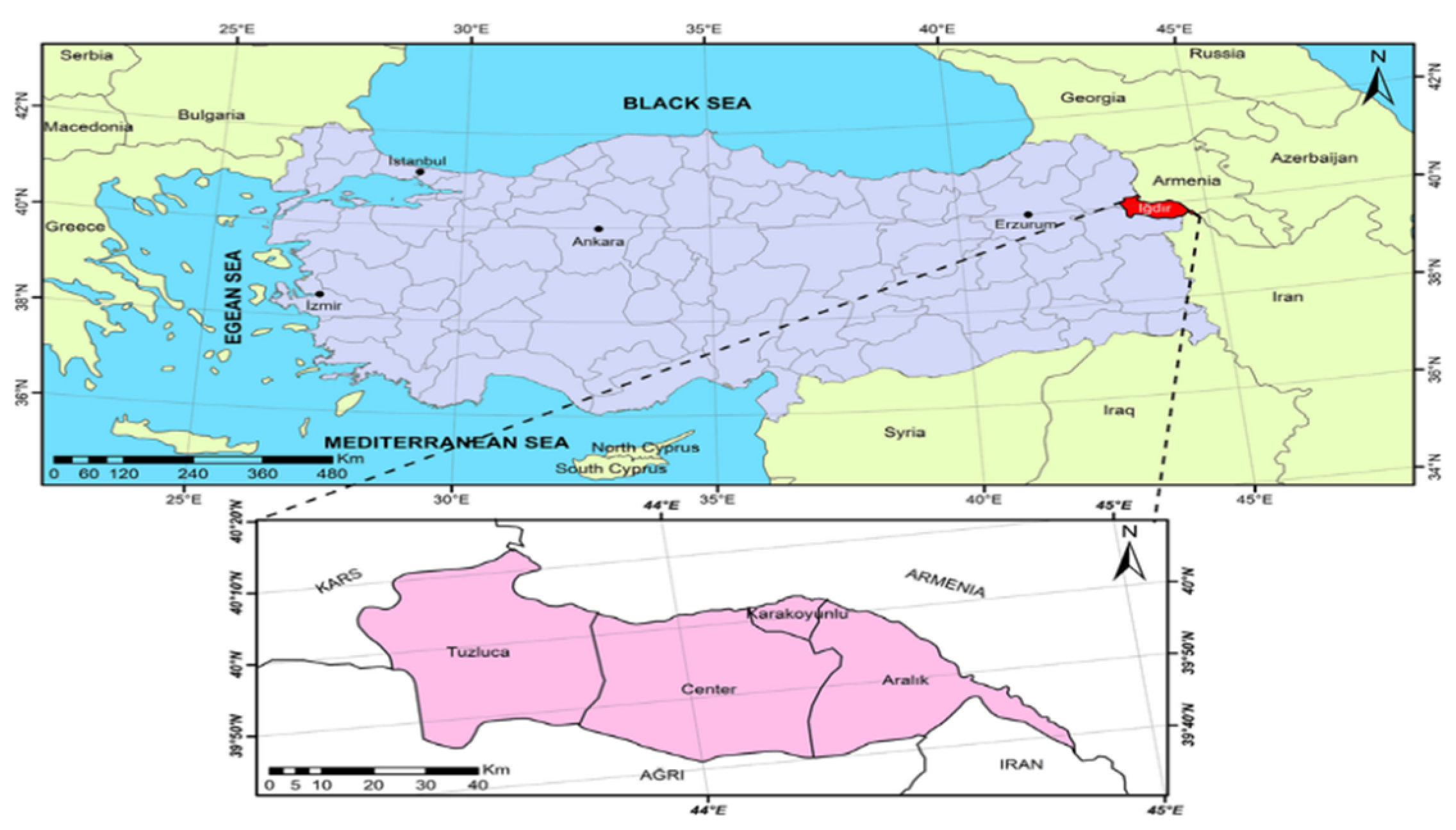
2.2. Working Area
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusion
References
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Yang, X. et al., Natural Resources Depletion, Financial Risk, and Human Well-Being: What is the Role of Green Innovation and Economic Globalization. Soc Indic Res 2023, 167, 269–288. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G. M.; Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) Environmental solution and climate change adaptation, Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 297, 126604. [CrossRef]
- Allan, C.; Xia, J.; Pahl-Wostl, C. Climate change and water security: challenges for adaptive water management, Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2013, 5 (6), 625-632. [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, M. H. Farmers Attitudes to the Pricing of Natural Resources for Sustainability: GAP-Şanlıurfa Sampling of Turkey. Water 2019, 11(9), 1772. [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, M. H.; Kaya, F. Factors Affecting Consumers’ Consumption of Organic Foods: A Case Study in GAP-Şanlıurfa in Turkey. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology 2020, 22 (2), 347-359.
- Aydogdu, M. H.; Aydoğdu, İ.; Cevheri, A. C.; Sevinç, M. R.; Küçük, N. Şanlıurfa’daki yem bitkileri eken çiftçilerin sosyo-ekonomik profilinin analizi, Journal of Ekonomi 2020, 10-15, 2687-2390.
- Aydogdu, M. H.; Sevinç, M. R.; Cançelik, M.; Parlakçı Doğan, H., Şahin, Z. Determination of Farmers’ Willingness to Pay for Sustainable Agricultural Land Use in the GAP-Harran Plain of Turkey. Land 2020, 9, 261. [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, M.H.; Yenigün K. Farmers’ Risk Perception towards Climate Change: A Case of the GAP-Sanlıurfa Region, Turkey. Sustainability 2016, 8, 806.
- Baran, M. F.; Gökdoğan, O. Karpuz ve Kavun Yetiştiriciliğinde Enerji Girdi-Çıktı Analizi: Kırklareli İli Örneği, Anadolu Tarım Bilim. Dergisi 2014, 29(3), 217-224.
- Bashimov, G. Elma İhracatında Türkiye’nin Karşılaştırmalı Üstünlüğü, Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Dergisi 2016, 13(2), 9-15.
- Beckman, J,; Countryman, A.M.The Importance of Agriculture in the Economy: Impacts from COVID-19. Am J Agric Econ. 2021, 103(5), 1595-1611. [CrossRef]
- BUGEM. Tarım ve Orman Bakanlığı, Bitkisel Üretim Verileri, https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/sgb/Belgeler/SagMenuVeriler/BUGEM.pdf 2022.
- Cançelik, M.; Şahin, Z.; Sevinç, M.R.; Küçük, N.; Aydoğdu, M. H. The Analysis of the Recent Periods of Wheat Market in Turkey, Journal of Engineering and Technology for Industrial Applications (ITEGAM-JETIA) 2021, 7(27), 57-62.
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Bertaki, M. Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture under Climate Change, Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2015, 4, 88-98. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, D.; Ming, G.; Hussain, F.; Ma, L.; Huang, Q.; Meng, X. Evaluation of Water Balance and Water Use Efficiency with the Development of Water-Saving Irrigation in the Yanqi Basin Irrigation District of China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2990. [CrossRef]
- Chu, E. W,; Karr, J.R. Environmental Impact: Concept, Consequences, Measurement. Reference Module in Life Sciences. 2017, B978-0-12-809633-8.02380-3.
- Demirok, A.; Tuylu, G. İ. Harran Ovası’nda Mısır Bitkisi (Zea mays L.) için Planlanan ve Gerçekleşen Sulama Zamanı Programının Değerlendirilmesi, Harran Tarım ve Gıda Bilimleri Dergisi 2017, 21(1), 84 – 90.
- Devi, K. P.; Chaturvedi, H. Chapter 9 - An overview of nanotechnology in water treatment applications and combating climate change, Binota Thokchom, Pengpeng Qiu, Pardeep Singh, Parameswar K. Iyer, Water Conservation in the Era of Global Climate Change, Elsevier 2021, 191-212.
- DSİ, DSİ 24. Bölge Müdürlüğü, Toprak ve Su Kaynakları 2023a, https://bolge24.dsi.gov.tr/Sayfa/Detay/967.
- DSİ, DSİ 24. Bölge Müdürlüğü, Toprak ve Su Kaynakları, Sulama Randımanları 2023b, https://bolge24.dsi.gov.tr/Sayfa/Detay/957.
- FAO, Food and Agriculture Organizations of United Nations, CROPWAT, Land-Water 1996, https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/cropwat/en/.
- Filho, W.L.; Wall, T.; Mucova, S. A. R.; Nagy, G. J.; Balogun, A.; Luetz, J. M.; Artie W. Ng.; Kovaleva, M.; Azam, F. M. S.; Alves, F.; Guevara, Z.; Matandirotya, N. R.; Skouloudis, A.; Tzachor, A.; Malakar, K.; Gandhi, O. Deploying artificial intelligence for climate change adaptation, Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2022, 180, 121662. [CrossRef]
- Fredrick, M. K. E.; Mwanzia, J.; Nyabuto, W. Influencers of Performance Contracting in Service Delivery: A Trend Analysis in the State Department of Water and Irrigation of Kenya. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences 2020, 10(11), 193-214. [CrossRef]
- Gago, J.; Douthe, C.; Florez-Sarasa I.; Jose M. E.; Jeroni G.; Alisdair R. F.; Jaume F.; Hipolito M. Opportunities for improving leaf water use efficiency under climate change conditions, Plant Science 2014, 226, 108-119.
- Gürgülü, H.; Ul, M. A. İzmir’de Yetiştirilen Bazı Bitkiler İçin Bitki Su Tüketimi Değerleri ve Sulama Programları, Ege Üniv. Ziraat Fak. Derg., 2017, 54 (3):311-317.
- He, D.; Gao, P.; Sun, Z.; Lau, Y. Measuring Water Transport Efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Zone, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2278. [CrossRef]
- Hedley, C. B.; Yule, I. J.; Tuohy, M. P.; Vogeler I. Key Performance Indicators for Simulated Variable-Rate Irrigation of Variable Soils in Humid Regions. The American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, the ASABE 2009, 52(5): 1575-1584. [CrossRef]
- Hemathilake, D.M.K.S.; Gunathilake, D.M.C.C. Chapter 31-Agricultural productivity and food supply to meet increased demands, Editor(s): Rajeev Bhat, Future Foods, Academic Press 2022, 539-553.
- Hong, N.B., Yabe, M. Improvement in irrigation water use efficiency: a strategy for climate change adaptation and sustainable development of Vietnamese tea production. Environ Dev Sustain 2017, 19, 1247–1263. [CrossRef]
- Jerry L. H.; Christian D. Water-Use Efficiency: Advances and Challenges in a Changing Climate. Front. Plant Sci., Sec. Plant Physiology 2019,10.
- Karam, F.; Nassif, N.; Mouneimne, A.H.; El Hachem, C.; Saadeh, I. Determination of some Key Performance Indicators for some strategic crops within South Bekaa Irrigation scheme in Lebanon. 2022, Available online at: www.crea.uclm.es.
- Kazak, G.; Özşenler, S.; Artukoğlu, M. M.; Yıldız, Ö. 2018. Sanayi Domatesi Üretimi ve Pazarlamasında Karşılaşılan Sorunlar: İzmir İli Torbalı İlçesi Örneği, Tarım Ekonomisi Dergisi, 2018, 24(2), 215-223.
- Lencucha, R.; Pal, N.E.; Appau, A. et al. Government policy and agricultural production: a scoping review to inform research and policy on healthy agricultural commodities. Global Health 2020, 16, 11. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo R.; Adapting agriculture to climate change via sustainable irrigation: biophysical potentials and feedbacks, Environ. Res. Lett. 17 063008, 2022 17, 6.
- Maimun, R.; Abdullah, N.; Dan, S.The Field application efficiency Assessment of Paddy Field inAceh Irrigation Scheme, Aceh, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2023, 012008.
- Maja, M. M.; Ayano, S. F. The Impact of Population Growth on Natural Resources and Farmers’ Capacity to Adapt to Climate Change in Low-Income Countries, Earth Systems and Environment 2021, 5(2), 271–283. [CrossRef]
- Malek, K.; Adam, J.; Stockle, C.; Brady, M.; Rajagopalan, K. Water Resources Research, When Should Irrigators Invest in More Water-Efficient Technologies as an Adaptation to Climate Change? 2018, 54(11):8999-9032. [CrossRef]
- Mangrio, M.; Mirjat, M.; Leghari, N.; Zardari, N, H.; Shaikh, I. Evaluatıng Water Applıcatıon Effıcıencıes Of Surface Irrıgatıon Methods At Farmer’s Fıeld. Pakistan Journal of Agriculture, Agricultural Engineering & Veterinary Sciences 2015, 279-288.
- MGM,. Meteoroloji Genel Müdürlüğü, Iğdır İklim Verileri, https://www.mgm.gov.tr/veridegerlendirme/il-ve-ilceler-istatistik.aspx?m=IGDIR 2023a.
- MGM, Meteoroloji Genel Müdürlüğü, yılı Türkiye iklim raporu ve değerlendirmeleri, https://www.mgm.gov.tr/iklim/iklim-raporlari.aspx 2023b.
- Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Christou, A.; Kitta, E.; Katsoulas, N. Implementing Sustainable Irrigation in Water-Scarce Regions under the Impact of Climate Change. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1120. [CrossRef]
- Ogata, R.; Mahasneh, S.; Alananbeh, A.; Fujii, N. Insights into water service quality in Jordan from key performance indicators and consumer perceptions, Utilities Policy 2022, 78101406. [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, Y.; Yulu, A,; Turgay, O. Remote sensing supported analysis of the effect of wind erosion on local air pollution in arid regions: A case study from Iğdır province in eastern Türkiye. Environmental Systems Research 2023. [CrossRef]
- Özüpekçe, S. Malatya’da Tarımsal Arazi Kullanımı ve Kayısı Tarımının Önemi, Al-Farabi International Journal on Social Sciences, 2021, 6(1), 62-77.
- Parlakçı, D.; H., Aydogdu, M. H.; Sevinç, M. R.; Cançelik, M.; Farmers’ Willingness to Pay for Services to Ensure Sustainable Agricultural Income in the GAP-Harran Plain, Sanlıurfa, Turkey. Agriculture 2020 10, 152.
- Parra, L.; Botella-Campos, M.; Puerto, H.; Roig-Merino, B.; Lloret, J. Evaluating Irrigation Efficiency with Performance Indicators: A Case Study of Citrus in the East of Spain. Agronomy 2020 10, 1359. [CrossRef]
- Qilong, W.; Xiaodong, M.; Sahar, A.; 2022. Dynamic effects of natural resource abundance, green financing, and government environmental concerns toward the sustainable environment in China, Resources Policy 2022, 79, 102954.
- Rafiei-Sardooi, E.; Azareh, A.; Shooshtari, S. J.; Parteli, E.J.R. Long-term assessment of land-use and climate change on water scarcity in an arid basin in Iran, Ecological Modelling, 2022, 467, 109934. [CrossRef]
- Sanjeet, S.; Gagan, D. S.; Magdalena, R., Daniel, B. L and Pooja, B. Do natural resources impact economic growth: An investigation of P5 + 1 countries under sustainable management, Geoscience Frontiers 2023, 101595.
- Sheikha-Bagem, Ghaleh, S.; Babazadeh, H.; Rezaie, H. et al. The effect of climate change on surface and groundwater resources using WEAP-MODFLOW models. Appl Water Sci 2023 13, 121.
- 2021; 51. SYGM, Methodological Guide on Water Efficiency in the Agriculture Sector, General Directorate of Water Management, Ankara, 2021a.
- SYGM, 2021b. Su Yönetimi Genel Müdürlüğü, Aras Havzası Kuraklık Yönetim Planının Hazırlanması Projesi, Ön Raporu, SUPEK, Aralık, Ankara 2021b.
- Şimşek, M.; Gülsoy, E.; Karadaş, K.; Iğdır İlinin Meyvecilik Potansiyeli ve İl Ekonomisine Katkısı, Iğdır Üni. Fen Bilimleri Enst. Dergisi 2018,8(3), 39-44.
- TAGEM. Türkiye’de Sulanan Bitkilerin Su Tüketim Rehberi https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/TAGEM/Belgeler/yayin/Tu%CC%88rkiyede%20Sulanan%20Bitkilerin%20Bitki%20Su%20Tu%CC%88ketimleri.pdf 2017.
- TOB IĞDIR. Iğdır Tarım ve Orman İl Müdürlüğü, Iğdır Büyük Ova Koruma Alanı Genişletme Çalışmaları, https://igdir.tarimorman.gov.tr/Haber/599/Igdir-Buyukova-Koruma-Alani-Genisletme-Calismalari-Baslatildi 2023.
- TOB. Tarım ve Orman Bakanlığı, TEPGE, Tarım Ürünleri Piyasaları, Elma, https://arastirma.tarimorman.gov.tr › Belgeler 2021.
- TOB. Tarım ve Orman Bakanlığı, İstatistikler, https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/Konular/Bitkisel-Uretim/Organik-Tarim/Istatistikler 2022.
- TOB. Bitkisel Üretim Destekleme Tebliği, https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/Duyuru/1716/2022-Yili-Havzalarda-Desteklenecek-Urun-Listeleri 2023a.
- TOB. Tarım ve Orman Bakanlığı, Buğday Tarımı, https://arastirma.tarimorman.gov.tr › Buğday Tarımı 2023b.
- TÜİK, Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu, Tarım, Bitkisel Üretim İstatistikleri, https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Kategori/GetKategori?p=Tarim-111 2022.
- TÜİK,. Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu, Adrese Dayalı Nüfus Kayıt Sistemi Sonuçları, 2022, https://data.tuik.gov.tr › Bulten › Index 2023.
- UN Water.Water Scarcity, https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/water-scarcity 2023.
- Vural, H.; Çakan, V. A.. Türkiye Şeftali Piyasasının Ekonomik Analizi ve Pazarlama Marjları. KSÜ Tarım ve Doğa Dergisi 2021, 24 (2), 379-387.746725.
- Wassie, S.B. Natural resource degradation tendencies in Ethiopia: a review. Environ Syst Res 2020, 9, 33. [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, O. Sulama. Ankara Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Yayın No: 1540, Ders Kitabı: Ankara 2004, 493, 292.
- Zhang, F.; Ju, W.; Shen, S. et al. How recent climate change influences water use efficiency in East Asia. Theor Appl Climatol 2014, 116, 359–370. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T. Water saving efficiency and reliability of rainwater harvesting systems in the context of climate change, Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 196, 1341-1355. [CrossRef]
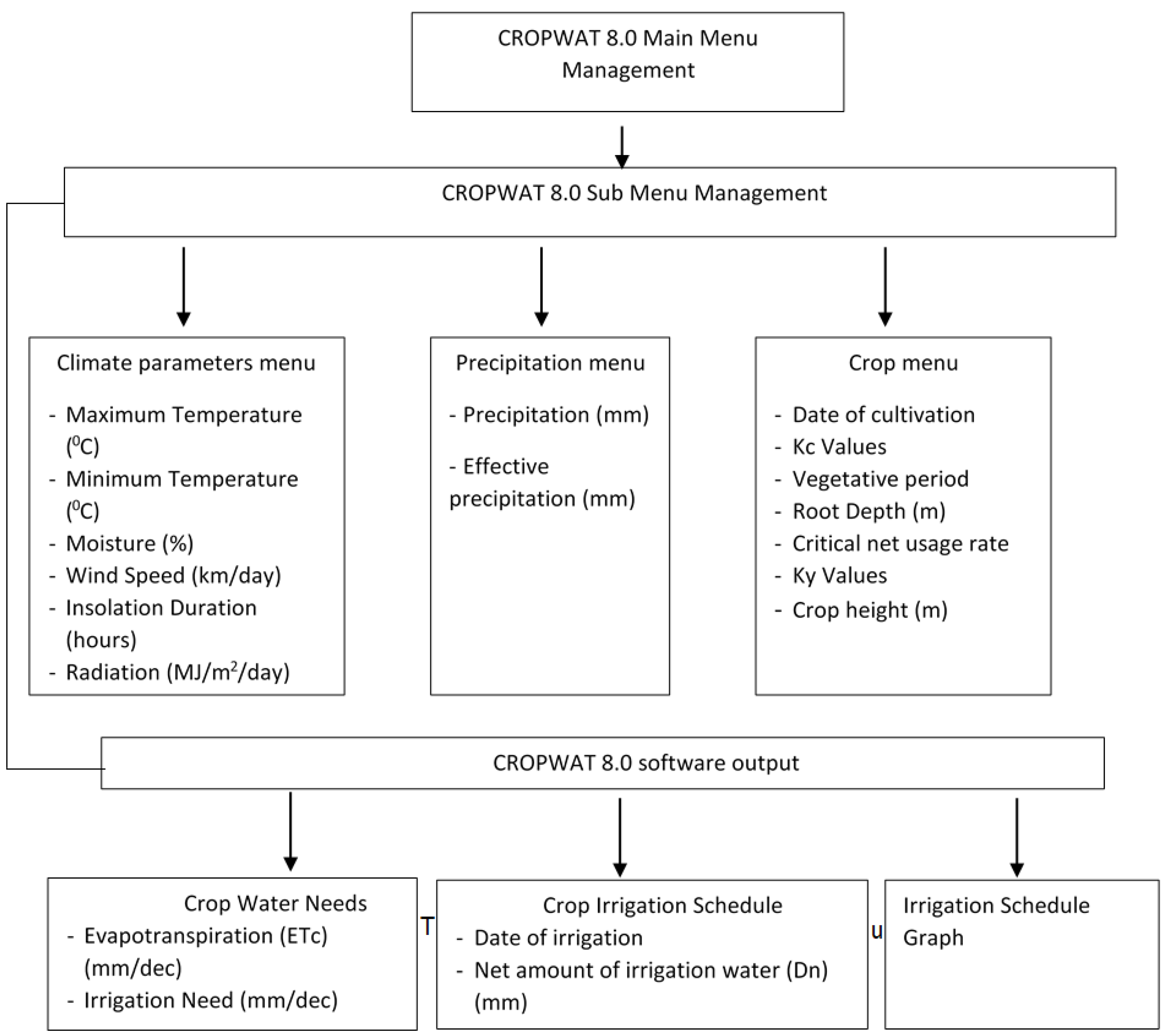
| Key performance indicators for water production and transmission performance |
Abstraction Performance (%): The ratio of the water volume at the beginning of the transmission line to the water volume abstracted from the resource (x100). Transmission Performance (%): The ratio of water directed for irrigation to the water volume at the beginning of the transmission line (x100). Water Losses Per the Length of Infrastructure (m³/km): The ratio of the volume of water loss to the length of the pipeline (ducts or pipes). Water Losses Per Irrigation Area (m³/ha): The ratio of the amount of water loss to the surface area of the irrigation area served. |
| Key performance indicators for irrigation and agricultural performance |
Crop Demands (m³/ha): The ratio of the amount of water used for each crop to the surface area of the crop considered. Irrigation System Performance (for flood, sprinkler and drip irrigation systems) (%): The ratio of the evapotranspiration of the considered crop to the volume used for irrigation by the system considered (x100). Application Performance (%): The ratio of the evapotranspiration of the considered crop to the volume of water allocated for irrigation of the crop considered (x100). Crop Yield Performance (m³/kg): The ratio of the volume of water allocated for irrigation of the crop considered (m³/ha) to the crop yield (kg/ha). Water Use Performance (kg/m³): The ratio of (yield of the irrigated crop-yield of the non-irrigated crop) to the volume of water allocated for irrigation of the crop considered (x100). |
| Crop pattern in the plain | Total (Hectares) | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Barley | 3,067.70 | 0.057 |
| Wheat* | 11,455.00 | 0.212 |
| Bean (dried) | 57.00 | 0.001 |
| Vetch (Green Grass) | 200.00 | 0.004 |
| Sainfoin (green grass) | 1,450.00 | 0.027 |
| Maize (Grain) - First Cultivation | 2.595,00 | 0.048 |
| Maize (Silage) * | 6,327.60 | 0.117 |
| Chickpeas | 31.50 | 0.001 |
| Cotton (Unseed) - First Cultivation | 310.00 | 0.006 |
| Potato (Other) - First Cultivation | 60.20 | 0.001 |
| Sugar Beet | 146.60 | 0.003 |
| Clover (greengrass)* | 28,115.00 | 0.520 |
| Paddy - First Cultivation | 205.00 | 0.004 |
| Total of Field Crops | 54,020.60 | 100.00 |
| Pepper | 150.30 | 0.042 |
| Tomato (Table)* | 949.70 | 0.267 |
| Beans (Fresh) | 104.30 | 0.029 |
| Cucumber (Table) | 234.30 | 0.066 |
| Spinach | 45.00 | 0.013 |
| Watermelon* | 858.30 | 0.242 |
| Melon* | 1,066.30 | 0.300 |
| Aubergine | 142.50 | 0.040 |
| Total of Vegetables | 3,550.70 | 100.00 |
| Pear | 35.00 | 0.006 |
| Apple* | 1,898.30 | 0.324 |
| Plum | 29.70 | 0.005 |
| Apricot* | 3,530.00 | 0.602 |
| Cherries | 40.00 | 0.007 |
| Peach* | 209,30 | 0.036 |
| Walnut | 110.00 | 0.019 |
| Cherry | 13.50 | 0.002 |
| Total of Fruits | 5,865.80 | 100.00 |
| Total of Irrigated Crops | 63,437.10 | 100.00 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 357.57 | 1,051.68 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12,046.95 | 0.00 | ----- |
| 321.80 | 946.47 | 90 | 1.80 | 81.00 | 927.86 | 10,841.81 | 163.17 | 0.02 |
| 286.07 | 841.38 | 80 | 3.13 | 140.85 | 1,613.44 | 9,638.01 | 283.73 | 0.03 |
| 250.27 | 736.09 | 70 | 5.03 | 226.35 | 2,592.84 | 8,431.91 | 455.96 | 0.05 |
| 214.53 | 630.97 | 60 | 6.83 | 307.35 | 3,520.69 | 7,227.76 | 619.13 | 0.09 |
| 178.80 | 525.88 | 50 | 8.80 | 396.00 | 4,536.18 | 6,023.96 | 797.70 | 0.13 |
| 143.03 | 420.68 | 40 | 9.67 | 435.15 | 4,984.64 | 4,818.89 | 876.57 | 0.18 |
| 107.30 | 315.59 | 30 | 11.87 | 534.15 | 6,118.69 | 3,615.08 | 1075.99 | 0.30 |
| 71.50 | 210.29 | 20 | 16.53 | 743.85 | 8,520.80 | 2,408.87 | 1498.41 | 0.62 |
| 35.77 | 105.21 | 10 | 19.57 | 880.65 | 10,087.85 | 1,205.18 | 1773.98 | 1.47 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 486.13 | 1,4291.80 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5,980.30 | 0.00 | ----- |
| 437.50 | 1,286.76 | 90 | 2.20 | 953.33 | 3,987.41 | 5,382.00 | 116.39 | 0.02 |
| 388.90 | 1,143.82 | 80 | 4.33 | 1,877.78 | 7,853.99 | 4,784.14 | 229.26 | 0.05 |
| 340.30 | 1,000.88 | 70 | 7.80 | 3,380.00 | 14,137.19 | 4,186.28 | 412.67 | 0.10 |
| 291.67 | 857.84 | 60 | 10.70 | 4,636.67 | 19,393.32 | 3,588.00 | 566.10 | 0.16 |
| 243.10 | 715.00 | 50 | 14.03 | 6,081.11 | 25,434.85 | 2,990.56 | 742.45 | 0.25 |
| 194.47 | 571.96 | 40 | 17.83 | 7,727.78 | 32,322.20 | 2,392.28 | 943.49 | 0.39 |
| 145.83 | 428.92 | 30 | 29.43 | 12,754.44 | 53,346.74 | 1,794.00 | 1557.20 | 0.87 |
| 87.23 | 256.57 | 20 | 33.40 | 14,473.33 | 60,536.16 | 1,073.13 | 1767.06 | 1.65 |
| 48.63 | 143.04 | 10 | 47.03 | 20,381.11 | 85,246.03 | 598.28 | 2488.35 | 4.16 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 568.37 | 1,671.67 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 46,999.00 | 0.00 | ---- |
| 511.53 | 1,504.51 | 90 | 1.40 | 20,066.66 | 5,641.74 | 42,299.30 | 54225.11 | 1.28 |
| 454.70 | 1,337.35 | 80 | 2.30 | 32,966.66 | 9,268.58 | 37,599.60 | 89084.12 | 2.37 |
| 397.87 | 1,170.20 | 70 | 4.53 | 64,977.76 | 18,268.50 | 32,900.17 | 175586.07 | 5.34 |
| 341.00 | 1,002.94 | 60 | 7.20 | 103,199.98 | 29,014.67 | 28,197.66 | 278872.02 | 9.89 |
| 284.23 | 835.98 | 50 | 8.97 | 128,522.19 | 36,134.01 | 23,503.58 | 347298.93 | 14.78 |
| 227.37 | 668.73 | 40 | 11.97 | 171,522.18 | 48,223.46 | 18,801.35 | 463495.60 | 24.65 |
| 170.53 | 501.57 | 30 | 15.57 | 223,122.17 | 62,730.80 | 14,101.64 | 602931.61 | 42.76 |
| 113.67 | 334.31 | 20 | 23.93 | 343,044.36 | 96,446.92 | 9,399.13 | 926991.20 | 98.63 |
| 56.87 | 167.25 | 10 | 32.27 | 462,488.78 | 130,028.72 | 4,702.24 | 1249759.74 | 265.78 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 560.00 | 1,647.06 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1,564.21 | 0.00 | ---- |
| 504.00 | 1,482.35 | 90 | 2.20 | 836.00 | 793.95 | 1,407.79 | 74.90 | 0.05 |
| 448.00 | 1,317.65 | 80 | 4.90 | 1,862.00 | 1,768.34 | 1,251.37 | 166.82 | 0.13 |
| 392.00 | 1,152.94 | 70 | 8.57 | 3,255.33 | 3,091.59 | 1,094.95 | 291.64 | 0.27 |
| 335.97 | 988.14 | 60 | 13.57 | 5,155.33 | 4,896.02 | 938.44 | 461.86 | 0.49 |
| 280.03 | 823.63 | 50 | 18.90 | 7,182.00 | 6,820.75 | 782.20 | 643.43 | 0.82 |
| 224.03 | 658.92 | 40 | 25.30 | 9,614.00 | 9,130.42 | 625.78 | 861.31 | 1.38 |
| 168.00 | 494.12 | 30 | 31.23 | 11,868.67 | 11,271.67 | 469.27 | 1063.30 | 2.27 |
| 112.00 | 329.41 | 20 | 43.60 | 16,568.00 | 15,734.63 | 312.84 | 1484.31 | 4.74 |
| 56.00 | 164.71 | 10 | 51.93 | 19,734.67 | 18,742.01 | 156.43 | 1768.01 | 11.30 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450.57 | 1,325.20 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1,137.42 | 0.00 | ----- |
| 405.50 | 1,192.65 | 90 | 1.97 | 662.11 | 568.29 | 1,023.65 | 49.36 | 0.05 |
| 360.47 | 1,060.20 | 80 | 4.20 | 1,414.00 | 1,213.64 | 909.97 | 105.41 | 0.12 |
| 315.40 | 927.65 | 70 | 6.60 | 2,222.00 | 1,907.14 | 796.20 | 165.65 | 0.21 |
| 270.33 | 795.10 | 60 | 10.40 | 3,501.33 | 3,005.19 | 682.44 | 261.03 | 0.38 |
| 225.23 | 662.45 | 50 | 14.93 | 5,027.56 | 4,315.15 | 568.58 | 374.81 | 0.66 |
| 180.23 | 530.10 | 40 | 18.60 | 6,262.00 | 5,374.68 | 454.99 | 466.84 | 1.03 |
| 135.17 | 397.55 | 30 | 23.83 | 8,023.89 | 6,886.90 | 341.22 | 598.19 | 1.75 |
| 90.10 | 265.00 | 20 | 27.53 | 9,269.56 | 7,956.06 | 227.45 | 691.05 | 3.04 |
| 45.07 | 132.55 | 10 | 33.83 | 11,390.56 | 9,776.51 | 113.77 | 849.18 | 7.46 |
| Dn |
Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 465.33 | 1,368.63 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1,459.37 | 0.00 | ---- |
| 418.83 | 1,231.86 | 90 | 2.10 | 471.74 | 503.02 | 1,313.53 | 62.67 | 0.05 |
| 372.27 | 1,094.90 | 80 | 3.67 | 823.67 | 878.28 | 1,167.49 | 109.43 | 0.09 |
| 325.73 | 958.04 | 70 | 6.63 | 1,490.10 | 1,588.89 | 1,021.56 | 197.96 | 0.19 |
| 279.20 | 821.18 | 60 | 11.63 | 2,613.29 | 2,786.55 | 875.63 | 347.18 | 0.40 |
| 232.70 | 684.41 | 50 | 14.63 | 3,287.20 | 3,505.14 | 729.79 | 436.71 | 0.60 |
| 186.13 | 547.45 | 40 | 17.90 | 4,021.02 | 4,287.61 | 583.75 | 534.20 | 0.91 |
| 139.63 | 410.69 | 30 | 22.80 | 5,121.75 | 5,461.32 | 437.92 | 680.44 | 1.55 |
| 93.07 | 273.73 | 20 | 27.17 | 6,102.67 | 6,507.27 | 291.88 | 810.76 | 2.78 |
| 46.53 | 136.86 | 10 | 36.30 | 8,154.36 | 8,694.99 | 145.93 | 1083.33 | 7.42 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 604.20 | 1,777.06 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3,373.39 | 0.00 | ---- |
| 543.80 | 1,599.41 | 90 | 2.00 | 600.00 | 1,138.98 | 3,036.16 | 144.34 | 0.05 |
| 483.37 | 1,421.67 | 80 | 4.97 | 1,490.00 | 2,828.47 | 2,698.76 | 358.45 | 0.13 |
| 422.93 | 1,243.92 | 70 | 7.37 | 2,210.00 | 4,195.24 | 2,361.33 | 531.66 | 0.23 |
| 362.50 | 1,066.18 | 60 | 10.37 | 3,110.00 | 5,903.71 | 2,023.93 | 748.17 | 0.37 |
| 302.10 | 888.53 | 50 | 13.53 | 4,060.00 | 7,707.10 | 1,686.70 | 976.71 | 0.58 |
| 241.70 | 710.88 | 40 | 17.97 | 5,390.00 | 10,231.84 | 1,349.46 | 1296.66 | 0.96 |
| 181.27 | 533.14 | 30 | 22.23 | 6,670.00 | 12,661.66 | 1,012.06 | 1604.59 | 1.59 |
| 120.83 | 355.39 | 20 | 28.53 | 8,560.00 | 16,249.45 | 674.64 | 2059.26 | 3.05 |
| 60.40 | 177.65 | 10 | 35.40 | 10,620.00 | 20,159.95 | 337.23 | 2554.84 | 7.58 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 589.97 | 1,735.20 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6,125.26 | 0.00 | ----- |
| 531.07 | 1,561.96 | 90 | 2.20 | 321.04 | 1,133.27 | 5,513.72 | 282.39 | 0.05 |
| 472.03 | 1,388.33 | 80 | 4.23 | 617.76 | 2,180.68 | 4,900.81 | 543.40 | 0.11 |
| 413.03 | 1,214.80 | 70 | 9.57 | 1,396.03 | 4,927.99 | 4,288.24 | 1227.98 | 0.29 |
| 354.00 | 1,041.18 | 60 | 15.80 | 2,305.64 | 8,138.92 | 3,675.37 | 2028.09 | 0.55 |
| 295.07 | 867.84 | 50 | 19.60 | 2,860.16 | 10,096.38 | 3,063.48 | 2515.86 | 0.82 |
| 236.07 | 694.31 | 40 | 25.80 | 3,764.91 | 13,290.13 | 2,450.91 | 3311.70 | 1.35 |
| 177.03 | 520.69 | 30 | 31.33 | 4,572.37 | 16,140.47 | 1,838.04 | 4021.96 | 2.19 |
| 118.03 | 347.16 | 20 | 36.80 | 5,370.10 | 18,956.46 | 1,225.48 | 4723.66 | 3.85 |
| 59.00 | 173.53 | 10 | 40.50 | 5,910.03 | 20,862.41 | 612.56 | 5198.59 | 8.49 |
| Dn | Dt (34%) | Irrigation rate (%) | Decrease in the yield (%) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Total Yield Loss (Tons) | Total Water Need (Thousand m3) |
Loss of Revenue (Thousand $) | Constraint Value of Water ($/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 571.55 | 1,681.03 | 100 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 351.84 | 0.00 | ----- |
| 514.40 | 1,512.94 | 90 | 2.85 | 513.00 | 107.37 | 316.66 | 24.46 | 0.08 |
| 457.25 | 1,344.85 | 80 | 7.00 | 1,260.00 | 263.72 | 281.48 | 60.08 | 0.21 |
| 400.05 | 1,176.62 | 70 | 9.35 | 1,683.00 | 352.25 | 246.27 | 80.25 | 0.33 |
| 342.90 | 1,008.53 | 60 | 13.90 | 2,502.00 | 523.67 | 211.09 | 119.31 | 0.57 |
| 285.80 | 840.59 | 50 | 19.70 | 3,546.00 | 742.18 | 175.94 | 169.09 | 0.96 |
| 228.65 | 672.50 | 40 | 22.35 | 4,023.00 | 842.01 | 140.76 | 191.83 | 1.36 |
| 171.50 | 504.41 | 30 | 25.65 | 4,617.00 | 966.34 | 105.57 | 220.16 | 2.09 |
| 114.30 | 336.18 | 20 | 34.60 | 6,228.00 | 1,303.52 | 70.36 | 296.98 | 4.22 |
| 57.15 | 168.09 | 10 | 41.70 | 7,506.00 | 1,571.01 | 35.18 | 357.92 | 10.17 |
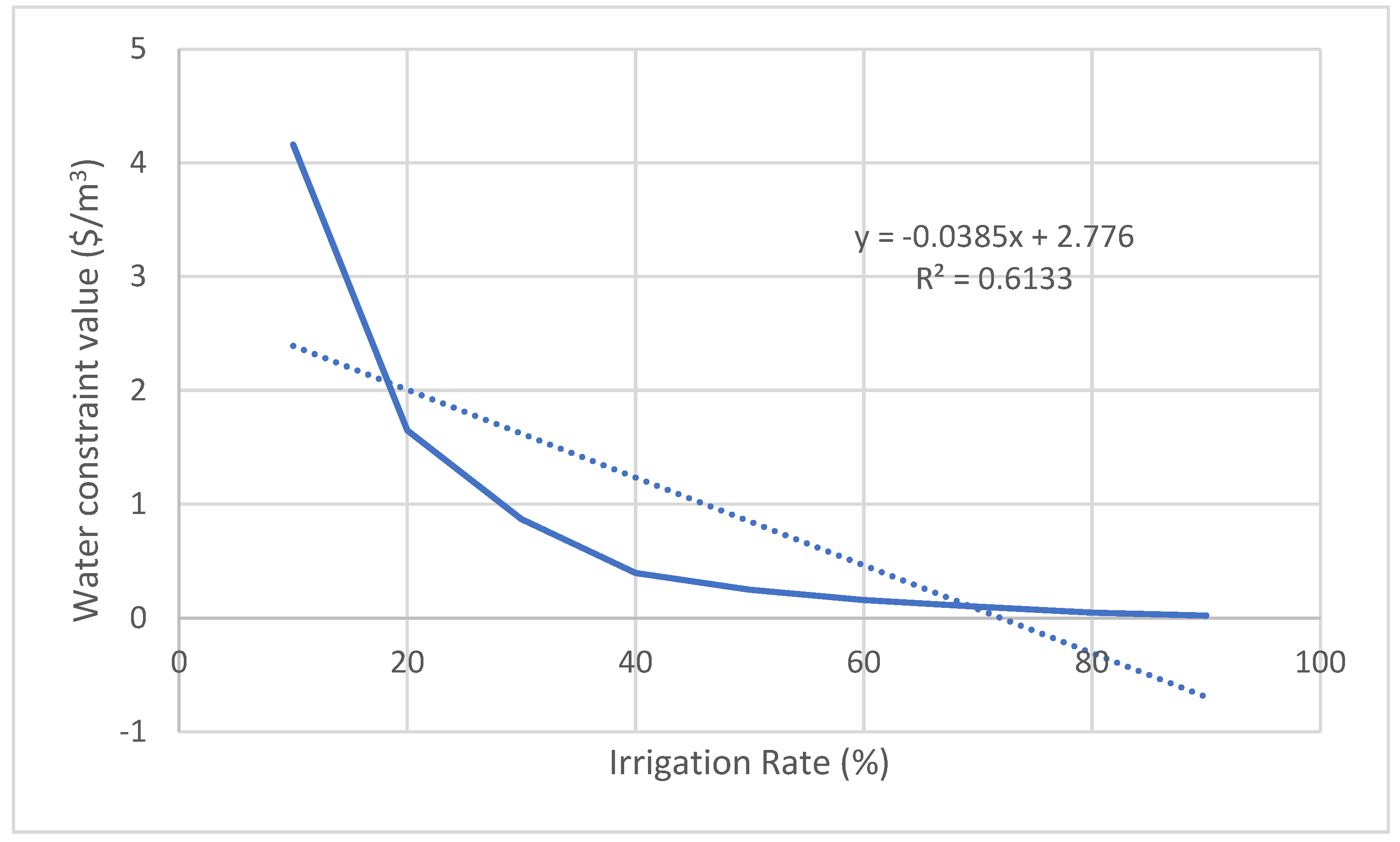
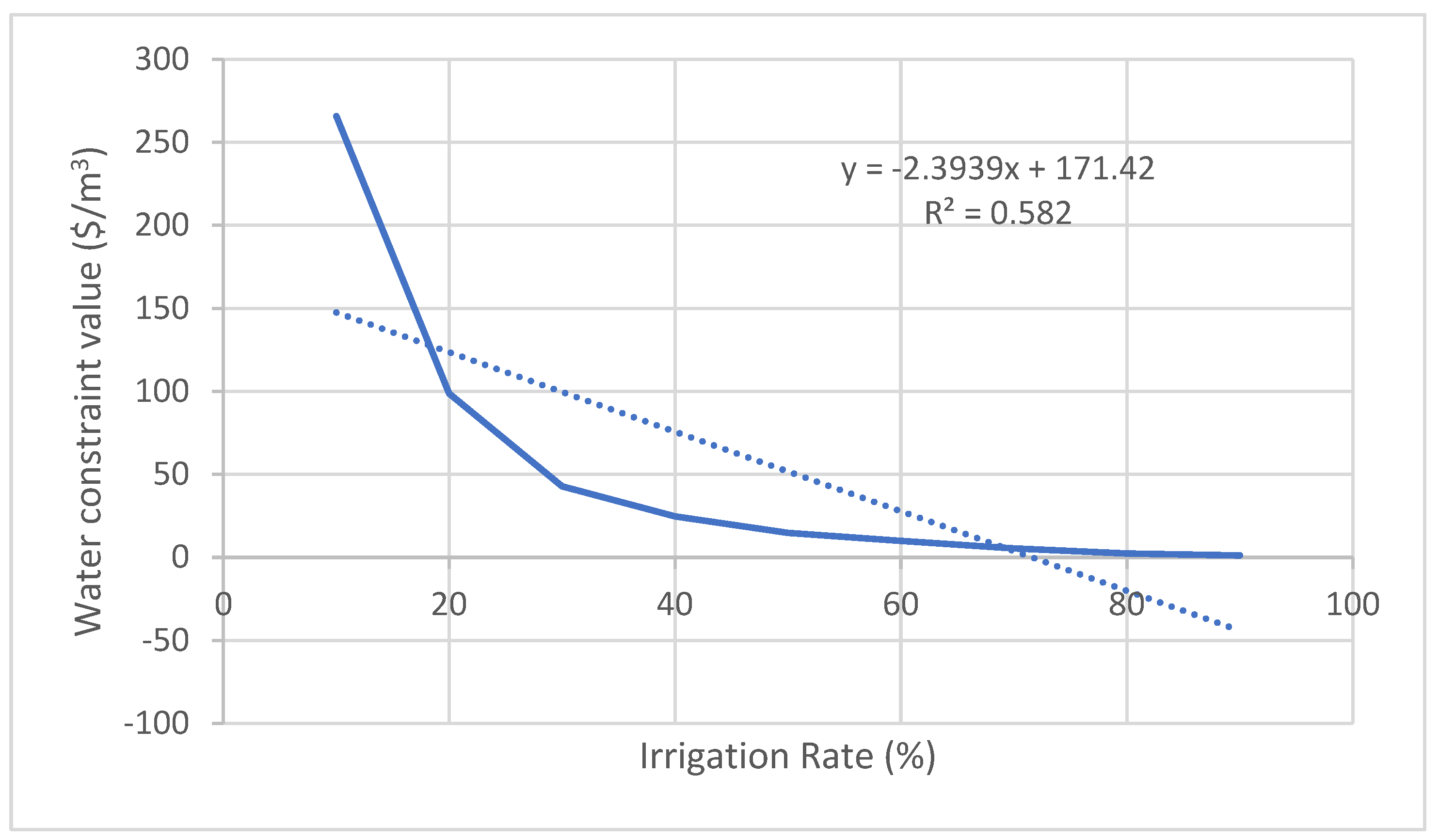
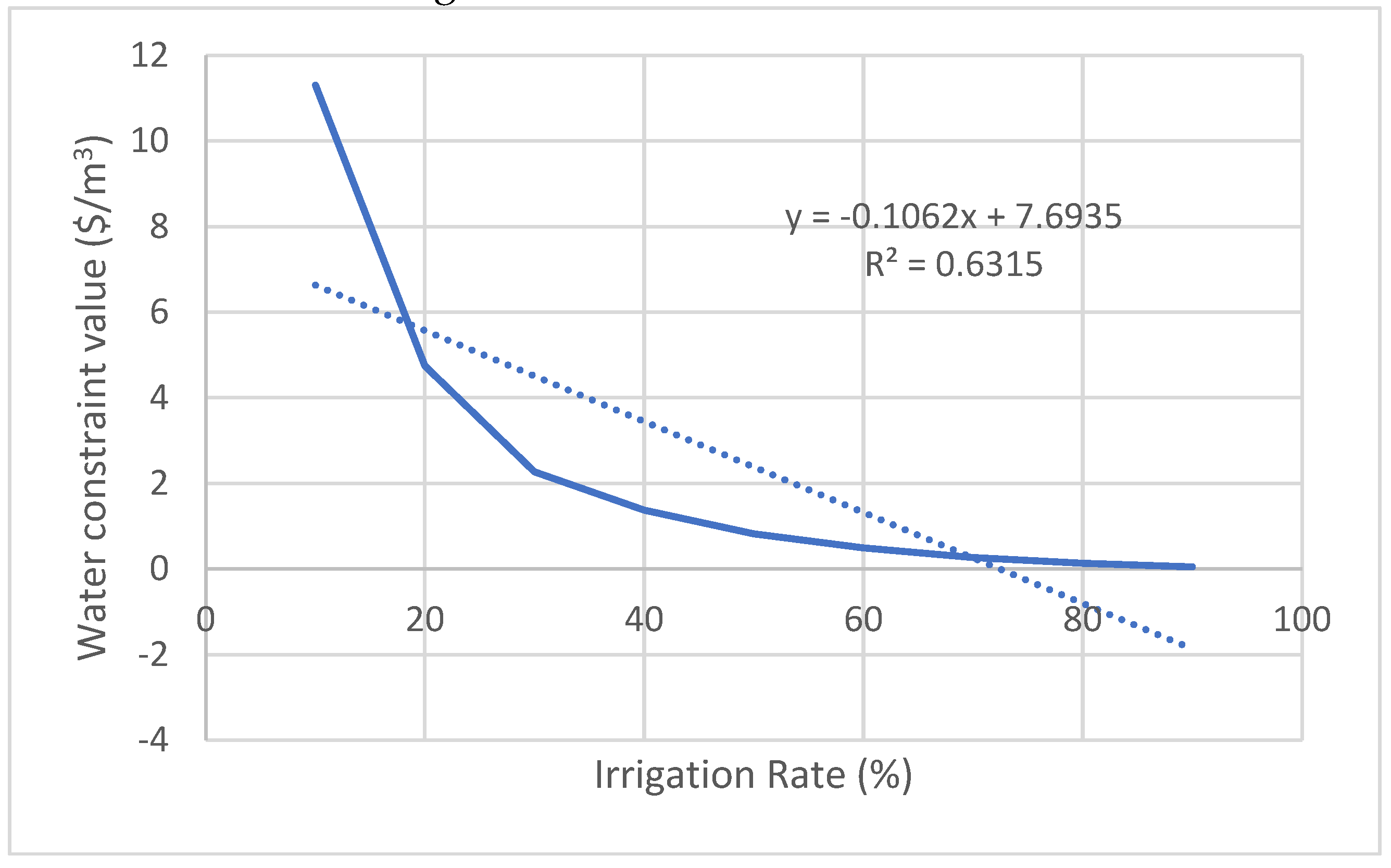
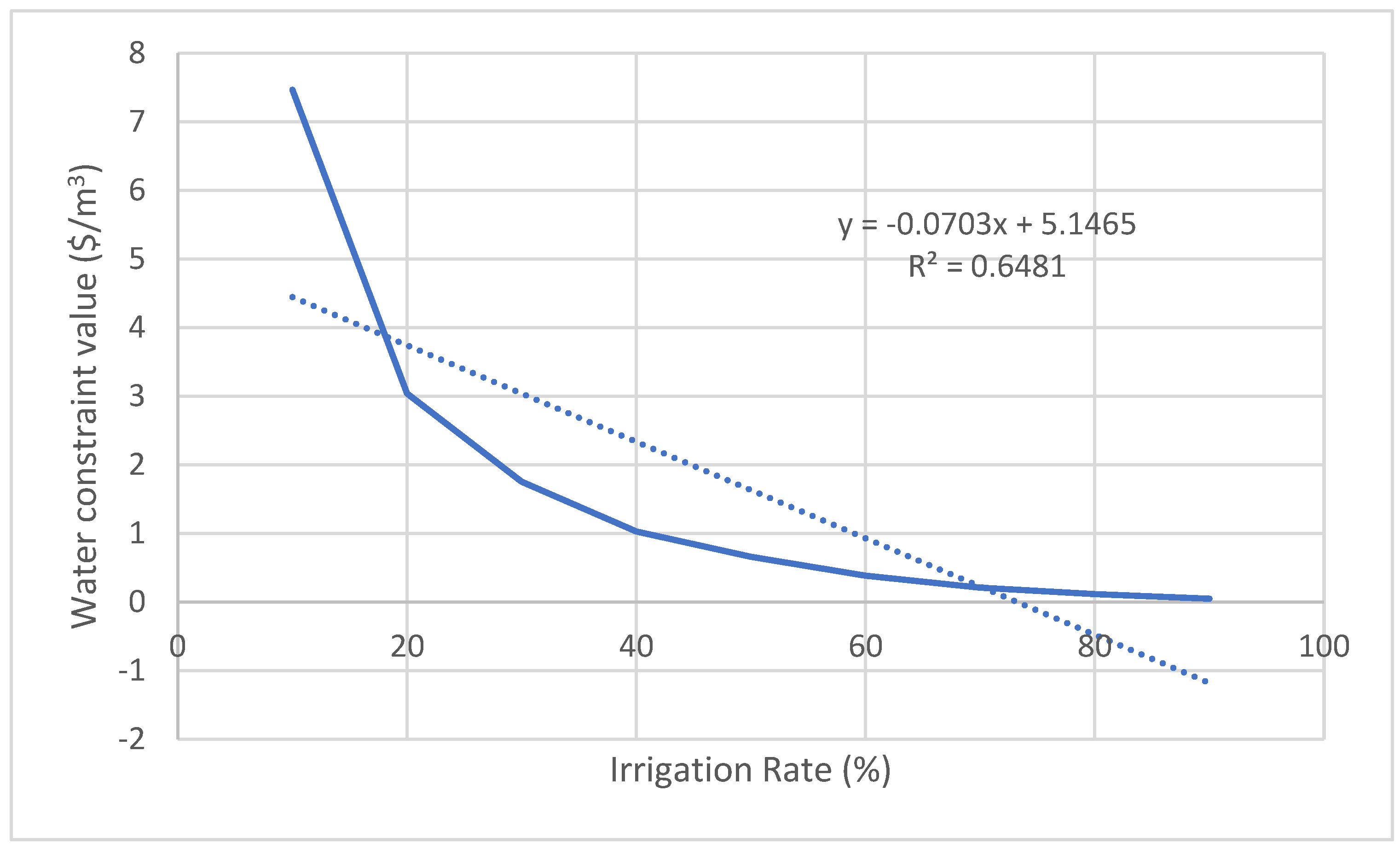
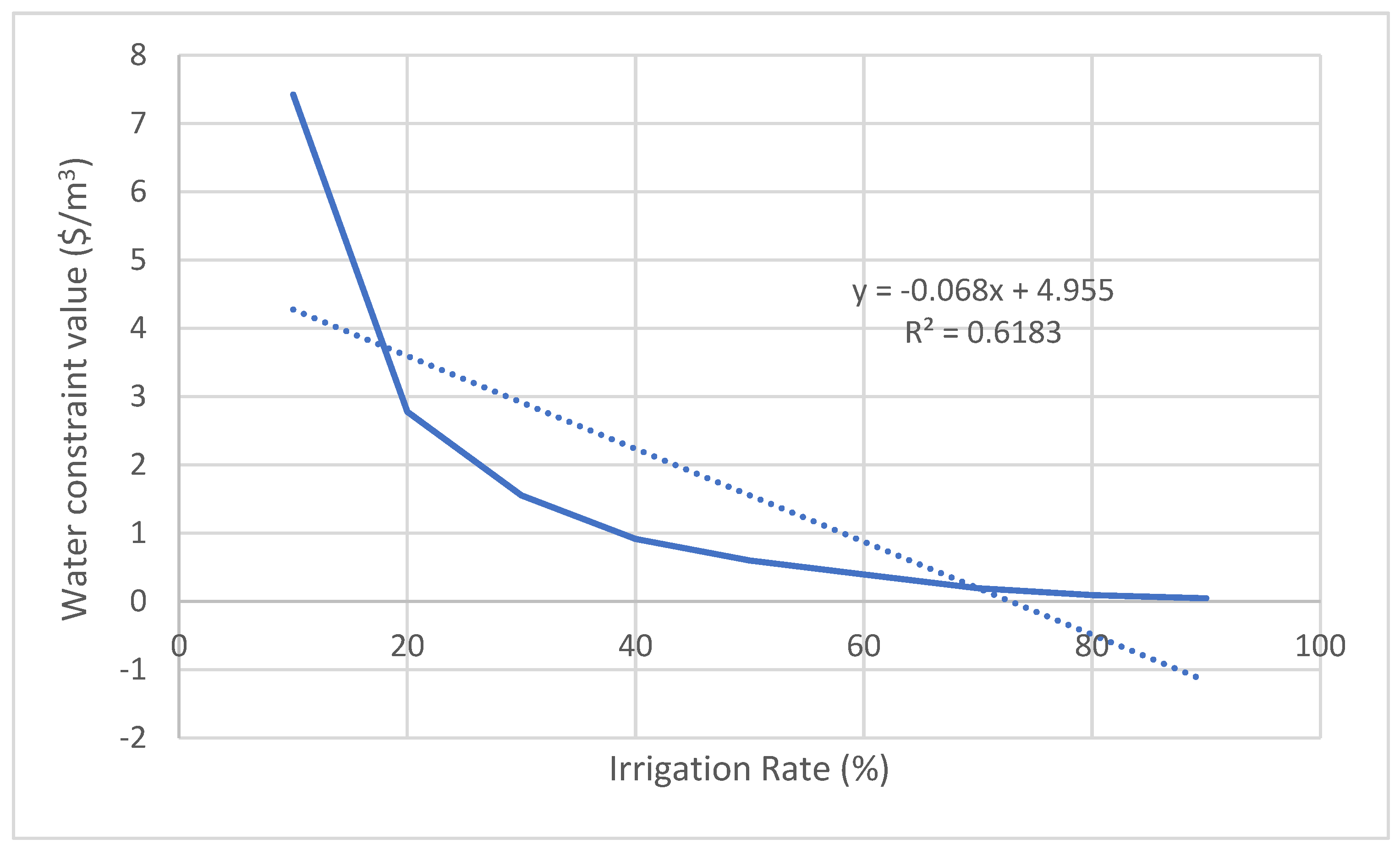
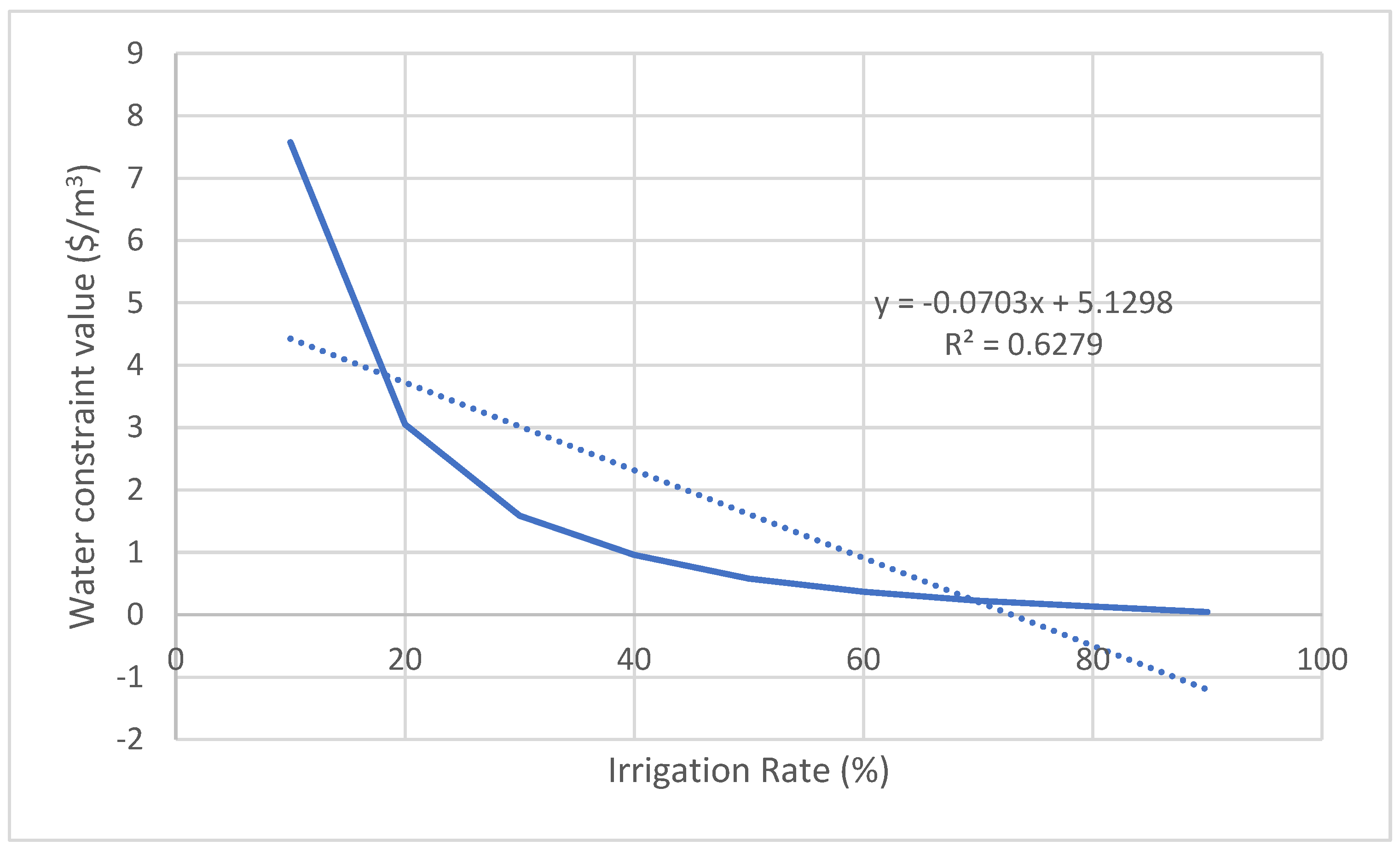
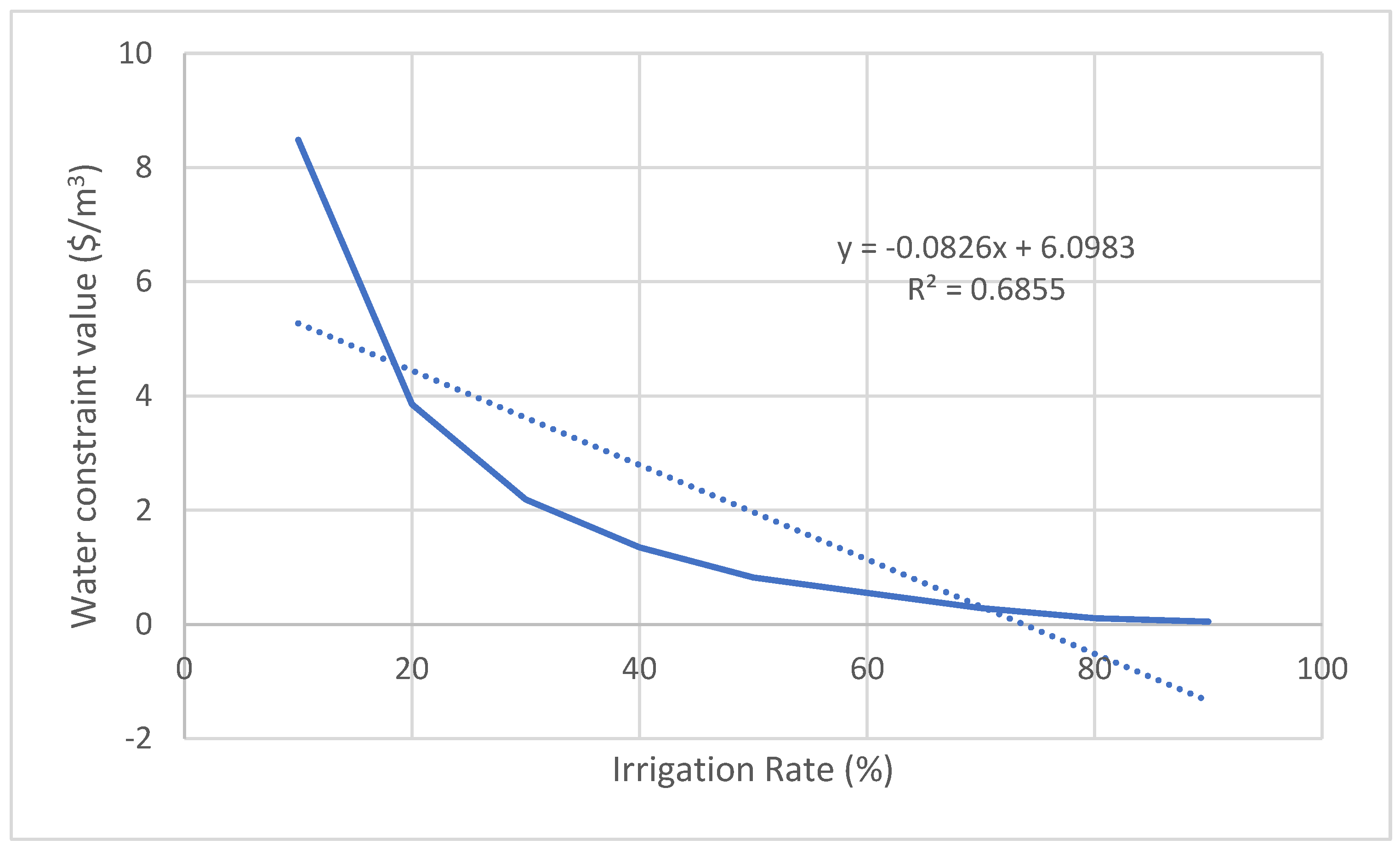
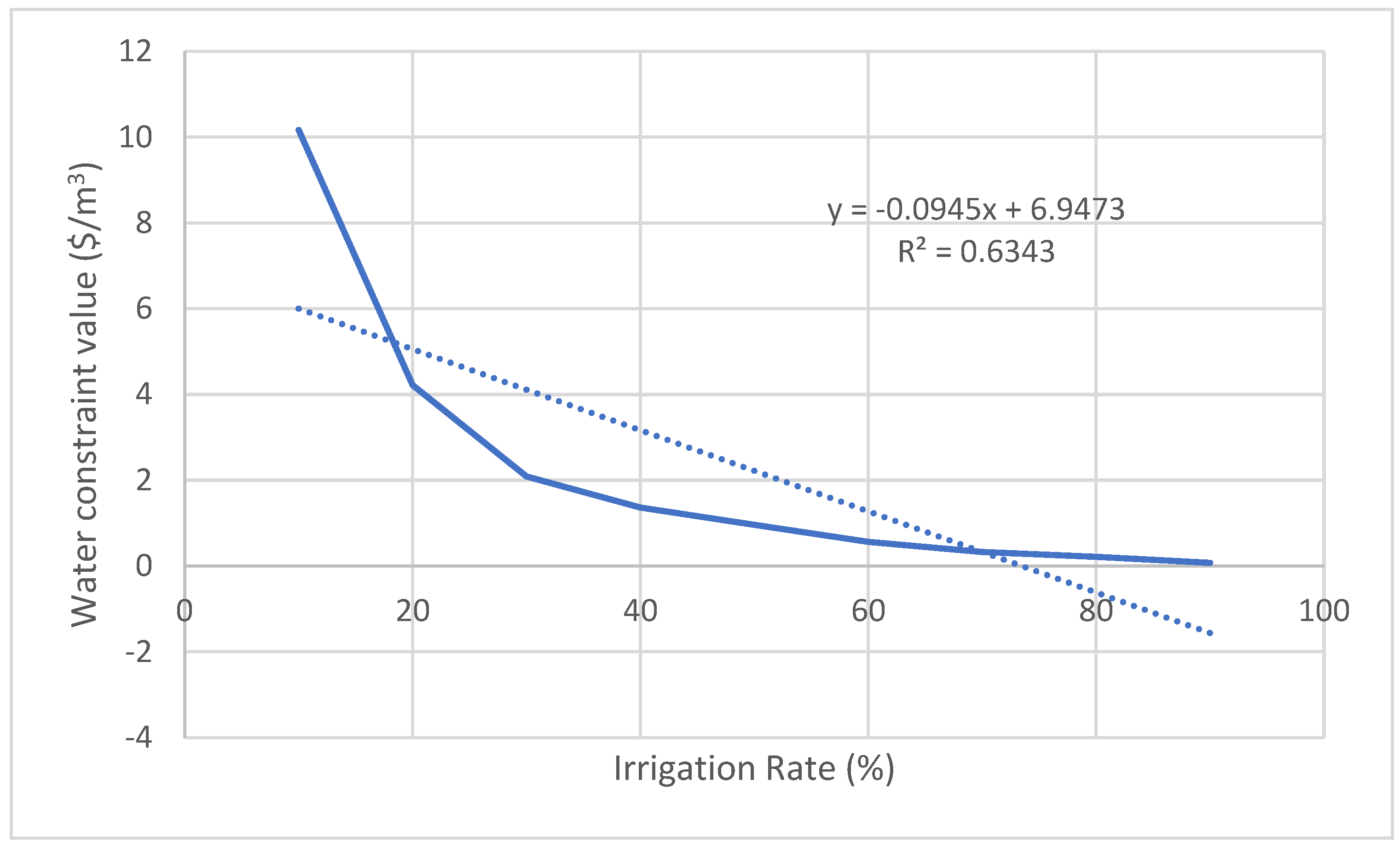
| Crop | Relation between the irrigation rate (x) and the constraint value of water (y) | R2 | Average constraint value of water ($/m3) | Average product loss (Tons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apricot | y = -0.0826x + 6.0983 | 0.6855 | 1.96 | 10636 |
| Watermelon | y = -0.0703x + 5.1465 | 0.6481 | 0.80 | 3469 |
| Peach | y = -0.0945x + 6.9473 | 0.6343 | 2.22 | 741 |
| Tomato | y = -0.1062x + 7.6935 | 0.6315 | 2.39 | 5945 |
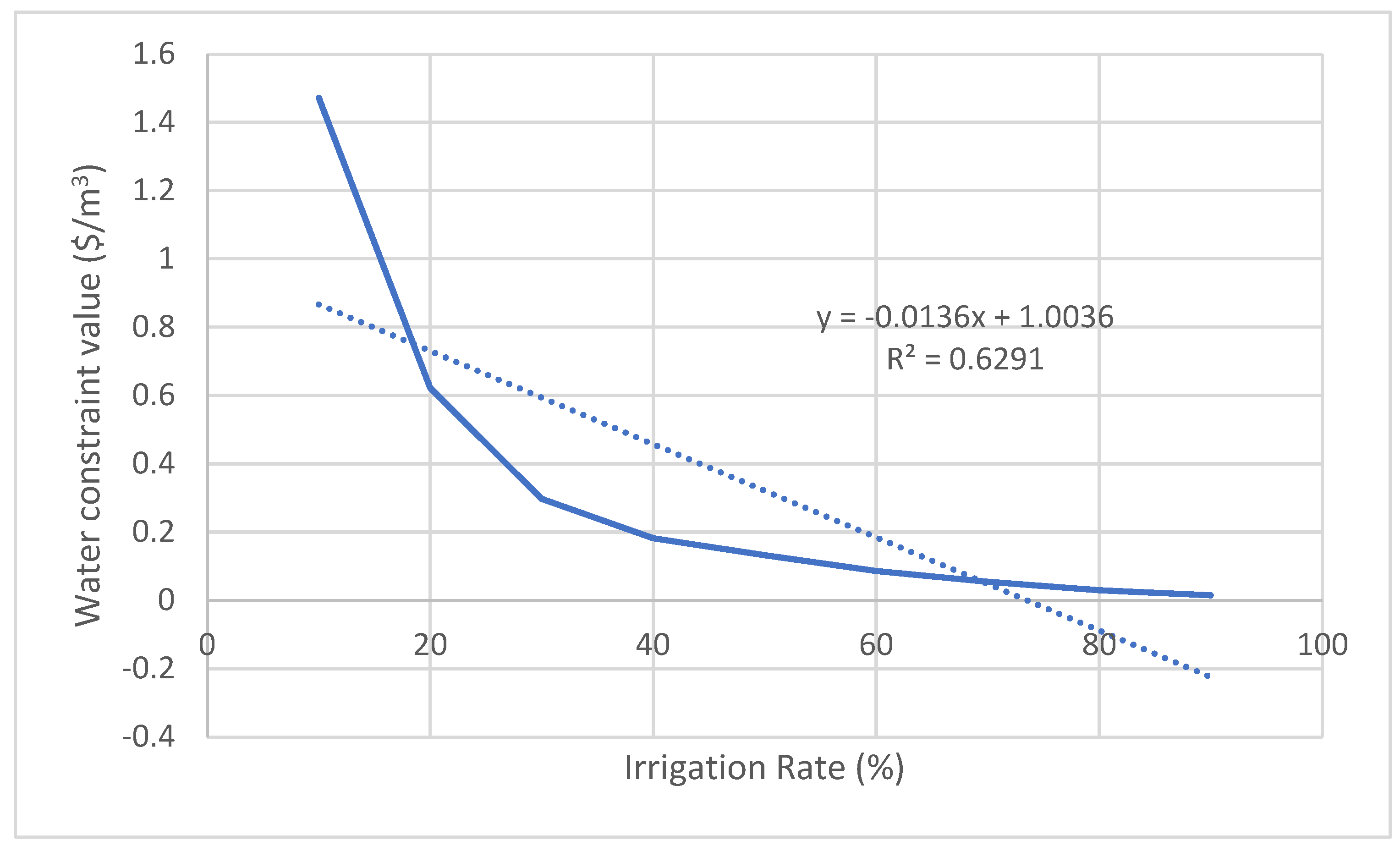
| Wheat | y = -0.0136x + 1.0036 |
0.6291 | 0.32 | 4767 |
| Apple | y = -0.0703x + 5.1298 | 0.6279 | 1.61 | 9008 |
| Melon | y = -0.068x + 4.955 | 0.6183 | 1.56 | 3801 |
| Maize | y = -0.0385x + 2.776 | 0.6133 | 0.85 | 33584 |
| Clover | y = -2.3939x + 171.42 | 0.5820 | 51.69 | 48417 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




