Submitted:
17 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Modeling
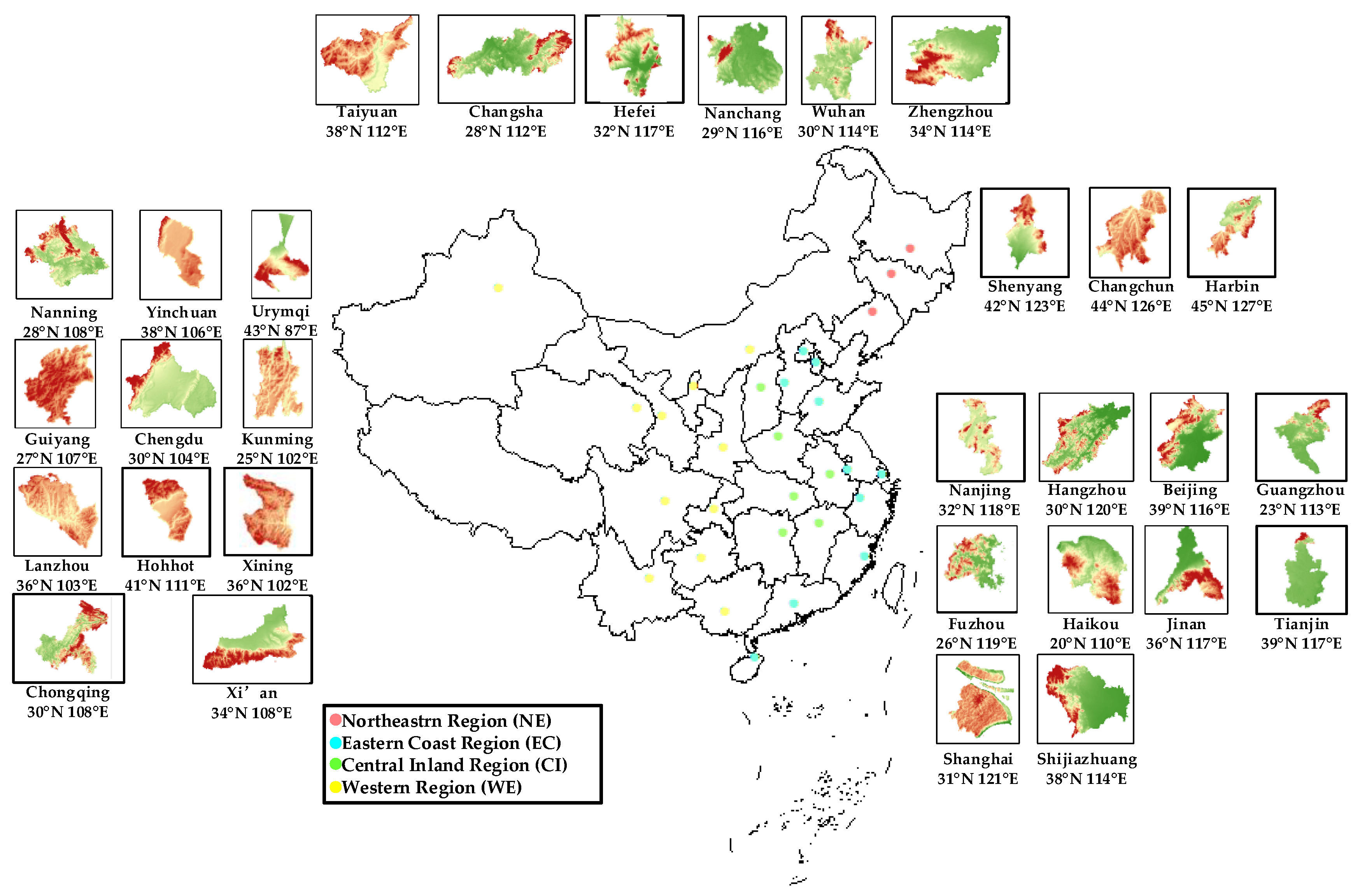
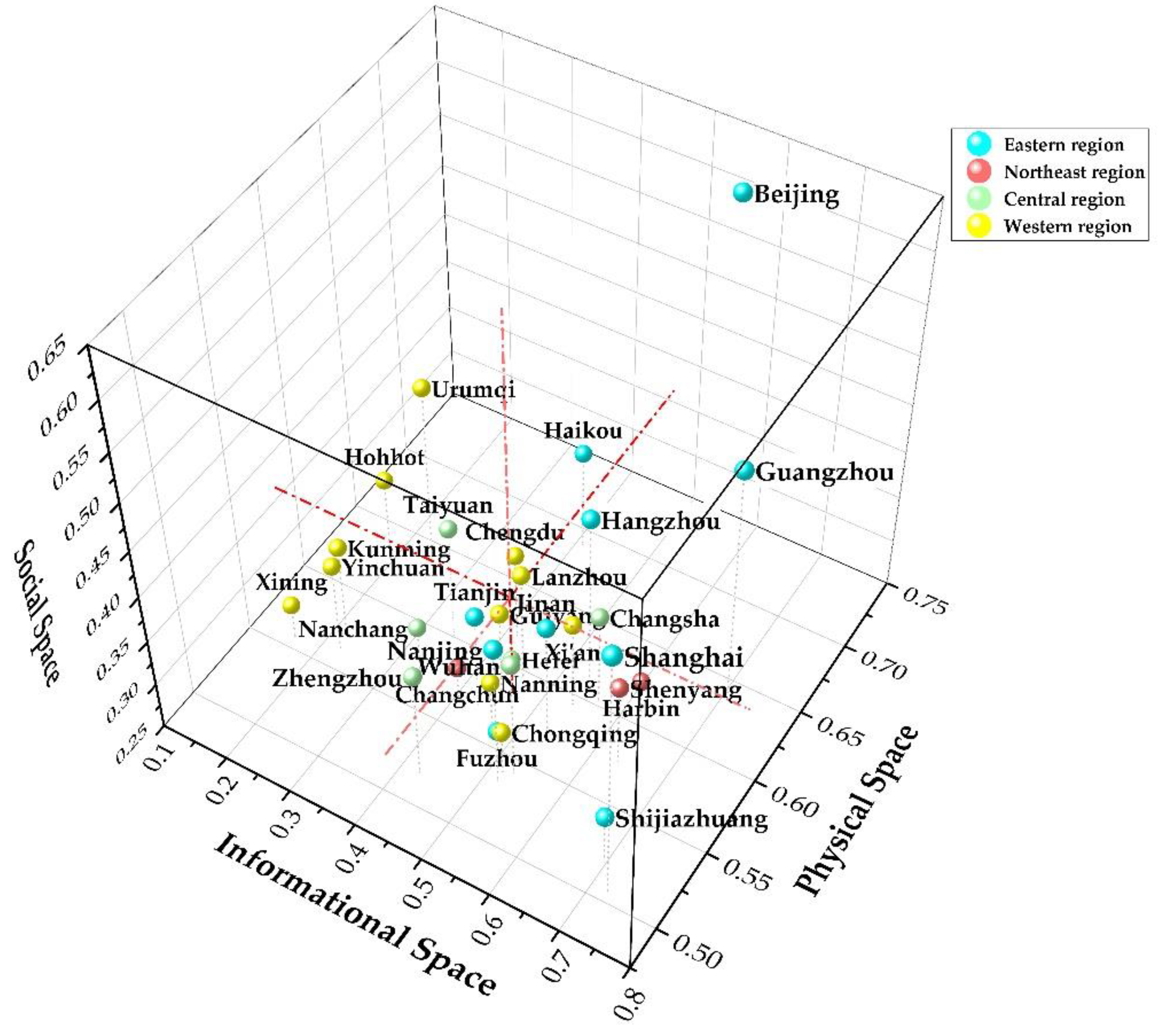
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Literature Review and Modeling
2.3. Data Source and Processing
3. Methods
3.1. Entropy Weight Method
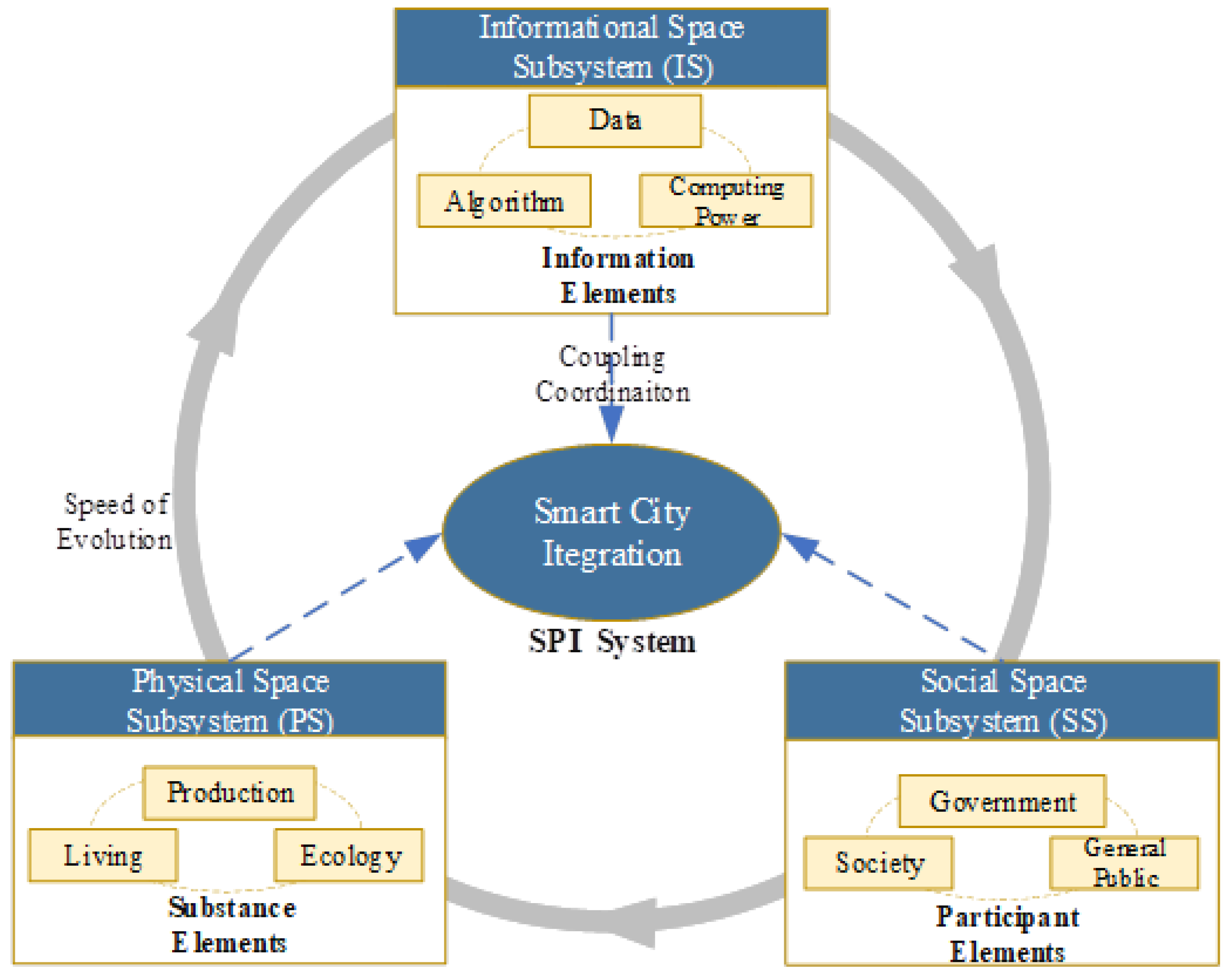
3.2. Revised Coupling Coordination Model
- U1, U2 and U3 respectively represent the comprehensive evaluation indexes of the dimensions of information space, physical space, and social space;
- C represents the coupling degree of the tri-dimensional space in smart city governance;
- D represents the fusion coordination index of the tri-dimensional space in smart city governance, with a value range of [0,1];
- T represents the comprehensive development index of the coupling system in smart city governance, reflecting the synergistic effects among the tri-dimensional space in smart city governance;
- α, β and γ respectively refer to the contribution degrees of information space, physical space, and social space in the coupling system;
- α + β + γ = 1 . The closer the value is to 1, the greater the contribution degree. This study considers the equal importance of the tri-dimensional space, hence .
3.3. Dagum Gini Coefficient Decomposition Method
- n represents the number of cities;
- k represents the number of subgroups, representing the eastern, central, western, and northeastern regions in this study;
- nj(nh) represents the number of cities in the j(h)-th subgroup;
- j(h) represents the number of divisions in the subgroup, and i and r represent the number of cities within the subgroup;
- G represents the overall Gini coefficient;
- represents the coordination level of any city in the j(h)-th subgroup;
- represents the average coordination level of the tri-dimensional space for all cities, calculated by ;
- Gjh represents the Gini coefficient between the j-th subgroup and the j-th subgroup;
- represents the average coordination level of the j-th subgroup's tri-dimensional space;
- Djh represents the relative influence between region j and region h.
3.4. Kernel Density Estimation Method
- N represents the number of study objects, representing the number of smart cities in the observed area in this study;
- Xi represents the observation value of each smart city's spatial coupling coordination in the observed area;
- X represents the mean value of observation;
- K(·) is the kernel function;
- h represents the bandwidth which determines the precision of the Kernel density and the smoothness of the density graph. is usually adopted (N is the sample size, S is the sample standard deviation).
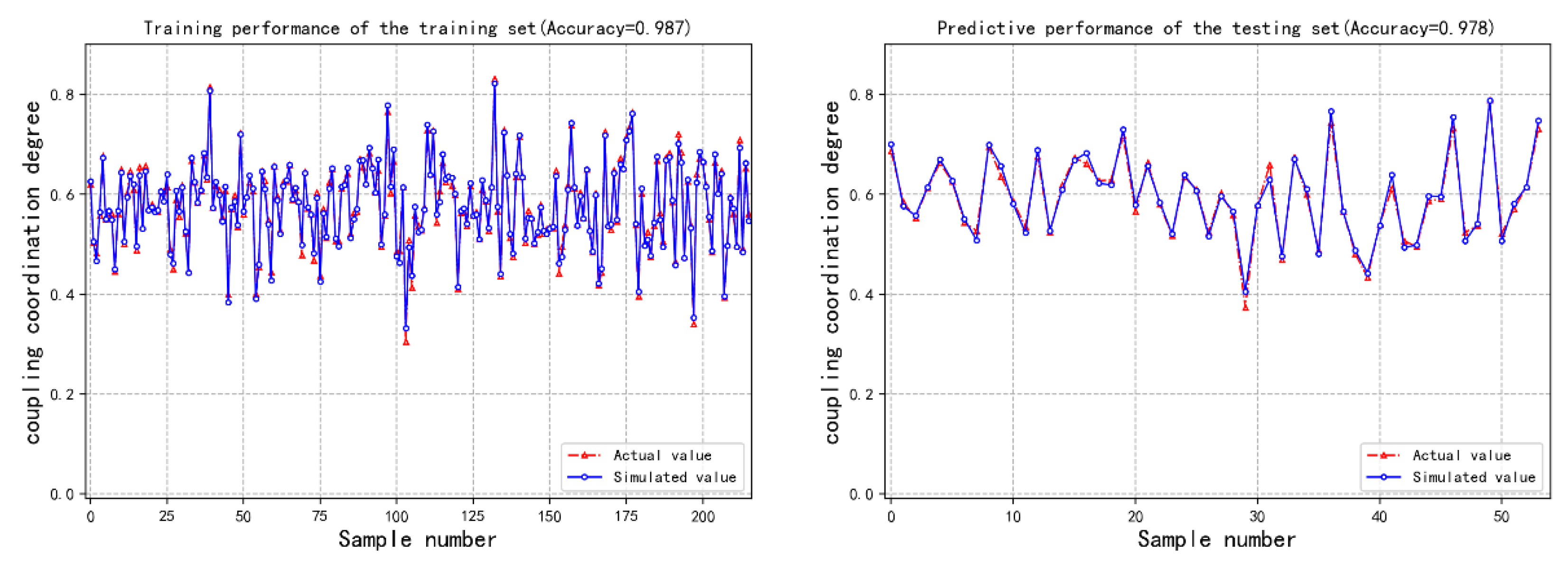
3.5. BP Neural Network
- m represents the number of input layer nodes;
- n represents the number of output layer nodes;
- α represents a constant between [0,10];
- K represents the number of hidden layer nodes.
- By observing the trend of mean square error (MSE) under different numbers of nodes using a step-by-step experimental method, the MSE value is minimized when the number of nodes increases to 13. Therefore, the optimal structure of the network is determined to be "31-13-1". Furthermore, using the constructed neural network for model training, the relationship between various factors and coupling coordination is identified. After all samples are trained and meet the accuracy requirements, the influence weights of various factors are obtained.
4. Results
4.1. Assessment of Smart City Spatial Development
4.1.1. Comprehensive Assessment of Smart City Spatial Development
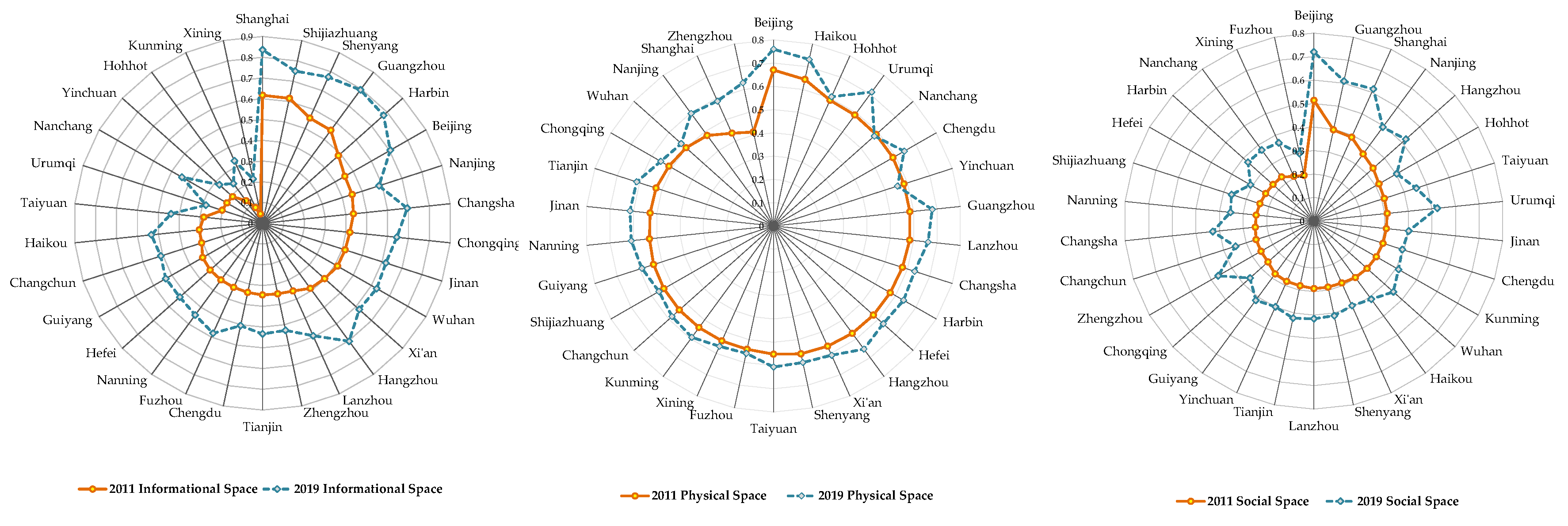
4.1.2. Subsystems Assessment of Smart City Spatial Development
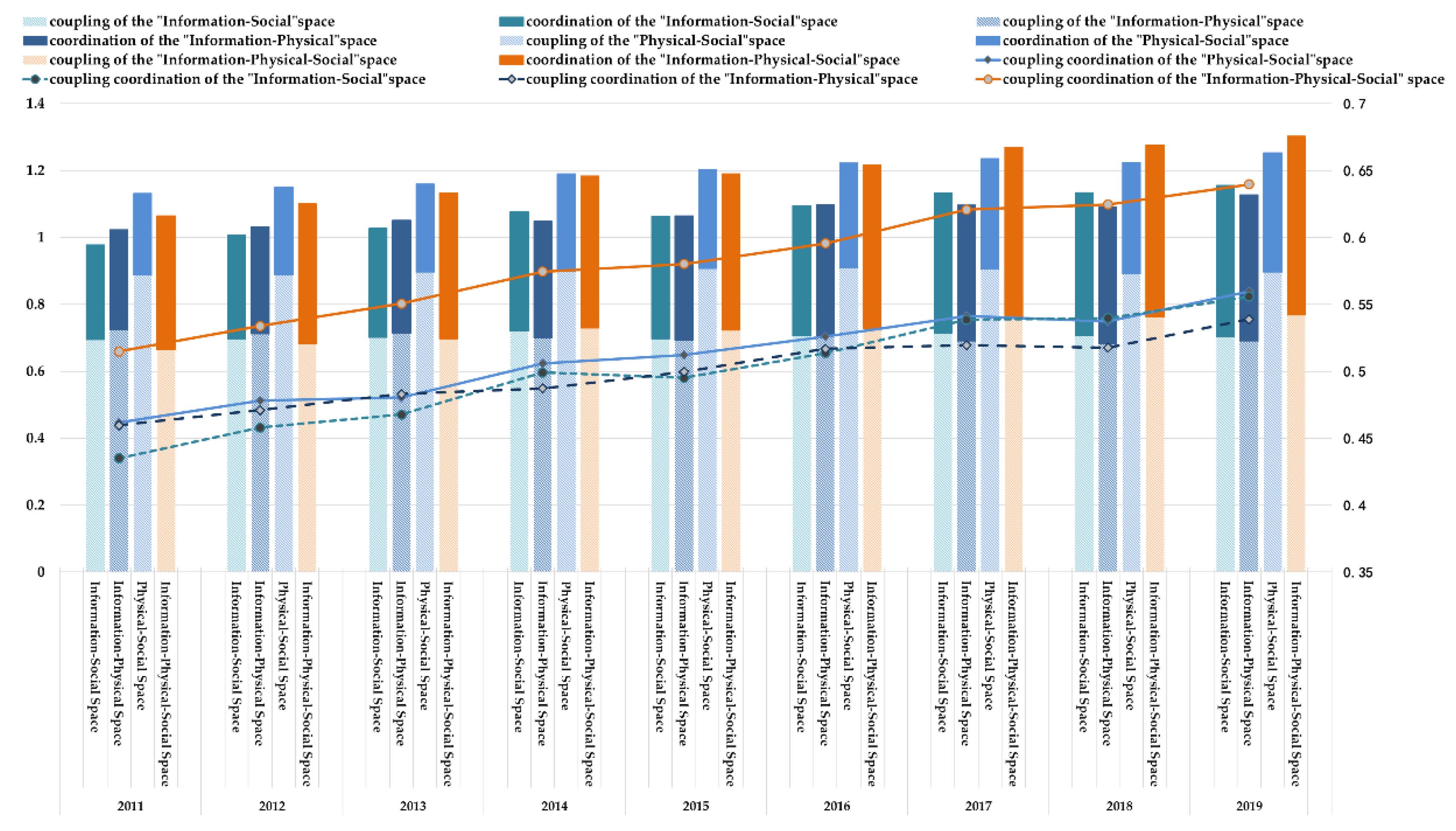
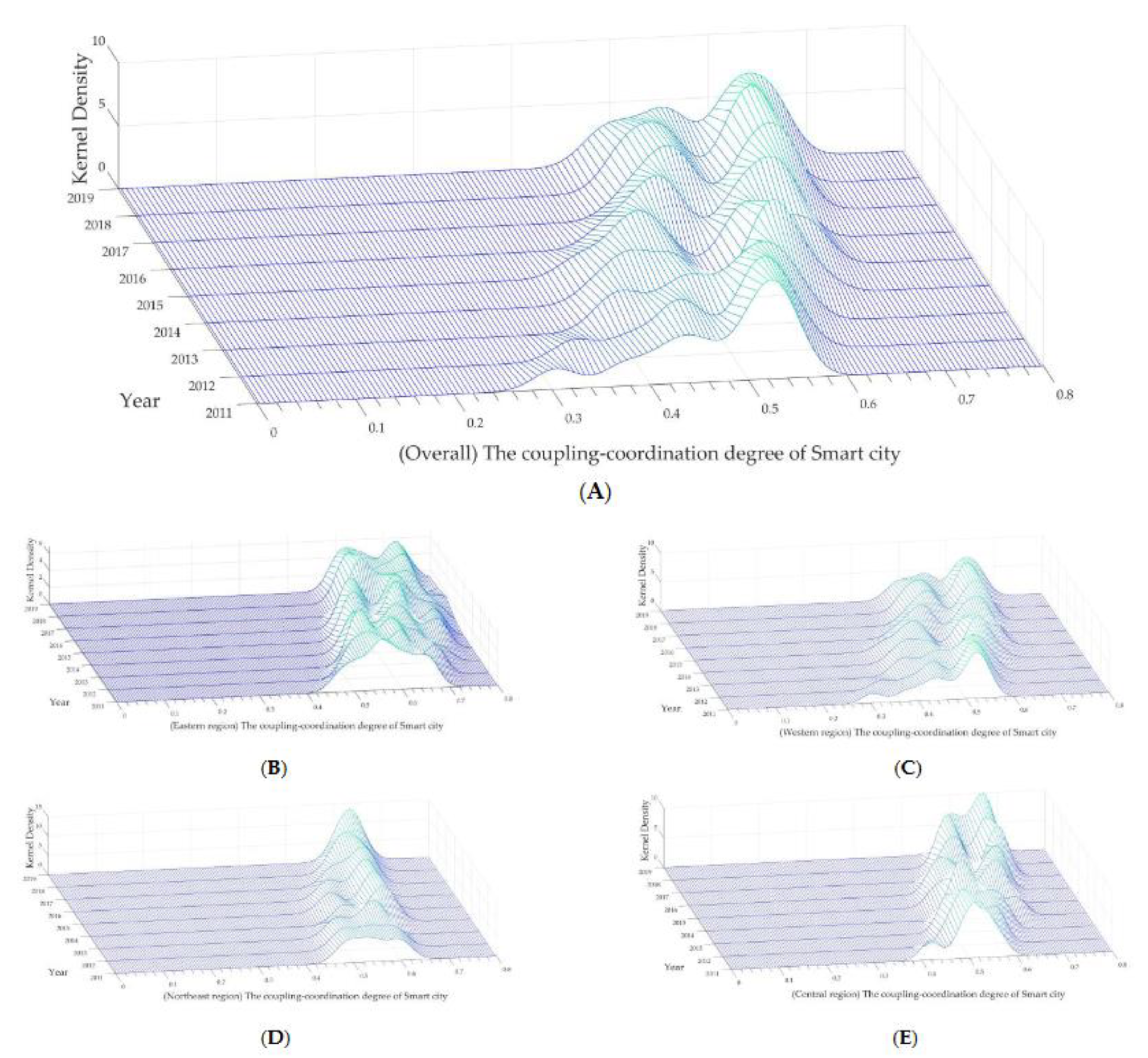
4.2. Descriptive Analysis of Smart City Spatial Coupling Coordination
4.2.1. Overall Characteristics
4.2.3. Regional Disparities
4.2.4. Dynamic Evolution
4.3. Inferential Analysis of Smart City Spatial Coupling Coordination
5. Discussion
5.1. Pathways of Development
5.2. Innovations and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shelton T, Zook M, Wiig A. The ‘actually existing smart city’. Cambridge journal of regions, economy and society 2015, 8, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, H.; Wilkinson, S.; Sweya, L.N.; Baghersad, M.; Dianat, H. Navigating Climate Change Challenges through Smart Resilient Cities: A Comprehensive Assessment Framework. Land 2024, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu Z. Establishment and Countermeasures of Smart City Security Risk Assessment Model. Advances in Computer and Communication 2023, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Laufs J, Borrion H, Bradford B. Security and the smart city: A systematic review. Sustainable cities and society 2020, 55, 102023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuhai N,Kexin Z,Juan Z, et al. How Does Industrial Upgrading Affect Urban Ecological Efficiency? New Evidence from China. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade. 2024, 60, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng Lei. Content, Path and Direction of Urban Digital Transformation. Exploration and Free Views 2021, 4, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Al Sharif R, Pokharel S. Smart city dimensions and associated risks: Review of literature. Sustainable Cities and Society 2022, 77, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrão C, Moura P, Almeida A T. Review of smart city assessment tools. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. A typology of smart city assessment tools and indicator sets. Sustainable cities and society 2020, 53, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y D,K. F A,A. A M B.Developing a Comprehensive Smart City Rating System: Case of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Urban Planning and Development 2024, 150, 04024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 11. Joyce A ,Javidroozi V .Smart city development: Data sharing vs. data protection legislations. Cities.
- 12. Sorri K ,Yrjönkoski K ,Seppänen M .Smart cities, smarter values: Unpacking the ecosystem of urban innovation. Technology in Society.
- José R,Rodrigues H. A Review on Key Innovation Challenges for Smart City Initiatives. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha M M,Golden E J. Smarter and resilient smart contracts applications for smart cities environment using blockchain technology. Automatika 2024, 65, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyworks Showcases Technologies for Smart Cities, Automotive and More at CES. Telecomworldwire 2024.
- Deveci M, Pekaslan D, Canıtez F. The assessment of smart city projects using zSlice type-2 fuzzy sets based Interval Agreement Method. Sustainable cities and society 2020, 53, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang Yuqiong, Xie Xinshui. Digital twin city governance: changes, dilemmas and countermeasures. E-Government 2021, 10, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mei Jie. Technology adapts to the city: Subject oppression and ethical dilemmas in digital transformation. Theory and Reform 2021, 3, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Mao Zijun, Huang Yingxu, Xu Xiaolin. Information Security Risk Analysis and Countermeasures of Smart City from the Perspective of Information Ecology. Chinese Public Administration 2019, 9, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zou Weizhong,Zhang Liyun. From Compartmentalization to Integration:The Compartmentalization Dilemma of Smart Cities and Strategies for Reconfiguring the Socio-Technical Imagination. Journal of Tianjin Administration Institute 2023, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya T R, Bhattacharya A, Mclellan B, et al. Sustainable smart city development framework for develo** countries. Urban Research & Practice 2020, 13, 180–212. [Google Scholar]
- Richey B, F. Risk Management Framework 2.0[D]. Iowa State University.
- Hiller J S, Russell R S. Privacy in crises: The NIST privacy framework. Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management 2017, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdullahH A,Nizam HT,KutubT. The Evolution of Information Security Strategies: A Comprehensive Investigation of INFOSEC Risk Assessment in the Contemporary Information Era. Computer and Information Science 2023, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Xiangqian, Liu Na. The Governance of Urban Community Public Space from the Perspective of Space Theory. Shanghai Urban Management 2022, 31, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yang Liu, Gan Quanxin, Ma Deshui. Public environmental concern and corporate environmental investment—from the perspective of the moderating effect of green image. Finance and Accounting Monthly 2020, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shan Zhiguang, Xu Qingyuan, Ma Chaojiang, et al. Digital economy development evaluation system and prospects based on ternary space theory. Macroeconomic Management 2020, 2, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- LIU Xizhao, LI Xiaoshun, HE Weikang, et al. The Coupling Coordination Degree of Human-Land and the Spatial Allocation of “Production-Living-Ecological”: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Modern Urban Research 2022, 10, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Juntao, Zhai Jingtong. Measurement of coupling coordination degree in China’s “Three Living Spaces”. Urban Problems 2019, 11, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xie Guogen, Jiang Shiquan, Zhao Chunyan. Analysis of the coupling coordination level of regional economy, urbanization and social governance. Statistics & Decision 2020, 36, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zou Xiuqing, Xie Meihui, Xiao Zegan, et al. EVALUATION OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF OBSTACLE FACTORS BASED ON ENTROPY WEIGHT TOPSIS METHOD. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning 2021, 42, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- LI Ruzi, HUANG Xiaoling, LIU Yaobin. Spatio-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of China's urbanization from 2010 to 2020. Acta Geographica Sinica 2023, 78, 777–791. [Google Scholar]
- WANG Shu-jia, KONG Wei, REN Liang, et al. Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China. Journal of Natural Resources 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU Chuangqing, ZHOU Xiyimin, HuangCheng. Study on the coupling and coordination relationship between the optimization of industrial structure and the construction of ecological civilization of ecological civilization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Journal of Central China Normal University(Natural Sciences) 2020, 54, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- GE Shi-shuai, ZENG Gang, YANG Yang, et al. The coupling relationship and spatial characteristics analysis between ecological civilization construction and urbanization in the Yellow River Economic Belt. Journal of Natural Resources 2021, 36, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHEN Hua-yu, WANG Zhao-xia, GAO Cheng-yao, et al. Determining the number of BP neural network hidden layer units. Journal of Tianjin University of Technology 2008, 5, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- MengFankun,WuXiangling. Revisiting “Smart City” : Three Basic Research Questions———Based on a Systematic Review of English Literature. Public Administration and Policy Review.
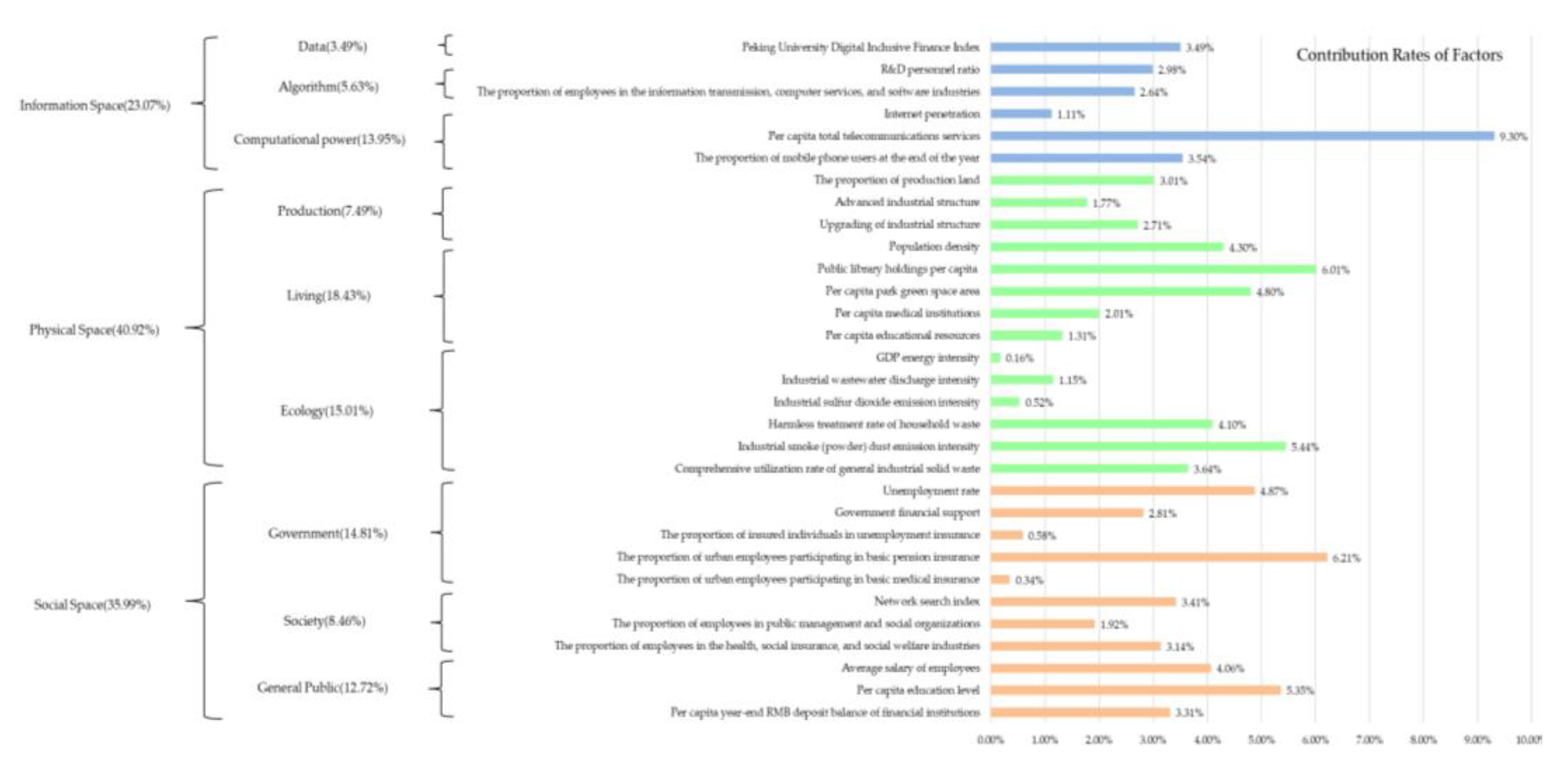
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Index Layer | Index Properties | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informational Space subsystem indices | Data | Peking University Digital Inclusive Finance Index | + | 0.167 |
| Algorithm | R&D personnel ratio(%) | + | 0.168 | |
| The proportion of employees in the information transmission, computer services, and software industries(%) | + | 0.163 | ||
| Computational power |
Internet penetration(%) | + | 0.170 | |
| Per capita total telecommunications services(yuan) | + | 0.169 | ||
| The proportion of mobile phone users at the end of the year(%) | + | 0.164 |
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Index Layer | Index Properties | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Space subsystem indices |
Production | The proportion of production land(%) | + | 0.067 |
| Advanced industrial structure(%) | + | 0.071 | ||
| Upgrading of industrial structure(%) | + | 0.068 | ||
| Living | Population density(%) | − | 0.073 | |
| Public library holdings per capita (volumes) | + | 0.072 | ||
| Per capita park green space area(square meters) | + | 0.073 | ||
| Per capita medical institutions | + | 0.067 | ||
| Per capita educational resources(persons) | + | 0.067 | ||
| Ecology | GDP energy intensity(yuan/billion kilowatt hours) | − | 0.074 | |
| Industrial wastewater discharge intensity(%) | − | 0.074 | ||
| Industrial sulfur dioxide emission intensity(%) | − | 0.074 | ||
| Harmless treatment rate of household waste(%) | + | 0.074 | ||
| Industrial smoke (powder) dust emission intensity(%) | − | 0.074 | ||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste(%) | + | 0.073 |
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Index Layer | Index Properties | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Space subsystem indices |
Government | Unemployment rate(%) | − | 0.096 |
| Government financial support(%) | + | 0.091 | ||
| The proportion of insured individuals in unemployment insurance(%) | + | 0.087 | ||
| The proportion of urban employees participating in basic pension insurance(%) | + | 0.089 | ||
| The proportion of urban employees participating in basic medical insurance(%) | + | 0.089 | ||
| Society | Network search index | + | 0.093 | |
| The proportion of employees in public management and social organizations(%) | + | 0.093 | ||
| The proportion of employees in the health, social insurance, and social welfare industries(%) | + | 0.091 | ||
| General Public | Average salary of employees(yuan) | + | 0.091 | |
| Per capita education level(year) | + | 0.092 | ||
| Per capita year-end RMB deposit balance of financial institutions(yuan) | + | 0.090 |
| Coordination Phase | Degree of Coupling Coordination | Coordination Index |
|---|---|---|
| Disordered type | Extremely disordered | (0,0.1] |
| Severely disordered | (0.1,0.2] | |
| Mildly disordered | (0.2,0.3] | |
| Endangered coordination | (0.3,0.4] | |
| Transition type | Fragile coordination | (0.4,0.5] |
| Barely coordination | (0.5,0.6] | |
| Basic coordination | (0.6,0.7] | |
| Coordinated development | Intermediate coordination | (0.7,0.8] |
| Well-coordinated | (0.8,0.9] | |
| High-quality coordination | (0.9,1] |
| City (Ranked) | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.655 | 0.687 | 0.717 | 0.733 | 0.744 | 0.765 | 0.790 | 0.815 | 0.832 |
| Guangzhou | 0.655 | 0.685 | 0.668 | 0.724 | 0.728 | 0.730 | 0.738 | 0.734 | 0.765 |
| Shanghai | 0.602 | 0.614 | 0.659 | 0.647 | 0.663 | 0.696 | 0.709 | 0.721 | 0.725 |
| Hangzhou | 0.561 | 0.617 | 0.618 | 0.683 | 0.664 | 0.673 | 0.717 | 0.729 | 0.731 |
| Nanjing | 0.610 | 0.615 | 0.609 | 0.648 | 0.650 | 0.671 | 0.668 | 0.683 | 0.715 |
| Jinan | 0.562 | 0.563 | 0.606 | 0.629 | 0.652 | 0.660 | 0.673 | 0.675 | 0.672 |
| Wuhan | 0.562 | 0.580 | 0.608 | 0.652 | 0.642 | 0.649 | 0.663 | 0.662 | 0.666 |
| Changsha | 0.530 | 0.566 | 0.588 | 0.601 | 0.626 | 0.651 | 0.678 | 0.675 | 0.678 |
| Shenyang | 0.597 | 0.604 | 0.590 | 0.624 | 0.612 | 0.618 | 0.634 | 0.647 | 0.645 |
| Xi'an | 0.540 | 0.565 | 0.586 | 0.621 | 0.635 | 0.626 | 0.647 | 0.627 | 0.666 |
| Lanzhou | 0.521 | 0.528 | 0.570 | 0.585 | 0.627 | 0.625 | 0.641 | 0.641 | 0.664 |
| Zhengzhou | 0.523 | 0.527 | 0.561 | 0.567 | 0.606 | 0.619 | 0.657 | 0.647 | 0.673 |
| Tianjin | 0.520 | 0.561 | 0.557 | 0.604 | 0.596 | 0.606 | 0.624 | 0.635 | 0.656 |
| Harbin | 0.539 | 0.551 | 0.566 | 0.606 | 0.613 | 0.609 | 0.620 | 0.610 | 0.636 |
| Guiyang | 0.511 | 0.554 | 0.553 | 0.579 | 0.598 | 0.597 | 0.640 | 0.650 | 0.657 |
| Average | 0.515 | 0.534 | 0.551 | 0.574 | 0.580 | 0.596 | 0.621 | 0.625 | 0.640 |
| Chongqing | 0.539 | 0.513 | 0.527 | 0.584 | 0.565 | 0.618 | 0.618 | 0.623 | 0.626 |
| Shijiazhuang | 0.554 | 0.538 | 0.543 | 0.556 | 0.558 | 0.571 | 0.610 | 0.603 | 0.613 |
| Nanning | 0.495 | 0.531 | 0.553 | 0.559 | 0.571 | 0.585 | 0.603 | 0.608 | 0.624 |
| Chengdu | 0.524 | 0.531 | 0.524 | 0.572 | 0.558 | 0.572 | 0.605 | 0.615 | 0.624 |
| Haikou | 0.498 | 0.502 | 0.533 | 0.540 | 0.560 | 0.580 | 0.606 | 0.614 | 0.630 |
| Fuzhou | 0.468 | 0.518 | 0.546 | 0.561 | 0.571 | 0.574 | 0.627 | 0.599 | 0.600 |
| Taiyuan | 0.503 | 0.503 | 0.539 | 0.538 | 0.558 | 0.565 | 0.586 | 0.586 | 0.635 |
| Changchun | 0.488 | 0.495 | 0.501 | 0.535 | 0.523 | 0.536 | 0.564 | 0.591 | 0.613 |
| Hefei | 0.485 | 0.507 | 0.492 | 0.534 | 0.539 | 0.513 | 0.549 | 0.566 | 0.590 |
| Nanchang | 0.419 | 0.475 | 0.488 | 0.522 | 0.501 | 0.534 | 0.575 | 0.579 | 0.603 |
| Urumqi | 0.455 | 0.443 | 0.485 | 0.481 | 0.485 | 0.506 | 0.544 | 0.537 | 0.561 |
| Yinchuan | 0.437 | 0.466 | 0.475 | 0.434 | 0.445 | 0.508 | 0.524 | 0.525 | 0.536 |
| Kunming | 0.373 | 0.396 | 0.450 | 0.479 | 0.469 | 0.475 | 0.528 | 0.548 | 0.564 |
| Hohhot | 0.413 | 0.442 | 0.412 | 0.436 | 0.447 | 0.490 | 0.482 | 0.500 | 0.507 |
| Xining | 0.304 | 0.341 | 0.394 | 0.401 | 0.400 | 0.444 | 0.506 | 0.495 | 0.487 |
| Year | The overall Gini coefficient |
The intra-group Gini coefficient |
The inter-group Gini coefficient |
The contribution of hyperdensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.080 | 0.020 | 0.047 | 0.013 |
| 2012 | 0.076 | 0.019 | 0.047 | 0.011 |
| 2013 | 0.071 | 0.017 | 0.043 | 0.011 |
| 2014 | 0.076 | 0.019 | 0.045 | 0.012 |
| 2015 | 0.077 | 0.019 | 0.044 | 0.014 |
| 2016 | 0.070 | 0.017 | 0.039 | 0.014 |
| 2017 | 0.062 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.010 |
| 2018 | 0.062 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.010 |
| 2019 | 0.060 | 0.015 | 0.036 | 0.009 |
| Decomposition | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The intra-group Gini coefficient |
EC | 0.059 | 0.058 | 0.054 | 0.058 | 0.055 | 0.056 | 0.048 | 0.054 | 0.056 |
| NE | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.021 | 0.011 | |
| CI | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.046 | 0.043 | 0.049 | 0.051 | 0.044 | 0.038 | 0.029 | |
| WE | 0.085 | 0.077 | 0.069 | 0.077 | 0.083 | 0.065 | 0.056 | 0.054 | 0.058 | |
| The inter-group Gini coefficient |
EC-WE | 0.109 | 0.106 | 0.099 | 0.106 | 0.105 | 0.094 | 0.085 | 0.087 | 0.087 |
| EC-CI | 0.075 | 0.069 | 0.066 | 0.069 | 0.067 | 0.065 | 0.060 | 0.058 | 0.056 | |
| EC-NE | 0.059 | 0.060 | 0.061 | 0.058 | 0.064 | 0.070 | 0.061 | 0.062 | 0.056 | |
| NE-WE | 0.088 | 0.081 | 0.066 | 0.077 | 0.077 | 0.058 | 0.049 | 0.048 | 0.047 | |
| NE-CI | 0.056 | 0.048 | 0.043 | 0.045 | 0.046 | 0.046 | 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.027 | |
| CI-WE | 0.073 | 0.068 | 0.067 | 0.074 | 0.078 | 0.066 | 0.060 | 0.057 | 0.055 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




