Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CTAB Modified CNCs (CTAB-CNCs)
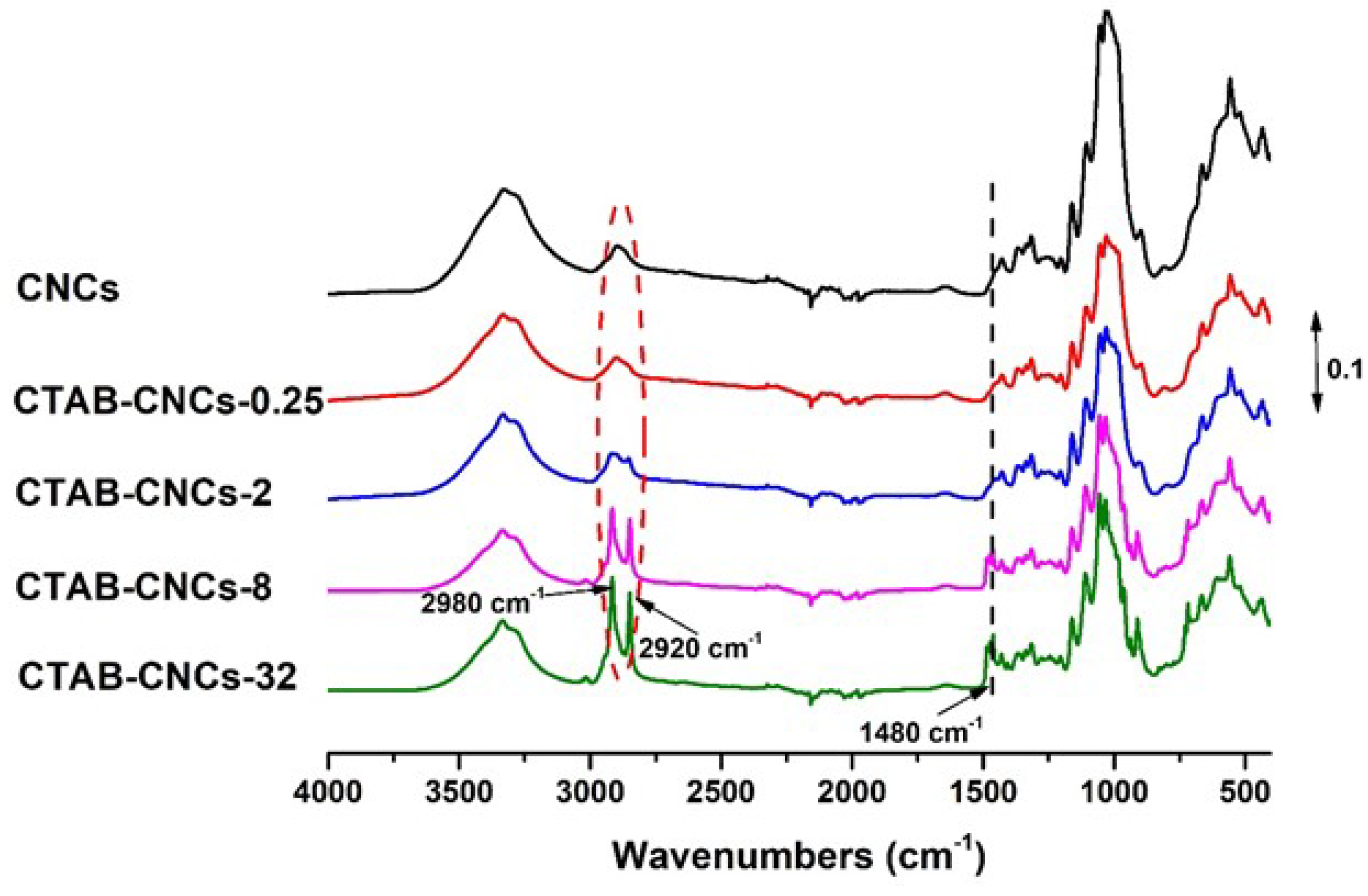
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
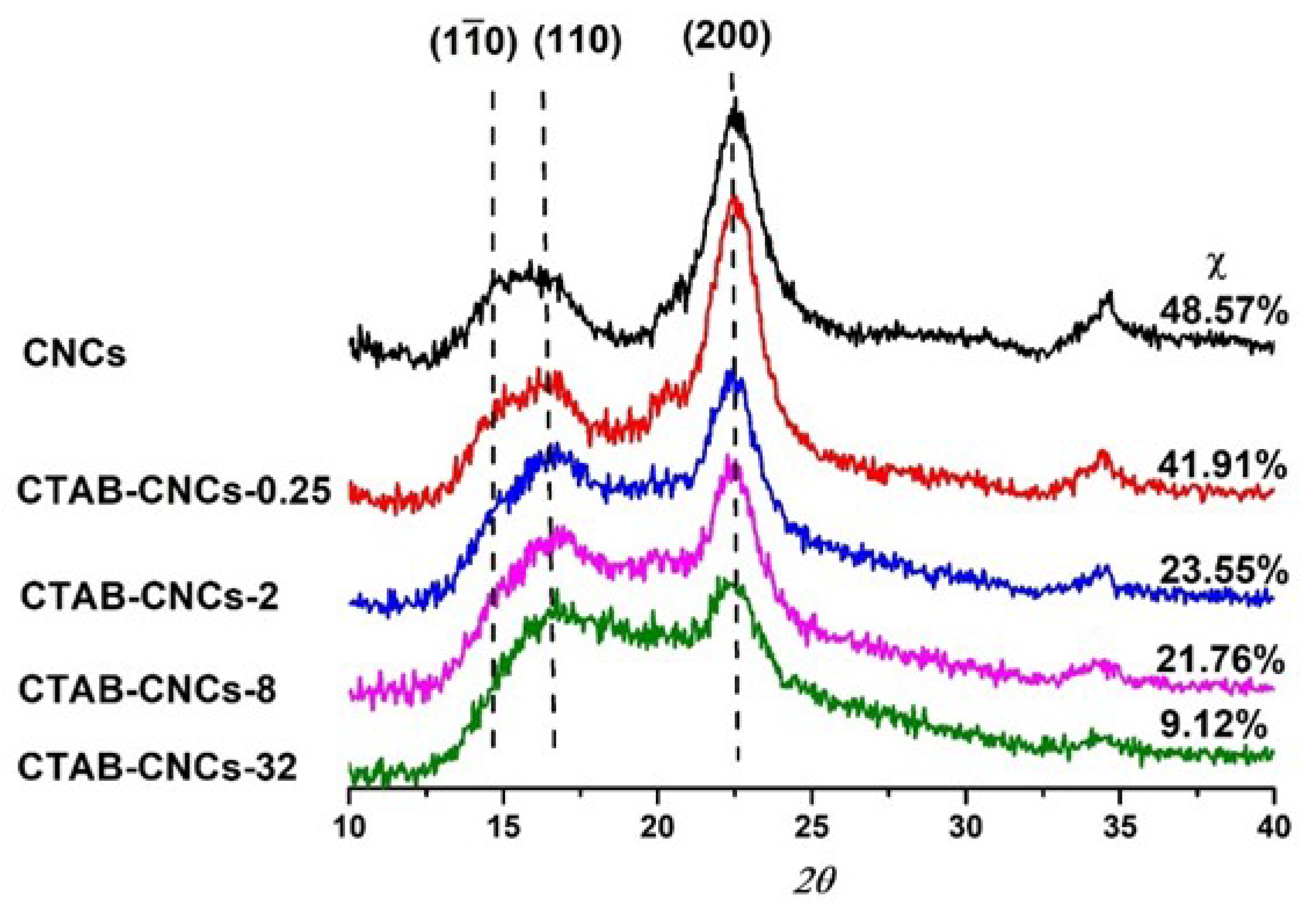
2.4. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
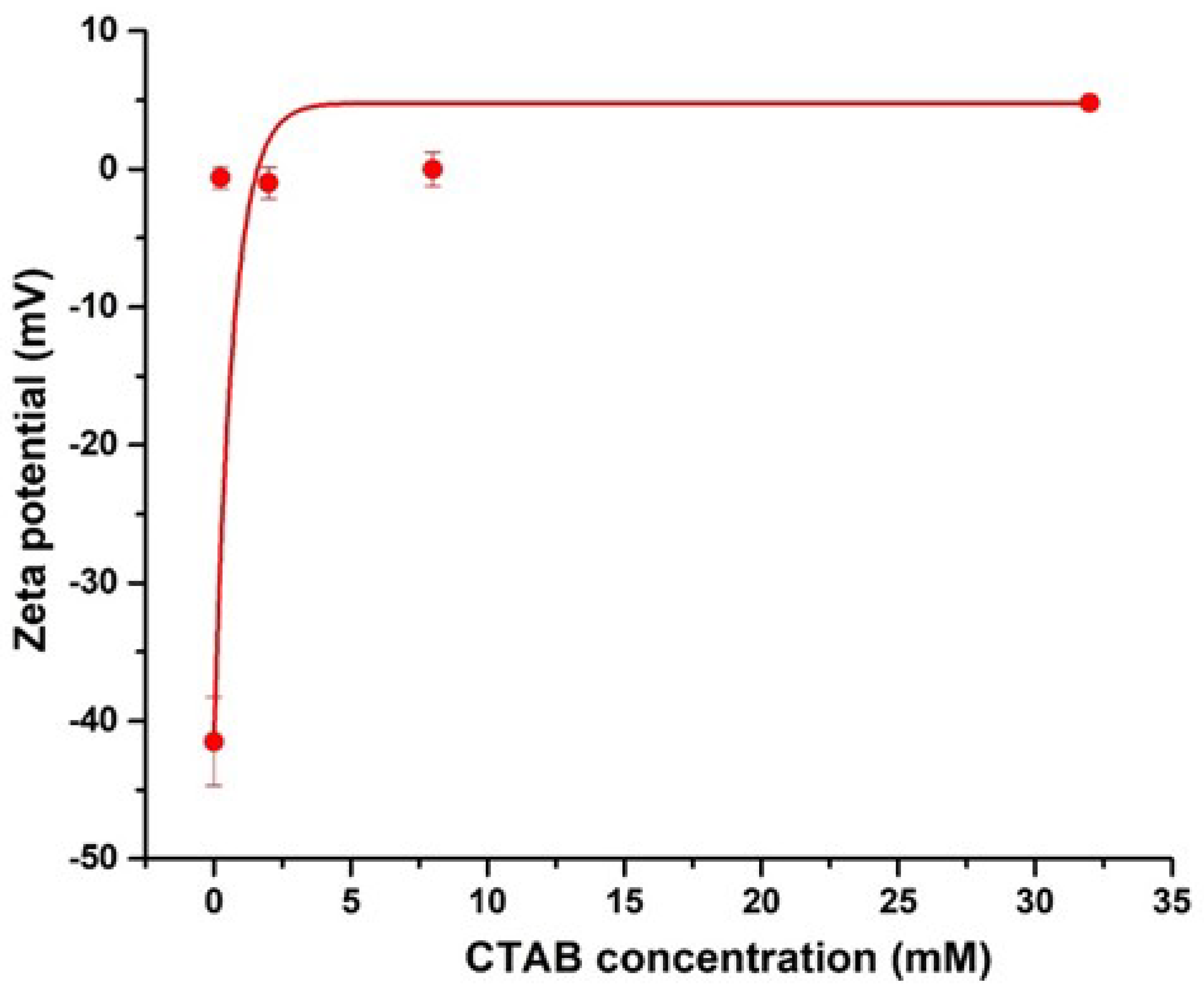
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
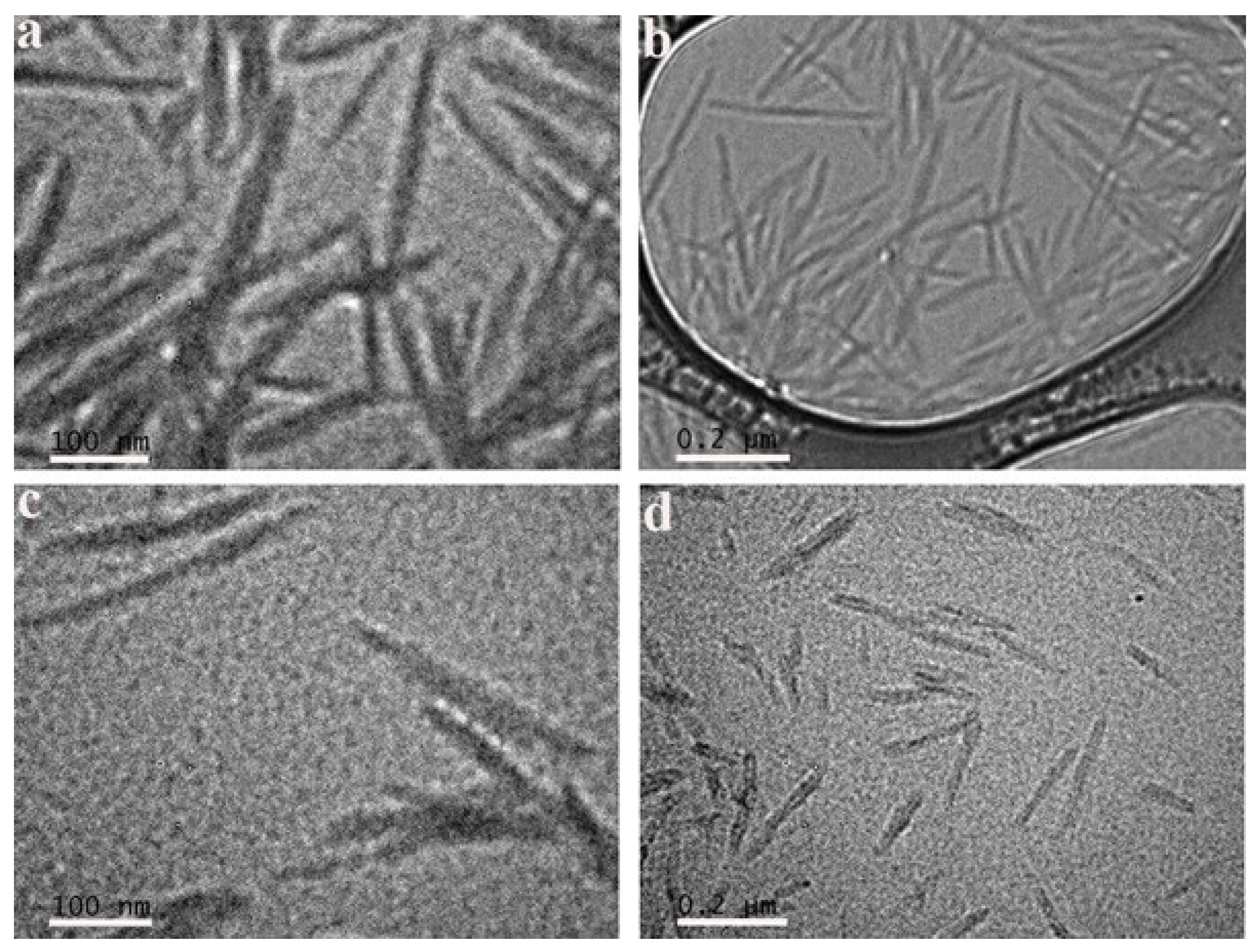
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
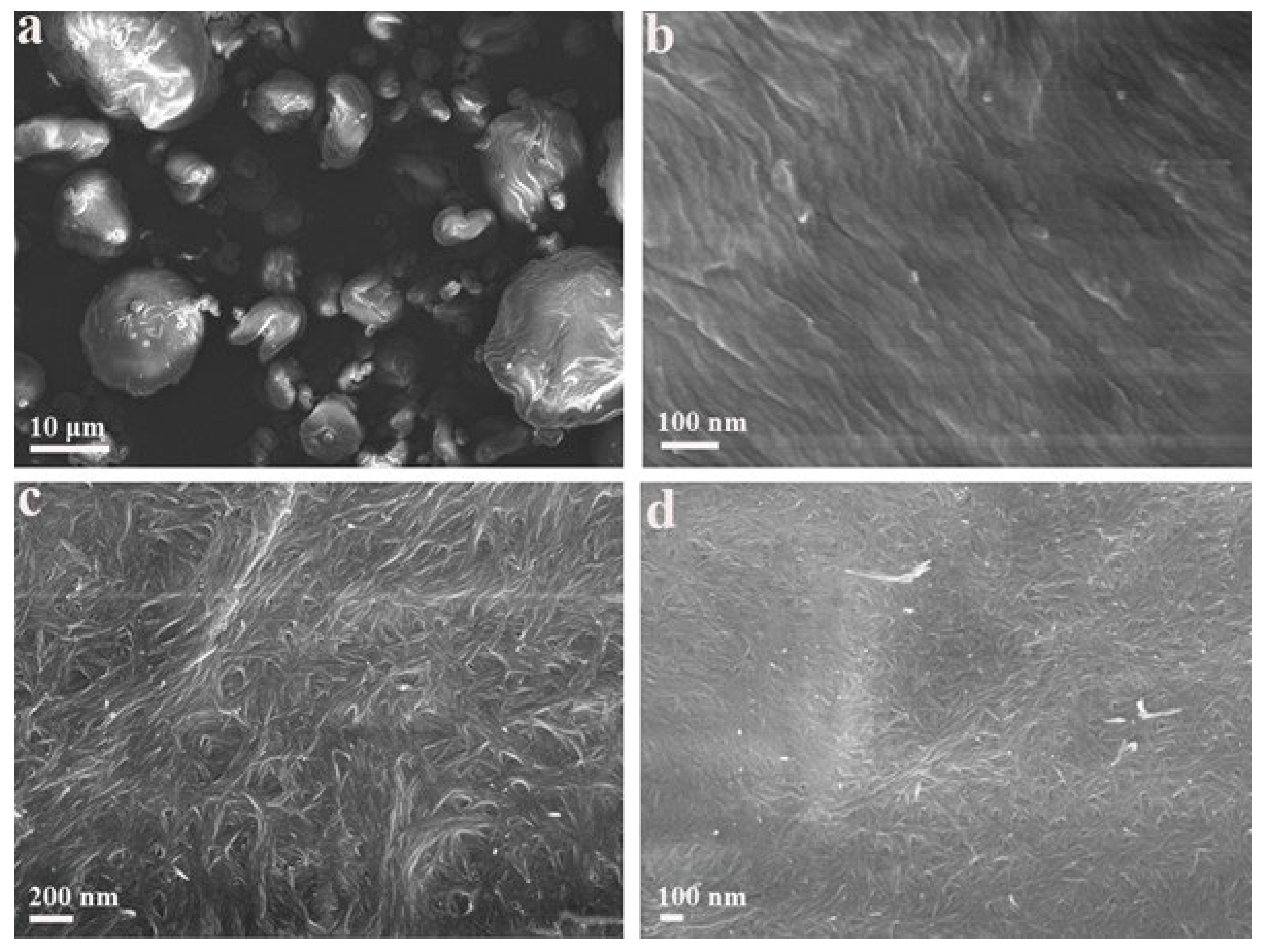
2.7. Scanning Electrical Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Spin Coating of the CNC and CTAB-CNC Dispersions
2.9. Wettability and Surface Energy
2.10. Immersion Coating of CNC and CTAB-CNC Dispersions
2.11. Ellipsometry
3. Results
3.1. Adsorption of CTAB Molecules on CNCs
3.2. Effects of CTAB Adsorption on CNCs
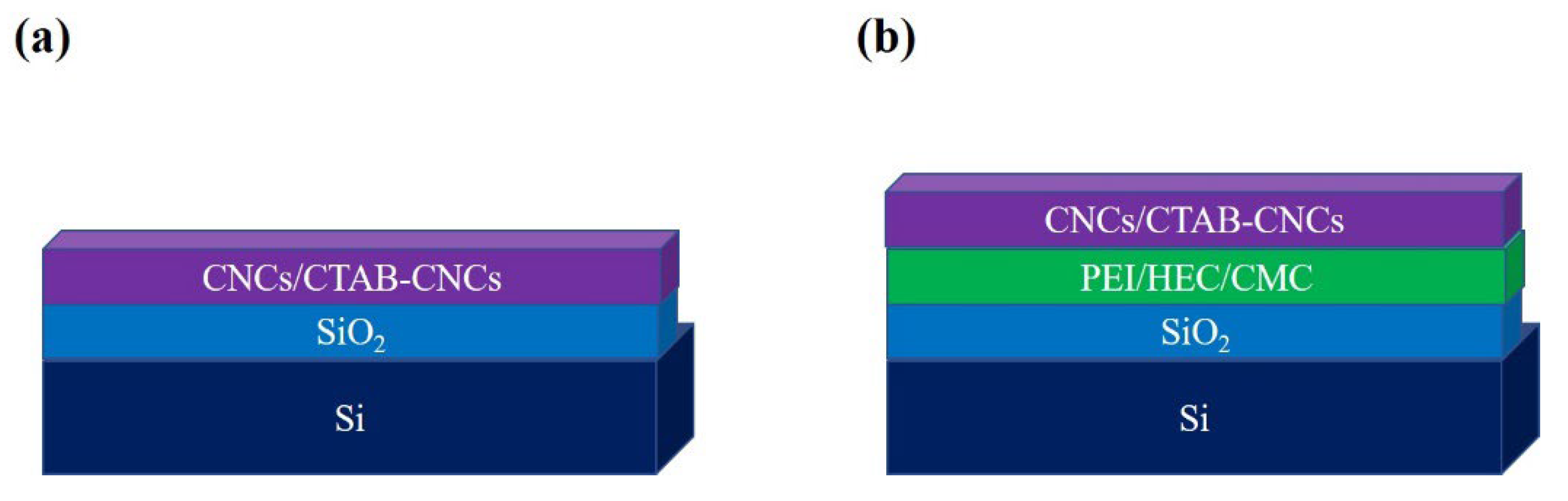
3.3. Ellipsometric Study and Adsorption of CNCs and CTAB-CNCs onto Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ranjbar, D.; Raeiszadeh, M.; Lewis, L.; MacLachlan, M. J.; Hatzikiriakos, S. G. Adsorptive removal of Congo red by surfactant modified cellulose nanocrystals: a kinetic, equilibrium, and mechanistic investigation. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3211–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, L. Controlled production of spruce cellulose gels using an environmentally “green” system. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluk, Y.; Lahiji, R.; Zhao, L.; McDermott, M. T. Suspension viscosities and shape parameter of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2011, 377, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishkewich, N.; Mohammed, N.; Tang, J.; Tam, K. C. Recent advances in the application of cellulose nanocrystals. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2017, 29, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Elanthikkal, S.; Francis, T.; Sangeetha, C.; Unnikrishnan, G. Cellulose Whisker-Based Green Polymer Composites. Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials, ed. VK Thakur, MK Thakur, and MR Kessler. Wiley: USA, 2017; pp. 461–494. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L. A.; Rojas, O. J. Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chemical reviews 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K. E.; Qi, H.; Hamad, W. Y.; MacLachlan, M. J. Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures. Nature 2010, 468, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: a review. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3274–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Gray, D. G. Parabolic focal conics in self-assembled solid films of cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5555–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunasee, R.; Hemraz, U. D.; Ckless, K. Cellulose nanocrystals: A versatile nanoplatform for emerging biomedical applications. Expert opinion on drug delivery 2016, 13, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, I.; Cathala, B. Surfactant-free high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Boluk, Y. Release of cellulose nanocrystal particles from natural rubber latex composites into immersed aqueous media. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2021, 4, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, Z.; Niazi, M. B. K.; Gregersen, Ø. W. Mechanical, thermal and swelling properties of cellulose nanocrystals/PVA nanocomposites membranes. Journal of industrial and engineering chemistry 2018, 57, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, O. V.; Voronova, M. I.; Afineevskii, A. V.; Zakharov, A. G. Polyethylene oxide films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: Microstructure-properties relationship. Carbohydrate polymers 2018, 181, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nessi, V.; Falourd, X.; Maigret, J.-E.; Cahier, K.; D’orlando, A.; Descamps, N.; Gaucher, V.; Chevigny, C.; Lourdin, D. Cellulose nanocrystals-starch nanocomposites produced by extrusion: Structure and behavior in physiological conditions. Carbohydrate polymers 2019, 225, 115123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunati, E.; Armentano, I.; Zhou, Q.; Iannoni, A.; Saino, E.; Visai, L.; Berglund, L. A.; Kenny, J. M. Multifunctional bionanocomposite films of poly (lactic acid), cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Carbohydrate polymers 2012, 87, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusin, C. J.; El Bakkari, M.; Du, R.; Boluk, Y.; McDermott, M. T. Plasmonic cellulose nanofibers as water-dispersible surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2020, 3, 6584–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salajková, M.; Berglund, L. A.; Zhou, Q. Hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals modified with quaternary ammonium salts. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2012, 22, 19798–19805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Enhanced emulsifying properties of wood-based cellulose nanocrystals as Pickering emulsion stabilizer. Carbohydrate polymers 2017, 169, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboorani, A.; Riedl, B. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) by a cationic surfactant. Industrial Crops and Products 2015, 65, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Marway, H.; Cranston, E. D. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal 2014, 29, 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Prathapan, R.; Thapa, R.; Garnier, G.; Tabor, R. F. Modulating the zeta potential of cellulose nanocrystals using salts and surfactants. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2016, 509, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Long, Y.; Ni, Y. Cellulose nanocrystal/hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide/silver nanoparticle composite as a catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Carbohydrate polymers 2017, 156, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, Y.; Foulon, L.; Aguié-Béghin, V.; Molinari, M.; Douillard, R. Langmuir–Blodgett films of cellulose nanocrystals: Preparation and characterization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2007, 316, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, P.; Choi, S.-Y.; Shim, B.; Lee, J.; Cuddihy, M.; Kotov, N. A. Molecularly engineered nanocomposites: layer-by-layer assembly of cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2914–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, Y.; Ngo, T.-D.; Fraschini, C.; Boluk, Y. Aggregate morphology and aqueous dispersibility of spray-dried powders of cellulose nanocrystals. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2019, 58, 19926–19936. [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer, J. M. [18] Detergents: an overview. Methods in enzymology 1990, 182, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habibi, Y.; Hoeger, I.; Kelley, S. S.; Rojas, O. J. Development of Langmuir− Schaeffer cellulose nanocrystal monolayers and their interfacial behaviors. Langmuir 2010, 26, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; French, A. D.; Condon, B. D.; Concha, M. Segal crystallinity index revisited by the simulation of X-ray diffraction patterns of cotton cellulose Iβ and cellulose II. Carbohydrate polymers 2016, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Kalantari, M.; Aslanzadeh, S.; Boluk, Y. Interfacial interactions and electrospinning of cellulose nanocrystals dispersions in polymer solutions: a review. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology 2022, 43, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, F.; Su, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, X. Investigation of adsorption and photocatalytic activities of in situ cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-modified Bi/BiOCl heterojunction photocatalyst for organic contaminants removal. RSC advances 2016, 6, 93309–93317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirich, C. L.; Picheth, G. F.; Machado, J. P. E.; Sakakibara, C. N.; Martin, A. A.; de Freitas, R. A.; Sierakowski, M. R. Influence of mechanical pretreatment to isolate cellulose nanocrystals by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. International journal of biological macromolecules 2019, 130, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, S.-J.; Adhikari, B. Effects of drying methods on the functional properties of flaxseed gum powders. Carbohydrate polymers 2010, 81, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvério, H. A.; Neto, W. P. F.; Dantas, N. O.; Pasquini, D. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from corncob for application as reinforcing agent in nanocomposites. Industrial crops and products 2013, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of freezing/thawing cycles and cellulose nanowhiskers on structure and properties of biocompatible starch/PVA sponges. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering 2010, 295, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, N.; Ahmad, I.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Ramli, S. Hydrophobic kenaf nanocrystalline cellulose for the binding of curcumin. Carbohydrate polymers 2017, 163, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Berg, J. C. A review of the different techniques for solid surface acid–base characterization. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2003, 105, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R. J.; Chaudhury, M. K.; van Oss, C. J. Theory of Adhesive Forces Across Interfaces: 2. Interfacial Hydrogen Bonds as Acid—Base Phenomena and as Factors Enhancing Adhesion. In Fundamentals of adhesion, Springer: 1991; pp 153-172.
- Gassan, J.; Gutowski, V. S. Effects of corona discharge and UV treatment on the properties of jute-fibre epoxy composites. Composites science and technology 2000, 60, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Liao, W.; Qi, L. Wettability alteration by CTAB adsorption at surfaces of SiO2 film or silica gel powder and mimic oil recovery. Applied surface science 2004, 221, 6114–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluk, Y.; Zhao, L.; Incani, V. Dispersions of nanocrystalline cellulose in aqueous polymer solutions: structure formation of colloidal rods. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6114–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Solvent | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) |
| DI water | 72.80 | 21.80 | 25.50 | 25.50 |
| Formamide | 58.00 | 39.00 | 2.28 | 39.60 |
| Diiodomethane | 50.80 | 50.80 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sample | θwater | θdiiodomethane | θformamide |
| Glass | 12±2 | 18±2.5 | 8±1 |
| CNCs | 16±2 | 22±3 | 11±2 |
| CTAB-CNCs-2 | 56±1.5 | 45±1 | 38±2 |
| Sample | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) |
| Glass | 40.2 | 31.71 | 8.38 | 29.99 | 71.91 |
| CNCs | 39.42 | 31.34 | 8.4 | 29.23 | 70.76 |
| CTAB-CNCs-2 | 34.22 | 16.16 | 5.97 | 11.0 | 50.38 |
| Direct Immersion coating | |
| Layer | Thickness |
| CNCs | 19.5 nm ± 3 nm |
| CTAB-CNCs | 39.67 nm ± 5 nm |
| Polymer-Based Immersion coating | |
| Layer | Thickness |
| Si | 2 mm |
| SiO2 | 508nm ± 5nm |
| PEI (100 ppm) | 90nm ± 12nm |
| CNCs (0.05 w/w%) | 54.5 nm ± 14nm |
| CNCs (0.5 w/w%) | 103.5 nm ± 13nm |
| Polymer coating (nm) thickness (nm) | CNCs (nm) | CTAB-CNCs (nm) |
| CMC: 40±4 | 60+5 | 105±8 |
| HEC: 70±8 | 140±10 | 206±8 |
| PEI: 120±7 | 160±14 | 70±11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





