1. Introduction
The specific detection of the human papillomavirus (HPV) subtype has favored the reduction of the mortality and morbidity rate in women due to cervical cancer (CC) worldwide [
1]. This reduction has been achieved due to the widespread use of liquid-based cytology preparations to obtain cervical samples, and the implementation of new molecular technologies for HPV genotyping by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [
2,
3,
4,
5].
Globally, CC is the fourth most common cancer in women, with 604,000 new cases in 2020 [
5]. About 90% of the 342,000 deaths caused by CC occurred in low and middle-income countries [
6,
7]. The highest rates of this tumor incidence and mortality are in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), Central America, and South-East Asia. Regional differences in the CC burden are related to inequalities in access to vaccination, screening and treatment services, risk factors (including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevalence, and social and economic determinants such as sex), gender biases, and poverty. Women living with HIV are six times more likely to develop CC compared to the general population, with an estimated 5% of all cases attributable to this infection. The contribution of HIV to CC disproportionately affects younger women, and as a result, 20% of children who lose their mother to cancer do so due to this neoplasia [
8].
In Mexico, this neoplasm represents the second cause of cancer in women, with 9,440 new cases per year, and the second cause of death, with 4,340 cases [
9]. Among women with invasive CC, around 70% are diagnosed with locally advanced disease, which highlights deficiencies in timely diagnosis [
9]. All these data reinforce the need to continue implementing early screening strategies for CC in Mexico and in other Latin American countries with similar incidences.
In recent years, the diagnosis of HPV infections by detection of viral DNA and PCR genotyping of high-risk (HR) variants in cervical samples has replaced the traditional Pap smear due to its higher sensitivity [
1,
10]. The improvement in the HR HPV detection capacity offered by PCR and its automation has led various countries, such as Australia, to abandon the Papanicolaou test as a CC screening [
11]. On the other hand, in Latin America, the efforts to implement HPV genotyping by PCR continue to be limited, and greater awareness of this serious female health problem is necessary in public institutions and private hospitals [
12].
HPV is a highly transmissible virus that leads to transient infections, with several factors increasing the risk of its persistence, including genetics, age, smoking, and the specific genomic sequence of the infecting virus [
13]. To date, more than 150 subtypes of papillomavirus viruses have been described that, based on their association with CC, have been classified as very high risk (HPV-16 and HPV-18), twelve high-risk subtypes (HR12), and other low-risk (LR) types that are associated with benign mucosal lesions [
14]. The high- and very-high-risk HPV subtypes (16, 18, and HR12) are associated with malignant lesions and cause approximately 70% of CC cases worldwide [
15,
16].
The cytological course caused by transient HPV infection begins with low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, of which 90% revert to healthy epithelium. However, HR-HPV-specific infections aggravated by host risk factors are more difficult to reverse, and their persistence leads to high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (moderate or high dysplasia) that can progress to CC [
15]. Cytological assessment by the expert cytotechnologist is highly relevant for predicting the course of HPV infection, although it has its limitations, such as low sensitivity and the impossibility of distinguishing persistent infection from reinfection [
17]. These are examples in which molecular tools such as PCR, given their greater sensitivity and ability to identify the infection HPV subtype, outperform traditional diagnostics [
4,
5].
To date, seven PCR assays for the detection and genotyping of HPV from cervical cell samples have been validated. Three of them are tests aimed at amplifying a region of the L1 gene (Abbott RealTime High-Risk HPV Test, Anyplex II HPV HR Detection, and Cobas 4800 HPV Test). While another four are assays that amplify early region genes (BD Onclarity HPV Assay, HPV-Risk Assay, PapilloCheck HPV-Screening Test, and Xpert HPV) [
18].
In Mexico and the rest of Latin America, strategies have been developed to implement these molecular PCR tests for HPV detection in both public and private institutions [
12]. However, automated PCR methods, such as those used in our laboratories (Cobas 4800 HPV Test), stand out from other methods, not only for their ability to process many simultaneous samples but also for their speed and diagnostic accuracy [
19]. The use of an internal control for co-amplification of a human gene makes it possible to practically eliminate the analysis of invalid samples, and the obtaining of false negatives [
19].
Although the specific detection of HPV genotyping by PCR is currently the “gold-standard” technique in the early diagnosis of CC, complementary techniques have been developed for the detection of premalignant cervical lesions in liquid cytology samples [
20]. The p16INK4a (p16) protein is a regulatory protein of the cell cycle under normal physiological conditions [
21]. This biomarker is effective in histological samples and is widely used to improve the reproducibility of cervical biopsy assessment and improves the accuracy in detecting premalignant lesions [
20,
22,
23,
24]. Likewise, the simultaneous detection of p16 and Ki67 (a proliferation biomarker) within the same cervical epithelial cell has been proposed as a marker of cellular transformation mediated by infections with the 12 high-risk HPV genotypes (HR12) [
25]. This combination of biomarkers (p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology, Cintec-Plus) has provided excellent results in cervical cytological samples where it has been used for the detection of premalignant and malignant lesions of CC [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30].
Given the proven advantages of the herein-described molecular tests, we have been implementing them in our laboratories and boosting their adoption among private practicing gynecologists in Mexico.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples and Diagnostic Algorithms
A total of 4,499 cervix samples received consecutively in our laboratories were analyzed for three strategies: (a) molecular PCR analyses (to screen for the presence of HPV infections); (b) liquid-based cytology was performed to search for cellular alterations suggestive of HPV infections and (c) finally, if the medical expert followed the triage, they requested to the laboratory dual-staining cytology (to assess if cellular transformation process has already started). All samples were analyzed by PCR, 3806 by liquid-based cytology, and 567 samples by p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology.
2.2. Clinical Specimen Sampling
Cervical samples from the cervix were taken by gynecologists in private clinical practice using a cervix brush and deposited in a transport medium (ThinPrep or Roche Cell Collection Medium). The vials with the samples were sent at room temperature to the laboratory, where they were stored and refrigerated (4 degrees Celsius) until processing.
2.3. Liquid-Based Cytology (PAP Test)
Liquid-based cytology slides were prepared by a cytotechnologist and interpreted according to the Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology (third edition, 2017), whereas for quality control and quality assurance, a pathologist reviewed 50% of negative samples and 100% of the positive ones.
2.4. HPV PCR Assay
The COBAS 4800 HPV Test (Roche) is an FDA-approved and validated qualitative test device for the detection of HPV DNA in swabs from the cervical canal. This test amplifies target DNA isolated from cervical epithelium by real-time PCR to detect HPV 16 and HPV 18, along with a simultaneous pooled result for 12 other HR genotypes in a single test. The entire procedure is automated, and the manufacturer's instructions were followed. The COBAS 4800 HVPV Test Primers are used to amplify DNA from 14 HR-HPV types (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68) in a single analysis, where probes with four different reporter dyes screen different targets in the multiplex reaction: dye 1 screens 12 pooled HR-HPVs (31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68), dyes 2 and 3 screen for HPV 16 and 18, respectively, while dye 4 targets the human β-globin gene to provide a control for uterine cervical cell adequacy of, extraction, and amplification.
2.5. p16/Ki67 Dual-Stain Cytology
One slide for each sample was prepared as a PAP test, using a Cytospin chamber adapter and subsequently subjected to p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology using the CINtec Plus Cytology Kit (Roche Laboratories) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Staining was performed using a BenchMark GX Stainer. All samples were evaluated by a trained cytotechnologist. An initial evaluation was performed to confirm the presence of the minimal criteria for squamous cellularity defined by the Bethesda terminology. Subsequently, the slide was checked for the presence of double-immunoreactive cervical epithelial cells, that is, cells with simultaneous brown cytoplasmic p16 immunostaining and Ki67 red nuclear immunostaining, which were interpreted as positive by double-stained cytological analysis, regardless of the morphological interpretation. A pathologist reviewed all cases with positive cells for double staining to confirm the result.
3. Results
Four thousand and four hundred ninety-nine liquid-based cervical samples were performed on samples from patients referred by private gynecologists mostly from central regions of Mexico. A molecular PCR study for genotyping of HPV was performed on all samples to detect the 14 most common HR genotypes of HPV to contribute to the early prevention of CC. In parallel, Pap test was performed in 84.6% (n=3,806) samples.
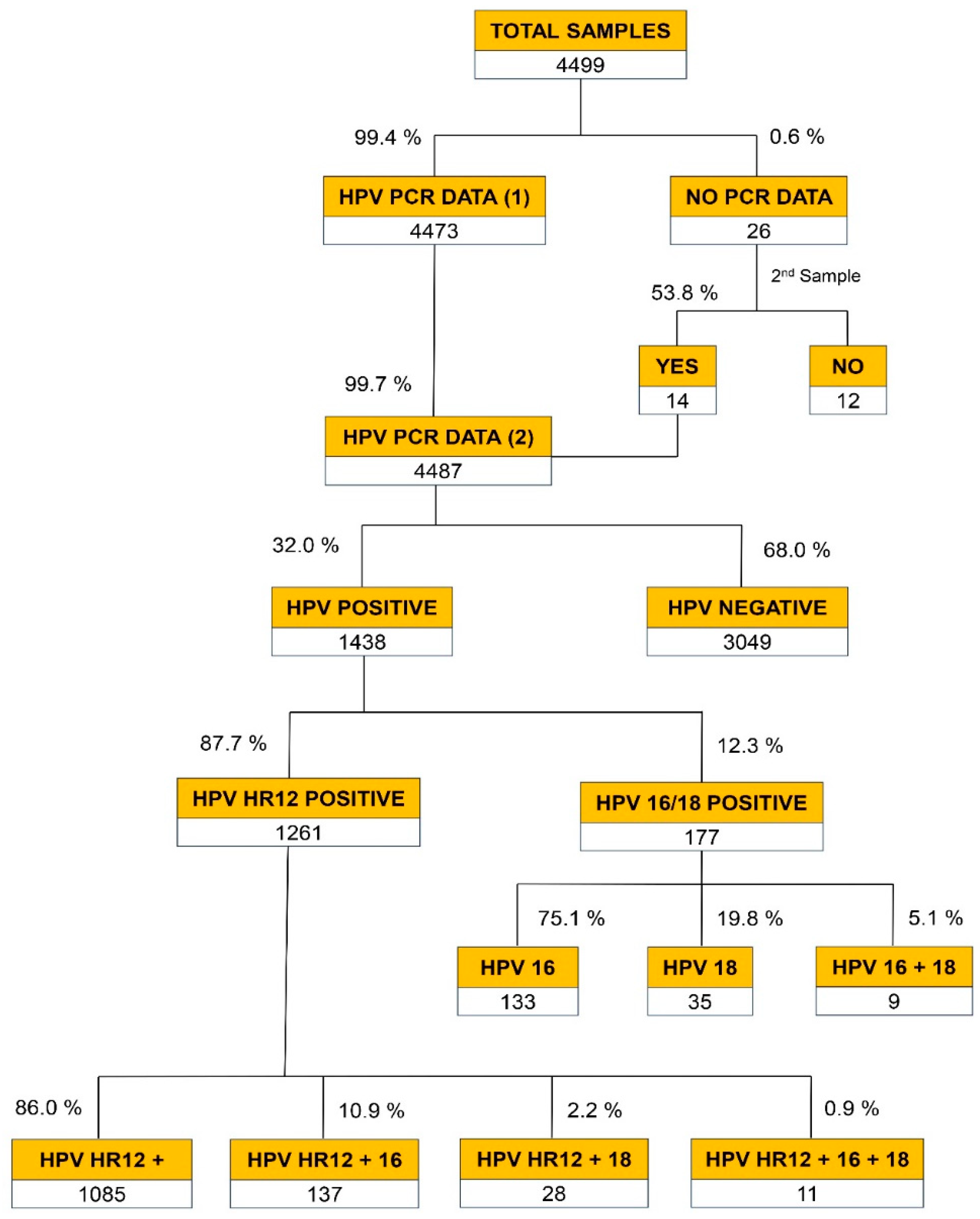
The global distribution of the results of the viral genotypes revealed by the PCR analysis is described in
Figure 1. In 99.4% of the cases, the samples received were considered adequate for this test given that they rendered positive for the amplification of the internal control, i.e. the genomic β-globin gene. In cases where samples did not pass this control (0.6%), a second sample was requested from the gynecologist. This request was met on 53.8% of the occasions (14/26). Thus, the final number of PCR results was 4,487, or 99.7% of the samples received.
Of the total results obtained (n=4,487), 68% rendered negative results (n=3,049) for any of the 14 HR-HPV genotypes analyzed. Of the 1,438 samples that tested positive for HR HPV-PCR (32%), 1,261 (87.7%) gave positive for any of the 12 HR-HPV subtypes present in the pool (HR12). In 12.3% (n=177) the positive result corresponded to either HPV16 and/or HPV18 subtypes, considered of very high risk for CC.
Figure 1, bottom part, shows the distribution results of the 1,261 positive PCRs for HR12: 86% presented an isolated viral genotype without involving genotypes 16 or 18 (n=1,085), 10.9% involved coinfections with HPV16, 2.2% presented coinfection with HPV18, and 0.9% (11 patients) showed triple infections involving the three of them. Overall, 14.0% of the samples positive for HR HPV from the pool showed coinfection with one of the two HR HPV more oncogenic (viral genotype 16 or 18.)
Figure 1 also details the distribution of positive HPV-PCR results (n=1,438) for the different viral genotypes, either in isolation or in combination (double or triple infection). The most common sample (75.5%) corresponded to positive PCRs for pool of the 12 high-risk subtypes (HR12). Next, with 9.5%, samples with coinfection with HR12 and HPV16 were detected. Thirdly, with 9.2% of the cases, positive PCR for the highly oncogenic HPV16 was detected. Overall, 353 patients (24.5%) had PCR results involving very high-risk viruses (HPV16 and/or HPV18), alone or in combination with viral types on HR12.
Figure 1 also shows that in 87.1% of the patients (n=1,253) an isolated HPV infection was detected [1,085+133+35)/1,438]. However, with this PCR methodology, the existence of some cases of coinfection within the HR12 pool of viral types, cannot be excluded. It also shows that in 185 patients (12.9%) a coinfection of two or more high or very high-risk viruses was detected [9+137+28+11)/1,438]. The results of the PCR viral genotyping distributed by age range are shown in
Table 1.
The data shown in
Table 1 corresponds to 3,826 samples for which data on the age of the patients were available, amounting to 85.3% of the PCR tests performed (3,826/4,487). In this group of patients analyzed, 45.1% (n=1,724) correspond to an age range of 25 to 35 years, 44.2% (n=1,691) correspond to women over 35 years of age, and 10.7% (n=411) are patients under 25 years of age. Overall, the population between 25 and 35 years of age showed 51% positive results for HPV-PCR (614/1,204), followed by 34% of the population over 35 years of age (409/1,204), and 15% for those under 25 years of age (181/1,204). However, if the results are stratified by age ranges, the population under 25 years of age was the one that showed the highest percentage of overall positive HPV-PCR results: 44% (181/411) tested positive for one of the high or very high-risk subtypes. Next, with 35.6% positive results (614/1724), is the population with an age range between 25 and 35 years. Finally, with 24.2% positive results (409/1,691) the population over 35 years of age occupies the third place.
If the results distributed by viral subtype are analyzed, the population between 25 and 35 years of age always shows a higher risk of infection with high or very high-risk genotypes. More than 50% of the results were positive in this age range for any viral genotype alone or in coinfection: 50.1% (450/898) for HR12, 51.8% (57/110) for HPV16, 55.2% (16/29) for HPV18, and 54.5% (91/167) for a viral coinfection.
If the different positive subtypes are analyzed by age range, the HR12 subgroup always shows the highest percentage: 84% (152/181) in patients younger than 25 years, 73.3% (450/614) for the age range of 25 to 35 years, and 72.4% (296/409) for those over 35 years. However, for the other subtypes, their behavior by age is very different. For HPV16, 5% (9/181) was obtained for those under 25 years of age, 9.3% (57/614) for the range of 25 to 35 years, and 10.8% (44/409) for others over 35 years of age. For HPV18, the data were 0.6% (1/181) for those under 25 years of age, 2.6% (16/614) for those 25 to 35 years of age, and 2.9% (12/409) for those over 35 years of age. The data for viral coinfections showed that 10.5% (19/181) correspond to those under 25 years of age, 14.8% (91/614) for the age range of 25 to 35 years, and 13.9% (57/409) for those over 35 years of age.
Analyzing the results globally, it stands out that: (a) The population under 25 years of age presented a higher percentage of positive results for HR12 viral types (84%), compared to 77.3% of the group between 25 and 35 years of age and a figure of 72.4% for those over 35 years of age. (b) The population between 25 and 35 years of age presented a higher percentage of results for coinfection, with 14.8%, compared to 13.9% in the group over 35 years of age and 10.5% in those under 25 years of age. (c) The population over 35 years of age presented a higher percentage of positive results for HPV16, 10.8% compared to 9.3% for the age range 25 to 35, and 5% for those under 25. Likewise, the population over 35 years of age presented a higher percentage of positive results for HPV18 (2.9%), compared to 2.6% for the age range of 25 to 35, and 0.6 % for those under 25 years of age.
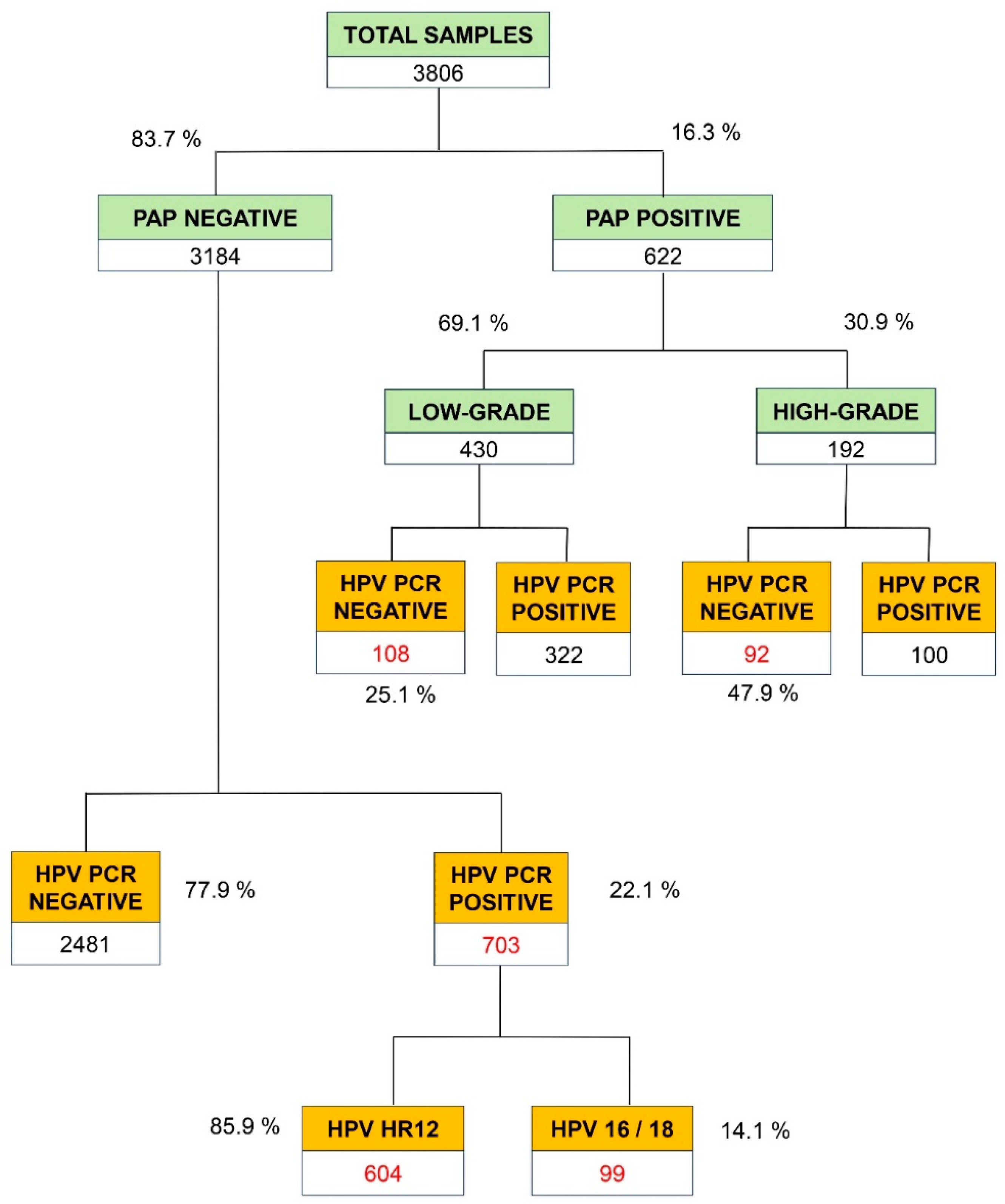
The global distribution of the 3,806 Pap test results, which represent 84.6% of the total 4,499 PCR tests, is shown in
Figure 2. 83.7% (n=3,184) gave a negative result and 16.3% a positive one (n=622). These positive results were sub-classified as low grade (69.1%), and high grade (30.9%). All the negative and positive samples for PAP underwent the PCR test for the detection of high or very high-risk HPVs. As shown in the figure, in the low-grade positive samples (n=430), a total of 108 samples were HPV-negative (25.1%). In the high-grade PAP samples (n=192), a total of 92 samples (47.9%) gave a negative PCR result. Taken together, these results show a low correlation between the positive results of PAP test (PAP) and the molecular results designed to identify HR HPV viral subtypes with a high (HR12) or very high (16 or 18) risk for CC.
Figure 2 also shows the results of HR HPV-PCR in the 3,184 samples reported as negative in the PAP test. In 703 samples (22.1%) a positive result was obtained for the viral genotypes of high or very high risk of CC. In this subgroup of false negatives from cytology for HPV detection, 85.9% (n=604) corresponded to the 12 high-risk subtypes (HR12) and 14.1% (n=99) to the HPV16 or HPV-18 very high-risk genotypes.
Table 2 shows the distribution by age of the 622 samples with a positive result for PAP, whether they are low or high grade. The most striking results correspond to patients over 35 years of age: a total of 110 samples (45 low-risk and 65 high-risk) gave negative results in the PCR, which represents 45.6% of potential false positives (110/241). The percentages of lack of correlation between PAP and HPV-PCR were lower in the other age ranges: 25.4% in the age range of 25 to 35 years, [(53+21)/291], and 17.7% for those under 25 years [(10+6)/90].
Table 3 shows the HR HPV-PCR genotyping results in the 422 double-positive samples in both the HPV-PCR and the PAP test (n=322 low-grade and n=100 high-grade). 61.8% of the samples were positive for HR12, 16% were positive for HR12 plus HPV16, and 15.2% were positive for isolated HPV16. Overall, 79.6% of the analyses obtained an isolated infection [(261+64+11)/422], and 20.4% corresponded to double or triple coinfections [(4+67+1+41)/422].
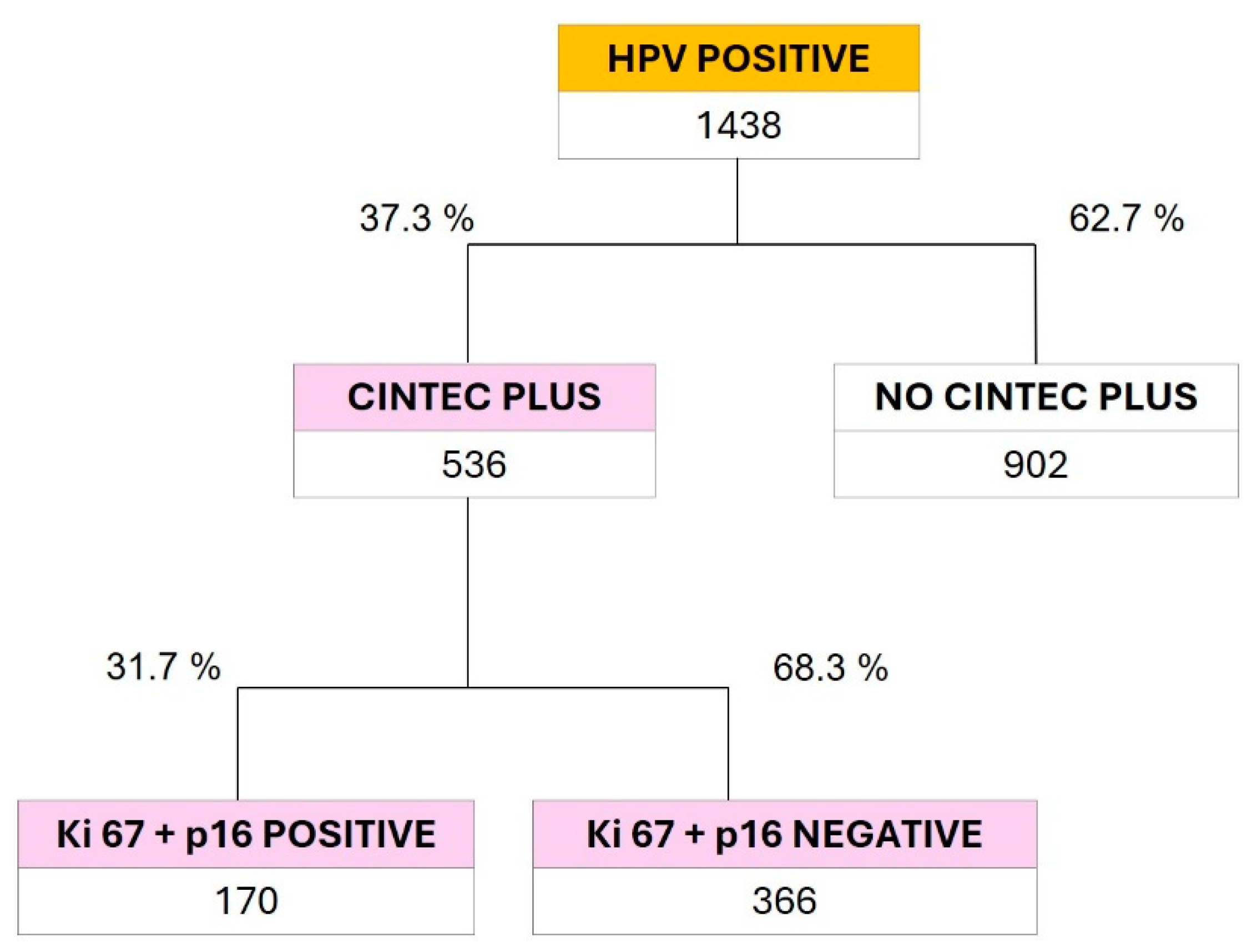
Figure 3 shows the results of the confirmation tests for CC performed using p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology (CINTEC PLUS). A total of 536 samples (37.3%) from the subgroup of 1438 positive results for 14 HR HPV types were tested. A total of 31.7% were positive for dual staining. These results also confirm that 68.3% of the positive results for any of the high-risk HPV subtypes do not present cellular transformation, which highlights the importance of performing p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology after PCR to avoid unnecessary colposcopy in the screening of possible CC patients.
These samples came from private practice gynecologists in private hospitals. In 100% of the cases, the gynecologists continued to perform the traditional Pap test in parallel with the HPV genotyping analysis using PCR (Cobas). Although this double screening for the early diagnosis of CC represents an extra cost for their patients, gynecologists argue that the traditional Pap allows them to identify other gynecological lesions (suspected infections by bacteria, fungi, or other viruses) than the PCR test alone does not offer them. In our experience, gynecologists are aware of the good sensitivity and specificity of the molecular PCR test and the costs of the study for their patients are the only reason for not requesting the HPV genotyping test, together with the traditional PAP test.
Regarding the possible reasons why the dual stain test is not widely requested within the global detection program for CC in our private gynecology sector, we can include the following: (1) Extra cost for the economy of many patients, for whom the cost of the PCR study already represents a large increase over the expense of the traditional PAP; (2) Ignorance on the part of the patients of the objective and scope of the staining in cervical cancer screening, which implies a longer explanation time in the private medical consultation; and (3) Reticence from a subgroup of gynecologists (colposcopists) since the positive/negative result of the dual stain test determines (or relativizes) the need to require surgical intervention (colposcopy) in their patients. This result seems to interfere with their area of expertise and business, which may be one of the causes of the low return rate in the confirmatory dual stain test.
4. Discussion
The results presented here correspond to a total of 4,499 samples received in our laboratories during three years for CC screening. The distribution of HPV subpopulations in the total samples is comparable to other results published internationally, although this study shows for the first time the results in the Mexican population within a private medicine market [
1,
9].
It should be noted that if we analyze the results within each age range, the population under 25 years of age was the one that showed the highest percentage of overall positive HR HPV-PCR results: 44% tested positive for one of the risk subtypes, high or very high, compared to 35.6% of positive results in the population between 25 and 35 years of age, and 24.2% of positive results in the population over 35 years of age.
Likewise, our results make it possible to highlight that the population between 25 and 35 years of age presented a higher percentage of results for viral coinfections with high or very high risk for CC viral types, with 14.8%, compared to 13.9% in the group over 35 years of age and 10.5% in those under 25 years of age. On the other hand, the population over 35 years of age was the one that presented a higher percentage of positive results for HPV16 and HPV18.
In our studies, a low correlation is observed between the positive results of PAP test (PAP) and the molecular results designed to identify HPV viral subtypes with a high (HR12) or very high (16 or 18) risk for CC. The most striking results correspond to patients over 35 years of age, who show 45.6% potential false positives. The percentages of PAP vs. HR HPV-PCR non-correlation were lower in the other age ranges: 25.4% in the age range of 25 to 35 years, and 17.7% for those under 25 years of age. These results may suggest the existence of an age bias when interpreting the PAP results in the older population, theoretically more prone to presenting CC.
Our results also allowed us to confirm the greater sensitivity of PCR tests compared to traditional PAP tests, since they allowed us to detect 22.1% of positive PCR results in samples reported as negative in the PAP test (false negatives).
Likewise, our data allowed us to detect a percentage of 68.3% negative results using confirmatory p16/Ki67 dual-stain cytology in the population of positive patients in the HR HPV. These results made it possible, on the one hand, to reassure the patients who had initially received a worrying result from the PCR test, to reduce the performance of unnecessary invasive tests (for example, colposcopy).
Although the PCR test for HPV screening is well known by gynecologists, the p16/Ki67 dual stain cytology is not a widely requested test for CC screening. Of the total HR HPV positive samples, only 37.3% were requested for reanalysis with confirmatory dual staining.
The most important challenges encountered after carrying out these works are: 1) Continue promoting among gynecologists that the papillomavirus PCR technique (HR HPV-PCR) is the best method for CC screening due to the lower presence of false negatives and false positives. 2) Stimulate the study of dual staining in HR12 positive patients mainly, to focus colposcopy procedures on those patients who have cancer cells. 3) Promote the establishment of new protocols agreed between the Medical Societies of specialists (Gynecology and/or Colposcopy) for a better diagnosis and treatment of patients with CC [
31,
32]. 4) Recently, a new global WHO strategy to achieve the elimination of CC as a public health problem by 2030 has been launched. It is called “Strategy 90-70-90”: 90% of girls (and boys in countries where resources allow) fully vaccinated with HPV vaccine by age 15, 70% of people screened with a high-performance test, and 90% of persons identified with cervical disease having received treatment [
33]. However, there are large inequities still to be resolved. Significant disparities continue to increase between countries and within different regions of the same country. Large differences persist between sociodemographic groups, household income, and children’s access to health insurance. The aspects in which we should improve to achieve these objectives are: (a) Accelerate the implementation of HPV screening programs, (b) Take advantage of diagnostic and therapeutic innovations, and (c) Focus on equity [
33].
To address these challenges, we are considering and propose to 1) Disseminate in gynecology congresses in our countries the benefits of molecular diagnosis of HR HPV by PCR, insisting on its greater speed, specificity, and sensitivity. 2) Carry out dissemination campaigns of these new technologies, in social networks aimed at the neediest female population in the prevention of CC. 3) Inform and achieve scientific discussion in specialized societies on the clinical risks associated with the unnecessary performance of many colposcopy procedures, for example, infertility or miscarriages. 4) Implement two innovations in our countries: (a) Promote self-collection programs to perform the HR HPV-PCR screening, and (b) Test and validate new detection procedures close to the patient, such as point-of-care (POC) testing. The self-collection programs have already been validated by many countries around the world [
34]. The sensitivity and specificity of self-sample HPV tests are like provider-collected HPV tests, and some devices are excellently accepted by women from very different countries [
34,
35,
36]. Regarding the accessibility of less expensive and convenient methodologies than automated laboratory machines, especially for developing countries, there is great interest in POC testing instruments that could be fast, low cost, and with a minimal training requirement [
33].
5. Conclusions
The HR HPV genotyping results by PCR show the low specificity and selectivity of the PAP test for CC screening. Up to 47.9% false positives have been observed in samples with a cytology diagnosed as high-grade positive. Likewise, 22.1% of false negatives have been observed in samples diagnosed as negative in the PAP test. The results of p16/Ki67 dual stain cytology in positive PCR samples for any of the HR HPV subtypes, show that 68.3% do not present cancer cells, highlighting the importance of performing these tests to avoid unnecessary colposcopies after the screening of possible patients with CC.
The results of our interactions with practicing gynecologists can be summarized as follows: There is deeply embedded societal reluctance to abandon traditional PAP tests given the long history of public relations campaigns to convince women and their doctors of their value as the preferred prevention tool for the diagnosis of CC. In the opinion of some specialists, colposcopy remains preferred to dual staining protocols despite the invasive and frequently unnecessary practice.
Eradicating CC still is a challenge in Mexico due to the poor prevention education and the inefficacy of current PAP technology. Our goal is to educate doctors and their patients about the benefits of the new molecular screening technologies for effective primary screening for HPV and the diagnosis of CC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; methodology, J.L.C.D., C.R.S., S.M.A.F., S.A.B.B and H.A.B.S.; software, J.L.C.D., H.A.B.S.; validation, J.L.C.D., C.R.S., S.M.A.F., and H.A.B.S.; formal analysis, J.L.C.D., C.R.S., S.M.A.F., and H.A.B.S.; investigation, J.L.C.D., C.R.S., S.M.A.F., and H.A.B.S.; resources, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; data curation, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; writing—review and editing, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; visualization, J.L.C.D., C.R.S., S.M.A.F., S.A.B.B and H.A.B.S.; supervision, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; project administration, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S.; funding acquisition, J.L.C.D. and H.A.B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study and their identification was protected by assigning a laboratory code.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the staff of our laboratories for their valuable technical support, especially HD Cervantes Santiago, MA Mora-Jiménez, JI Andrade-Sashida, and Luis E Fernandez-Garza.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Perkins R.B.; Wentzensen N.; Guido R.S.; Schiffman M. Cervical Cancer Screening: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330(6), 547-558. [CrossRef]
- Weintraub J.; Morabia A. Efficay of a liquid-based thin layer method for cervical cancer screening in a population with a low incidence of cervical cancer. Diagn Cytopathol 2000, 22(1), 52-59.
- Hoda R.S.; Loukeris K.; Abdul-Karim F.W. Gynecologic cytology on conventional and liquid-based preparations: a comprehensive review of similarities and differences. Diagn Cytopathol 2013, 41(3), 257-278. [CrossRef]
- Cuzick J.; Arbyn M.; Sankaranarayanan R.; Tsu V.; Ronco G.; Mayrand M.H.; Dillner J.; Meijer C.J. Overview of human papillomavirus-based and other novel options for cervical cancer screening in developed and developing countries. Vaccine 2008, 26(S10), 29-41. [CrossRef]
- Olivas A.D.; Barroeta J.E.; Lastra R.R. Overview of Ancillary Techniques in Cervical Cytology. Acta Cytol 2023, 67(2), 119-128. [CrossRef]
- Arbyn M.; Weiderpass E.; Bruni L.; de Sanjosé S.; Saraiya M.; Ferlay J.; Bray F. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2020, 8(2), 191-203. [CrossRef]
- Bruni L.; Serrano B.; Roura E.; Alemany L.; Cowan M.; Herrero R.; Poljak M.; Murillo R.; Broutet N.; Riley L.M.; et al. Cervical cancer screening programmes and age-specific coverage estimates for 202 countries and territories worldwide: a review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2022, 10(8), 1115-1127. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Comprehensive cervical cancer control. A guide to essential practice – Second edition.: WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1-364.
- Arango-Bravo E.A.; Cetina-Pérez L.D.C.; Galicia-Carmona T.; Castro-Equiluz D.; Gallardo-Rincón D.; Cruz-Bautista I.; Duenas-Gonzalez A. The health system and access to treatment in patients with cervical cancer in Mexico. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 1028291. [CrossRef]
- Davies-Oliveira J.C.; Smith M.A.; Grover S.; Canfell K.; Crosbie E.J. Eliminating Cervical Cancer: Progress and Challenges for High-income Countries. Clin Oncol 2021, 33(9), 550-559. [CrossRef]
- Morris B.J. The advent of human papillomavirus detection for cervical screening. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2019, 31(5), 333-339. [CrossRef]
- Rol M.L.; Picconi M.A.; Ferrera A.; Sánchez G.I.; Hernández M.L.; Lineros J.; Peraza A.; Brizuela M.; Mendoza L.; Mongelós P.; et al. Implementing HPV testing in 9 Latin American countries: The laboratory perspective as observed in the ESTAMPA study. Front Med 2022, 9, 1006038. [CrossRef]
- Koliopoulos G.; Arbyn M.; Martin-Hirsch P.; Kyrgiou M.; Prendiville W.; Paraskevaidis E. Diagnostic accuracy of human papillomavirus testing in primary cervical screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis of non-randomized studies. Gynecol Oncol 2007, 104(1), 232-246. [CrossRef]
- Tommasino M. The human papillomavirus family and its role in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 2014, 26, 13-21. [CrossRef]
- Hareza D.A.; Wilczyński J.R.; Paradowska E. Human Papillomaviruses as infectious Agents in Gynecological Cancers. Oncogenic Properties of Viral Proteins. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(3), 1818. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Bello J.O.; Carrillo-García A.; Lizano M. Epidemiology and Molecular Biology of HPV Variants in Cervical Cancer: The State of the Art in Mexico. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(15), 8566. [CrossRef]
- Scymonowicz K.A.; Chen J. Biological and clinical aspects of HPV-related cancers. Cancer Biol Med 2020, 17(4), 864-878.
- Arbyn M.; Simon M.; Peeters E.; Xu L.; Meijer C.J.L.M; Berkhof J.; Cuschieri K.; Bonde J.; Ostrbenk Vanlencak A.; Zhao F.H.; et al. 2020 list of human papillomavirus assays suitable for primary cervical cancer screening. Clin Microbiol Infect 2021, 27(8), 1083-1095. [CrossRef]
- Arbyn M.; Snijders P.J.; Meijer C.J.; Berkhof J.; Cuschieri K.; Kocjan B.J.; Poljak M. Which high-risk HPV assays fulfill criteria for use in primary cervical cancer screening? Clin Microbiol Infect 2015, 21(9), 817-826.
- Galgano M.T.; Castle P.E.; Atkins K.A.; Brix W.K.; Nassau S.R.; Stoler M.H. Using biomarkers as objective standards in the diagnosis of cervical biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol 2010, 34(8), 1077-1087. [CrossRef]
- Von Knebel Doeberitz M.; Reuschenbach M.; Schmidt D.; Bergeron C. Biomarkers for cervical cancer screening: the role of p16(INK4a) to highlight transforming HPV infections. Expert Rev Proteomics 2012, 9(2), 149-163. [CrossRef]
- Bergeron C.; Ordi J.; Schmidt D.; Trunk M.J.; Keller T.; Ridder R.; European CINtec Histology Study Group. Conjunctive p16INK4a testing significantly increases accuracy in diagnosing high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 2010, 133(3), 395-406. [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra M.G.; Heideman D.A.; de Roy S.C.; Rozendaal L.; Berkhof J.; van Krimpen K.; van Groningen K.; Snijders P.J.; Meijer C.J.; van Kemenade F.J. p16(INK4a) immunostaining as an alternative to histology review for reliable grading of cervical intraepithelial lesions. J Clin Pathol 2010, 63(11), 972-977. [CrossRef]
- Denton K.J.; Bergeron C.; Klement P.; Trunk M.J.; Keller T.; Ridder R; European CINtec Cytology Study Group. The sensitivity and specificity of p16(INK4a) cytology vs HPV testing for detecting high-grade cervical disease in the triage of ASC-US and LSIL papa cytology results. Am J Clin Pathol 2010, 134(1), 12-21.
- Schmidt D.; Bergeron C.; Denton K.J; Ridder R.; European CINtec Cytology Study Group. p16/ki-67 dual-stain cytology in the triage of ASCUS and LSIL Papanicolaou cytology: results from the European equivocal or mildly abnormal Papanicolaou cytology study. Cancer Cytopathol 2011, 119(3), 158-166.
- Petry K.U.; Schmidt D.; Scherbring S.; Luyten A.; Reinecke-Lüthge A.; Bergeron C.; Kommoss F.; Löning T.; Ordi J.; Regauer S.; et al. Triaging Pap cytology negative, HPV positive cervical cancer screening results with p16/Ki-67 Dual-stained cytology. Gynecol Oncol 2011, 121(3), 505-509.
- Wentzensen N.; Schwartz L.; Zuna R.E.; Smith K.; Mathews C.; Gold M.A.; Allen R.A.; Zhang R.; Dunn S.T.; Walker J.L.; et al. Performance of p16/Ki-67 immunostaining to detect cervical cancer precursors in a colposcopy referral population. Clin Cancer Res 2012, 18(15), 4154-4162.
- Edgerton N.; Cohen C.; Siddiqui M.T. Evaluation of CINtec PLUS® testing as an adjunctive test in ASC-US diagnosed SurePath® preparations. Diagn Cytopathol 2013, 41(1), 35-40.
- Tjalma W.A.A. Diagnostic performance of dual-staining cytology for cervical cancer screening: A systematic literature review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2017, 210, 275-280.
- Ryu A.; Honma K.; Shingetsu A.; Tanada S.; Yamamoto T.; Nagata S.; Kamiura S.; Yamasaki T.; Ohue M.; Matsuura N. Utility of p16/Ki67 double immunocytochemistry for detection of cervical adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cytopathol 2022, 130(12), 983-992.
- Kyrgiou M.; Arbyn M.; Bergeron C.; Bosch F.X.; Dillner J.; Jit M.; Kim J.; Poljak M.; Nieminem P.; Sasieni P.; et al. Cervical screening: ESGO-EFC position paper of the European Society of Gynaecologic Oncology (ESGO) and the European Federation of Colposcopy (EFC). Br J Cancer 2020, 123(4), 510-517. [CrossRef]
- Sharma J.; Yennapu M.; Priyanka Y. Screening Guidelines and Programs for Cervical Cancer Control in Countries of Different Economic Groups: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15(6), e41098. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global strategy to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer as a public health problem and its associated goals and targets for the period 2020-2030. Seventy-third world health Assembly. Agenda item 11.4. WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1-3.
- Serrano B.; Ibáñez R.; Robles C.; Peremiquel-Trillas P.; de Sanjosé S.; Bruni L. Worldwide use of HPV self-sampling for cervical cancer screening. Prev Med 2022, 154, 106900. [CrossRef]
- Arbyn M.; Verdoodt F.; Snijders P.J.; Verhoef V.M.; Suonio E.; Dillner L.; Minozzi S.; Bellisario C.; Banzi R.; Zhao F.H.; et al. Accuracy of human papillomavirus testing on self-collected versus clinician-collected samples: a meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2014, 15(2), 172-183. [CrossRef]
- Arbyn M.; Latsuzbaia A.; Castle P.E.; Sahasrabuddhe V.V.; Broeck D.V. HPV testing of self-samples: Influence of collection and sample handling procedures on clinical accuracy to detect cervical precancer. Lancet Reg Health Eur 2022, 14, 100332. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).