Submitted:
07 April 2024
Posted:
09 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
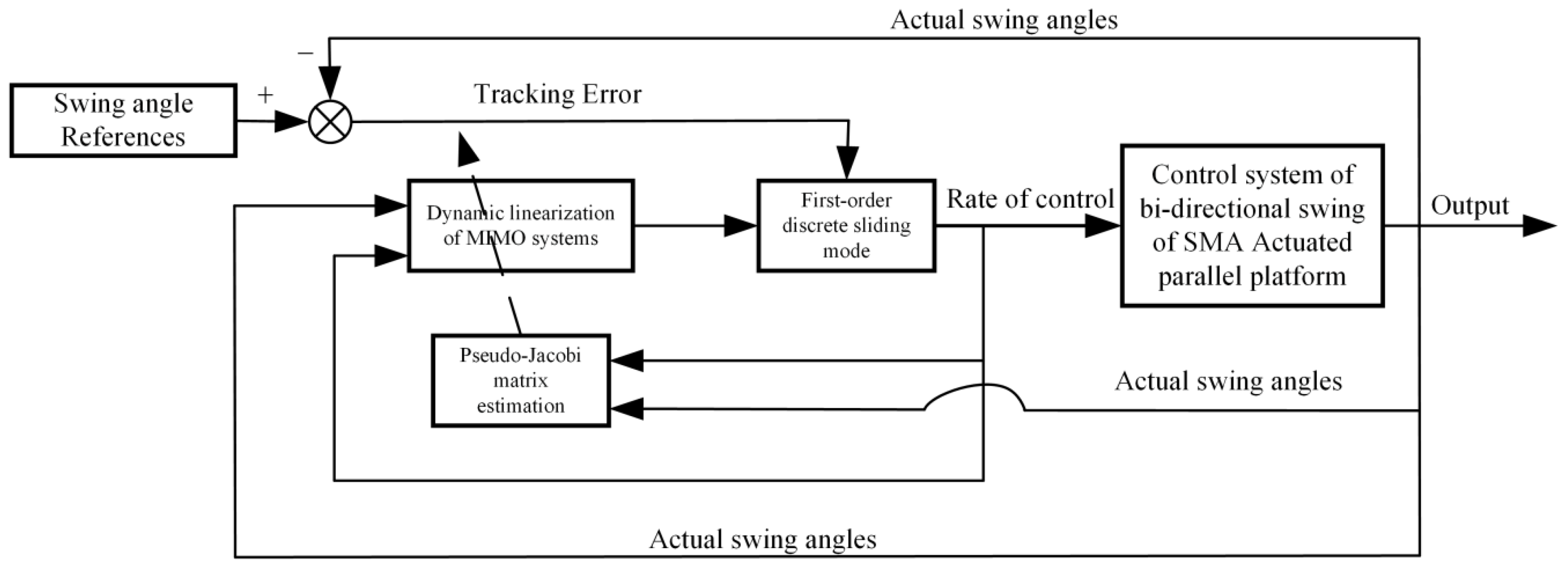
2. Model-Free Adaptive Sliding Mode Control
2.1. Dynamic Data Model of MIMO System
2.2. Design of Sliding Mode Control
3. Stability
4. Experiment
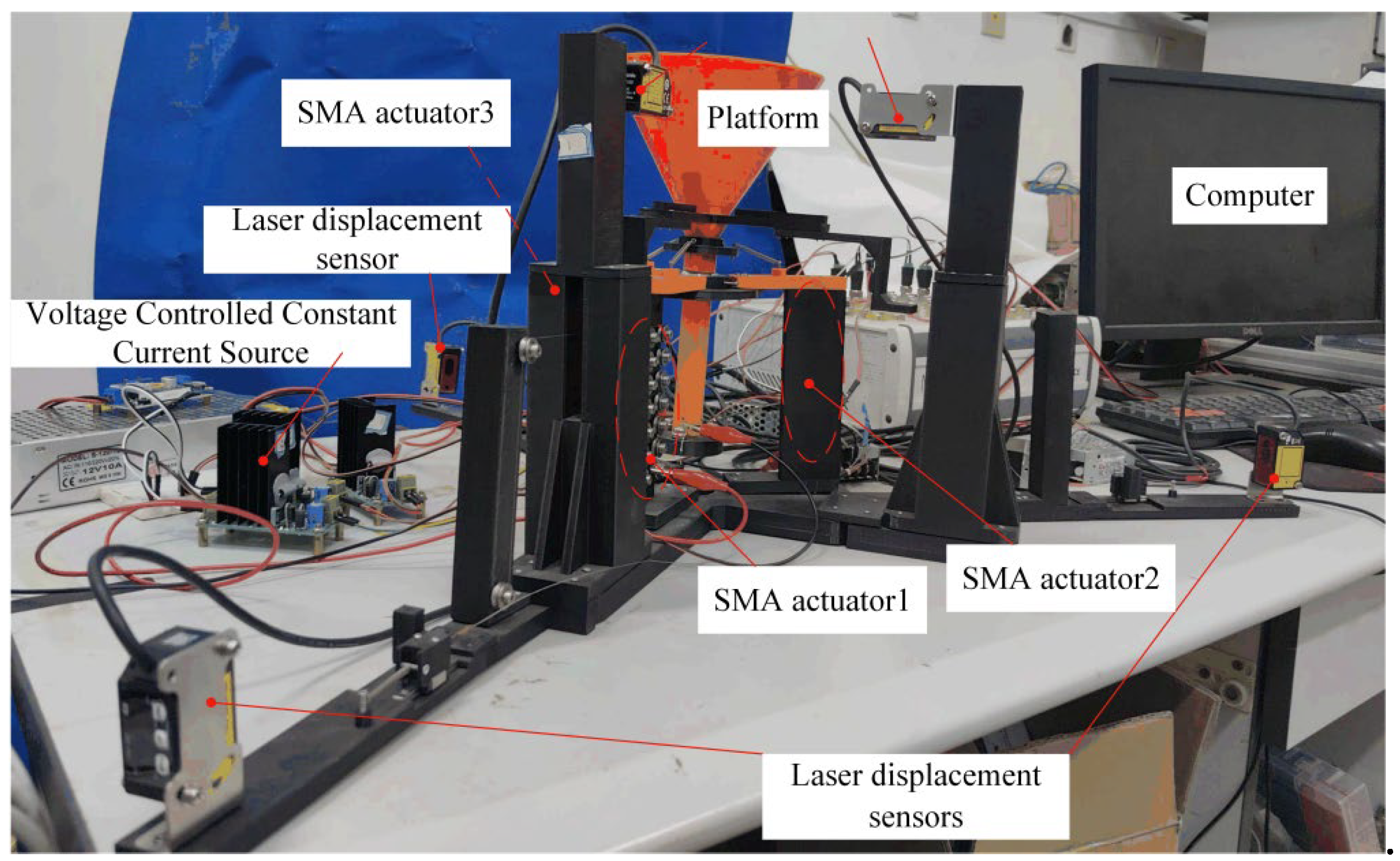
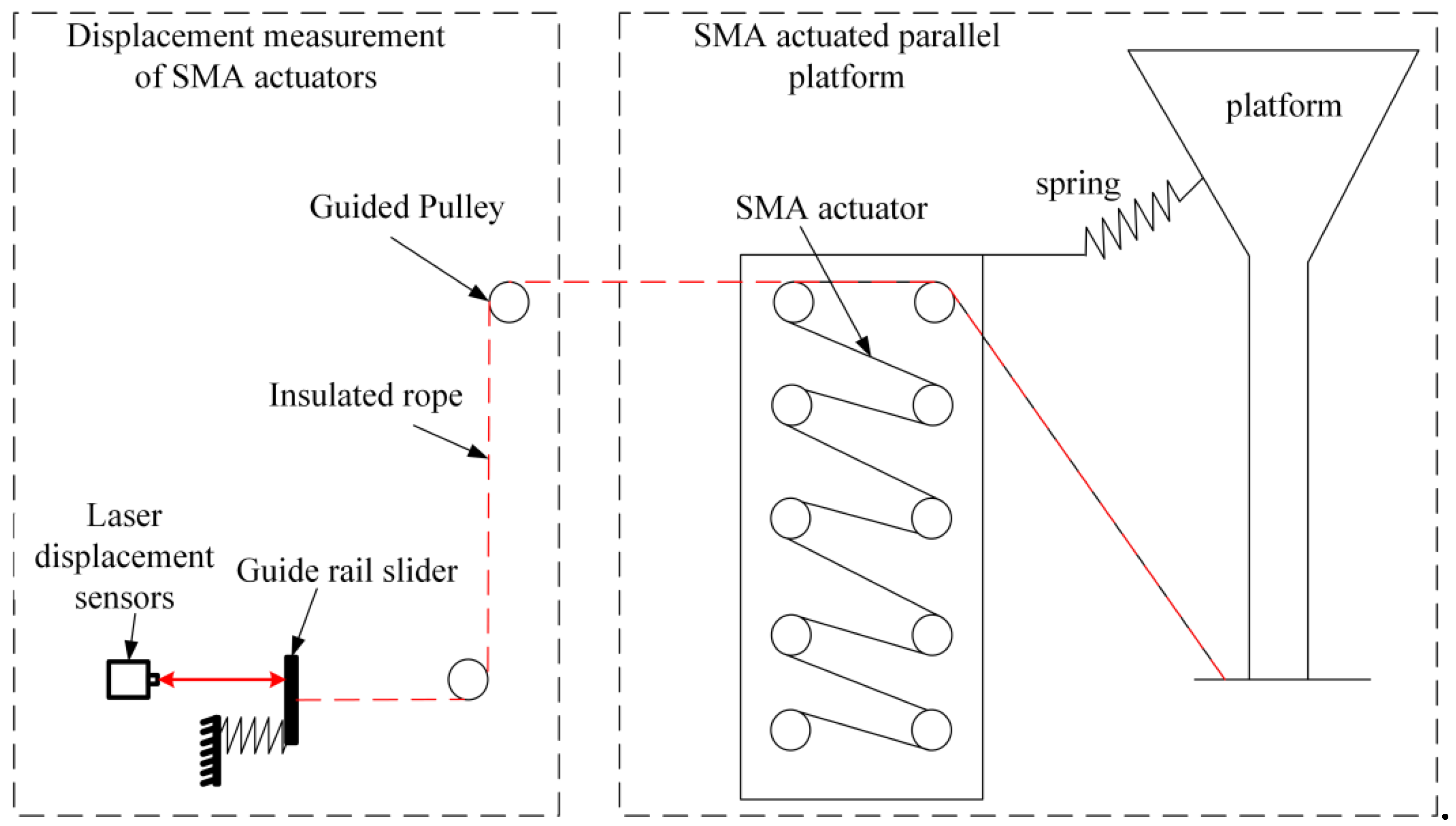
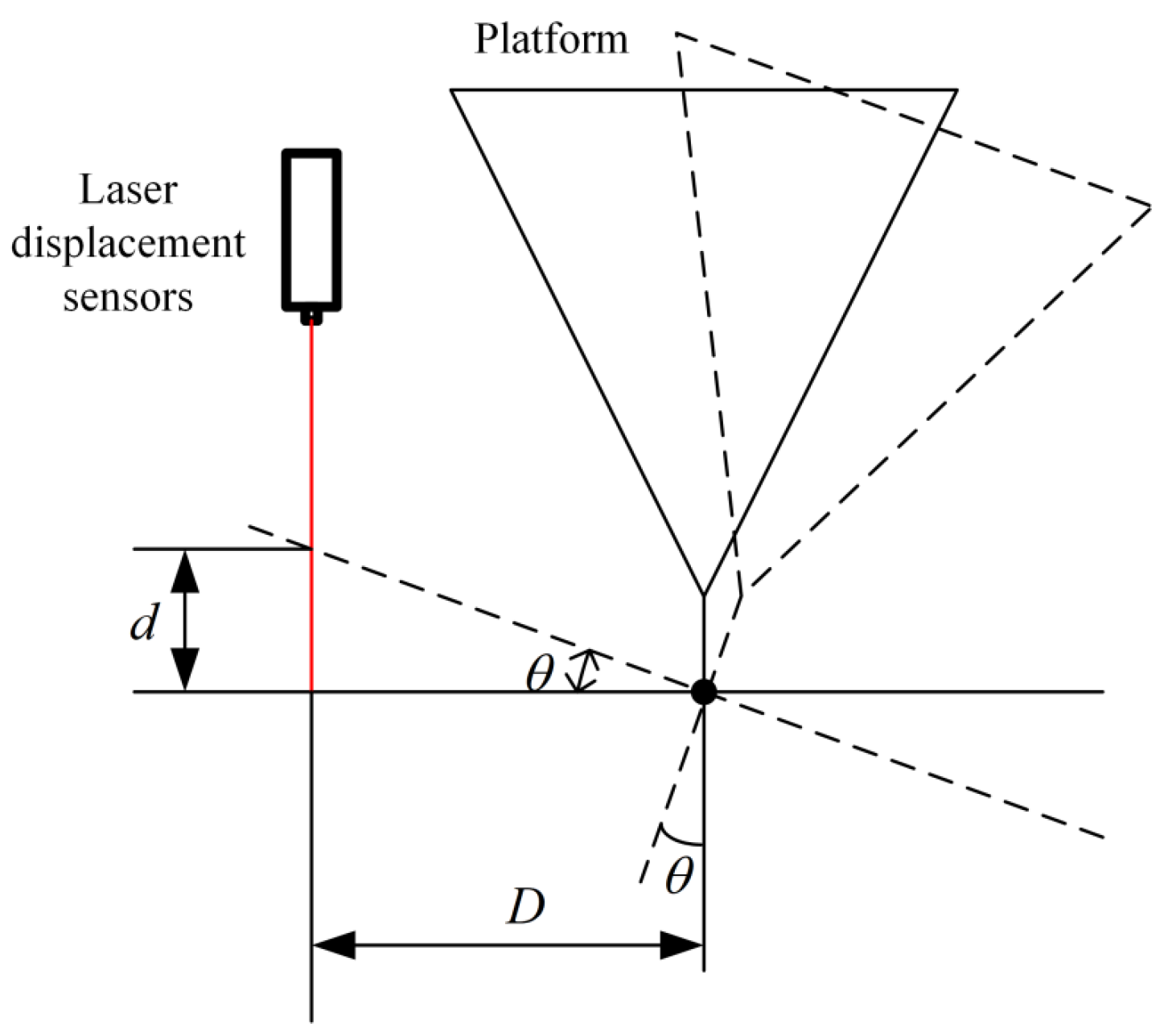
4.1. Experimental Platform
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Jani, J.M.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Materials & Design 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.; O’Neill, C.T.; et al. Robotic artificial muscles: Current progress and future perspectives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2019, 35, 761–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fang, B.; et al. A Review of Smart Materials for the Boost of Soft Actuators, Soft Sensors, and Robotics Applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering 2022, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, N.B. Medical shape memory alloy applications—the market and its products[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A 2004, 378, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Castro Sundin, R.; Loidi Eguren, I.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; Treviño-Quintanilla, C.D. Neural network direct control with online learning for shape memory alloy manipulators. Sensors 2019, 19, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, M.; Wu, Z.; Yin, H. Design, analysis, and grasping experiments of a novel soft hand: hybrid actuator using shape memory alloy actuators, motors, and electromagnets. Soft Robotics 2020, 7, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.F.; Digumarti, K.M.; Le, N.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Carreira, S.C.; Zaghloul, N.S.; Rossiter, J. B: Ionic Glove: A soft smart wearable sensory feedback device for upper limb robotic prostheses. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 3311–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A.; Colli, M.; Dragoni, E. Mechatronic design of a shape memory alloy actuator for automotive tumble flaps: a case study. ieee transactions on industrial electronics 2009, 56, 2644–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradin, H.; Braun, S.; Stemme, G.; van der Wijngaart, W. SMA microvalves for very large gas flow control manufactured using wafer-level eutectic bonding. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2011, 59, 4895–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bena, R.M.; Nguyen, X.T.; Calderón, A.A.; Rigo, A.; Pérez-Arancibia, N.O. SMARTI: A 60-mg Steerable Robot Driven by High-Frequency Shape-Memory Alloy Actuation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 8173–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Aramaki, S.; Yanagisawa, K. (1995, July). Feedback linearization for SMA (shape memory alloy). In SICE'95. Proceedings of the 34th SICE Annual Conference. International Session Papers (pp. 1383-1386). IEEE.
- Moallem, M.; Tabrizi, V.A. Tracking control of an antagonistic shape memory alloy actuator pair. IEEE Transactions on control systems technology 2008, 17, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianagui, A.; Tannuri, E.A. A sliding mode torque and position controller for an antagonistic SMA actuator. Mechatronics 2015, 30, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, A.; Liu, T.I.; Hozian, P. Control of shape memory alloy actuators with a neuro-fuzzy feedforward model element[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 2006, 17, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, H. Position control of SMA actuator based on inverse empirical model and SMC-RBF compensation[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2018, 108, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Lee, J.; Ahn, K.K. Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of shape memory alloy actuators using time delay estimation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 2014, 20, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.; Tannuri, E.A. Modeling, control and experimental validation of a novel actuator based on shape memory alloys[J]. Mechatronics 2009, 19, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.G.; Li, X.G.; et al. Robust indirect adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems and its application to shape memory alloy actuators[J]. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35809–35823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kha, N.B.; Ahn, K.K. Position control of shape memory alloy actuators by using self tuning fuzzy PID controller[C]//2006 1ST IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. IEEE, 2006: 1-5.
- Song, G.; Ma, N. Control of shape memory alloy actuators using pulse-width pulse-frequency (PWPF) modulation[J]. Journal of intelligent material systems and structures 2003, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, Á.; Escudero, N.; Martín, F.; et al. Position control of a shape memory alloy actuator using a four-term bilinear PID controller[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2015, 236, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, N.T.; Ahn, K.K. Output feedback direct adaptive controller for a SMA actuator with a Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on control systems technology 2011, 20, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominik, I. Type-2 fuzzy logic controller for position control of shape memory alloy wire actuator[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures 2016, 27, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntanapreeda, S. Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding-Mode Position Control of A Shape Memory Alloy Actuated System[C]//Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2015, 789, 946–950. [Google Scholar]
- Elwaleed, A.K.; Mohamed, N.A.; Nor MJ, M.; et al. A new method for actuating parallel manipulators[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2008, 147, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copaci, D.; Muñoz, J.; González, I.; et al. SMA-Driven Soft Robotic Neck: Design, Control and Validation[J]. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 199492–199502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhang, K.; Dai, J.S. Constraint-based design and analysis of a compliant parallel mechanism using SMA-spring actuators[C]//International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers 2014, 46360, V05AT08A035. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Jing, Z.; Pan, H.; et al. Distance-directed target searching for a deep visual servo sma driven soft robot using reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering 2020, 17, 1126–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Cheng, J.; Huang, W. Design and development of a novel SMA actuated multi-DOF soft robot[J]. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75073–75080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.R.; Ganesan, M. Mechatronics design and kinematic analysis of SMA spring actuated parallel manipulator[C]//Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing 2021, 1969, 012011. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Jin, S. Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems[J]. IEEE transactions on neural networks 2011, 22, 2173–2188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
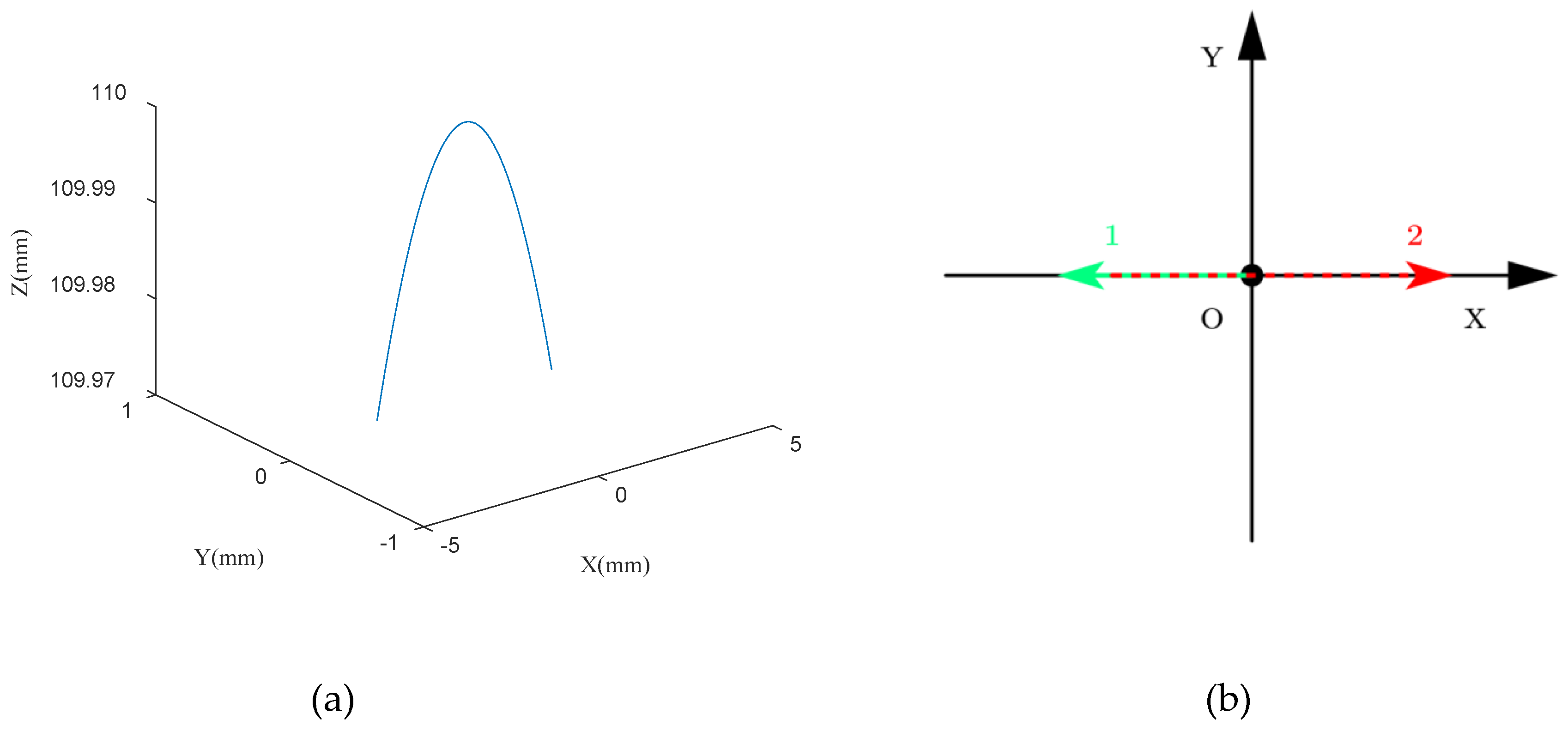
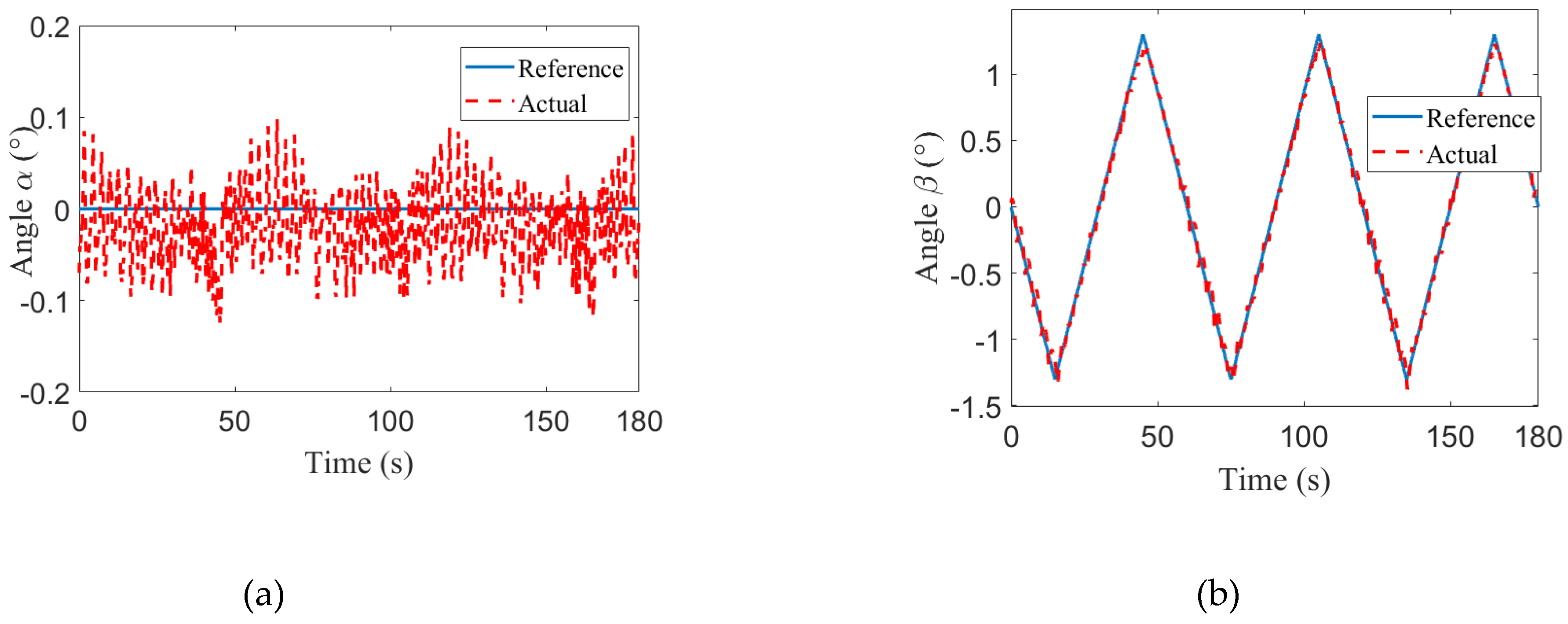
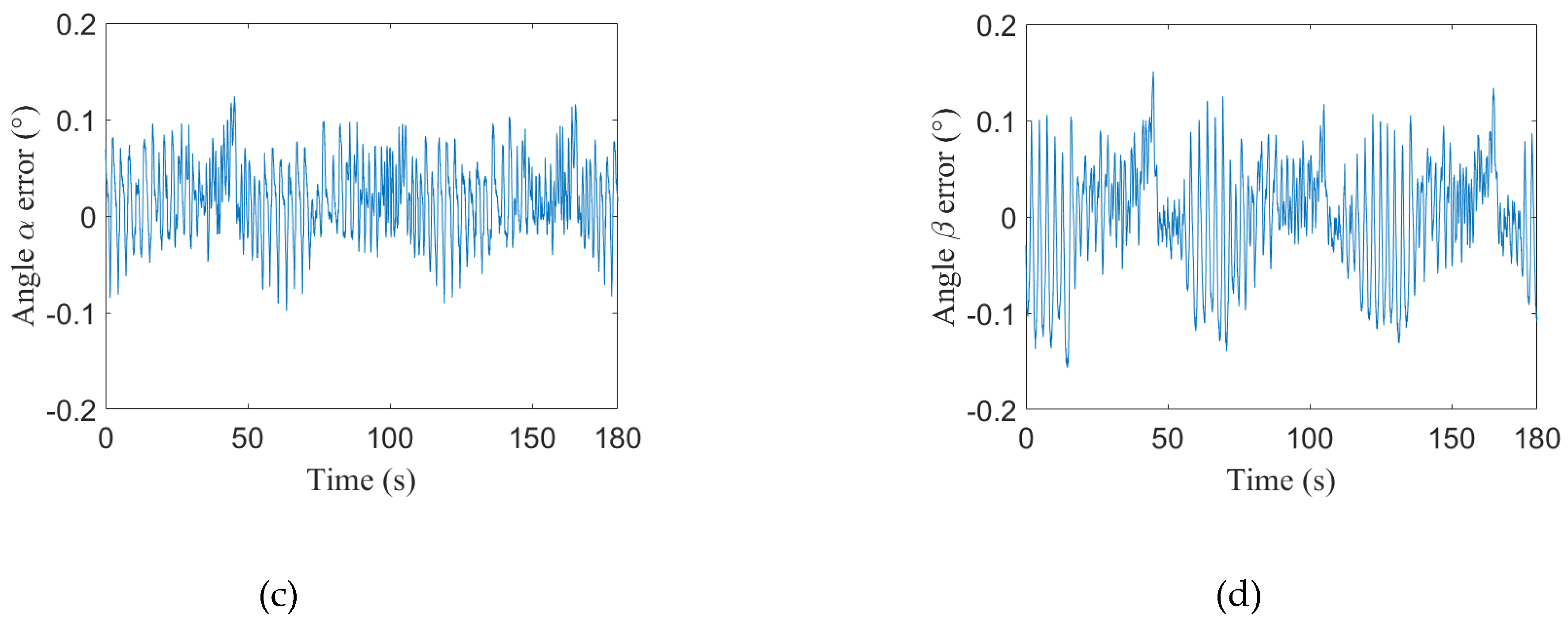
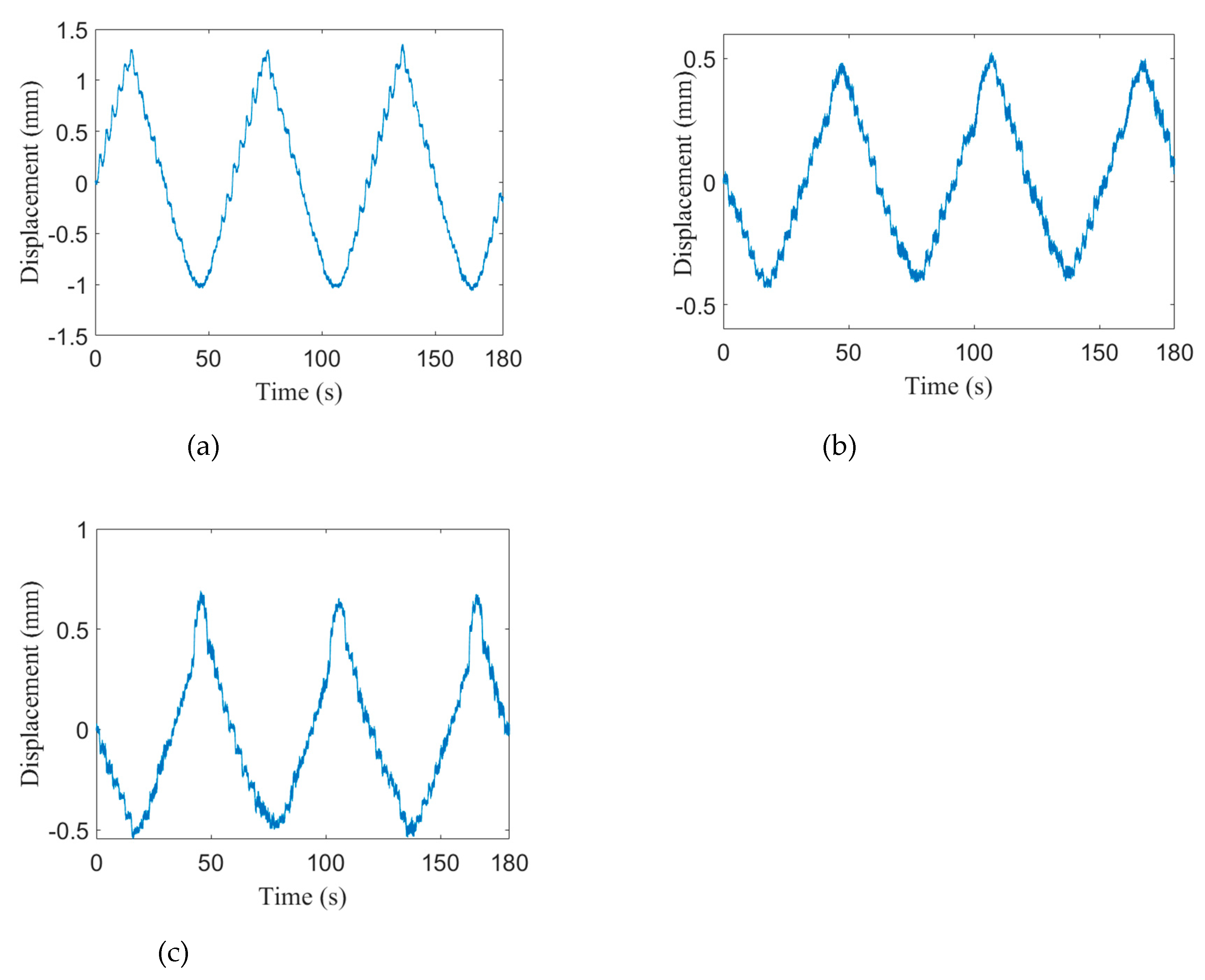
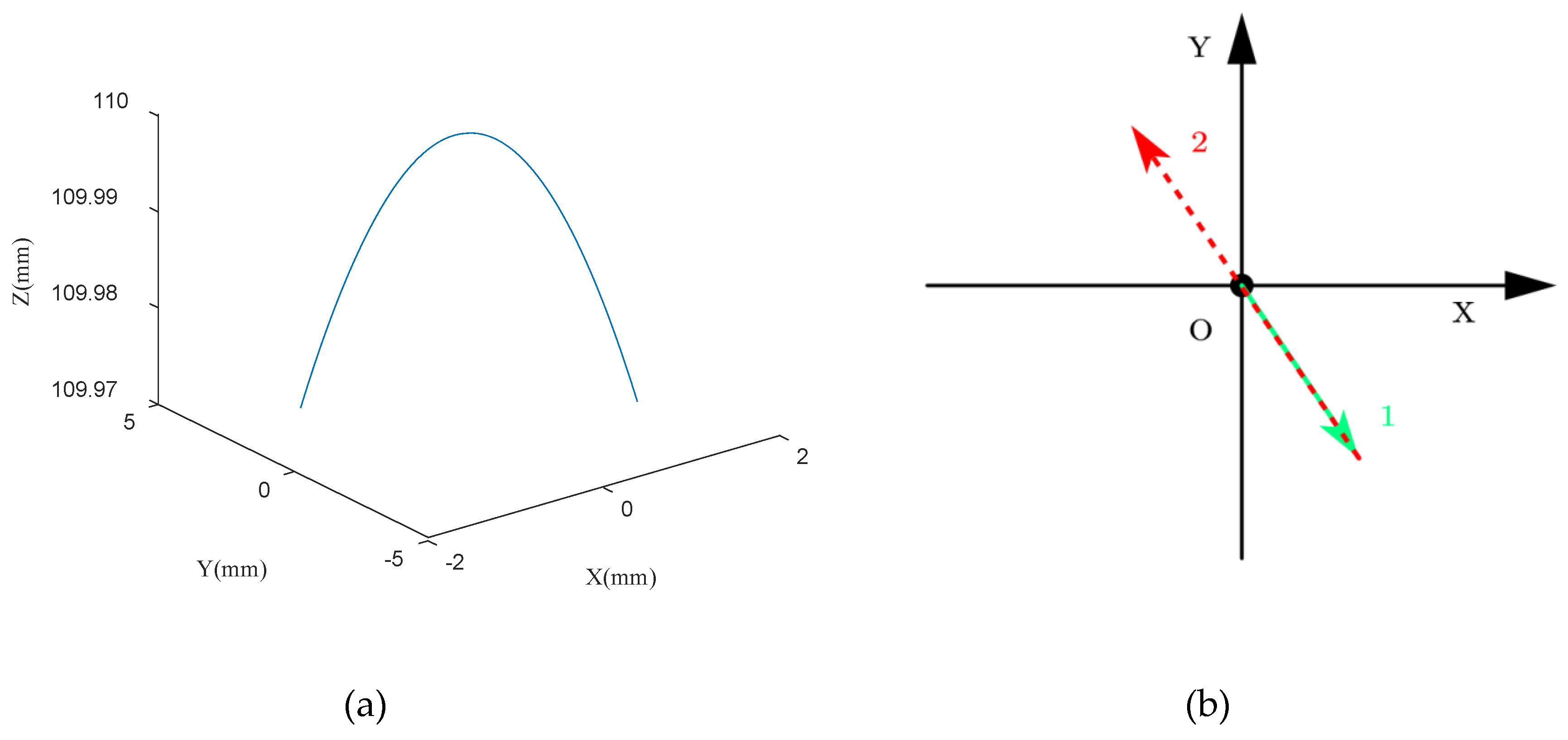
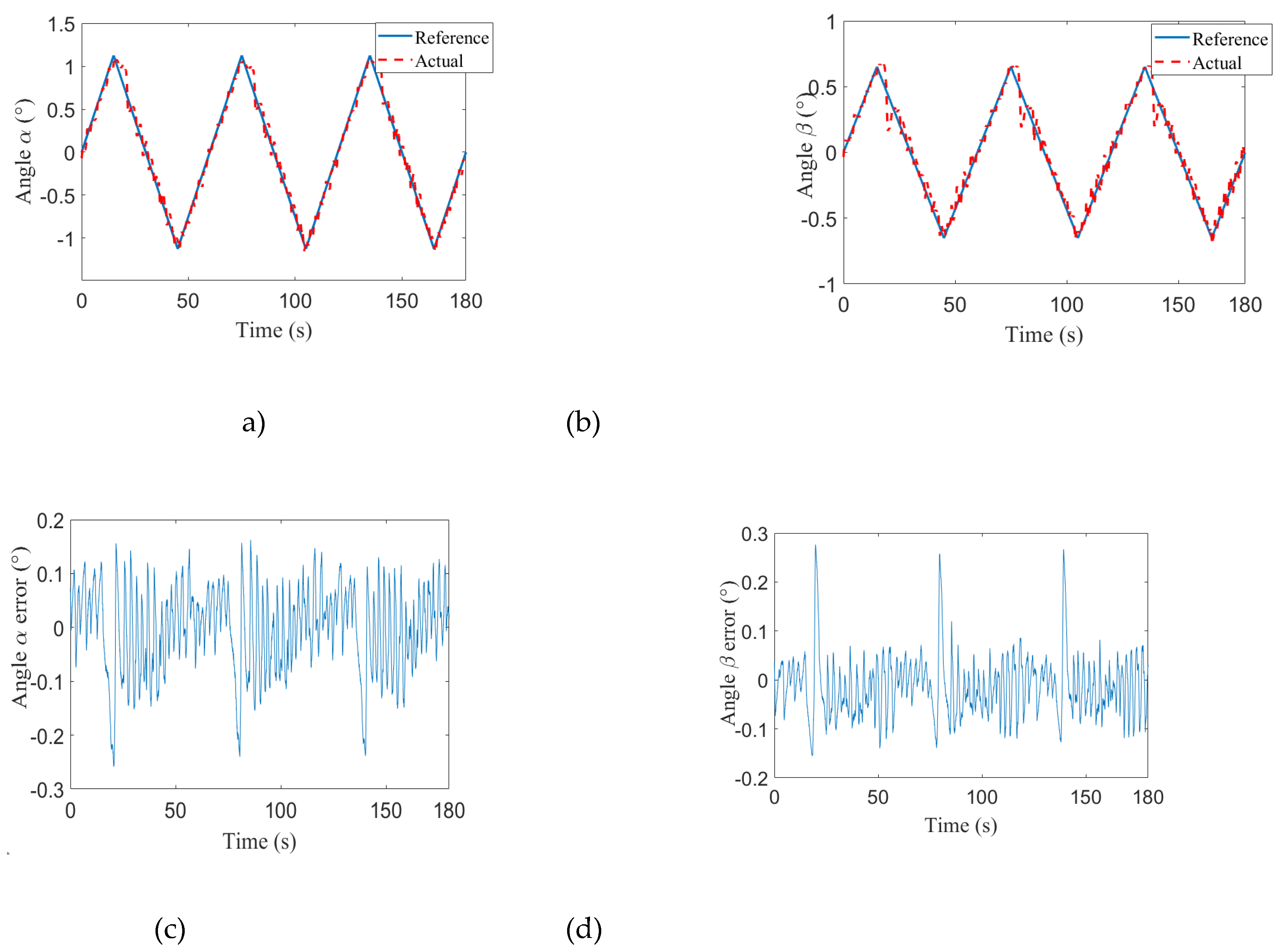
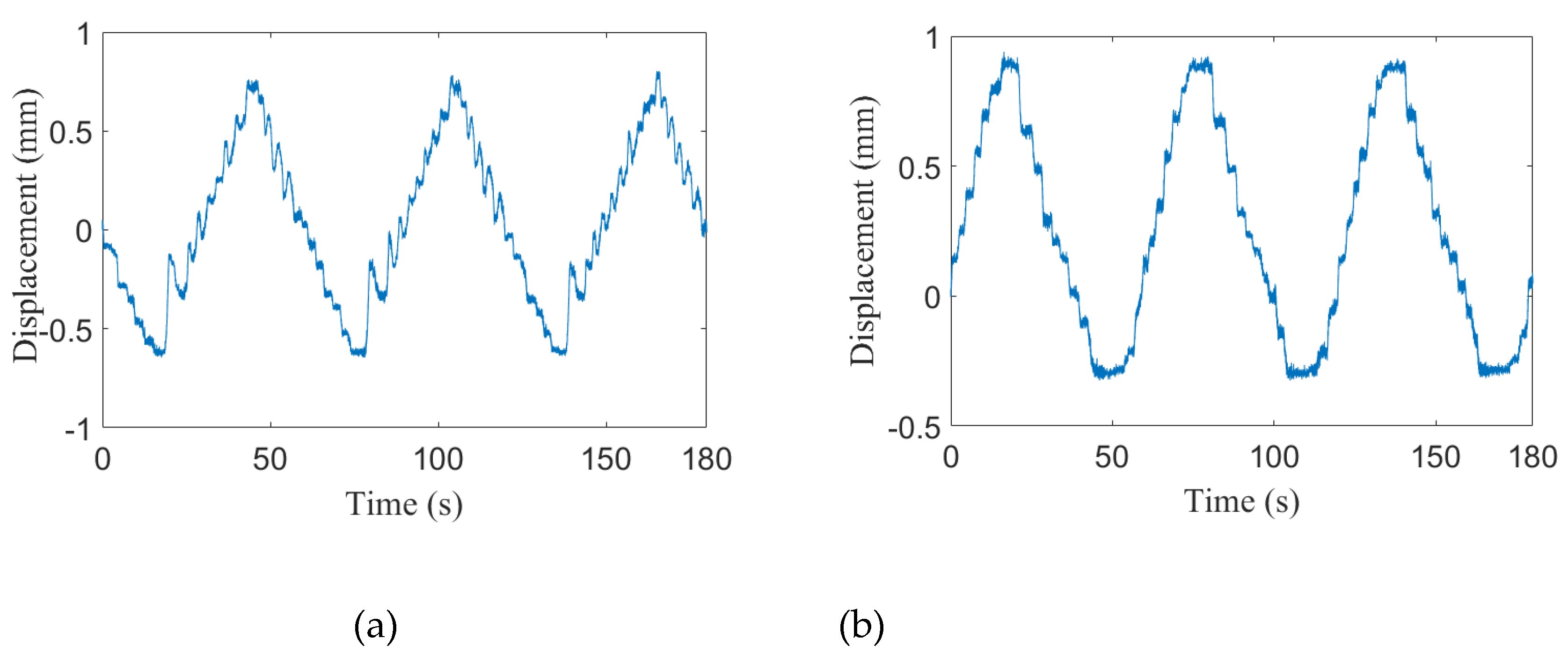
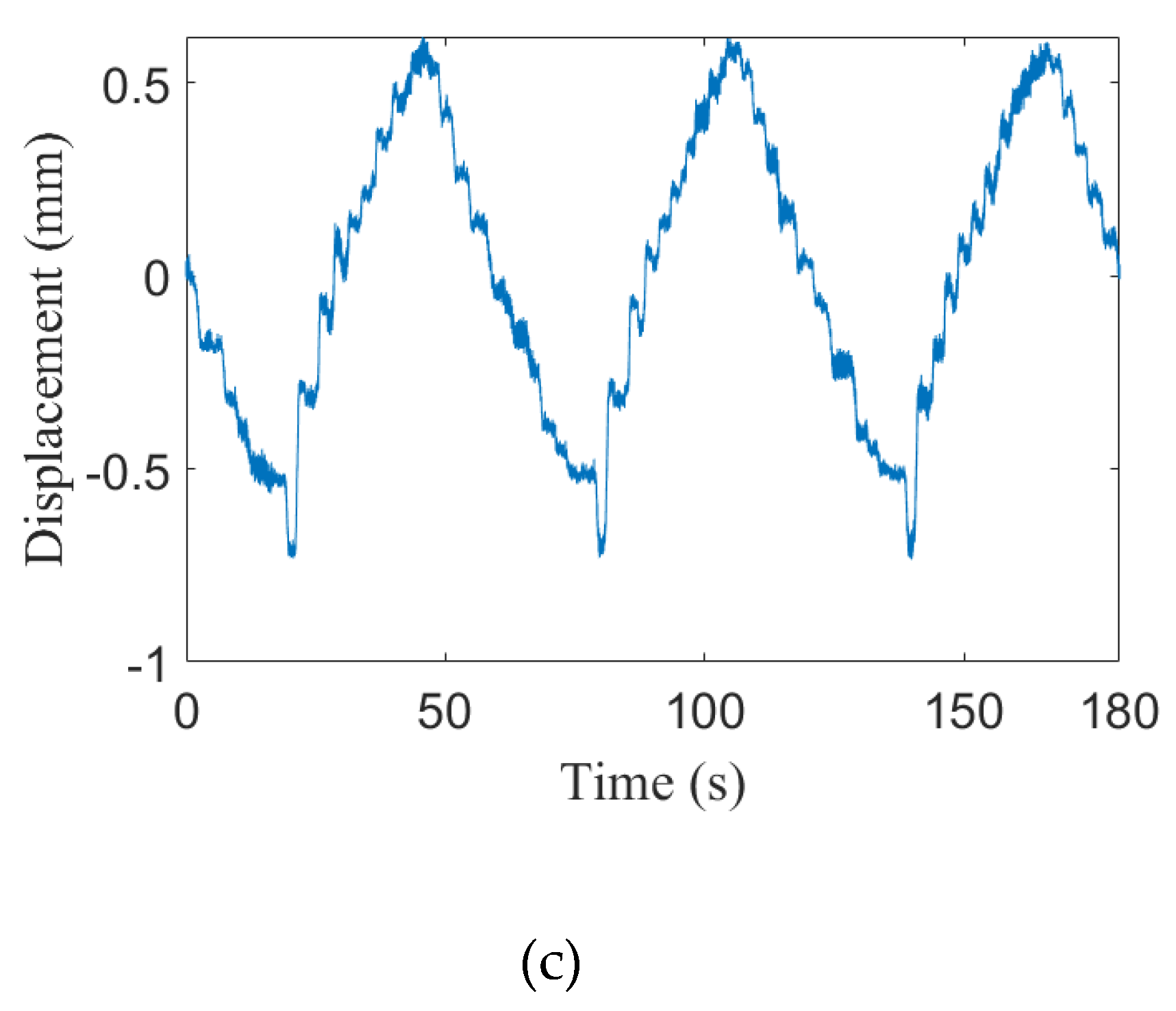
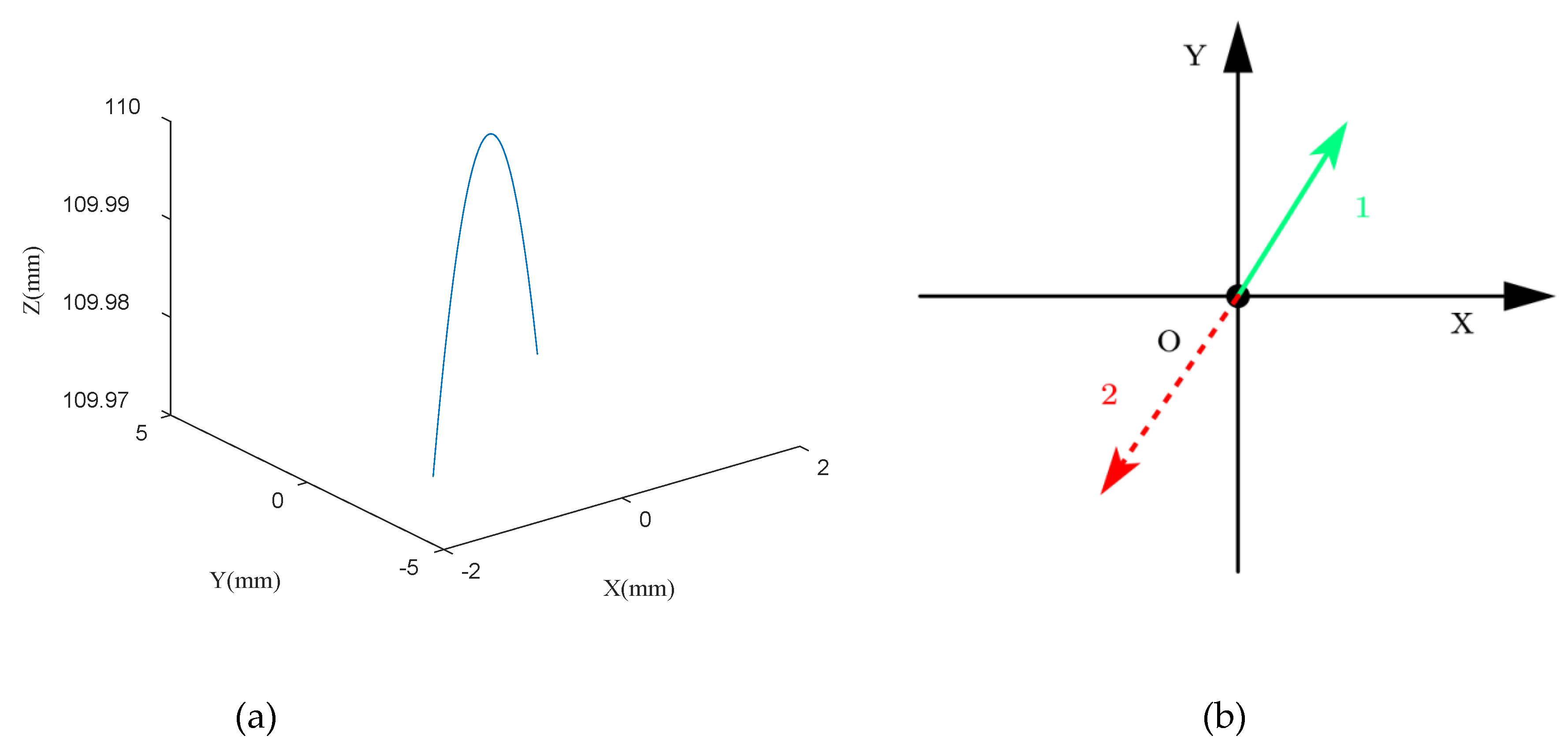
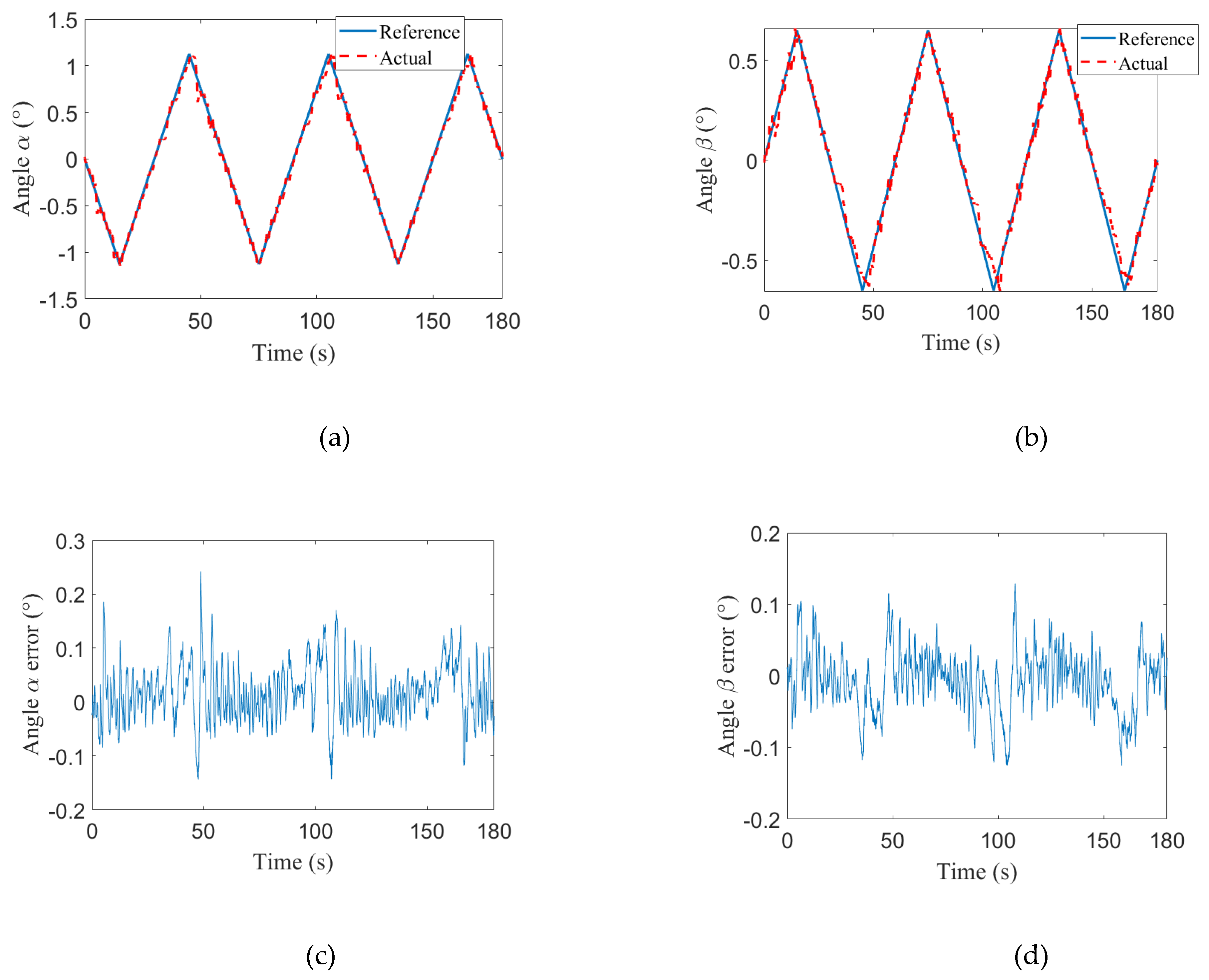
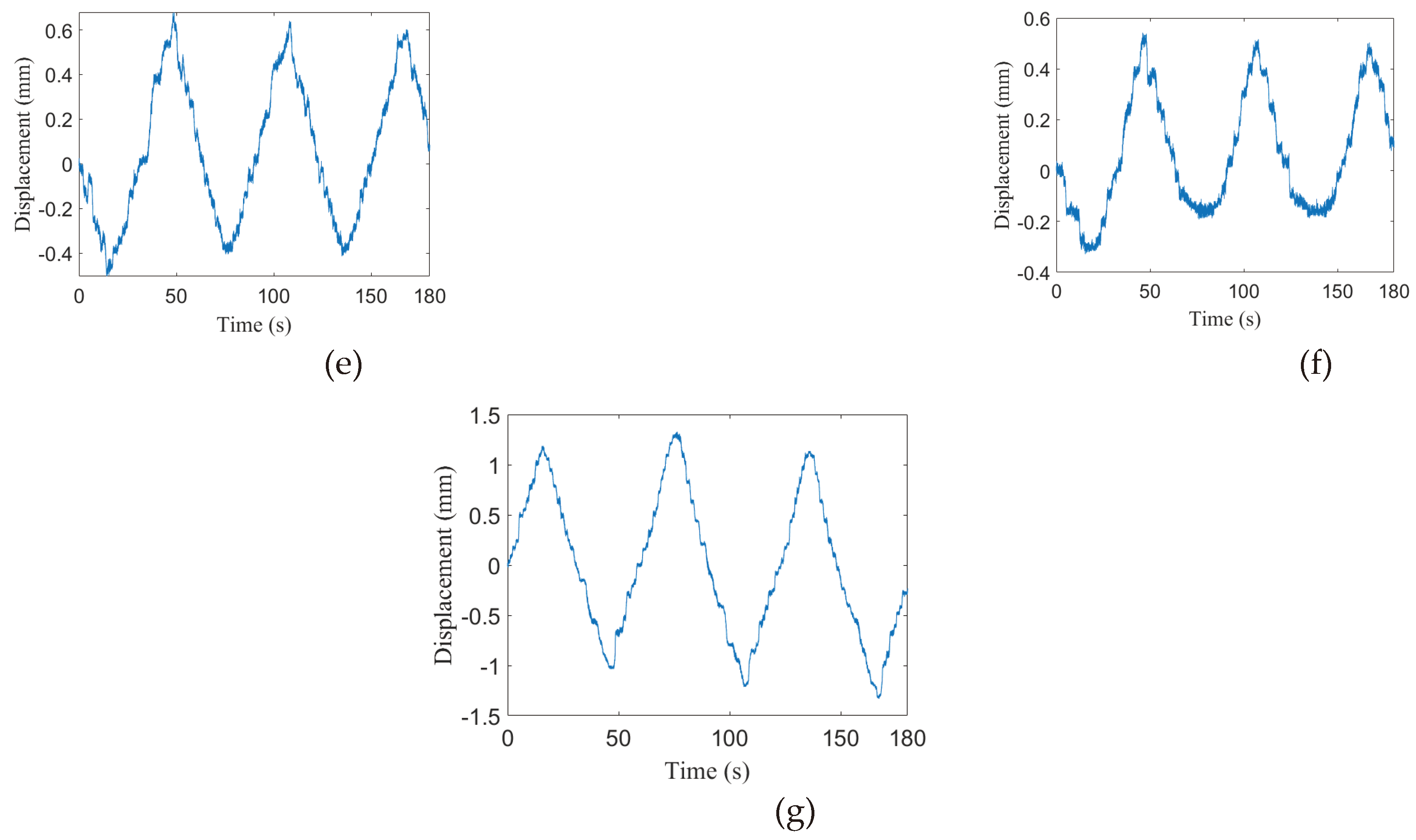
| Angles | α | ||
| Swing mode | β | ||
| 1 | 0.0340° | 0.0447° | |
| 2 | 0.0629° | 0.0465° | |
| 3 | 0.0423° | 0.0323° | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




