Submitted:
04 April 2024
Posted:
07 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Spinal Cord Stimulation and Waveforms
2.1. Conventional/ Tonic Stimulation
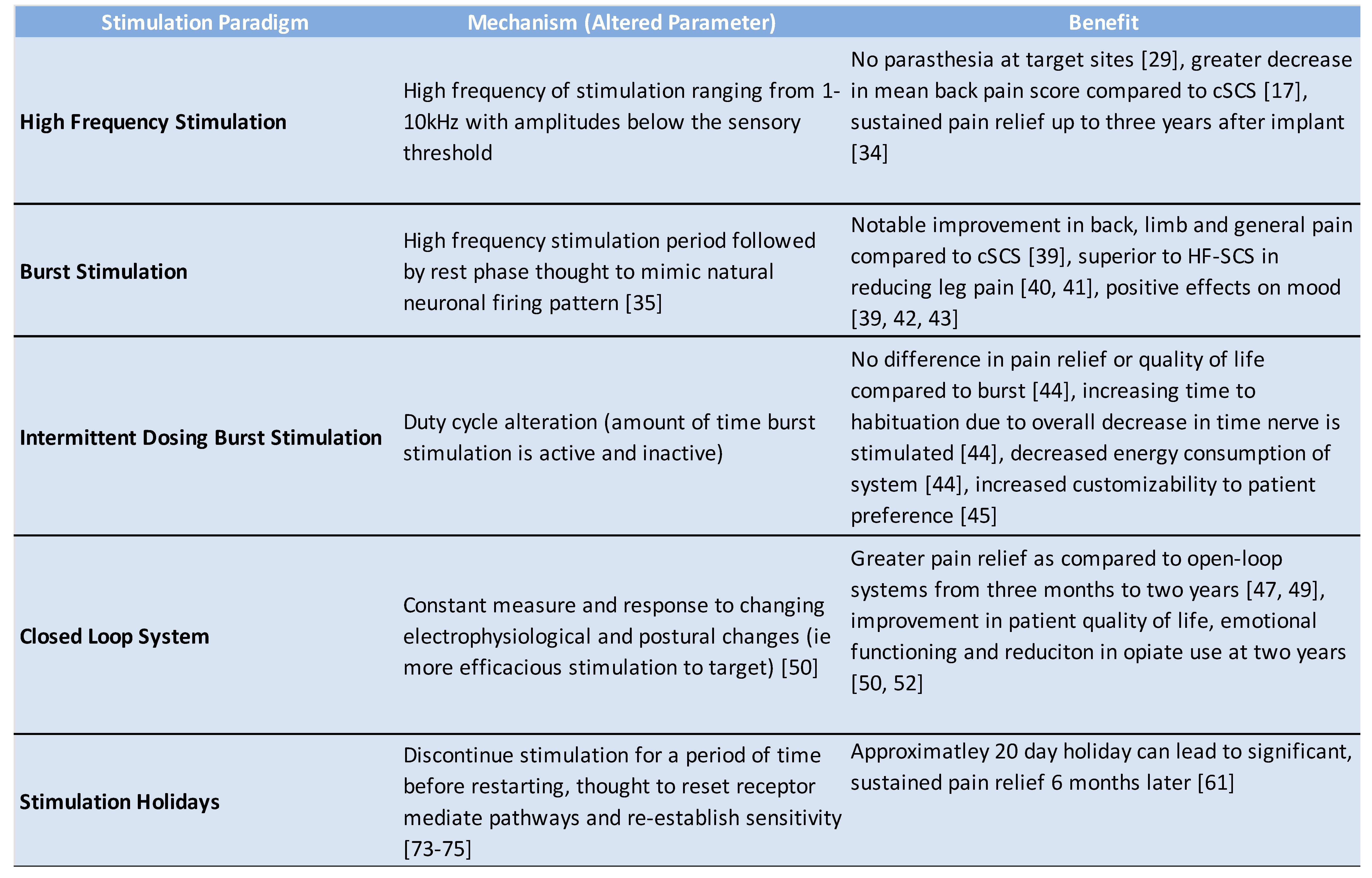
2.2. High Frequency Stimulation
2.3. Burst Stimulation
2.4. Intermittent Dosing Burst Paradigm
3. Closed-Loop Spinal Cord Stimulation
4. Habituation and Spinal Cord Stimulator Explantation
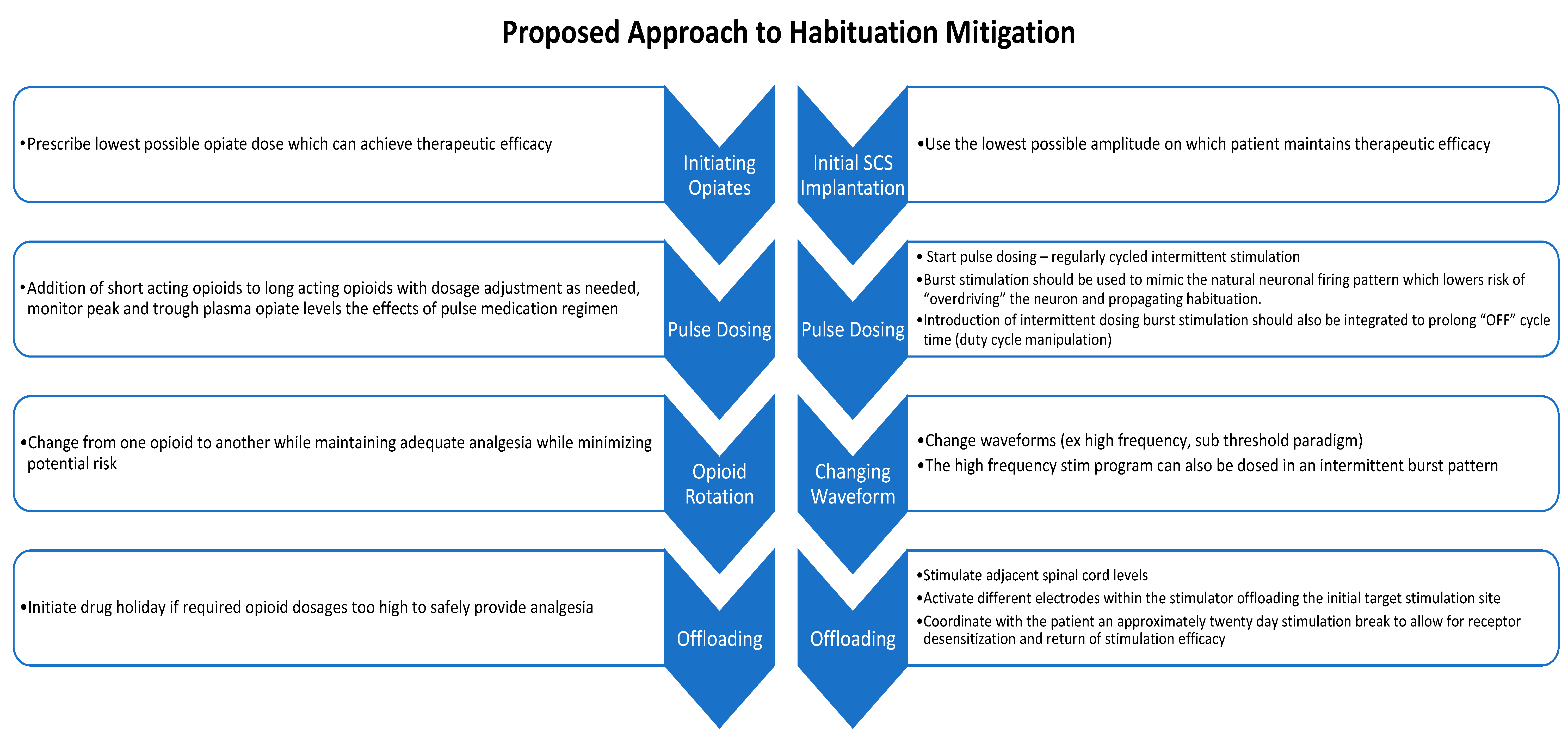
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. (2023) Estimated Rates of Incident and Persistent Chronic Pain Among US Adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Network Open.6(5):e2313563-e.
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. (2022) Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain.163(2):e328-e32. [PubMed]
- Gaskin DJ, Richard P. (2012) The economic costs of pain in the United States. The journal of pain.13(8):715-24.
- Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. (2014) Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol.69(2):119-30. [PubMed]
- Dale R, Stacey B. (2016) Multimodal treatment of chronic pain. Medical Clinics.100(1):55-64.
- Vakkala M, Järvimäki V, Kautiainen H, Haanpää M, Alahuhta S. (2017) Incidence and predictive factors of spinal cord stimulation treatment after lumbar spine surgery. J Pain Res.10:2405-11. PMCID: PMC5634380. [PubMed]
- Shealy CN, Mortimer JT, Reswick JB. (1967) Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns: preliminary clinical report. Anesth Analg.46(4):489-91. [PubMed]
- Knotkova H, Hamani C, Sivanesan E, Le Beuffe MFE, Moon JY, Cohen SP, Huntoon MA. (2021) Neuromodulation for chronic pain. The Lancet.397(10289):2111-24.
- Duarte RV, Nevitt S, Maden M, Meier K, Taylor RS, Eldabe S, de Vos CC. (2021) Spinal cord stimulation for the management of painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient and aggregate data. Pain.162(11):2635-43.
- Al-Kaisy A, Van Buyten J, Kapural L, Amirdelfan K, Gliner B, Caraway D, Subbaroyan J, Edgar D, Rotte A. (2020) 10 kHz spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of non-surgical refractory back pain: subanalysis of pooled data from two prospective studies. Anaesthesia.75(6):775-84.
- Eckermann JM, Pilitsis JG, Vannaboutathong C, Wagner BJ, Province-Azalde R, Bendel MA. (2022) Systematic literature review of spinal cord stimulation in patients with chronic back pain without prior spine surgery. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.25(5):648-56.
- Vannemreddy P, Slavin KV. (2011) Spinal cord stimulation: Current applications for treatment of chronic pain. Anesth Essays Res.5(1):20-7. PMCID: PMC4173369. [PubMed]
- Lam CM, Latif U, Sack A, Govindan S, Sanderson M, Vu DT, Smith G, Sayed D, Khan T. (2023) Advances in Spinal Cord Stimulation. Bioengineering (Basel).10(2). PMCID: PMC9951889. [PubMed]
- Miller JP, Eldabe S, Buchser E, Johanek LM, Guan Y, Linderoth B. (2016) Parameters of spinal cord stimulation and their role in electrical charge delivery: a review. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.19(4):373-84.
- Brill S, Defrin R, Aryeh IG, Zusman AM, Benyamini Y. (2022) Short-and long-term effects of conventional spinal cord stimulation on chronic pain and health perceptions: A longitudinal controlled trial. European Journal of Pain.26(9):1849-62.
- Hayek SM, Veizi E, Hanes M. (2015) Treatment-Limiting Complications of Percutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulator Implants: A Review of Eight Years of Experience From an Academic Center Database. Neuromodulation.18(7):603-8; discussion 8-9. [PubMed]
- Kapural L, Yu C, Doust MW, Gliner BE, Vallejo R, Sitzman BT, Amirdelfan K, Morgan DM, Brown LL, Yearwood TL. (2015) Novel 10-kHz high-frequency therapy (HF10 therapy) is superior to traditional low-frequency spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of chronic back and leg pain: the SENZA-RCT randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology.123(4):851-60.
- Reddy RD, Moheimani R, Yu GG, Chakravarthy KV. (2020) A Review of Clinical Data on Salvage Therapy in Spinal Cord Stimulation. Neuromodulation.23(5):562-71. PMCID: PMC7202967. [PubMed]
- Melzack R, Wall PD. (1965) Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science.150(3699):971-9. [PubMed]
- Linderoth B, Meyerson BA. (2010) Spinal cord stimulation: exploration of the physiological basis of a widely used therapy. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists.113(6):1265-7.
- Jeon, YH. (2012) Spinal cord stimulation in pain management: a review. Korean J Pain.25(3):143-50. PMCID: PMC3389317. [PubMed]
- Barolat G, Massaro F, He J, Zeme S, Ketcik B. (1993) Mapping of sensory responses to epidural stimulation of the intraspinal neural structures in man. J Neurosurg.78(2):233-9. [PubMed]
- Kumar K, North R, Taylor R, Sculpher M, Van den Abeele C, Gehring M, Jacques L, Eldabe S, Meglio M, Molet J. (2005) Spinal cord stimulation vs. conventional medical management: a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter study of patients with failed back surgery syndrome (PROCESS study). Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.8(4):213-8.
- Levy RM. (2014) Anatomic considerations for spinal cord stimulation. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.17:2-11.
- Schultz DM, Webster LR, Kosek P, Dar U, Tan Y, Sun M. (2012) Sensor-driven position-adaptive spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain. Pain physician.15(1):1.
- Barolat G, Oakley JC, Law JD, North RB, Ketcik B, Sharan A. (2001) Epidural spinal cord stimulation with a multiple electrode paddle lead is effective in treating intractable low back pain. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.4(2):59-66.
- Turner JA, Loeser JD, Bell KG. (1995) Spinal cord stimulation for chronic low back pain: a systematic literature synthesis. Neurosurgery.37(6):1088-95; discussion 95-6. [PubMed]
- Aló KM, Redko V, Charnov J. (2002) Four Year Follow-up of Dual Electrode Spinal Cord Stimulation for Chronic Pain. Neuromodulation.5(2):79-88. [PubMed]
- Caylor J, Reddy R, Yin S, Cui C, Huang M, Huang C, Rao R, Baker DG, Simmons A, Souza D. (2019) Spinal cord stimulation in chronic pain: evidence and theory for mechanisms of action. Bioelectronic medicine.5:1-41.
- Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L, Eldabe S, Meglio M, Molet J, Thomson S, O'Callaghan J, Eisenberg E, Milbouw G. (2008) The effects of spinal cord stimulation in neuropathic pain are sustained: a 24-month follow-up of the prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial of the effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery.63(4):762-70.
- Kapural L, Yu C, Doust MW, Gliner BE, Vallejo R, Sitzman BT, Amirdelfan K, Morgan DM, Yearwood TL, Bundschu R, Yang T, Benyamin R, Burgher AH. (2016) Comparison of 10-kHz High-Frequency and Traditional Low-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Back and Leg Pain: 24-Month Results From a Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Pivotal Trial. Neurosurgery.79(5):667-77. PMCID: PMC5058646. [PubMed]
- Al-Kaisy A, Palmisani S, Smith TE, Pang D, Lam K, Burgoyne W, Houghton R, Hudson E, Lucas J. (2017) 10 kHz High-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation for Chronic Axial Low Back Pain in Patients With No History of Spinal Surgery: A Preliminary, Prospective, Open Label and Proof-of-Concept Study. Neuromodulation.20(1):63-70. [PubMed]
- Al-Kaisy A, Van Buyten JP, Smet I, Palmisani S, Pang D, Smith T. (2014) Sustained effectiveness of 10 kHz high-frequency spinal cord stimulation for patients with chronic, low back pain: 24-month results of a prospective multicenter study. Pain Med.15(3):347-54. PMCID: PMC4282782. [PubMed]
- Al-Kaisy A, Palmisani S, Smith TE, Carganillo R, Houghton R, Pang D, Burgoyne W, Lam K, Lucas J. (2018) Long-Term Improvements in Chronic Axial Low Back Pain Patients Without Previous Spinal Surgery: A Cohort Analysis of 10-kHz High-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation over 36 Months. Pain Med.19(6):1219-26. [PubMed]
- De Ridder D, Vanneste S, Plazier M, van der Loo E, Menovsky T. (2010) Burst spinal cord stimulation: toward paresthesia-free pain suppression. Neurosurgery.66(5):986-90.
- Kirketeig T, Schultheis C, Zuidema X, Hunter CW, Deer T. (2019) Burst Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Clinical Review. Pain Med.20(Suppl 1):S31-s40. PMCID: PMC6544556. [PubMed]
- de Vos CC, Bom MJ, Vanneste S, Lenders MW, De Ridder D. (2014) Burst spinal cord stimulation evaluated in patients with failed back surgery syndrome and painful diabetic neuropathy. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.17(2):152-9.
- Schu S, Slotty PJ, Bara G, von Knop M, Edgar D, Vesper J. (2014) A prospective, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to examine the effectiveness of burst spinal cord stimulation patterns for the treatment of failed back surgery syndrome. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.17(5):443-50.
- De Ridder D, Vanneste S. (2016) Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation: Different and Common Brain Mechanisms. Neuromodulation.19(1):47-59. [PubMed]
- Kinfe TM, Pintea B, Link C, Roeske S, Güresir E, Güresir Á, Vatter H. (2016) High frequency (10 kHz) or burst spinal cord stimulation in failed back surgery syndrome patients with predominant back pain: preliminary data from a prospective observational study. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.19(3):268-75.
- Muhammad S, Roeske S, Chaudhry SR, Kinfe TM. (2017) Burst or high-frequency (10 kHz) spinal cord stimulation in failed back surgery syndrome patients with predominant back pain: one year comparative data. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.20(7):661-7.
- De Ridder D, Plazier M, Kamerling N, Menovsky T, Vanneste S. (2013) Burst spinal cord stimulation for limb and back pain. World neurosurgery.80(5):642-9. e1.
- Yearwood T, De Ridder D, Yoo HB, Falowski S, Venkatesan L, Ting To W, Vanneste S. (2020) Comparison of Neural Activity in Chronic Pain Patients During Tonic and Burst Spinal Cord Stimulation Using Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography. Neuromodulation.23(1):56-63. [PubMed]
- Vesper J, Slotty P, Schu S, Poeggel-Kraemer K, Littges H, Van Looy P, Agnesi F, Venkatesan L, Van Havenbergh T. (2019) Burst SCS microdosing is as efficacious as standard burst SCS in treating chronic back and leg pain: results from a randomized controlled trial. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.22(2):190-3.
- Deer TR, Patterson DG, Baksh J, Pope JE, Mehta P, Raza A, Agnesi F, Chakravarthy KV. (2021) Novel intermittent dosing burst paradigm in spinal cord stimulation. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.24(3):566-73.
- Ranger M, Irwin G, Bunbury K, Peutrell J. (2008) Changing body position alters the location of the spinal cord within the vertebral canal: a magnetic resonance imaging study. British journal of anaesthesia.101(6):804-9.
- Parker JL, Karantonis DM, Single PS, Obradovic M, Cousins MJ. (2012) Compound action potentials recorded in the human spinal cord during neurostimulation for pain relief. Pain.153(3):593-601.
- Russo M, Brooker C, Cousins MJ, Taylor N, Boesel T, Sullivan R, Holford L, Hanson E, Gmel GE, Shariati NH, Poree L, Parker J. (2020) Sustained Long-Term Outcomes With Closed-Loop Spinal Cord Stimulation: 12-Month Results of the Prospective, Multicenter, Open-Label Avalon Study. Neurosurgery.87(4):E485-e95. PMCID: PMC8184296. [PubMed]
- Deer TR, Jain S, Hunter C, Chakravarthy K. (2019) Neurostimulation for Intractable Chronic Pain. Brain Sci.9(2). PMCID: PMC6406470. [PubMed]
- Mekhail N, Levy RM, Deer TR, Kapural L, Li S, Amirdelfan K, Hunter CW, Rosen SM, Costandi SJ, Falowski SM. (2020) Long-term safety and efficacy of closed-loop spinal cord stimulation to treat chronic back and leg pain (Evoke): a double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology.19(2):123-34.
- Russo M, Cousins MJ, Brooker C, Taylor N, Boesel T, Sullivan R, Poree L, Shariati NH, Hanson E, Parker J. (2018) Effective Relief of Pain and Associated Symptoms With Closed-Loop Spinal Cord Stimulation System: Preliminary Results of the Avalon Study. Neuromodulation.21(1):38-47. [PubMed]
- Mekhail N, Levy RM, Deer TR, Kapural L, Li S, Amirdelfan K, Hunter CW, Rosen SM, Costandi SJ, Falowski SM. (2022) Durability of clinical and quality-of-life outcomes of closed-loop spinal cord stimulation for chronic back and leg pain: a secondary analysis of the evoke randomized clinical trial. JAMA neurology.79(3):251-60.
- Dupré DA, Tomycz N, Whiting D, Oh M. (2018) Spinal Cord Stimulator Explantation: Motives for Removal of Surgically Placed Paddle Systems. Pain Pract.18(4):500-4. [PubMed]
- Deer TR, Pope JE, Falowski SM, Pilitsis JG, Hunter CW, Burton AW, Connolly AT, Verrills P. (2023) Clinical Longevity of 106,462 Rechargeable and Primary Cell Spinal Cord Stimulators: Real World Study in the Medicare Population. Neuromodulation.26(1):131-8. [PubMed]
- Simopoulos T, Aner M, Sharma S, Ghosh P, Gill JS. (2019) Explantation of Percutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulator Devices: A Retrospective Descriptive Analysis of a Single-Center 15-Year Experience. Pain Med.20(7):1355-61. [PubMed]
- Van Buyten JP, Wille F, Smet I, Wensing C, Breel J, Karst E, Devos M, Pöggel-Krämer K, Vesper J. (2017) Therapy-Related Explants After Spinal Cord Stimulation: Results of an International Retrospective Chart Review Study. Neuromodulation.20(7):642-9. PMCID: PMC5656934. [PubMed]
- Al-Kaisy A, Royds J, Al-Kaisy O, Palmisani S, Pang D, Smith T, Padfield N, Harris S, Wesley S, Yearwood TL, Ward S. (2020) Explant rates of electrical neuromodulation devices in 1177 patients in a single center over an 11-year period. Reg Anesth Pain Med.45(11):883-90. [PubMed]
- Kumar K, Hunter G, Demeria D. (2006) Spinal cord stimulation in treatment of chronic benign pain: challenges in treatment planning and present status, a 22-year experience. Neurosurgery.58(3):481-96.
- Hayek SM, Veizi E, Hanes M. (2015) Treatment-limiting complications of percutaneous spinal cord stimulator implants: a review of eight years of experience from an academic center database. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.18(7):603-9.
- Hagedorn JM, Layno-Moses A, Sanders DT, Pak DJ, Bailey-Classen A, Sowder T. (2020) Overview of HF10 spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of chronic pain and an introduction to the Senza Omnia™ system. Pain management.10(6):367-76.
- D'Souza RS, Her YF. (2022) Stimulation holiday rescues analgesia after habituation and loss of efficacy from 10-kilohertz dorsal column spinal cord stimulation. Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.47(12):722-7.
- Reddy RD, Moheimani R, Gregory GY, Chakravarthy KV. (2020) A review of clinical data on salvage therapy in spinal cord stimulation. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.23(5):562-71.
- Levy RM, Mekhail N, Kramer J, Poree L, Amirdelfan K, Grigsby E, Staats P, Burton AW, Burgher AH, Scowcroft J, Golovac S, Kapural L, Paicius R, Pope J, Samuel S, McRoberts WP, Schaufele M, Kent AR, Raza A, Deer TR. (2020) Therapy Habituation at 12 Months: Spinal Cord Stimulation Versus Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I and II. J Pain.21(3-4):399-408. [PubMed]
- Chapman KB, Spiegel MA, van Helmond N, Patel KV, Yang A, Yousef TA, Mandelberg N, Deer T, Mogilner AY. (2022) Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation as a Salvage Therapy Following Failed Spinal Cord Stimulation. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.25(7):1024-32.
- Bateson, A. (2002) Basic pharmacologic mechanisms involved in benzodiazepine tolerance and withdrawal. Current pharmaceutical design.8(1):5-21.
- Glajchen, M. (2001) Chronic pain: treatment barriers and strategies for clinical practice. The Journal of the American Board of Family Practice.14(3):211-8.
- Rauck RL, Loudermilk E, Thomson SJ, Paz-Solis JF, Bojrab L, Noles J, Vesper J, Atallah J, Roth D, Hegarty J. (2023) Long-term safety of spinal cord stimulation systems in a prospective, global registry of patients with chronic pain. Pain management.13(2):115-27.
- Kapural L, Sayed D, Kim B, Harstroem C, Deering J. (2020) Retrospective assessment of salvage to 10 kHz spinal cord stimulation (SCS) in patients who failed traditional SCS therapy: RESCUE study. Journal of Pain Research.2861-7.
- Andrade P, Heiden P, Visser-Vandewalle V, Matis G. (2021) 1.2 kHz high-frequency stimulation as a rescue therapy in patients with chronic pain refractory to conventional spinal cord stimulation. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.24(3):540-5.
- Kumar V, Prusik J, Lin Y, Hwang R, Feustel P, Pilitsis JG. (2018) Efficacy of alternating conventional stimulation and high frequency stimulation in improving spinal cord stimulation outcomes: a pilot study. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.21(5):466-71.
- Cordero Tous N, Sanchez Corral C, Ortiz Garcia IM, Jover Vidal A, Galvez Mateos R, Olivares Granados G. (2021) High-frequency spinal cord stimulation as rescue therapy for chronic pain patients with failure of conventional spinal cord stimulation. European Journal of Pain.25(7):1603-11.
- Courtney P, Espinet A, Mitchell B, Russo M, Muir A, Verrills P, Davis K. (2015) Improved pain relief with burst spinal cord stimulation for two weeks in patients using tonic stimulation: results from a small clinical study. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface.18(5):361-6.
- Breitfeld C, Eikermann M, Kienbaum P, Peters J. (2003) Opioid “holiday” following antagonist supported detoxification during general anesthesia improves opioid agonist response in a cancer patient with opioid addiction. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists.98(2):571-3.
- Howland, RH. (2009) Medication holidays. Journal of psychosocial nursing and mental health services.47(9):15-8.
- Corona T, Rivera C, Otero E, Stopp L. (1995) A longitudinal study of the effects of an L-dopa drug holiday on the course of Parkinson's disease. Clinical neuropharmacology.18(4):325-32.
- Mirzakhalili E, Rogers ER, Lempka SF. An optimization framework for targeted spinal cord stimulation. J Neural Eng. 2023;20(5):056026. Published 2023 Sep 28. [CrossRef]
- Rigoard P, Ounajim A, Moens M, et al. Should we Oppose or Combine Waveforms for Spinal Cord Stimulation in PSPS-T2 Patients? A Prospective Randomized Crossover Trial (MULTIWAVE Study). J Pain. 2023;24(12):2319-2339. [CrossRef]
- Provenzano D, Tate J, Gupta M, et al. Pulse Dosing of 10-kHz Paresthesia-Independent Spinal Cord Stimulation Provides the Same Efficacy with Substantial Reduction of Device Recharge Time. Pain Med. 2022;23(1):152-163. [CrossRef]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





