Submitted:
05 April 2024
Posted:
07 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Reconstituted Skim Milk (RSM)-Based Fermentates
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Metabolomics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Statement
3. Results
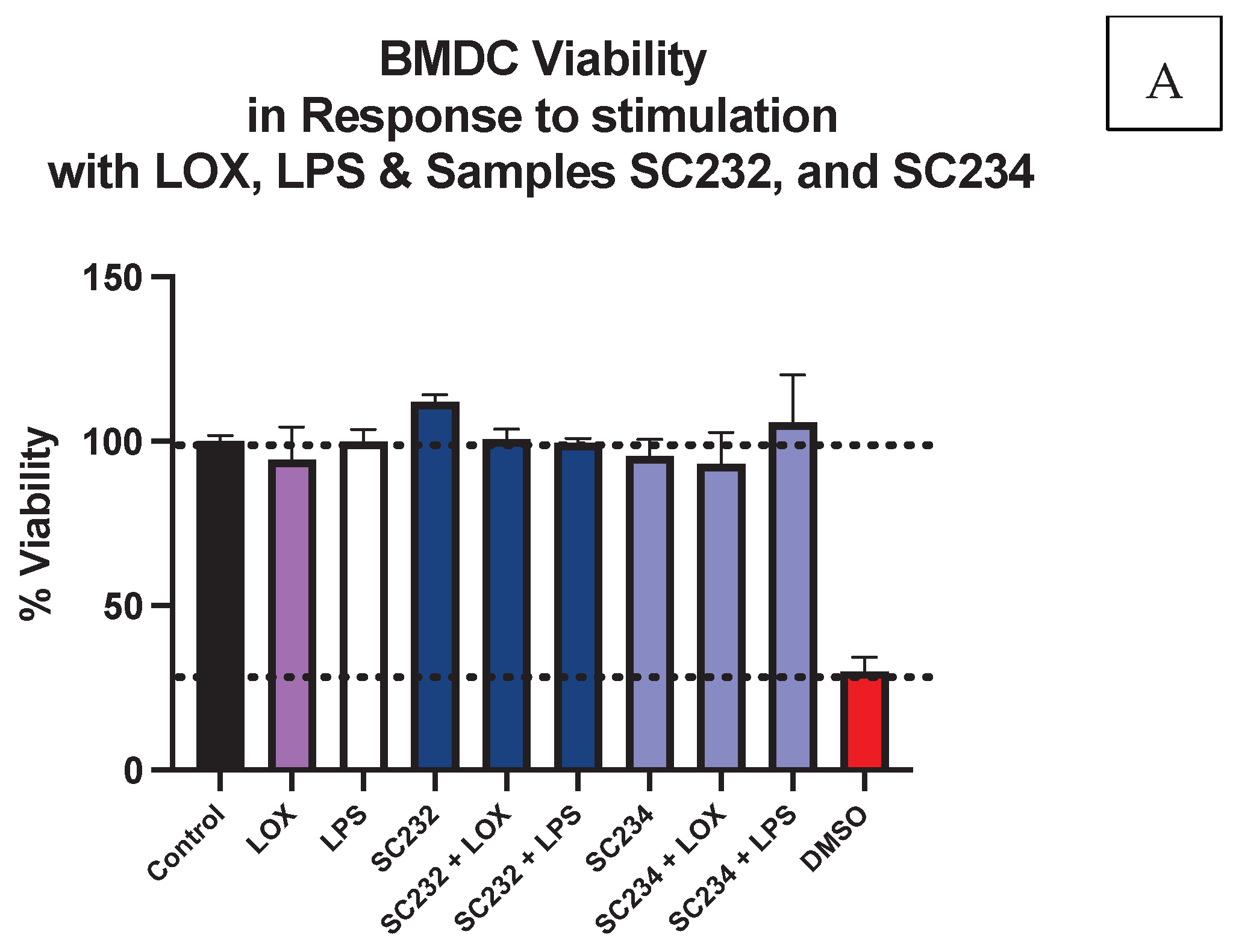
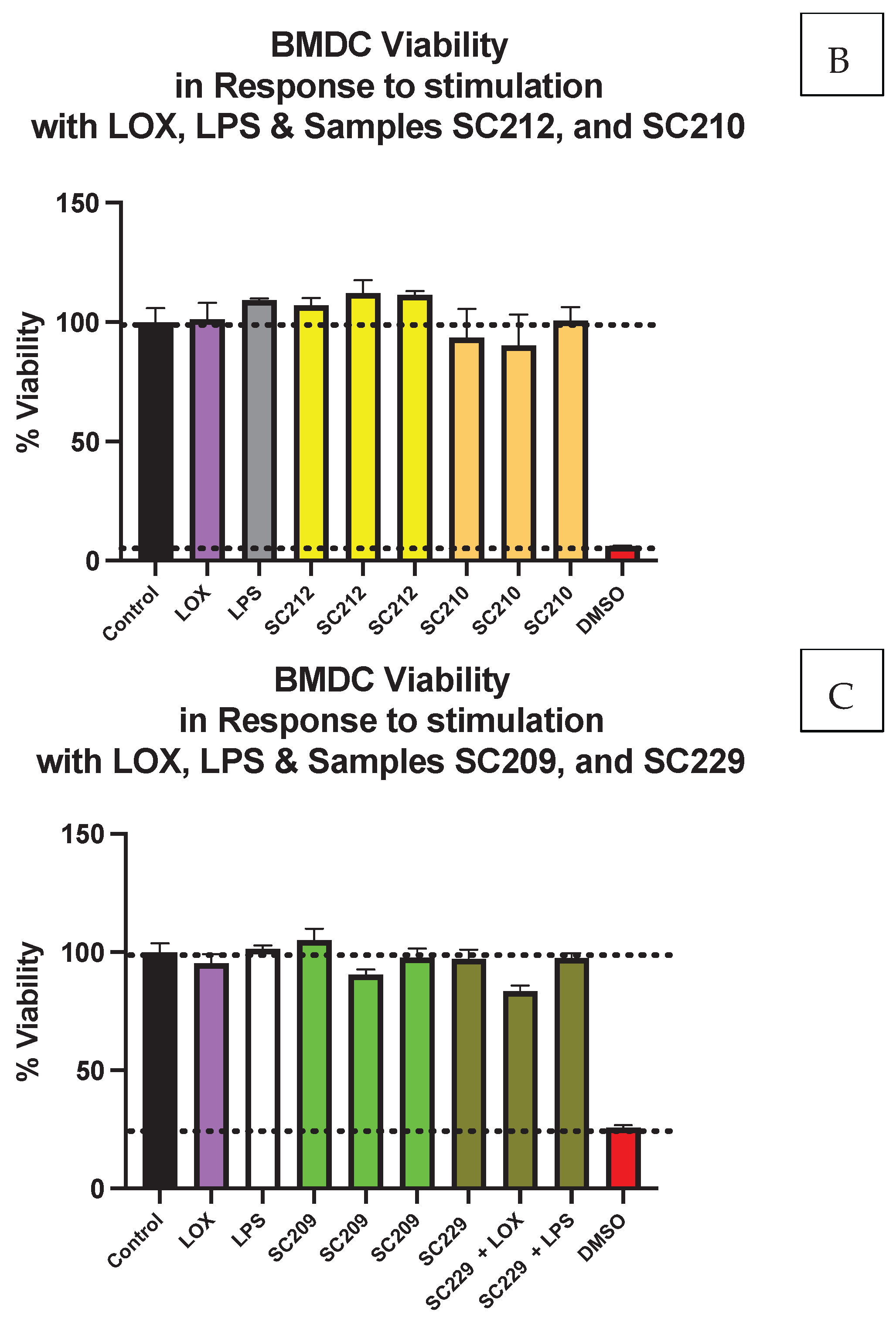
3.1. Cell Viability Is Not Affected by the Presence of Fermentate Samples
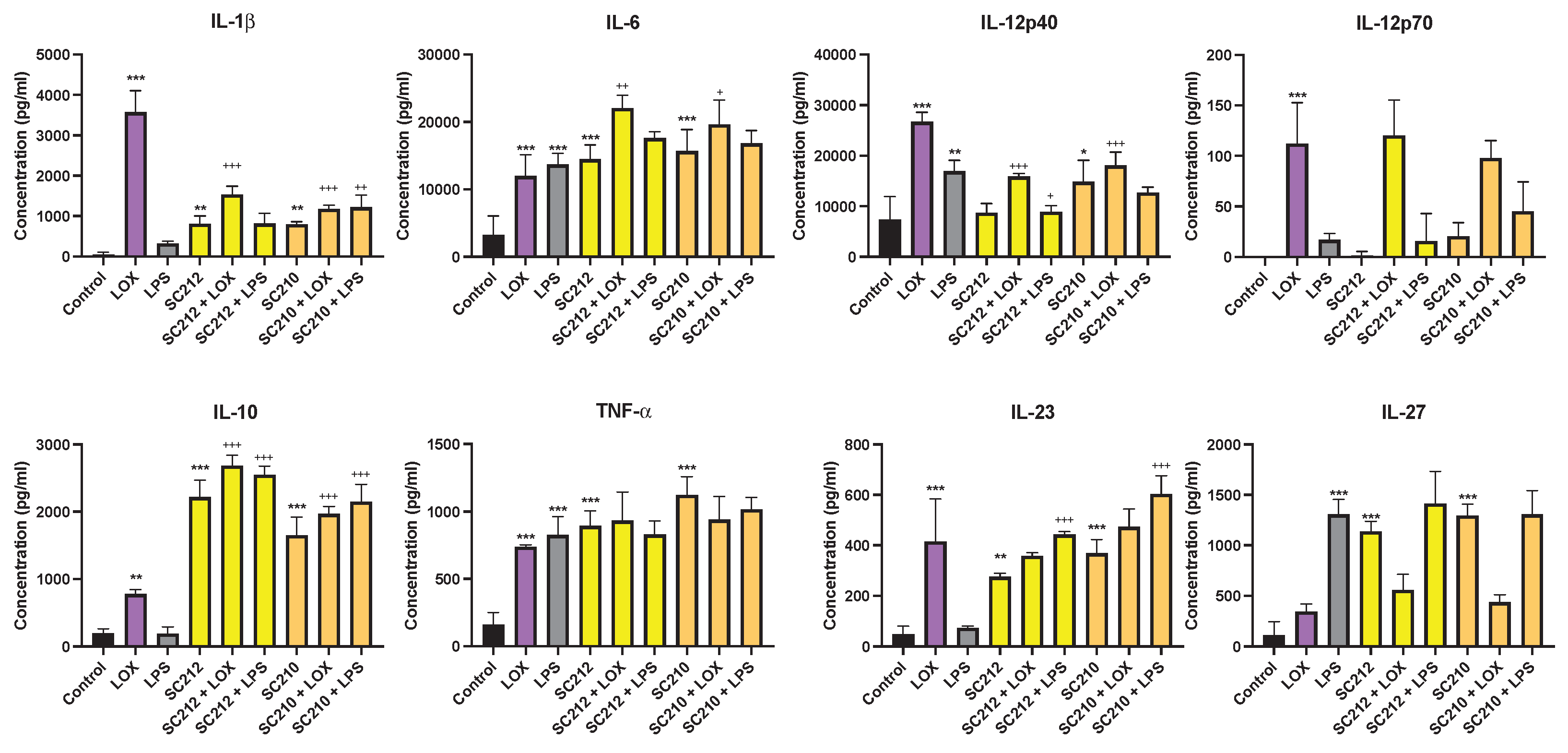
3.2. Effects of Fermentates on Cytokine Secretion
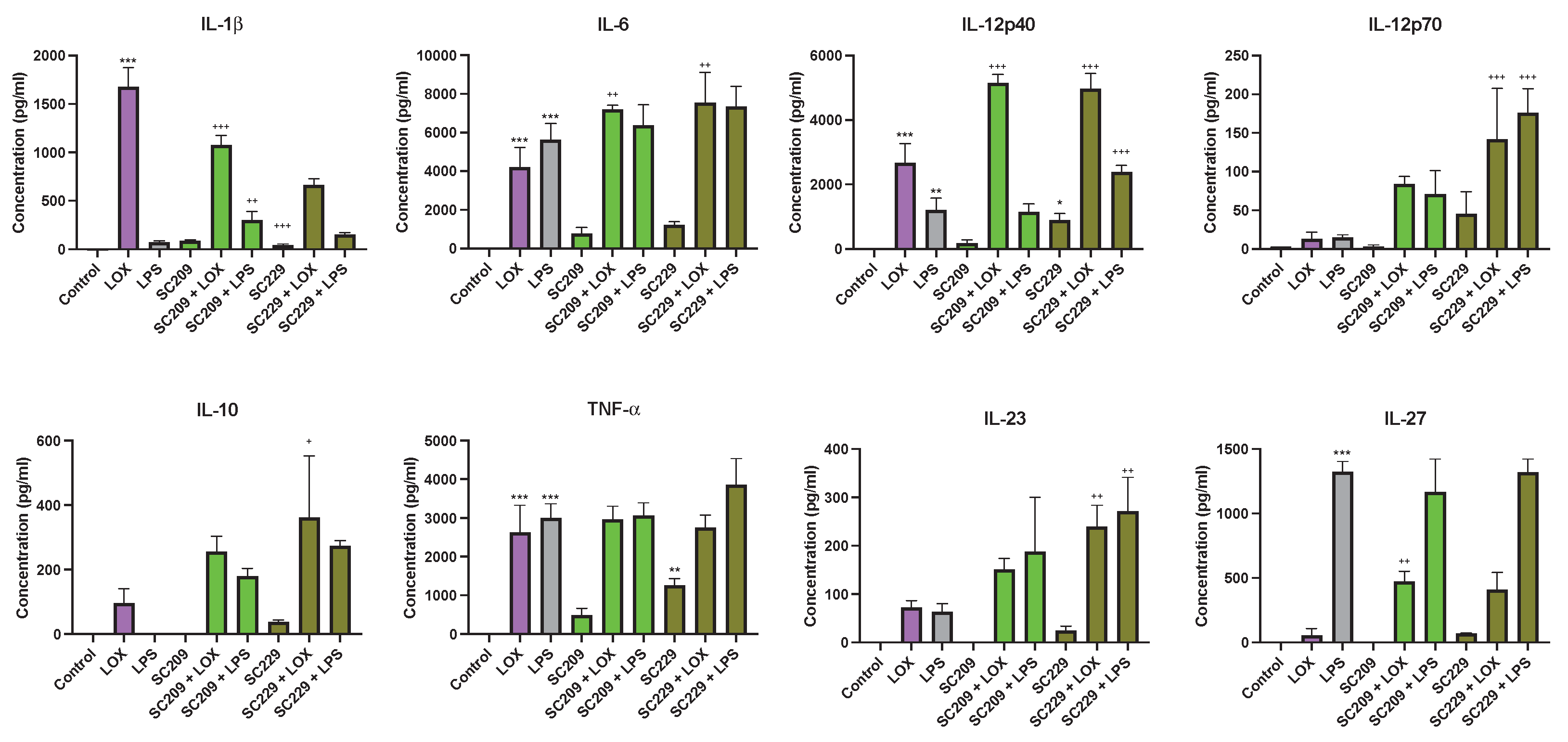
3.5. Metabolite Levels in Fermentates
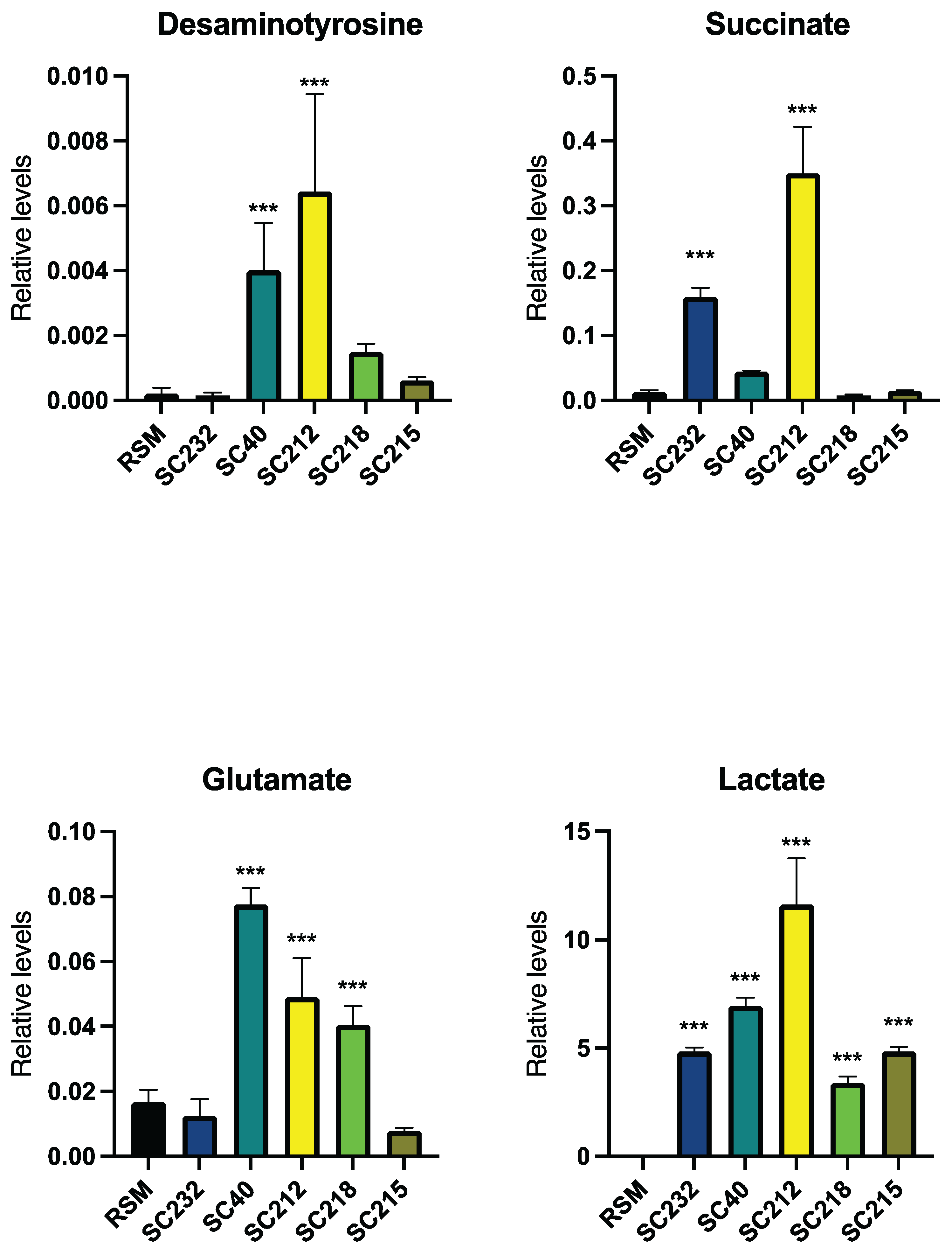
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fadnes, L.T.; Økland, J.-M.; Haaland, Ø.A.; Johansson, K.A. Estimating Impact of Food Choices on Life Expectancy: A Modeling Study. PLOS Medicine 2022, 19, e1003889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koithan, M.; Devika, J. New Approaches to Nutritional Therapy. J Nurse Pract 2010, 6, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lewis, E.D.; Pae, M.; Meydani, S.N. Nutritional Modulation of Immune Function: Analysis of Evidence, Mechanisms, and Clinical Relevance. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, H.; Beresford, T.P.; Cotter, P.D. Health Benefits of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Fermentates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, D.; Tocmo, R.; Loscher, C. Targeted Application of Functional Foods as Immune Fitness Boosters in the Defense against Viral Infection. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D. The Role of Diet in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2016, 12, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EFCCA About IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Diseases) Organisations | World IBD Day. Available online: https://worldibdday.org/about-us (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- de Mattos, B.R.R.; Garcia, M.P.G.; Nogueira, J.B.; Paiatto, L.N.; Albuquerque, C.G.; Souza, C.L.; Fernandes, L.G.R.; Tamashiro, W.M. da S.C.; Simioni, P.U. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Overview of Immune Mechanisms and Biological Treatments. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015, 493012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland Clinic Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Symptoms, Treatment & Diagnosis. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15587-inflammatory-bowel-disease-overview (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Head, K.; Jurenka, J. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Part II: Crohn’s Disease - Pathophysiology and Conventional and Alternative Treatment Options. Alternative Medicine Review 2004, 9, 360–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alatab, S.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Ikuta, K.; Vahedi, H.; Bisignano, C.; Safiri, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Nixon, M.R.; Abdoli, A.; Abolhassani, H.; et al. The Global, Regional, and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Prevalence of IBD | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/data-and-statistics/prevalence.html (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Song, L.; Dong, G.; Guo, L.; Graves, D.T. The Function of Dendritic Cells in Modulating the Host Response. Mol Oral Microbiol 2018, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Agrawal, S.; Gupta, S. Role of Dendritic Cells in Inflammation and Loss of Tolerance in the Elderly. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollara, G.; Kwan, A.; Newton, P.J.; Handley, M.E.; Chain, B.M.; Katz, D.R. Dendritic Cells in Viral Pathogenesis: Protective or Defective? Int J Exp Pathol 2005, 86, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazersaheb, S.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Hejazi, M.S.; Tarhriz, V.; Farjami, A.; Ghasemian Sorbeni, F.; Farahzadi, R.; Ghasemnejad, T. COVID-19 Infection: An Overview on Cytokine Storm and Related Interventions. Virology Journal 2022, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanvand, A. COVID-19 and the Role of Cytokines in This Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brydon, E.W.A.; Morris, S.J.; Sweet, C. Role of Apoptosis and Cytokines in Influenza Virus Morbidity. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2005, 29, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, K.; Crowe, S.M. Cytokines and HIV-1: Interactions and Clinical Implications. Antivir Chem Chemother 2001, 12, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, L.E.; Hatton, R.D.; Mangan, P.R.; Turner, H.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M.; Weaver, C.T. Interleukin 17–Producing CD4+ Effector T Cells Develop via a Lineage Distinct from the T Helper Type 1 and 2 Lineages. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Barlow, A.T.; Young, H.; Valencia, J.C. Interferon γ: An Overview of Its Functions in Health and Disease. In Encyclopedia of Immunobiology; Ratcliffe, M.J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2016; pp. 494–500. ISBN 978-0-08-092152-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzeni, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics - 2nd Edition; 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, 2013; ISBN 978-0-08-096156-9. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.H.; Webster, R.G. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Exerts Powerful Anti-Influenza Virus Effects in Lung Epithelial Cells. J Virol 2002, 76, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rook, G.A.; Taverne, J.; Playfair, J.H. Evaluation of TNF as Antiviral, Antibacterial and Antiparasitic Agent. Biotherapy 1991, 3, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, J.; Bluethmann, H.; Peschon, J.J. Antiviral Activity of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Is Mediated via P55 and P75 TNF Receptors. J Exp Med 1997, 186, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Mitoma, H.; Harashima, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Shimoda, T. Transmembrane TNF-α: Structure, Function and Interaction with Anti-TNF Agents. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, J.M.; Avia, M.; Martín, V.; Sevilla, N. IL-10: A Multifunctional Cytokine in Viral Infections. J Immunol Res 2017, 2017, 6104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Ikari, N.; Kouchi, T.; Kowatari, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Shimojo, N.; Tsuji, N.M. The Molecular Mechanism for Activating IgA Production by Pediococcus Acidilactici K15 and the Clinical Impact in a Randomized Trial. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Kawahara, S.; Hidaka, M.; Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, W.; Takeshita, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Bumbein, D.; Muguruma, M.; Kurokawa, M. Effects of Oral Administration of Probiotics from Mongolian Dairy Products on the Th1 Immune Response in Mice. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 2013, 77, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Takeshita, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Dashnyam, B.; Kawahara, S.; Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, W.; Muguruma, M.; Kurokawa, M. Efficacy of Oral Administration of Heat-Killed Probiotics from Mongolian Dairy Products against Influenza Infection in Mice: Alleviation of Influenza Infection by Its Immunomodulatory Activity through Intestinal Immunity. International Immunopharmacology 2011, 11, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, Z.; Yu, T.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhai, P.; He, L.; et al. The Antiviral Effects of Jasminin via Endogenous TNF-α and the Underlying TNF-α-Inducing Action. Molecules 2022, 27, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.-G.; Jang, M.; Cho, C.-W.; Hong, H.-D.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, S.-Y.; Jung, S.K.; Rhee, Y.K. White Ginseng Extract Induces Immunomodulatory Effects via the MKK4-JNK Pathway. Food Sci Biotechnol 2016, 25, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, Y.; Eo, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Jeon, K.S.; Jeong, J.B. Wild Simulated Ginseng Activates Mouse Macrophage, RAW264.7 Cells through TRL2/4-Dependent Activation of MAPK, NF-κB and PI3K/AKT Pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 263, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughran, S.T.; Power, P.A.; Maguire, P.T.; McQuaid, S.L.; Buchanan, P.J.; Jonsdottir, I.; Newman, R.W.; Harvey, R.; Johnson, P.A. Influenza Infection Directly Alters Innate IL-23 and IL-12p70 and Subsequent IL-17A and IFN-γ Responses to Pneumococcus in Vitro in Human Monocytes. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0203521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Ye, D.; Dokladny, K.; Ma, T.Y. Mechanism of IL-1β-Induced Increase in Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Permeability. J Immunol 2008, 180, 5653–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Mejía, J.; Jakesevic, M.; Krych, Ł.; Nielsen, D.S.; Hansen, L.H.; Sondergaard, B.C.; Kvist, P.H.; Hansen, A.K.; Holm, T.L. Treatment with a Monoclonal Anti-IL-12p40 Antibody Induces Substantial Gut Microbiota Changes in an Experimental Colitis Model. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016, 2016, 4953120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosh, R.H.; Jordan-Mahy, N.; Sammon, C.; Le Maitre, C. Interleukin 1 Is a Key Driver of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Demonstration in a Murine IL-1Ra Knockout Model. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3559–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitselou, A.; Grammeniatis, V.; Varouktsi, A.; Papadatos, S.S.; Katsanos, K.; Galani, V. Proinflammatory Cytokines in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Comparison with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Intest Res 2020, 18, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecker, H.C.; Steffen, M.; Witthoeft, T.; Pflueger, I.; Schreiber, S.; MacDermott, R.P.; Raedler, A. Enhanced Secretion of Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 Beta by Isolated Lamina Propria Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Clin Exp Immunol 1993, 94, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H. Tackling Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Targeting Proinflammatory Cytokines and Lymphocyte Homing. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, F.; Peng, Y.; Yi, X.; He, Y.; Shi, Y. Research Progress of Interleukin-27 in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 2023, izad153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarreberg, L.D.; Wilkins, C.; Ramos, H.J.; Green, R.; Davis, M.A.; Chow, K.; Gale, M. Interleukin-1β Signaling in Dendritic Cells Induces Antiviral Interferon Responses. mBio 2018, 9, e00342–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, R.N.; Dotan, S.; Elkabets, M.; White, M.R.; Reich, E.; Carmi, Y.; Song, X.; Dvozkin, T.; Krelin, Y.; Voronov, E. The Involvement of IL-1 in Tumorigenesis, Tumor Invasiveness, Metastasis and Tumor-Host Interactions. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2006, 25, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, E.P. An Interleukin-1 Beta-Encoding Retrovirus Exhibits Enhanced Replication In Vivo. Journal of Virology 2015, 89, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, A.; Horng, T. IL-6 Strikes a Balance in Metabolic Inflammation. Cell Metab 2014, 19, 898–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Blood 2011, 117, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 Family in Innate Inflammation and Acquired Immunity. Immunol Rev 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Immunoregulatory Functions of the IL-12 Family of Cytokines in Antiviral Systems. Viruses 2019, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker, J.A.; Wong, K.A.; Dallari, S.; Bao, P.; Dolgoter, A.; Jo, Y.; Wehrens, E.J.; Macal, M.; Zuniga, E.I. Interleukin-27R Signaling Mediates Early Viral Containment and Impacts Innate and Adaptive Immunity after Chronic Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection. Journal of Virology 2018, 92, e02196–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideshima, T.; Nakamura, N.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C. Biologic Sequelae of Interleukin-6 Induced PI3-K/Akt Signaling in Multiple Myeloma. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5991–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, B.S. Th17 Cells Enhance Viral Persistence and Inhibit T Cell Cytotoxicity in a Model of Chronic Virus Infection. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2009, 206, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komastu, T.; Ireland, D.D.C.; Reiss, C.S. IL-12 and Viral Infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1998, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.; Ghilardi, N.; Li, J.; de Sauvage J., F. IL-27 Regulates IL-12 Responsiveness of Naïve CD4+ T Cells through Stat1-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2003, 100, 15047–15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A. The Cytokine Handbook; 2nd, *!!! REPLACE !!!* (Eds.) L: Academic Press, 1996.
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the Regulation of Innate Resistance and Adaptive Immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2003, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.V.; Hunter, C.A. Biology of Recently Discovered Cytokines: Discerning the pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Interleukin-27. Arthritis Res Ther 2004, 6, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, E.J.; Wong, K.A.; Gupta, A.; Khan, A.; Benedict, C.A.; Zuniga, E.I. IL-27 Regulates the Number, Function and Cytotoxic Program of Antiviral CD4 T Cells and Promotes Cytomegalovirus Persistence. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0201249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.B.; Brooks, D.G. The Role of IL-10 in Regulating Immunity to Persistent Viral Infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2011, 350, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the Interleukin-10 Receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of Interleukin 10 Transcriptional Regulation in Inflammation and Autoimmune Disease. Crit Rev Immunol 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, N.; Freitas, R.H.C.N.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Fernandes, P.D. Therapeutic Effects of Anti-Inflammatory N -Acylhydrazones in the Resolution of Experimental Colitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2020, 374, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abron, J.D.; Singh, N.P.; Price, R.L.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Singh, U.P. Genistein Induces Macrophage Polarization and Systemic Cytokine to Ameliorate Experimental Colitis. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0199631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Zuo, X.; Fu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; et al. Saccharomyces Boulardii Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021, e1622375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhan, L.; Liao, H.; Chen, L.; Lv, X. Curcumin Improves TNBS-Induced Colitis in Rats by Inhibiting IL-27 Expression via the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Planta Med 2013, 29, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caban, M.; Lewandowska, U. Polyphenols and the Potential Mechanisms of Their Therapeutic Benefits against Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Journal of Functional Foods 2022, 95, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.-P.; Wang, M.-X.; Wu, T.-T.; Liu, D.-Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Long, J.; Zhao, H.-M.; Zhong, Y.-B. Curcumin Alleviated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Regulating M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization and TLRs Signaling Pathway. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2021, 2021, e3334994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Lv, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, J. Curcumin Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice via Regulation of Autophagy and Intestinal Immunity. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019, 30, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-B.; Kang, Z.-P.; Wang, M.-X.; Long, J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Huang, J.-Q.; Wei, S.-Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, H.-M.; Liu, D.-Y. Curcumin Ameliorated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis via Regulating the Homeostasis of DCs and Treg and Improving the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Journal of Functional Foods 2021, 86, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, H.C.; Herrmann, B.; Wiredu, D.; Thaiss, C.A. The Path toward Using Microbial Metabolites as Therapies. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, A.L.; Christophi, G.P.; Kaiko, G.E.; Sun, L.; Goodwin, V.M.; Jain, U.; Esaulova, E.; Artyomov, M.N.; Morales, D.J.; Holtzman, M.J.; et al. The Microbial Metabolite Desaminotyrosine Protects from Influenza through Type I Interferon. Science 2017, 357, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Lu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X. Lactiplantibacillus Pentoses CCFM1227 Produces Desaminotyrosine to Protect against Influenza Virus H1N1 Infection through the Type I Interferon in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, J.; Kou, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, L.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Liang, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; et al. The Intestinal Microbial Metabolite Desaminotyrosine Is an Anti-Inflammatory Molecule That Modulates Local and Systemic Immune Homeostasis. The FASEB Journal 2020, 34, 16117–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harber, K.J.; de Goede, K.E.; Verberk, S.G.S.; Meinster, E.; de Vries, H.E.; van Weeghel, M.; de Winther, M.P.J.; Van den Bossche, J. Succinate Is an Inflammation-Induced Immunoregulatory Metabolite in Macrophages. Metabolites 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhu, W. Succinate Modulates Intestinal Barrier Function and Inflammation Response in Pigs. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.-C.; Wang, X.-Q.; Gao, C.-Q. Succinate Metabolism and Its Regulation of Host-Microbe Interactions. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, A.; Brea-Diakite, D.; Cezard, A.; Wacquiez, A.; Baranek, T.; Bourgeais, J.; Picou, F.; Vasseur, V.; Meyer, L.; Chevalier, C.; et al. Host Succinate Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection through Succinylation and Nuclear Retention of the Viral Nucleoprotein. EMBO J 2022, 41, e108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Quan, J.; Zhao, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, H.; Di, Q.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W. Succinate Is a Natural Suppressor of Antiviral Immune Response by Targeting MAVS. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, J.; Dawe, N.; Van Limbergen, J. The Role of Succinate in the Regulation of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Veledo, S.; Vendrell, J. Gut Microbiota-Derived Succinate: Friend or Foe in Human Metabolic Diseases? Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2019, 20, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caslin, H.L.; Abebayehu, D.; Pinette, J.A.; Ryan, J.J. Lactate Is a Metabolic Mediator That Shapes Immune Cell Fate and Function. Frontiers in Physiology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraporda, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Bengoa, A.A.; Errea, A.J.; Cayet, D.; Foligné, B.; Sirard, J.-C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Rumbo, M. Local Treatment with Lactate Prevents Intestinal Inflammation in the TNBS-Induced Colitis Model. Front Immunol 2016, 7, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Fan, Z.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Yu, J.; Mao, X.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Dietary Lactate Supplementation Can Alleviate DSS-Induced Colitis in Piglets. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 158, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Bilotta, A.J.; Zhao, X.; Cong, Y.; Li, Y. L-Lactate Promotes Intestinal Epithelial Cell Migration to Inhibit Colitis. FASEB J 2021, 35, e21554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




