1. Introduction
The past decades have witnessed a booming of urban populations with ever-increased municipal facilities to serve all citizens. An effective solution to manage these facilities is smart city with Internet of Things (IoT), which is mostly benefitted from the recent development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) [
1,
2,
3]. To support the smart city, an economic but efficient electric power management system is indispensable [
4].
A cloud-end administrator monitors electricity consumptions of all users and loads, presents analyses of all electricity usages, and provides advices to users or directly manages electricity usage of all loads. As a result, the overall electricity consumptions are saved to support sustainable developments of cities and environments.
An efficient electric power management system is dependent on its electric load monitoring module [
5,
6,
7], which can be realized by intrusive or non-intrusive approaches. Compared with Intrusive Load Monitoring (ILM), Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) has more advantages (see Section II for details). In the design of NILM, Load Recognition Algorithm (LRA) plays an essential role and thus attracts attention from researchers. Despite of these great efforts, there still exists a need to further improve the accuracy of LRA. Generally, load recognition may lead to inaccurate results when using inappropriate feature extraction and neural networks, or false recognising loads under masking effect – features of low power load are usually hard to be identified under high power loads.
To address these issues, we present a NILM method based on current feature visualization and a Deep Load Recognition Network (DLRN), as shown in
Figure 1. The NILM method enables precise load recognition in smart homes, facilitating more effective energy management.
In summary, our contributions are summarized as follows:
We propose a current feature visualization method based on signal transforms and Gramian Angular Field (GAF). By this operation, the feature differences between loads are highlighted to make ease of vision-based recognition.
We propose a DLRN based on multi-scale feature extraction and attention mechanism. This design aims to further enhance the recognition accuracies and generalization abilities of our method, especially at low power conditions.
Our NILM approach demonstrates its high efficiency in both public and our private datasets. To examine the generalization ability of proposed approach, we introduce a new dataset with 12 types of electric loads with powers from 24W to 1800W. Experimental results in this dataset as well as the public PLAID dataset validate our design.
The rest of paper is organized as follows. Section II reviews the related work on load monitoring. Sections III presents our contributions in current feature visualization and load recognition based on deep neural networks. Comprehensive experiments and analyses are presented in Section IV. Finally, Section V concludes this paper.
2. Related Works
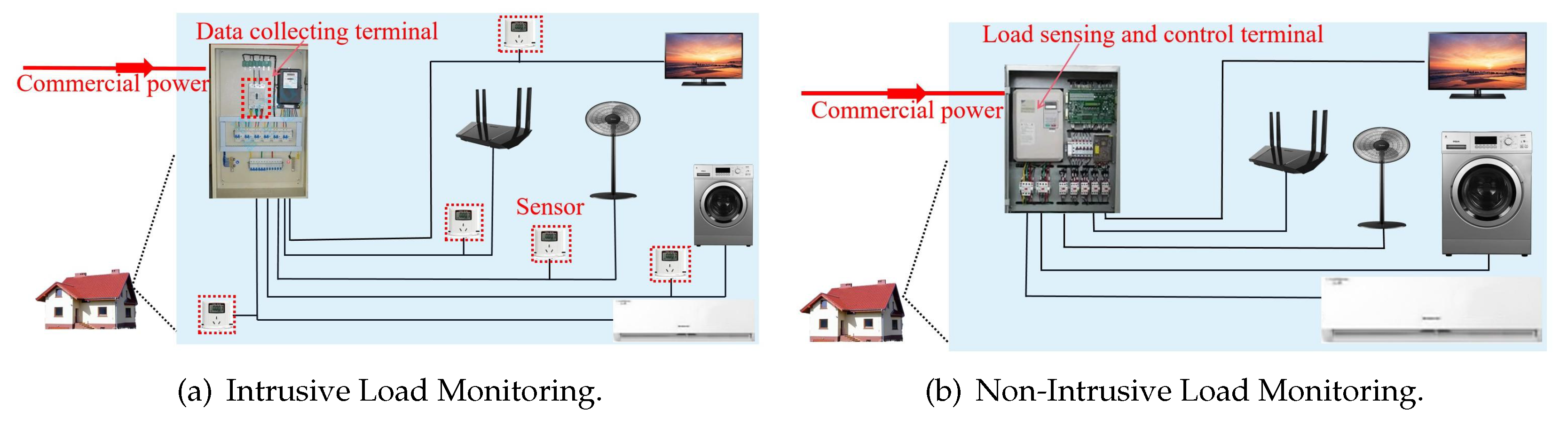
As pointed out in Section I, there are two types of methods of load monitoring: ILM and NILM. In ILM [
8,
9], each electric load is monitored by a separate sensor and the information acquired from all sensors can be centrally processed by cloud-end. While in NILM [
6,
7,
10], only one monitor is required for each family or cell. It captures electric signals (such as voltage, current, and so on) at the commercial power input and transimits them to cloud server in which workload information of all loads are interpreted with algorithms. These differences can be shown in
Figure 2. Apparently, the NILM is preferrable in smart city infrastructure for its simple design, energy-efficient and low setup/maintenance cost.
In the NILM design of
Figure 2b, only one terminal is deployed at the access point of family/cell. It sees the electrical loads in room within a black box. How to design an effective LRA model to recognize or interpret these loads is thus critical.
Traditional LRA methodologies compared the feature of an unknown load with those of known loads in dictionary. They made judgments through a metric set consisting of matching degree [
11], similarity degree [
12], Hellinger distance [
13], etc. The performance of LRA was also benefited from the development of machine learning, resulting in recognition methods with K-means clustering [
14] and fuzzy C-means [
15]. However, these methods basically utilized single feature without consideration on subtle differences between similar signals. Therefore, the problem of recognition confusion was not well addressed.
Researchers considered to introduce more types of signal features to improve the accuracy of LRA. [
16] proposed a load recognition model with a feature combination of transient waveform and power change value during load switching. Kang
et al. [
17] employed fast Fourier transform to extract the amplitude and phase of odd harmonics of the current, and then used them as key features for recognition. To improve the recognition accuracies of loads, [
18] constructed a hybrid feature set by the parameters of active power, reactive power and harmonic amplitude.
In the past decade, deep learning has demonstrated its strengths in AI-driven tasks, such as computer vision, natural language processing, human-computer interaction, and IoT. These successes also inspired the researchers to introduce deep neural networks in LRA. [
19] designed a sequence-to-sequence Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network for load recognition. The authors in [
20] designed a capsule-network-based LRA, in which Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) extracted latent features from a set of non-overlapping energy measurement data segments. [
21] proposed a dual-stream neural network to extract features from current signals. [
22] proposed to extract features with Siamese neural networks and then used them in load recognition. These works have revealed the strong feature extraction abilities of neural networks with promising performance in load recognition.
To further promote the LRA accuracy, researchers also attempted to visualize the features of voltage or current and then employed image-alike processing techniques in load recognition. Owing the advantage of recent booming of computer vision technologies, more accurate and robust LRA methods were developed. [
23] presented an image-classification-based LRA, where the image was obtained with voltage-current (V-I) trajectory. [
24] provided a CNN-based LRA with weighted pixel V-I trajectory map as features. Liu
et al. employed color-coded V-I trajectory map as the input of their AlexNet-based load recognition model [
25]. In [
26], the V-I trajectory and amplitudes of current and voltage were mapped as a color image, which provided richer feature information to CNN-based load recognition. Wenninger
et al. [
27] mapped a cycle of V-I trajectories as a threshold-free recursive graphs, and subsequently designed a Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) convolutional neural network for load recognition.
Our proposed method is also an image-based recognition approach that maps current features and employs image-alike recognition. Compared with its peers, we design a more effective feature mapping framework and a more reliable deep neural network for load recognition. Experimental results validate its design.
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Motivation and Our Framework
It is clear that the choice of input signal has a significant impact on the performance of load recognition. Most traditional approaches [
26,
28,
29] directly input signals such as voltage, current and V-I trajectory diagram into a feature extraction network and carry out the subsequent load recognition accordingly. However, studies [
30,
31,
32] have shown that there are a large amount of noise with a great negative impact on current and voltage signals. It will lead to a decrease in the accuracy of subsequent recognition algorithm, which also leaves room for performance improvement. In other words, preprocessing the signal before entering the recognition network is expected to improve the performance of recognition algorithm.
Considering the excellent results of frequency domain analysis (e.g., wavelet transform, discrete Fourier transform) signal processing, we introduce them into the preprocessing in our method. Firstly, we decompose the current signal into approximation and detail coefficients by wavelet transform. The approximation coefficient represents envelope information of the current signal, which can be used as the main information to distinguish the load; the detail coefficient represents texture information of the current signal, which can distinguish the details of different loads and consequently improve the accuracy of load recognition. Secondly, we use harmonic information of coefficients for load recognition to reduce the impact of noise on recognition accuracy. Our experiments have shown that harmonics are generated during the operation of power equipment, and the harmonics generated by different types of power equipment are different (see below for validation experiments).
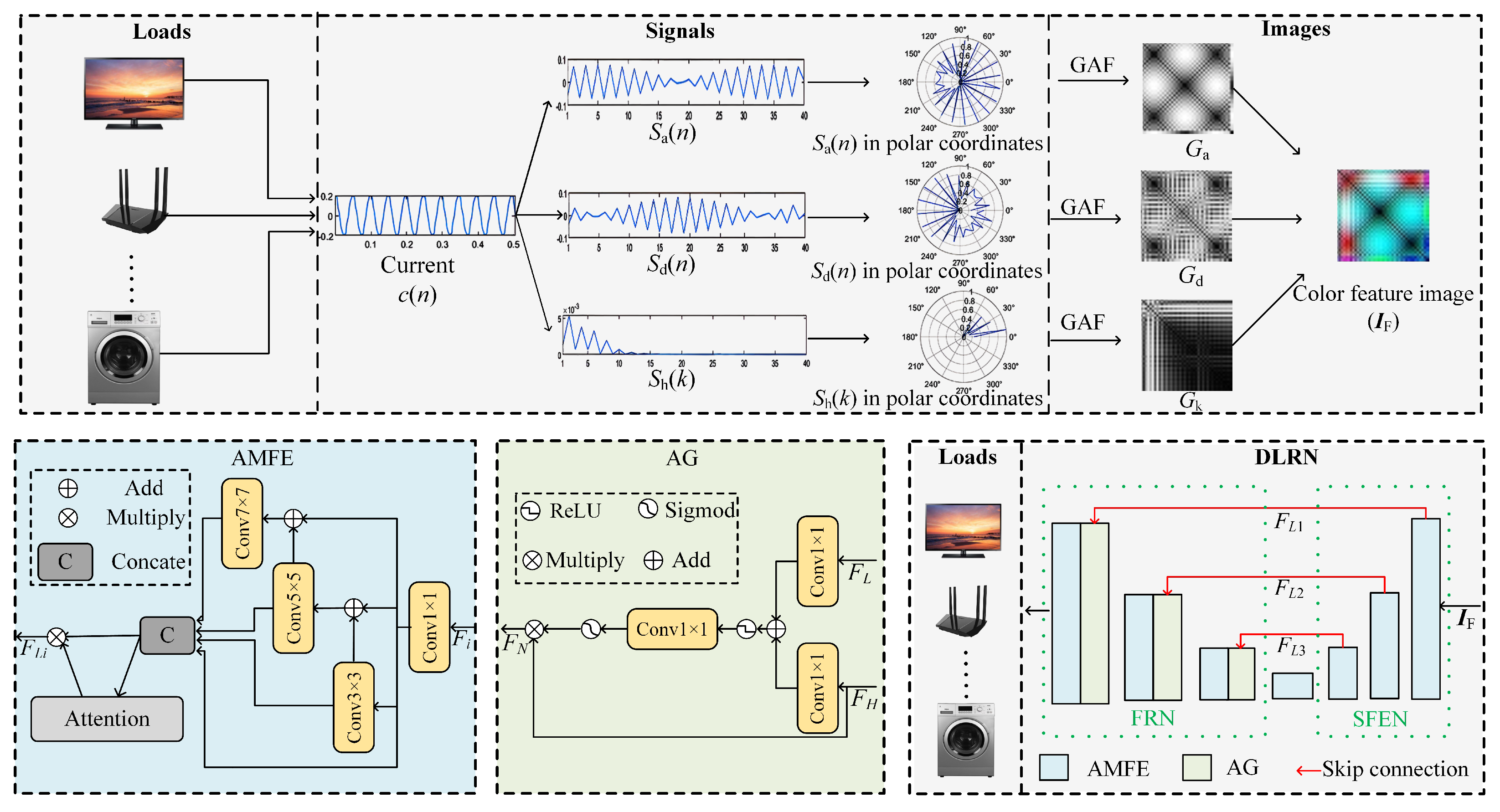
Inspired by the avove analysis, we propose a NILM method, as shown in
Figure 3. First of all, we employ wavelet transform and Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to decompose the current signal into three feature sequence: (i) approximation coefficient sequence with envelope feature of the current signal; (ii) detail coefficient sequence with texture feature of the current signal; (iii) harmonic ratio sequence with harmonic feature of the current signal. After that, we utilize the GAF method to convert the above three sequences into gray-scale images, and further set them as R, G, B channels of a color image. By this operation, the differences between loads are highlighted to make ease of load recognition. Finally, we propose a DLRN based on multi-scale features and visual attention mechanism. These steps will be elaborated as follows.
3.2. Proposed Current Feature Visualization
In a NILM system, the terminal at commercial power input is able to capture the voltage and current signals. Between them, the voltage keeps almost intact while the current fluctuates with the electric usage on loads. Therefore, we select the current signal as the input of our load recognition model. To visualize the current signal as a two-dimensional image, we first extract its features and then convert them into gray-scale images, which are further set as channels of the visualized color image.
Denote the current signal by
with a length
N. It can be expanded into wavelet series as [
33]:
where
j represents wavelet decomposition scale that determines the length of wavelet coefficient,
k.
and
represent the scaling and wavelet functions, respectively.
and
are approximation coefficient and detail coefficient, respectively. For ease of presentation, we denote them as
and
,
. They are calculated as [
34]:
According to [
35],
and
represent the envelope feature and texture feature of the current signal, respectively. This paper uses them as two features that will be visualized and recognized.
Another feature used in this paper is harmonic content which refers to the percentage of the
k-th order harmonic component in the total harmonic components. As the
k-th order harmonic component of the current signal can be obtained by DFT [
36]:
the harmonic content (denoted by
) is formulated as:
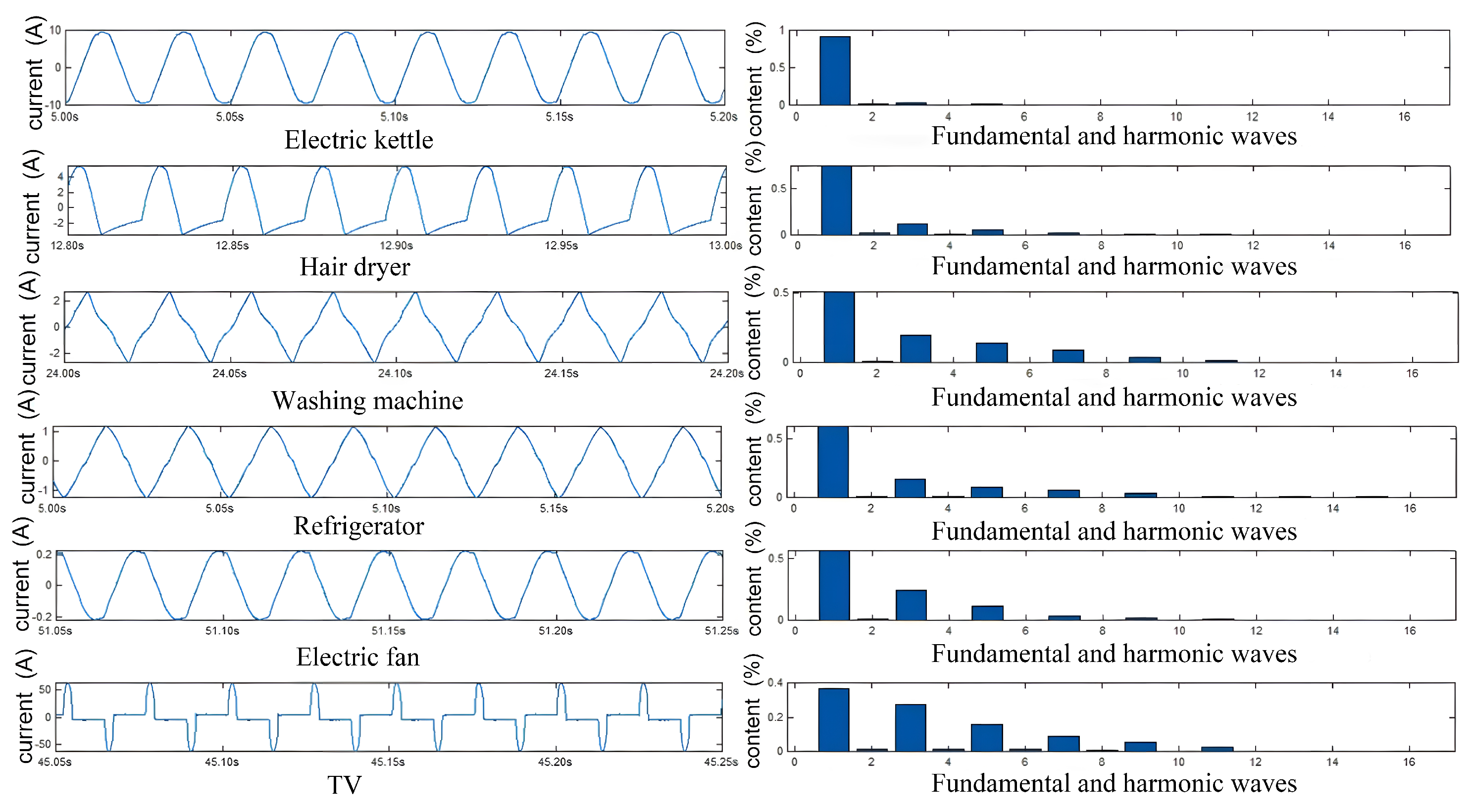
The harmonic contents of loads vary subject to electrical components and circuit systems. To verify the above assumption, we explored the harmonic contents of different types of loads: resistive, pump-driven, motor-driven and switching-powered. The results are shown in
Figure 4 where the left part shows the current waves while the right part shows their corresponding harmonic contents. From this figure, the resistive loads (
e.g., electric kettle, hair dryer) heat with resistors and barely have harmonic components. The pump-driven loads (
e.g., washing machine, refrigerator) works mainly with fundamental wave, but with more 3rd, 5th and 7th harmonic components. The motor-driven loads (
e.g., electric fan) are similar to pump-driven loads. They have 3rd, 5th, 7th and 9th harmonic components that are lower than fundamental wave. The switching-powered loads (
e.g., TV, computer) adjust output voltages with high-frequency switches. They generate rich high-order harmonic components, such as 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th, 11th and 13th harmonic components, which are comparable with fundamental wave. Obviously, the harmonic content,
i.e., , is an effective feature to identify different types of loads.
We then map all extracted features of
,
and
into grayscale images with GAF method. Take
for example. Firstly,
,
are transferred from Cartesian coordinate system to polar coordinate system:
Then, an
Gramian matrix
is obtained in which
Similarly, we also obtain the Gramian matrixes of
and
, respectively denoted by
and
. We use the following equations to map these Gramian matrixes to the R, G and B channels of a color image:
The flowchart of our proposed current feature visualization can be summarized on the top of
Figure 3. The fused color image,
, with a resolution of 40×40, has its unique texture information and chroma components. It includes low-frequency envelope features, high-frequency texture details and all harmonic ratios. Compared with the original one-dimensional current signal, it visualized and highlighted all hidden features whilst keeping timestamp of the original signal. As a result, we are allowed to use CNN methods to recognize all loads with a high accuracy.
3.3. Proposed DLRN
3.3.1. Overview of the Network
To recognize load from
, a critical issue is how to effectively extract both global and local features and avoid the influence of noise. To this end, we designed a deep feature extraction neural network (
i.e., DLRN), which is illustrated on the bottom of
Figure 3. DLRN consists primarily of Shallow Feature Extraction Network (SFEN), intermediate layer module, Feature Recombination Network (FRN), and skip connections. SFEN employs continuous attention-based multi-scale feature dense extraction modules (denoted by AMFEs) to extract various feature information from the
. The intermediate layer AMEF further processes the output of SFEN to capture important load features. To preserve shallow features, the output of each AMEF (denoted as
) is fed into FRN through skip connections.
where
represents the output of the
i-th layer’s AMFE, and
represents AMFE. In FRN, Atention Gates (AGs) and AMEFs make progress on between shallow and crucial load features. Ultimately, the output from FRN is subjected to average global pooling, fully connected layer, and a softmax function for precise load recognition.
3.3.2. AMFE
In order to effectively extract features about envelope information, texture details, and all harmonic ratios in load images, we have designed AMFE in both SFEN and FRN, which is depicted in
Figure 3. First, it utilizes a 1×1 convolution to extract coarse-grain features and further divides them into four feature sub-sets with the same space size. Second, it employs four different convolution kernels to extract features from different sub-sets:
where
,
and
are 3×3, 5×5 and 7×7 convolutions, respectively. Third, it concatenates all inputs
,
and uses a 1×1 convolution to fuse all features from different scales. Finally, it employs attention mechanism to adaptively allocate weights to multi-scale features. Attention mechanism allows the network to adaptively adjust the importance of each channel. By weighting operations on the feature maps, attention mechanism highlights important features and depresses the other features, thus it degrades the impacts of non-relevant features in load recognition.
By using AMFE, the proposed network deeply exploits the image features at different scales that benefit the feature extraction ability of our model.
3.3.3. Attention Gate
During the process of the FRN, low-level load features will be replaced by high level load features. To address this issue, we introduce an AG before each addition operation to better recombination high-level and low-level features.
Figure 3 shows the network structure of AG, which incorporates both low-level and high-level features for load recognition. In this structure, the low-level feature from skip connection (
) serves as a gate control signal, while high-level feature (
) acts as a input signal. To combine these two signals, both two signals are separately convoluted by 1×1 and added into a new signal. Then, the new signal is activated by ReLU function, convoluted by 1×1 and filtered by a Sigmoid function to obtain a weight matrix. Finally, the feature
is multiplied element-wise with the weight matrix obtained earlier, resulting in a new feature
that integrates both low-level and high-level features for load recognition. The features are passed through the AG network, which can be represented by:
where
denotes a convolution of 1×1,
represents Sigmod function,
represents ReLU function, and
is the weight matrix of the AG network.
By incorporating the AG network, the model selectively enhances important low-level features while preserving the information from high-level features.
3.4. The Overall Algorithm for the Proposed NILM
In summary, the steps of proposed NILM method are as follows.
Step 1. Obtain the current signal .
Step 2. Calculate the three feature sequences, approximation coefficient , detail coefficient and harmonic content , with Eqs. (2), (3) and (5).
Step 3. Use the GAF method, as shown in Eqs. (6)-(9) to convert these feature sequences into a color image .
Step 4. Identify the electric load with the image
, and the proposed DLRN in
Figure 3.
4. Experiments and Simulations
To examine the performance of our method, we compare it with the state-of-the-art methods on popular datasets. We also present the ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of our network design. In addition, we discuss the use of the proposed method of NILM in smart cities.
4.1. Datasets
We compare all methods in a publicly available dataset, Plug Load Appliance Identification Dataset (PLAID) [
37], with electric usage data of 11 types of loads. To increase the data samples for training, we also design a load sensing terminal and capture electric usage of 12 types of popular loads. The powers of these loads range from 24W to 1800W, which are representative to test the LRAs under similar electric loads or masking effect of loads.
4.2. The Performance of Our Method
The tested results of our method are summarized in
Table I, including results on both PLAID and our datasets. For each dataset, we split it into a 70:30 ratio for training and testing. From the table, our method achieves a promisingly high accuracy of 98.26% on our dataset with an F1 score of 0.9819. It also achieves an accuracy of 97.71% and an F1 score of 0.9743 on the PLAID dataset. These results have fully demonstrated the efficiency of our load recognition model.
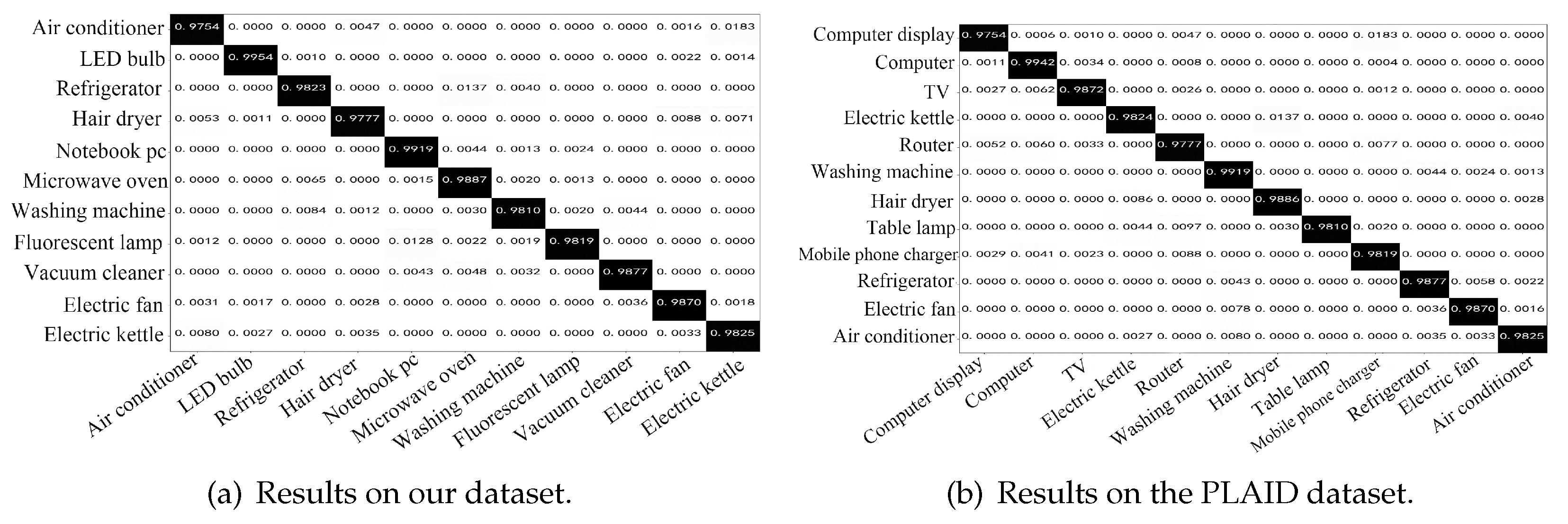
To analyze the recognition accuracies of different types of loads, we present the confusion matrixes on testing sets in
Figure 5. From
Figure 5, all resistive loads,
e.g., electric kettle (1800W) and hair dryer (1200W), can be well recognized with a high accuracy of 98.20%. This fact is mainly attributed to their distinct features of high powers and low harmonic contents. As discussed in Section III, pump-driven loads have similar feature distributions to those of motor-driven loads. In these categories, our model successively identifies washing machine, electric fan, air conditioner and vacuum cleaner with a low probability of incorrect recognition or confusion. switching-powered loads have high harmonic contents, but also with low powers that might be covered by high-power loads. From
Figure 5, our method is well capable of addressing this issue. Its recognition accuracies of notebook, TV and router exceed 96.88% even when high-power loads (
e.g., electric kettle, air conditioner) are working at full powers.
4.3. Comparison with Popular Methods
To examine the superiority of our proposed method, we compare it with references [
24,
25,
26] under the same conditions. The evaluation results on PLAID dataset are shown in
Table II. From the table, our method surpasses all compared algorithms on PLAID with an average accuracy of 97.71%. This fact validates the effectiveness of our method in electric load recognition. It is thus capable of identifying all types of loads after a fine training in a large-scale electricity management system for smart city.
In addition, both the two stages of our model, current feature visualization and deep load recognition, contribute to the final performance. With our current feature visualization and Ding’s CNN model, the hybrid method also achieves an accuracy of 96.91% that outperforms Ding’s method. By using both current feature visualization and deep load recognition, our method outperforms Ding’s by 1.08%. This fact also validates our design.
4.4. Ablation Study
We also perform ablation experiments to examine the design of our DLRN. Experiments are run on both PLAID and our dataset.
1) The Effectiveness of Our Features Extraction: In our method, we employ approximation coefficient, detail coefficient and harmonic ratio as the three features for load recognition, as shown on the top of
Figure 3. To validate the effectiveness of these features, we implemented an experiment in which we input the features used in tradtional methods [
26,
28,
29] to our network and then compared its performance with our method. The results are shown in
Table III. From this table, our features extraction method achieves apparently higher accuracy compared to the traditional method.
2) The Effectiveness of Multi-scale Feature Extraction: Our deep network utilizes multi-scale convolution kernels 1×1, 3×3, 5×5, 7×7, as shown in network part of
Figure 3. To validate its effectiveness, we compare it with identical kernel settings,
e.g., 1×1, 3×3, 5×5 or 7×7, with results summarized in
Table IV. All settings are retrained for fair comparison. From the table, our multi-scale feature extraction design is superior to all other settings. Therefore, our deep model can well extract all critical information from the visualized current and thus is more suitable for load recognition.
3) The Effectiveness of AG: The AGs are utilized to add multi-scale features after skip connections. From
Table V, our method achieves inferior performance without these AGs. Therefore, both multi-scale feature extraction and attention mechanism contribute to the final recognition performance.
4.5. Discussion on Practical Use
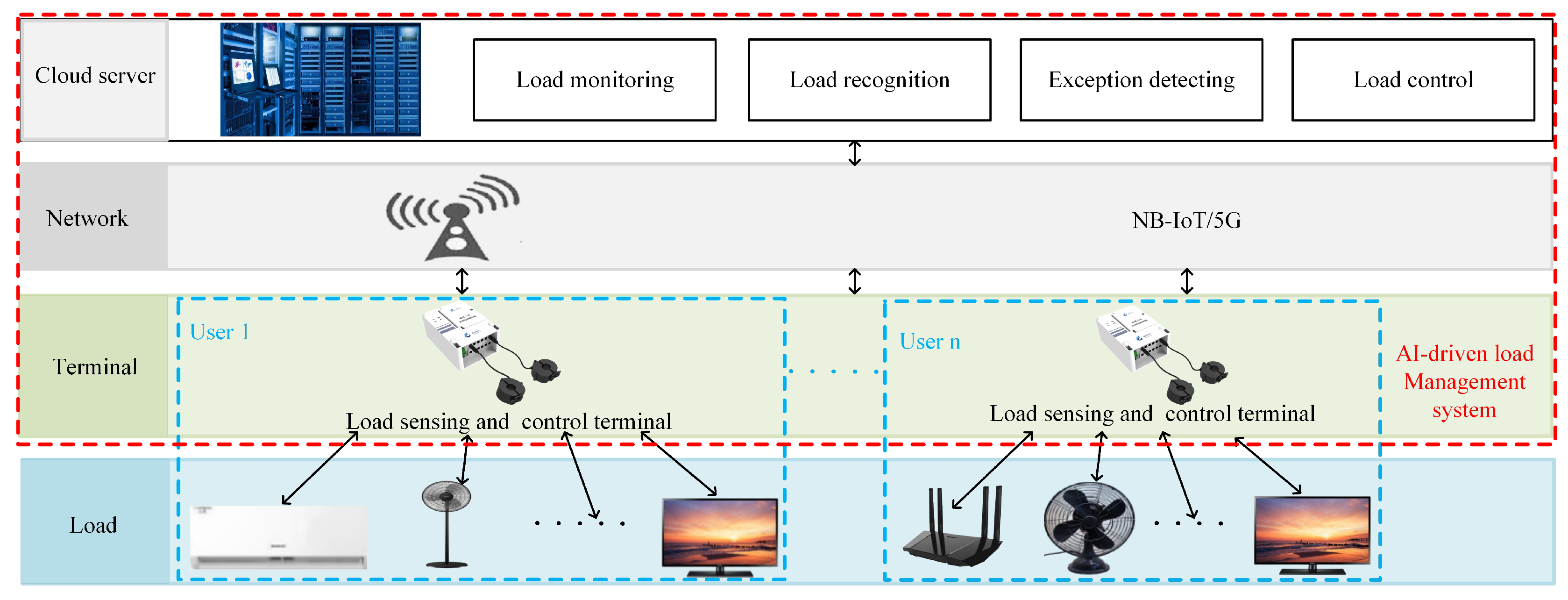
A practical AI-driven load management system can be implemented with the proposed load recognition method, as shown in
Figure 6. This system is designed as a joint Terminal-Network-Cloud infrastructure for smart cities.
At the terminal-end, a load sensing and control terminal is in charge of managing all loads in a family or cell. It collects load information (e.g., the current signal) and sends it to a cloud server for further analysis. It also receives and executes all commands from the cloud server to control loads for energy saving. The network is utilized to transmit all data and commands, which can be based on technologies like Narrow Band IoT (NB-IoT) or 5G.
At the cloud-end, a cloud-based service platform is responsible for load recognition, monitoring, and control. It analyzes the electricity consumption of all loads and provides suggestions for smart control of switches. By controlling the loads, unnecessary (e.g., lighting under daylight) or dangerous (e.g., abnormal use in factory) usage of electricity can be avoided. The cloud-based service platform runs the proposed NILM method only when necessary, so computational cost is not a critical issue. The experiments also demonstrate that the NILM approach can run on a laptop, as the proposed deep model processes a 40×40 color image only.
In summary, the joint Terminal-Network-Cloud infrastructure enables efficient electricity management over large-scale IoT in smart cities, allowing for load monitoring, analysis, and control for each family or cell. The proposed NILM approach can be deployed in the smart electricity management system of smart cities.
5. Conclusion
This paper proposes a NILM method based on current feature visualization and deep recognition network. It first converts current signals into color images with a combination of signal transform and GAF method. Then, it utilizes multi-scale feature extraction and attention mechanism to design a deep recognition network. Experimental results demonstrate its efficiency in both public and our own datasets, as well as its performance superiority compared with its peers. The proposed method can be embedded into the load monitoring and management system to control the electric usage and save energy in smart city.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. and T.Z.; methodology, Y.X. and D.L.; software, Z.L. and D.L.; validation, Y.X. and T.Z.; formal analysis, N.H.; investigation, N.H. and D.L.; resources, Y.X. and T.Z.; data curation, N.H. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X. and D.L.; writing—review and editing, N.H. and D.L.; visualization, Z.L. and D.L.; supervision, Y.X. and T.Z.; project administration, Y.X. and T.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.X. and T.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by National Key R and D Program, MOST, China (No. 2022YFB3603704) and Foundation for Middle-aged and Young Educational Committee of Fujian Province (No. JAT200024).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some or all data, models, or code generated or used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, G.; Kim, M. Deepfake Detection Using the Rate of Change between Frames Based on Computer Vision. Sensors 2021, 21. [CrossRef]
- Muzzini, F.; Montangero, M. Exploiting Traffic Light Coordination and Auctions for Intersection and Emergency Vehicle Management in a Smart City Mixed Scenario. Sensors 2024, 24. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ho, D.W.C.; Huang, T.; Yu, J.; Abu-Rub, H.; Li, C. Second-Order Continuous-Time Algorithms for Economic Power Dispatch in Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 2018, 48, 1482–1492. [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.Z.; Das, R. Smart Grid Security: An Effective Hybrid CNN-Based Approach for Detecting Energy Theft Using Consumption Patterns. Sensors 2024, 24. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Delcroix, B.; Henao, N.; Agbossou, K.; Kelouwani, S. Towards Feasible Solutions for Load Monitoring in Quebec Residences. Sensors 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Lazzaretti, A.E.; Renaux, D.P.B.; Lima, C.R.E.; Mulinari, B.M.; Ancelmo, H.C.; Oroski, E.; Pöttker, F.; Linhares, R.R.; Nolasco, L.d.S.; Lima, L.T.; others. A multi-agent NILM architecture for event detection and load classification. Energies 2020, 13, 4396. [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, L.; Buscarino, A. Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Ridi, A.; Gisler, C.; Hennebert, J. A Survey on Intrusive Load Monitoring for Appliance Recognition. 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2014, pp. 3702–3707. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Helfenstein, A.; Mattern, F.; Staake, T. Leveraging smart meter data to recognize home appliances. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2012, pp. 190–197. [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, M.; Sheikh, S.R.; Naseer, N.; Din, Z.M.U.; Rehman, H.Z.U.; Naved, M. Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring of Buildings Using Spectral Clustering. Sensors 2022, 22, 4036. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shaowei, S. A Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Method Based on Multi-scale Wavelet Packet Optimization and Transient Feature Matching. 2021 12th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 113–117. [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z. An online transient-based electrical appliance state tracking method via Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling. 2020 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Basu, K.; Debusschere, V.; Douzal-Chouakria, A.; Bacha, S. Time series distance-based methods for non-intrusive load monitoring in residential buildings. Energy and Buildings 2015, 96, 109–117. [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, P.G.; Gkaidatzis, P.A.; Christoforidis, G.C.; Bouhouras, A.S. Unsupervised NILM Implementation Using Odd Harmonic Currents. 2021 56th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC). IEEE, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Lin, W.; Li, M.; Wu, Q. Non-intrusive load monitoring using additive factorial approximate maximum a posteriori based on iterative fuzzy c-means. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6667–6677. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Luan, W.; Yu, Y. Dynamic time warping based non-intrusive load transient identification. Applied energy 2017, 195, 634–645. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kim, H.; others. Household appliance classification using lower odd-numbered harmonics and the bagging decision tree. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 55937–55952. [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.J. Simultaneous Load Identification Method Based on Hybrid Features and Genetic Algorithm for Nonintrusive Load Monitoring. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2022, 2022, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.H.; Heo, S.; Kim, H. Toward Load Identification Based on the Hilbert Transform and Sequence to Sequence Long Short-Term Memory. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3252–3264. [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Hossain, E.; Islam, M.M. Comprehensive NILM framework: Device type classification and device activity status monitoring using capsule network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179995–180009. [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, B.; Du, Z.; Sun, Y. A Nonintrusive load identification model based on time-frequency features fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 1376–1387. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z. Research on non-intrusive unknown load identification technology based on deep learning. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 131, 107016. [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Li, Y.; Du, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, B. Non-intrusive load identification using reconstructed voltage–current images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 77349–77358. [CrossRef]
- De Baets, L.; Ruyssinck, J.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D. Appliance classification using VI trajectories and convolutional neural networks. Energy and Buildings 2018, 158, 32–36. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; You, W. Non-intrusive load monitoring by voltage–current trajectory enabled transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 10, 5609–5619. [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Le, Y.; Hongling, S.; Hong, S. Realize intelligent non-intrusive load identification by using data visualization. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition) 2021, pp. 010–049.
- Wenninger, M.; Bayerl, S.P.; Maier, A.; Schmidt, J. Recurrence Plot Spacial Pyramid Pooling Network for Appliance Identification in Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. 2021 20th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA). IEEE, 2021, pp. 108–115. [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Yu, M.; Lu, L.; Wang, B.; Bao, Z. Adaptive Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on Feature Fusion. IEEE Sensors Journal 2022, 22, 6985 – 6994. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Q. Household Load Identification Based on Multi-label and Convolutional Neural Networks. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series 2022, pp. 42 – 48. [CrossRef]
- Jayant, H.K.; Rana, K.; Kumar, V.; Nair, S.S.; Mishra, P. Efficient IIR notch filter design using Minimax optimization for 50Hz noise suppression in ECG. 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), 2015, pp. 290–295. [CrossRef]
- Bouny, L.E.; Khalil, M.; Adib, A. Removal of 50Hz PLI from ECG signal using undecimated wavelet transform. 2017 International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications (WINCOM), 2017, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Dhayabarani, R.; Balachandar, P.; Arunkumar, R.; Elakkiyaselvan, M. Design of FIR Filter for Reduction of Power Line Interference from ECG Signal. 2018 Second International Conference on Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies (ICICCT), 2018, pp. 1205–1208. [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Park, J.H.; Choo, K.B.; Kim, M.; Ji, D.H.; Choi, H.S. Unmanned Surface Vehicle Thruster Fault Diagnosis via Vibration Signal Wavelet Transform and Vision Transformer under Varying Rotational Speed Conditions. Sensors 2024, 24. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.y.; Zhang, R.j. The technology research in decomposition and reconstruction of image based on two-dimensional wavelet transform. 2012 9th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. IEEE, 2012, pp. 1998–2000. [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.S.M.; Sharif, S.M. Computation reduction of haar wavelet coefficients. 2017 2nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), 2017, pp. 832–835. [CrossRef]
- Sankoh, A.; Jin, W.; Zhong, Z.; He, J.; Hong, Y.; Giddings, R.; Tang, J. DFT-Spread Spectrally Overlapped Hybrid OFDM–Digital Filter Multiple Access IMDD PONs. Sensors 2021, 21. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Giri, S.; Kara, E.C.; Bergés, M. Plaid: A public dataset of high-resoultion electrical appliance measurements for load identification research: Demo abstract. proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, 2014, pp. 198–199. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).