Submitted:
03 April 2024
Posted:
04 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Feeding Tests
2.3. Frass Collection and Characterization
2.3.1. Weight Variation and Survival Rate
2.3.2. FT-IR Analysis
2.3.3. Morphological Analysis
2.3.4. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Variation and Survival Rate of T. Molitor and Z. Morio Larvae
3.2. SEC analysis
3.3. Spectroscopy Analysis
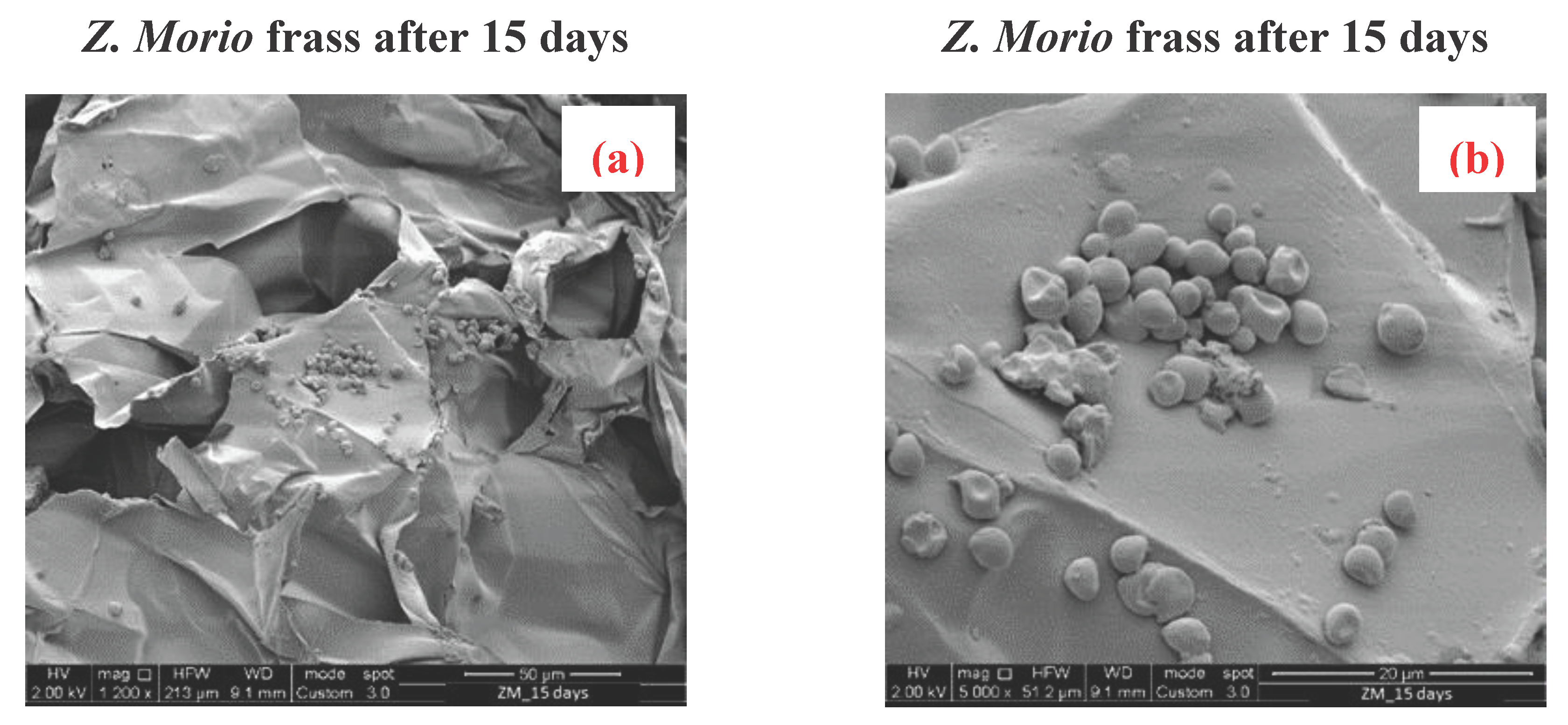
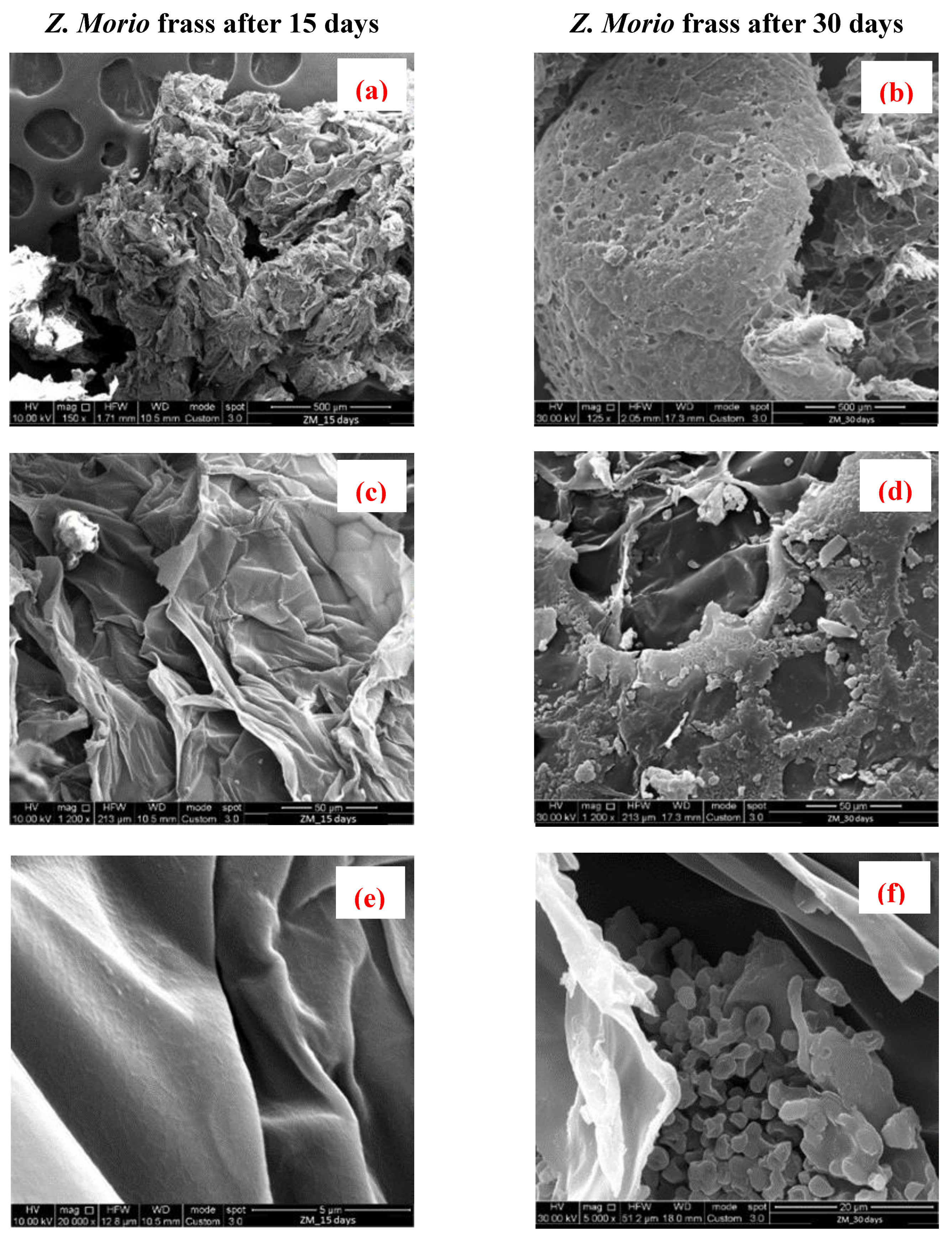
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pastic Europe Plastics – The Fast Facts 2023. Https://Plasticseurope.Org/Knowledge-Hub/Plastics-the-Fast-Facts-2023/ (Accessed 20 February 2024) 2023.
- Beghetto, V.; Gatto, V.; Samiolo, R.; Scolaro, C.; Brahimi, S.; Facchin, M.; Visco, A. Plastics Today: Key Challenges and EU Strategies towards Carbon Neutrality: A Review. Environmental Pollution 2023, 334, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Jia, P. Recent Advances in Degradation of Polymer Plastics by Insects Inhabiting Microorganisms. Polymers 2023, 15, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolo, A.; Infurna, G.; Dintcheva, N.T. A Review of Bioplastics and Their Adoption in the Circular Economy. Polymers 2021, 13, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqattaf, A. Plastic Waste Management: Global Facts, Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2020 Second International Sustainability and Resilience Conference: Technology and Innovation in Building Designs(51154); IEEE: Sakheer, Bahrain, November 11, 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira-Filipe, D.A.; Paço, A.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Patrício Silva, A.L. Are Biobased Plastics Green Alternatives?—A Critical Review. IJERPH 2021, 18, 7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Shafea, L.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N.; Qingyue, W.; Chowdhury, T.; Paredes, M. Microplastics Exposure Routes and Toxicity Studies to Ecosystems: An Overview. Environ Anal Health Toxicol 2020, 35, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Dong, Y.; Nadir, S.; Schaefer, D.A.; Mortimer, P.E.; Xu, J.; Ye, L.; Gui, H.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Dossa, G.G.O.; et al. Valorizing Plastic Waste by Insect Consumption. C 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Das, A. The Ability of Insects to Degrade Complex Synthetic Polymers. In Arthropods - New Advances and Perspectives; D.C. Shields, V., Ed.; IntechOpen, 2023 ISBN 978-1-80355-612-3.
- Jiang, S.; Su, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Tenebrio Molitor, Galleria Mellonella, and Zophobas Atratus Larvae and Comparison of Their Degradation Effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivato, A.F.; Miranda, G.M.; Prichula, J.; Lima, J.E.A.; Ligabue, R.A.; Seixas, A.; Trentin, D.S. Hydrocarbon-Based Plastics: Progress and Perspectives on Consumption and Biodegradation by Insect Larvae. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-S.; Brandon, A.M.; Andrew Flanagan, J.C.; Yang, J.; Ning, D.; Cai, S.-Y.; Fan, H.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Ren, J.; Benbow, E.; et al. Biodegradation of Polystyrene Wastes in Yellow Mealworms (Larvae of Tenebrio Molitor Linnaeus): Factors Affecting Biodegradation Rates and the Ability of Polystyrene-Fed Larvae to Complete Their Life Cycle. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastic Europe Plastics – the Facts 2022 Https://Plasticseurope.Org/Knowledge-Hub/Plastics-the-Facts-2022/ (Accessed 20 February 2024).
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 1. Chemical and Physical Characterization and Isotopic Tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12080–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilias, D.S. Polymer Degradation Under Microwave Irradiation. In Microwave-assisted Polymer Synthesis; Hoogenboom, R., Schubert, U.S., Wiesbrock, F., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; Vol. 274, pp. 309–346; ISBN 978-3-319-42239-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Ramanathan, S.; Basak, T. Microwave Material Processing—a Review. AIChE Journal 2012, 58, 330–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles-Arriaga, C.A.; López-Hernández, J.; Hernández-Ordoñez, M.; Echavarría-Solís, R.A.; Ovando-Medina, V.M. Thermal Characterization of Microwave Assisted Foaming of Expandable Polystyrene. Ingeniería, Investigación y Tecnología 2016, 17, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.-Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Benbow, M.E.; Criddle, C.S.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhang, Y. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Dark ( Tenebrio Obscurus ) and Yellow ( Tenebrio Molitor ) Mealworms (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5256–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulak, P.; Proc, K.; Pytlak, A.; Puszka, A.; Gawdzik, B.; Bieganowski, A. Biodegradation of Different Types of Plastics by Tenebrio Molitor Insect. Polymers 2021, 13, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, C.; Samperi, F.; Carroccio, S.; Montaudo, G. Analysis of Poly(Bisphenol A Carbonate) by Size Exclusion Chromatography/Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization. 2. Self-Association Due to Phenol End Groups. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, M.V.; Carroccio, S.C.; Dattilo, S.; Cocca, M.; Nicosia, A.; Torri, M.; Bennici, C.D.; Musco, M.; Masullo, T.; Russo, S.; et al. Polymer Aging Affects the Bioavailability of Microplastics-Associated Contaminants in Sea Urchin Embryos. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, M. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Superworms Zophobas Atratus. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 708, 135233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
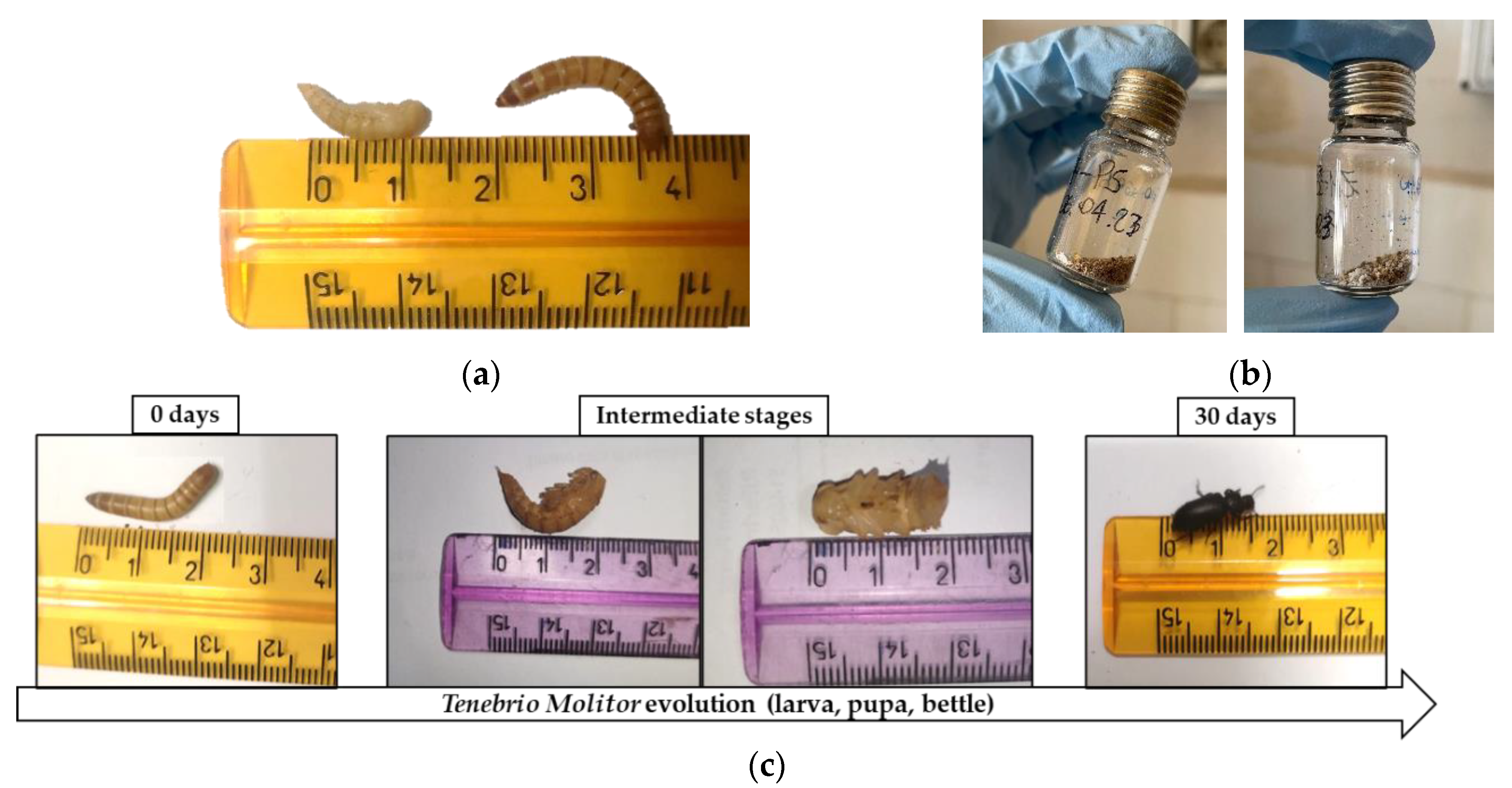
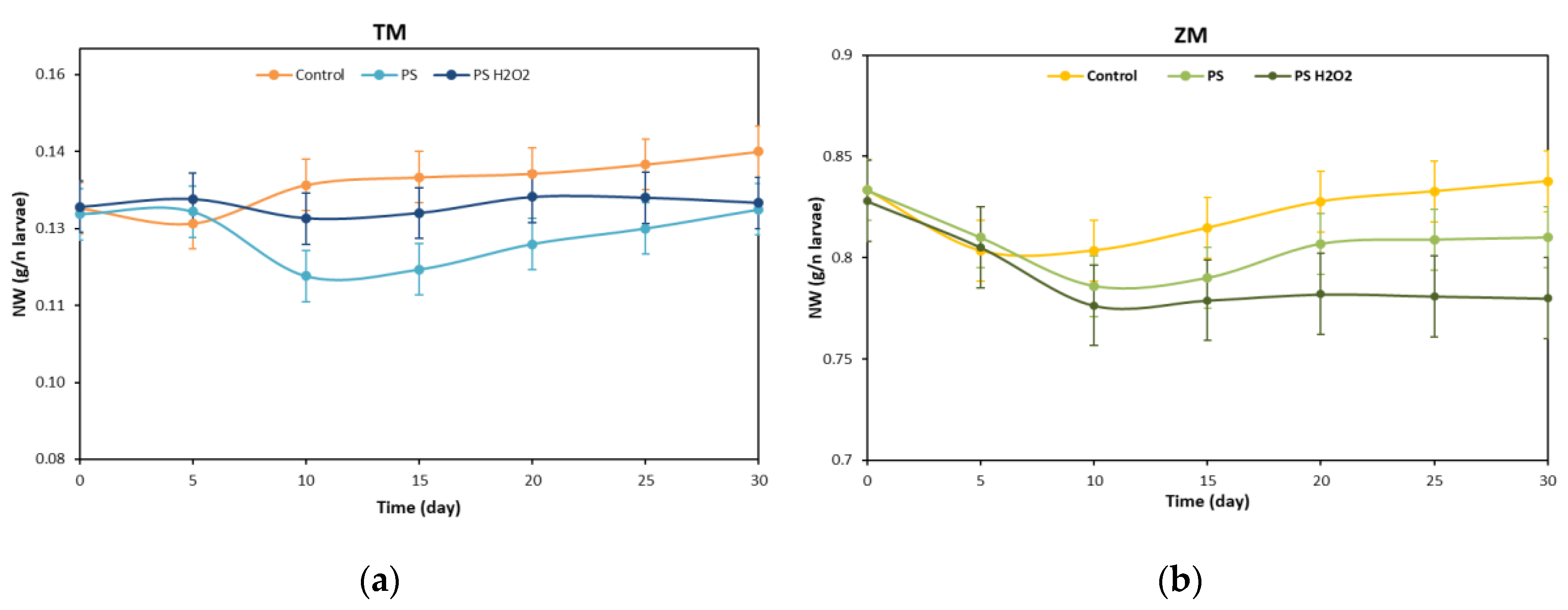
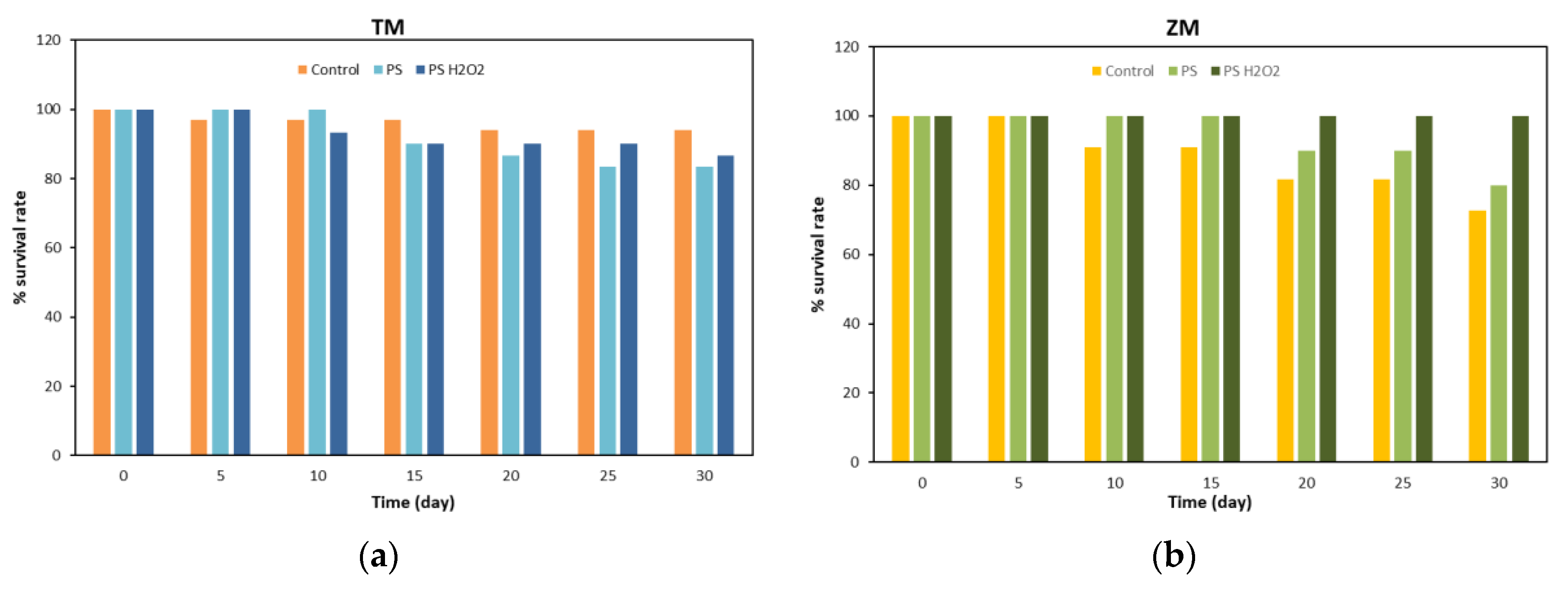
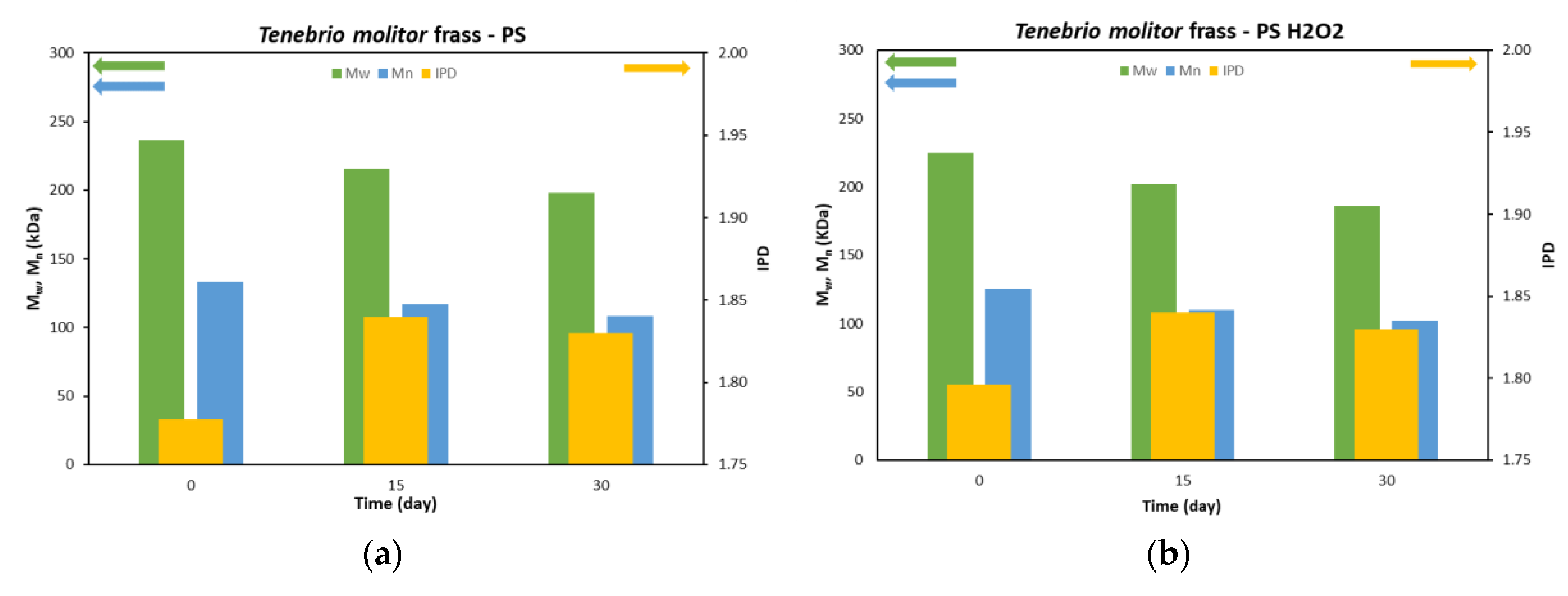
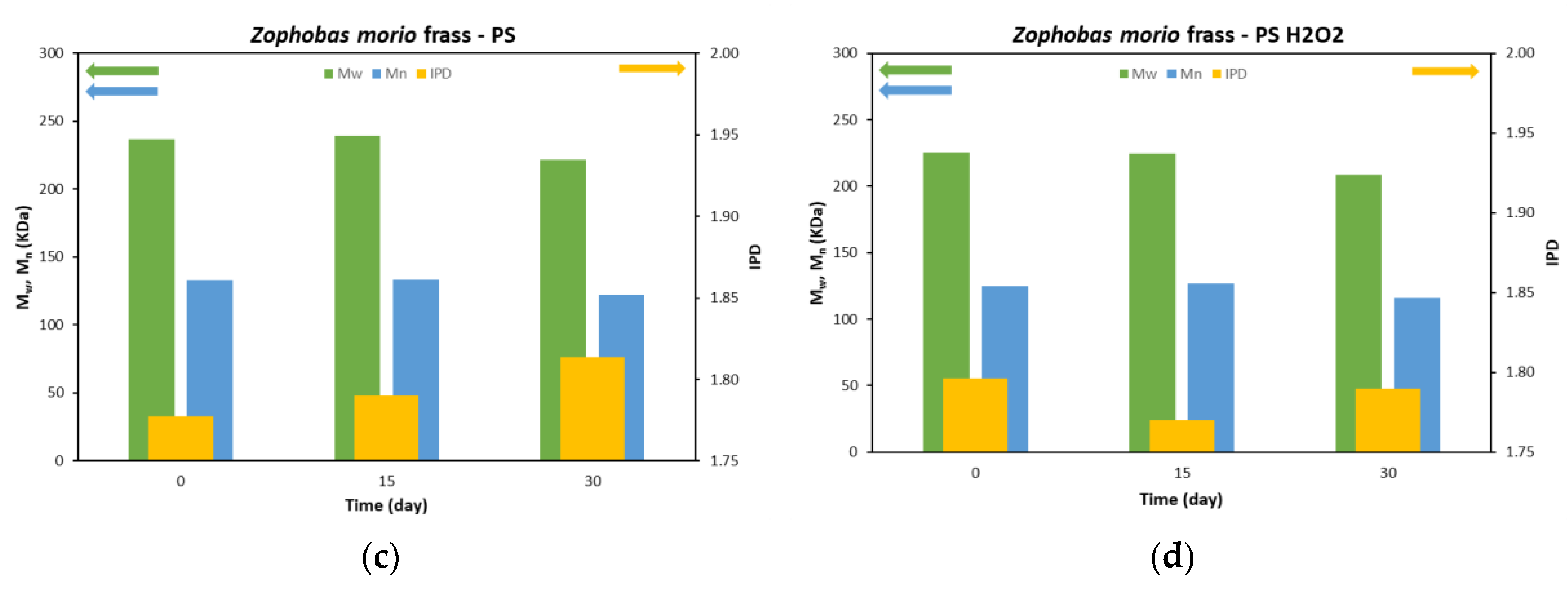
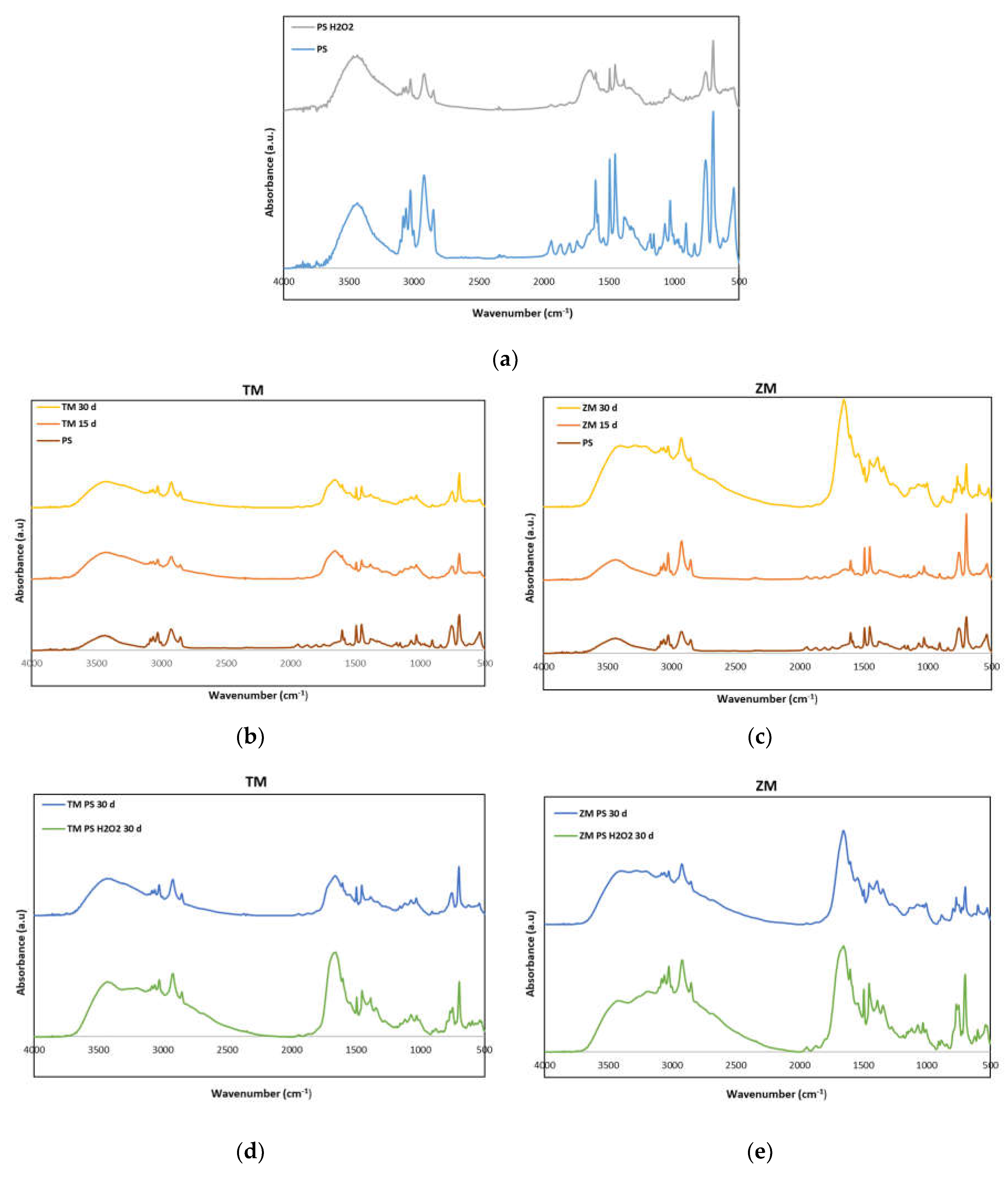
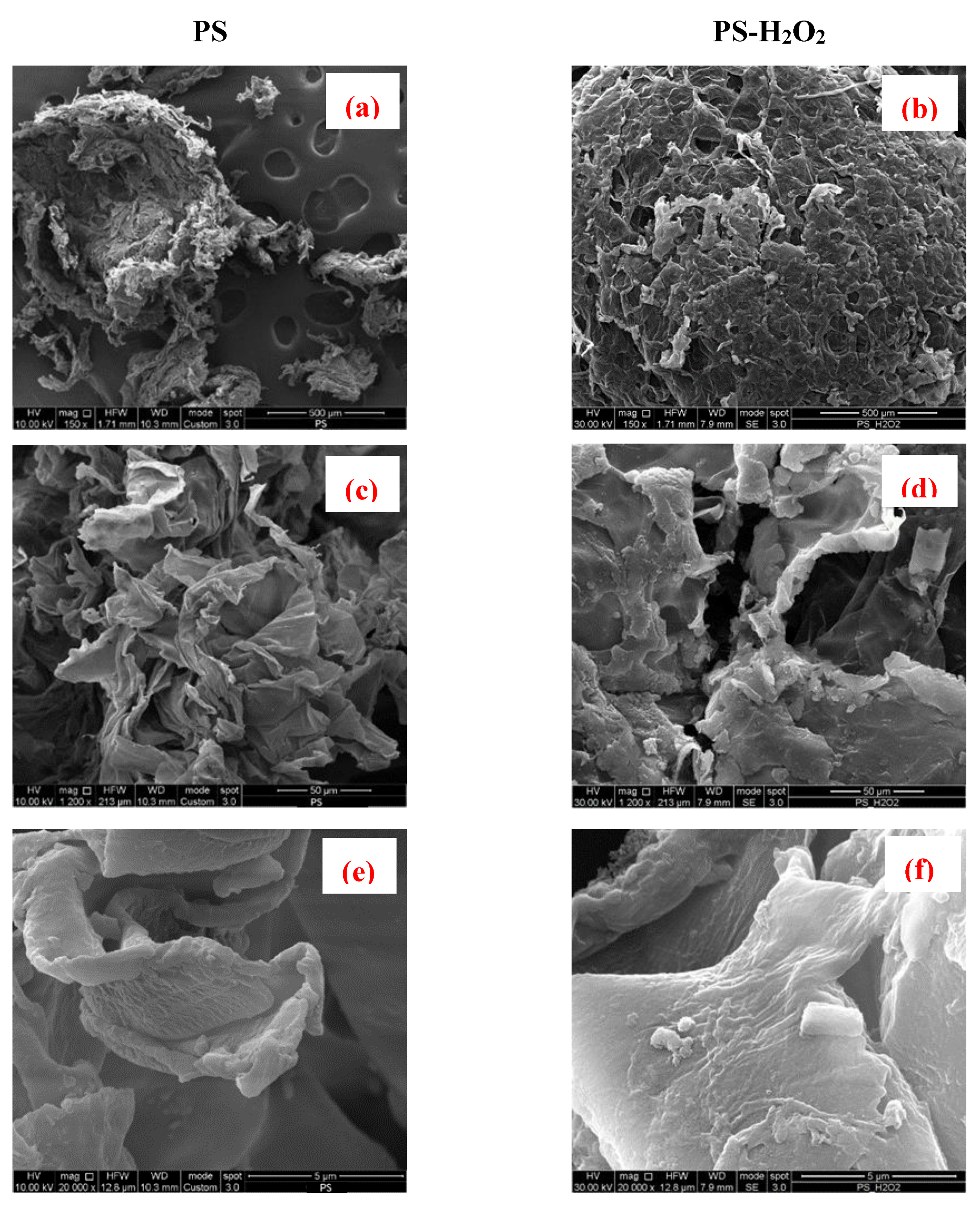
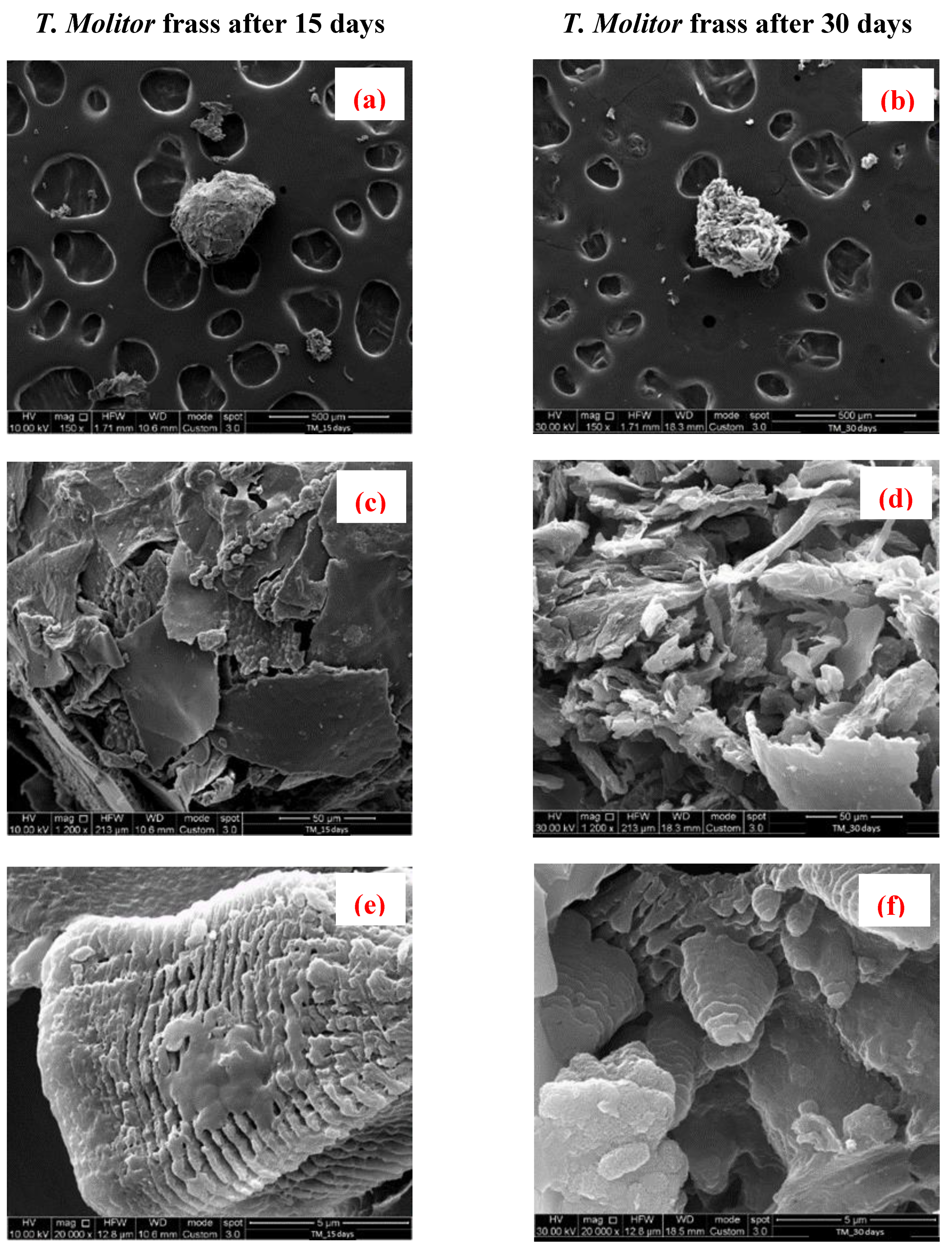

| Worm source | Initial weight (g) | Feedstocks | Survival rate (%) | Mw of frass (kDa) | Mw reduction (%) | Mn of frass (kDa) | Mn reduction (%) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. Molitor | 3.8 | Bran PS PS-H2O2 |
94 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 83 | 197.8 | 16.4 | 108.4 | 18.6 | 1.83 | ||||
| 87 | 186.0 | 17.3 | 101.8 | 18.7 | 1.83 | ||||
| Z. Morio | 8.3 | Bran | 73 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| PS | 80 | 221.9 | 6.3 | 122.3 | 8.1 | 1.81 | |||
| PS-H2O2 | 100 | 208.5 | 7.3 | 116.2 | 7.1 | 1.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





