1. Introduction
GBMs are the most frequent brain tumors and are characterised by a very poor prognosis. Typical survival after diagnosis is approximately 14.6 months, and only 20-25% of patients show improvement in 2-year survival with approved [
1,
2]. Attempts to extend median survival with central nervous system (CNS) drugs have been limited by the complexity of the brain, particularly the difficulty of penetrating the blood-brain barrier (BBB)[
1,
3]. The BBB is a major barrier to drug delivery in most brain tumors [
4,
5,
6,
7]. As the tumor progresses, the BBB is referred to as the blood–tumor barrier (BTB), which differs from the BBB in that it is damaged and new blood vessels are formed. In GBM, the permeability of the BTB is high in the bulk of the tumor, but there is very little permeability in the periphery [
2]. Accordingly, a GBM cell-specific target binding strategy may be required for drug delivery across the BTB.
Nanopharmaceutical research has been continuously reported in cancer treatment applications, and numerous nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems have been attempted, including the development of specific tumor-targeted drug delivery systems [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. In addition, nanocarrier designs using biomolecules such as DNA, aptamers and proteins have been reported to minimise side effects [
14,
15,
16]. Among the nanocarrier synthesis studies using biomaterials, it is highly efficient to induce self-assembled hybrid systems through biotin-streptavidin hydrogen-bonding interactions and complementary base pairs of DNA [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. DNA has excellent cell permeability and relative resistance to enzymatic degradation, and the streptavidin-biotin interaction has the advantages of high specific molecular recognition and resistance to changes in temperature or pH, which can form a stable structure [
21,
22,
23,
24]. Here, we intend to apply previous research techniques to synthesise nanocarriers using only biopolymers that induce biotin-streptavidin molecular binding based on DNA structures.
An aptamer is a DNA or RNA oligonucleotide that can recognise a specific three-dimensional structure even with a short base sequence and can bind to a target protein [
25,
26,
27]. In addition, the aptamer is used as a suitable candidate for target delivery due to its low molecular weight, small size, non-immunogenicity, inherent biocompatibility, and stable structure in biological environments [
28,
29,
30]. In particular, AS1411 is a guanine-rich DNA oligonucleotide and is known as one of the aptamers reported to be fully effective as an anticancer drug in phase 1/2 of clinical trials [
31,
32,
33]. AS1411 recognises NCL proteins expressed in tumor cell membranes through the high affinity of guanine domains, and internalisation of AS1411-NCL complexes results in significant inhibition of DNA synthesis, destabilisation of bcl2 mRNA, and induction of cell apoptosis [
16,
34,
35,
36].
NCL is expressed on the cell surface and inside the cell and is overexpressed in highly proliferating cells of many types of cancer cells, including GBM cell lines, and mediates the binding of AS1411 and intracellular uptake [
37,
38,
39,
40]. Therefore, the main target for improving GBM treatment in this study was the AS1411-NCL recognition and interactive drug delivery system.
Here, we selectively identified tumor cells overexpressing NCL proteins using AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres. AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres showed stronger affinity for target U87 and U251 cells than non-target NHA cells. In addition to the 2D cell culture model, anti-tumor activity was confirmed in 3D spheroid and xenograft models derived from GMB, confirming that drugs penetrated by the high permeability of BTB are selectively targeted to cancer cells, resulting in fewer side effects and precise drug delivery potential. Furthermore, Dox can be easily loaded into nanospheres for selective drug delivery to GBM cells, with excellent structural stability and biocompatibility.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell lines and Cell Culture
The cell lines (human GBM cells, U87 and U251) used in this study were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank, Seoul, Korea. The normal human astrocytes (NHA) cell line was purchased from iXCells Biotechnologies, San Diego, California. These cell lines were grown and maintained in culture with Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Biowest, France) supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum (FBS; Biowest, France) and 1 % penicillin–streptomycin. The The BBB hCMEC/D3 cell line and media were purchased from Millipore, Temecula, California and cultured in EndoGRO™-MV Complete Media Kit (Cat. No. SCME004) supplemented with 1 ng/mL FGF-2 (Cat.No. GF003). All cells were maintained at 37 °C in a 5 % CO₂ atmosphere.
2.2. Quantitative Real Time RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from cultured cells using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After DNase treatment with RQ1 RNase-free DNase (Promega), 1 µg of total RNA was used for first-strand cDNA synthesis with oligo-dT primers using the ProtoScript M-MuLV Taq RT-PCR system (New England Biolabs).
Q-PCR amplification was performed in a Quantstudio 7 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems) using 96 well plates. The reaction was performed with a final volume of 25 µl using ABSOLUTETM QPCR SYBR Absolute QPCR Green Rox Mix (Thermo Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The qPCR conditions were as follows: an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles with denaturation at 95 °C for 5 s, and the annealing/elongation at 60 °C for 30 s, followed a dissociation phase at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 15 s and 95 °C for 15 s. The primer sequences are as follows: Hu NCL (5’-AGGAGGAGGAAGAAGAGGAG-3’ and 5’-ACAAAGAGATTGAAAGCCGTAG-3’; product size 148 bp); Hu GAPDH (5’-GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAA-3’ and 5’-AGGGATCTCGCTCCTGGAA-3’; product size 75 bp). The primer sequences and conditions used in qPCR to investigate the expression of NCL mRNA were as previously reported [
41].
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
Cells were washed with ice-cold PBS and lysed on ice with RIPA buffer (Thermo Scientific) containing Halt protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Scientific). The protein concentration of the supernatant was measured using the Pierce BCA (bicinchoninic acids) protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific) and the lysates were resolved on a 4–20 % Mini-PROTEAN TGX precast gel (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The samples were then transferred to 0.45 µm methanol-activated polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Thermo Scientific) and the membranes were blocked with 5 % skim milk solution. The membranes were washed three times with TBS-T, followed by primary antibody incubation overnight. The primary antibodies used were rabbit anti-NCL (D4C7O) monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) and rabbit anti-beta actin (13E5) monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling Technology). The next day, the membranes were washed three times each with TBS-T and incubated with the anti-rabbit IgG HRP- conjugated secondary anti-body (Cell Signaling Technology). HRP antibodies were detected using the SuperSignal West Pico PLUS chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Scientific).
2.4. Synthesis of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres
An equimolar mixture of the complementary strands (5’-ACGGCTGCGCGACGTAGGTACGGCAACTCGCGGCTATGCA-3’ and 5’-BiotinTEG-TACCTACGTCGCGCAGCCGTTGCATAGCCGCGAGTTGCCG-3’) was dissolved in PBS to a final concentration of 50 µM. FAM labelled nanospheres were used as follows: (5’-FAM-ACGGCTGCGCGACGTAGGTACGGCAACTCGCGGCTATGCA-3’ and 5’-BiotinTEG-TACCTACGTCGCGCAGCCGTTGCATAGCCGCGAGTTGCCG-3’). The solution was heated in a water bath at 95 °C for 5 min and slowly cooled to room temperature. Meanwhile, Dox-loaded nanospheres were synthesised by inducing DNA intercalation at a ratio of 1:10 between dsDNA and Dox in a mixture of complementary strands. After the formation of a linear DNA chain, streptavidin (Invitrogen) and an equivalent amount of DNA monomer were mixed, stored at 4 °C for 3 hours, and then used. The complementary strand of sequences and synthesis conditions were performed as previously reported [
42,
43]. To construct aptamer conjugated nanospheres, biotinylated AS1411 aptamer (5’-BiotinTEG-GGTGGTGGTGGTTGTGGTGGTGGTGG-3’) was added and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. Prior to use, the AS1411 aptamer was dissolved in nuclease-free water and heated to 85°C for 2 minutes and cooled to room temperature for 10 minutes [
44]. Each nanosphere sample was prepared by diluting to a final concentration of particles between 106 and 109 in a 1 ml volume of PBS, and the size distribution was measured by injecting into NanoSight NS300 (Malvern) with a syringe. Confocal imaging of the FAM-labelled nanospheres was performed using a Zeiss LSM710 confocal laser scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss).
2.5. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
A 3 % agarose gel was prepared in 1 × TBE buffer (890mM Tris-borate, 890mM boric acid, 20mM EDTA, pH8.0) and stained with SYBR Safe DNA gel stain (Invitrogen). The sample solution (10 µl) was mixed with 2 µl of 6 × loading buffer. The prepared samples were then subjected to electrophoresis (Mupid-exU) in 1 × TBE buffer at 100 V for 30 min. The gel was imaged using the Gel Doc EZ imaging system (Bio-Rad).
2.6. Characterization of Drug Loading and Release
To quantify drug loading on the nanospheres, dsDNA was synthesised with Dox at various concentration ratios (dsDNA:Dox = 1:2, 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50, 1:100). Fluorescence spectra were collected in the wavelength range 350-700 nm, with both absorbance and emission slit widths of 10 nm, using an Epoch-2 microplate spectrophotometer (BioTek Instruments). To study Dox release under the influence of nuclease degradation, 10uM Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treated with DNAse I (1U/ml; more than twice the level in human serum) [
45,
46] was transferred to a dialysis tube (Pur-A-Lyzer™ Midi Dialysis Kit, Sigma-Aldrich) and immersed in PBS (pH 7.4) at 37°C. The fluorescence of Dox (Ex/Em: 470/560) in PBS was measured and the amount of drug released was calculated at different time intervals (1, 3, 6, 24, 48 h) using an Epoch-2 microplate spectrophotometer (BioTek Instruments).
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
Cells (5 × 103 cells per well) were seeded in 100 µl DMEM medium supplemented with 10 % FBS in 96 well plates. After overnight incubation, different concentrations of Free Doxorubicin (Dox), Dox-loaded nanosphere (Dox-Nanosphere) and Dox-loaded aptamer conjugated nanosphere (Dox-Apt-Nanosphere) were added to the fresh medium and incubated for 24 h in a humidified atmosphere with 5 % CO₂ at 37 °C. After incubation, 10 µl of cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) solution (Dojin Laboratory) was added and incubated for 3 h. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using an Epoch-2 microplate spectrophotometer (BioTek Instruments).
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
Flow cytometric analysis was performed to evaluate the selective binding ability of AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanospheres to target cells. Cells (1 × 105 cells per well) were seeded in 500 µl DMEM medium supplemented with 10 % FBS in 24 well plates. After overnight incubation, a brief wash with 500 µl of PBS, cells were incubated with 500 nM of FAM-labelled nanosphere, and aptamer conjugated nanosphere (Apt-Nanosphere) in 200 µl of serum-free DMEM medium for 24 h. After incubation, the cells were washed twice with PBS and resuspended in 500 µl of PBS prior to flow cytometric analysis on a FACS Calibur flow cytometry (Becton Dickinson). Data analysis was performed using FlowJo 10.8.1 software.
2.9. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
Cells were plated in 24-well culture plates (1 × 105 cells per well) at 37 °C overnight. After incubation, FAM-labelled nanosphere and Apt-Nanosphere (100 nM equivalents) were added and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C to assess selective cellular internalisation. To compare the cellular uptake of nanospheres, Free Dox, Dox-Nanosphere and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere (1 µM Dox equivalent) were inoculated into the media and incubated for 4 h and 24 h. The cells were then washed with PBS and fixed with 4 % paraformaldehyde. Cell nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Thermo Scientific). Confocal imaging was performed using a Zeiss LSM710 confocal laser scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss). Sum fluorescence intensity values were calculated using the ZEN lite software (Carl Zeiss).
2.10. 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation
U87 cells were seeded at 6 × 105 cells per well in a Stem FIT 3D cell culture dish (C100600, MicroFIT, Inc., Korea). Cells were incubated in 500 µl DMEM medium supplemented with 10 % FBS. After overnight incubation, 200 µl of PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere (10 µM Dox equivalent) were added to each well and incubation was continued for 72 h in a humidified atmosphere with 5 % CO₂ at 37 °C. After 72 h, the radius of 3D tumor spheroids was estimated using an inverted microscope (Olympus CKX53, Japan) at 4 × magnification and the spheroid areas were measured using iSolution Lite software (IMT i-solution, Canada). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s HSD.
2.11. In Vitro BTB Penetration Assays
The in vitro BTB model by coculture of hCMEC/D3 and U87 cells was established as previously described [
47,
48]. Briefly, U87 cells were seeded into the basolateral chambers of the transwell plates at a density of 1.12 × 10
6 per well, and after 3days, hCMEC/D3 were seeded onto the upper inserts of the transwell plates at a density of 1.12 × 10
5 per well. The co-cultured cells were incubated for 5 days, and the culture medium (0.5 mL) was changed once. After incubation, the transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) of the hCMEC/D3 cell monolayer was measured using an EVOM3 device (WPI, USA). After removal of the entire medium from both sides, 0.1 mM Free Dox and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere in 0.5 mL of fresh complete cell culture medium was added to the apical chamber and incubated with the cell monolayer for 30, 60, 120, 300 min. At each time point, the fluorescence of Dox (Ex/Em: 470/560) from the basolateral side of the medium containing the different samples was determined using a BioTek Cytation 5 fluorescence microplate reader The transport efficiency (TE) of each sample across the BTB model was calculated as TE = (
-
)/(
-
), where
,
and
represent the fluorescence signals from the basolateral side of the media containing the different samples at each time point, the basolateral side containing the full amount of each sample and the blank control, respectively. In addition, the transport ratio (%) of each sample, normalised to each transwell membrane TE only, was calculated as transport ratio (TR) =
.
2.12. In vivo Antitumor Experiments
To generate a GBM xenograft model, 6-week-old male Balb/c nude mice were injected subcutaneously into the right thigh with U87 cells at a dose of 1 × 106 cells in 100 µl PBS and randomly divided into four groups: PBS, Free Dox, Apt-Nanosphere and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere when tumours in tumour bearing mice reached approximately 2 mm in diameter (n=3). Samples in a volume of 100 µl per group were administered by tail vein injection with an equivalent concentration of Dox at 2 mg/kg administered intravenously every 3 days for a total of 5 injections. Fluorescence images (660/710 nm) of the mice were acquired using an IVIS Caliper Lumina imaging system (Perkin Elmer, Connecticut, USA) to monitor the Cy5.5 labelled nanosphere. Tumor-bearing mice were sacrificed on day 5 after full treatment. Tumour-bearing mice were sacrificed on day 5 after full treatment, and tumour tissues were resected, fixed in formalin, and embedded in paraffin. Tumour tissues were sectioned at 4 μm thickness and stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and DAPI using ProLong gold mounting medium with DAPI (Invitrogen). Tissue sections were examined using a Zeiss LSM710, a confocal laser scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss).
2.13. Statical Analysis
Results are expressed as mean and standard error of the mean. Significance (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05) was assessed using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test using GraphPad Prism 9.0 (San Diego, CA).
3. Results
3.1. Generation and Characterisation of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres
The nanosphere synthesis was designed as a two-step self-assembly process in which the ssDNA oligonucleotides of the semi-complementary sequences were hybridised to form a dsDNA chain, and then the self-assembled structure was extended by a system in which biotin linked to ssDNA binds to streptavidin. The ssDNA oligonucleotide sequences,[
43] and the process for synthesising a stabilised dsDNA-streptavidin hybrid nanosphere were obtained in previous studies [
42,
49,
50]. In addition, a dsDNA-streptavidin hybrid nanosphere was developed that selectively targeting GBM cells was developed based on the AS1411 aptamer targeting NCL proteins.
To synthesise the AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanosphere structure, it was necessary to verify the optimisation of the AS1411 aptamer ratio for binding to the nanosphere. Residues of ssDNA were observed when the nanosphere and AS1411 aptamer were combined in a ratio of 1:1 and 1:2 (lane 4, 5), but no residual ssDNA was observed when the nanospheres and aptamers were combined in a ratio of 1:3 (lane 6) in
Figure 1B. In this study, a self-assembly process was performed using a ratio where no dimer was formed, and the ratio was as follows: [ssDNA (40 bp)]: [biotin-linked to ssDNA (40 bp)]: [streptavidin]: [biotin-linked to 1411 aptamer (26 bp)] = 1:1:1:3.
With the addition of biotinylated AS1411 aptamer, it is assumed that ssDNA residues and dimers can be generated due to tertiary structure loss or non-specific binding during recombination with complementary strands [
51,
52]. Rather, it was assumed that the balance of hydrophobic and van der Waals forces between biotin and streptavidin may be a suitable ratio for reconstruction into the nanosphere when a 3-fold ratio of biotinylated AS1411 aptamer is added.
The size distribution of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres was measured by injecting them into the NanoSight NS300 using a syringe (
Figure 1E and 1F). In
Figure 1E shows the measurement of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated dsDNA-streptavidin hybrid nanospheres at a concentration of 1.48E+8 particles per 1 ml, with an average size of 234.6 ± 44.2 nm (mean ± SD). The size of the AS1411 aptamer-conjugated dsDNA-streptavidin hybrid nanospheres with Dox was measured at a concentration of 1.74E+8 particles per 1 ml, with an average size of 260.4 ± 84.9 nm (mean ± SD). The addition of Dox increased the size by approximately 25 nm (
Figure 1F).
Dox, used as an anticancer drug, can be intercalate into the "GC" or "CG" sequence of DNA due to aromatic rings [
53,
54]. In addition, previous studies reported that 94% of the fluorescence signal of Free Dox was quenched in PBS when the concentration ratio of dsDNA to Dox was 1:10[
42]. Therefore, the concentration ratio of dsDNA to Dox was treated as 1:10 in order to quantitatively predict the Dox released from nanosphere-encapsulated drugs.
3.2. Ability to Selectively Bind to Glioblastoma Cells of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres
Multifunctional NCL proteins, which promote tumor initiation and progression, are highly expressed in various tumors. AS1411 is a 26-mer G-rich DNA aptamer used as a targeting agent to deliver small molecules to cancer cells that overexpress NCL [
34,
55]. In addition, NCL acts as a molecular chaperone to support the cell entry of AS1411 [
34] and was therefore used in this study for the purpose of GBM cell-specific binding and cellular internalisation.
The expression of NCL mRNA and protein was detected in NHA cells and GBM cells (U87 and U251) using real-time RT-PCR and Western blot assay. The qRT-PCR results showed that the NCL mRNA levels were significantly higher in GBM cells (U87 and U251) compared to non-target NHA cells (3.41 ± 1.09, 2.90 ± 0.03 vs. 1 ± 0.09, p < 0.05,
Figure 2G). Similarly in Western blot analysis, expression of NCL protein expression was significantly higher in GBM cells (U87 and U251) than in NHA cells (
Figure 2F).
After incubation of FAM-labelled nanospheres and FAM-labelled AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres in each cell for 24 h, the selective target affinity of GBM cells (U87 and U251) compared to non-target NHA cells was analysed by flow cytometry (
Figure 2). As a result, only U87 and U251 cells (
Figure 2A and 2B) confirmed their binding ability due to the fluorescence (FL-1) peak shifts compared to NHA cells (
Figure 2C), and AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres selectively recognised GBM cells.
In the results of confocal laser scanning microscopy (Carl Zeiss), sum fluorescence intensity (SFI) values were significantly different in U87 and U251 cells compared to NHA cells (p < 0.01), confirming selective binding between FAM-labelled AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres and GBM cells (
Figure 2D and 2E).
3.3. Transport Efficiency and Cellular Uptake of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres with Doxorubicin
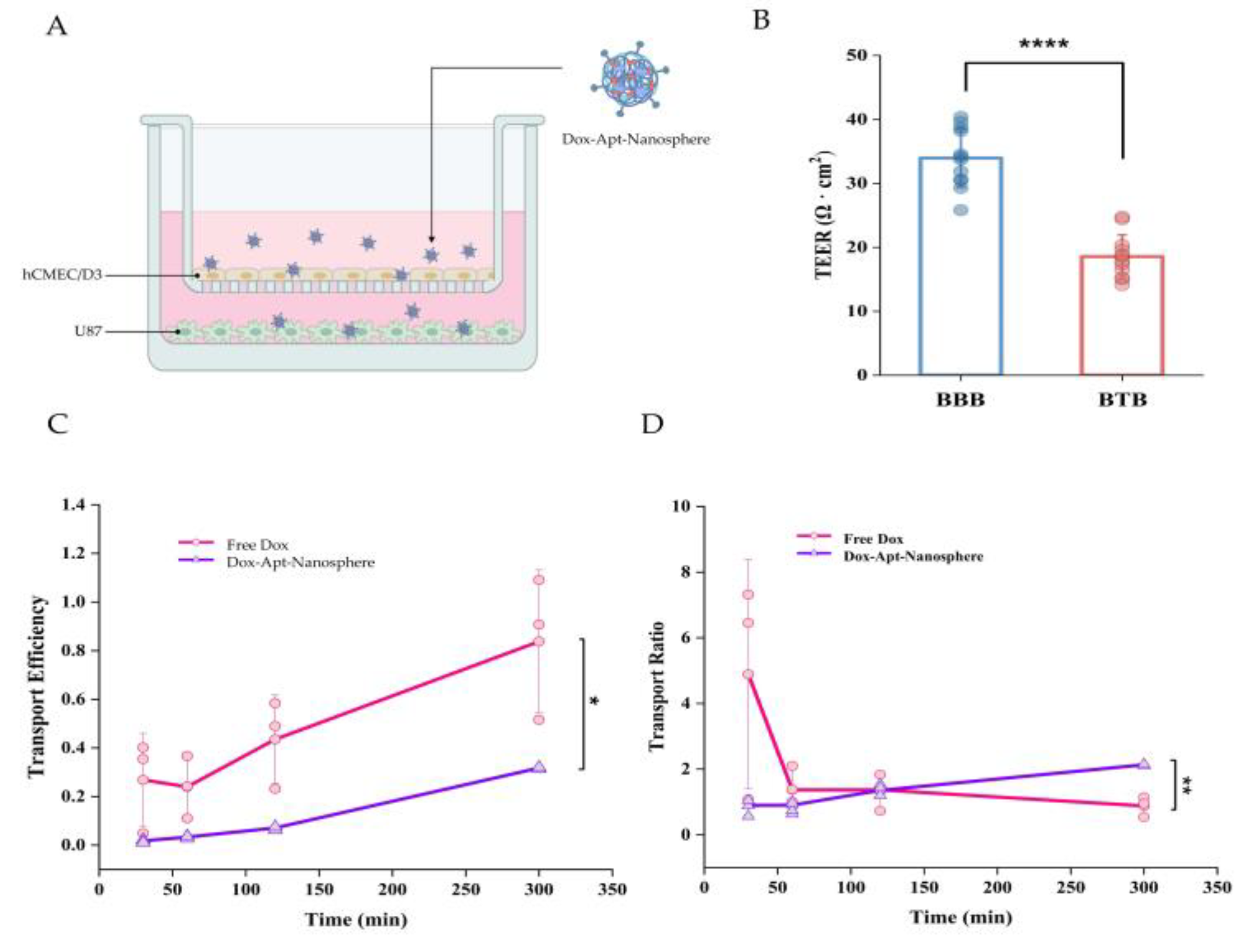
We have previously confirmed the binding of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles to GBM-specific NCL for cancer cell-targeted drug delivery and investigated the permeation efficiency of BTBs in Dox-loaded nanospheres, a step prior to binding. In the case of GBM, the drug permeability of BTBs is high in the bulk tumor site, but low permeability in the periphery [
2], so we established an in vitro hCMEC/D3 and U87 cell co-culture model to investigate drug penetration efficiency and whether it could reduce drug release. In this culture system, U87 cells stimulated a monolayer of hCMECs seeded in an insert chamber to confer an angiogenic phenotype that could mimic BTBs in vivo (
Figure 3A). To assess the integrity of the BTBs, we measured the TEER after 5 days of co-culture and found that the TEER of BTBs (18.56 ± 3.39) was significantly reduced compared to small BBB monolayers (33.95 ± 4.57) (
Figure 3B). As expected, the transport efficiency of low molecular weight Free Dox was consistently found to be higher than that of the aptamer conjugated nanospheres, with a 2-fold difference in efficiency across the BTB (
Figure 3C). However, for the spherical aptamer-conjugated nanosphere, the efficiency increased steadily with little variation over time. For the transport ratio, Free Dox was more than 3-fold higher than the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere within 30 minutes, but the transport ratio decreased after 1 hour, whereas the transport ratio of the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere increased continuously and the transport ratio was significantly higher than Free Dox after 3 hours. (p < 0.01) (
Figure 3D). It was suggested that more and more AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanospheres were captured by NCL on the cell membrane and gradually migrated to the basolateral surface of the cell over time after penetrating the BTB.
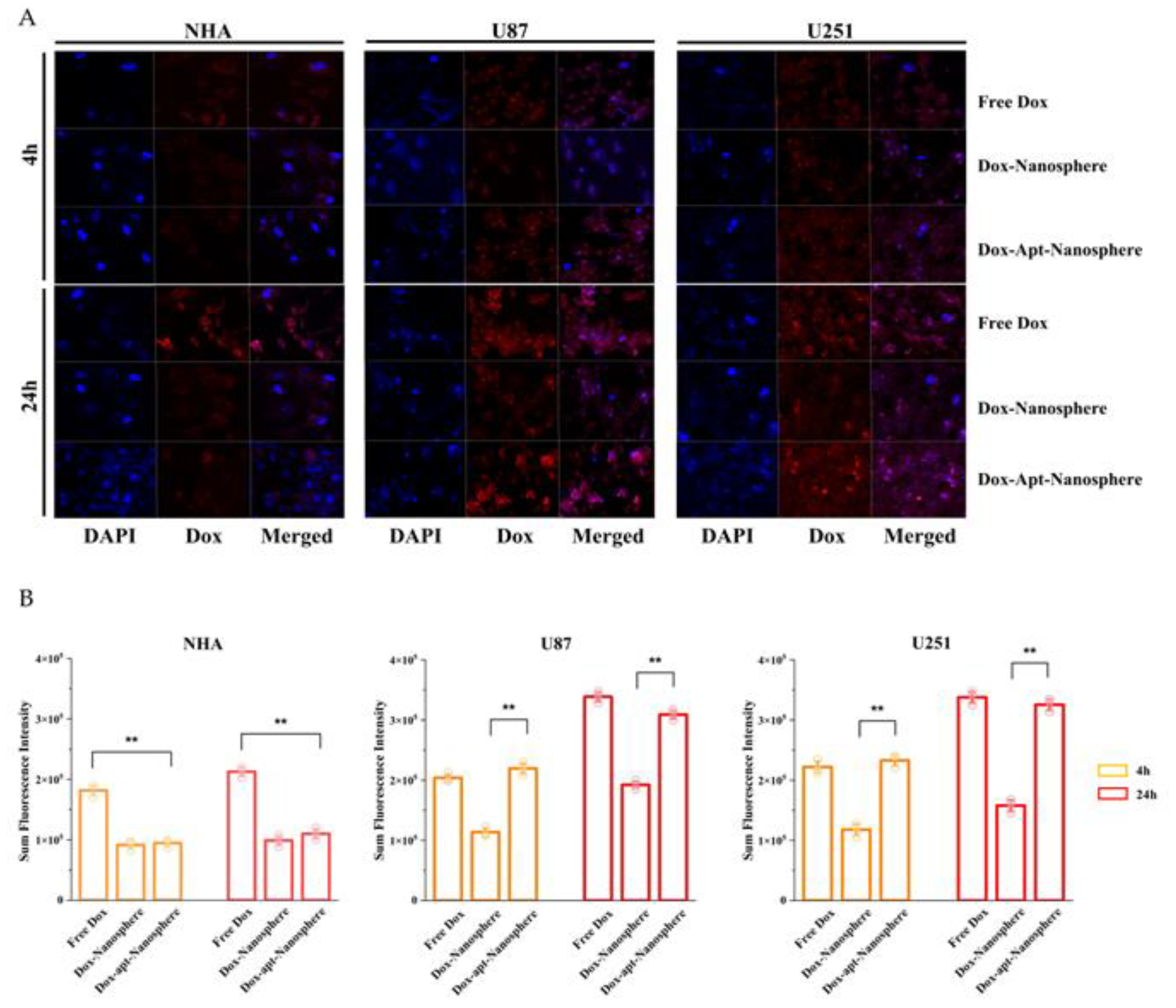
To evaluate whether AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres could selectively deliver Dox to target GBM, Free Dox, Dox-Nanospheres and Dox-Apt-Nanospheres were inoculated into U87, U251 target cells or NHA non-target cells and evaluated with confocal laser scanning microscopy (Carl Zeiss). As shown in
Figure 4A and B, drug accumulation by Free Dox was observed in both GBM (U87 and U251) and NHA cells, and an increase in Dox fluorescence intensity was observed at 24 hours rather than 4 hours. The Dox-Apt-Nanospheres were observed at a level equivalent to the fluorescence intensity of Free Dox and showed Dox accumulation over time in U87 and U251 cells. In GBM cells, Dox-Nanospheres had a significantly lower cell accumulation of Dox than Dox-Apt-Nanospheres (p < 0.01). In NHA cells, Dox-Apt-Nanospheres and Dox-Nanospheres showed no increase in Dox accumulation over time, and the Dox fluorescence intensities of Free Dox and Dox-Apt-Nanospheres showed a significant difference (p < 0.01). The AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanospheres with AS1411-NCL interactions in GBM cells with high NCL expression clearly showed a selective drug delivery ability similar to Free Dox.
3.4. Cytotoxicity of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres with Doxorubicin
The CCK-8 cytotoxicity assay was performed to determine whether Dox-loaded AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres could target GBM cells to promote drug-induced killing in target cells (
Figure 5).
First, to assess the toxicity of the nanosphere itself, nanospheres and aptamer-conjugated nanospheres were inoculated into U87 and U251 target cells and NHA non-target cells, respectively, and no evidence of cytotoxicity was observed in the nanosphere without Dox loading (
Figure 5A). Free Dox showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity against both NHA and GBM U87 and U251 target cells. However, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere showed drug-induced cell death effects specific to GBM U87 (
Figure 5C) and U251 (
Figure 5D) cells at a concentration around IC50 but showed no difference in NHA cells (
Figure 5B). These comparisons of targeted and non-targeted cells demonstrated that selective cell killing can be achieved by the precise delivery of anticancer drugs using AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres with Dox.
3.5. Antitumor effect of AS1411 Aptamer-Conjugated Nanospheres with Doxorubicin
Drug delivery and efficacy were evaluated in 3D models of U87 spheroids, which more closely resemble in vivo tumor characteristics than 2D models (
Figure 5). In the 2D model, Apt-Nanosphere alone did not inhibit tumor growth, but in the 3D model, Apt-Nanosphere inhibited cell growth significantly more than PBS (p < 0.05), and the AS1411 aptamer itself had some effect on growth inhibition by binding to cells. Both Free Dox and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere showed significant inhibition of tumorigenesis compared to PBS and Apt-nanosphere at 1 µM (p < 0.001) (
Figure 5E and 5G), a concentration similar to that in the 2D model, but at 10 µM, which is 10 times higher than in the 2D model, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere showed significantly higher tumorigenesis inhibition efficacy than Free Dox (p < 0.05) (
Figure 5F and 5H). We confirmed that the 3D model requires a higher concentration of drug to be induced than the 2D model [
56] and that at the same concentration of Dox, the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere would adhere to the GBM cells and inhibit the cell growth with a higher drug delivery efficiency than Free Dox.
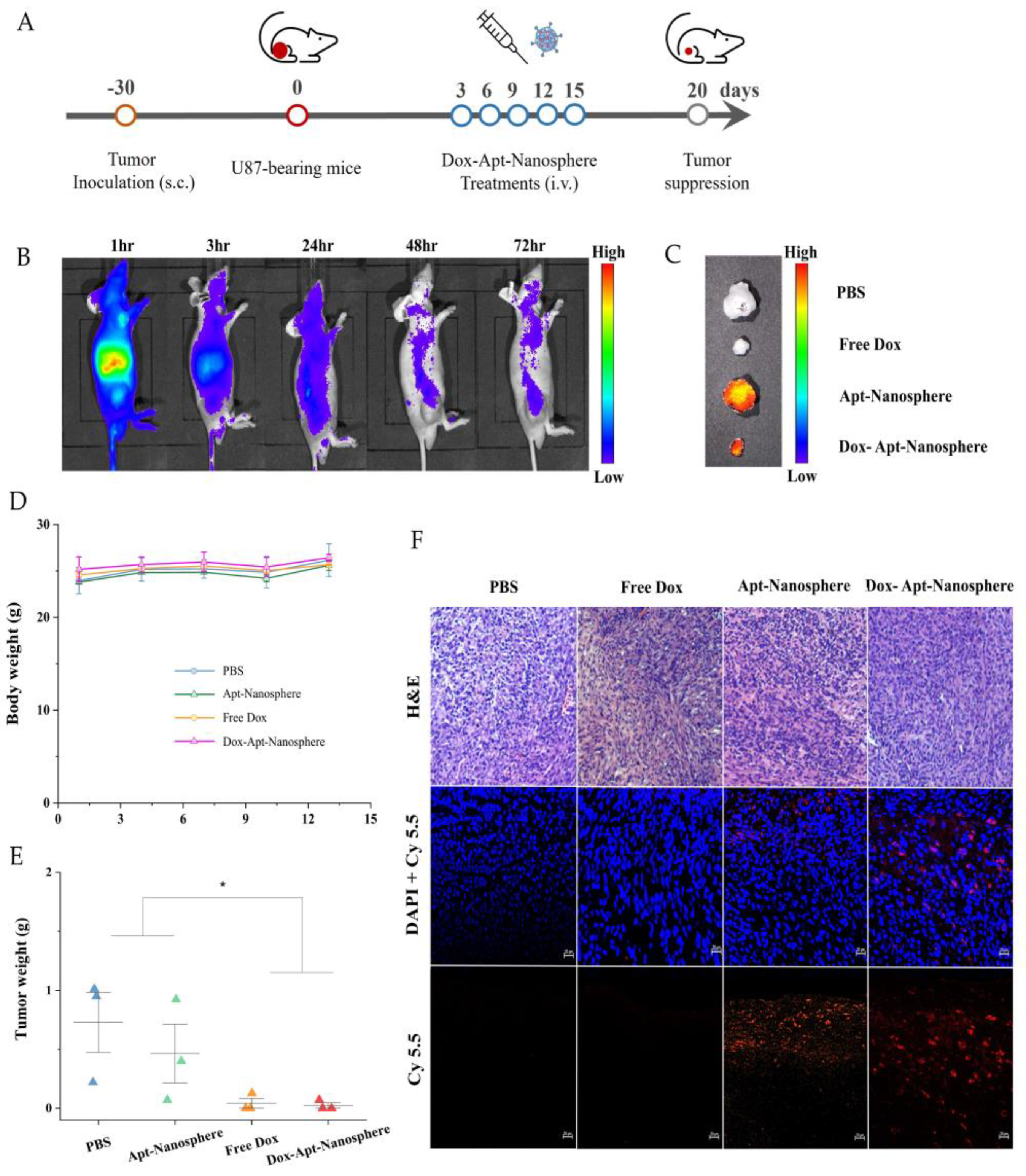
In addition, after the injection of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres using a GBM xenograft tumor model in nude mice, the biodistribution imaging of the drug delivery to the tumor target and the tumor suppression effect were observed (
Figure 6). Nanospheres were labelled with Cy5.5 and injected intravenously into the tail of U87 tumor-bearing mice. Based on the distribution of nanospheres, the fluorescence signal was found to be the strongest mainly in organs, so the degradation of nanospheres appeared to be active [
57], followed by the tumor target delivery image of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere by checking the strong signal in the tumor tissue. As the signal strength of the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere distributed throughout the body of U87 tumor-bearing mice decreased after 48 hours of fluorescence, the researchers were able to estimate that the drug had been released gradually over a 72-hour period (
Figure 6B). To confirm that the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere accumulated directly in the tumor tissue, the ex vivo fluorescence signal and direct delivery to the tumor tissue was verified (
Figure 6C). H&E staining of tumor tissue showed no significant tissue necrosis, biological stability was confirmed, and fluorescence signals from the Cy5.5 labelled Dox-Apt-Nanosphere in tissue sections demonstrated target binding and penetration into tumor tissue adjacent to blood vessels. (
Figure 6F). After confirming the drug delivery to the tumor tissue, the anti-tumor effect of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere was evaluated in U87 tumor-bearing mice at the end of the PBS, Free Dox, Apt-Nanosphere and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treatment groups. As a result, similar to the experimental results in the 3D spheroid model, the tendency of volume reduction in the Apt-Nanosphere group compared to the PBS group was confirmed in the U87 tumor-bearing mice model, but no statistically significant anti-tumor effect was observed (
Figure 6E). The Dox-Apt-Nanospheres also showed a tendency to have a lower volume than the Free Dox, but no statistically significant difference in the anti-tumor capacity was observed. In addition, there was no significant change in body weight in either Apt-Nanosphere or Dox-Apt-Nanospheres treated animals, confirming the biosafety of the drug (
Figure 6D). This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
4. Discussion
GBM has a high recurrence rate and poor prognosis, and various treatment strategies are needed to prolong survival. Post-operative chemotherapy is still needed to treat GBM, and the development of tumor-targeted drug delivery treatment using the nanoplatform system is under development.
A multi-faceted understanding of the BBB/BTB is essential for CNS therapy or drug delivery strategies to the brain. As cancer progresses, it degenerates into BTB, and even within the microenvironment of the same lesion, it differs from the characteristics of the intact BBB, which may not be treatable when designing drug delivery. The angiogenesis process surrounding tumors, including GBM, has irregular and inadequate underlying barriers with discontinuous epithelium. BTB forms a leaky vascular structure with 40-200 nm of fenestration [
58]. This vascular structure causes the passive accumulation of drugs in tumors due to the effect of EPR in drug delivery using nanocarriers. A size of 40 to 200 nm may be suitable for nanoplatforms used for diagnosis and treatment, and even if the nanocarrier is smaller than 5 nm, it is easily excreted by the kidneys during long-term circulation of the drug [
59]. It is essential that BBB/BTB drug delivery is designed to accurately target and deliver drugs to cancer cells.
The nanoparticle size used in this study was confirmed to be around 100-300 nm, and it was designed to accumulate Dox specifically to GBM cells. In addition, the drug was reasonably stable in the treatment of DNAse I, which was more than twice the human blood concentration, and the drug transport ratio into tumor cells was stable and active compared to Free Dox. NCL was overexpressed in renal vascular endothelial cells and GBM cells, and specific targeting of cancer cells was possible through the interaction of the AS1411 aptamer with NCL. Cellular selective binding and drug uptake in cytotoxicity analysis showed a significant improvement and increase in cytotoxicity in U87 and U251 cells upon inoculation with AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanospheres. The high rate of apoptosis of U87 and U251 cells reflected the increased toxicity as active drug delivery with the function of AS1411. As a result, drug delivery inhibited cell growth with similar levels of Free Dox and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere, but importantly, NHA control cells showed less accumulation due to significant differences when drugs were delivered with AS1411 aptamer conjugated nanospheres. The GBM xenograft tumor model also confirmed the biosafety of the tumor tissue after drug treatment while confirming the direct delivery of Dox-Apt-Nanospheres, and in the 3D spheroid model, Dox-Apt-Nanospheres significantly inhibited cell growth compared to Free Dox. Non-specific drug delivery can damage normal tissue while accumulating in GBM tissue. Therefore, it is designed to enhance drug accumulation in tumor cells by targeting molecules that are over-expressed on the surface of tumor cells.
The nanodrug carriers used in this study have been shown in previous studies to have the following advantages It consists only of biomolecules containing DNA and proteins, so high biocompatibility and biodegradability are expected. Nanopharmaceutical transporters could be induced to self-assemble biomolecules with specific molecular recognition interactions between biotin and streptavidin for cross-linking of DNA nanostructures. In addition, the possibility of encapsulation could be explored by intercalating Dox into the DNA duplex and combining it with an aptamer that can carry cancer cell targeting functions.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres drug delivery system was developed for dual-target treatment of GBM. AS1411-mediated specific recognition and drug accumulation significantly improved NCL-positive U87 and U251 cell binding, and improved cytotoxicity. Improving the ability to penetrate and retain anti-tumor drugs is known to be important in clinical treatment [
60]. In this study, compared to non-specific EPR-mediated delivery and passive drug delivery to tumor cells, the active targeting model through aptamer-mediated drug delivery did not confirm the absolute amount in improving drug penetration and retention, but the potential was confirmed through 3D spheroid and in vivo GBM xenograft tumor model experiments. These results suggest that AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres may have excellent biocompatibility, specifically targeted drug delivery capability, and the potential to exert anti-tumor effects in targeted therapy of GBM cells.
Author Contributions
K.S., original draft preparation, conceptualization, reviewing; K.H., conceptualization, reviewing; K.-M.N., methodology, investigation; M.-J.K., methodology, investigation; S.S., investigation; Y.-K.S., conceptualization, supervision, reviewing; C.-Y.K., conceptualization, supervision, reviewing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This study was supported by grants (No. 18-2021-0005) from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Taylor, O.G.; Brzozowski, J.S.; Skelding, K.A. Glioblastoma Multiforme: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tellingen, O.; Yetkin-Arik, B.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T.; de Vries, H.E. Overcoming the blood-brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment. Drug Resist Updat 2015, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingineni, K.; Belekar, V.; Tangadpalliwar, S.R.; Garg, P. The role of multidrug resistance protein (MRP-1) as an active efflux transporter on blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Mol Divers 2017, 21, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Niksic, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Esteve, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Patel, B.M. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery to the Brain. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X. Current Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoenix, T.N.; Patmore, D.M.; Boop, S.; Boulos, N.; Jacus, M.O.; Patel, Y.T.; Roussel, M.F.; Finkelstein, D.; Goumnerova, L.; Perreault, S.; et al. Medulloblastoma Genotype Dictates Blood Brain Barrier Phenotype. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xiang, M.H.; Liu, J.W.; Tang, H.; Jiang, J.H. DNA Polymer Nanoparticles Programmed via Supersandwich Hybridization for Imaging and Therapy of Cancer Cells. Anal Chem 2018, 90, 12951–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, A.N.; Joseph, M.M.; Maniganda, S.; Karunakaran, V.; Sreelekha, T.T.; Maiti, K.K. Emergence of Gold-Mesoporous Silica Hybrid Nanotheranostics: Dox-Encoded, Folate Targeted Chemotherapy with Modulation of SERS Fingerprinting for Apoptosis Toward Tumor Eradication. Small 2021, 17, e2007852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Li, N.; Dai, L.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Ding, B.; et al. DNA origami as an in vivo drug delivery vehicle for cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6633–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Guo, D.S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Multistimuli responsive supramolecular vesicles based on the recognition of p-Sulfonatocalixarene and its controllable release of doxorubicin. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Xiong, S.; Lin, C.; Shen, Y.Z.; Wang, L. Multistimuli-responsive supramolecular vesicles based on water-soluble pillar[6]arene and SAINT complexation for controllable drug release. J Am Chem Soc 2014, 136, 10762–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaikherd, A.; Nagamani, C.; Thayumanavan, S. Multi-stimuli sensitive amphiphilic block copolymer assemblies. J Am Chem Soc 2009, 131, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, S.; Alibolandi, M.; Tehranizadeh, Z.A.; Oskuee, R.K.; Nosrati, R.; Soltani, F.; Ramezani, M. Self-assembly of an aptamer-decorated chimeric peptide nanocarrier for targeted cancer gene delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelu, H.V.P.; Atchimnaidu, S.; Perumal, D.; Harikrishnan, K.S.; Vijayan, S.; Varghese, R. Self-Assembly of an Aptamer-Decorated, DNA-Protein Hybrid Nanogel: A Biocompatible Nanocarrier for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2019, 2, 5227–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Girvan, A.C.; Casson, L.K.; Pierce, W.M., Jr.; Qian, M.; Thomas, S.D.; Bates, P.J. AS1411 alters the localization of a complex containing protein arginine methyltransferase 5 and nucleolin. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.M.; Dietz, H.; Liedl, T.; Hogberg, B.; Graf, F.; Shih, W.M. Self-assembly of DNA into nanoscale three-dimensional shapes. Nature 2009, 459, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothemund, P.W. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xia, D.; Klausen, L.H.; Dong, M. The self-assembled behavior of DNA bases on the interface. Int J Mol Sci 2014, 15, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbandt, M.; Bruns, O.; Vallazza, M.; Lamla, T.; Betzel, C.; Erdmann, V.A. High resolution structure of streptavidin in complex with a novel high affinity peptide tag mimicking the biotin binding motif. Proteins 2007, 67, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilkoti, A.; Tan, P.H.; Stayton, P.S. Site-directed mutagenesis studies of the high-affinity streptavidin-biotin complex: contributions of tryptophan residues 79, 108, and 120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995, 92, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.P.; Lee, Z.W.; Choi, S.K.; Jung, H.C.; Pan, J.G.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, I.S. Micropatterns of spores displaying heterologous proteins. J Am Chem Soc 2004, 126, 10512–10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.K.; Petkau, K.; Brunsveld, L. Protein assembly along a supramolecular wire. Chem Commun (Camb) 2011, 47, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, P.C.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Wendoloski, J.J.; Salemme, F.R. Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science 1989, 243, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Aptamer-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2012, 2, 418–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerchia, L.; de Franciscis, V. Targeting cancer cells with nucleic acid aptamers. Trends Biotechnol 2010, 28, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, J.K.; Smith, J.E.; Medley, C.D.; Shangguan, D.; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for selective collection and detection of cancer cells. Anal Chem 2006, 78, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tian, T.; Zhou, R.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Shi, S.; Li, Q.; Xie, X.; et al. Design, fabrication and applications of tetrahedral DNA nanostructure-based multifunctional complexes in drug delivery and biomedical treatment. Nat Protoc 2020, 15, 2728–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidfar, N.; Aghanejad, A.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Farzanehfar, S.; Eppard, E. Theranostic Advances in Breast Cancer in Nuclear Medicine. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberian, M.; Hamzeiy, H.; Aghanejad, A.; Asgari, D. Aptamer-based Nanosensors: Juglone as an Attached-Redox Molecule for Detection of Small Molecules. Bioimpacts 2011, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Shen, N.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, S.; Meguellati, K.; Yan, F. Targeting epigenetic pathway with gold nanoparticles for acute myeloid leukemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 167, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Bambury, R.M.; Van Allen, E.M.; Drabkin, H.A.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Harzstark, A.L.; Wagle, N.; Figlin, R.A.; Smith, G.W.; Garraway, L.A.; et al. A phase II trial of AS1411 (a novel nucleolin-targeted DNA aptamer) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 2014, 32, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunka, D.H.; Platonova, O.; Stockley, P.G. Development of aptamer therapeutics. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2010, 10, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.J.; Reyes-Reyes, E.M.; Malik, M.T.; Murphy, E.M.; O'Toole, M.G.; Trent, J.O. G-quadruplex oligonucleotide AS1411 as a cancer-targeting agent: Uses and mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 2017, 1861, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Hamhouyia, F.; Thomas, S.D.; Burke, T.J.; Girvan, A.C.; McGregor, W.G.; Trent, J.O.; Miller, D.M.; Bates, P.J. Inhibition of DNA replication and induction of S phase cell cycle arrest by G-rich oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 43221–43230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. RNA-binding protein nucleolin in disease. RNA Biol 2012, 9, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galzio, R.; Rosati, F.; Benedetti, E.; Cristiano, L.; Aldi, S.; Mei, S.; D'Angelo, B.; Gentile, R.; Laurenti, G.; Cifone, M.G.; et al. Glycosilated nucleolin as marker for human gliomas. J Cell Biochem 2012, 113, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldshmit, Y.; Trangle, S.S.; Kloog, Y.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R. Interfering with the interaction between ErbB1, nucleolin and Ras as a potential treatment for glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8602–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Yan, Z.; Jin, K.; Pang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Lu, H.; Liu, X.; Pang, Z.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X. Precise glioblastoma targeting by AS1411 aptamer-functionalized poly (l-gamma-glutamylglutamine)-paclitaxel nanoconjugates. J Colloid Interface Sci 2017, 490, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Xu, A.M.; White, F.M. Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signal 2009, 2, re6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovanessian, A.G.; Soundaramourty, C.; El Khoury, D.; Nondier, I.; Svab, J.; Krust, B. Surface expressed nucleolin is constantly induced in tumor cells to mediate calcium-dependent ligand internalization. PLoS One 2010, 5, e15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Baek, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Bang, Y.; Jung, H.N.; Im, H.J.; Song, Y.K. Self-Assembled DNA-Protein Hybrid Nanospheres: Biocompatible Nano-Drug-Carriers for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2022, 14, 37493–37503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, J.R.; Hayes, O.G.; Remis, J.P.; Mirkin, C.A. Programming Protein Polymerization with DNA. J Am Chem Soc 2018, 140, 15950–15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, S.; Ardestani, M.S. Novel nanosized AS1411-chitosan-BODIPY conjugate for molecular fluorescent imaging. Int J Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 3543–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanova, A.; Tamkovich, S.; Pyshnyi, D.; Kharkova, M.; Vlassov, V.; Laktionov, P. Immunochemical assay for deoxyribonuclease activity in body fluids. J Immunol Methods 2007, 325, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S.N.; Cherepanova, A.V.; Kolesnikova, E.V.; Rykova, E.Y.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Circulating DNA and DNase activity in human blood. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006, 1075, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.; Marques, C.; Carvalho, I.; Costa, P.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B. Influence of glioma cells on a new co-culture in vitro blood-brain barrier model for characterization and validation of permeability. Int J Pharm 2015, 490, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Fu, Y.; Lin, F.; Pan, X.; Li, L.; et al. Enhanced in Vivo Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration by Circular Tau-Transferrin Receptor Bifunctional Aptamer for Tauopathy Therapy. J Am Chem Soc 2020, 142, 3862–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, Y.H. The effect of limited monomer solubility in heterogeneous step-growth polymerization. Acc Chem Res 2001, 34, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fu, H.; Shih, K.C.; Jia, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ekatan, S.; Nieh, M.P.; Lin, Y.; et al. DNA-Mediated Step-Growth Polymerization of Bottlebrush Macromonomers. J Am Chem Soc 2020, 142, 10297–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, A.; Blomstergren, A.; Nord, O.; Lukacs, M.; Lundeberg, J.; Uhlen, M. The biotin-streptavidin interaction can be reversibly broken using water at elevated temperatures. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, C.; Tang, T.H.; Tominaga, J.; Tan, S.C.; Gopinath, S.C. Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) production in DNA aptamer generation. Analyst 2012, 137, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Arnaiz, C.; Busto, N.; Leal, J.M.; Garcia, B. New insights into the mechanism of the DNA/doxorubicin interaction. J Phys Chem B 2014, 118, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali-Boucetta, H.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; McCarthy, D.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Multiwalled carbon nanotube-doxorubicin supramolecular complexes for cancer therapeutics. Chem Commun (Camb) 2008, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.J.; Laber, D.A.; Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Trent, J.O. Discovery and development of the G-rich oligonucleotide AS1411 as a novel treatment for cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 2009, 86, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.; Hoang, H.H.; You, D.; Han, J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.; Park, S. Formation of size-controllable tumour spheroids using a microfluidic pillar array (muFPA) device. Analyst 2018, 143, 5841–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, K.M.; MacParland, S.A.; Ma, X.Z.; Spetzler, V.N.; Echeverri, J.; Ouyang, B.; Fadel, S.M.; Sykes, E.A.; Goldaracena, N.; Kaths, J.M.; et al. Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver. Nat Mater 2016, 15, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlageter, K.E.; Molnar, P.; Lapin, G.D.; Groothuis, D.R. Microvessel organization and structure in experimental brain tumors: microvessel populations with distinctive structural and functional properties. Microvasc Res 1999, 58, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhan, M.A.; Yalamarty, S.S.K.; Filipczak, N.; Parveen, F.; Torchilin, V.P. Recent Advances in Tumor Targeting via EPR Effect for Cancer Treatment. J Pers Med 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, N.; Shen, Y. Rational Design of Cancer Nanomedicine: Nanoproperty Integration and Synchronization. Adv Mater 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Generation of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres. (A) Schematic of the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere self-assembling to transport drugs targeting tumor cells for antitumor effects. The biopolymer that intercalates Dox into the dsDNA structure and induces biotin-streptavidin molecular binding. (B) Determination of the optimisation of the aptamer ratios that combine with the nanospheres. 2 µl of the samples were loaded on a 3% agarose gel. Lanes 1 to 3 correspond to a ssDNA (100 µM), dsDNA and nanosphere, respectively. Lanes 4 to 6 correspond to different ratios of aptamers to nanospheres correspond to 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, respectively. Samples of each lane were prepared by mixing a material at 20 µM concentration, respectively. (C) Images of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere identified by the NanoSight NS300 system and (D) FAM-labelled Dox-Apt-Nanosphere identified by confocal microscopy. (E), (F) Size distribution of Apt-Nanosphere and Dox-Apt-Nanospheres were analysed using the NanoSight NS300 system. (G) The fluorescence spectra of Dox at various concentration ratios (dsDNA:Dox = 1:2, 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50, 1:100). (H) Fluorescence signals of Dox accumulated release in Dox-Apt-Nanosphere under treatment with DNase I enzyme (1U/ml).
Figure 1.
Generation of AS1411 aptamer-conjugated nanospheres. (A) Schematic of the Dox-Apt-Nanosphere self-assembling to transport drugs targeting tumor cells for antitumor effects. The biopolymer that intercalates Dox into the dsDNA structure and induces biotin-streptavidin molecular binding. (B) Determination of the optimisation of the aptamer ratios that combine with the nanospheres. 2 µl of the samples were loaded on a 3% agarose gel. Lanes 1 to 3 correspond to a ssDNA (100 µM), dsDNA and nanosphere, respectively. Lanes 4 to 6 correspond to different ratios of aptamers to nanospheres correspond to 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, respectively. Samples of each lane were prepared by mixing a material at 20 µM concentration, respectively. (C) Images of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere identified by the NanoSight NS300 system and (D) FAM-labelled Dox-Apt-Nanosphere identified by confocal microscopy. (E), (F) Size distribution of Apt-Nanosphere and Dox-Apt-Nanospheres were analysed using the NanoSight NS300 system. (G) The fluorescence spectra of Dox at various concentration ratios (dsDNA:Dox = 1:2, 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50, 1:100). (H) Fluorescence signals of Dox accumulated release in Dox-Apt-Nanosphere under treatment with DNase I enzyme (1U/ml).
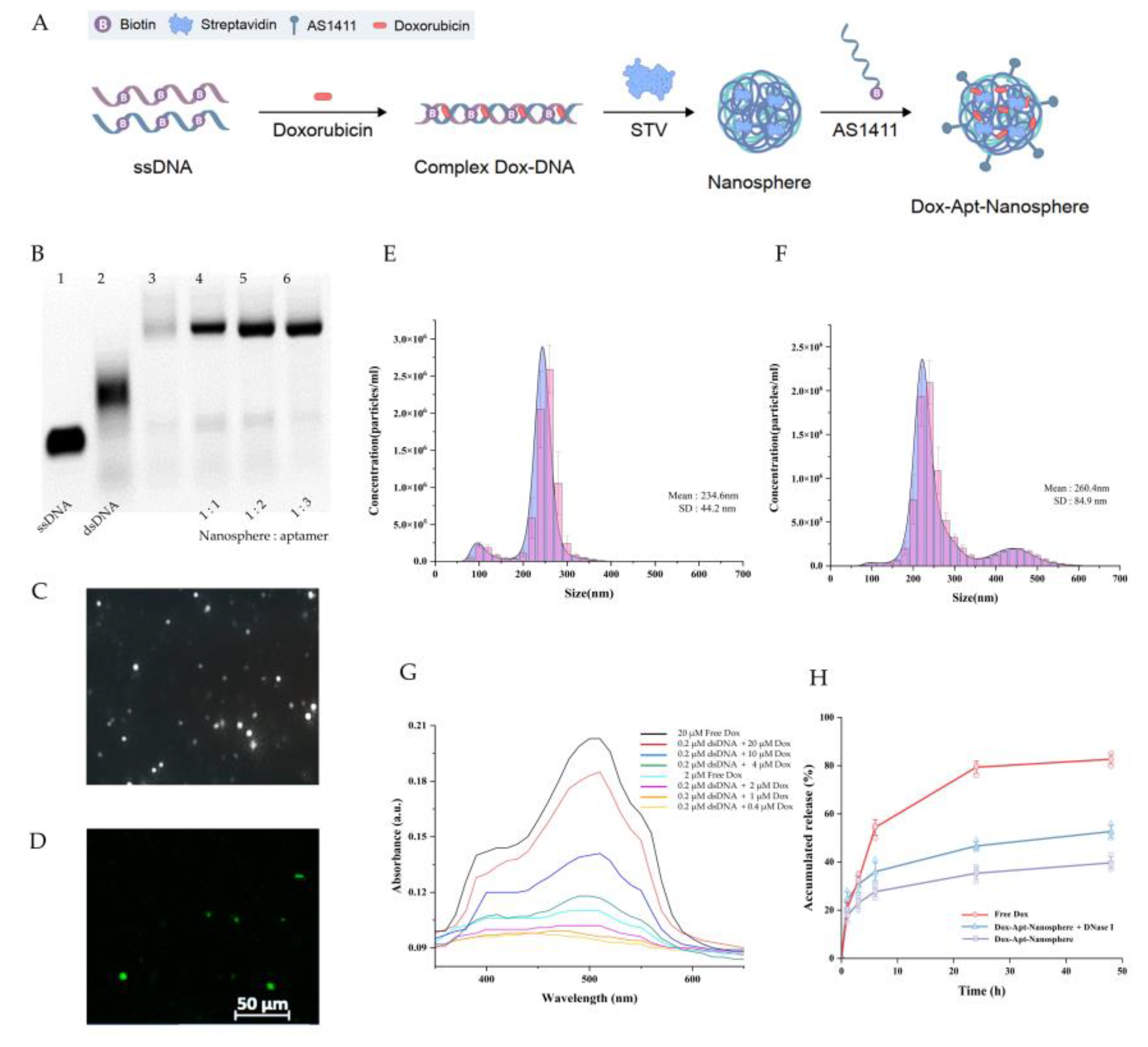
Figure 2.
Nucleolin mRNA and protein expression analysis and flow cytometry and confocal microscopy images of nontarget NHA cells and target U87 and U251 glioblastoma cells treated with nanosphere and apt-nanosphere. Selective binding of AS1411 apt-nanosphere to target U87 (A) and 251 glioblastoma cells (B), nontarget NHA cells (C). (D) The comparison of binding affinity of the FAM labelled nanosphere and 1411 aptamer conjugated FAM labelled nanosphere in target U87 and 251 glioblastoma cells, nontarget NHA cells. (E) Sum fluorescence intensity values were calculated using the ZEN lite software. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=6). (F) Western blot analysis NCL mRNA expression level of NHA, U87 and U251 cells and β-actin was used as internal control. (G) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of NCL mRNA expression level of NHA, U87 and U251 cells and GAPDH was used as an internal control. Relative quantification was performed using the comparative Ct method (2 –ΔΔCt). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=4).
Figure 2.
Nucleolin mRNA and protein expression analysis and flow cytometry and confocal microscopy images of nontarget NHA cells and target U87 and U251 glioblastoma cells treated with nanosphere and apt-nanosphere. Selective binding of AS1411 apt-nanosphere to target U87 (A) and 251 glioblastoma cells (B), nontarget NHA cells (C). (D) The comparison of binding affinity of the FAM labelled nanosphere and 1411 aptamer conjugated FAM labelled nanosphere in target U87 and 251 glioblastoma cells, nontarget NHA cells. (E) Sum fluorescence intensity values were calculated using the ZEN lite software. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=6). (F) Western blot analysis NCL mRNA expression level of NHA, U87 and U251 cells and β-actin was used as internal control. (G) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of NCL mRNA expression level of NHA, U87 and U251 cells and GAPDH was used as an internal control. Relative quantification was performed using the comparative Ct method (2 –ΔΔCt). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=4).
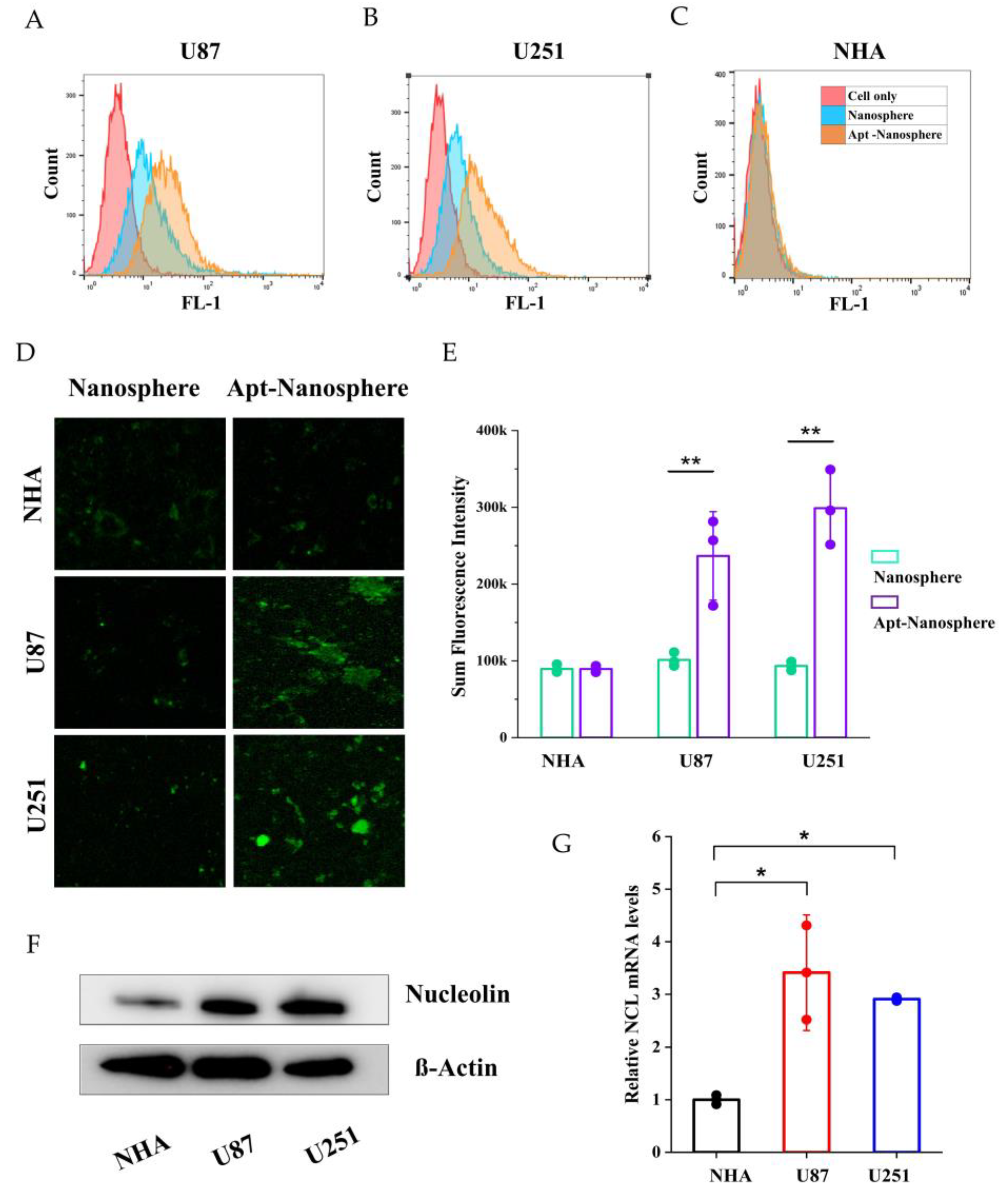
Figure 3.
The penetration of aptamer-conjugated nanospheres with doxorubicin across the in vitro BTB model. (A) Schematic of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere crossing the in vitro BTB model. (B) TEER values of BBB and BTB were expressed as Ω ∙ cm2. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 12, each). (C) Transport efficiency (TE) of Free Dox, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere samples across the BTB in vitro. Transport efficiency (TE) = (- )/( - ). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) Transport ratio (%) of Free Dox, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere, as normalised to each TE in the transwell membrane. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Transport ratio (TR) = . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
Figure 3.
The penetration of aptamer-conjugated nanospheres with doxorubicin across the in vitro BTB model. (A) Schematic of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere crossing the in vitro BTB model. (B) TEER values of BBB and BTB were expressed as Ω ∙ cm2. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 12, each). (C) Transport efficiency (TE) of Free Dox, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere samples across the BTB in vitro. Transport efficiency (TE) = (- )/( - ). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) Transport ratio (%) of Free Dox, Dox-Apt-Nanosphere, as normalised to each TE in the transwell membrane. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Transport ratio (TR) = . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
Figure 4.
Confocal microscopy images of cellular uptake of doxorubicin by nontarget NHA cells and target U87 and U251 glioblastoma cells. (A) Comparison of cellular uptake of Free Dox, Dox-Nanosphere and Dox-AS1411 apt-Nanosphere (1µM Dox equivalent) were inoculated into the media and incubated for 4h and 24h. The cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. (B) Sum fluorescence intensity values were calculated using the ZEN lite software. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=6).
Figure 4.
Confocal microscopy images of cellular uptake of doxorubicin by nontarget NHA cells and target U87 and U251 glioblastoma cells. (A) Comparison of cellular uptake of Free Dox, Dox-Nanosphere and Dox-AS1411 apt-Nanosphere (1µM Dox equivalent) were inoculated into the media and incubated for 4h and 24h. The cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. (B) Sum fluorescence intensity values were calculated using the ZEN lite software. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=6).
Figure 5.
In vitro selective cytotoxicity of Dox-loaded AS1411 apt-nanosphere and evaluation of the differences in the radius of 3D tumor spheroids after treatment with PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere. (A) Cell viability of nanosphere without Dox against NHA, U87 and U251 cells was determined using CCK-8 assay. NCL-negative NHA (B) cells and positive U87 (C) and U251 (D) glioblastoma cells were incubated with Free Dox, Dox-nanosphere and Dox-AS1411 apt-nanosphere for 24hr. The treatment concentrations of Dox are 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 µM, respectively. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=5). (E) Optical microscopy images of U87 spheroids were captured after treatment with PBS (n=78), Apt-Nanosphere (n=78), Free Dox(n=83), and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere(n=84) for 0 and 3 days. (F) Optical microscopy images of U87 spheroids were captured after treatment with PBS (n=76), Apt-Nanosphere (n=49), Free Dox (n=41), and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere (n=58) for 0 and 3 days. (G) The differences in the radius of the U87 spheroids were calculated after 3 days of treatment with 1 µM Dox. (H) The differences in the radius of the U87 spheroids were calculated after 3 days of treatment with 10 µM Dox. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc test. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
Figure 5.
In vitro selective cytotoxicity of Dox-loaded AS1411 apt-nanosphere and evaluation of the differences in the radius of 3D tumor spheroids after treatment with PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere. (A) Cell viability of nanosphere without Dox against NHA, U87 and U251 cells was determined using CCK-8 assay. NCL-negative NHA (B) cells and positive U87 (C) and U251 (D) glioblastoma cells were incubated with Free Dox, Dox-nanosphere and Dox-AS1411 apt-nanosphere for 24hr. The treatment concentrations of Dox are 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 µM, respectively. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (n=5). (E) Optical microscopy images of U87 spheroids were captured after treatment with PBS (n=78), Apt-Nanosphere (n=78), Free Dox(n=83), and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere(n=84) for 0 and 3 days. (F) Optical microscopy images of U87 spheroids were captured after treatment with PBS (n=76), Apt-Nanosphere (n=49), Free Dox (n=41), and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere (n=58) for 0 and 3 days. (G) The differences in the radius of the U87 spheroids were calculated after 3 days of treatment with 1 µM Dox. (H) The differences in the radius of the U87 spheroids were calculated after 3 days of treatment with 10 µM Dox. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc test. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
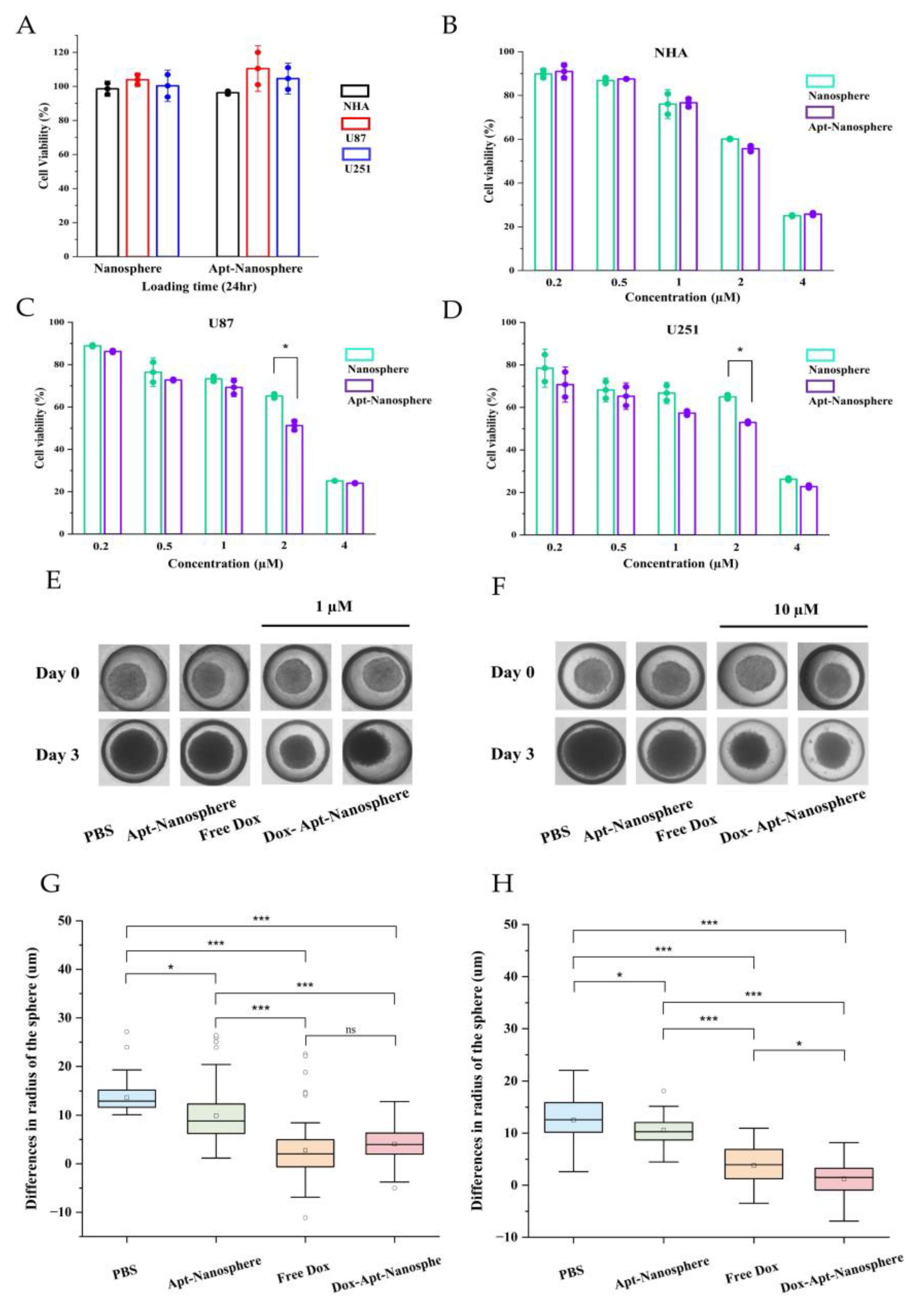
Figure 6.
Antitumor effects of PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere in a xenograft tumor model. (A) Schematic of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treatment to suppress tumor growth (B) In vivo biodistribution analysis by IVIS imaging of U87 cell tumor-bearing BALB/c mice after intravenous injection of Cy5.5-labeled Apt-Nanosphere (C) Ex vivo imaging of tumors dissected from the mice at the end of the experiment (D) Changes in body weight of mice during treatment. (E) The weights of tumors derived from the mice were measured at day 15. (F) Confocal microscopy images of DAPI-stained nuclei merged images of the DAPI and Cy-5.5 and H&E staining of tumor sections in the PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treated groups. The scale bar for all images is 20 µm.
Figure 6.
Antitumor effects of PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere in a xenograft tumor model. (A) Schematic of Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treatment to suppress tumor growth (B) In vivo biodistribution analysis by IVIS imaging of U87 cell tumor-bearing BALB/c mice after intravenous injection of Cy5.5-labeled Apt-Nanosphere (C) Ex vivo imaging of tumors dissected from the mice at the end of the experiment (D) Changes in body weight of mice during treatment. (E) The weights of tumors derived from the mice were measured at day 15. (F) Confocal microscopy images of DAPI-stained nuclei merged images of the DAPI and Cy-5.5 and H&E staining of tumor sections in the PBS, Apt-Nanosphere, Free Dox, and Dox-Apt-Nanosphere treated groups. The scale bar for all images is 20 µm.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).