Submitted:
01 April 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
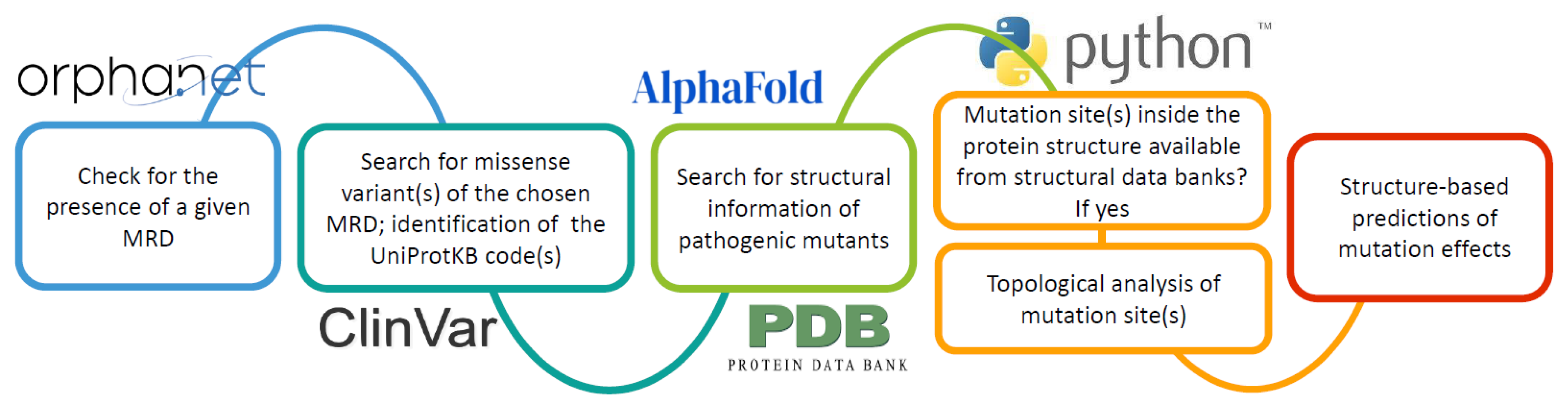
1. Introduction
2. Results
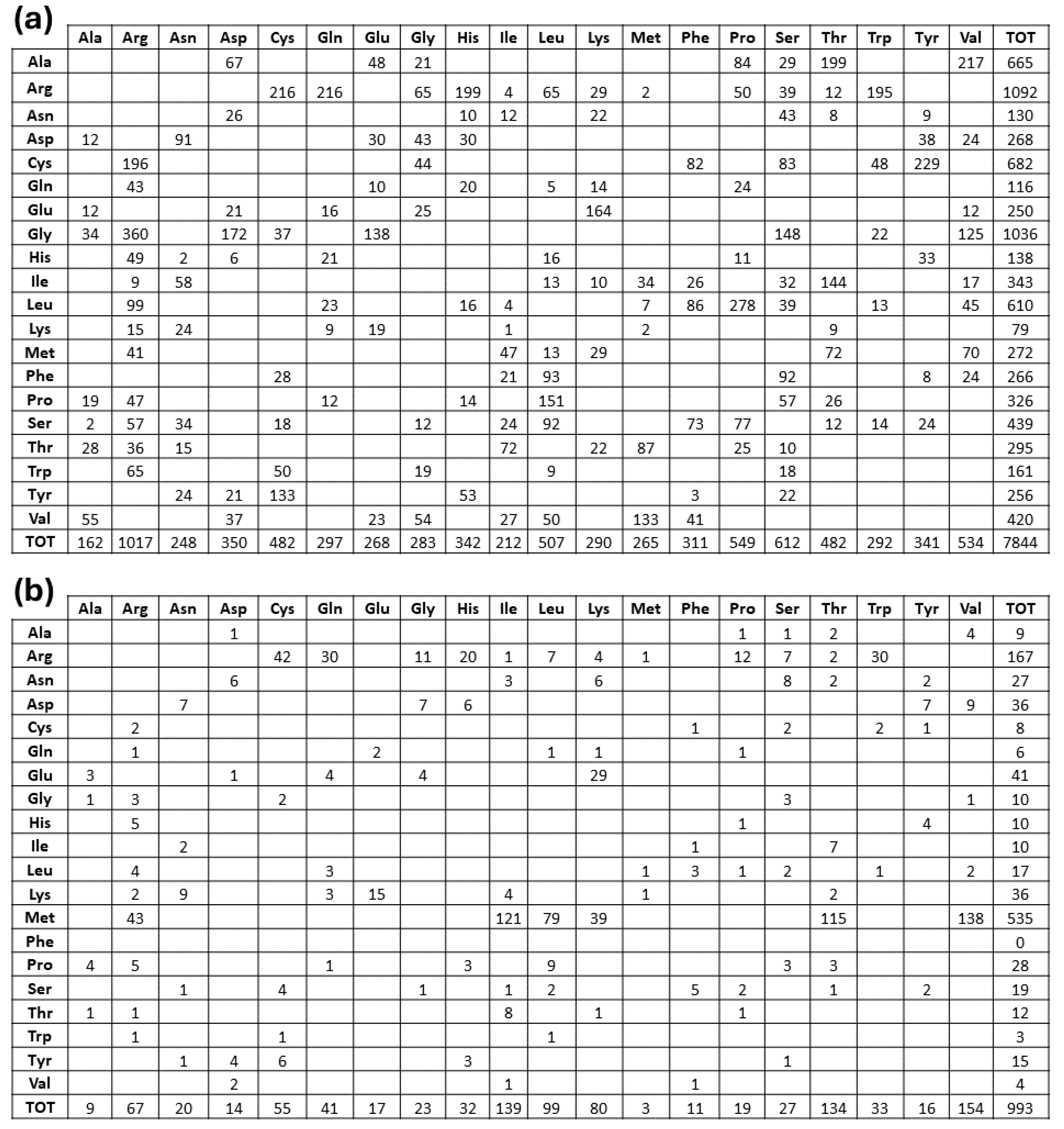
2.1. Deriving Structural Information from the Orpha.net Database
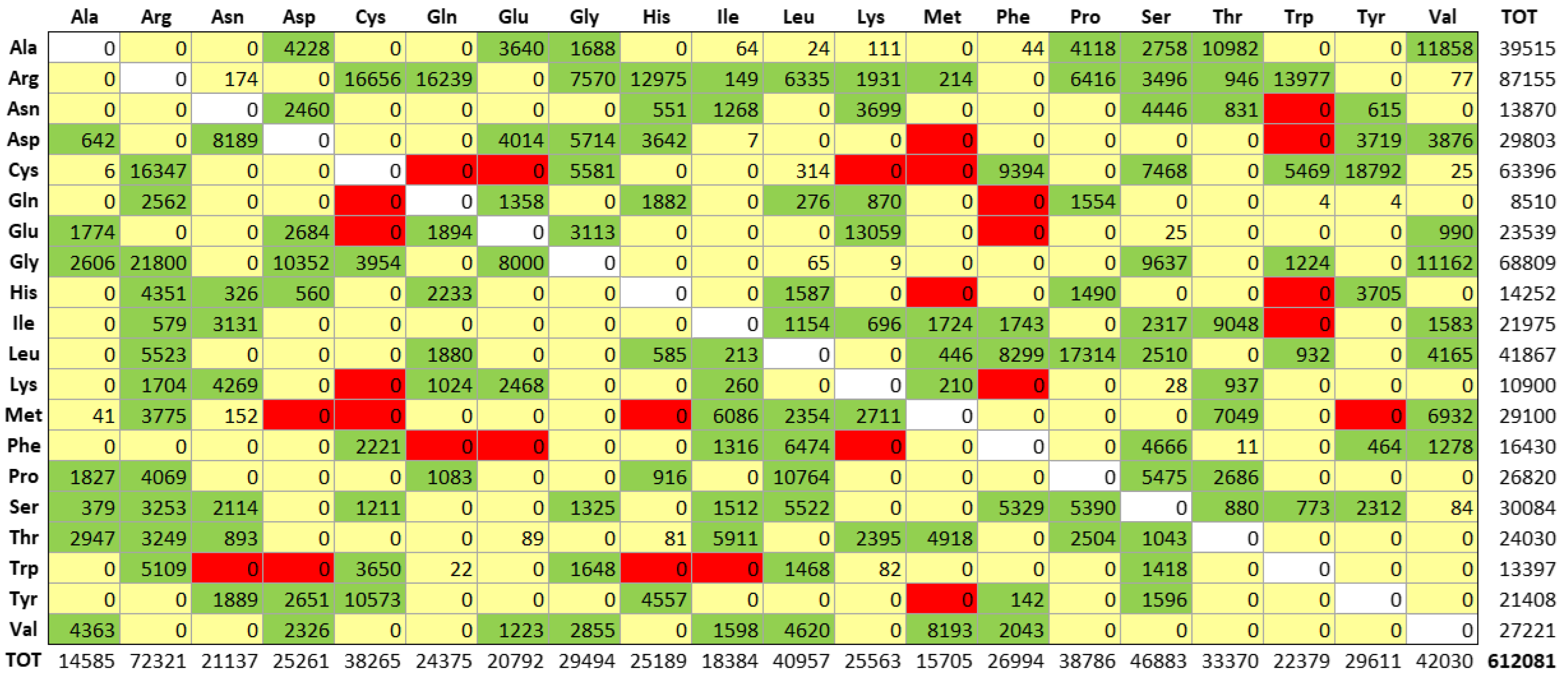
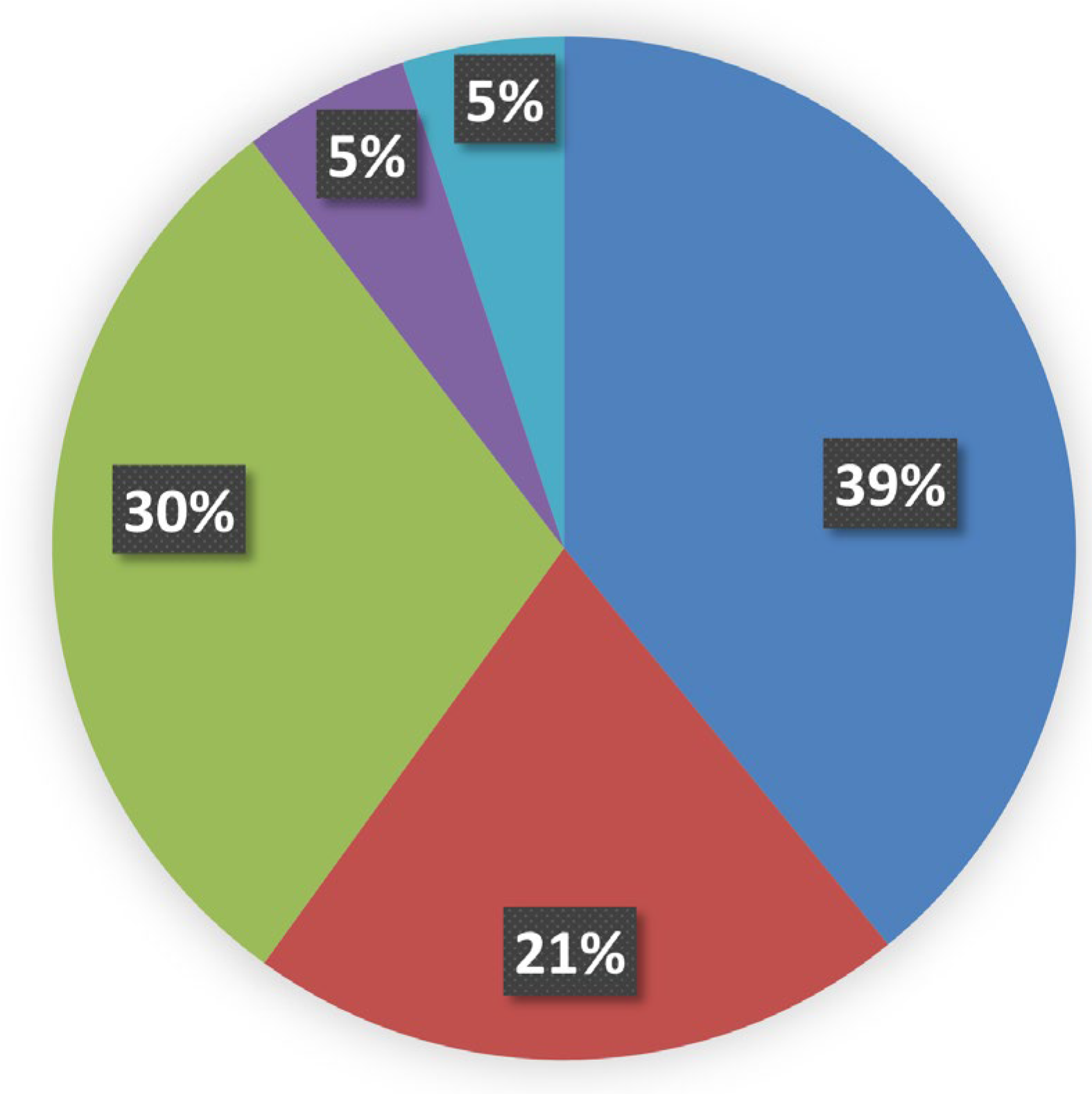
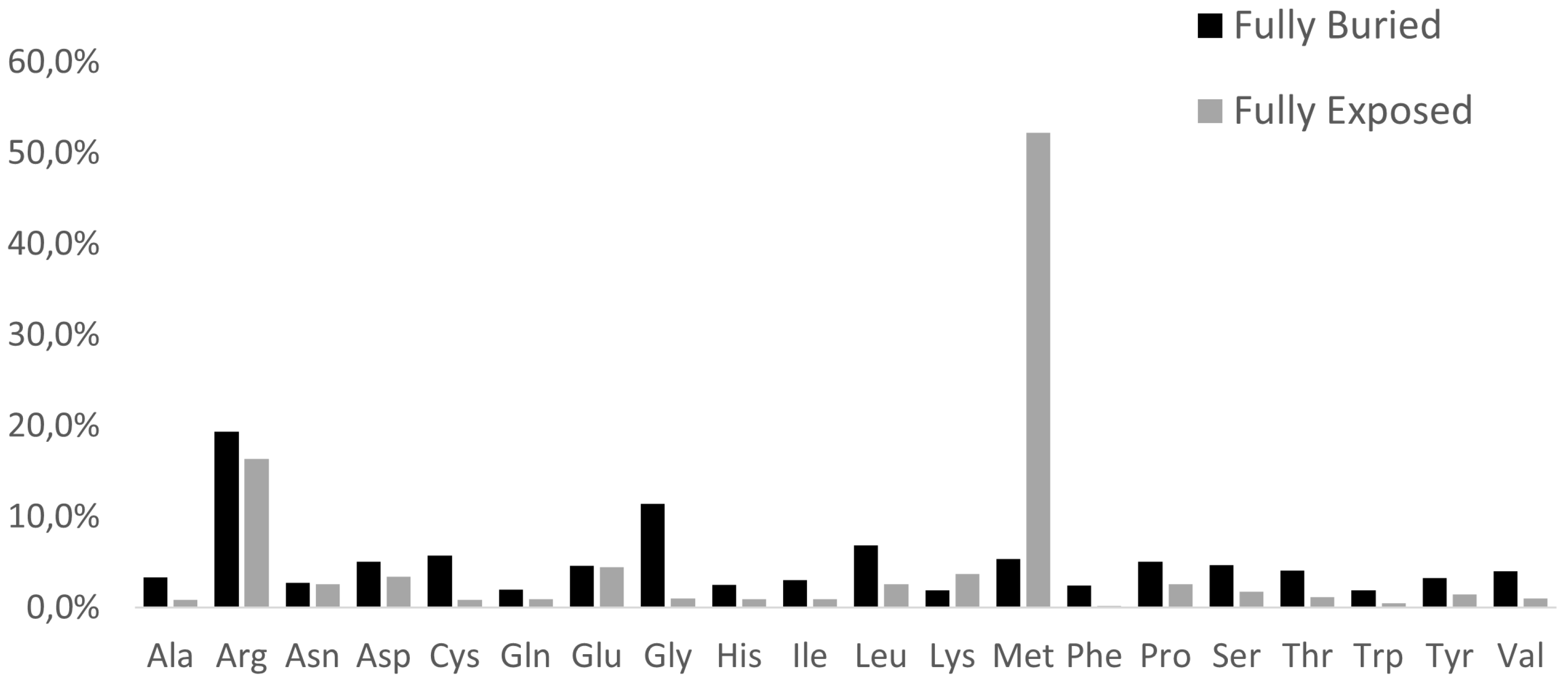
2.2. Topological Assignments of Protein Mutants Responsible for MRD
2.3. Predicting the Structural Effects of Specific Amino Acid Replacements
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Dataset of Missense Variants
5.2. Structural Analysis
5.3. Atom Depth Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S. Nguengang Wakap et al., ‘Estimating cumulative point prevalence of rare diseases: analysis of the Orphanet database’, European Journal of Human Genetics, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 165–173, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. P. O’Connor and R. G. Crystal, ‘Genetic medicines: Treatment strategies for hereditary disorders’, Nature Reviews Genetics, vol. 7, no. 4. pp. 261–276, Apr. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Landrum et al., ‘ClinVar: Public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants’, Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 44, no. D1, pp. D862–D868, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Laddach, J. C. Fung Ng, and F. Fraternali, ‘Pathogenic missense protein variants affect different functional pathways and proteomic features than healthy population variants’, PLoS Biol, vol. 19, no. 4, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. M. Berman et al., ‘The Protein Data Bank’, 2000. [Online]. Available: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/status.html.
- J. Jumper et al., ‘Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold’, Nature, vol. 596, no. 7873, pp. 583–589, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Bateman et al., ‘UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023′, Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 51, no. D1, pp. D523–D531, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Cheng et al., ‘Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense’, Science (1979), vol. 381, no. 6664, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Pavan, K. Rommel, M. E. M. Marquina, S. Höhn, V. Lanneau, and A. Rath, ‘Clinical practice guidelines for rare diseases: The orphanet database’, PLoS One, vol. 12, no. 1, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Bongini et al., ‘Structural Bioinformatic Survey of Protein-Small Molecule Interfaces Delineates the Role of Glycine in Surface Pocket Formation’, IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 1881–1886, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Grantham R, ‘Amino acid difference formula to help explain protein evolution.’, Science (1979), pp. 862–864, 1974.
- Epstein C, ‘Non-randomness of Ammo-acid Changes in the Evolution of Homologous Proteins.’, Nature, vol. 215, pp. 355–359, 1967.
- T. Miyata, S. Miyazawa, and T. Yasunaga, ‘Journal of Molecular Evolution Two Types of Amino Acid Substitutions in Protein Evolution’, 1979.
- S. Teng et al., ‘Structural assessment of the effects of Amino Acid Substitutions on protein stability and protein-protein interaction’, 2010.
- L. Cavallo, J. Kleinjung, and F. Fraternali, ‘POPS: A fast algorithm for solvent accessible surface areas at atomic and residue level’, Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 31, no. 13, pp. 3364–3366, Jul. 2003. [CrossRef]
- D. Vitkup, C. Sander, and G. M. Church, ‘The amino-acid mutational spectrum of human genetic disease’, 2003. [Online]. Available: http://genomebiology.com/2003/4/11/R72.
- M. Hackel, H.-J. Hinz, and G. R. Hedwig, ‘Partial molar volumes of proteins: amino acid side-chain contributions derived from the partial molar volumes of some tripeptides over the temperature range 1090C’, 1999.
- M. J. Harms, J. L. Schlessman, G. R. Sue, and B. García-Moreno, ‘Arginine residues at internal positions in a protein are always charged’, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Antonarakis, M. Krawczak, and D. N. Cooper, ‘Disease-causing mutations in the human genome’. [Online]. Available: http://www.kazusa.or.jp/codon/.
- T. J. Branden C, Introduction to Protein Structure Second Edition.
- Parrini et al., ‘Glycine residues appear to be evolutionarily conserved for their ability to inhibit aggregation’, Structure, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 1143–1151, Aug. 2005. [CrossRef]
- S. A. G. Guarnizo, M. K. Kellogg, S. C. Miller, E. B. Tikhonova, Z. N. Karamysheva, and A. L. Karamyshev, ‘Pathogenic signal peptide variants in the human genome’, NAR Genom Bioinform, vol. 5, no. 4, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Evans et al., ‘Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer’, 2022. [CrossRef]
| Electrically charged side chains |
Polar uncharged side chains |
Hydrophobic side chains |
Special cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive: Arg, His, Lys Negative: Asp, Glu |
Small size: Ser, Thr Large size: Asn, Gln, Tyr |
Small size: Ala, Val Medium size: Ile, Leu, Met Large size: Phe, Trp |
Cys; Gly; Pro |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





