1. Introduction
Electroencephalography (EEG) records electrical activity produced in the cerebral cortex of the brain and contains information about the brain’s neuronal electrical activities [
2]. EEG has been used for clinical purposes to predict outcomes such as depression [
3]. The extraction of time-series features from the EEG signal is an important approach to identify signals that can differentiate healthy subjects from patients. However, additional improvements are needed to improve sensitivity and specificity [
1].
Diagnostic interviews are commonly used to assess PTSD and determine if an individual meets criterion for a PTSD diagnosis. They can provide detailed info of the individual’s symptoms, with their overall functioning, medical and psychiatric history, and the presence of other conditions. Advantages of diagnostic interviews include their comprehensive nature, ability to evaluate the existence and seriousness of symptoms, and the fact that they are well validated and widely used in clinical settings. Disadvantages of diagnostic interviews include their time-consuming nature and the potential for bias in the interviewer’s assessment. Interviews provide an opportunity for direct assessment of symptoms and diagnosis of PTSD based on specific criteria. Many discussions, like the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS), have established clinical validity and reliability. Interviews can be adapted to different populations and can be modified based on the specific needs of the individual being assessed. But Interviews may be subject to bias, such as interviewer bias, recall bias, and social desirability bias. They can be time-consuming and may require a trained interviewer. Interviews can be costly, especially if a trained interviewer is required. [
4,
5].
Psychological assessments refer to a range of measures that are used to evaluate an individual’s mental health and functioning. This can include self-report questionnaires, behavioral assessments, and clinical interviews. Advantages of psychological assessments include their ease of administration, cost-effectiveness, and the fact that they can be administered in a variety of settings. Disadvantages of psychological assessments include the potential for response bias and limitations in the interpretation of results. The advantage of Self-report measures is that many psychological assessments for PTSD are self-report measures, which can be completed in a relatively short amount of time and may be less expensive than diagnostic interviews. Psychological assessments for PTSD often use standardized measures, which can help to ensure consistent and reliable assessments. Many psychological assessments for PTSD have established validity and reliability. But they may only provide a limited assessment of other factors, such as physical health, that may also impact PTSD symptoms [
6,
7].
Neuroimaging studies refer to the use of various imaging techniques. Disadvantages of neuroimaging studies include the need for specialized equipment and the potential for exposure to ionizing radiation. Neuroimaging studies can provide a direct assessment of brain activity and may help to identify specific brain regions associated with PTSD. Neuroimaging studies provide objective measures, which can help to reduce bias in assessments. They may have the potential to identify biomarkers for PTSD, which can help to diagnose the condition and guide treatment [
8].
An important biomedical application of EEG signal is investigating PTSD cases, which is indicated by sleep disturbances, and several symptoms related to a traumatic event [
9]. Previously, we employed a time series Hurst analysis of EEG signals to recognize healthy controls and PTSD subjects. We found the Hurst exponent in channel F3 to be smaller in PTSD subjects compared to healthy controls [
1]. In another study, Kim et al. (2002) applied Non-linear interdependence (NI) determined from EEG data with 16 channels of 18 healthy controls and 18 PTSD cases. This study showed the growth of nonlinear functional connectivity in cortical networks in PTSD in channels of F7, F3, T3, C3, T5, and P3 and decreases in F4, C4, P4, and O2 [
10].
In addition to standard statistical methods and feature extraction, machine learning methods are increasingly popular for prediction and modeling in biomedical research. Many machine learning algorithms can extract feature importance that indicates the role of variables in prediction models. In addition, some methods can compute indirect feature importance from machine learning models. Based on Amin Zandvakili (2019) project, Support Vector Machine (SVM) weights show that after treatment, the depressive disorder almost got down to the half [
11].
The study is organized with three main parts. First, we describe the EEG data that is available for the study. Next, the new analytical approach of k-mean clustering and linear SVM is explained. Finally, we apply this new approach to an EEG study of PTSD and discuss challenges and potential applications.
2. Data Description
The data was assembled at the Laureate Institute of Brain Research [
12]. The ethical code of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for human tests was applied to the implements on human subjects.
The data included 12 male subjects: 6 PTSD (P) cases and 6 Heathy (H) controls, with average age 27 ± 5 years. For each subject, there is a dataset with 31 EEG channels x 50,000 time points. The 31 channel names, 1 to 31 respectively, are Fp1, Fp2, F3, F4, C3, C4, P3, P4, O1, O2, F7, F8, T7, T8, P7, P8, Fz, Cz, Pz, Oz, FC1, FC2, CP1, CP2, FC5, FC6, CP5, CP6, TP9, TP10, POz. The signals of the channels were collected with electrodes placed at AFz and FCz and taged at a testing space of 5000 samples/second and resolution 0.1μV. The study used software BrainVision Analyzer2 (
https://brainvision.com/products/analyzer-2/) to do the processing of EEG signals. For advance assessment we employed EEGLAB software (
http://sccn.ucsd.edu/eeglab) [
14].
There was millions of data per channel. The first 50000 data was cut off and the second 50000 data points taken as a sample.
The study applied the template deduction method to remove MRI gradient artifact and cardio ballistic (BCG) artifact for EEG processing [
15]. A sample of 250 samples/second (4ms temporal resolution) to 40Hz was selected. We removed the artifacts and subject head movement to use in independent component analysis (ICA). The scanning spanned 526s. For signals consistent, the initial 6s were removed. Each channel has 130,000 timepoints. We selected 50,000 reliable data points after the subject’s movement.
3. Methods
The overall approach is first to identify clusters of EEG channels from the time series for each subject. In other words, each subject will have a separate set of channel clusters. We then apply SVM to each subject, where the inputs are the cluster ids of the 31 channels and the class label is PTSD. We find the model and the weight of each channel. This dimensionality reduction maps each channel’s time series to an SVM weight and results in a derived data matrix with SVM weights as the predictor features. Finally, we use the clinical outcome variable to test the ability of the SVM-based features to discriminate between PTSD cases and healthy people.
3.1. K-Means Clustering
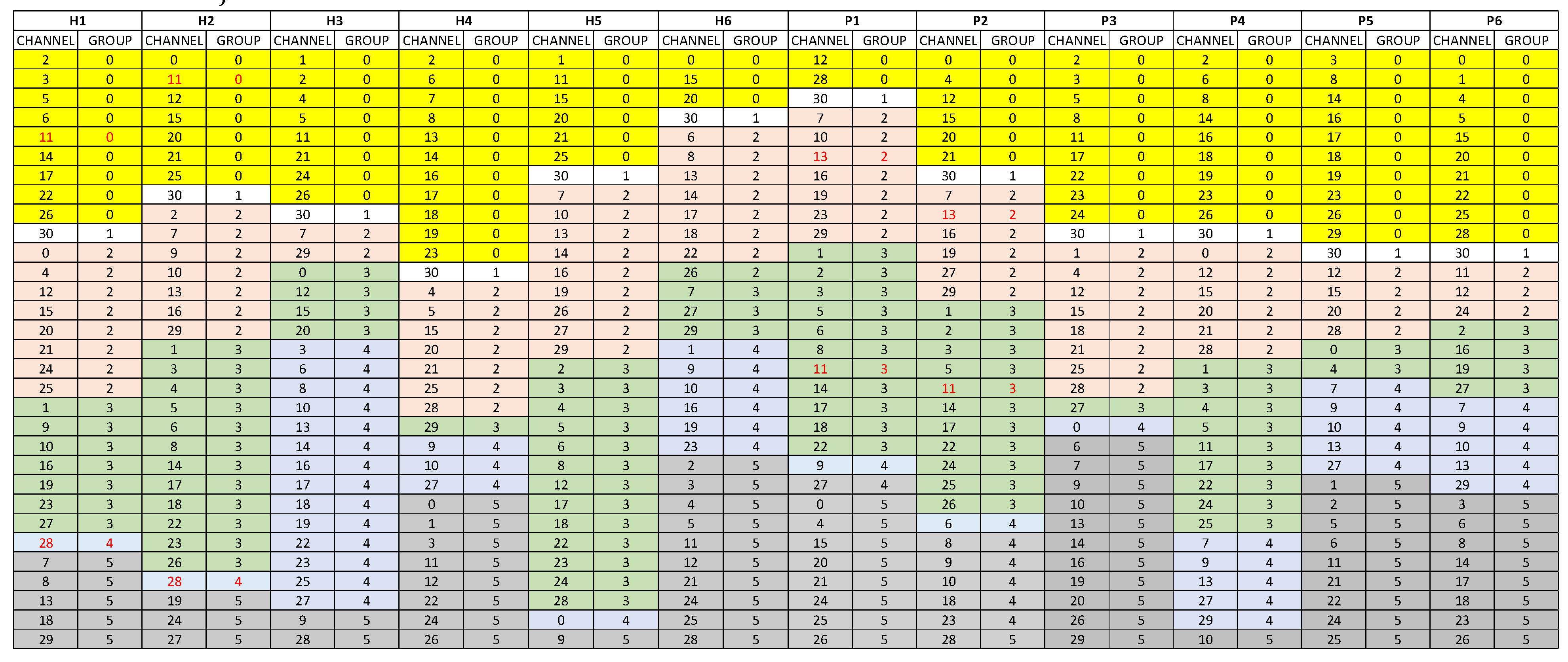
We use k-means to cluster channel time series into six groups within each subject. We computed k-means clusters for k=1-31, and based on the size of clusters, we noticed that 6 is the best For lower or higher number of clusters, many groups had only 2 or 3 channels and even there were some groups with no element. We used the Euclidean distance to find the clusters. We calculated the distance between channels and used k-means clustering to classify the channels. This clustering is repeated to determine groups of channels for each subject.
3.2. Linear SVM Classification
SVM identifies a hyperplane or decision boundary that separates instances (in this case channels) with maximum margin of the support vectors to separate instances into classes (in this case clusters) [
15]. The hyperplane for 12 subjects is specified by weights, are used to construct a new dataset.
In n-dimensional space, the vector
presents a combination of data points. Here, x is the vector of 31 channel cluster ids. The values of x can be integers 0 to 5, corresponding to six clusters. A 12 * 31 matrix for 12 subjects and 31 channels will be obtained. The main task of linear SVM is finding the linear model [
11]:
that is defined by the best hyper-lane:
and b need to be determined. It is equivalent to the objective of maximizing the margin:
So, the main factor that affects the classification is vector
which is the weight in the linear model. Assessment of this vector
can help to show how the data points are classified and how the classification is determined. The weights,
, indicate
the importance of each channel for separating the channels into 6 groups for a given subject [
3]
.
k-mean SVM boosting method was defined by Dr. Chen and his research group in 2013 [
16]. Then it was applied to predict the cancer by Dr. Kim in 2016 [
17].
SVM model is applied to each subject based on the k-means cluster labels of the EEG time series. Then, the weights (
) can be aggregated across subjects to construct a subject by weight dataset to test the most important channels for distinguishing between PTSD and healthy control (
Figure 1).
3.3. K-Mean SVM Method
For each subject, we cluster the EEG time series into six sets of channels by k-means.
Figure 2 shows the subjects and sets of channels in different colors.
We then apply SVM to each subject to classify the six sets of channels and identify hyperplane weights for each one. This results in a dataset (12 subjects x 31 channels) where each subject has an SVM weight for each channel.
Finally, we use this derived dataset to perform hypothesis testing (T-tests) to test channel weights that may distinguish between PTSD and controls.
4. Results and Discussion
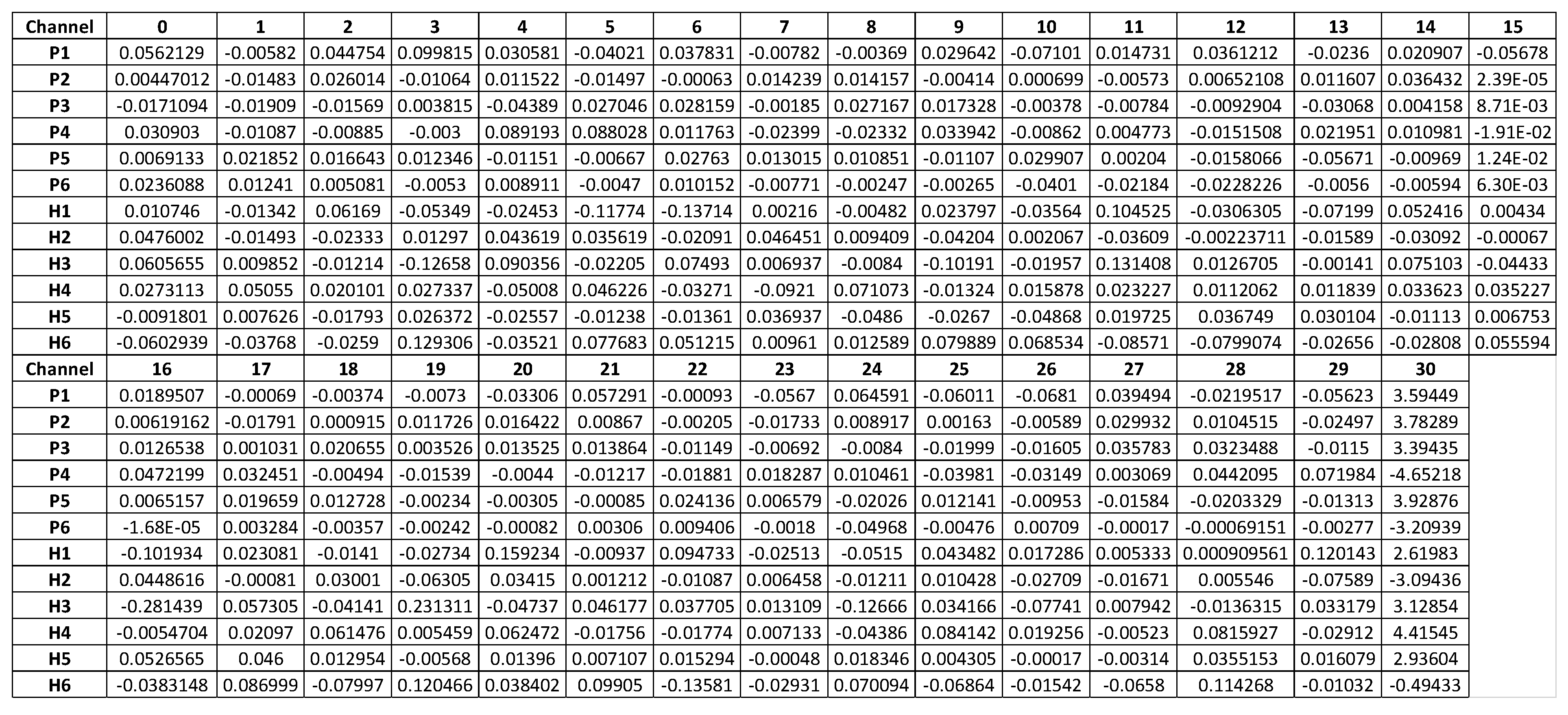
There are 6 healthy controls and 6 PTSD cases. In each subject, the data of 31 channels presented as a time-series dataset with a size of 31 x 50,000. After applying k-means (k =6) we applied SVM and then get 31 values of weight showing respectively the importance of 31 channels in classifying 6 clusters of 12 subjects. With the same combination of k-means and SVM, we got the fixed matrix of weights (size 12 x 31 for 31 channels in 12 data subjects). To compute the importance of each channel for differentiating healthy subjects and PTSD subjects, we compare how different the weight of each channel over 12 data subjects by 31 line graphs, matching respectively 31 channels. When we compare these 31 line graphs, we define a common pattern in 3 channels, F4, F8 and Pz. It is that more than 90% of weights in healthy controls are higher than in PTSD cases (
Figure 3). This may imply the significant difference between 2 groups of subjects, healthy and PTSD, which needs to be checked by Hypothesis Testing.
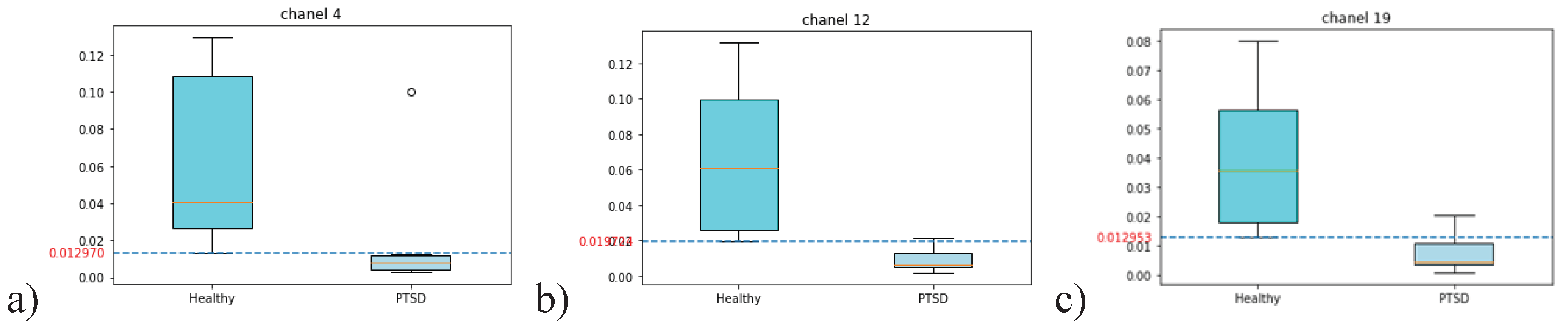
The weights of channel 4 (channel F4), channel 12 (channel F8) and channel 19 (channel Pz) are significantly higher in the healthy control group (H) versus PTSD (P) (
Figure 4). All channel weights are higher in healthy subjects than in PTSD subjects except for three values: subject P1 in channel 4 (F4), subject P5 in channel 8 (P4), and subject P3 in channel 19 (Pz).
In channel F4, all weights in healthy subjects are equal to or greater than 0.01297 while all of the weights in PTSD subjects are lower than this value (
Figure 3). The pattern is similar in channel F8 and Pz with the different bordering values of 0.019724 in channel F8 and 0.012953 in channel Pz.
We test the hypothesis of difference of channel weights between the healthy and PTSD groups using the Mann-Whitney U test (
Table 1).
The P-values of the Mann-Whitney U test for channels F4, F8, and Pz are statistically significant for average weights in healthy subjects ≠ average of weights in PTSD cases (
Table 1). These findings suggest that channels F4, F8, and Pz may differentiate PTSD and healthy controls based on our combination of machine-learning-based weight extraction method.
These results are consistent with previous reports for channels F4 and Pz as important channels to differentiate healthy and PTSD subjects [
12,
18]. The study by Rutter (2014) found F4 and Pz to be channels associated with the disorder [
18].
The main function of channel F4 is similar to channel F3; namely, motor planning for right arm while channel F4 mainly motor planning for left arm [
15]. This symmetry explains the similarity in channel F4 and channel F3 in discrimination of healthy and PTSD controls. Previous studies have reported association of these channels with PTST in Refs. and [
12]. Our previous Hurst exponent analysis found an association of channel F3 with PTSD [
1]. The current study suggests that channels F4, F8 and Pz are important factors in discrimination of healthy and PTSD subjects. These results may find practical application in the diagnosis of PTSD, and the channel weight construction approach may be useful in combination with other machine learning methods.
A study over veterans with PTSD syndrome confirmed our results about diagnostic F3-F4 channels [
19].
Data Availability Statement
All data will be released for the journal editors as supplementary attachments.
Acknowledgement
This paper and the research behind it would not have been possible without the exceptional support of Dr. Jerzy Bodurka who passed away on Friday, August 13, 2021. He provided the EEG data for our projects.
https://www.laureateinstitute.org/in-memoriam.html
References
- Bahareh Rahmani, Chung Ki Wong, Payam Norouzzadeh, Jerzy Bodurka, Brett McKinney. “Dynamical Hurst analysis identifies EEG channel differences between PTSD and healthy controls.” , PLOS One, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Paudel Bishnu Hari, Limbu Nirmala, Panta Raju, Ghimire Nisha, Shrestha Binu, Deo Santosh. Neurophysiology Application Notes (pp.7-18), Edition: 1, Chapter: Electroencephalography (EEG). 2012.
- Kristin Köhler-Forsberg, Anders Jorgensen, Vibeke H. Dam, Dea Siggaard Stenbæk, Patrick M. Fisher, Cheng-Teng, Melanie Ganz, Henrik Enghusen Poulsen, Annamaria Giraldi, Brice Ozenne, Martin Balslev Jørgensen, Gitte Moos Knudsen, and Vibe Gedsoe Frokjaer “Predicting Treatment Outcome in Major Depressive Disorder Using Serotonin 4 Receptor PET Brain Imaging, Functional MRI, Cognitive-, EEG-Based, and Peripheral Biomarkers: A NeuroPharm Open Label Clinical Trial Protocol,” Frontiers in Psychiatrics, 2020.
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing. Breslau, N., Peterson, E. L., Schultz, L. R., & Kessler, R. C. (1998). The Stressor Criterion in DSM-IV Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: An Empirical Investigation. Biological Psychiatry, 44(9), 1099-1105.
- Blake, D. D., Weathers, F. W., Nagy, L. M., Kaloupek, D. G., Klauminzer, G., Charney, D. S., & Keane, T. M. (1995). A clinician rating scale for assessing current and lifetime PTSD: The CAPS-1. Behavior Therapy, 26(1), 177-188.
- Foa, E. B., Cashman, L., Jaycox, L., & Perry, K. (1997). The validation of a self-report measure of posttraumatic stress disorder: The Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale. Psychological Assessment, 9(4), 445-451. [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, I., Martis, B., Phan, K. L., Liu, J., Taylor, S. F., & Falk, W. (2003). Frontolimbic brain activity in posttraumatic stress disorder: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1008(1), 236-240.
- Shin, L. M., Rauch, S. L., & Pitman, R. K. (2006). Interoception, emotion and the biological substrates of PTSD. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 8(1), 35-48.
- Mo H. Modarres, Ryan A. opel, Kristianna B. Weymann, Miranda M. Lim. Strong Correlation of Novel Sleep Electroencephalography Coherence Markers with Diagnosis and Severity of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. 2019.
- Jinho Kim, Jeong-Ho Chae, Hee-kyoung Ko, Charles-Francois Vincent Latchoumane, Aveek Banerjee, Donald J. Mandell, Christina W. Hoven, Jaeseung Jeong. Hemispheric Asymmetry in Non-Linear Interdependence of EEG In Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. 2012.
- Amin Zandvakili, Noah S.Philip, Stephanie R.Jones, Audrey R.Tyrka, Benjamin D.Greenberg, Linda L. Carpenter. Use of Machine Learning in Predicting Clinical Response to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Comorbid Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Major Depression: A Resting State Electroencephalography Study. 2019.
- Mulert C, Lemieux L. EEG-fMRI: Physiological Basis, Technique, and Applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. 2010.
- Analyser-2, Brain Vision supports all HD-EEG labs, https://brainvision.com/products/analyzer-2/.
- EEGLAB, Swartz Center for Computational Neuroscience, UC San Diego, Regents of the University of California, http://sccn.ucsd.edu/eeglab.
- Madeleine Bullock, Graeme D. Jackson, David F. Abbott, Artifact Reduction in Simultaneous EEG-fMRI: A Systematic Review of Methods and Contemporary Usage, Madeleine Bullock, Graeme D. Jackson, David F. Abbott, Frontiers in Neurology, 2021.
- Thomas F. Collura. “Functional Analysis Of MINI-Q II Positions, And Use with Live Z-Scores A Window To 4-Channel EEG Assessment and Training”. Brain Master Technologies, 2007.
- Yukai Yao, Yang Liu, Yongqing Yu, Hong Xu, Weiming Lv, Zhao Li, Xiaoyun Chen, K-SVM: An effective SVM algorithm based on K-means clustering, Journal of Computers 8(10), 2013.
- SungHwan Kim, Weighted K-means support vector machine for cancer prediction, Springerplus. 2016; 5(1): 1162. [CrossRef]
- Penijean Rutter, LMHC, BCN. Five Case Studies Using Live Z-Score Training Percent-Z Dk On Individuals Diagnosed With PTSD. 2012.
- Identification of Veterans With PTSD Based on EEG Features Collected During Sleep, Srinivas Laxminarayan, Chao Wang, Tatsuya Oyama, J. David Cashmere, Anne Germain, Jaques Reifman, Frontiers, Volume 11, 2020.
- Etkin, A., & Wager, T. D. (2007). Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: a meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(10), 1476-1488. [CrossRef]
- Felmingham, K. L., Williams, L. M., & Kemp, A. H. (2010). Changes in regional brain activation in response to emotional faces before and after treatment in posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 23(2), 259-266.
- Olff, M., Langeland, W., Draijer, N., & Gersons, B. P. (2007). The role of neuroimaging in understanding neurobiological mechanisms of PTSD. European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 28(1), 65-75.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).