Submitted:
29 March 2024
Posted:
31 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
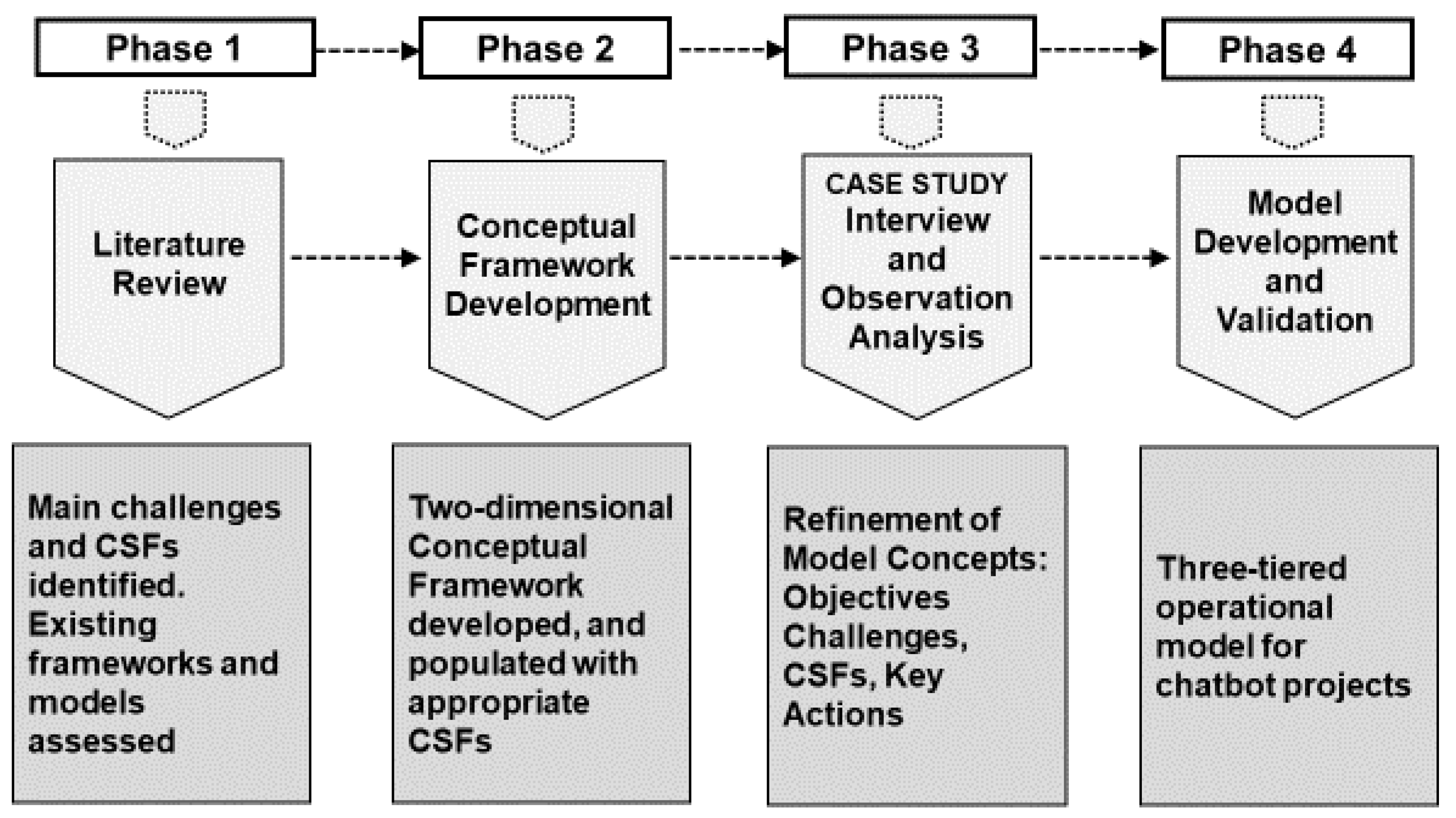
2. Research Method
2.1. The Case Study Approach and Research Philosophy
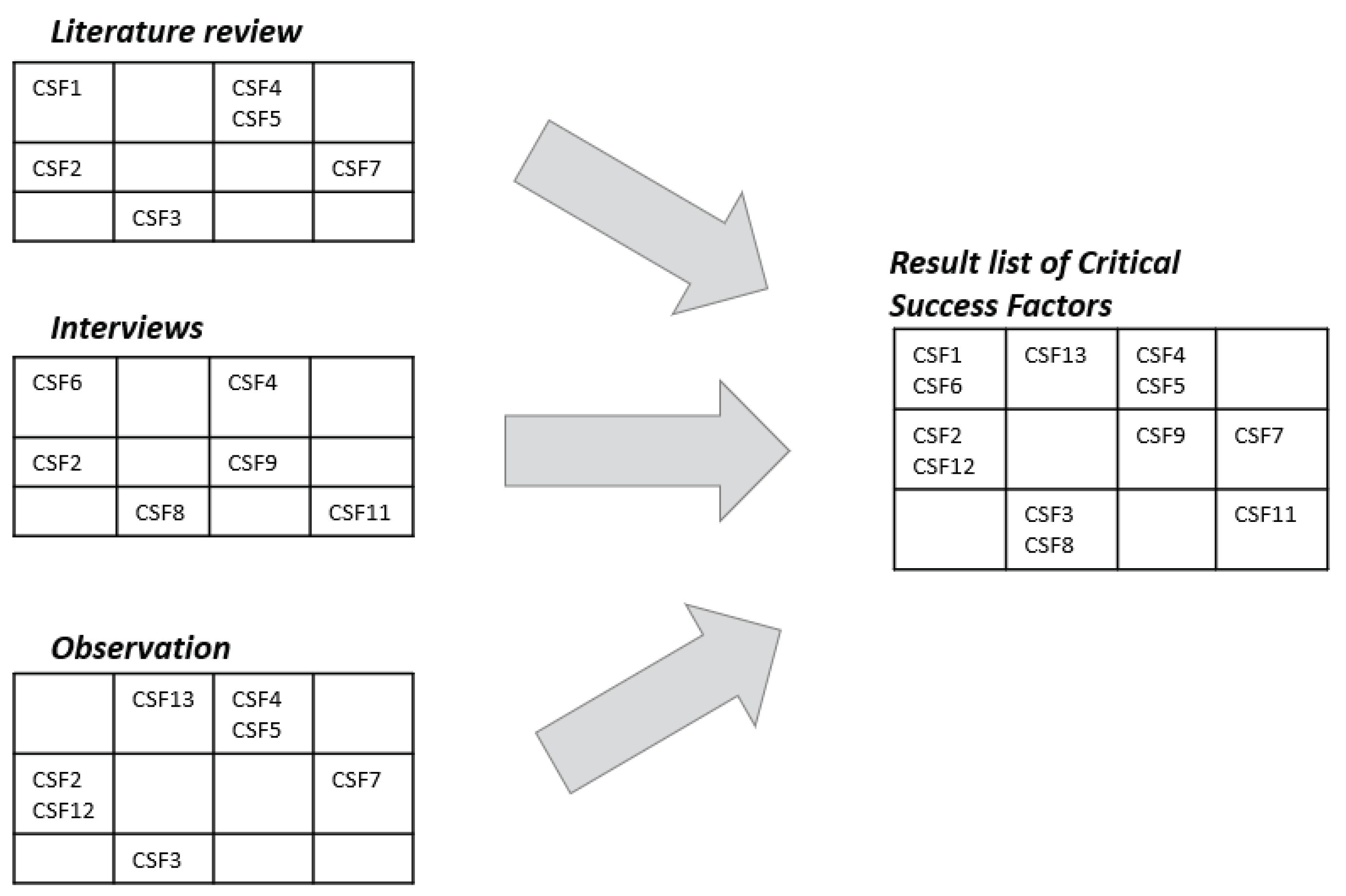
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Results Validation
3. Relevant Literature and Provisional Conceptual Framework
3.1. Chatbot Implementation Challenges
- Setup challenges. Activities related to obtaining, preparing and processing of big data, bot training, implementation and launch, support and maintenance.
- User/customer acceptance. Not all users are ready to interact with virtual agents. This situation is expected to gradually improve, so in the long term, such difficulties should not prevent the introduction of new technology.
- Language challenges. Effective communicating with users can be hampered by technical limitations, difficulties in understanding various accents, as well as the ability of developers to deal with natural language processing (NLP) tasks.
- Regulatory restrictions and data security. Both internal company guidelines and national or international regulations (for example, GDPR) can impact system architecture and methods of receiving and storing customer data. This complicates the process of developing virtual assistants in practice and increases the cost of implementation.
- Technology-related challenges need to be addressed. It is advisable to implement technologies from strong vendors that have mature solutions, innovative features, and flexible APIs for integration with other company systems.
- This categorisation overlaps considerably with the perspectives given by Srinivasan et al. [29] and other authors.
3.2. Critical Success Factors for Chatbot Projects
3.3. Relevant Models, Methods and Frameworks
3.5. Provisional Conceptual Framework
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. RQ1. What Are the Main Challenges Which Companies Face When Implementing Chatbot Projects?
4.2. RQ2. What Are the Critical Success Factors (CSFs) That Contribute to the Successful Implementation of Chatbots in Companies?
4.3. RQ3. What Operational Model can Support the Chatbot Implementation Process and Help Responsible Managers to Deliver Expected Chatbot Project Outcomes?
4.4. Model Application and Guidance
5. Conclusions
5.1. Contribution to the Theory and Practice
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McTear, M. Conversational AI, 1st ed.; Springer, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jurafsky, D.; Martin, J.H. Speech and Language Processing. In Speech and Language Processing; Taylor & Francis, 2010; pp. 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambridge Dictionary. https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/chatbot (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Hoy, M. Alexa, Siri, Cortana, and More: An Introduction to Voice Assistants. Medical Reference Services Quarterly 2018, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y. Neural Network Methods for Natural Language Processing. Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technologies 2017, 10, 1–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, A.; Sônego, A.; Pozzebon, E. Chatbots: An Analysis of the State of Art of Literature. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Advanced Virtual Environments and Education; 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805v2. [Google Scholar]
- Horev, R. BERT Explained: State of the art language model for NLP. Medium. November 17, 2018. https://towardsdatascience.com/bert-explained-state-of-the-art-language-model-for-nlp-f8b21a9b6270.
- Floridi, L.; Chiriatti, M. GPT-3: Its Nature, Scope, Limits, and Consequences. Minds and Machines 2020, 30, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. GPT-4. 2023, March 14. https://openai.com/research/gpt-4.
- Chui, M. The state of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s breakout year. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai-in-2023-generative-ais-breakout-year (accessed on 01 March 2024).
- Williams, S. Hands-On Chatbot Development with Alexa Skills and Amazon Lex: Create Custom Conversational and Voice Interfaces for Your Amazon Echo Devices and Web Platforms. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CB Insights. Lessons from the Failed Chatbot Revolution — And 7 Industries Where the Tech Is Making A Comeback. CB Insights Research 2021, January 14. https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/most-successful-chatbots/.
- Fach, P.; Tranker, N.; Schüssler, S. Deloitte Survey | Chat Talk Touch. Deloitte 2019, December 20. https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/de/Documents/financial-services/deloitte-survey-chat-talk-touch.pdf.
- Gwendal, D.; Cabot, J.; Deruelle, L.; Derras, M. Xatkit: A Multimodal Low-Code Chatbot Development Framework. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15332–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.; Grützner, L.; Breitner, M.H. Why do Chatbots fail? A Critical Success Factors Analysis. ICIS 2021 Proceedings.
- Skuridin, A. Chatbot Implementation in a Steel Company in Russia. In Handbook of Research on Digital Transformation, Industry Use Cases, and the Impact of Disruptive Technologies; Wynn, M., Ed.; IGI-Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R. Case Study Research. Design and Methods, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications Inc.: London, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.; Lewis, J. Qualitative Research Practice—A Guide for Social Science Students and Researchers; Sage Publications Ltd: London, Thousand Oaks, CA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guest, G.; Bunce, A.; Johnson, L. How Many Interviews Are Enough? An Experiment with Data Saturation and Variability. Field Methods. 2006, 18, pp. 59–82. Available online: http://fmx.sagepub.com/cgi/content/abstract/18/1/59 (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Kuzel, A. Sampling in qualitative inquiry. In Doing qualitative research; Crabtree, B., Miller, W., Eds.; SAGE Publications Ltd: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1992; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R. Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners, 4th ed.; Sage, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Trochim, W.M.K.; Donnelly, J.P. Research Methods Knowledge Base, 3rd ed.; Thomson Custom Pub, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, M.; Lewis, P.; Thornhill, A. Research Method for Business Students; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, United Kingdom, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guba, E.G.; Lincoln, Y.S. Competing Paradigms in Qualitative Research. In Handbook of Qualitative Research; Denzin, N.K., Lincoln, Y.S., Eds.; Sage Publications, Inc., 1994; pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, M.Q. Enhancing the Quality and Credibility of Qualitative Analysis. Health Serv. Res. 1999, 34 5 Pt 2, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, E.; Bryman, A.; Harley, B. Business Research Methods; Oxford University Press: Oxford, England, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, A.L.; Kongthon, A.; Lu, J.C. Research Profiling: Improving the Literature Review. Scientometrics 2002, 53, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Nguyen, C.; Tanguturi, P. Chatbots Are Here to Stay. Accenture, February 6, 2021. https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/pdf-77/accenture-research-conversational-ai-platforms.pdf.
- Kaushal, V.; Yadav, R. Exploring B2B Chatbots Adoption Experiences: Lessons for Successful Implementation in Businesses. Research Square. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmegani, C. An Assessment in 2022 For Why Chatbots Fail. AIMultiple, June 14, 2022. https://research.aimultiple.com/why-chatbots-fail/.
- Varitimiadis, S.; Kotis, K.; Pittou, D.; Konstantakis, G. Graph-Based Conversational AI: Towards a Distributed and Collaborative Multi-Chatbot Approach for Museums. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drift. The State of Chatbots Report: How Chatbots Are Reshaping Online Experiences. Drift, January 23, 2018. https://www.drift.com/blog/chatbots-report/.
- Atkinson, R. Project Management: Cost, Time, and Quality, Two Best Guesses and a Phenomenon, It’s Time to Accept Other Success Criteria. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1999, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockart, J.F. Chief Executives Define Their Own Data Needs. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1979, 57, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bullen, C.; Rockart, J. A Primer on Critical Success Factors. Sloan School of Management, 1981.
- Franke, A. How May A.I. Assist You? KPMG, January 10, 2018. https://advisory.kpmg.us/articles/2018/how-may-ai-assist-you.html.
- Henke, N.; Bughin, J.; Chui, M.; Manyika, J.; Saleh, T.; Wiseman, B.; Sethupathy, G. The Age of Analytics: Competing in a Data-Driven World. McKinsey & Company, December 20, 2016. https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Industries/Public%20and%20Social%20Sector/Our%20Insights/The%20age%20of%20analytics%20Competing%20in%20a%20data%20driven%20world/MGI-The-Age-of-Analytics-Full-report.pdf.
- Sengupta, R.; Lakshman, S. Conversational Chatbots – Let's Chat. Deloitte, February 6, 2017. https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/in/Documents/strategy/in-strategy-innovation-conversational-chatbots-lets-chat-final-report-noexp.pdf.
- Bakhshi, N.; van den Berg, H.; Broersen, S.; de Vries, D.; El Bouazzaoui, H.; Michels, B. Chatbots Point of View. Deloitte, 2018. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/nl/Documents/deloitte-analytics/deloitte-nl-chatbots-moving-beyond-the-hype.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Robinson, M.; Gray, J.; Cowley, A.; Tan, R. Adopting the Power of Conversational UX. Deloitte, 2017. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/nl/Documents/financial-services/deloitte-nl-fsi-chatbots-adopting-the-power-of-conversational-ux.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Dasgupta, A.; Wendler, S. AI Adoption Strategies; Working Paper Series, No. 9; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bughin, J.; Hazan, E.; Ramaswamy, S.; Chui, M.; Allas, T.; Dahlström, P.; Henke, N.; Trench, M. Artificial Intelligence: The Next Digital Frontier? McKinsey Global Institute, 2017. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/advanced%20electronics/our%20insights/how%20artificial%20intelligence%20can%20deliver%20real%20value%20to%20companies/mgi-artificial-intelligence-discussion-paper.ashx (accessed on 01 March 2024).
- Fokina, M. The Future of Chatbots: 80+ Chatbot Statistics for 2023. Tidio, January 18, 2023. https://www.tidio.com/blog/chatbot-statistics/.
- Brandtzaeg, P.B.; Folstad, A. Why People Use Chatbots. In Internet Science; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Isbister, K.; Nass, C. Consistency of personality in interactive characters: verbal cues, non-verbal cues, and user characteristics. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 2000, 53, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S. The Ultimate Guide to Chatbot Personality. Chatbots Magazine, November 20, 2019. Available at: https://chatbotsmagazine.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-chatbot-personality-b9665ab5e99d (accessed on 20 March, 2021).
- Liew, T.W.; Tan, S. Virtual Agents with Personality: Adaptation of Learner-Agent Personality in a Virtual Learning Environment. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eleventh International Conference on Digital Information Management (ICDIM); pp. 157–162.
- Ruane, E.; Farrell, S.; Ventresque, A. User Perception of Text-Based Chatbot Personality. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; 2021; pp. 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smestad, T.L. Personality Matters! Improving the User Experience of Chatbot Interfaces - Personality Provides a Stable Pattern to Guide the Design and Behaviour of Conversational Agents. 2018.
- Overend, R.; Stefanoff, S.; Jackson, P.; Rayment, S.; Cooper, S.; Taylor, D. Conversational AI. The Next Wave of Customer and Employee Experiences. Deloitte, 2019. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/au/Documents/strategy/au-deloitte-conversational-ai.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2023).
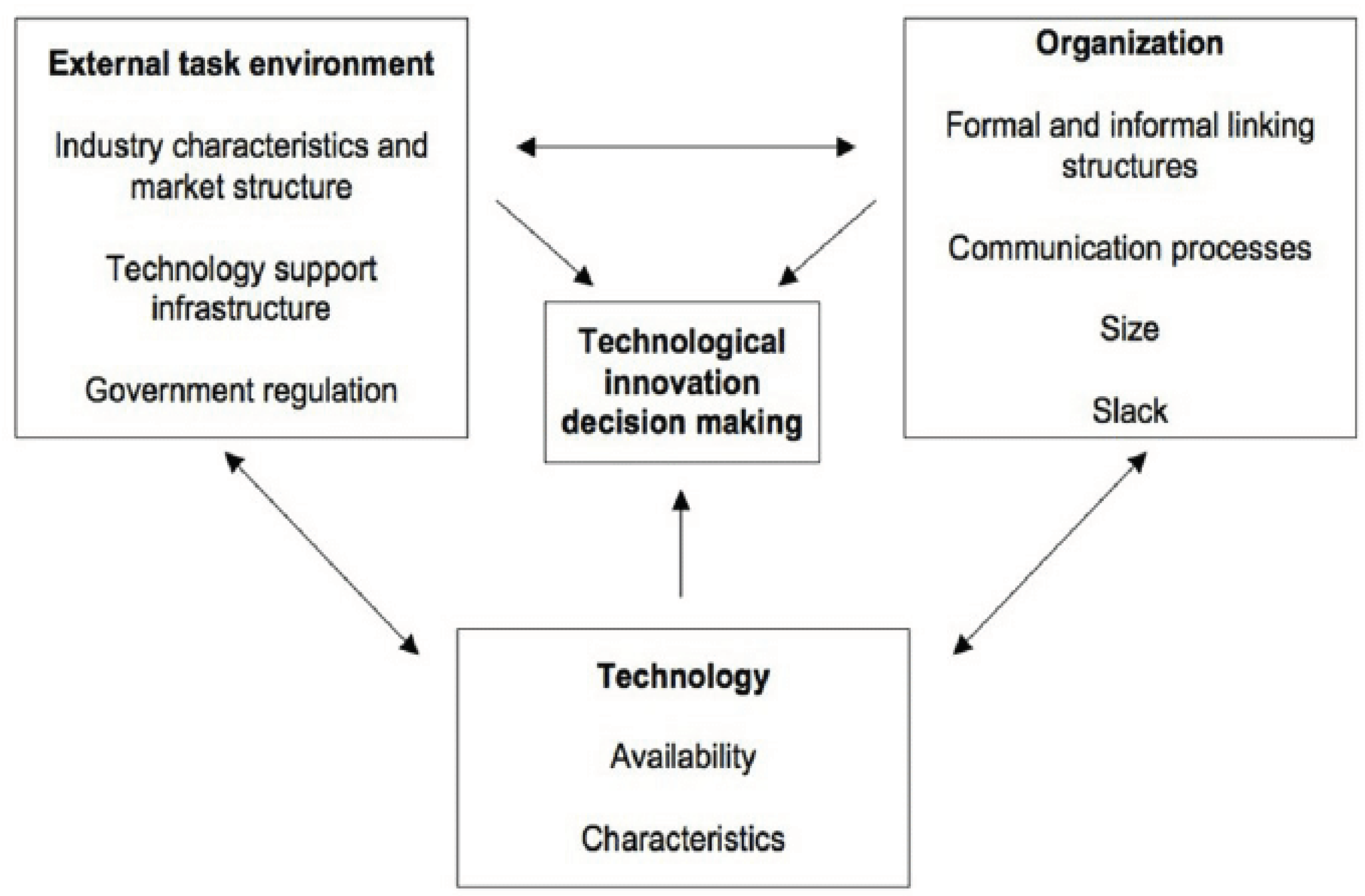
- DePietro, D.; Wiarda, E.; Fleischer, M. Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington Books: Massachusetts, MA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Awa, H.O.; Ukoha, O.; Emecheta, B.C. Using T-O-E Theoretical Framework to Study the Adoption of ERP Solution. Cogent Business & Management 2016, 3, 1196571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racherla, P.; Hu, C. ECRM System Adoption by Hospitality Organizations: A Technology-Organization-Environment (TOE) Framework. J. Hosp. & Leis. Mark. 2008, 17, 30–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Martins, M.F.O. Understanding the Determinant Factors of Internet Business Solutions Adoption: The Case of Portuguese Firms. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’in, V.I.; Ivetić, J.; Simić, D. Understanding the Determinants of E-Business Adoption in ERP-Enabled Firms and Non-ERP-Enabled Firms: A Case Study of the Western Balkan Peninsula. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 125, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, M.; Bakeer, A.; Forti, Y. E-Government and Digital Transformation in Libyan Local Authorities. Int. J. Teach. and Case Stud. 2021, 12, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, M.J. Management Strategies for Information Technology, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J. Project Managing the SDLC: Using Milestones to Align Project Management and System Development Lifecycles and Report Project Success. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2004, North America, Anaheim, CA; Project Management Institute: Newtown Square, PA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Buede, D.M.; Miller, W.D. The Engineering Design of Systems: Models and Methods; Wiley, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, E.C. Software Engineering: A Methodical Approach; Apress, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.M.; Steyn, H. Project Management for Engineering, Business, and Technology, 5th ed.; Routledge: London, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Atlassian. What is the Agile methodology? Atlassian. https://www.atlassian.com/agile (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Dingsoyr, T.; Nerur, S.; Balijepally, V.; Moe, N.B. A Decade of Agile Methodologies: Towards Explaining Agile Software Development. J. Syst. Softw. 2012, 85, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J. Scrum: A Revolutionary Approach to Building Teams, Beating Deadlines, and Boosting Productivity; Random House, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ries, E. Minimum Viable Product: A Guide. Startup Lessons Learned, August 3, 2009. Available at: http://www.startuplessonslearned.com/2009/08/minimum-viable-product-guide.html (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Abrahamsson, P.; Conboy, K.; Wang, X.; Baskerville, R.; Fitzgerald, B.; Morgan, L. Agile Processes in Software Engineering and Extreme Programming; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, A.; Salwan, S.; Thakker, V. Chatbots. Riding the Next-Gen Technology Wave to Operational Success. Deloitte, 2019. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/in/Documents/technology-media-telecommunications/in-tmt-chatboats-noexp.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Guenole, N.; Feinzig, S. The Business Case for AI in HR. IBM Watson Talent, 2018. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/AGKXJX6M (accessed on 2 March 2024).
| Interviewee code | Job title | Industry | Country | Interview language | Internal or external |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Project manager | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 02 | Project manager | IT integration | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 03 | Analyst | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 04 | Analyst | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 05 | Senior Marketing Manager | Pharmaceutical | Germany | English | External |
| 06 | Business Processes Director | Pharmaceutical | Germany | English | External |
| 07 | Project manager | Banking | Russia | Russian | External |
| 08 | Product owner | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 09 | Analyst | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 10 | Marketing director | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 11 | CRM director | Online retail | Russia/China | Russian | External |
| 12 | Director | Metallurgy | Russia | Russian | Internal |
| 13 | IT Director | Online retail | Russia | Russian | External |
| 14 | IT Director | Fintech | Russia | Russian | External |
| 15 | IT developer | Online retail | Russia | Russian | External |
| Expert No. | Was involved as an interviewee? | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Yes | Senior IT manager and department head in a large company. Responsible for managing a programme of new IS integration projects including CRM, e-commerce platforms, AI application and chatbots. Experienced methodologist who organised the production of IT projects in an international IT integrator. Participated in several chatbot implementation projects as project leader. |
| 02 | No | Head of project implementation department in a large IT integrator. Leads the development of multiple projects including new CRM integration, website development and chatbot integration. |
| 03 | No | Professor in Digital Skills with experience in AI, cyber security, and data science. |
| 04 | Yes | Director of digital transformation in a large enterprise. Responsible for managing a programme of IT projects including ERP, CRM, websites and various AI application projects including chatbots. Previously involved in several chatbot implementation projects, either as project lead or key stakeholder. Holds a PhD. |
| 05 | No | IT Director in a medium-sized company. Experienced in managing IS integration projects that include ERP, CRM, eCommerce platforms, AI applications and chatbots. |
| No. | Critical success factor |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify use cases and assess suitability of using a conversational User Interface (UI) [37,38,39] |
| 2 | Focus on one business objective [40,41] |
| 3 | Analyse integration capabilities of the selected platform [37,40] |
| 4 | Define business value metrics aligned to the organisation strategy [37] |
| 5 | Consider security and compliance requirements [29] |
| 6 | Explore vendor options in selected industry field and locality [40] |
| 7 | Analyse build and buy approaches to define the strategy [42] |
| 8 | Use the buy (not build) approach and explore your local vendors [42] |
| 9 | Choose a platform that can provide detailed reports about chatbot performance [40] |
| 10 | Offer users an option to chat in their favourite messenger and provide multiple messenger support [39] |
| 11 | Apply agile iterative approach and MVP method [38,40,41] |
| 12 | Design an experience that provides value for both to the customer and business [41] |
| 13 | Use information about the customers to offer personalised service [43,44] |
| 14 | Focus on chatbot productivity. The ease, speed, and convenience of using chatbots is vital. Bots should solve users’ problems in a more efficient way than any other communication channel [41,45] |
| 15 | Use entertainment elements and social interaction elements for additional motivation [45] |
| 16 | Design chatbot personality [37,39,44,46,47,48,49,50] |
| 17 | Evaluate performance and identify which requests were not processed properly [40,41] |
| 18 | Invest time and resources in bot training [38,41,51] |
| 19 | Blended communication enables excellent service. Switch dialog to a human when a bot can't handle a user's request [34,39,44] |
| 20 | Create dashboard that displays key chatbot performance metrics [41] |
| 21 | Study the users' needs by collecting feedback and plan new features accordingly [37,41] |
| 22 | Continuously improve the chatbot by applying recent AI technologies [41] |
| 23 | Advertise bot’s capabilities to its users [37] |
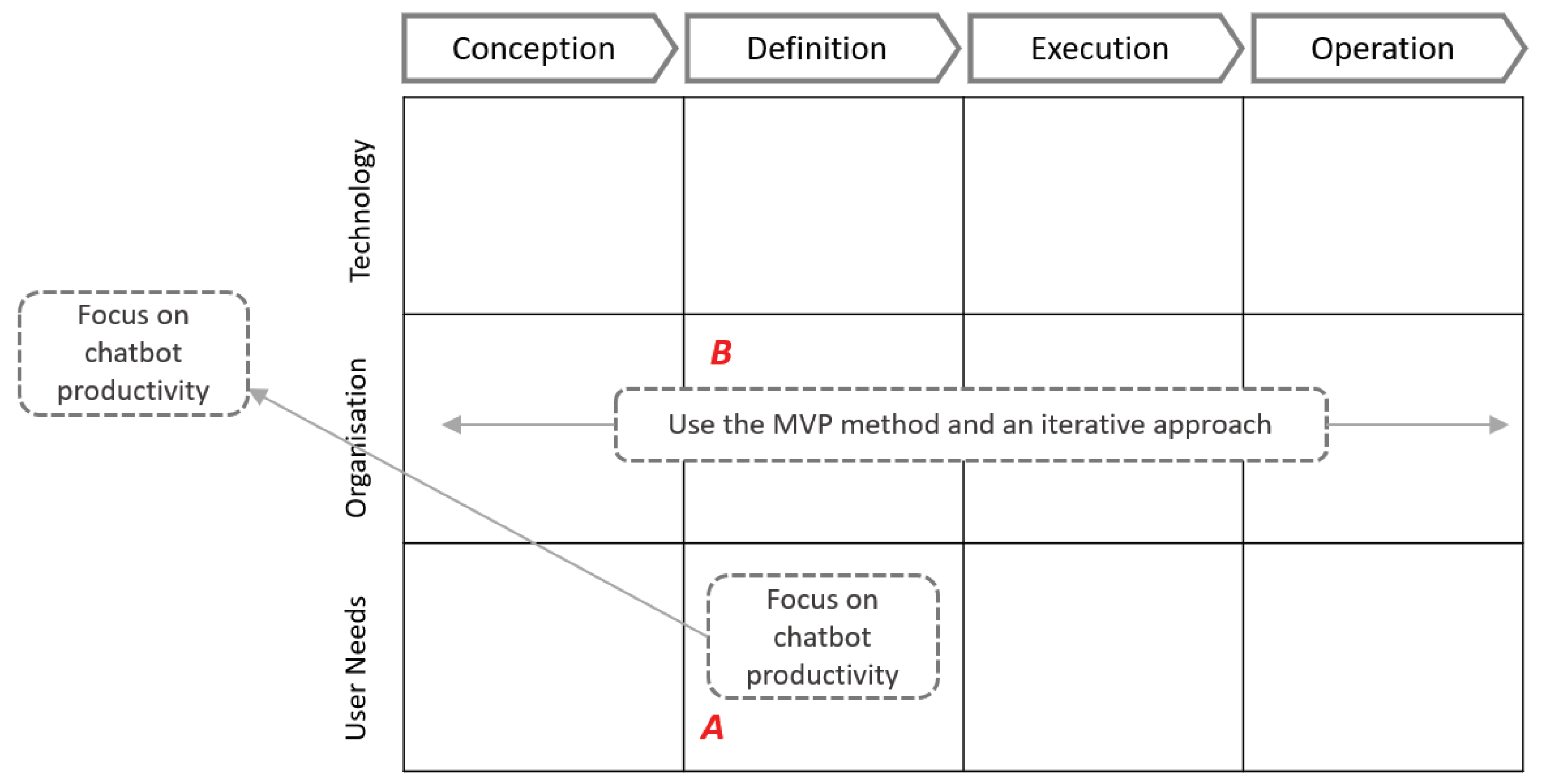
| Project Stages/Change Categories | Conception | Definition | Execution | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Analyse build and buy approaches to define the strategy Explore vendor options in selected industry field and locality Analyse integration capabilities of the selected platform Choose a platform that can provide detailed reports about chatbot performance |
Consider security and compliance requirements Offer users an option to chat in their favourite messenger and provide multiple messenger support |
Create dashboard that displays key chatbot performance metrics | Continuously improve the chatbot by applying recent AI technologies |
| Organisation | Identify use cases and assess suitability of using conversational User Interface Focus on one business objective Define business value metrics aligned to the organisation strategy |
Apply agile iterative approach and MVP method | Invest time and resources in bot training Advertise bot’s capabilities to its users |
|
| User Needs | Design an experience that provides value for both to the customer and business Use information about the customers to offer personalised service Apply blended communication approach |
Focus on chatbot productivity. The ease, speed, and convenience of using chatbots is vital Use entertainment elements and social interaction elements for additional motivation Design chatbot personality |
Evaluate performance and identify which requests were not processed properly Study the users' needs by collecting feedback and plan new features accordingly |
| No. | Challenge | Score |
|---|---|---|
| TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY | ||
| Challenge 1 | Complexity and amount of system integration work. | 23 |
| Challenge 2 | Difficulty in finding the best product and vendor which can solve your problem and will offer its service for a long time | 15 |
| Challenge 3 | Overall complexity of chatbot projects and necessity to deal with many software systems and IT technologies | 13 |
| Challenge 4 | Chatbots require much calculation resources. Many companies are not ready to purchase required hardware | 10 |
| Challenge 5 | Few companies are able to collect, analyse and use their internal data to develop appropriate chatbot behaviour | 9 |
| Challenge 6 | The complexity of regulation and information security tasks | 9 |
| Challenge 7 | Current chatbot technologies are complex but not yet perfect and bots often fail to process users' requests properly | 9 |
| Challenge 8 | The license and support costs of a chatbot systems from leading vendors is too high, what forces teams to create their own solution | 6 |
| ORGANISATION CATEGORY | ||
| Challenge 9 | Difficulty in formulating project objectives, success criteria and measuring KPIs | 24 |
| Challenge 10 | Lack of in-house chatbot expertise and limited availability of relevant specialists in the market | 21 |
| Challenge 11 | Top managers are often underestimate chatbot integration projects complexity and costs and not ready to invest significant budget in a new technology adoption | 17 |
| Challenge 12 | Planning and managing chatbot projects is challenging due to their unpredictability and high uncertainty | 11 |
| Challenge 13 | Low quality of integration services provided by vendors and IT integrators | 10 |
| USER NEEDS CATEGORY | ||
| Challenge 14 | User scepticism about the capabilities of chatbots and unwillingness to interact with them | 27 |
| Challenge 15 | User behaviour in chats is very different from other channels like phone, website, mobile app. High-quality UX design skills and user training are required. | 11 |
| Challenge 16 | The scenario-based approach for creating bots prevails, but limits their capabilities | 8 |
| Challenge 17 | Difficulty in creating a chatbot which solves the company’s problem and provides users with an excellent service the same time. | 4 |
| Project Stages/Change Categories | Conception | Definition | Execution | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Identify and choose the most suitable technology and vendor which meet your business requirements. (Score=26) Explore vendor options and external service availability in your field and locality. (Score=24) Choose a platform that can provide detailed reports about your chatbot performance. (Score=19) Analyse build and buy approaches to define your strategy. (Score=17) Analyse API of the selected platform and how to integrate it with the company's IS. (Score=10) Study project portfolio of vendor candidates, request recommendations from their clients. (Score=9) The selected platform should have a powerful dialog editor. (Score=6) |
Invest in analysis and planning of system integration and data migration tasks. (Score=23) Define scalability requirements and realistically estimate the required hardware. (Score=13) Obtain necessary access to IS and solve information security issues. (Score=13) Strategically plan the compatibility of the bot platform with the company's internal IT systems. (Score=12) Make sure you know exactly how you can develop the bot on your own or change the integrator company, if necessary. (Score=8) Formulate comprehensive functional requirements that determine the result. (Score=5) |
Create dashboard for tracking chatbot behavioural metrics and success indicators after the launch. (Score=11) Perform load testing, plan and prepare infrastructure for high load. (Score=9) Prepare and use development, testing and production environment. (Score=9) Use SLAs (service level agreements) to set performance requirements for involved IS. (Score=6) |
Monitor a chatbot availability and usage. (Score=19) Continuously improve the chatbot by applying recent AI technologies, updating language models, and installing the platform updates. (Score=14) |
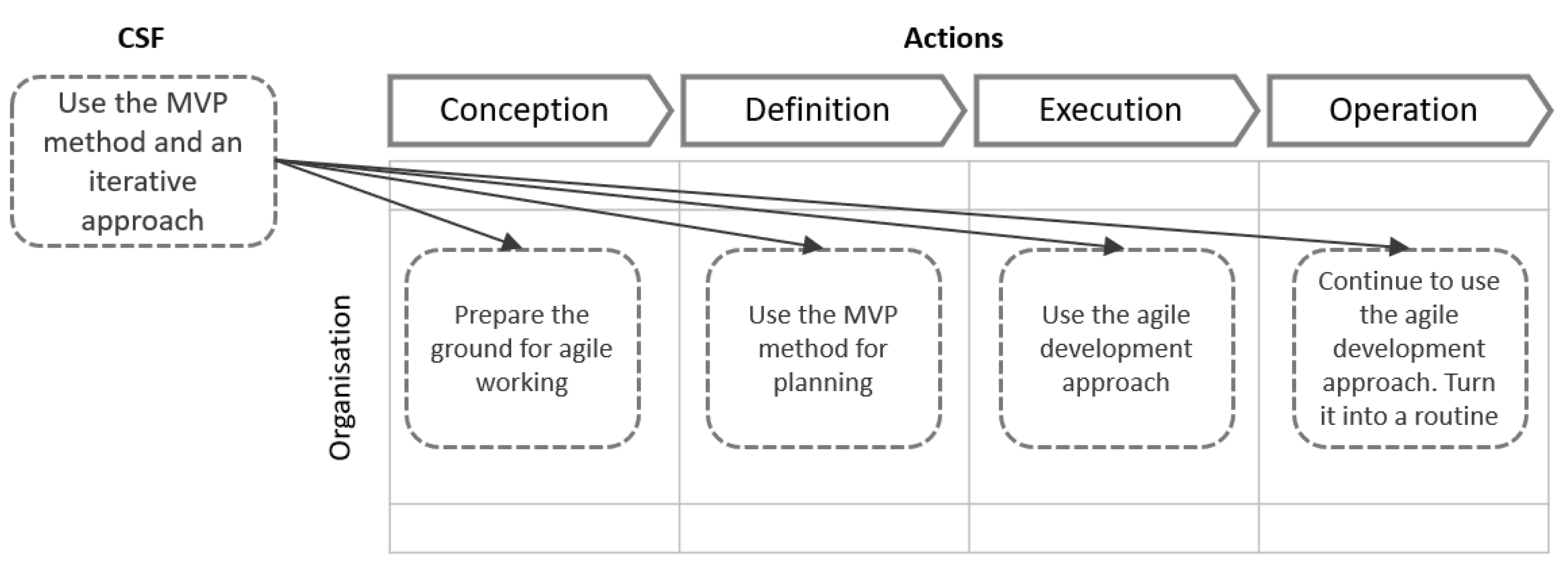
| Organisation | Identify your aim, key success indicators and associated improvement metrics. (Score=24) Identify use cases and assess suitability of using a conversational UI. (Score=19) Find an expert to join your team. (Score=10) Prepare the ground for agile working. (Score=9) |
Form a product team on the company's side which includes a product owner, analyst or dialog designer, data scientist, UX-designer, technical leader. (Score=23) Use the MVP method and an iterative approach. (Score=18) Find a responsible project leader from the business team who has the necessary expertise. (Score=9) Involve top management into the process. (Score=6) Communicate your aim to your team, contractors, and top management. (Score=5) |
Apply an agile iterative approach and MVP method. (Score=23) Define the chatbot maintenance team, their responsibilities and train the key users. (Score=9) Test your bot internally with your team, and with business experts in the company. (Score=7) Pay attention to project control, reporting and communication with the contractor. (Score=4) |
Collect dialog data and invest time and resources in bot training. (Score=13) Develop the chatbot expertise and grow your team in-house. (Score=9) Continue to use the agile development approach. Turn it into a routine. (Score=9) Make sure that the chatbot systems are accepted by IT support technical specialists. (Score=7) Advertise bot features and share success stories within your company. (Score=5) |
| User Needs | Focus on one business objective. (Score=20) Analyse alternatives to the chatbot service. Specify why the chatbot is the best way to solve your problem. (Score=13) Make sure the chatbot is not only good for the company but designed to make the customer’s life better. (Score=10) Make sure the chatbot is the most convenient way for users to solve their problems. (Score=5) |
Focus on chatbot productivity. The ease, speed, and convenience of using chatbots are vital. (Score=16) Use CJM and Jobs-To-Be-Done methods to capture user experience and specify chatbot requirements. (Score=16) Choose the “easy-to-develop” functionality. Publish limited but well-developed functionality. (Score=14) Design a chatbot personality which fits your brand communication style. (Score=13) Focus on intuitive and simple UX. (Score=9) Apply blended communication approach. (Score=9) Plan methods and tools for collecting user feedback. (Score=8) |
Test every product iteration on a small pilot group of real customers using real data. (Score=23) Test UX and employ measurement tools which your platform offers. (Score=13) Determine your bot personality which fits your brand communication style. (Score=10) |
Monitor chatbot performance and identify which requests were not processed properly. (Score=23) Study your user needs by collecting feedback and plan new features accordingly. (Score=20) Monitor chatbot behavioural metrics and success indicators. Ensure that the chatbot achieves its objectives. (Score=20) Advertise bot capabilities to its users and create respective promotion plan. (Score=15) Collect qualitative data about chatbot performance to improve functionality. (Score=12) |
|
Objective |
 |
||||
 |
|||||
| CSFs | 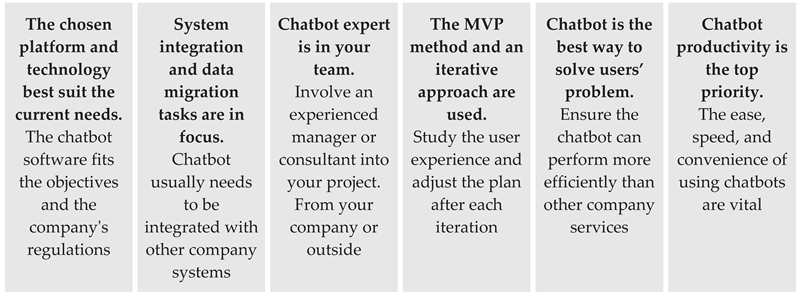 |
||||
 |
|||||
| Conception ► | Definition ► | Execution ► | Operation ► | ||
| Recommended Key Actions | Technology | Identify and choose the most suitable technology and vendor which meet your business requirements. (Score=26) Explore vendor options and external service availability in your field and locality. (Score=24) Choose a platform that can provide detailed reports about your chatbot performance. (Score=19) Analyse build and buy approaches to define your strategy. (Score=17) Analyse API of the selected platform and how to integrate it with the company's IS. (Score=10) Study project portfolio of vendor candidates, request recommendations from their clients. (Score=9) The selected platform should have a powerful dialog editor. (Score=6) |
Invest in analysis and planning of system integration and data migration tasks. (Score=23) Define scalability requirements and realistically estimate the required hardware. (Score=13) Obtain necessary access to IS and solve information security issues. (Score=13) Strategically plan the compatibility of the bot platform with the company's internal IT systems. (Score=12) Make sure you know exactly how you can develop the bot on your own or change the integrator company, if necessary. (Score=8) Formulate comprehensive functional requirements that determine the result. (Score=5) |
Create dashboard for tracking chatbot behavioural metrics and success indicators after the launch. (Score=11) Perform load testing, plan and prepare infrastructure for high load. (Score=9) Prepare and use development, testing and production environment. (Score=9) Use SLAs (service level agreements) to set performance requirements for involved IS. (Score=6) |
Monitor a chatbot availability and usage. (Score=19) Continuously improve the chatbot by applying recent AI technologies, updating language models, and installing the platform updates. (Score=14) |
| Organisation | Identify your aim, key success indicators and associated improvement metrics. (Score=24) Identify use cases and assess suitability of using a conversational UI. (Score=19) Find an expert to join your team. (Score=10) Prepare the ground for agile working. (Score=9) |
Form a product team on the company's side which includes a product owner, analyst or dialog designer, data scientist, UX-designer, technical leader. (Score=23) Use the MVP method and an iterative approach. (Score=18) Find a responsible project leader from the business team who has the necessary expertise. (Score=9) Involve top management into the process. (Score=6) Communicate your aim to your team, contractors, and top management. (Score=5) |
Apply an agile iterative approach and MVP method. (Score=23) Define the chatbot maintenance team, their responsibilities and train the key users. (Score=9) Test your bot internally with your team, and with business experts in the company. (Score=7) Pay attention to project control, reporting and communication with the contractor. (Score=4) |
Collect dialog data and invest time and resources in bot training. (Score=13) Develop the chatbot expertise and grow your team in-house. (Score=9) Continue to use the agile development approach. Turn it into a routine. (Score=9) Make sure that the chatbot systems are accepted by IT support technical specialists. (Score=7) Advertise bot features and share success stories within your company. (Score=5) |
|
| User Needs | Focus on one business objective. (Score=20) Analyse alternatives to the chatbot service. Specify why the chatbot is the best way to solve your problem. (Score=13) Make sure the chatbot is not only good for the company but designed to make the customer’s life better. (Score=10) Make sure the chatbot is the most convenient way for users to solve their problems. (Score=5) |
Focus on chatbot productivity. The ease, speed, and convenience of using chatbots are vital. (Score=16) Use CJM and Jobs-To-Be-Done methods to capture user experience and specify chatbot requirements. (Score=16) Choose the “easy-to-develop” functionality. Publish limited but well-developed functionality. (Score=14) Design a chatbot personality which fits your brand communication style. (Score=13) Focus on intuitive and simple UX. (Score=9) Apply blended communication approach. (Score=9) Plan methods and tools for collecting user feedback. (Score=8) |
Test every product iteration on a small pilot group of real customers using real data. (Score=23) Test UX and employ measurement tools which your platform offers. (Score=13) Determine your bot personality which fits your brand communication style. (Score=10) |
Monitor chatbot performance and identify which requests were not processed properly. (Score=23) Study your user needs by collecting feedback and plan new features accordingly. (Score=20) Monitor chatbot behavioural metrics and success indicators. Ensure that the chatbot achieves its objectives. (Score=20) Advertise bot capabilities to its users and create respective promotion plan. (Score=15) Collect qualitative data about chatbot performance to improve functionality. (Score=12) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





