1. Introduction
Modern dental prosthetic crowns predominantly utilize ceramic materials and their composites, chosen based on aesthetic and mechanical requirements, often involving tradeoffs. Among available options, dental zirconias are renowned for their superior strength and wear resistance, albeit potentially presenting challenges in machinability and aesthetics compared to less robust materials such as glass-ceramics or ceramic-polymer composites [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8].
Zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate (ZLS) materials represent an advancement in dental glass-ceramics, offering enhanced strength and durability while maintaining excellent aesthetics. This is achieved by incorporating 10% zirconium oxide to the glass matrix to bolster strength and by limiting the size of lithium silicate crystallites [
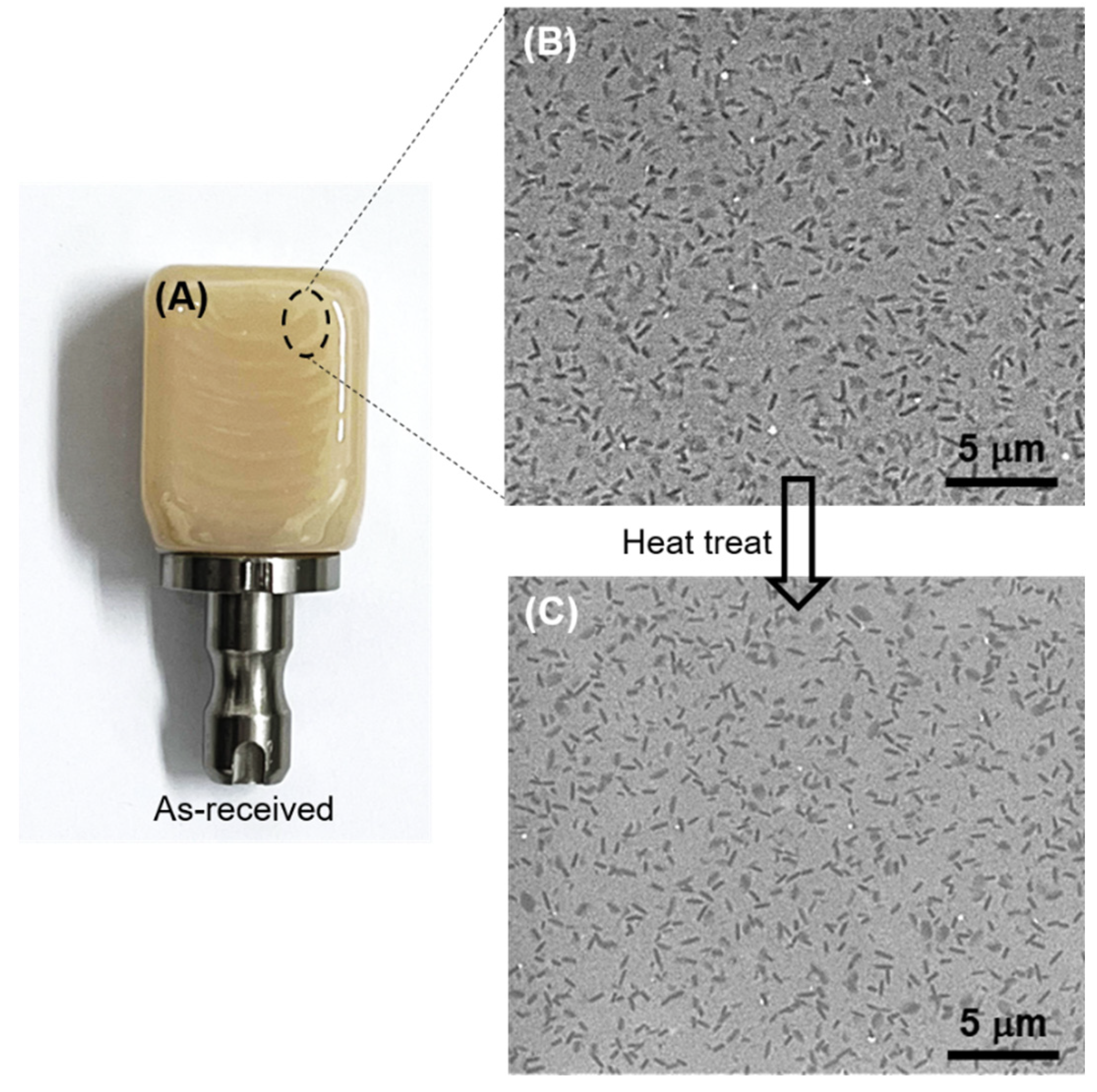
9]. Commercial ZLS dental materials are typically sourced in blocks (
Figure 1(A)) ready for use in computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) dentistry. According to the manufacturer specifications [
9], one of such ZLS materials can be employed in as-received, already fully-crystallized condition which possess a natural tooth colour. An optional heat treatment (post-processing) is recommended to further enhance flexural and biaxial fracture strength by approximately ~150/160 MPa without changing the aesthetics.
A gap in the literature exists regarding the systematic examination of how post-processing treatments may impact the contact damage (
e.g., fracture-induced chipping) of ZLS dental materials, beyond conventional mechanical property measurements. This is relevant because dental prosthetic crowns experience cyclic contacts against opposing dentition during chewing, involving a complex combination of axial and lateral forces, occasional bite overloads, and exposure to aggressive media where micron-sized abrasive particles may be present [
6,
10,
11]. Mechanical degradation in the form of fracture and wear in turn has the potential to compromise the performance, strength and durability of the crown. Notably, the ability to resist mechanical degradation does not necessarily correlate with single-valued mechanical properties as measured from standardized tests [
8].
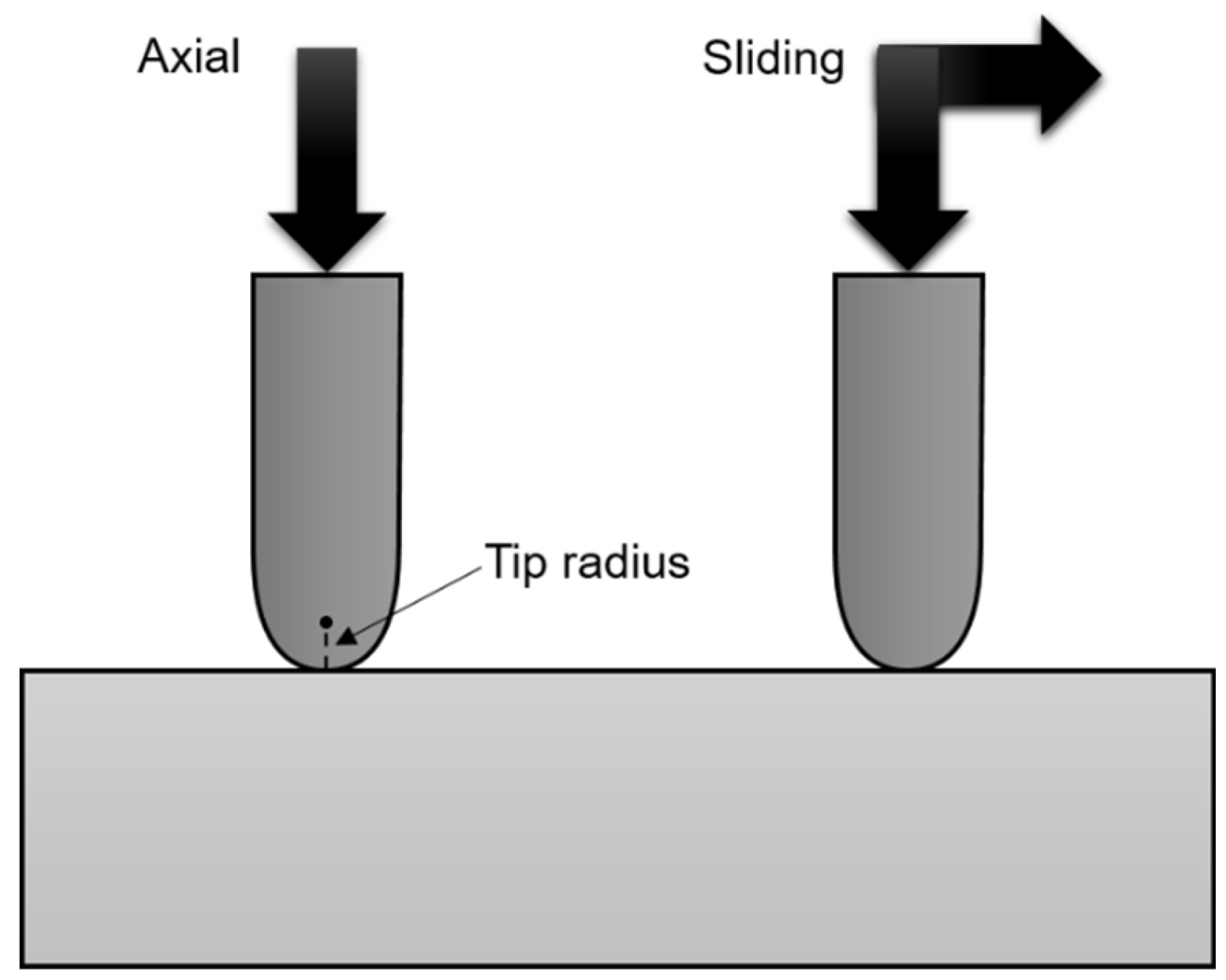
To address this gap, we investigate the fundamental contact damage of as-received (untreated) and heat-treated commercial ZLS glass-ceramics using controlled
in-vitro indentation tests, in both axial and sliding configurations (
Figure 2). The effects of contact/abrasive size are evaluated using tips of varying radii. Results are analysed with respect to the materials’ microstructure, within the framework of contact fracture mechanics. Furthermore, we briefly discuss the implications for prosthetic dentistry, with a view to providing insights for the selection of dental materials.
2. Experimental Procedure
The ZLS materials employed were obtained from commercially available CAD/CAM blocks (Celtra Duo HT, Dentsply Sirona, NC, USA). Plane parallel specimens for testing of thickness ≈1.2-1.5 mm were obtained by mechanical cutting from as-received (untreated) blocks. Half of the specimens were subsequently heat-treated in a dedicated furnace (Multimap Touch, Dentsply, PA, USA) in a dental/prosthetic facility (Clínica David Maestre, Valverde de Leganés, and LAB Dental, Badajoz, Spain), following the manufacturer’s specifications: initial heating to 500 ºC (soaking 3 min), followed by heating to 820ºC at 60ºC/min (soaking 1 min), and gradual cooling with the chamber closed until 500ºC, and then opening the furnace doors [
7].
The test surfaces of all specimens were gently ground with fine sandpaper, lapped (30 μm), and polished with diamond suspensions using routine ceramographic methods. The polishing routine consisted of the following steps: 15 μm (10 min), 9 μm (10 min), 6 μm (10 min), 3 μm (15 min), and 1 μm (20 min).
The microstructure and fracture surface of the materials were observed by scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM; Quanta 3D FEG, FEI, The Netherlands) using secondary and backscattered electrons at intermediate accelerating voltages (10-20 kV), without gold coating.
Relevant contact mechanical properties were measured by conventional indentation tests at room temperature in air. First, Hertzian tests were conducted (5535, Instron, Canton, MA, USA) on sputter-gold coated specimens, using loads in between 15 N and 1500 N, applied by WC spheres of radii 7.94 and 4.76 mm. The dimensions of the scars were subsequently measured by optical microscopy (Epiphot 300, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and, following procedures described elsewhere [
12], stress-strain curves were constructed. For each material, the elastic modulus (
E) was estimated from the linear part of the stress-strain curve [
12,
13]. Second, Vickers tests were performed with a diamond tip (MV-1, Matsuzawa, Japan), using a load of 9.8 N. A total of 10 indentations per material were conducted to determine the hardness (
H) and fracture toughness (
KIC) from the scar dimensions (measured by optical microscopy), using standard formulae [
13,
14].
Advanced indentation experiments were used to investigate micro-contact damage. Tests were performed at room temperature in air, using dedicated, computer-controlled equipment (Revetest RST3, Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). Rockwell-C (sphero-conical), diamond indenters of different radii (200 μm, and 20 μm) were employed. Tests were conducted in both axial and sliding loading configurations (see
Figure 2). In the axial tests, for each material and tip size, separate pre-tests were performed at 50 N/min, progressively increasing maximum load at initial intervals of 20 N. The test surfaces were subsequently inspected by optical microscopy to determine the load range within which chipping takes place first. Such intervals were subsequently scanned in more detail, using loading steps between 1N and 5N. Every test was repeated ×3. Surfaces were again inspected after testing to accurately determine critical chipping loads. The criterion employed was that the critical chipping load was the smallest load for which all 3 of the 3 indentations at such load showed a well-formed chip particle. Tests were also conducted in sliding mode, ×3 for each material and tip size, using a sliding speed of 5 mm/min, at progressively increasing normal load from an initial value of 1 N (loading rate 100 N/min with the large tip; 25 N/min with the small tip). Test surfaces were subsequently examined by optical microscopy. For each test, critical chipping load was calculated from the corresponding microscopy image using the sliding speed and loading rate (more details in [
6]).
Sliding tests using the larger tip (200 µm) were also employed to estimate the resistance to sliding fracture (σ*) of the materials. Tests were conducted in progressive loading under the following conditions: initial normal load 1 N, final normal load of 25 N, loading rate 25 N/min, and sliding rate 3 mm/min. A total of
N=25 tests per material were performed. After each scratch test, the track was inspected in detail using the optical microscope to assess the critical fracture (normal) load (
FC) and the contact radius (
a) at the onset of cracking, as well as the coefficient of friction (
f) logged by the equipment at that point. For each material, the σ* values were obtained from the experimental (
FC,
a,
f) values using a contact mechanics model [
15]. These were then sorted in ascending order, and a probability of failure value (
Pf) was assigned to each one of them, using
Pf =(
i-0.5)/
N, for the
i-th value. A two-parameter Weibull probability function was employed to fit the data, from which the characteristic resistance to sliding fracture (σ
0*) and Weibull modulus (
m) were determined [
16] (more details in [
17]).
In selected cases, contact stresses were simulated using the software package FilmDoctor
® (SIO
®, Saxonian Institute of Surface Mechanics, Ruegen, Germany). The software calculates the elastic stress field in single-layer and multilayer systems, from the contact conditions and the materials’ elastic property values, using the extended Hertzian model [
18].
3. Results and Discussion
Figures 1(B) and 1(C) show SEM micrographs representative of the microstructure of as-received and heat-treated ZLS dental glass-ceramics, respectively. At the microstructural scale, no significant differences can be detected between the two. Both microstructures exhibit a distribution of lithium-based crystals within a zirconia silicate glassy matrix. Crystal phase content is ≈50 vol%, and their compositions are known to be primarily Li
2SiO
3, followed by Li
2Si
2O
5 and Li
3PO
4 [
9,
19,
20]. Crystal sizes range from nanometric, beyond the current resolution, to micrometric. The majority of observed crystals appear rod-shaped, with an average size of 0.7 ± 0.1 μm and an aspect ratio of 3.5 ± 0.6 [
7]. Hence, based on the SEM observations, the optional post-processing heat treatment does not significantly alter the relative phase content and crystallinity of the ZLS investigated materials. It is worth noting that this contrasts with other commercially available ZLS materials, which are supplied in pre-crystallized form and require a crystallization treatment to achieve both aesthetic and strength requirements [
20].
The contact-mechanical properties of the ZLS materials investigated also appear to remain unaffected by the post-processing heat treatment. Elastic modulus, hardness and indentation fracture toughness values of 99 ± 6 GPa, 6.2 ± 0.2 GPa, and 0.70 ± 0.03 MPa·m
1/2, respectively, were measured through Hertzian and Vickers tests in both as-received and heat-treated materials. In comparison to other dental glass-ceramics, ZLS materials generally exhibit improved mechanical properties, except for fracture toughness [
4,
6,
7,
17]. Lithium disilicate glass-ceramics, with their larger, interconnected crystals, demonstrate significantly higher toughness [
7,
17]. It is important to note that, while the Vickers indentation method may be considered less accurate than other techniques, it proves suitable for measuring the fracture toughness of the ZLS materials investigated and assessing any potential differences. This is because, under the load applied in our tests, the materials exhibit the required response, characterized by clean radial cracks observed on the surface [
21,
22].
Controlled indentation tests with sphero-conical tips in both axial and sliding modes enable simulations of the fundamental modes of dental contact.
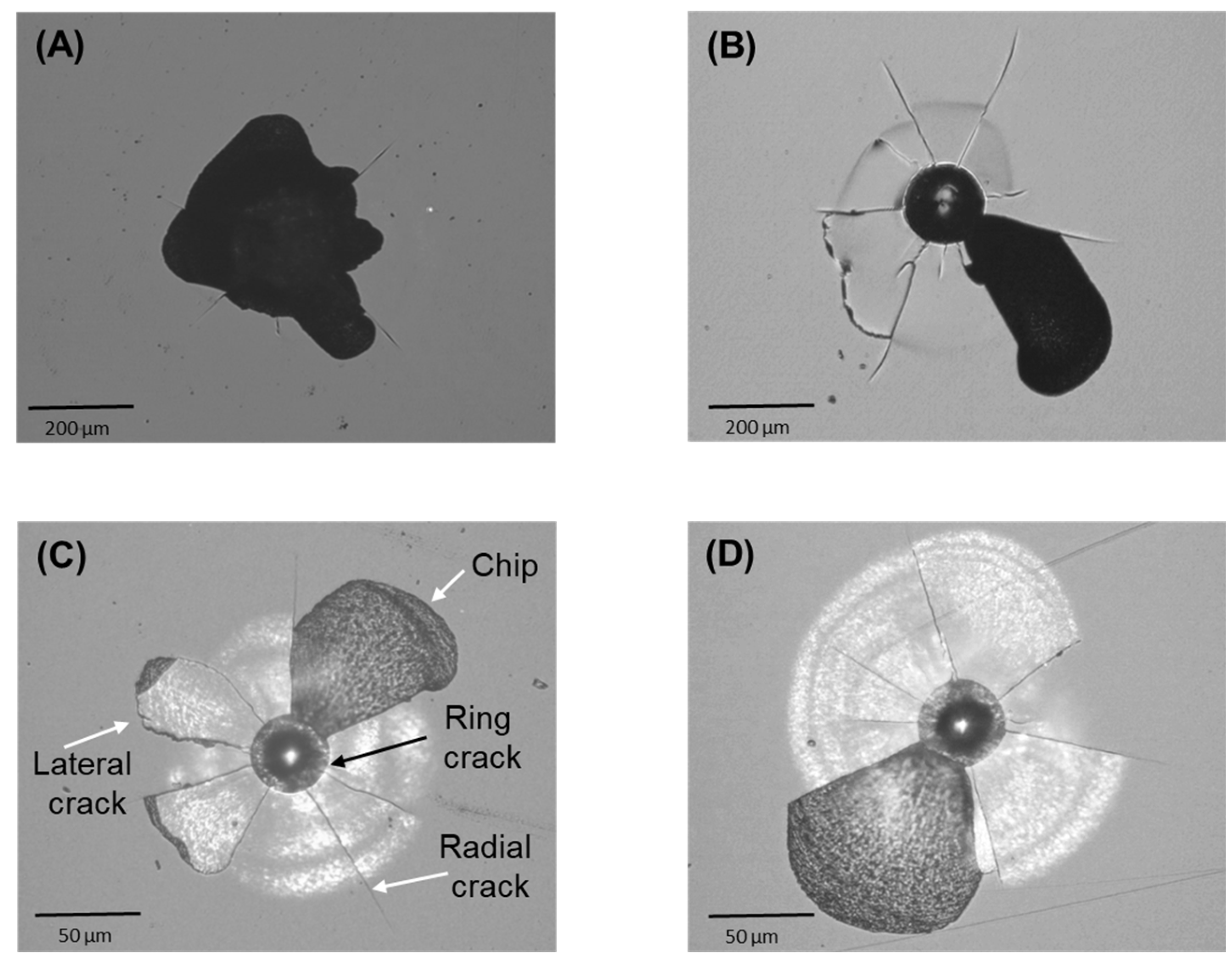
Figure 3 presents micrographs illustrating the damage generated by axial contacts of different size (radius 200 μm and 20 μm) on both as-received and heat-treated ZLS glass-ceramics. When the applied load is sufficiently high, the concentrated stresses induce different fracture modes around the indentation site, including ring-like cracks around the circular contact, radial cracks perpendicular to the loading axis, and sub-surface lateral cracks (some reaching the surface). Of particular relevance in dentistry is the phenomenon of
chipping, characterized by the wholesale dislodgement of material fragments (chips) due to the coalescence of cracks (typically radial and lateral) [
23]. The loads required for the onset of fracture and chipping decrease with decreasing the tip radius from 200 μm to 20 μm. It is noteworthy that, in contrast with the previous single-value mechanical properties, the critical chipping load is influenced by the heat treatment. With the larger tip radius (200 μm), the critical chipping load for the as-received material was measured at 115 ± 5 N, while for the heat-treated material it was 130 ± 5 N—a 13 % increase. Similarly, with the smaller tip radius (20 μm), the critical chipping loads measured in as-received and heat-treated materials were 10 ±± 1 N and 12 ± 1 N, respectively, representing a 20 % increase.
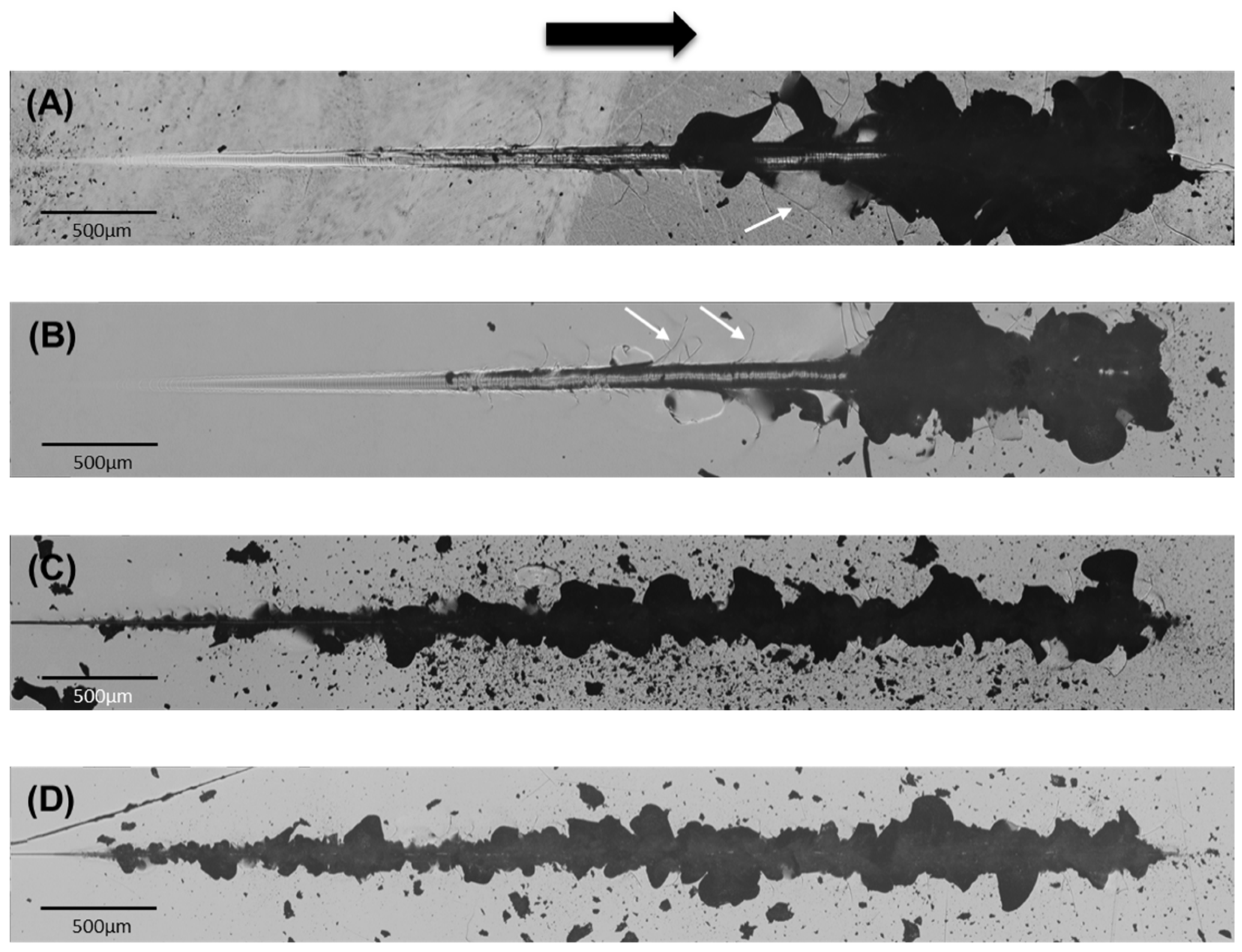
Figure 4 presents panoramic micrographs of the damage resulting from sliding contacts of different size, at progressively increasing normal load, on the investigated ZLS glass-ceramics. With the larger tip (200 μm), low initial loads lead to surface smearing and deformation, evolving into fracture at intermediate loads. The first fracture mode is partial ring cracks, perpendicular to the sliding direction. Subsequent sliding leaves behind a series of parallel cracks in the wake of the contact, with progressively decreasing spacing. At higher loads, radial cracks extend outwards from the scratch track at an angle with the sliding direction. Ultimately, the coalescence of radial and partial ring/cone cracks results in material removal through chipping. As in the axial case, the loads required for the onset of fracture and chipping decrease with decreasing tip radius from 200 μm to 20 μm, with the heat treatment influencing the critical loads. With the larger tip (200 μm), the measured critical fracture and chipping loads were 5.4 ± 0.1 N and 54 ± 4 N (as-received), and 7.2 ± 0.1 N and 64 ± 4 N (heat-treated). With the smaller tip (20 μm), the critical fracture and chipping loads were 2.2 ± 0.1 N and 2.5 ± 0.3 N (as-received), and 2.5 ± 0.1 N and 2.7 ± 0.3 (heat-treated).
The fracture modes observed can be explained based on the analysis of the main components of the stress field generated by axial and sliding contacts.
Figure 5 shows simulations of the cross-sectional distribution of normal and Von Mises stresses, induced by axial contacts of radii 200 μm and 20 μm, at a low reference load (1 N). The maximum tensile stress is located on the surface, right outside the contact circle. Because the maximum tensile stresses have radial direction, when their magnitude exceeds a critical value, they open ring-shaped cracks, as shown in the inset of
Figure 5 (A) (high magnification detail) [
12]. On the other hand, the maximum shear stress (Von Mises) is located below the surface, approximately at ~0.5
a, with
a the Hertzian contact radius, and is responsible for plastic and quasi-plastic deformation processes. Upon unloading, the residual elastic-plastic indentation stress field propagates some of the sub-surface microcracks previously generated, which eventually reach the contact surface with radial orientation (
i.e., radial cracks,
Figure 5(A) inset). Depending on the specific micro-crack orientation, propagation may be parallel to the contact surface, developing lateral cracks as observed for example in
Figure 3(C) [
12,
13,
14]. The simulations indicate that the greater pressures attained using smaller tips translate into an increase in both the maximum surface tensile stress and the sub-surface Von Mises stress with decreasing the contact size (Figures 5(C) and 5(D)). This explains, qualitatively, the lower loads required for chipping using the 20 μm tip compared to the 200 μm tip.
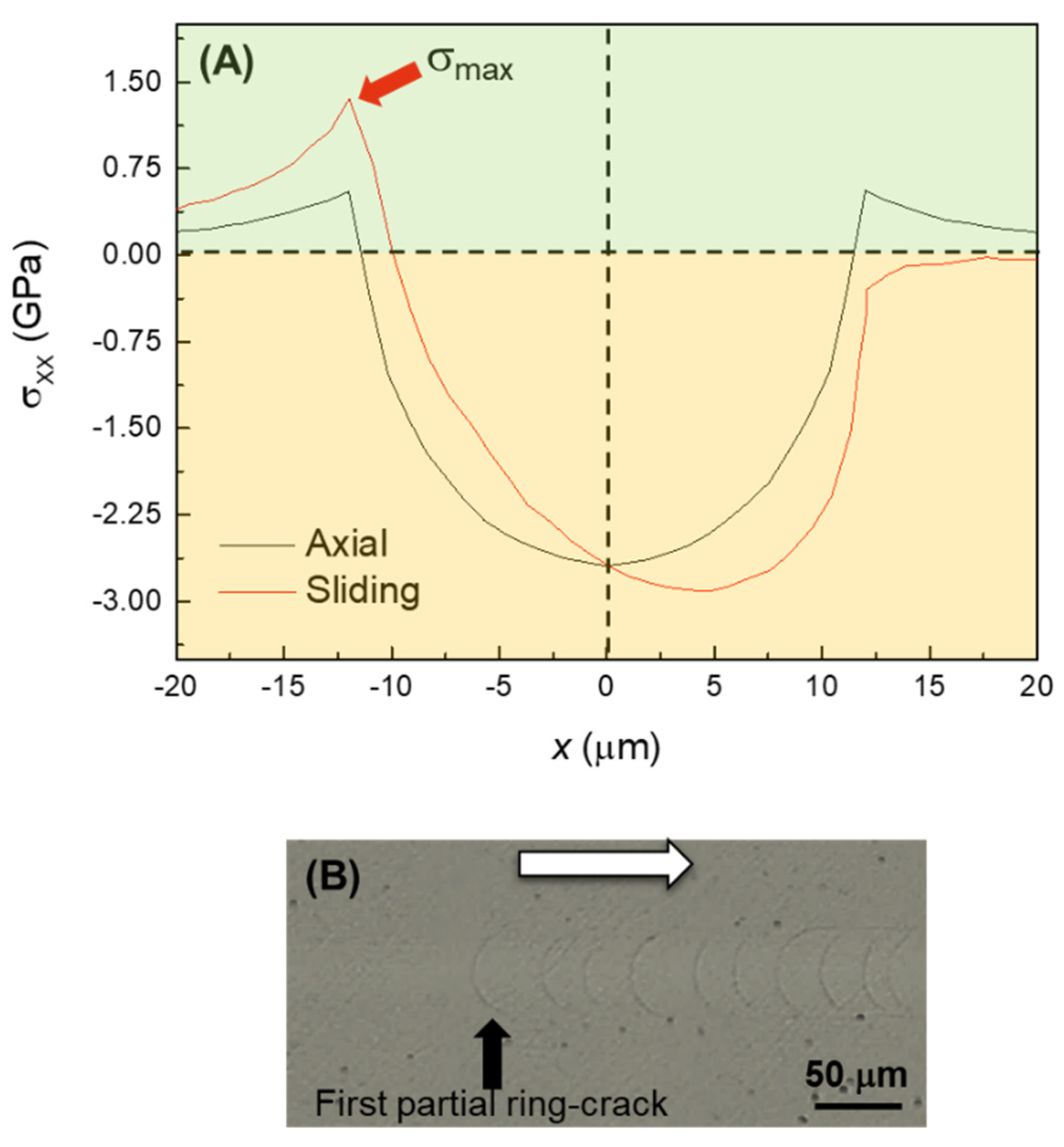
The addition of a lateral force upon sliding has a relatively minor effect on the Von Mises stress?it basically shifts the maximum slightly ahead of the normal axis [
15]. However, it has a significant impact on the stress at the contact surface. In particular, friction increases the maximum tensile stress at the trailing half of the contact, while the stress at the leading half becomes compressive, as observed in the line graphs (
Figure 6) of the normal stress distributions on the surface for the 200 μm tip (axial/frictionless vs. sliding/friction) [
15]. This asymmetry of the maximum contact stress leads to the initial opening not of fully developed ring cracks, but of half rings (
i.e., only in the rear edge of the contact, the so-called partial ring/cone cracks) [
24]. A detail of such partial ring cracks upon sliding contact can be observed in
Figure 6 (C). As in the axial case, subsequent increases in the applied load lead to the formation of radial cracks. In the sliding case, the moving tensile component of the stress field pulls the radial cracks forward, explaining the angle with respect to the sliding direction (
e.g., white arrows in Figures 4(A) and 4(B)). Decreasing the contact size also translates into an increase of the magnitude of the stresses, again explaining the lower chipping loads measured with the 20 μm tip compared to the 200 μm tip. In fact, as a result of the greater contact pressure even at low loads, partial ring cracks are not observed with the smaller tip, and the initial fracture mode is radial cracking followed by chipping at low loads.
The fact that the initial fracture mode of the ZLS materials upon scratching with the larger 200 μm tip is that of partial ring cracks allows this test to be employed to assess the resistance to sliding fracture. The theoretical framework is provided by the expression from Hamilton and Goodman for the maximum tensile stress at the rear edge of a sliding Hertzian contact [
15]:
where
P0 and f are the applied Hertzian pressure and coefficient of friction at that contact point, and υ the Poisson’s ratio of the material. Thus, measurement of the critical load
FC and
f at which the first partial ring crack appears (data collected by the equipment), allows an estimation of the material’s resistance to sliding fracture (σ*) using (1). To deal with the intrinsic variability of the fracture phenomenon in brittle materials, several tests were performed in as-received and heat-treated ZLS materials and analysed using Weibull statistics [
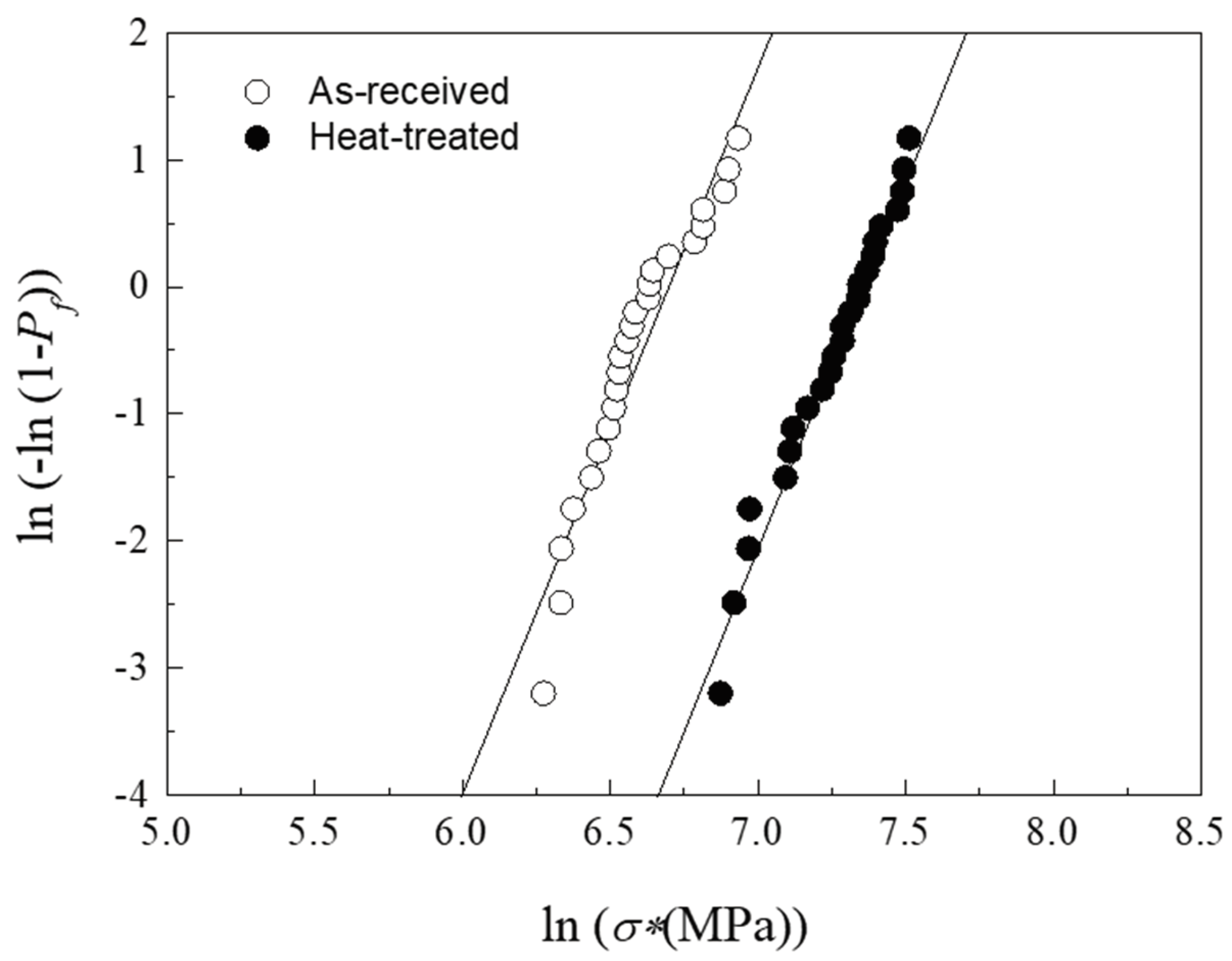
17]. The results are shown in
Figure 7, where
Pf represents the probability of failure. As with the critical chipping loads, the post-processing heat treatment has a positive impact on the resistance to sliding fracture. However, in this case the extent of the improvement is significantly greater, with the heat-treated material showing a characteristic resistance σ
0*=1587.6 MPa and Weibull modulus/reliability
m=5.8 vs. σ
0*=804.3 MPa and
m=5.7 in the the as-received material.
The results obtained demonstrate that the optional post-processing heat treatment applied to ZLS materials does not significantly alter their single-value mechanical properties (
E,
H,
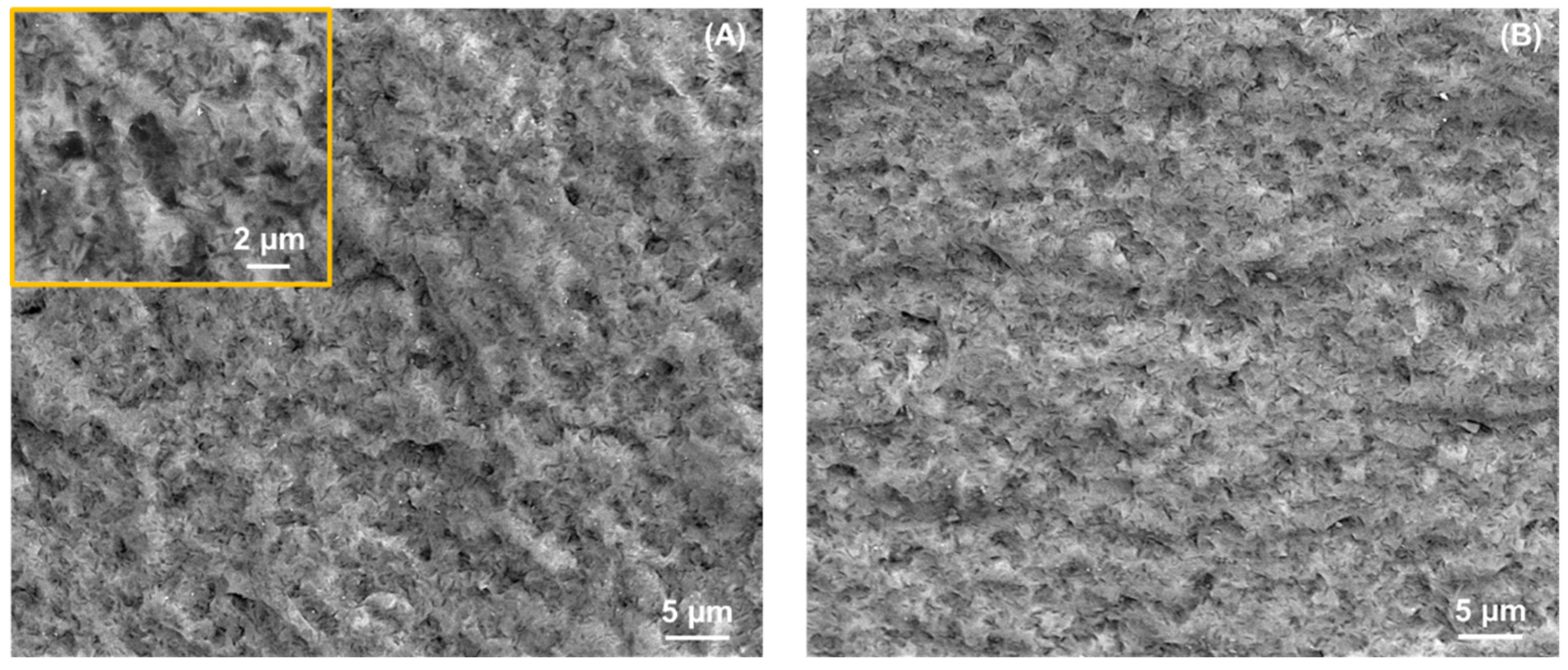
KIC). However, it does increase the critical loads for chipping under any given contact configuration (axial, sliding) and size, as well as the sliding fracture strength. In essence, this treatment makes the materials more resistant to the initiation of cracks, and to material removal by crack coalescence processes. Given that the heat treatment does not significantly affect the observed crystallinity of the glass-ceramics (
Figure 1), this effect is attributed to a refinement of the flaw population. Such defects are traditionally challenging to detect on polished surfaces such as the ones in
Figure 1 [
25,
26], but they become apparent on fracture surfaces, as illustrated in
Figure 8. The SEM images reveal the presence of defects, such as µm-sized voids [
14], in both the as-received and the heat-treated materials. However, the frequency and size of these defects appear to be relatively smaller after the heat treatment. According to Griffith’s fracture mechanics relation (σ
F~
c-1/2, with
c representing the size of the critical defect precursor for fracture [
13,
14]), a reduction in the average defect size can in turn lead to an increase in the fracture strength of the heat-treated material without compromising aesthetics, aligning with the manufacturer’s specifications [
9].
This study has significant implications in prosthetic dentistry and may aid in selecting materials with improved durability. Although the post-processing heat treatment for ZLS glass-ceramics involves greater processing cost and time, it results in improved mechanical stability of the prosthesis without sacrificing aesthetics. Similar treatments could be considered for other types of dental materials. Furthermore, the findings emphasize that single-value mechanical properties such as elastic modulus, hardness and fracture toughness may not adequately reflect prosthesis durability, adding to previous evidence obtained from wear tests on biphasic dental materials [
8]. Material removal processes, such as chipping, involving complex interactions between different fracture modes, are best assessed by considering both mechanical properties
and microstructural features (
e.g., weak interfaces, defects).