Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem Description and Assumptions
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. Model Assumptions
3. Model Construction and Solution
3.1. Model Building
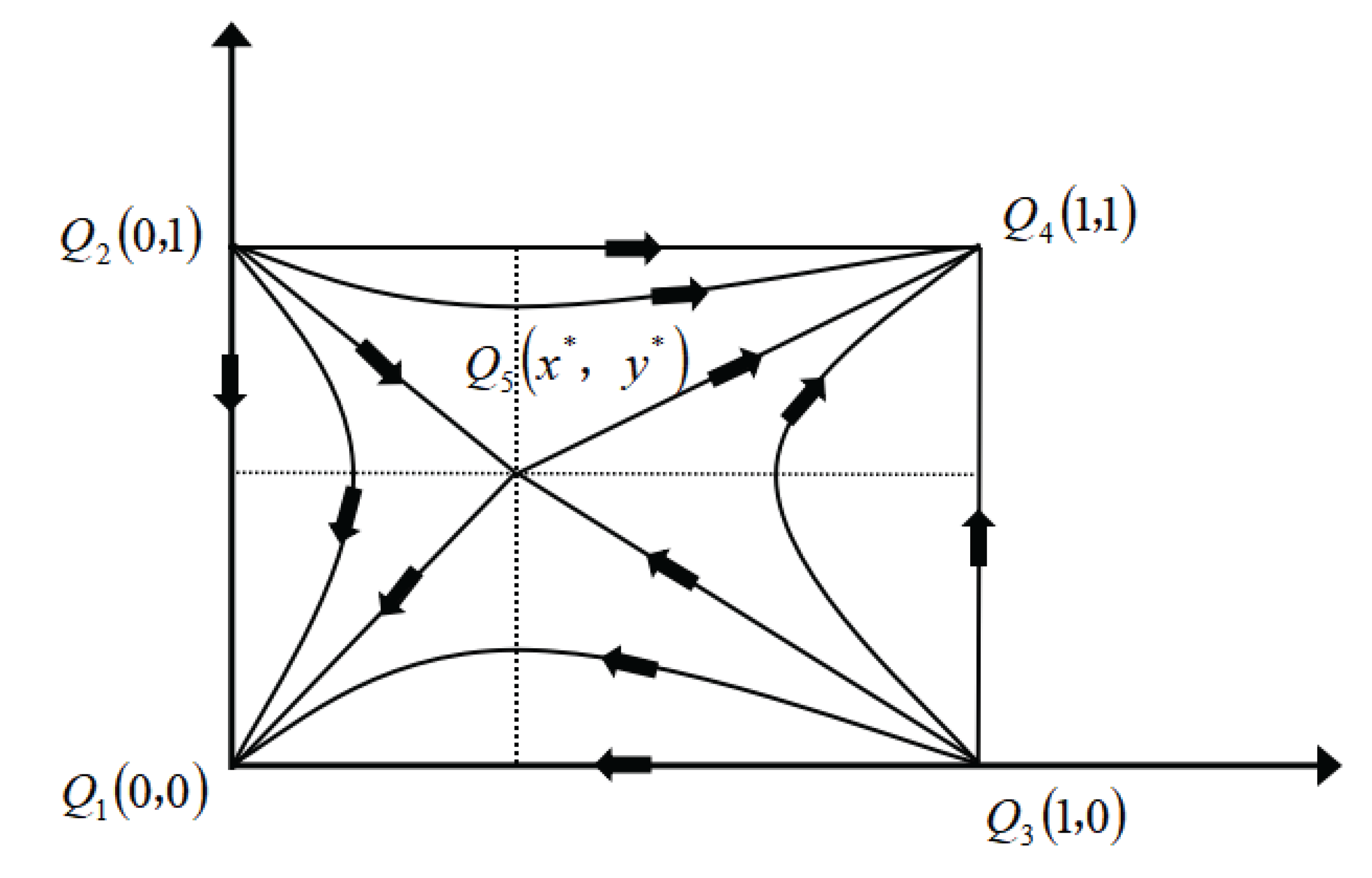
3.2. Model Analysis
4. Numerical Simulation
4.1. Parameter Assignment of Related Variables
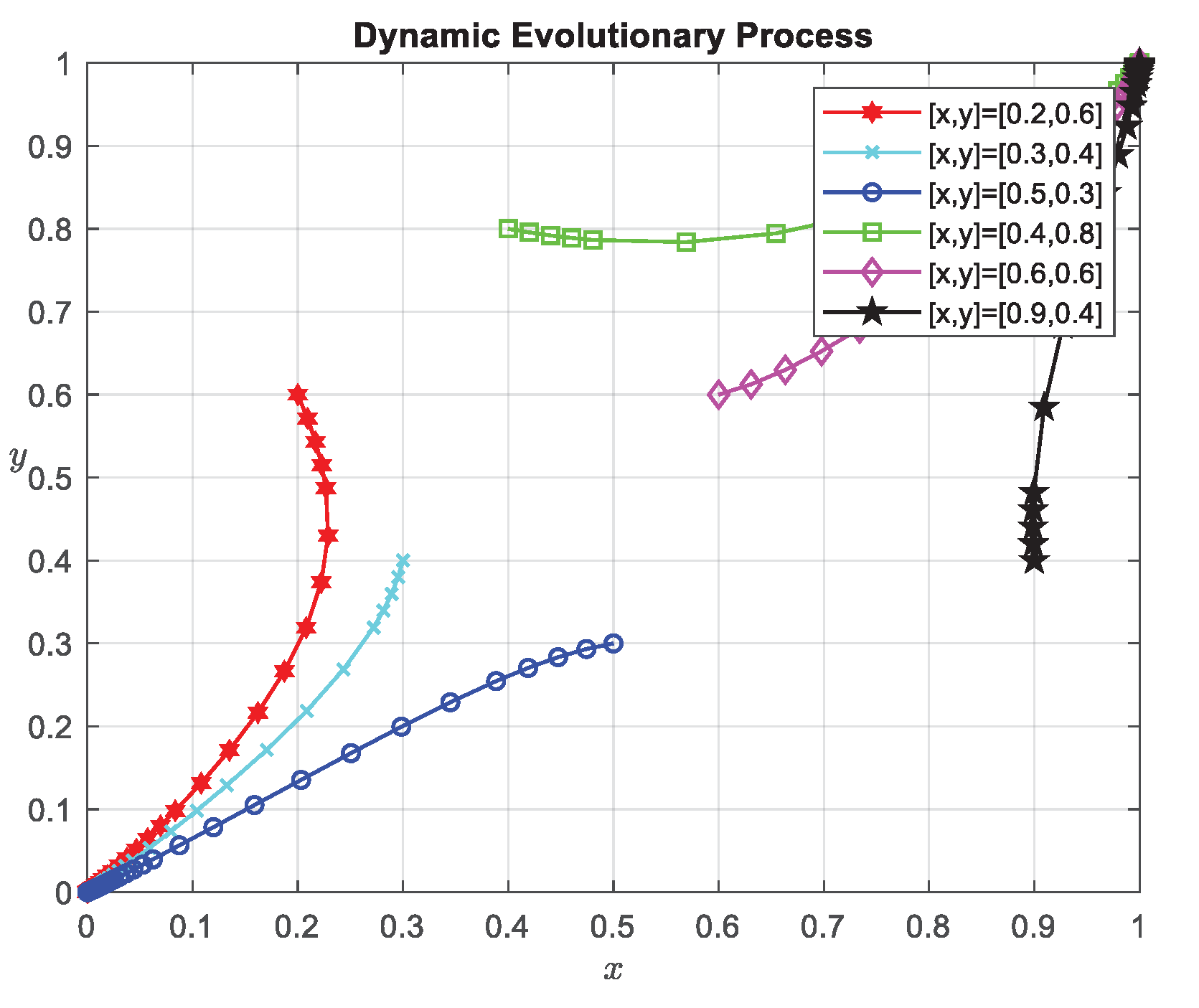
4.2. Influence of Initial Probability on System Evolution Process
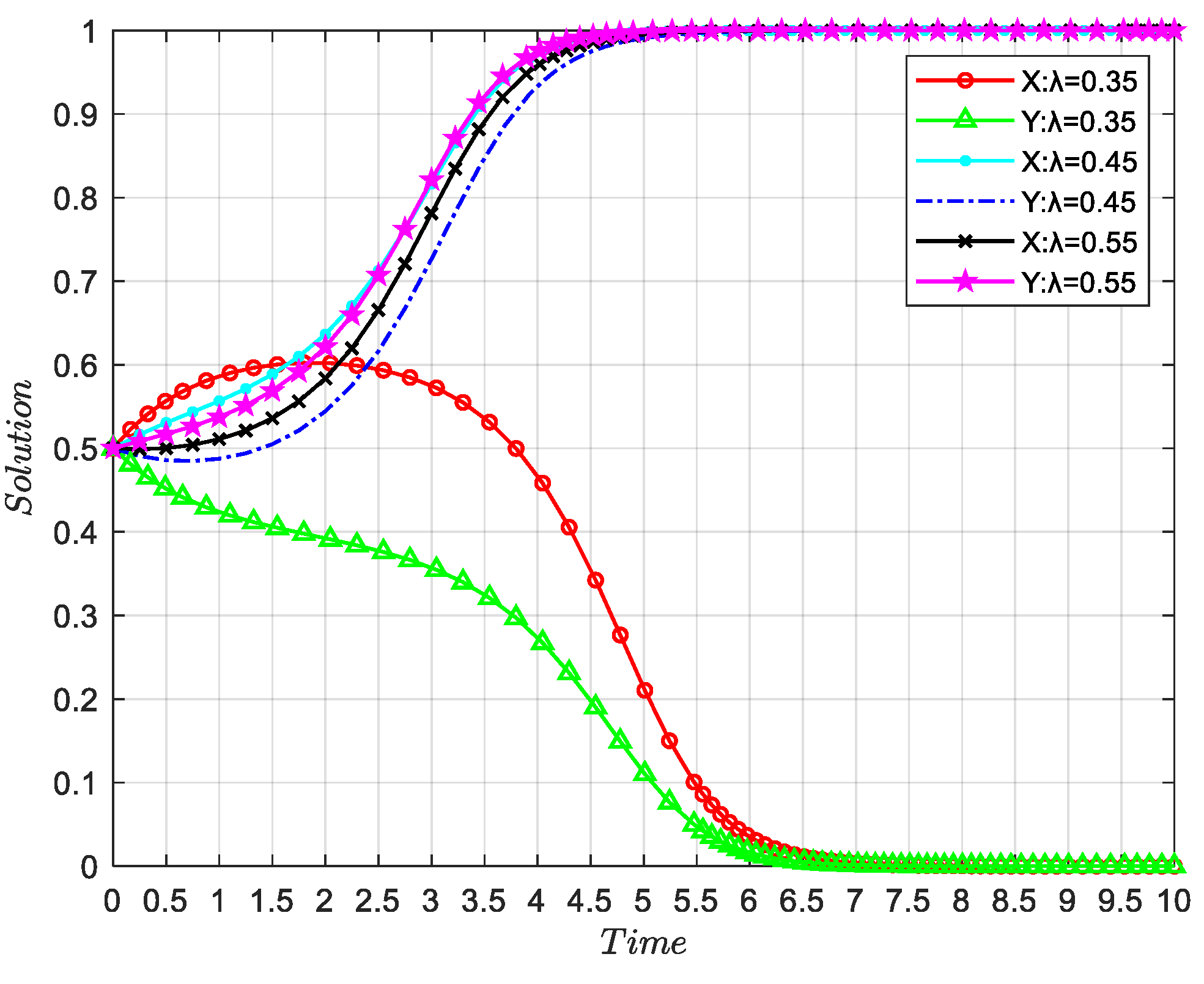
4.3. The Influence of λ on the Evolution Results of Both Parties
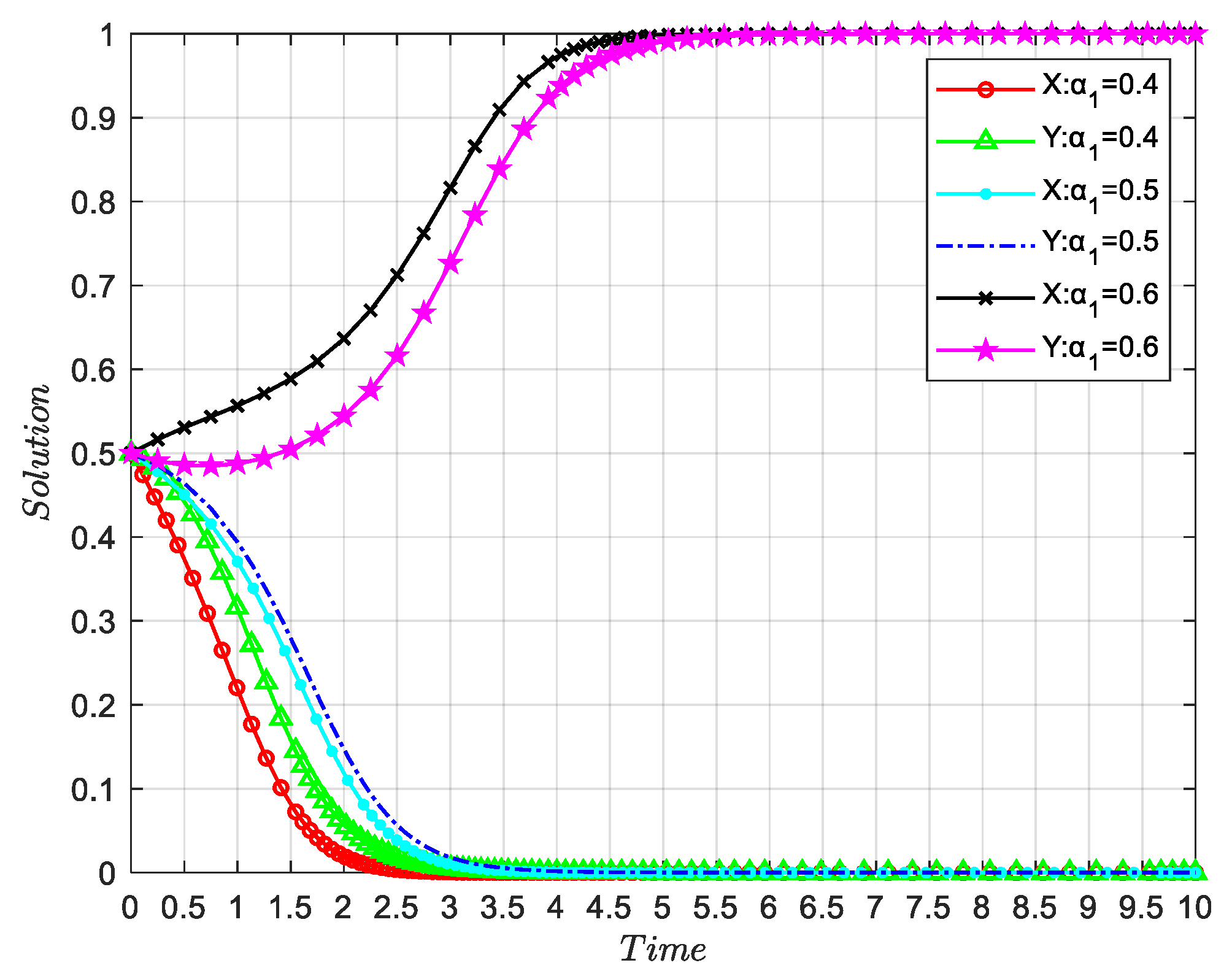
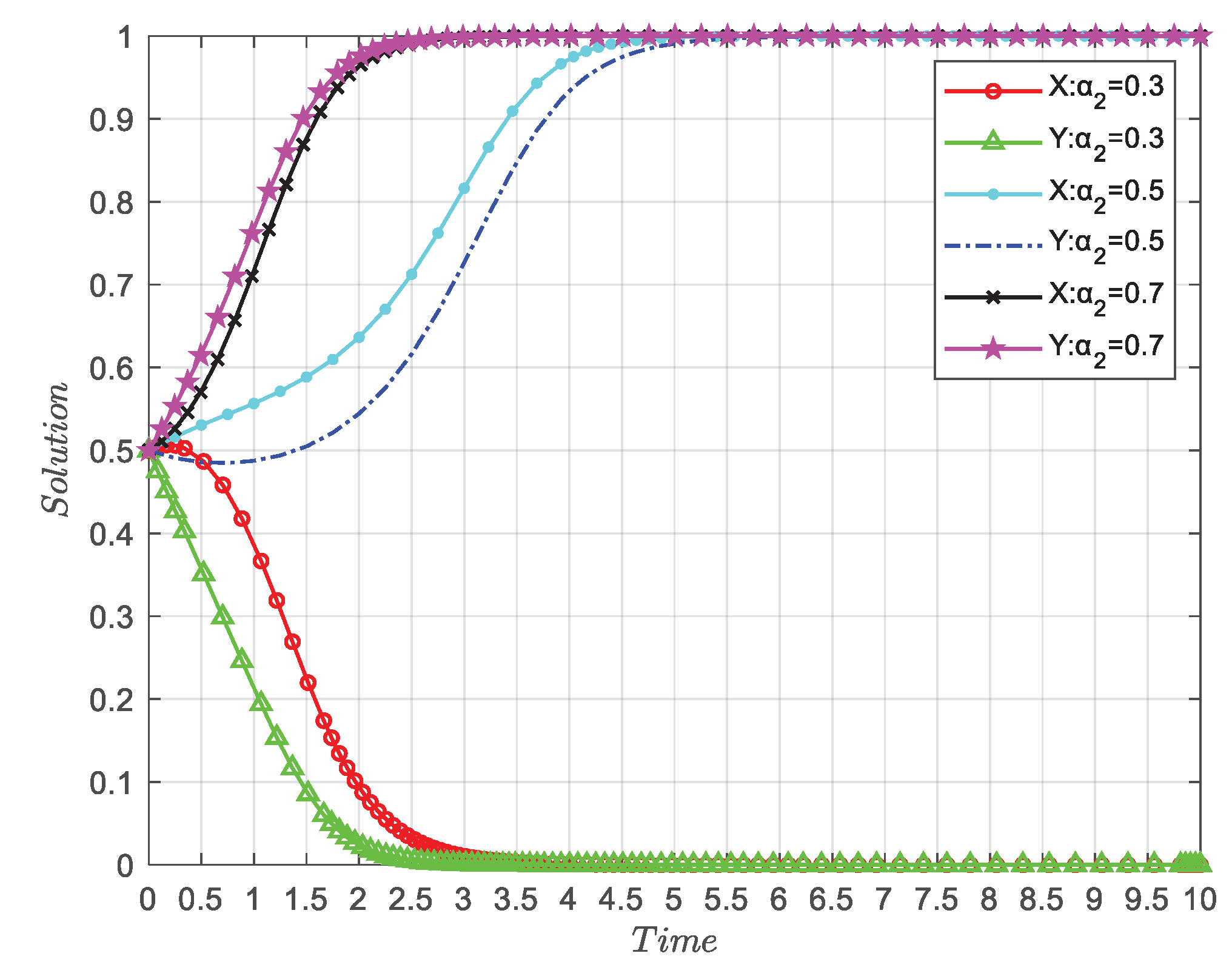
4.4. The Influence of αi(i=1,2) on the Evolution Results of Both Parties
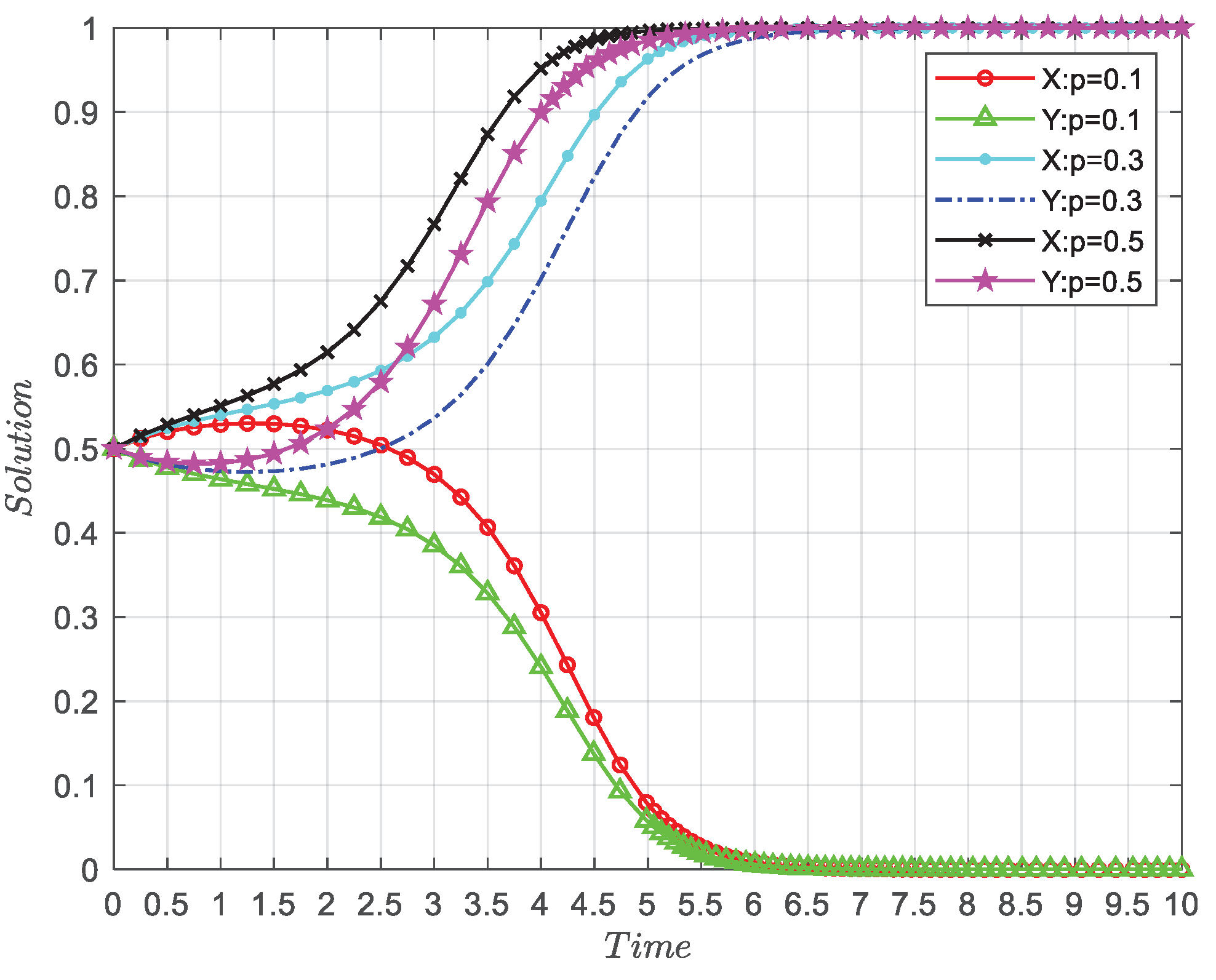
4.5. The Influence of p on Evolution Results of Both Parties
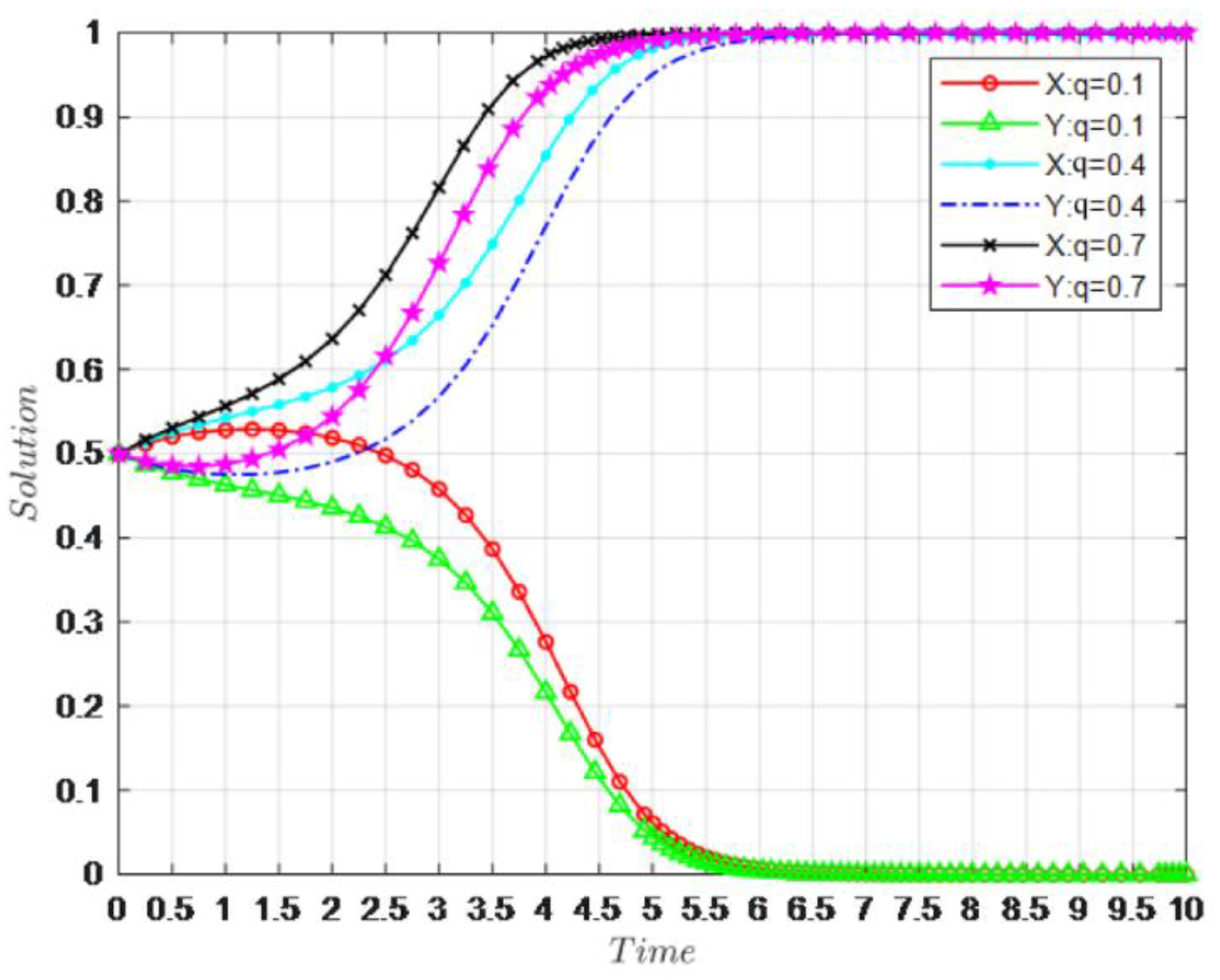
4.6. The Influence of q on Evolution Results of Both Parties
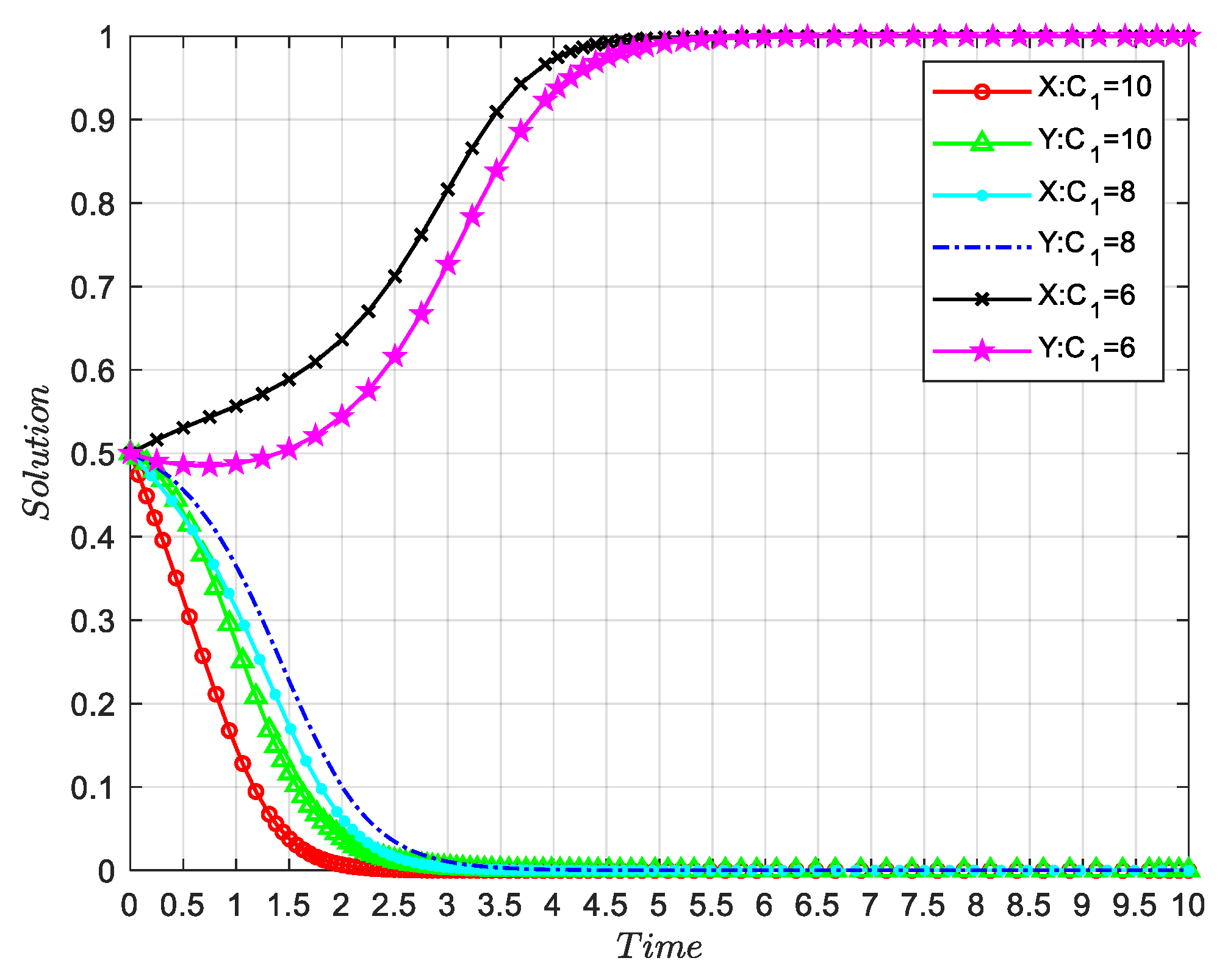
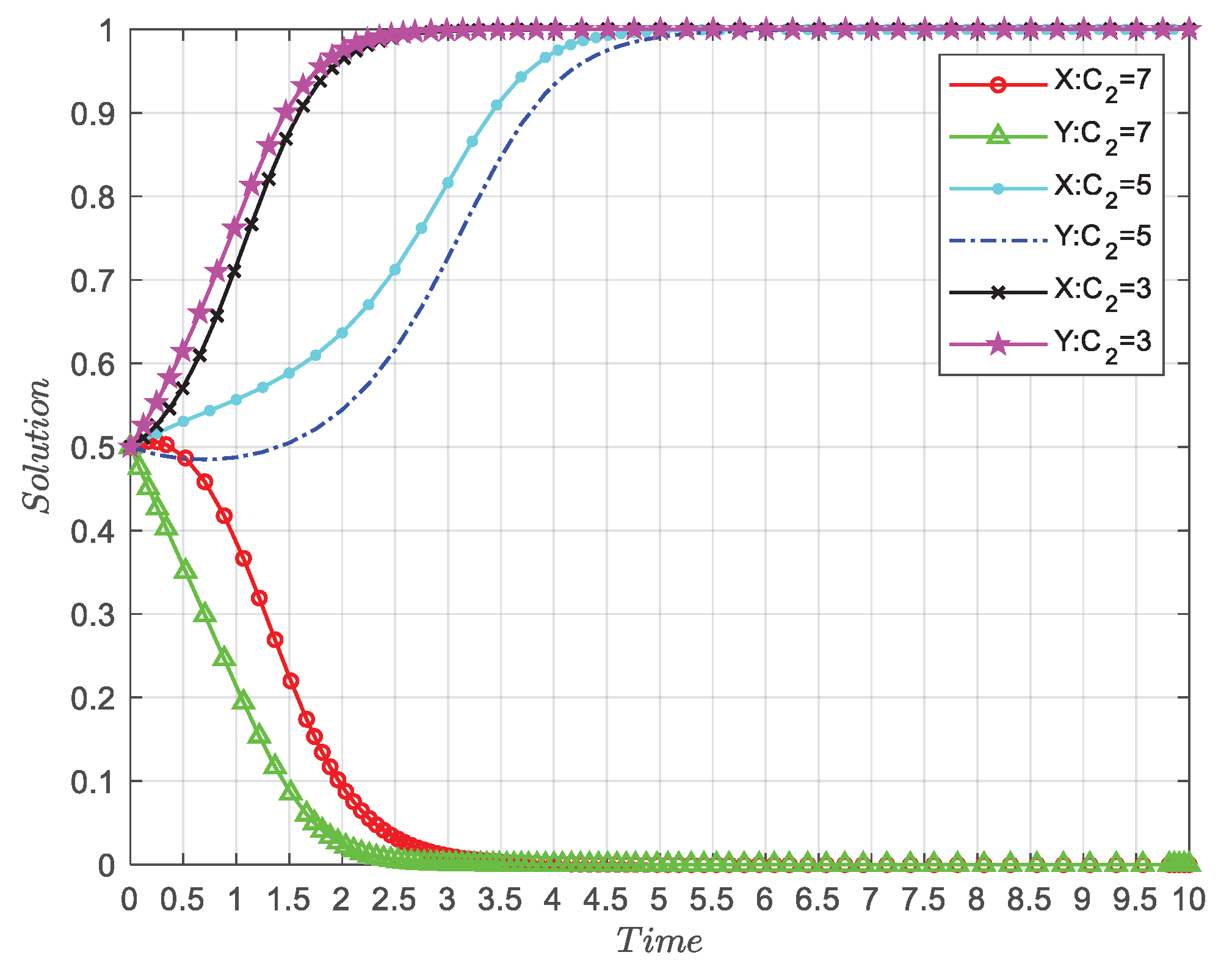
4.7. The Influence of Ci(i=1,2) on the Evolution Results of Both Parties
5. Research Conclusions and Suggestions
- (1)
- Government can balance the problems in the income distribution by means of financial subsidies and innovation incentives. Major projects are the symbol of economic development, which can not only enhance China's comprehensive national strength and international status, but also accelerate China's modernization process. Because general contractors are in a dominant position in the construction process, unfairness will inevitably appear in the distribution of benefits, thus damaging the interests of subcontractors and leading them to choose negative cooperative behaviors. The behavior of participants in major project construction has an important impact on project quality and project cycle, so it is necessary to distribute the income reasonably, and the government should take financial means to balance the unfair distribution when necessary.
- (2)
- Participants in major projects should actively strengthen themselves and enhance their innovation ability. The innovation ability of participants will directly affect the promotion of major projects' technology innovation process. In the process of technological innovation, innovation cost is one of the important factors that restrict innovation enthusiasm, and innovation subjects are unwilling to bear huge cost pressure. Therefore, the innovation subjects should strive to improve the innovation ability, because the stronger the innovation ability, the lower the innovation cost. In addition, due to the large number of participants in major projects' technology innovation, in the early stage of project construction, the innovation ability of participants should be included in the assessment criteria when building a cooperative team with strong innovation abilities.
- (3)
- We propose to increase public participation in major projects' innovations. Major projects not only play an important role in the development of national economy, but also have a far-reaching impact on the public. For example, the completion of the Three Gorges Dam project not only solved the flood problem in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, but also effectively alleviated the shortage of electricity in our society. Improving public participation can not only make the public perceive the social benefits brought by the construction of major projects, but to a certain extent they can also play a supervisory role on the participants in major projects and technological innovation. In addition, the government can also set up effective reward and punishment measures to improve the enthusiasm of public participation, and then promote the development of major projects and technological innovation.
- This study reveals the role of the general contractor and subcontractor in the process of major projects' technological innovation behavior decision-making, and refers to both development of major projects and technological innovation. However, this paper is from the theoretical point of view, and lacks engineering construction and technological innovation data, so there will be differences between the research conclusions and actual major projects. In addition, this paper selects only a few of the major projects' technology innovation influencing factors for research. In spite of these limitations, this research can act as a comprehensive reference point for more for in-depth studies.
Funding
References
- Flyvbjerg, B. What you should know about megaprojects and why: an overview[J]. Project Management Journal, 2014, 45:6-19.
- Chen, H.Q.; Jin, Z.Z.; Su, Q.K.; Yue, G.Y. The roles of captains in megaproject innovation ecosystems: the case of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge[J]. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 2020, 28(3):662-680.
- Damayanti, R.W.; Hartono, B.; Wijaya, A.R. Clarifying megaproject complexity in developing countries: A literature review and conceptual study[J]. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 2021, 13:18479790211027414.
- He, Q.H.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, T.; Chan, A.P.C. Identifying the driving factors of successful megaproject construction management: Findings from three Chinese cases[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2021, 8(1):5-16.
- Liu, Y.; Houwing, E.J.; Hertogh, M.; Yuan, Z.W.; Liu, H.M. Explorative learning in infrastructure development megaprojects: The case of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge[J]. Project Management Journal, 2022, 53(2):113-127.
- Davies, A.; MacAulay, S.; DeBarro, T.; Thurston, M. Making innovation happen in a megaproject: London's Crossrail Suburban Railway System[J]. Project Management Journal, 2014, 45(6):25-37.
- Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.J.; Chang, R.D. Governing behavioral relationships in megaprojects: examining effect of three governance mechanisms under project uncertainties[J]. Journal of Management in Engineering, 2019, 35(5):04019016.
- Brockman, P.; Khurana, I.K.; Zhong, R. Societal trust and open innovation[J]. Research Policy, 2018, 47(10):2048-2065.
- Ge, Z.H.; Hu, Q.Y.; Goh, C.H.; Zhao, R. Action-dependent commitment in vertical collaborations: The effect of demand-creating innovations in a supply chain[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2021, 147:102164.
- Ozorhon, B.; Oral, K. Drivers of innovation in construction projects[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2017, 143(4):04016118.
- Han, Z.Y. Research on influencing factors and mechanism of railway engineering technology innovation [J]. Building Materials and Decoration,2018(17):239-240.
- Xue, X.L.; Zhang, R.X.; Wang, L.; Fan, H.Q.; Yang, R.J.; Dai, J. Collaborative innovation in construction project: A social network perspective[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(2):417-427.
- Sergeeva, N.; Zanello, C. Championing and promoting innovation in UK megaprojects[J] International Journal of Project Management, 2018, 36(8):1068-1081.
- Chen, H.Q.; Su, Q.K.; Zeng, S.X.; Sun, D.X.; Shi, J.J. Avoiding the innovation island in infrastructure mega-project[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2018, 5(1):109-124.
- Liu, H.M.; Yu, Y.R.; Sun, Y.X.; Yan, X. A system dynamic approach for simulation of a knowledge transfer model of heterogeneous senders in mega project innovation[J]. Engineering Construction and Architectural Management, 2020, 28(3):681-705.
- Guo, B.; Cheng, Z.J.; Feng, T. Research on the influence of dual governance on the vulnerability of technology innovation network in major engineering projects[J]. International Journal of Electrical Engineering Education, 2020:0020720920940606.
- Qiu, Y.M.; Chen, H.Q.; Sheng, Z.H.; Cheng, S.P. Governance of institutional complexity in megaproject organizations[J]. International Journal of Project Management, 2019, 37(3):425-443.
- Xu, X.D.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, Y.F.; Luo, X.C. Subject behavior of collaborative innovation in civil-military integration: An evolutionary game analysis[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021:6698895.
- Chen, L.; Bai, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.J. Incentives for green and low-carbon technological innovation of enterprises under environmental regulation: From the perspective of evolutionary game[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2022, 9:793667.
- Ma, Y.H.; Kong, L.K.; Yang, X.M; Lin, C.R. Innovation cooperation network evolution about green building technology with government intervention: Based on evolutionary game theory[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9:142289-142301.
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Du, L.; Lin, C.R.; Lu, W. How does alliance-based government-university-industry foster cleantech innovation in a green innovation ecosystem?[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 283:124559.
- Wang, Q.E.; Lai, W.; Ding, M.M.; Qiu, Q. Research on cooperative behavior of green technology innovation in construction enterprises based on evolutionary game[J]. Buildings, 2022, 12(1):19.
- Zan, A.; Yao, Y.H.; Chen, H.H. University–Industry collaborative innovation evolutionary game and simulation research: The agent coupling and group size view[J]. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2021, 68(5):1406-1417.
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Feng, G.Z.; Zhou, K. A dynamic incentive model for the prepositioning system of supplies based on reputation effect[J]. Journal of Systems Management, 2022, 31(01):1-15.
- Fama, E.F. Agency problems and the theory of the firm[J]. Journal of Political Economy, 1980, 88(2): 288-307.
- Kreps, D.M.; Wilson, R. Sequential equilibria[J]. Econometrica,1982, 50(4):863-895.
- Shi, Q.Q.; Zhu, J.B.; Sheng, Z.H.; Liu, H.M. Dynamic incentive mechanism for the suppliers of mega project considering double reputation[J]. Journal of Systems Management, 2017, 26(02):338-345.
- Li., J.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.M. Li. J.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.M. Research on incentive mechanism of bank to logistic company in inventory financing considering reputation effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2017, 25(07):86-92.
- Galor, O.; Weil, D.N. Population, technology, and growth: From Malthusian stagnation to the demographic transition and beyond[J]. American economic review, 2000, 90(4): 806-828.
- Friedman, D. On economic applications of evolutionary game theory[J]. Journal of evolutionary economics, 1998, 8(1): 15-43.
| General Contractor | |||
| Active collaborative innovation(x) | Negative collaborative innovation(1-x) | ||
| Subcontractor | Active collaborative innovation(y) | ||
| Negative collaborative innovation(1-y) | |||
| Order | Equilibrium Point | Det(J) | Tr(J) | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q1(0,0) | + | - | Asymptotic Stable Point |
| 2 | Q2(0,1) | + | + | Instability Point |
| 3 | Q3(1,0) | + | + | Instability Point |
| 4 | Q4(1,1) | + | - | Asymptotic Stable Point |
| 5 | Q5(x*,y*) | - | 0 | Saddle Point |
| Parameter | R1 | R2 | M | η1 | η2 | V1 | V2 | λ | β | C1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | 0 | 0 | 6.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 4 | 6 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 6 |
| Parameter | C2 | α1 | α2 | ρ1 | ρ2 | b1 | b2 | p | q | |
| Data | 5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





