1. Introduction
Video streaming has been established as one of the primary uses of communication networks [
1]. It is estimated that 65.93% of current Internet traffic is related to video streaming [
2], underscoring the significance of these applications in today’s digital landscape. In the realm of real-time video streaming, a multitude of applications has emerged for purposes such as surveillance, entertainment, autonomous driving, text and object recognition, and social communications [
3]. These services meet strict requirements for Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE), necessitating minimal delay and negligible interruptions [
4]. In this context, technologies like 4G or 5G, and architectures such as cloud computing have provided significant advances [
5].
The improvement in communication technologies and cloud processing techniques has enabled an effective integration of real-time video flows into applications [
5]. Transmission protocols such as HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) [
6] or Dynamic Adaptative Streaming over HTTP (DASH) are applied in cloud architectures to provide large scale broadcasting, while meeting the high QoS requirements [
7]. However, there are contexts where these architectures are not applicable due to restrictions in connectivity, lack of infrastructure availability or exaggerated required investment. In these scenarios, alternatives such as Mobile Adhoc Networks (MANETs) become suitable approaches.
MANETs are a network typology which integrates autonomous independent mobile devices as nodes to perform data transmissions [
8]. In these networks, communications are handled by the nodes using range-limited wireless communication interfaces, without requiring a centralized coordinator element. Nodes may change their position in the context, changing dynamically the network topology and creating additional connectivity opportunities [
8]. As a result, MANETs become applicable in scenarios where Internet infrastructure is not available, relying in the autonomy and mobility of nodes to perform data transmissions. Thus, MANETs may provide a suitable alternative for live-video streaming in offline contexts, however, they face challenging limitations.
The inherent autonomy of the nodes in MANETs rises multiple challenges which may compromise QoS and QoE in live video streaming [
9]. The nodes mobility and the dynamic topology may lead to abrupt variations in the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) of nodes, affecting QoS by decreasing bit rate, increasing latency and, eventually, occasioning disconnections [
9,
10]. At the same time, nodes face power consumption and computing limitations, which may constraint their functions at processing incoming live video or acting as intermediate devices to route video streams [
9]. Considering these challenges, the present work proposes a software-driven architecture to adapt live video streaming using Machine Learning (ML) in offline MANETs.
The proposal enables the transmission and routing of real-time video, adapting the image compression individually to the network state. For this, ML classification techniques are applied to identify the stability of the link. Following this description, an implementation of the architecture has been developed and assessed in a laboratory context, training and applying a decision tree algorithm to achieve link quality prediction and adapting compression accordingly. As a result, QoS and QoE have been successfully satisfied.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: section 2 describes related works and compares them with the proposed technique. Next,
Section 3 details the functioning of the architecture and its components. Then, section 4 assess the implementation and analyzes the evaluation score of the model, in terms of QoS and QoE. Finally, section 5 draws draws conclusions and presents suggestions for further studies.
2. Related Works
The inherent nature of MANETs implies multiple challenges for delivering video, requiring measures to mitigate their impact on QoS. Some of their features often become obstacles to video streaming, such as the changing topology, node mobility, or limited bandwidth [
11][
9]. These factors lead to variations in RSSI, increased latency, decreased bit rates, and even route interruptions with the sender node. Consequently, live video streaming may experience delays and lack synchronization at destination nodes, while also encountering interruption periods.
In response to the challenge of streaming video in MANETs, the approaches presented in the literature may primarily focus on the routing process while also providing adjustments to enhance performance. Thus, these works can essentially be classified into three groups [
11]: multipath routing, QoS-aware routing, and prediction-based link routing.
Multipath routing is a technique based on maintaining multiple data flows towards a destination, aiming to improve QoS [
9]. To achieve this, multiple flows are employed to transmit a compressed version of the video stream and an enhanced version of the frames, respectively, through independent paths. Simultaneously, the use of several connections enables the aggregation of additional bandwidth while balancing the traffic load between nodes [
11]. Furthermore, the use of multiple paths reduces the potential impact of link failures, thanks to redundancy. Proposals such as [
12] and [
13] represent some of the most significant alternatives in the field, applying resources like distance-vector and memetic algorithms to enhance multimedia communication. Despite these advances, multipath streaming requires additional computational resources to prevent duplicated data at destinations [
11].
On the other hand, QoS-aware techniques focus on adapting video streaming to the estimation of the available network resources [
11]. Thus, the transmission rate is managed to adapt to the link state. Works such as [
14] and [
15] predict the required and available bandwidth to discover the optimal route toward the destination. To achieve this, a heuristic approach is applied, enabling the initial discovery of optimal paths. However, most of these QoS solutions focus on the optimization of low-level mechanisms, requiring specific underlying technologies for encoding and decoding. Therefore, most of them are not applicable for MANETs based on interfaces such as radio frequencies or Bluetooth.
Link-prediction routing is based on the estimation of a path between the sender and the destination to forward information [
16]. The most recurrent techniques applied to predict stable links include periodic patterns, decision trees, complex network predictions, deep learning, and reinforcement learning techniques [
17].
In the case of applying pattern-based predictions, models can be trained to predict links using historical contacts [
16]. Thus, by identifying patterns in past encounters, link stability can be forecasted. Proposals like [
18] explore the potential of this technique in networks, incorporating variables such as encounter time, recurrence, and distribution. However, the dynamic topology of MANETs often does not mirror social behaviors but is characterized by random and opportunistic encounters instead. As a result, this technique may exhibit limitations in its application to these contexts.
Decision trees are a potential classification mechanism to predict the quality of links. Relevant works such as [
19] utilize this technique to determine paths towards the destination. For this purpose, attributes such as the speed of the node, the link expiration time, the trip time, and the node lifetime are applied to classify encounters. However, the considered metrics may not be accurate for real-time video transmission, since essential parameters such as latency are not considered.
In the case of deep learning, neural networks are applied to classify links and determine eventual stable connections. Works such as [
20] utilize this technique to establish a graded relationship between nodes, facilitating the discovery of potential paths in networks and eventual recovery in case of link failures. However, its potential application for live-video streaming remains limited. Conversely, contributions such as [
21] showcase the utility of these technologies for audio streaming.
Reinforcement learning is conceived as a ML technique based on evaluating the actions of the model and rewarding it for good decisions [
22]. Proposals such as [
22] rely on reinforcement learning to provide routing based on energy consumption in MANETs, enabling its integration for data transmissions. For this, variables such as node energy levels, neighbor count, and traffic load are defined as the state space, while routing becomes the available actions. Then, the reward is defined as a function which quantifies energy efficiency. However, in spite of these advancements, [
22] is not adapted to video streaming.
After summarizing some of the most relevant related works, it is possible to highlight the most significant points. Video streaming in MANETs has mainly motivated works related to the routing process. Among the different approaches, ML-based ones have become the most relevant, offering adaptable functioning that enables effective evaluation of link stability. As a result, the application of these techniques may present a potential opportunity to enhance the performance of the proposed architecture.
3. ML-Driven Adaptive Streaming Quality in MANETs
The work presented in this paper proposes a software-based application to enable adaptive live-video transmission in MANETs. For this, a ML classification model is applied to evaluate the stability of links, enabling an individual adaptation of the image quality for each connection. Thus, the model makes use of communication metrics to classify alive connections, enabling the architecture to adapt the compression rate of the transmitting frames. As a result, frames are largely compressed when the connection becomes unstable. In this section, the working scheme of the proposal, the architecture , the routing process and the ML model are detailed.
3.1. Working Scheme
The proposed architecture follows two main stages which are regularly executed: scanning and analyzing the network context, and adapting video-streaming to contacted nodes. The combination of these tasks enables an accurate analysis of the nodes available in the context, while dynamics communications are carried out.
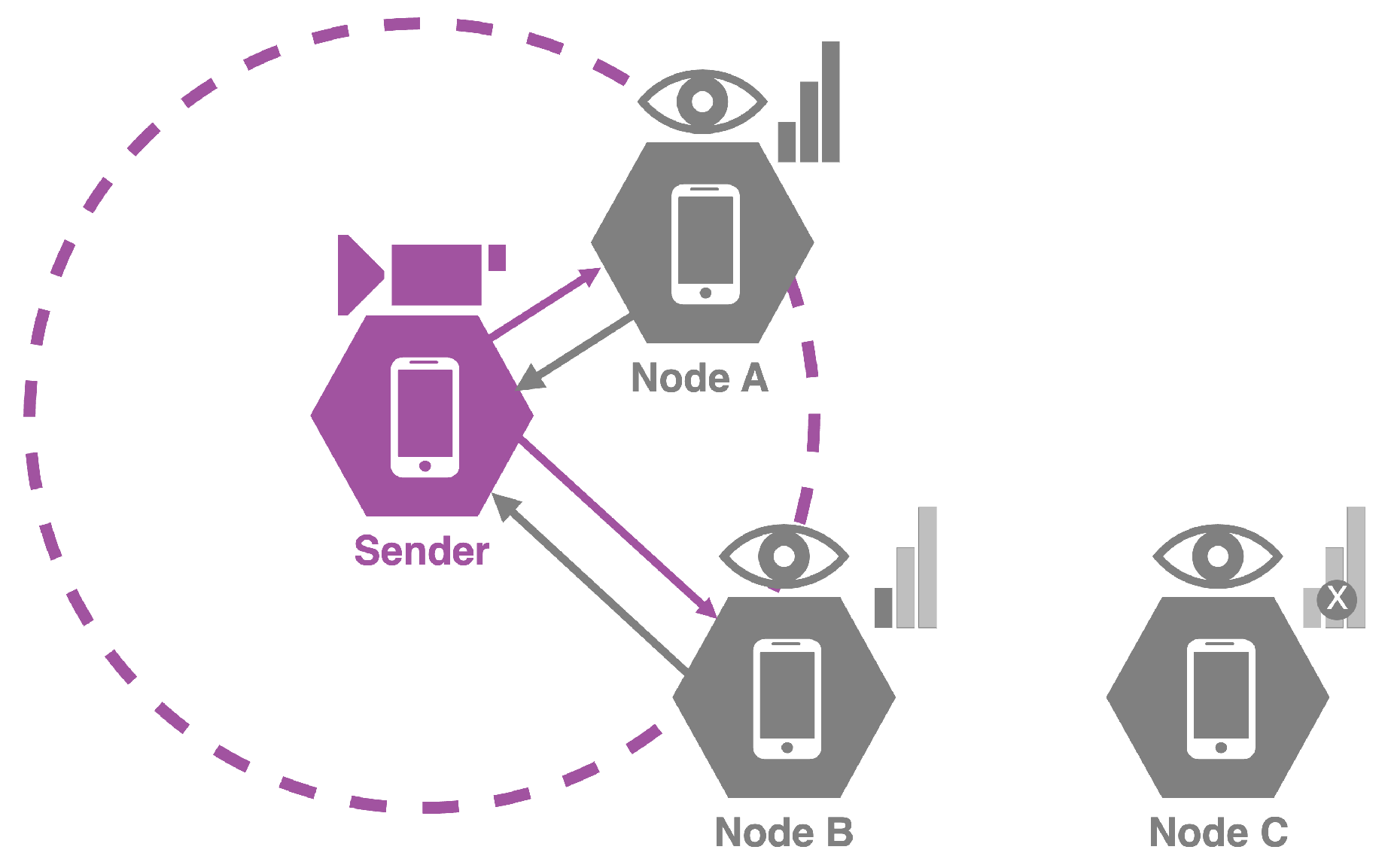
Figure 1 depicts an initial scenario for a MANET. In this case, four nodes are located in the context: Sender, Node A, B and C. In the case of the first one, it is in charge of broadcasting live-video streaming, while the remaining nodes are spectators. In order to scan and evaluate the network, sender performs multiple pings to surrounding nodes, registering the RSSI, throughput, Bit Error Rate (BER), number of connection attempts, latency and distance. These metrics are used by the model to evaluate the link stability (
Table 1), predicting if the current connection is stable or unstable. As a result, frames in the video streaming can be compressed accordingly.
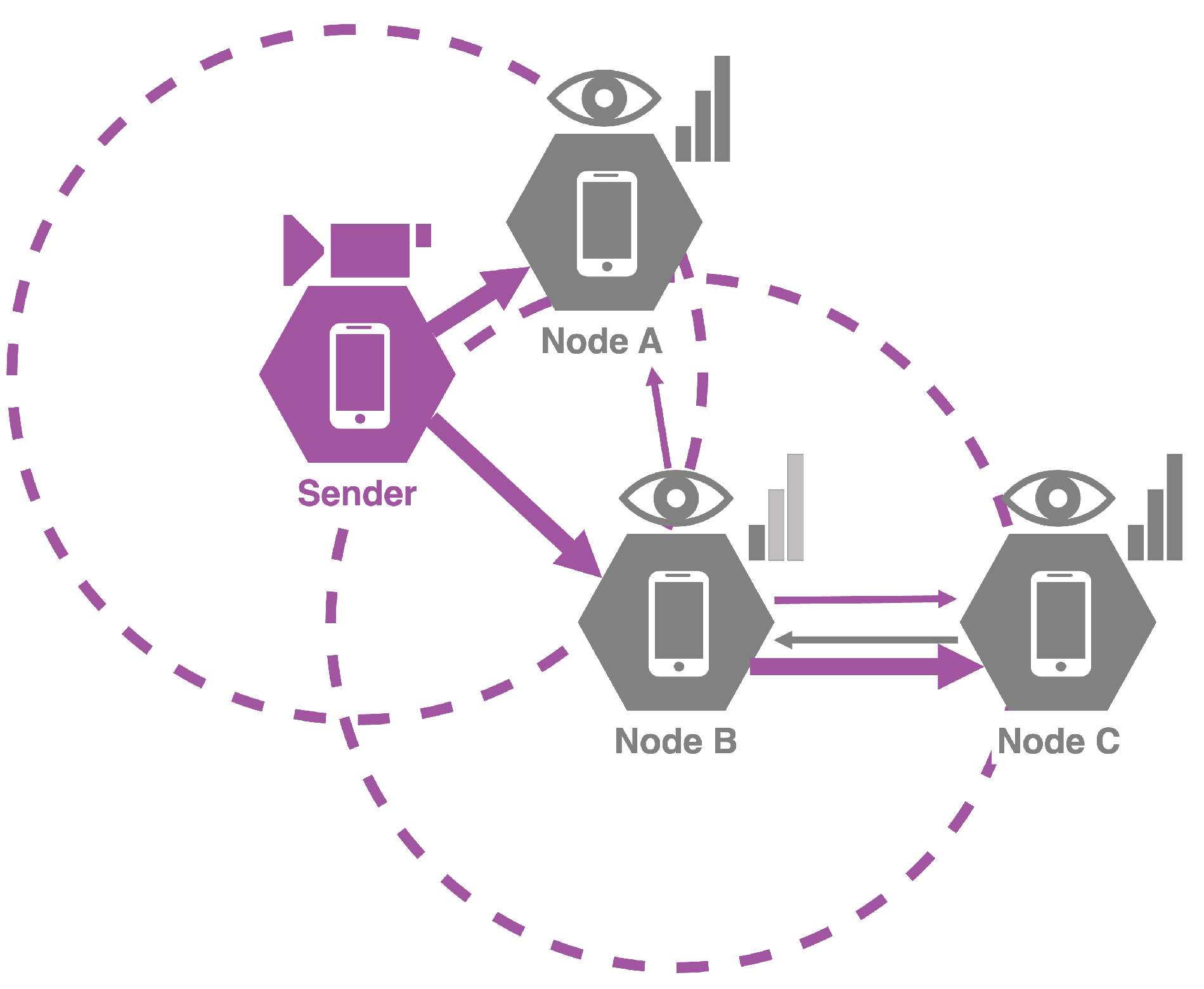
Figure 2 illustrates the progression of the first scenario. After the nodes are identified by the sender and their stability is classified, adaptive video streaming is transmitted to the connected nodes. Specifically, Node A receives frames with low compression due to its stable connection. Conversely, due to its unstable connection, Node B receives highly compressed frames. Initially, Node C is not recognized by the sender. Nonetheless, other nodes conduct pings to surrounding devices and evaluate the responses. In this scenario, Node B pings both A and C but only receives a response from C, as nodes do not accept more than one concurrent incoming communication if their current link is classified as stable. Consequently, Node C is recognized as a new node and receives video streaming, which is adapted by the intermediate node. This process facilitates routing in MANETs, with dynamic adaptation of compression.
These advances are made possible through the coordination of multiple transmission processes. Therefore, the proposed architecture comprises multiple elements dedicated to communication management, link prediction, and frame forwarding. With this in consideration, the following subsection will analyze the internal elements that constitute the proposal.
3.2. Architecture
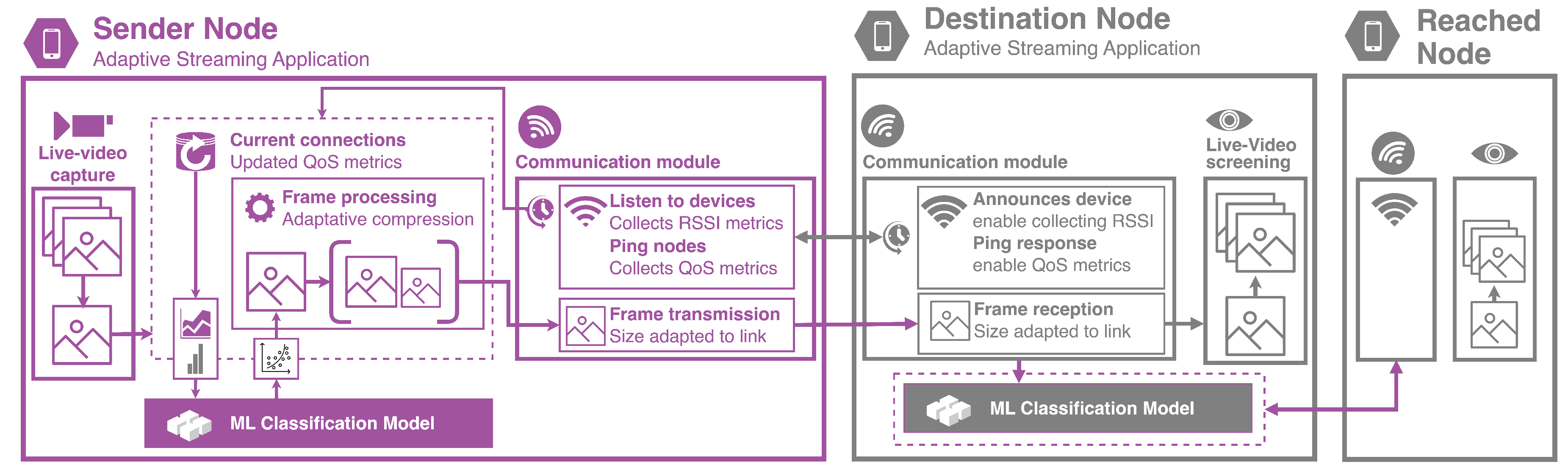
The proposed application relies on the integration of various software-based components, facilitating dynamic and individual adaptability of streaming. As depicted in
Figure 3, the functionality of the involved elements varies based on the node’s role. A device assumes the sender role when it is responsible for capturing live video, whereas it becomes a destination when receiving and displaying the live video streaming. Additionally, these nodes play a crucial role in routing the streaming to destination devices that are not directly reached by the sender.
The sender node performs three main tasks: scanning and analyzing the network context; capturing live-video; adapting frame compression and delivering frame.
Scanning and Analyzing the Network Context (Communication Module): The sender node monitors surrounding devices that announce their presence, identifying them as nodes within the MANET. Subsequently, the sender pings these devices to collect a set of performance metrics, which are utilized to classify the connection’s stability. A pre-trained ML-based classification model processes these parameters to determine if the link is stable. The insights gained from this scanning process are then used to adjust frame compression. Therefore, scanning and analysis are conducted periodically to keep the link states updated.
Capturing Live Video: Video streaming is initiated by the sender node, which captures a series of frames comprising the video flow. A lightweight buffer is employed to retain frames during the transmission process.
Adapting Frame Compression and Delivering Frame: After capturing a frame, its compression can be modified based on the stability prediction of the link. This adjustment takes into account the latest prediction for each individual connection. Given the frequent updates to the predictions, the system can respond to dynamic changes in network topology by adjusting frame quality accordingly.
Alongside these processes, destination nodes undertake a series of tasks aimed at receiving video streaming and simultaneously acting as intermediate nodes for devices beyond the sender’s direct reach. These tasks encompass three main activities: scanning and analyzing the context, screening the video, and re-transmitting the video.
Scanning and Analysis of the Network: Employing a strategy akin to that used by the sender, nodes conduct selective pings to assess the quality of their links. Consequently, the pool of connections is narrowed down to nodes not designated as senders. Furthermore, surrounding nodes only accept one concurrent incoming connection if their existing link is either predicted to be stable or originates directly from the sender. This policy is devised to prioritize traffic from the sender. Consequently, pings that are accepted are then utilized to gather metrics and forecast the quality of active links. To ensure this information remains current, this procedure is executed periodically.
Screening Video: After receiving the frames from the sender, the receiver stores these images in a flash buffer. This setup facilitates video screening for the user, allowing them to view the stream while concurrently re-transmitting content to other nodes. Given that images are dynamically compressed at the source, the resolution of the received stream may vary, reflecting the quality of the link.
Re-transmitting Video: Drawing on the data acquired during the scanning and analysis phase, the node may adjust the compression of frames based on the anticipated link quality. Nonetheless, with the intention of circumventing excessive compression of frames—which could diminish legibility after several hops—a minimum threshold is established.
Given the importance of the stages outlined, routing emerges as a crucial step for nodes within the MANET. Consequently, the following subsection will delve into the strategy employed and the principal decisions made regarding routing.
3.3. Routing Policy
Streaming in MANET networks presents a significant challenge due to frequent disconnections between nodes. The architecture introduces a strategy for establishing connections that focuses on prioritizing high-quality links and direct contact with the sender. Receiver nodes act as intermediate devices within the MANET, detecting nearby devices through pinging and assessing communication metrics. To maintain more stable connections, nodes that are already connected to the sender or another node refrain from accepting additional incoming transmissions. However, this approach may lead to nodes rejecting new links that could potentially offer greater stability than the existing ones. Therefore, it is crucial to establish a policy that ensures the optimization of current connections, guaranteeing that they are the most stable option available.
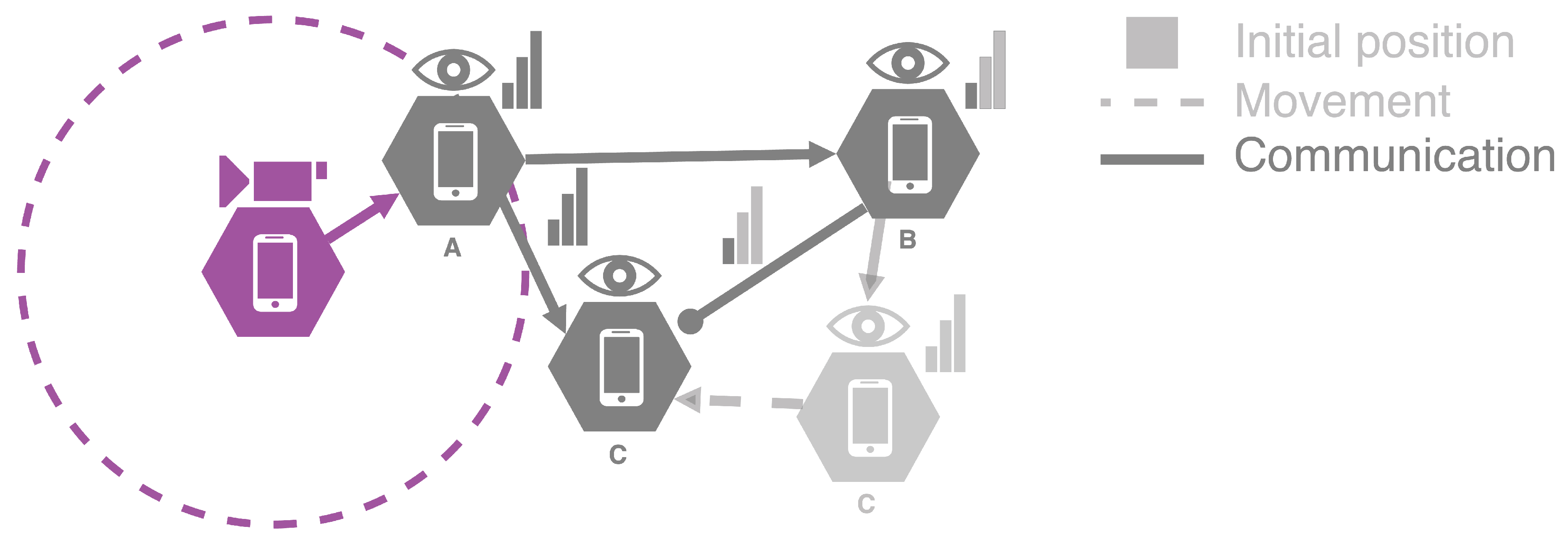
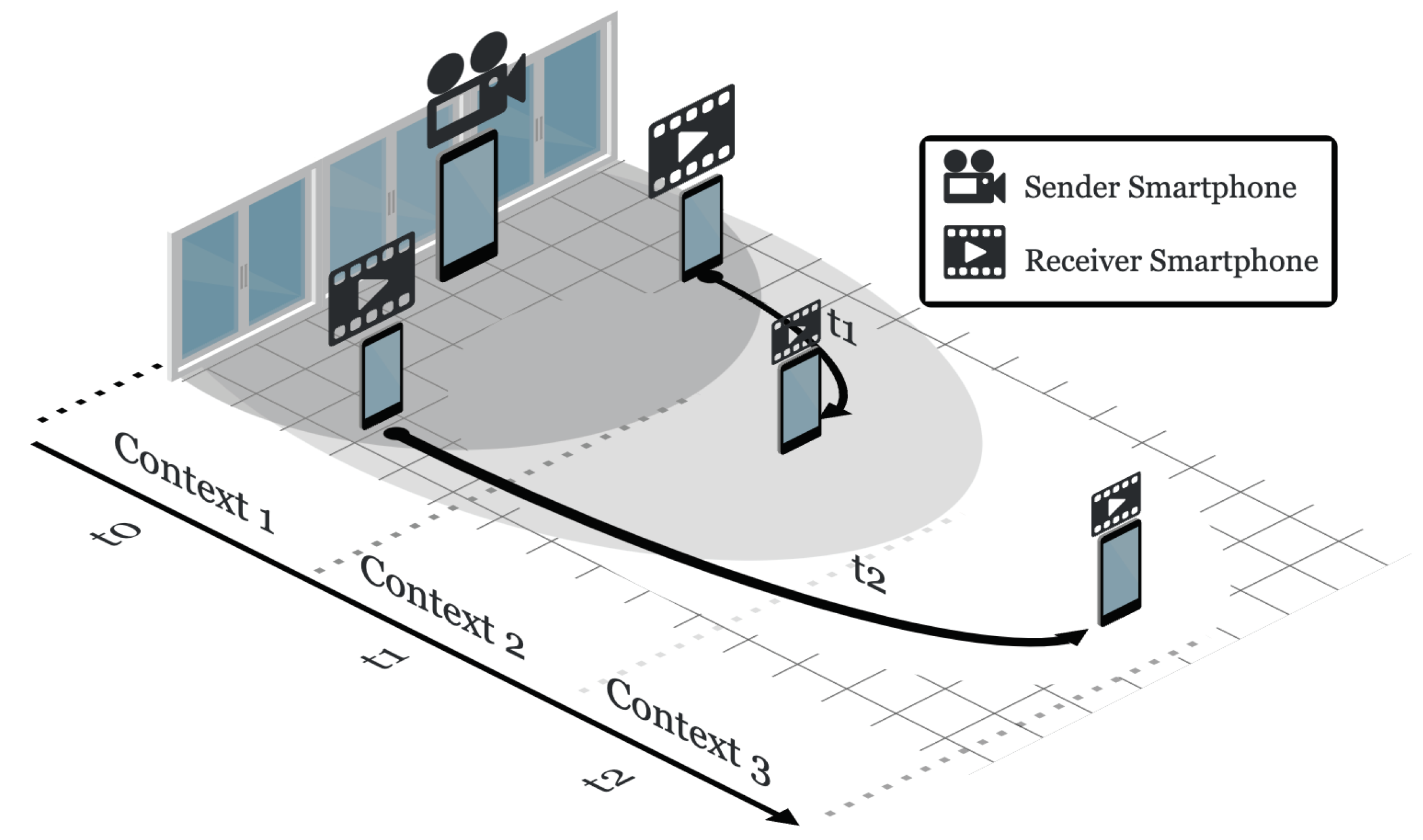
Figure 4 illustrates the routing policy implemented in the architecture, involving three nodes and the sender within a specific context. Initially, Node C is reachable only through Node B, which acts as a relay for video streaming transmission. Over time, Node C moves closer to Node A, resulting in Node A recognizing this link as stable. Concurrently, as Node B distances itself, its link with Node C is deemed unstable. Consequently, Node C has the option to switch to the newly established stable link with Node A, thereby disconnecting from Node B. This dynamic process underscores the architecture’s ability to adaptively manage connections based on evolving link stability.
This strategy facilitates dynamic connections between devices within the MANET, leveraging knowledge and predictions to improve the overall communication performance. Technically, Algorithms 1 and 2 detail the routing strategy. More specifically, Algorithm 1 involves checking surrounding connections and pinging them to gauge connection metrics. Algorithm 2, pinged nodes respond to requests only if they are not directly receiving streaming from the sender or if their current link to another node is unstable. Senders manage this scenario with timeouts, allowing them to stop waiting for a response. If pinged nodes are not connected to any node or their current link is deemed unstable, they reply to the ping, thereby enabling senders to assess communication metrics and predict link stability with their pre-trained classification model. Subsequently, the sender communicates the prediction results to the receiver, which then evaluates whether the stability of the new link is superior to the existing one. If the assessment is positive, the node discontinues the current link and starts receiving streaming from the new sender. If not, no changes to the link are made.
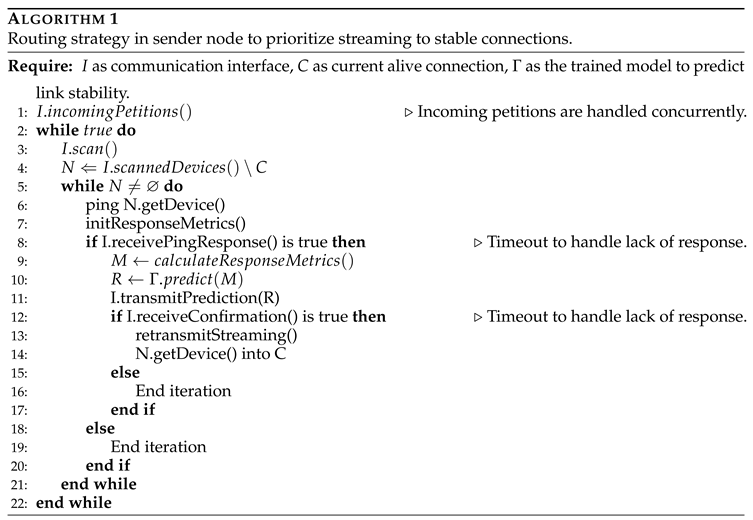
This strategy outlines a method to address the variability of links in MANETs, aiming to sustain communication stability. Here, ping processes play a vital role in identifying contextual variables, thus enabling a distributed, self-governed approach for video streaming retransmission. At the heart of the proposal is the ML-based classification model. The following subsection will elaborate on the key features involved in link stability prediction.
3.4. ML Classification Model
The architecture incorporates a pre-trained ML classification model designed to forecast the stability of network links. To achieve this, the model utilizes a collection of connection attributes both for training and making predictions. As outlined in
Table 1, the features include RSSI, throughput, BER, number of connection attempts, latency, and distance. These parameters equip the model with essential and streamlined insights into the potential stability of the link. For the purpose of classification, two distinct methodologies can be adopted: binary and multi-class classification, each offering a different level of granularity in assessing link stability.
In the context of binary classification, two primary categories can be distinguished: stable link and unstable link. This distinction allows for the adaptation of video streaming into two compression modes: highly compressed and lightly compressed. On the other hand, multi-class classification offers a more detailed level of granularity, enabling the categorization of links into a broader range of options. This approach contributes to a more precise identification and classification of link stability, facilitating tailored streaming adjustments.
The classification predictions offered by the model necessitate establishing a definitive hierarchy to assess the stability of the links. This enables prioritization of connections that demonstrate superior performance. Similarly, training the models demands datasets rich enough to deduce the stability of these links. Two methodologies can be pursued in this regard: one involves labeling connection sets for supervised learning, and the other relies on using unlabeled communication datasets, which steers the training towards unsupervised learning. The choice between these methods depends on the context’s specific nature and the data’s availability. Moreover, given that the architecture is intended for deployment on mobile nodes, federated learning [
23] emerges as a viable strategy for managing model updates and facilitating iterative enhancements.
Federated learning is a ML approach that involves deploying a pre-trained model across a set of nodes for individual predictions, which may include further training with newly introduced data [
23]. This method allows for the consolidation of advancements from various models into a central model, striving for a comprehensive understanding of all individual models’ insights. Additionally, the synchronization processes can be executed when devices have Internet access, facilitating autonomous operation in offline scenarios. Therefore, federated learning introduces an additional layer that could potentially enhance the overall performance of the architecture.
Leveraging the potential of the proposed model, the architecture integrates ML as a pivotal element to enhance video streaming performance in MANETs and serves as a foundation for adaptive streaming. A proof-of-concept has been developed to assess the technical feasibility and performance of the classification model, alongside analyzing QoS and QoE metrics derived from the testing phase.
4. Results
To evaluate the proposal presented in this paper, a proof of concept application for smartphones was developed. This implementation facilitates the examination of streaming transmission performance, adhering closely to the outlined architecture. A variety of contexts were established to conduct comprehensive assessments, focusing on evaluating model performance as well as the QoS and QoE outcomes. This section presents the testbed scenario, describes how the model was trained, and provides an analysis of QoS and QoE.
4.1. Testbed Scenario
The testbed has been carried out in a laboratory context, utilizing a proof-of-concept implementation that enables the transmission of real-time video streaming in MANETs. This is achieved by using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for context recognition and Bluetooth Classic for the transmission of frames between nodes. This technology was chosen due to its capability to broadcast information between smartphones without the need for prior pairing. Unlike Wifi Direct [
24], no prior configuration is necessary, thus enabling the opportunistic broadcasting of information.
The developed application was installed on three physical smartphones: one device had the task of capturing real-time video and two phones were responsible for receiving, screening, and routing the streaming. These nodes are engaged in three different scenarios. The experiments were conducted in a laboratory context, where the physical positions of the devices was changed. This setup allows for the assessment of the proof-of-concept implementation’s performance under multiple network conditions. Consequently, as
Figure 5 illustrates, three distinct contexts (
C) were considered: a first context where receiver nodes are in contact with the sender (
); a second context where one of the receiver devices moves to the edge of the communication range of the sender (
); and a third context where a receiver device moves out of the sender’s range, requiring the other receiver device to act as an intermediate node by routing the streaming (
). This enables the evaluation of the impact of the dynamic topology on the architecture and the resilience of the adaptive video streaming and routing strategy.
A sequence of four iterative tests was performed for each scenario, to minimize potential deviations. Before conducting these tests, the model integrated into the proof-of-concept was trained with real-world data on interactions in MANETs. The following subsection will provide a detailed analysis of this process.
4.2. Training the Model
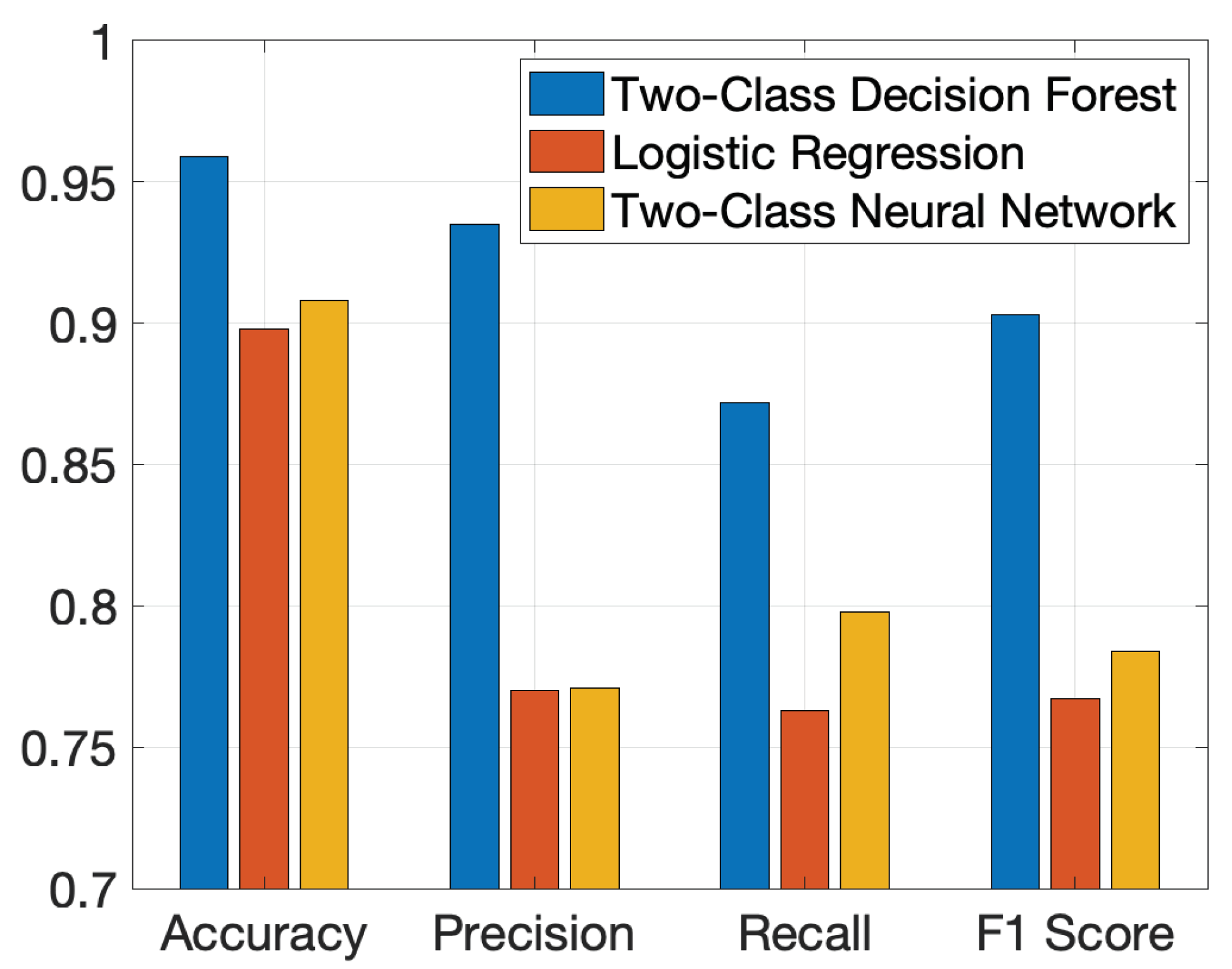
After conducting a sensitivity analysis, the Two-Class Decision Forest emerged as the model providing the best overall results, outperforming both Logistic Regression and the Two-Class Neural Network. As depicted in
Figure 6, the Two-Class Decision Forest achieved the highest scores across several metrics, including accuracy (0.959), precision (0.935), recall (0.872), and F1 Score (0.903). These results indicate that the model successfully predicted most of the evaluation data. The high accuracy score demonstrates effective classification in the majority of cases. Precision highlights that stable links were correctly identified in 93.5% of instances. The recall rate, closely mirroring precision, shows the model’s ability to accurately flag most unstable connections. Lastly, the F1 Score, representing the balance between precision and recall, attains a high value, reinforcing confidence in the model’s performance.
In this scenario, binary classification was chosen over multi-class classification primarily for the accuracy in generating training data. The dataset employed for training the model was created based on communication statistics from links within a physical MANET, comprising five dynamic devices. Links were self-labeled as stable when flows of ping messages were successfully received back by the sender. Conversely, transmission errors were marked as indicators of unstable links. Consequently, the model was trained using bagging as the resampling method, with a total of eight decision trees. Furthermore, each tree was restricted to a maximum depth of 32. This configuration was designed to mitigate overfitting during the training process. As a result, the training data facilitated the model’s training, adhering to a set of predefined configurations.
The input values proposed for the model are part of a strategy designed to achieve high accuracy in optimization, with a low tolerance value (10E-07) and elastic net parameters for L1 and L2 weights. After training, it was observed that attributes such as distance, disconnections, Bit Error Rate (BER), and latency are assigned negative weights, indicating their inverse impact on stability classification. Conversely, the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) is identified as having a direct positive impact on the outcomes, while parameters like throughput are not deemed significantly relevant.
As a result, the global evaluation score of the model is positive and encouraging. Predicting the stability of links in MANETs is a challenging task, since the network may behave randomly. However, the obtained results highlight a significative performance.
4.3. Analysis of QoS and QoE
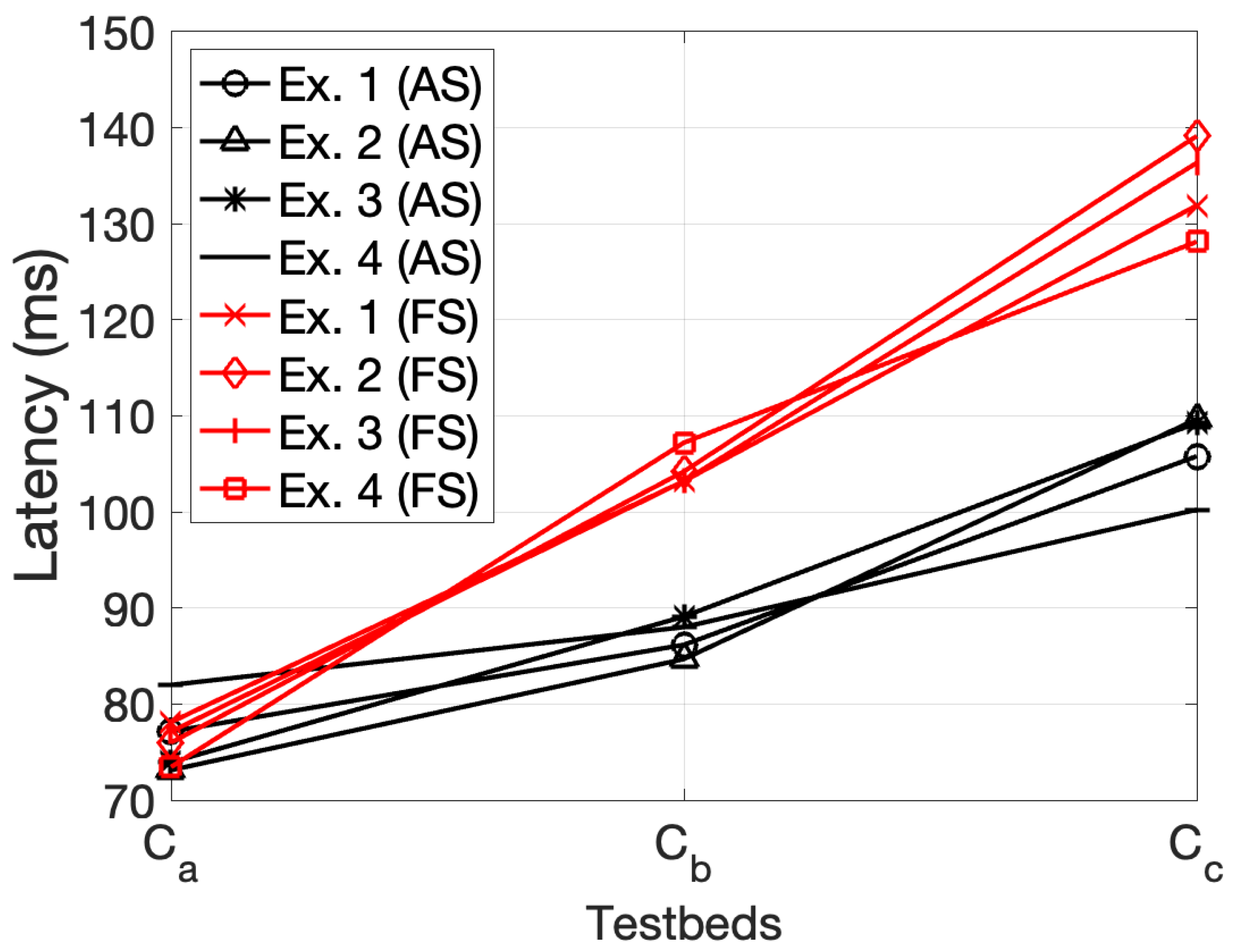
During the execution of the application in the different contexts, QoS and QoE parameters were used to evaluate the impact of adaptive video streaming. Aiming to compare the obtained results objectively, latency has also been measured applying fixed-compression transmission. Furthermore, latency values were also considered, due to its significant relevance in the communication. As a result,
Figure 7 represents the resulting values of latency for the adaptive video streaming (Adapted Streaming, AS) and for fixed-compression streaming (Fixed Streaming, FS), including individually the executions of the three contemplated scenarios.
Figure 7 displays lower latency values for adaptive streaming. It is possible to observe an increasing tendency as the distance between sender and nodes increases (
and
). However, dynamic frame compression improves fixed compression, easing transmission and improving latency. As a result, it is possible to observe a global stable tendency, viable for video streaming and resilient to node movements.
On the other hand, QoE can be assessed under variables such as the resolution of the received images. In this context, the proof-of-concept compresses around 40% the frames in case of the link is identified as unstable. Thus,
Figure 8 displays two frames, extracted from the live-video, one corresponding to low compression rate, and another with high compression rate.
In this visual comparison, differences in the quality of the images are noticeable. However, the loss is not pronounced in shape identification or resolution but rather in colors and sharpness. In subfigures 8a and 8b,, variations in color tones are observable, particularly in the blue color, clouds, and mountains in the background. Nonetheless, buildings are discernible in both frames in a very similar manner. As a result, variations in compression are not immediately obvious to the viewer.
The implemented proof-of-concept yields promising outcomes. Firstly, the trained classification model secures high evaluation scores, demonstrating its efficacy in accurately classifying encounters based on their stability. Secondly, applying this model within a physical MANET highlights the technical feasibility of the proposal and the effective latency reduction achieved through adaptive video compression. Additionally, from the user’s perspective, changes in compression have no discernible effect on the appearance. Therefore, even if there is a shift in link classification while video streaming is in progress, the variations in quality are not drastic. Consequently, the experimental results present encouraging findings that pave the way for further enhancements of the proposal in future research work.
5. Conclusion and Future Work
Live-video streaming in MANETs has emerged as a frequent area of research in recent years, driven by the unique challenges these networks present. The dynamic nature of MANETs, characterized by unstable and unpredictable topology and potential disconnections between nodes, poses considerable obstacles to maintaining QoS in live flow transmissions. This paper introduces a software-based architecture designed to facilitate adaptive streaming in MANETs by leveraging ML techniques. The objective of this approach is to alleviate the adverse effects posed by the inherent challenges of these networks, thereby ensuring a more stable and reliable live-video streaming experience in MANET environments.
The approach presented in this paper utilizes classification techniques to identify the potential stability of links between nodes. Consequently, based on the prediction, video streaming frames are compressed accordingly. This strategy can improve QoS by reducing the streaming size. This proposal has been implemented and evaluated in a physical MANET, using a decision tree classification model and Bluetooth as the communication interface. The model achieves an accuracy of 95.9% and an average latency ranging from 75 to 106 milliseconds. Additionally, adaptive compression does not critically affect quality, enabling smooth transitions if the link becomes unstable.
The future work will be mainly focused on refining the implementation of the proposed architecture. For this purpose, the proof-of-concept may evolve into a more robust solution, providing overall better performance. Enhancing routing could reduce the workload of sender nodes, aiming to distribute tasks. Additionally, exploring multi-class classification can achieve higher granularity, improving predictions about the stability of links by including intermediate states. As a result, the presented work becomes a solid initial approach towards improvement in video streaming in offline MANETs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.A., V.N.G.J.S and J.G.J.; software, M.J.A., V.N.G.J.S and J.G.J.; validation, M.J.A., V.N.G.J.S and J.G.J.; funding acquisition, V.N.G.J.S and J.G.J.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been partially funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/ 501100011033 and by the European Union “Next GenerationEU /PRTR”, by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (projects TED2021-130913B-I00, PDC2022-133465-I00), European Union’s Digital Europe Programme (DIGITAL) under grant agreement Nº101083667-TECH4EFFICIENCYEDIH. Co-funded by the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Tourism of the Government of Spain, within the framework of the Recovery and Resilience Mechanism. However, the views and opinions expressed are solely those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the Government of Spain. Also, Science and Digital Agenda of the Regional Government of Extremadura (GR21133) and the European Regional Development Fund. V.N.G.J.S. acknowledges that this work is funded by FCT/MCTES through national funds and when applicable co-funded EU funds under the project UIDB/50008/2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lüders, M.; Sundet, V.S.; Colbjørnsen, T. Towards streaming as a dominant mode of media use? A user typology approach to music and television streaming. Nordicom Review 2021, 42, 35–57. [CrossRef]
- Sandvine. The Global Internet Phenomena Report; Sandvine, 2023.
- Li, X.; Darwich, M.; Salehi, M.A.; Bayoumi, M. Chapter Four - A survey on cloud-based video streaming services. In Advances in Computers; Hurson, A.R., Ed.; Elsevier, 2021; Vol. 123, Advances in Computers, pp. 193–244. [CrossRef]
- Khan, K. A Taxonomy for Deep Learning in Dynamic Adaptive Video Streaming Over HTTP. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Analysis 2023, 06. [CrossRef]
- Baena, C.; Peñaherrera-Pulla, O.S.; Camacho, L.; Barco, R.; Fortes, S. Video Streaming and Cloud Gaming Services Over 4G and 5G: A Complete Network and Service Metrics Dataset. IEEE Communications Magazine 2023, 61, 154–160. [CrossRef]
- Pantos, R.; May, W. HTTP Live Streaming. RFC 8216, 2017. doi:10.17487/RFC8216. [CrossRef]
- Dao, N.N.; Tran, A.T.; Tu, N.H.; Thanh, T.T.; Bao, V.N.Q.; Cho, S. A Contemporary Survey on Live Video Streaming from a Computation-Driven Perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54. [CrossRef]
- Ramphull, D.; Mungur, A.; Armoogum, S.; Pudaruth, S. A Review of Mobile Ad hoc NETwork (MANET) Protocols and their Applications. 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), 2021, pp. 204–211. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Rishiwal, V.; Negi, A. A comprehensive survey on QoS for video transmission in heterogeneous mobile ad hoc network. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies 2023, 34, e4775, [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ett.4775]. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, Y.H.; Balaji, S.; Julie, E.G. FPSOEE: Fuzzy-enabled particle swarm optimization-based energy-efficient algorithm in mobile ad-hoc networks. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2019, 36, 3541–3553. [CrossRef]
- Fleury, M.; Kanellopoulos, D.; Qadri, N.N. Video streaming over MANETs: An overview of techniques. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2019, 78, 23749–23782. doi:10.1007/s11042-019-7679-0. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, J.; Singhal, A.; Yadav, R.N. Multipath routing in mobile Ad-hoc network using meta-heuristic approach. 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), 2017, pp. 1399–1406. [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.M.; Gasser, S.M.; El-Mahallawy, M.S.; Hammad, K.; El Bakly, A.M. A memetic optimization algorithm for multi-constrained multicast routing in ad hoc networks. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, W.E.; Guerri, J.C.; Arce, P. A QoS-aware routing protocol with adaptive feedback scheme for video streaming for mobile networks. Computer Communications 2016, 77, 10–25. [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Castellanos, W.; Guzmán, P.; Arce, P.; Guerri, J.C. Simulation and experimental testbed for adaptive video streaming in ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2016, 52, 89–105. Modeling and Performance Evaluation of Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Dixit, A.; Sethi, P. Link prediction techniques for opportunistic networks using machine learning. Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing & Communication (ICICC), 2021. [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.P.P.; Senthilkumar, V.; Kumar, G.; Rajendran, A.; Rajaram, A. Dynamic link utilization empowered by reinforcement learning for adaptive storage allocation in MANET. Soft Computing 2024, 28, 5275–5285. [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, A.; Yang, C.C. Frequent Pattern Mining in Continuous-Time Temporal Networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2024, 46, 305–321. [CrossRef]
- Gnana Prakasi, O.S.; Varalakshmi, P. Decision Tree Based Routing Protocol (DTRP) for Reliable Path in MANET. Wireless Personal Communications 2019, 109, 257–270. doi:10.1007/s11277-019-06563-z. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Classification of node degree based on deep learning and routing method applied for virtual route assignment. Ad Hoc Networks 2017, 58, 70–85. Hybrid Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. Adaptive video transmission in MANETs. 2009 2nd IEEE International Conference on Broadband Network & Multimedia Technology, 2009, pp. 749–754. doi:10.1109/ICBNMT.2009.5347782. [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathrao, B.A.; Vikhar, P.A. Reinforcement Machine Learning-based Improved Protocol for Energy Efficiency on Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering 2023, 12, 654–670.
- Mammen, P.M. Federated Learning: Opportunities and Challenges, 2021, [arXiv:cs.LG/2101.05428].
- Lagos Jenschke, T.; Dias de Amorim, M.; Fdida, S. Nearby connections strategies: Features, usage, and empirical performance evaluation. Internet of Things 2023, 23, 100895. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).