1. Introduction
Correct and consistent condom use is one of the key behavioral HIV prevention interventions that do not only limit the spread of sexually infections, including HIV prevention but also prevent unintended pregnancy particularly among the sexually active persons [
1].
Consistent and correct use of male latex condom reduces the risk of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission [
2]. Condom effectiveness for STDs and HIV prevention has been demonstrated by both laboratory and epidemiologic studies [
3], for instance laboratory studies have shown that latex condoms provide an effective barrier against even the smallest STD pathogens due to absence of microscopic holes [
4], it has also been reflected that the current levels of HIV would have been five times higher if it had not been for condom use [
5]. Similarly, epidemiologic studies have shown that condom use reduces the risk of many other STDs and provides greater protection against those that are transmitted only by genital fluids like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomonas [
3].
Currently, over 30% of all new HIV infections globally are estimated to occur among the youth of ages 15 to 25 years. Decreasing the number of sexual partners and increasing access to utilization of comprehensive prevention services, including prevention education and increasing access to condoms are essential for sexually active young people [
6].
Among university students, studies done on the prevalence of condom use and associated factors among female undergraduate students in Wuhan China showed that a larger subset of Chinese female undergraduate students engaged in unprotected, premarital sex [
7] and hence condom use among university students should be promoted from the onset of sexual activity to establish a habit of safe sex practices and improvement in self-efficacy [
8]; on exploring the determinants of condom use among university students in Sudan, the significant barriers towards condom use included misconception about condom use, negative attitudes towards condom use, lack of social support, low self-efficacy to use condoms and poor action planning [
9]. In addition to this, risky sexual behavior was associated with gender, age at first sexual intercourse, frequency of alcohol consumption, consumption of psychoactive substances before the last sexual intercourse and use of smartphone application for sexual purposes were found among the undergraduates of southern Brazil [
10] and similarly, condom use in the last sexual intercourse among undergraduate students of Rio Grande campuses in Brazil highlighted male gender, lower age group, condom use at first sexual intercourse, older age of onset of sexual activity, not having a partner and casual partner in the last sexual intercourse increased the likelihood of condom use [
11].
The prevalence of HIV among adults aged 15 to 64 in Uganda is 6.2%, 7.6% among females and 4.7% among males, this corresponds to approximately 1.2 million people aged 15 to 64 living with HIV in Uganda and HIV prevalence is higher among women living in urban areas (9.8%) than those in rural areas (6.7%) [
12]. The prevalence of HIV among children aged 0-14 is 0.5% which corresponds to approximately 95,000 children living with HIV in Uganda and looking more in depth at the HIV prevalence among young adults, the survey found that HIV prevalence estimates were higher among the 20 to 24 years age group than in the 15-to-19-year age group [
12] therefore, the above figures do show that condoms that play a significant role in HIV prevention has been used in a relaxed manner in the country.
Uganda as a nation has made considerable progress against the HIV epidemic in the recent years through provision of reproductive health services to its citizens. Condoms as one of the barrier contraceptive methods has been implemented by the Ministry of Health by advocating for nationwide distribution of condoms at a free cost or relatively very low cost that is affordable by the citizens. Studies done on condom use and its associated factors in Uganda particularly among Ugandan university students are still very low and basing on the available literature, currently there is no evidence of such a study in the northern part of the country especially in Gulu district yet it has the highest prevalence rate of HIV in the whole northern region and ranks among the top hotspots for HIV infection in the country.
This study is therefore, undertaken to determine the prevalence of condom use and associated factors among undergraduate students of Gulu university with a view of finding out public reaction and compliance towards the intervention of condom use as a strategy implemented by WHO, UNAIDS and MoH to combat transmission of HIV/AIDS and other STIs as well as unwanted pregnancy not only within countries but also globally.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
We conducted a cross-sectional study among undergraduate students of Gulu University, Gulu, Uganda between June and December 2023.
2.2. Study Area
Gulu University consists of three branches or campuses which include Gulu, Kitgum, and Hoima. The study was done at Gulu University main campus located in Pece-Laroo Division, Gulu City, Uganda.
Gulu main campus is approximately 5 kilometers, by road, northeast of the central business district of Gulu, the largest city in Uganda’s northern region. This is approximately 333 kilometers by road, north of Kampala, Uganda’s capital and largest city. The coordinates of the university’s main campus are 2
◦47’19.0” N, 32
◦19′01.0” E (Latitude:2.788620, Longitude:32.316946) [
13].
Gulu University’s main campus comprises of six faculties: Medicine, Agriculture and Environment, Science, Business and Development Studies, Education and Humanities, Law, and an Institute of Peace and Strategic Studies. All six faculties are confined within Pece-Laroo Division of Gulu City. Agricultural Business, Education, Management, Business Administration and Education, Communication Studies, Computer Education and Science, Agriculture, Art Education, Development Studies, Economics, Education, Food Bioscience, Humanities and Social Sciences Education, Information Technology, Medicine and Surgery, Public Health, Physical Education, Public Administration and Science Education are the various courses on the undergraduate scheme [
14]. It has an estimated population of at least over 3500 students enrolled in various programs from the different faculties. Gulu’s main campus was chosen because it has the biggest population of all the three branches and hence the required sample was easily met.
2.3. Study Population
The study participants were the undergraduate students of Gulu university, Gulu district, Uganda who provided written informed consent.
2.4. Sample Size Determination
The modified Kish Leslie was used to determine the size of the sample and generate the minimum number of participants required to participate in the study using the following assumptions; a margin error of 5% at 95% CI, and a 50% probable condom use was expected among the participants. Using a 0.95 response rate, the final estimated sample size was 404 participants.
2.5. Sampling Procedure
Gulu university main campus comprises of six faculties. The students were selected using a simple random sampling method following initial stratification of the different faculties into independent units. We obtained student lists from each faculty for all the students from the faculty Academic Registrars of the respective faculties and each faculty was sampled independently. Sequential numbers were assigned to each of the students in their respective faculties to establish the different sampling frames and available population for each faculty. A random number table was generated from Microsoft Excel and samples were continuously drawn until the required number of study participants for each faculty were met. The random numbers chosen from the generated random number table were matched against the student’s sequential numbers and names and these were selected for the study.
2.6. Data Collection
Data were collected for a period of 6 months. Data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire to assess condom use together with the associated factors among the students of Gulu university. Upon arrival at the respective faculties, the research participants were approached in correspondence to their names and random numbers assigned to them. This was done before the students exited their lecture halls upon request from their lecturers and the students themselves as their lectures came to an end. Written informed consent was obtained from them prior to participating in the study and whoever consented to take part in study was given the questionnaires to fill and those who declined consent were excused and we moved on to identify the next participants. Brief instructions were given to the study participants before the filling process and the investigators were available throughout the process to respond to any query, collect and secure the filled-up questionnaires. Codes were used instead of participants names on the questionnaires to ensure confidentiality. Every session for filling the questionnaire took at least 5 to 10 minutes.
2.7. Data Analysis
The filled questionnaires were checked for completeness and data was entered into Microsoft Excel and then cleaned and coded in Microsoft excel. The coded dataset was exported into Stata version 18.0 for analysis. Categorical variables were summarized using frequency and corresponding percentage. The prevalence of condom use was measured as the number of students who had ever used condoms in the last six months out of the total number of students that participated in the study and this was presented as a pie chart. Association between independent variables like year of education and faculty and dependent variable (Condom use) was assessed using either Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test depending on the number of cells on cross tabulation and was reported as p value. Variables with p<0.2 were taken for multivariable modified Poisson regression analysis to assess for factors independently associated with condom use. These were presented as adjusted prevalence ratio with corresponding 95% confidence interval and p value. A p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.8. Ethical Considerations
The study received ethical approval from the Gulu University Research Ethics Committee (approval number: GUREC-2023-520). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before the start of the study. Participants were informed of their right to withdraw from the study at any time and that their participation was voluntary. All data collected was kept confidential and anonymous. The ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki were all adhered to.
3. Results
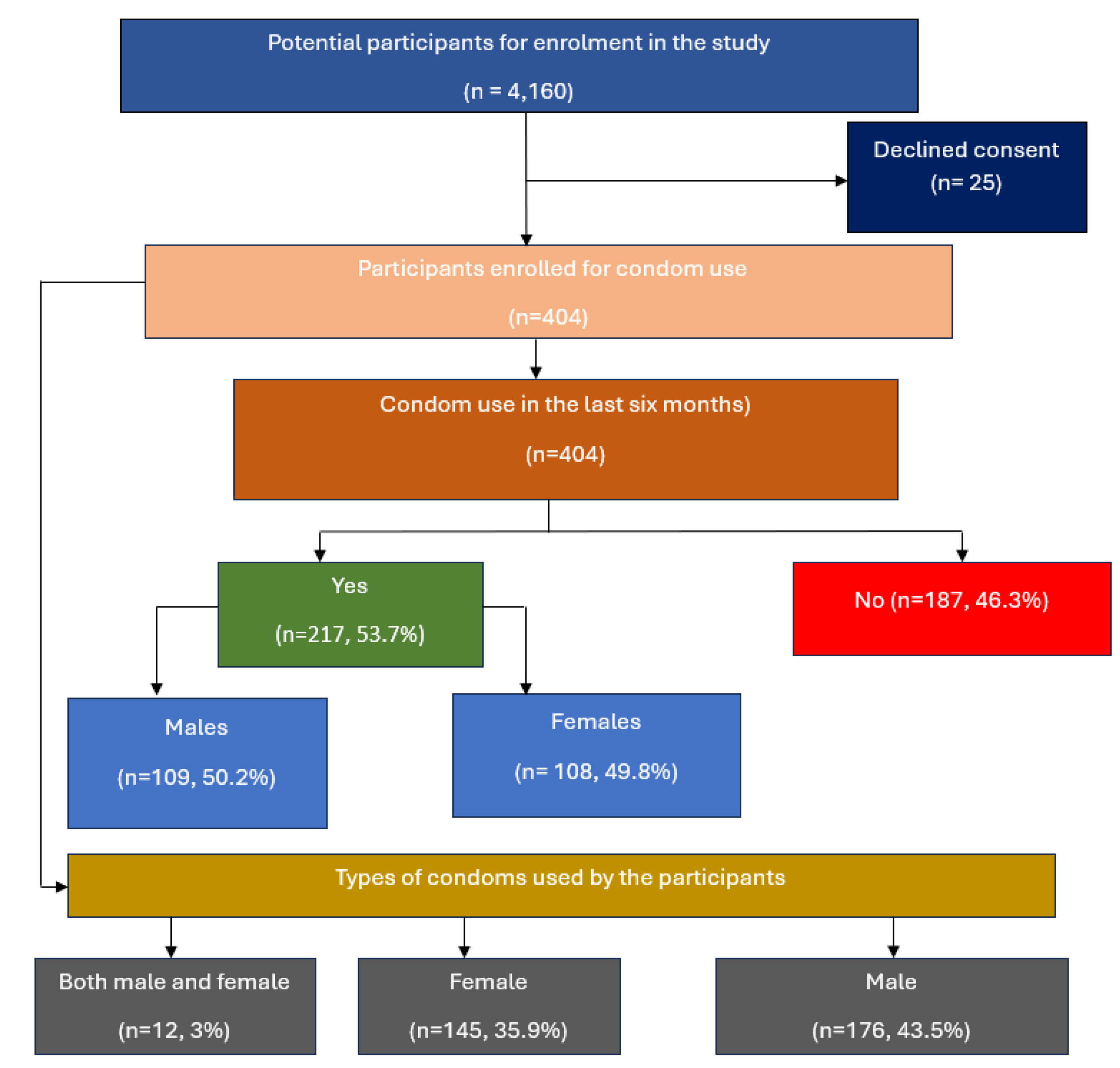
Study enrolment
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram.
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram.
3.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics
A total of 404 participants with a median age of 23 years (interquartile range (21.5-24) years) were enrolled in the study. More than half 54.2%(n=219) were male and 45.8%(n=185) were females. Majority 81.4%(n=329) were in senior classes (year 2,3,4, and 5) and 18.6%(n=75) were in their first year of study. At least half 51.5% (n =208) of the respondents had sexual partners and 63.9%(n=133) of these were in stable relationship, 30.3%(n=63) were casual and 5.8%(n=12) were married. Most of the participants 58.7%(n=237) had their sexual partners out of campus and 41.3%(n=167) had theirs within the campus and of these, the majority 68.1%(n=275) had had sexual intercourse in the last six months of which 78.9%(n=217) used a condom and 21.1%(n=58) did not. Majority 96.5%(n=389) did not engage in buying or selling sex. Most of the respondents knew their HIV status 87.6%(n=354) and of these, 99.1%(n=351) were negative. It was also found out that fewer respondents carried out HIV testing before sex 33.9%(n=137) and 46% (n =63) of these did their tests from the nearby clinic, 26.5%(n=107) had ever heard of PrEP whereas 41.6%(n=168) had ever heard of PEP. Majority of the study participants 84.5%(n=339) reported no experience of condom bursting while 28.8%(n=116) of the respondents reported the use of other methods of contraceptives and majority of these 88.1%(n=104) indicated emergency pills. Majority of the participants 62.1%(n=251) reported no sex in the absence of condoms and 68.8%(n=278) of participants reported no drinking of alcohol,
Table 1.
3.2. Prevalence of Condom Use
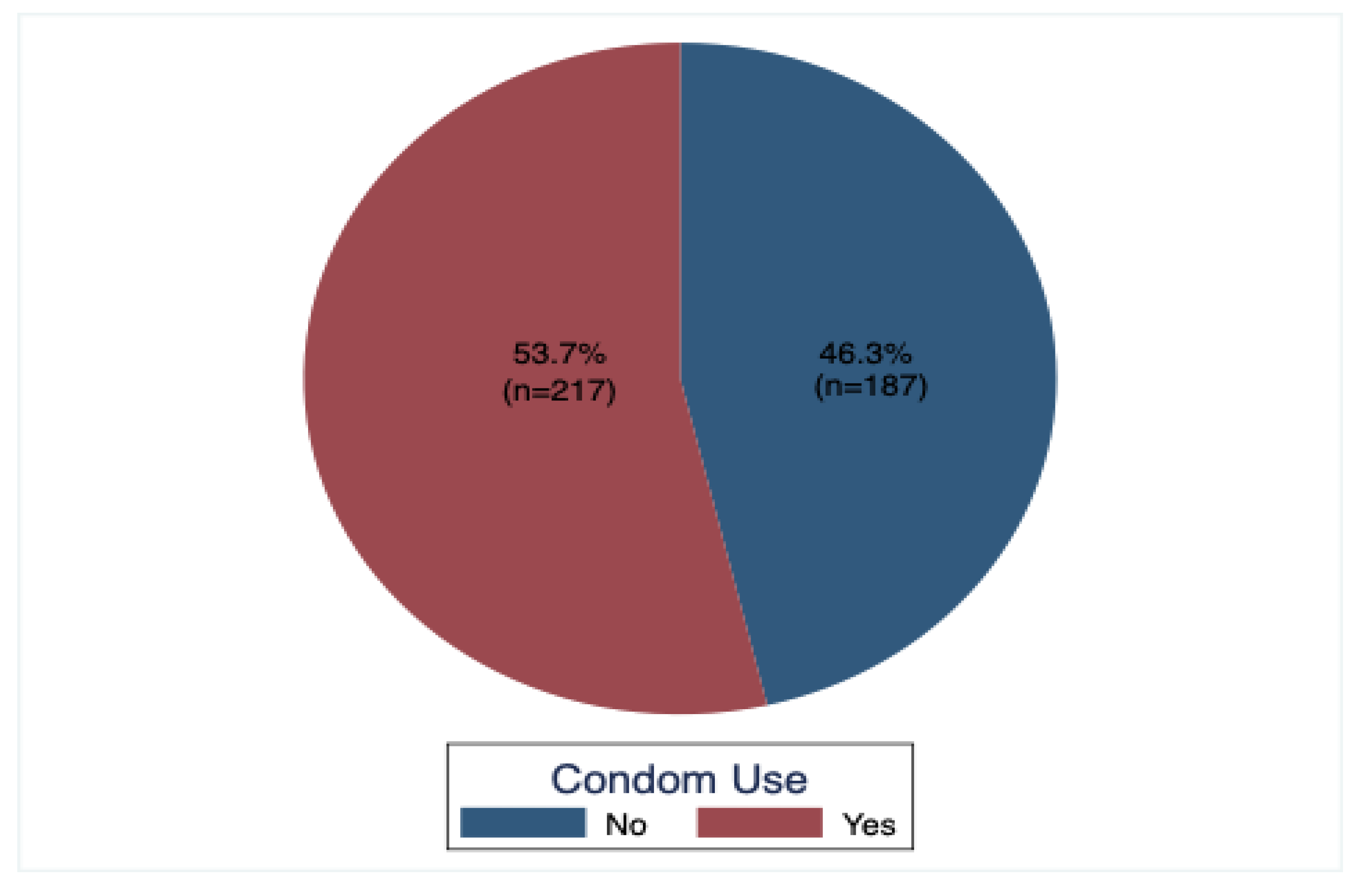
The study determined the prevalence condom use by asking the study participants if they had had sexual intercourse in the previous six months, those who answered yes were asked further question as to whether they had used a condom during that occasion or not, whoever acknowledged that they had indeed used a condom was considered and this study found out that the prevalence of condom use among the undergraduate students of Gulu university was 53.7% (n=217),
Figure 1.
3.3. Type of Condom Used
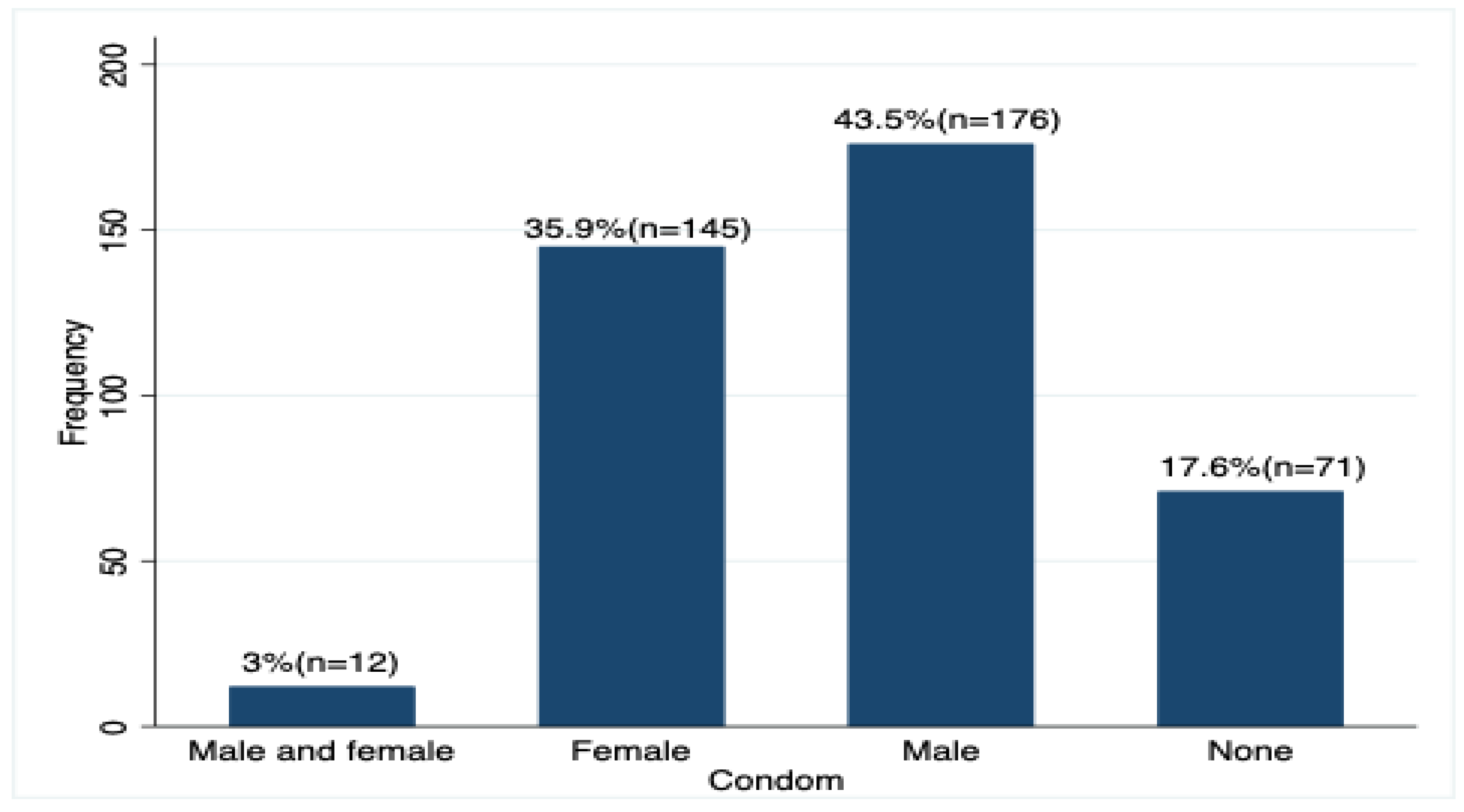
The study assessed use of both male and female condoms, female condoms and male condoms and those who didn’t use any and it was found out that the male dominated 43.5% (n=176) and this indicates that the male condoms were mostly being used compared to the female condoms,
Figure 2.
3.4. Consistency in Condom Use by the Participants
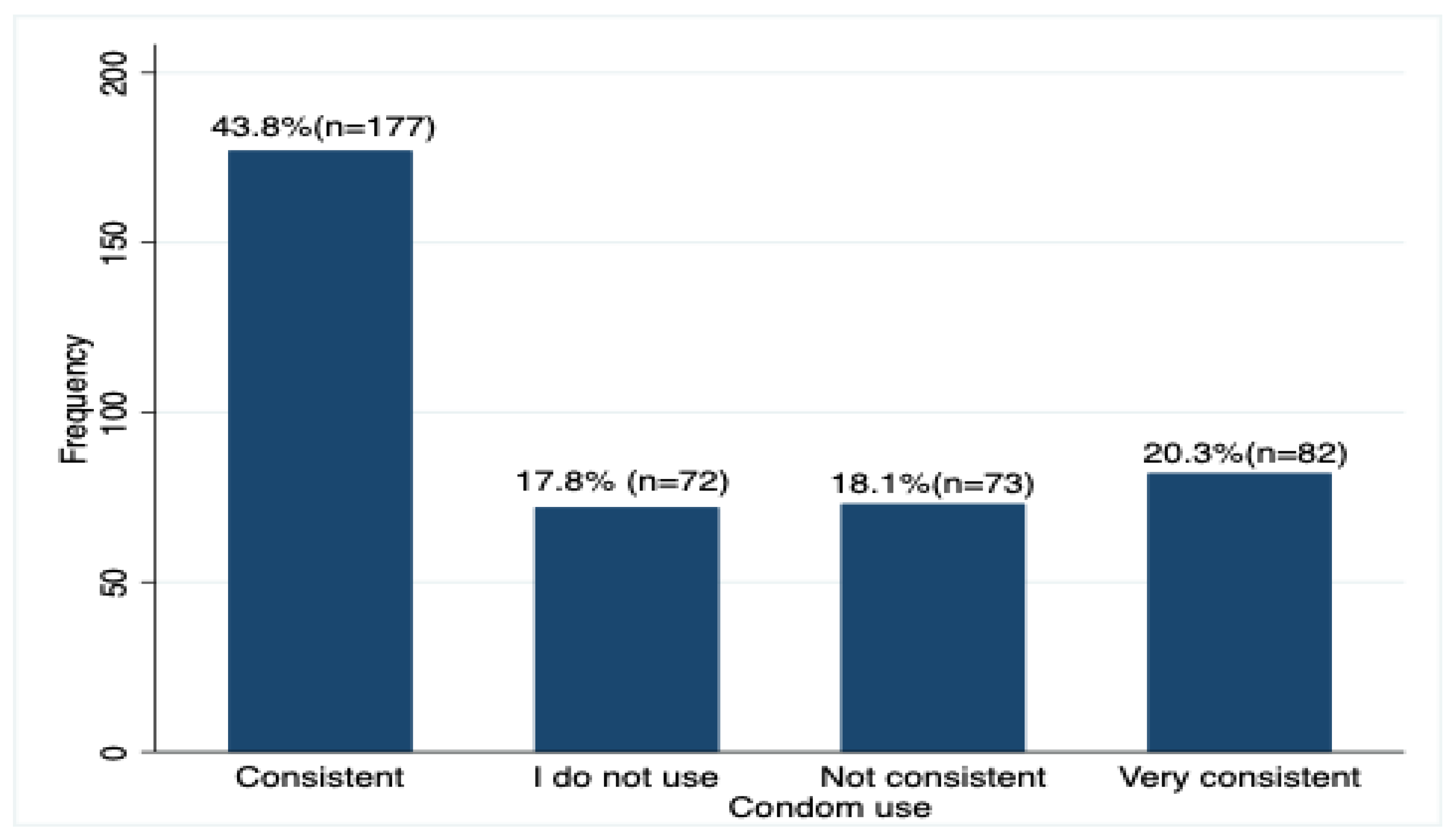
The study as well explored consistency in condom use by the study participants and it was found out that the majority 43.8% (n =177) of the respondents used condoms consistently,
Figure 3.
3.5. Factors Associated with Condom Use
Variables such as faculty(p=0.004), year of study(p<0.001), having a sexual partner(p<0.0001), source of sexual partner(p<0.0001), sex in the last six months(p<0.0001), experience of condom bursting(p=0.017), use of other methods of contraceptives(p=0.035), and absence of condoms(p<0.001) were all found to be significantly associated with condom use. These were determined using both chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test,
Table 2.
3.6. Factors Independently Associated with Condom Use
At multivariable modified Poisson regression analysis, year of study, having a sexual partner, source of sexual partner (within campus), experience of condom bursting, having sex in absence of condoms and drinking alcohol were the factors found to be independently associated with condom use. The findings showed that those in senior classes were 1.4 times (aPR = 1.4, 95% CI = 1.59, 3.54, p<0.0001) more likely to use condom than their counterparts in year 1. Respondents who had sexual partners were 2.4 times (aPR = 2.4, 95% CI = 1.89, 2.94, p<0.001) more likely to use condoms than those who did not have. Likewise, those who had their sexual partners within campus were 2 times (aPR =2, 95% CI = 1.69, 2.45, p<0.0001) were more likely to use condoms than their colleagues who had their sexual partners out of campus. Respondents who had ever experienced condom bursting were 1.3 times (aPR = 1.3, 95% CI = 1.08, 1.61, p=0.006) more likely to use condoms as compared to those who had never. Respondents who proceeded to have sex in absence of condoms were just 0.6 times (aPR = 0.6, 95% CI = 0.44, 0.70, p<0.0001) more likely to use condoms than those who withdrew from having sex. On the other hand, respondents who drink alcohol were 1.2 times (aPR = 1.2, 95% CI = 1.01, 1.45, p=0.037) than their counter parts who didn’t drink,
Table 3.
4. Discussion
Our study found out that the median age of 23 years (interquartile range (21.5-24) years) and this indicates that the majority of the undergraduates have their ages ranging between 20 to 29 [
11]. At least half of the respondents had sexual partners and majority of these were in a stable relationship with only very few of them being married and majority had had sexual intercourse in the previous six months. A significant number of the students also indicated that their source of sexual partner was out of campus. Majority 96.5%(n=389) did not engage in buying or selling sex and this indicated that the practice of prostitution was very minimal among the students though efforts to curb this vice should not be relaxed. Awareness on both PrEP and PEP were found to be high among the students, a possible explanation could have it that education together with reproductive health service awareness and trainings could be playing a significant role in empowering youth to take charge of their reproductive health [
15].
With the different studies that have been conducted so far about condom use among the population of students, the prevalence of condom use has greatly varied from low to high and this could be due to different study designs and methods used. This study found out that the prevalence of condom use was 53.7% (n = 217) and this showed consistency with some of the previous studies within Africa and beyond. A systematic and meta-analysis study conducted on low condom use at the last sexual intercourse among university students in sub-Saharan Africa revealed that the prevalence of condom use in the last sexual intercourse was 52.9% [
16]. Our results were also comparable to findings from studies conducted in Zimbabwe, Brazil and United States where the prevalence of condom use was found to range between 54.3% and 56.2% [
10,
17,
18]. The possible explanations given to this trend in similarity and consistency in prevalence could be due to similar socio demographic characteristics explored during the study and a number of studies showed linkage between socio demographic characteristics to condom use such as [
11,
17,
19,
20].
On the contrary, other studies found had a higher prevalence compared to the one that this study found, and this follows studies conducted in Southern Brazil and southwest Ethiopia with estimated prevalence of 60% and 66,1% respectively [
21,
22] and the possible explanations would be that condoms offer protection from both pregnancy and HIV infection [
23].
In a similar way some studies had a much lower prevalence compared to the one that this study found, a study conducted by Moreira and colleagues about condom use in the last sexual intercourse among undergraduates found a prevalence of 41.5% [
11] whereas another study conducted about factors associated with condom use among high school students of Natitingou Agricultural Technical school in Benin in 2017 found out that the prevalence of condom use was 40.63% [
24].
A cross-sectional survey of two Nigerian universities done by Ajayi and his colleagues on factors associated with consistent condom use in Nigeria found out the prevalence of condom use in the previous year was 38.6% [
25] and another population-based study explored condom use and its associated factors among Iranian youth in Iran and the prevalence of condom use was found to be 35.1%. The probable explanation that could have resulted into the low prevalence could have been abandoning condoms by the students for other contraceptive methods which reduced the probability of using it by 60% [
26].
4.1. Factors Associated with Condom Use among the Undergraduate Students
The following factors were found to be statistically significant and associated with condom use and these were year of study, having a sexual partner, source of sexual partner (within campus), experience of condom bursting, having sex in absence of condoms and drinking alcohol.
The study found out that students who drunk alcohol were less likely to use condoms and this finding was consistent with a study conducted in 2010 on 1954 Ugandan students where it was found that alcohol consumption mediated the association between low condom efficacy and inconsistent condom use [
27] which is further, more supported by alcohol myopia theory [
28] “that excessive alcohol consumption affects the mind and body in such a way it makes the person act mentally shortsighted” and this implies that intoxicated individuals are likely to get involved in risky sexual behaviors. A similar study done by Tara K. MacDonald and colleagues on effects of alcohol on intentions to use condoms also revealed that those who were intoxicated reported more positive intentions to have unprotected sex than sobber people [
29].
Having a sexual partner was found to be significantly associated with condom use and those who had sexual partners were 2.4 times more likely to use condoms than those who did not have. This could have been due to the nature of relationship and other factors like fear for unwanted pregnancies and this is supported by a study conducted by Valencia and colleagues on factors predisposing, facilitating and strengthening condom use among university students in Cali, Colombia which revealed that having both casual and habitual sexual partners increased the opportunity to use condoms 19-fold [
30]. A similar study done on factors associated with consistent condom in two Nigerian universities in Nigeria as well revealed that engaging in sex with only steady partner was associated with higher odds of consistent condom use [
25].
Having sex in absence of condoms; students were asked what they did in such situations and those who said they proceeded to have sex with their partners stood a much lower chance of using condoms than their counter parts who reported no sex. A possible explanation could have been that condom were not within their reach and this is supported by a study conducted on condom distribution intervention in the U.S. which indicated that interventions increasing the availability of or accessibility to condoms along with condom distribution were shown to be efficacious in increasing condom use behaviors [
31].
The study sought to find out if some of the students had ever experienced condom bursting and these were 15.5% (n = 404), this was as well found to be significantly associated with condom use. This finding was in line with some of the findings in other studies like; standardized protocols for condom breakage and slippage trials revealed that condom breakage rate went up to 12% [
32], Ankomah and colleagues also found out 17.4% of their study participants had experienced condom breakage [
33]. Another study also revealed that condom failure rate fell with its continuous use, out of 7895 female condoms and 12253 male ones that were given to the participants, 11% slipped off during first time and fell to less than 1% with continuous use for women, 7% broke during first time and fell to 2% with continuous use for the men [
34].
Senior class was the other factor that was significantly associated with condom use and students in higher years of study (year 2,3,4 and 5) showed higher chances of using condoms than their counterparts in the first year. A possible explanation could be that they had a higher condom negotiation efficacy [
18] though this study did not examine any association between self-efficacy and condom use among these undergraduates.
Lastly, this study also found out that the source of the sexual (within campus) partner was significantly associated with condom use as well. This study assessed source of partner as being within and out of campus. It could have been possible that those who stayed within campus and had their sexual partners within increased chances of physical intimacy than those who had theirs out, this is in line with a study conducted by Travis S.K Kong and colleagues in China which revealed that condom use decreased with increase in distance between the sexual partners [
35].
4.2. Study Limitations
The study could have not been a full representative of all the undergraduate students of Gulu university because the main campus was chosen leaving the other two branches of the university that also has students on undergraduate scheme. This study was done among an educated group of youth that were at their higher levels of education and hence pose a problem of generalizability of the findings with the entire population, in addition to this some specific variables associated with condom use like drinking alcohol did not confer causal relationships since the study was purely cross-sectional. The results of the studies entirely relied on self-administered structured questionnaires and there could have been cases of giving false information hence creating bias.
5. Conclusions
The prevalence of condom use was high 53.7% and having a sexual partner, source of sexual partner, year of study, experience of condom bursting, absence of condoms, and drinking alcohol were the factors that were positively associated with condom use. In regards to this, 51.5% had sexual partners and this gives an insight that indeed condom use was very likely, hence interventions such as condom distribution could help in availing condoms to the students. Besides, reproductive health talks and training would seem so useful in creating awareness.
Author Contributions
All the authors listed made outstanding contributions to drafting the article, editing, analysis, structure and design, critical screening and revision to identify errors, agreed to submit to this journal for publication and be accountable for any matter regarding the work.
Funding
This study did not receive any external source of funding from any organization or individual.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the administration of Gulu university and the study participants as well as our data collection assistants Nyakirya Joy, Abigaba Katushabe and Odida Joel for their significant contributions.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Treibich C, Lépine A. Estimating misreporting in condom use and its determinants among sex workers: Evidence from the list randomisation method. Heal Econ (United Kingdom). 2019;28(1).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Condoms and STDs: Fact Sheet for Public Health Personnel. Male Latex Condoms and Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 2011.
- CDC, Oid, NCHHSTP. CDC Fact Sheet: Consistent and Correct Condom Use. Dep Heal Hum Serv. 2018;
- SIECUS fact sheet: comprehensive sexuality education. The truth about latex condoms. SIECUS Rep. 1993;21.
- Stover J, Teng Y. The impact of condom use on the HIV epidemic. Gates Open Res. 2022;5.
- World Health Organisation W. WHO | HIV and youth. Who. 2017.
- Tang L, Chen R, Huang D, Wu H, Yan H, Li S, et al. Prevalence of condom use and associated factors among Chinese female undergraduate students in Wuhan, China. AIDS Care - Psychol Socio-Medical Asp AIDS/HIV. 2013;25(4).
- Pinyaphong J, Srithanaviboonchai K, Chariyalertsak S, Phornphibul P, Tangmunkongvorakul A, Musumari PM. Inconsistent Condom Use Among Male University Students in Northern Thailand. Asia-Pacific J Public Heal. 2018;30(2).
- Elshiekh HF, Hoving C, de Vries H. Exploring Determinants of Condom Use among University Students in Sudan. Arch Sex Behav. 2020;49(4).
- Gräf DD, Mesenburg MA, Fassa AG. Risky sexual behavior and associated factors in undergraduate students in a city in Southern Brazil. Rev Saude Publica. 2020;54.
- Moreira LR, Dumith SC, Paludo S dos S. Condom use in last sexual intercourse among undergraduate students: How many are using them and who are they? Cienc e Saude Coletiva. 2018;23(4).
- Fact sheet on the Uganda Population HIV Impact Assessment | WHO | Regional Office for Africa [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Feb 3]. Available from: https://www.afro.who.int/publications/fact-sheet-uganda-population-hiv-impact-assessment.
- Gulu University Main Campus / Branch - Admissions [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 12]. Available from: https://admissions.co.ug/gulu-university-main-campus/.
- List Of Gulu University Faculties and Schools - Admissions [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 May 12]. Available from: https://admissions.co.ug/list-of-gulu-university-faculties/.
- Labat A, Medina M, Elhassein M, Karim A, Jalloh MB, Dramaix M, et al. Contraception determinants in youths of Sierra Leone are largely behavioral. Reprod Health. 2018;15(1).
- Szucs LE, Lowry R, Fasula AM, Pampati S, Copen CE, Hussaini KS, et al. Condom and Contraceptive Use Among Sexually Active High School Students - Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2019. MMWR Suppl. 2020;69(1).
- Nkomazana N, Maharaj P. The prevalence of condom use among university students in Zimbabwe: Implications for planning and policy. J Biosoc Sci. 2013;45(5).
- Izudi J, Okello G, Semakula D, Bajunirwe F. Low condom use at the last sexual intercourse among university students in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vol. 17, PLoS ONE. 2022.
- Long L, Han Y, Tong L, Chen Z. Association between condom use and perspectives on contraceptive responsibility in different sexual relationships among sexually active college students in China: A cross-sectional study. Med (United States). 2019;98(1).
- Hernandez-Giron CA, Cruz-Valdez A, Quiterio-Trenado M, Uribe-Salas F, Peruga A, Hernández-Avila M. Factors associated with condom use in the male population of Mexico City. Int J STD AIDS. 1999;10(2).
- Costa LC, Rosa MI da, Battisti IDE. Prevalence of condom use and associated factors in a sample of university students in southern Brazil. Cad Saude Publica. 2009;25(6).
- Yosef T, Nigussie T. Behavioral Profiles and Attitude toward Condom Use among College Students in Southwest Ethiopia. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020.
- Maharaj P. Reasons for condom use among young people in KwaZulu-Natal: Prevention of HIV, pregnancy or both? Int Fam Plan Perspect. 2006;32(1).
- Houéto DS, N’Koué N’Da EB, Sambiéni EN. Factors Associated With Condom Use Among High School Students of Natitingou Agricultural Technical School, Benin, in 2017. Int Q Community Health Educ. 2021;41(4).
- Ajayi AI, Ismail KO, Akpan W. Factors associated with consistent condom use: A cross-sectional survey of two Nigerian universities. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1).
- Valencia CP, Canaval GE. [Factors predisposing, facilitating and strengthening condom use amongst university students in Cali, Colombia]. Rev Salud Publica (Bogota). 2012;14(5).
- Mehra D, Östergren PO, Ekman B, Agardh A. Inconsistent condom use among Ugandan university students from a gender perspective: a cross-sectional study. [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 May 12];8(1). Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3402/gha.v7.22942. [CrossRef]
- Steele CM, Josephs RA. Alcohol myopia: Its prized and dangerous effects. Am Psychol. 1990;45(8).
- MacDonald TK, Zanna MP, Fong GT. Why common sense goes out the window: Effects of alcohol on intentions to use condoms. Personal Soc Psychol Bull. 1996;22(8).
- Valencia CP, Canaval GE. Factores que predisponen, facilitan y refuerzan el uso del preservativo en jóvenes universitarios de Cali, Colombia. Rev Salud Publica. 2012;14(5).
- Charania MR, Crepaz N, Guenther-Gray C, Henny K, Liau A, Willis LA, et al. Efficacy of structural-level condom distribution interventions: A meta-analysis of U.S. and international studies, 1998-2007. Vol. 15, AIDS and Behavior. 2011.
- Steiner M, Trussell J, Glover L, Joanis C, Spruyt A, Dorflinger L. Standardized protocols for condom breakage and slippage trials: a proposal. Am J Public Health. 1994;84(12).
- Ankomah A, Habib HH, Atsu BK, Atuahene M, Nortey P, Afagbezi S, et al. Factors associated with condom breakage among female sex workers in the western region of ghana. Afr J Reprod Health. 2021;25(4).
- Hollander D. Failure rates of male and female condoms fall with use. Vol. 31, International Family Planning Perspectives. 2005.
- Kong TSK, Laidler KJ, Pang H. Relationship type, condom use and HIV/AIDS risks among men who have sex with men in six Chinese cities. AIDS Care - Psychol Socio-Medical Asp AIDS/HIV. 2012;24(4).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).