Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
21 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
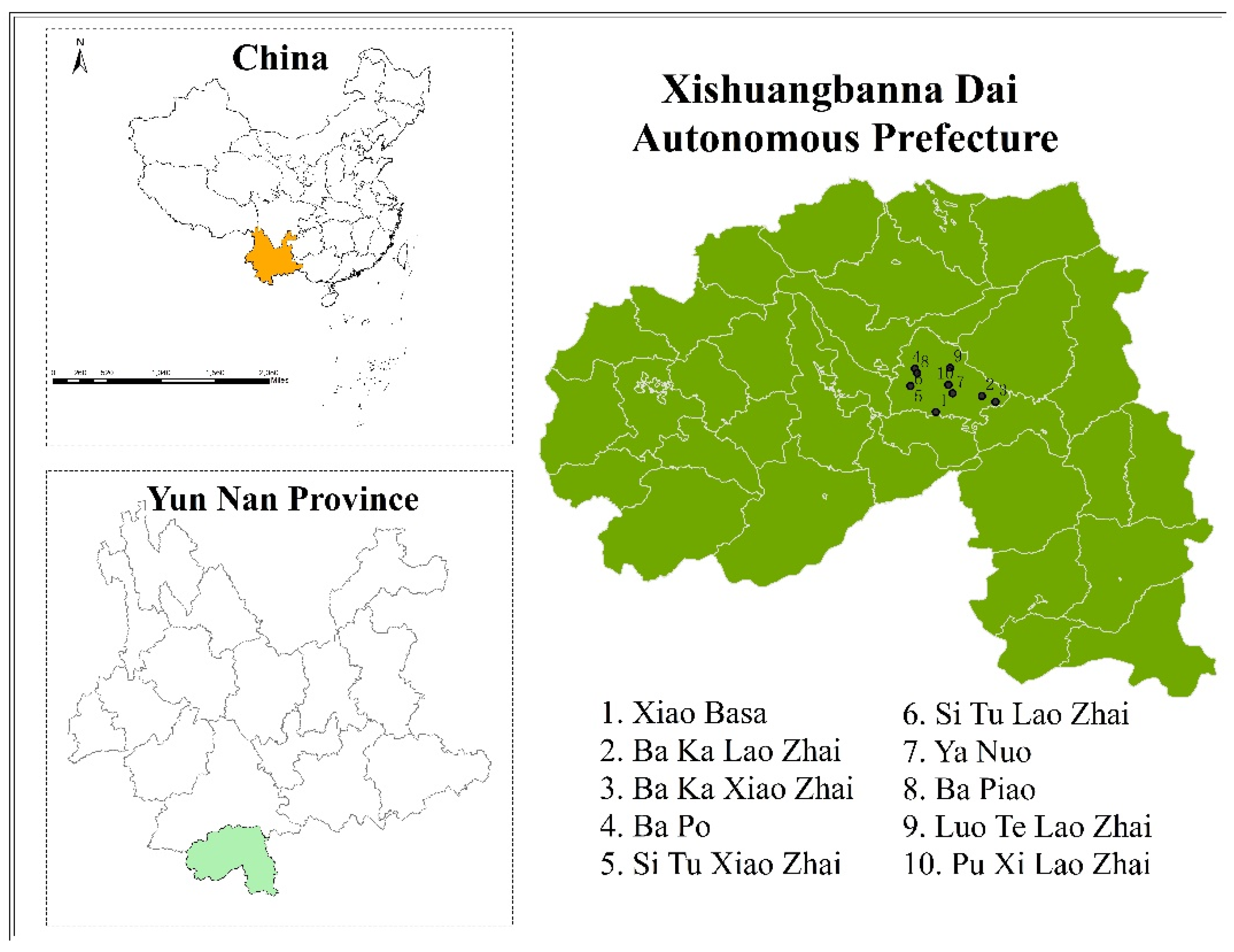
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Methods
2.2.1. Literature Research
2.2.2. Survey and Cataloging
2.2.3. Traditional Knowledge Diversity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protection of Traditional Knowledge Related to Biodiversity in Xishuangbanna
3.1.1. Survey and Cataloging of Traditional Knowledge Related to Biodiversity of the Jinuo people
3.1.2. Diversity Analysis of Traditional Knowledge Related to Biodiversity of the Jinuo People
3.2. Progress in Biodiversity Conservation in Xishuangbanna
3.2.1. In-situ Conservation in Xishuangbanna
3.2.2. Ex-situ Conservation in Xishuangbanna
3.3. Achievements in Biodiversity Conservation in Xishuangbanna
3.3.1. Ecosystem and National Key Protected Wildlife Protection
3.3.2. Increased Public Awareness of Biodiversity Conservation
4. Challenges
5. Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Huang, G.; Ping, X.; Xu, W.; Hu, Y.; Chang, J.; Swaisgood, R.R.; Zhou, J.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, Y.; et al. Wildlife conservation and management in China: achievements, challenges and perspectives. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab042, . [CrossRef]
- IPBES. Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019.
- Williams, B.A.; Watson, J.E.; Butchart, S.H.; Ward, M.; Brooks, T.M.; Butt, N.; Bolam, F.C.; Stuart, S.N.; Mair, L.; McGowan, P.J.K.; et al. A robust goal is needed for species in the Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework. Conserv. Lett. 2020, 14, . [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.J.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.S.; Xu, J. Progress and prospects of the Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28,238-243. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, M.; Hanson, J.O.; Wang, J.; Locke, H.; Watson, J.E.; Ellis, E.C.; Li, S.; Ma, K. Countries’ differentiated responsibilities to fulfill area-based conservation targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. One Earth 2023, 6, 548–559, . [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [CrossRef]
- CEPF (Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund). The biodiversity hotspots,2022; Available online: https://www.cepf.net/our-work/biodiversity (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Feng, X.; Uriarte, M.; González, G.; Reed, S.; Thompson, J.; Zimmerman, J.K.; Murphy, L. Improving predictions of tropical forest response to climate change through integration of field studies and ecosystem modeling. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, E213–E232, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F. Xishuangbanna Yearbook (Vol. 21); Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2021, ISBN 978-7-5587-3663-6. (in Chinese).
- Liu, H.M.; Xu, Z.F.; Xu, Y.K.; Wang, J.X. Practice of conserving plant diversity through traditional beliefs: a case study in Xishuangbanna, southwest China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2002, 11: 705-713. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, L.C. Wild Seed Plants in Xishuangbanna of Yunnan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012, pp.10-26, ISBN 978-7-03-033462-6. (in Chinese).
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Alatalo, J.M.; Bai, Y.; Fang, Z.; Liu, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Yang, S. Spatial heterogeneity analysis of matching degree between endangered plant diversity and ecosystem services in Xishuangbanna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 96891–96905, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Dao, T.; Guo, X. Sacred natural site and regional biodiversity conservation in Xishuangbanna. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 15, 1797-1800.
- Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, B.G.; Zhou, S.S.; Zhang, J.H. Study on forest vegetation in Xishuangbanna. Plant Sci. J. 2015, 33, 641-726. (in Chinese).
- Henle, K.; Alard, D.; Clitherow, J.; Cobb, P.; Firbank, L.; Kull, T.; McCracken, D.; Moritz, R.F.A.; Niemelä, J.; Rebane, M.; et al. Identifying and managing the conflicts between agriculture and biodiversity conservation in Europe–A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 124, 60–71, doi:10.1016/j.agee.2007.09.005.
- Jie, L.Y. A review of research on Yunnan’s biodiversity conservation and ecological views of ethnic minorities. J. Yunnan Minzu Univ. 2009, 26, 156-160. (in Chinese).
- Long, C.L.; Zhou, Y. Indigenous community forest management of Jinuo people's swidden agroecosystems in southwest China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 753-767. [CrossRef]
- Yin, L. Customary law of ethnic ecology and biodiversity protection: theory, value and approach. J. Ethn. Cult. 2022, 14, 15-28. (in Chinese).
- Shen, S.; Xu, G.; Li, D.; Clements, D.R.; Zhang, F.; Jin, G.; Wu, J.; Wei, P.; Lin, S.; Xue, D. Agrobiodiversity and in situ conservation in ethnic minority communities of Xishuangbanna in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2017, 13, 1–15, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Mammides, C.; Corlett, R.T. Reasons for the Survival of Tropical Forest Fragments in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Forests 2020, 11, 159, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, M. Tropical forest vegetation of Xishuangbanna, SW China and its secondary changes, with special reference to some problems in local nature conservation. Biol. Conserv. 1995, 73, 229–238, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Cheng, F.; Hou, X.; Dong, S.; Wu, X. Spatio-temporal variations of conservation hotspots based on ecosystem services in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0189368–e0189368, . [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Technical Regulation for Classification, Investigation, and Inventory of Traditional Knowledge Relating to Biological Diversity. China,2014.
- Swingland, I.R. Biodiversity, definition of. Encycl. Biodivers. 2001, 1, 377-391.
- Wang, G.P.; Xue, D.Y.; Wen, Y.; Cheng, G.; Min, Q.W. Diversity of traditional knowledge related to utilization of biological resources by Tu nationality in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, ,27, 735-742.
- Ogar, E.; Pecl, G.; Mustonen, T. Science Must Embrace Traditional and Indigenous Knowledge to Solve Our Biodiversity Crisis. One Earth 2020, 3, 162–165, . [CrossRef]
- Rundle, H. Indigenous knowledge can help solve the biodiversity crisis. Sci. Am. 2019, 12.
- Mekonen, S.; Roles of traditional ecological knowledge for biodiversity conservation. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2017, 7, 21-27.
- Langton, M.; Rhea, Z.M. Traditional Indigenous Biodiversity-related Knowledge. Aust. Acad. Res. Libr. 2005, 36, 45–69, . [CrossRef]
- CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity). Convention on Biological Diversity: Text and Annexes; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 1992.
- Xue, D.Y.; Guo, L. On the concept and protection of traditional knowledge. Biodivers. Sci. 2009, 17, 135-142. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Lu, F. Research Status and Trends of Agrobiodiversity and Traditional Knowledge Based on Bibliometric Analysis (1992–Mid-2022). Diversity 2022, 14, 950, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Stephen, S., Young. Differences in bird diversity between two swidden agricultural sites in mountainous terrain, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 110, 231-243. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C. People and Forests: Yunnan Swidden Agriculture in Human-Ecological Perspective. Agric. Hist. 2008, 82, 241.
- Liu, C.H.; Liu, D.M.; Yang, J.B.; Piao, J.L.; Xue, D.Y. Diversity analysis and protection countermeasure of traditional knowledge about biodiversity by Buyi ethnic group. J. Guizhou Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2020, 5, 140-148. (in Chinese).
- Xiong, Y.; Long, C.L. Investigation, collation and protection of traditional Buyi medicine. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2018, 41, 286-291. (in Chinese).
- Andermann, T.; Antonelli, A.; Barrett, R.L.; Silvestro, D. Estimating Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Diversity Through Deep Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 839407, . [CrossRef]
- Al-Robai, S.A.; Ahmed, A.A.E.; Mohamed, H.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Zabin, S.A.; Alghamdi, A.A.A. Qualitative and Quantitative Ethnobotanical Survey in Al Baha Province, Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Diversity 2022, 14, 867, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J. In-situ conservation of biodiversity in China: Advances and prospects. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 133–149, . [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, O.; Mossman, H.L.; Suggitt, A.J.; Curtis, R.J.; Maclean, I.M.D. Using in situ management to conserve biodiversity under climate change. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 885–894, . [CrossRef]
- Mestanza-Ramón, C.; Henkanaththegedara, S.M.; Vásconez Duchicela, P.; Vargas Tierras, Y.; Sánchez Capa, M.; Constante Mejía, D.; Jimenez Gutierrez, M.; Charco Guamán, M.; Mestanza Ramón, P. In-Situ and Ex-Situ Biodiversity Conservation in Ecuador: A Review of Policies, Actions and Challenges. Diversity 2020, 12, 315, doi:10.3390/d12080315.
- CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity). Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework; CBD: Montreal, Canada, 2022.
- Qiu, C.; Hu, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, F.; Li, X. Human Pressures on Natural Reserves in Yunnan Province and Management Implications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wen, Q.Z. Hua, Z.L. Yunnan Nature Reserve; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2018; pp. 20-35, ISBN 759-992-74. (in Chinese).
- Chen, F.; Tang, F.L.; Wang, D.T.; Wang, M.J.; Sun, H.Y.; Sun, G.Z.; Wang, J.S.; Zong, L.P.; Zhao, W.F.; Yang, Z.C. Research on Asian Elephant National Park. For. Constr. 2019, 6, 23-29. (in Chinese).
- Alves-Pinto, H.; Geldmann, J.; Jonas, H.; Maioli, V.; Balmford, A.; Latawiec, A.E.; Crouzeilles, R.; Strassburg, B. Opportunities and challenges of other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) for biodiversity conservation. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 19, 115-120. [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Pu, J.Y.; Ma, J.Z. Other-effective area-based measures of global experiences and implications for Post-2020 biodiversity conservation in China. J. West China For. Sci. 2022,51, 1-8.
- Xu, Z. Conservation of biodiversity and cultural diversity are two sides of a coin: Xishuangbanna Dai’s ecological culture as an example. Biodivers. Sci. 2015, 23, 126–130, . [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tam, C.; Li, T.; Yu, G.; Hu, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, R. Sacred natural sites classification framework based on ecosystem services and implications for conservation. Conserv. Sci. Pr. 2022, 4, e12638, . [CrossRef]
- Long, C.-L.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Trangmar, B. Strategies for agrobiodiversity conservation and promotion: a case from Yunnan, China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 1145–1156, . [CrossRef]
- Canessa, S.; Converse, S.J.; West, M.; Clemann, N.; Gillespie, G.; McFadden, M.; Silla, A.J.; Parris, K.M.; McCarthy, M.A. Planning for ex situ conservation in the face of uncertainty. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 30, 599–609, . [CrossRef]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Wang, M.; Lang, R.; Chen, H.; Metzger, M.J.; Smajgl, A.; Beckschäfer, P.; Xu, J. Environmental stratification to model climate change impacts on biodiversity and rubber production in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 264–273, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Shi, J.P.; Li, J.S.; Xiao, N.W. Biodiversity conservation measures under the ecological security barrier strategy in Yunnan Province. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 42, 26-29. (in Chinese).
- Huang, H.W.; Zhang, Z. Current status and prospects of ex situ cultivation and conservation of plants in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2012, 20, 559-571. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Glowka, L.; Burhenne-Guilmin, F.; Synge, H.; McNeely, J.A.; Gündling, L. A Guide to the Convention on Biological Diversity; IUCN Environmental Law Centre: Bonn, Germany, 1994.
- Song, Z.Y.; Dao, Y.Y. Resources status and management strategies of National Nature Reserve in Xishuangbanna. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 100-104. (in Chinese).
- Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture People's Government Protection Rate of National Key Protected Wild Animals and Plants in Xishuangbanna Prefecture. Available online: https://www.xsbn.gov.cn/lyj/81753.news.detail.dhtml?news_id=2865470.(accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Dou, L.; Zhang, W.; Deng, X.; Cao, M.; Tang, Y. Nine-year seed rain dynamics in Parashorea chinensis forest in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Biodivers. Sci. 2018, 26, 919–930, . [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.; Dai, J.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Du, F. Community structure and distribution of minimum population species of Myristica yunnanensis. Guihaia 2017, 37, 783-790. (in Chinese).
- Luo, M.; Guo, Y.; Ma, K.; Service, M.O.N.R.3.N.M.H.M. A brief introduction to the negotiations of the post-2020 global biodiversity framework. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 22654, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-G.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Yan, Y.; Beckschäfer, P.; Kleinn, C.; Dossa, G.G.; Huai, J.-J.; Zhai, D.-L.; Song, L. Encouraging the reconversion of rubber plantations by developing a combined payment system. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, . [CrossRef]
- Corlett, R.T. Achieving zero extinction for land plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 913–923, . [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.Y.; Cai, L. New hot topics in the Convention on Biological Diversity: Protection of traditional knowledge. Environ. Prot. 2006,24,72-74. (in Chinese).
- Yin, S.T. Research on the ethnic ecology of slash-and-burn farming of Jinuo people. Agric. Archaeol. 1988, 1, 318-334. (in Chinese).
- Huang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Yang, Z. Mapping biodiversity conservation priorities for protected areas: A case study in Xishuangbanna Tropical Area, China. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 249, 108741, . [CrossRef]
- Ahrends, A.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Ziegler, A.D.; Fox, J.M.; Chen, H.; Su, Y.; Xu, J. Current trends of rubber plantation expansion may threaten biodiversity and livelihoods. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 34, 48–58, . [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.W. Spatiotemporal changes and linear characteristics of rubber forests in Xishuangbanna from 1987 to 2018. Trop. Geogr. 2022,42, 1376-1385. (in Chinese).
- Min, S.; Huang, J.; Waibel, H.; Yang, X.; Cadisch, G. Rubber Boom, Land Use Change and the Implications for Carbon Balances in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 156, 57–67, . [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.B., Liu, S.Y. A re-examination of China’s legal system for biodiversity conservation in the context of the CBD negotiations. Yuejiang Acad. J. 2022, 14, 95-104. (in Chinese).
- Li, L.-L.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Yang, H.-P.; Tao, Y.-X.; Wang, L.-X.; Yang, Z.-B.; Campos-Arceiz, A.; Quan, R.-C. Mobile animals and immobile protected areas: improving the coverage of nature reserves for Asian elephant conservation in China. Oryx 2023, 57, 532–539, . [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.E.M.; Venegas-Li, R.; Grantham, H.; Dudley, N.; Stolton, S.; Rao, M.; Woodley, S.; Hockings, M.; Burkart, K.; Simmonds, J.S.; et al. Priorities for protected area expansion so nations can meet their Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework commitments. Integr. Conserv. 2023, 2, 140–155, . [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, C.; Abebe, Y.A.; Worthy, F.R.; Wijerathne, I.L.; Ma, H.; Yingfeng, B.; Jiayu, G.; Chen, H.; Yan, Q.; Geng, Y.; et al. Impact of land use and land cover changes on carbon storage in rubber dominated tropical Xishuangbanna, South West China. Ecosyst. Heal. Sustain. 2021, 7, . [CrossRef]
- James, H.; Yi, Z.F.; Timothy, M.; Zhao, J.W. Situational analysis report: Xishuangbanna autonomous Dai Prefecture Yunnan, China. World Agroforestry Center Working Paper 2015, 1-67.
| Category | Subcategory | Number of species under national first-grade protection | Number of species under national second-grade protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild plants | Gymnosperm | 4 | 5 |
| Angiosperm | 6 | 141 | |
| Lycophyte and Fern | - | 17 | |
| Bryophyte | - | 1 | |
| Total | 10 | 164 | |
| Wild animals | Bird | 15 | 117 |
| Mammal | 21 | 17 | |
| Amphibian | - | 1 | |
| Reptile | 3 | 5 | |
| Total | 39 | 140 | |
| Major Category | Subcategory | Number | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional knowledge related to breeding of agricultural genetic resources | TK related to breeding of crop genetic resources | 36 | 21.43% |
| TK related to breeding of domestic animal genetic resources | 6 | 3.57% | |
| TK related to breeding of aquatic organism genetic resources | 5 | 2.98% | |
| TK related to breeding of forest genetic resources | 20 | 11.90% | |
| TK related to breeding ornamental plant genetic resources | 22 | 13.10% | |
| TK related to wild plant genetic resources conservation | 49 | 29.17% | |
| TK related to terrestrial wild animal genetic resources | 20 | 11.90% | |
| TK related to breeding of microbial genetic resources | 10 | 5.95% | |
| Traditional knowledge related to medicine | TK on the introduction, domestication, cultivation and conservation of traditional medicinal biological resources | 223 | 92.53% |
| Traditional medicine theories | 5 | 2.07% | |
| Traditional therapies | 3 | 1.24% | |
| Traditional processing technology of medicinal materials | 3 | 1.24% | |
| Traditional prescriptions | 5 | 2.07% | |
| TK of health care and disease prevention | 2 | 0.82% | |
| Traditional technologies related to sustainable use of biological resources | Traditional agricultural production technologies | 8 | 29.63% |
| Traditional printing and dyeing and textile technologies | 5 | 18.52% | |
| Traditional food processing technologies | 8 | 29.63% | |
| Traditional planning, design and construction techniques | 3 | 11.11% | |
| Other traditional technologies | 3 | 11.11% | |
| Traditional culture related to biodiversity | Religious beliefs and ecological ethics | 6 | 13.33% |
| Traditional festivals | 13 | 28.89% | |
| Customary law | 4 | 8.89% | |
| Traditional literature and art | 14 | 31.11% | |
| Traditional food culture | 2 | 4.44% | |
| Other traditional cultures | 6 | 13.33% | |
| Traditional knowledge of biogeographical indication products | TK related to food indication products | 3 | 33.33% |
| TK related to craft-marked products | 5 | 55.56% | |
| TK related to other geographical indication products | 1 | 11.11% |
| Name | Total number | Number of subcategories | Diversity index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional knowledge related to breeding of agricultural genetic resources | 168 | 8 | DTK1=0.82 |
| Traditional knowledge related to medicine | 241 | 6 | DTK2=0.14 |
| Traditional technologies related to sustainable use of biological resources | 27 | 5 | DTK3=0.79 |
| Traditional culture related to biodiversity | 45 | 6 | DTK4=0.86 |
| Traditional knowledge of biogeographical indication products | 9 | 3 | DTK5=0.64 |
| No. | Name | Main protection type | Administrative region | Main protected object | Area (hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xishuangbanna National Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Jinghong City, Mengla County, Menghai County | Forest ecosystems such as tropical rain forest and tropical monsoon forest, and rare wild animals and plants such as Asian elephants and parashorea chinensis | 242510.0 |
| 2 | Xishuangbanna Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Jinghong City, Menghai County | Tropical forest ecosystems dominated by tropical rain forest and tropical seasonal rain forest, and rare wild animals and plants | 26600.0 |
| 3 | Xishuangbanna Lancang-Mekong River Watershed State Nature Reserve | Wild animal | Mongla County | Fish resources such as soft-shelled turtle and gyrinocheilus aymonieri | 67.0 |
| 4 | Xishuangbanna Luosuo River State Nature Reserve | Wild animal | Mongla County | Aquatic wildlife and their habitats | 600.0 |
| 5 | Xishuangbanna Bulong State Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Jinghong City, Menghai County | Forest ecosystems dominated by montane rain forest and rare wildlife resources | 35485.0 |
| 6 | Xishuangbanna Yiwu State Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Mongla County | Ancient tea tree resources and national key protected wildlife resources | 33369.9 |
| 7 | Jinghong County Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Jinghong City | Unique forest ecosystem and wild animals and plants under state key protection | 47258.0 |
| 8 | Menghai County Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Menghai County | Forest ecosystems and rare and endangered wild animal and plant resources | 28315.7 |
| 9 | Mengla County Lancang River Green Triangle County Nature Reserve | Forest ecosystem | Mongla County | Forest ecosystems dominated by mountain rain forest, and rare and endangered wildlife resources | 14752.0 |
| Plant group | Family | Chinese name | Scientific name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gymnosperm | Cycadaceae | Bichisutie篦齿苏铁 | Cycas pectinata |
| Cycadaceae | Changyesutie长叶苏铁 | Cycas dolichophylla | |
| Cycadaceae | Danyusutie单羽苏铁 | Cycas simplicipinna | |
| Taxaceae | Xumihongdoushan须弥红豆杉 | Taxus wallichiana | |
| Angiosperm | Dipterocarpaceae | Wangtianshu望天树 | Parashorea chinensis |
| Dipterocarpaceae | Guangxiqingmei广西青梅 | Vatica guangxiensis | |
| Combretaceae | Echiteng萼翅藤 | Getonia floribunda | |
| Nyssaceae | Yunnanlanguoshu云南蓝果树 | Nyssa yunnanensis | |
| Orchidaceae | Piaodaidoulan飘带兜兰 | Paphiopedilum parishii | |
| Orchidaceae | Zimaodoulan紫毛兜兰 | Paphiopedilum villosum |
| Animal groups | Family | Chinese name | Scientific name | Endemism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birds | Phasianidae | Heijingchangweizhi黑颈长尾雉 | Syrmaticus humiae | — |
| Phasianidae | Huikongquezhi 灰孔雀雉 | Polyplectron bicalcaratum | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Phasianidae | Lukongque绿孔雀 | Pavo muticus | — | |
| Columbidae | Xiaojuanjiu小鹃鸠 | Macropygia ruficeps | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Gruidae | Chijinghe赤颈鹤 | Grus antigone | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Laridae | Heyanou河燕鸥 | Sterna aurantia | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Threskiornithidae | Caihuan彩鹮 | Plegadis falcinellus | — | |
| Accipitridae | Heiwujiu黑兀鹫 | Sarcogyps calvus | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Accipitridae | Wudiao乌雕 | Clanga clanga | — | |
| Bucerotidae | Baihouxiniao 白喉犀鸟 | Anorrhinus austeni | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Bucerotidae | Guanbanxiniao 冠斑犀鸟 | Anthracoceros albirostris | — | |
| Bucerotidae | Shuangjiaoxiniao 双角犀鸟 | Buceros bicornis | — | |
| Bucerotidae | Zongjingxiniao 棕颈犀鸟 | Aceros nipalensis | — | |
| Leiothrichidae | Languanzaomei 蓝冠噪鹛 | Garrulax courtoisi | — | |
| Emberizidae | Huangxiongwu 黄胸鹀 | Emberiza aureola | — | |
| Reptiles | Testudinidae | Aojialugui 凹甲陆龟 | Manouria impressa | — |
| Testudinidae | Miandianlugui 缅甸陆龟 | Indotestudo elongatea | — | |
| Varanidae | Yuanbijuxi 圆鼻巨蜥 | Varanus salvator | — | |
| Mammals | Lorisidae | Fenghou蜂猴 | Nycticebus bengalensis | — |
| Cercopithecidae | Beitengweihou北豚尾猴 | Macaca leonina | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Cercopithecidae | Yinzhihuiyehou 印支灰叶猴 | Trachypithecus crepusculus | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Hylobatidae | Baijiachangbiyuan北白颊长臂猿 | Nomascus leucogenys | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Manidae | Chuanshanjia 穿山甲 | Manis pentadactyla | — | |
| Canidae | Chai豺 | Cuon alpinus | — | |
| Ursidae | Malaixiong马来熊 | Helarctos malayanus | — | |
| Viverridae | Dabanlingmao大斑灵猫 | Viverra megaspila | — | |
| Viverridae | Dalingmao大灵猫 | Viverra zibetha | — | |
| Viverridae | Xiaolingmao 小灵猫 | Viverricula indica | — | |
| Viverridae | Xiongli熊狸 | Arctictis binturong | — | |
| Viverridae | Xiaochili小齿狸 | Arctogalidia trivirgata | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Viverridae | Gaolingmao缟灵猫 | Chrotogale owstoni | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Felidae | Conglinmao丛林猫 | Felis chaus | — | |
| Felidae | Jinmao 金猫 | Catopuma temminckii | — | |
| Felidae | Yunbao云豹 | Neofelis nebulosa | — | |
| Felidae | Bao豹 | Panthera pardus | — | |
| Felidae | Hu虎 | Panthera tigris | — | |
| Elephantidae | Yazhouxiang亚洲象 | Elephas maximus | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Tragulidae | Weishixilu威氏鼷鹿 | Tragulus williamsoni | Endemic to Yunnan | |
| Bovidae | Yeniu 野牛 | Bos gaurus | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




