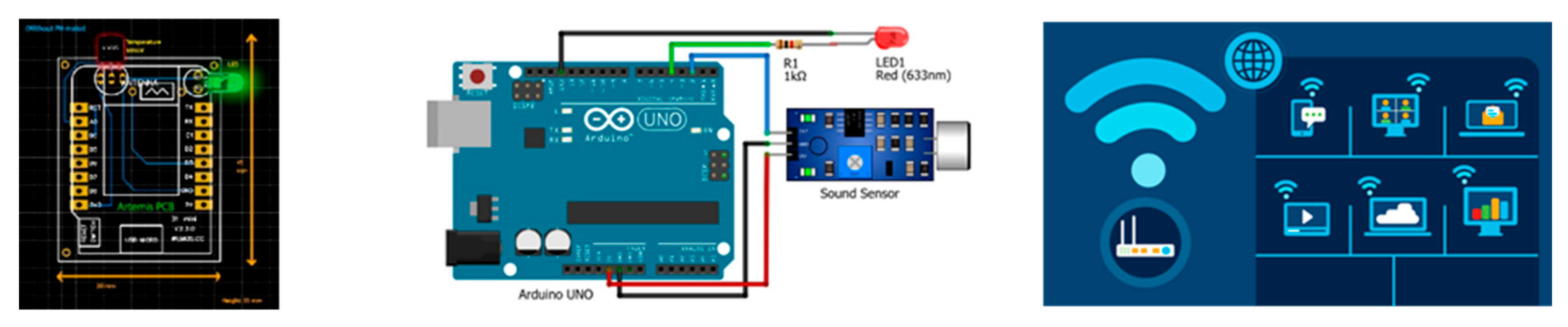
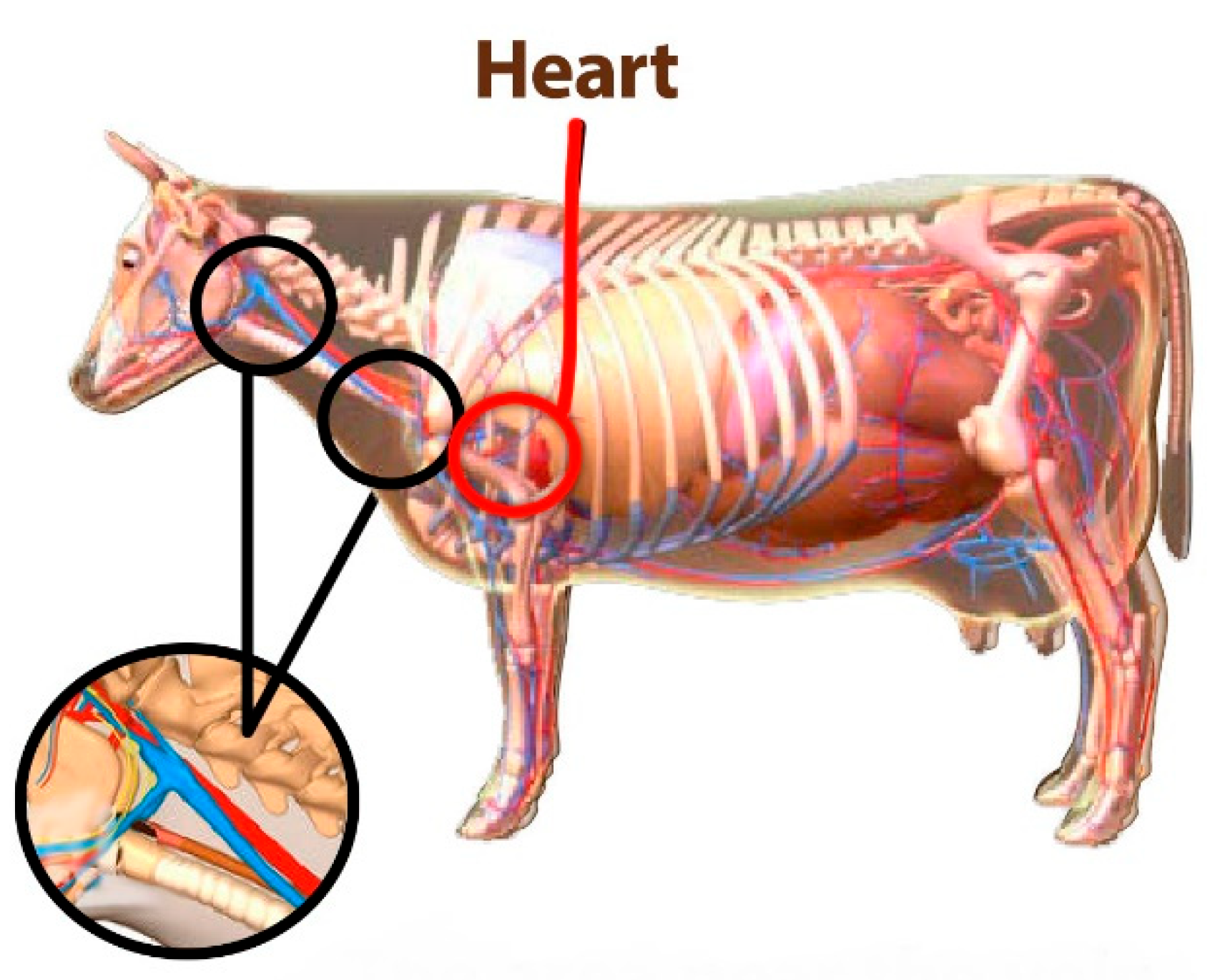
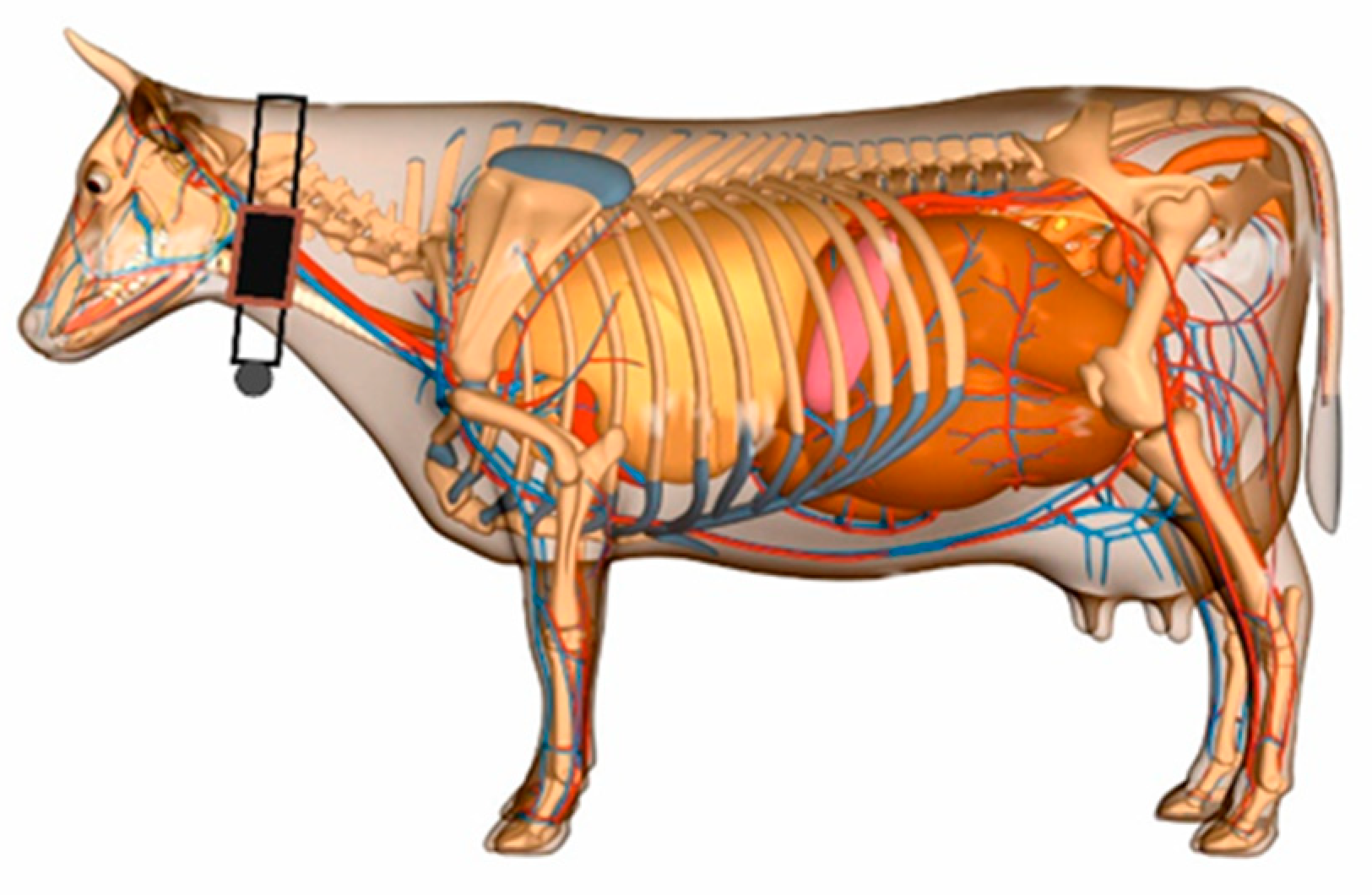
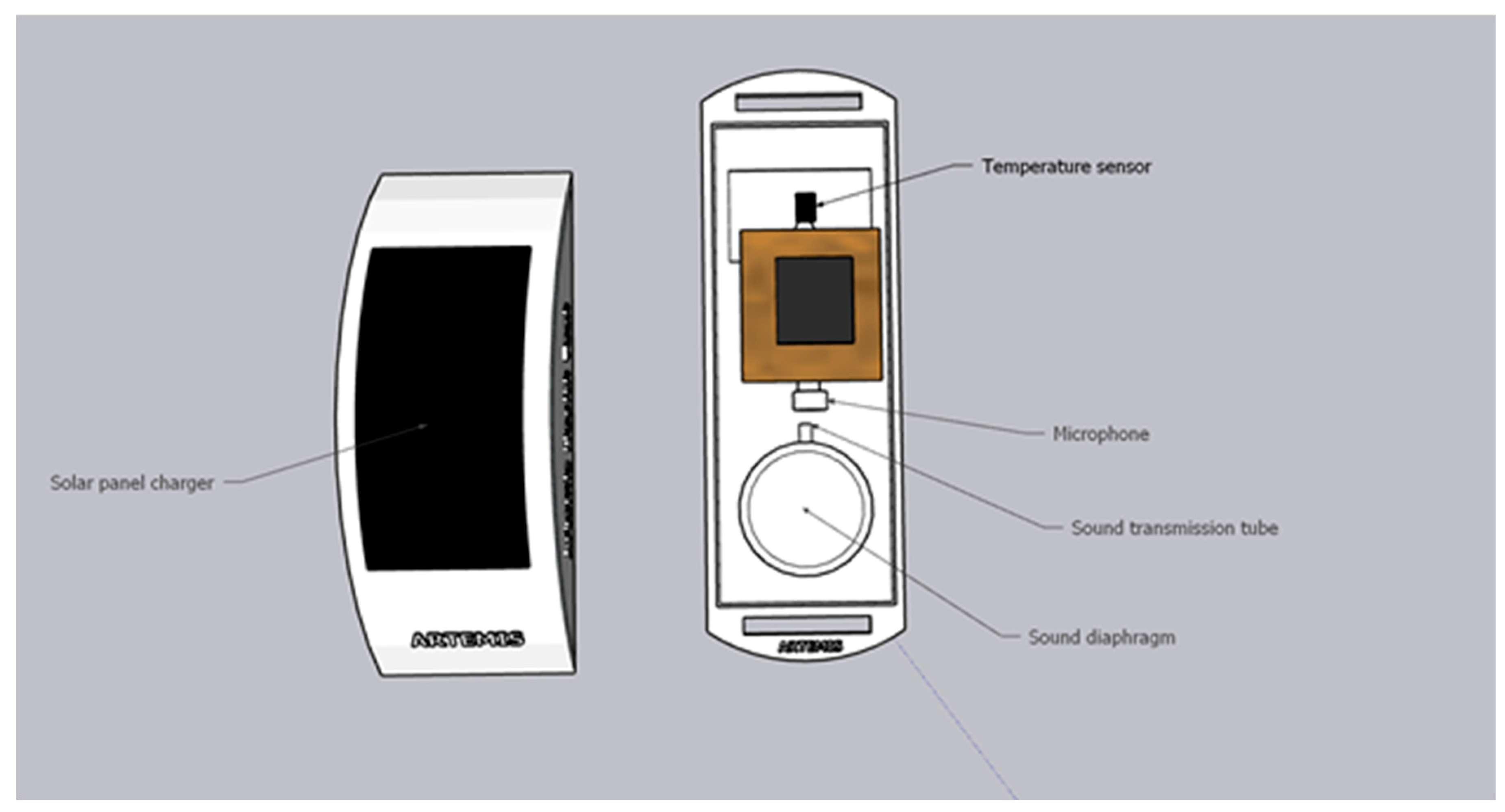
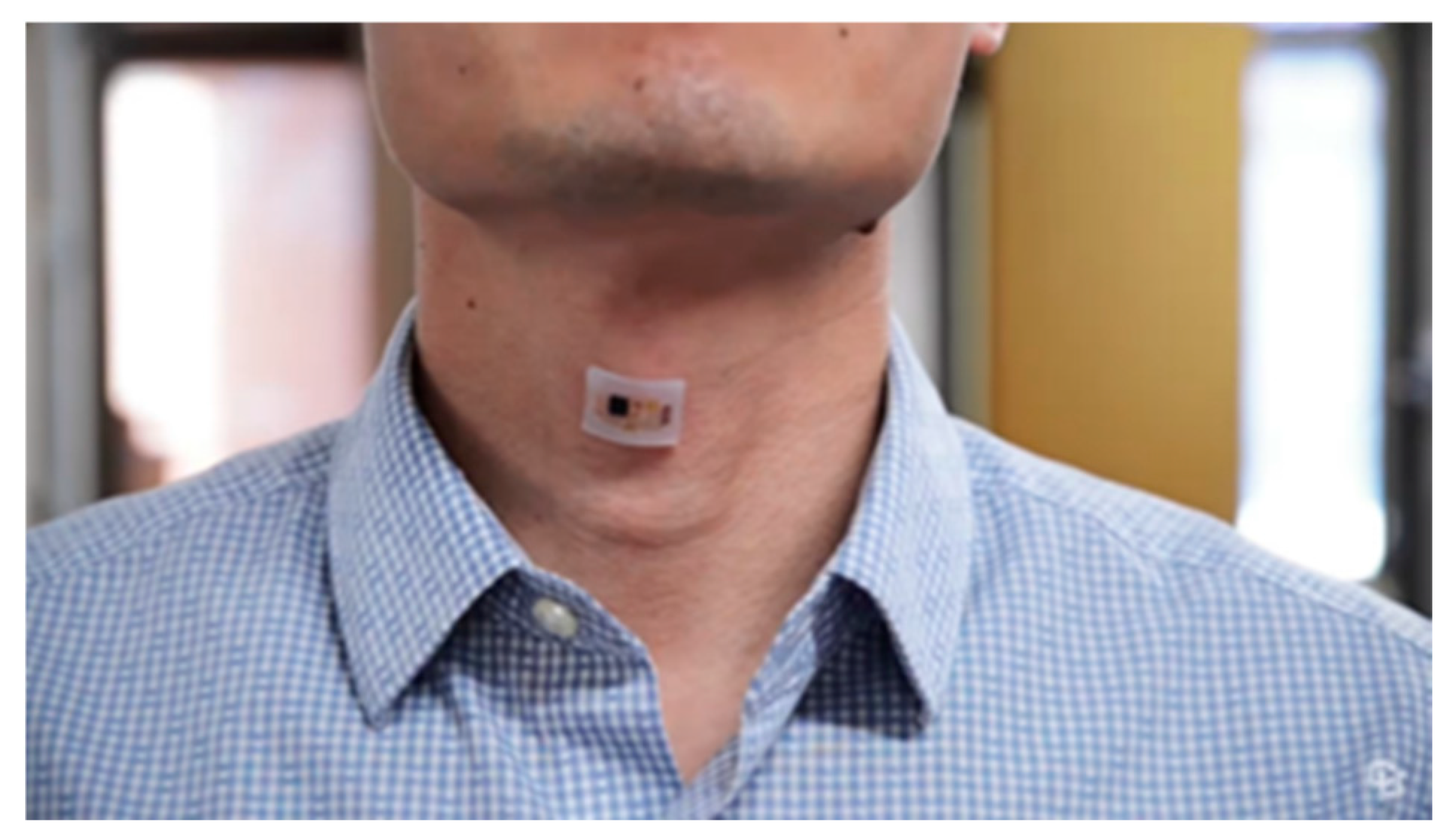
7. Results:
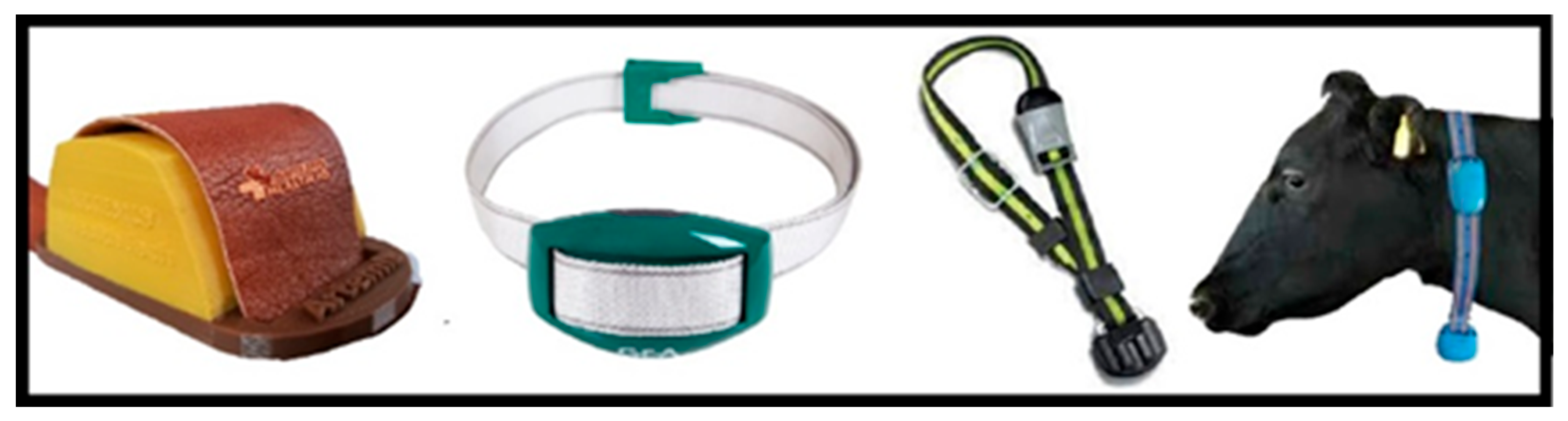
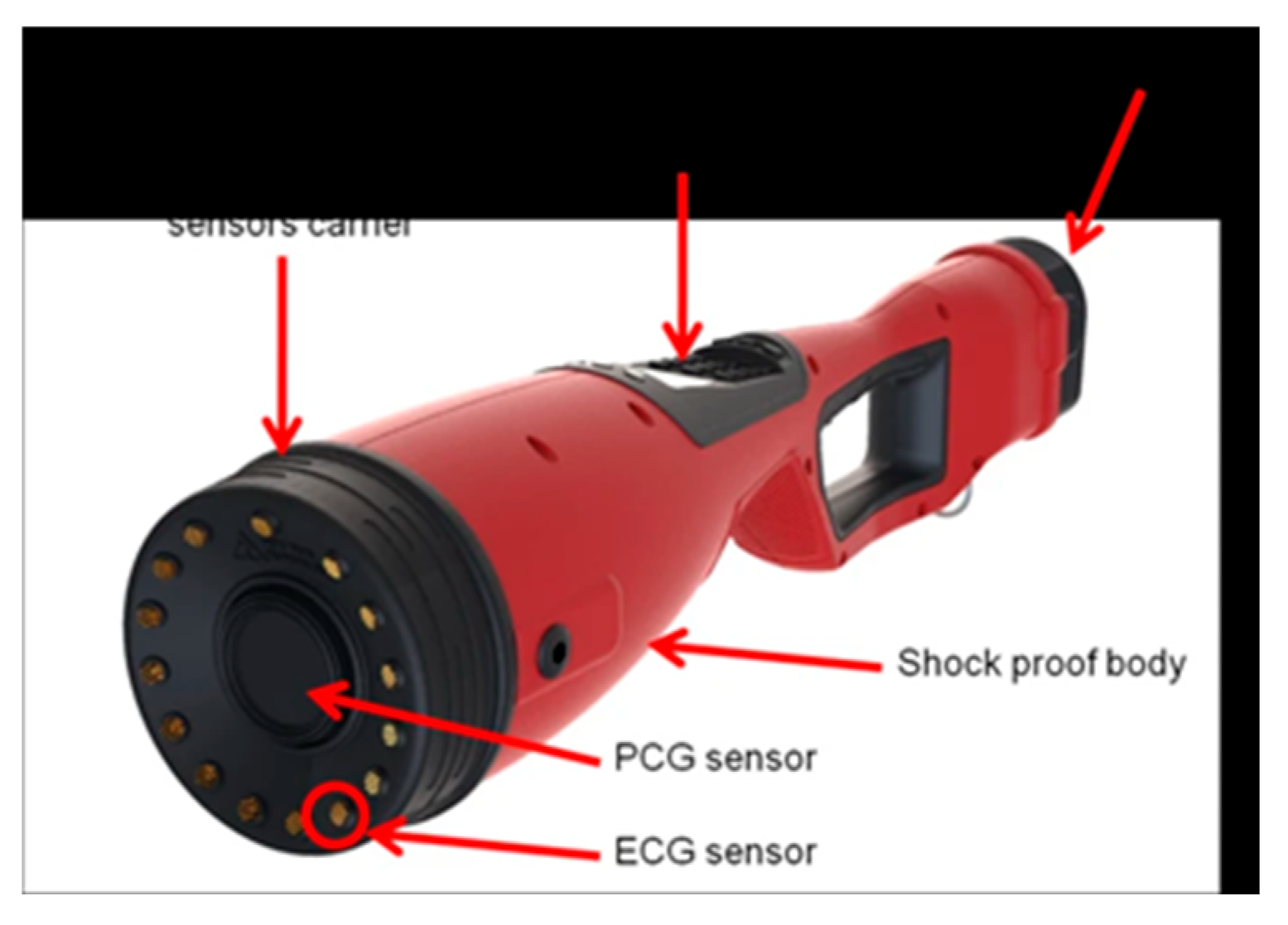
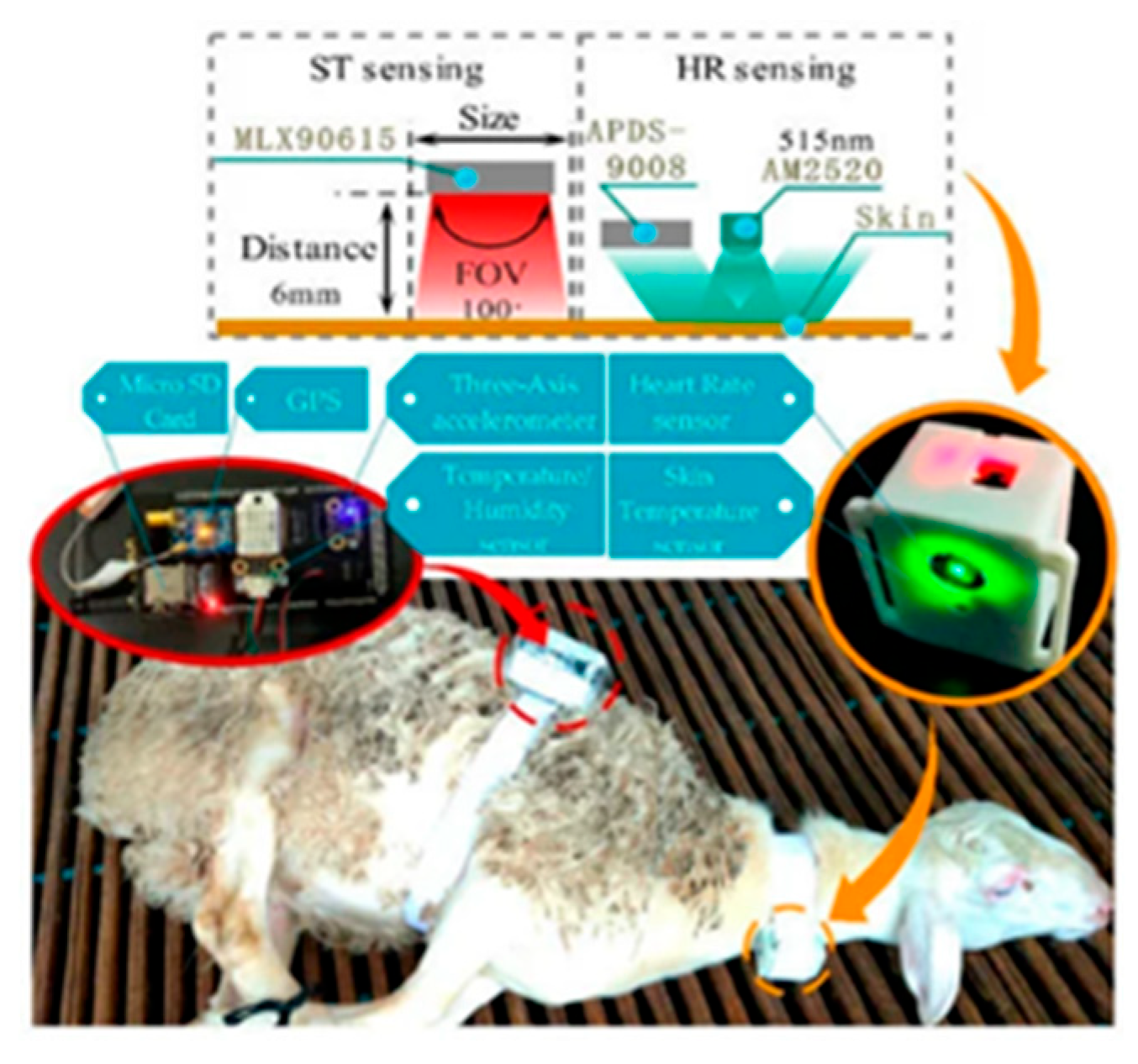
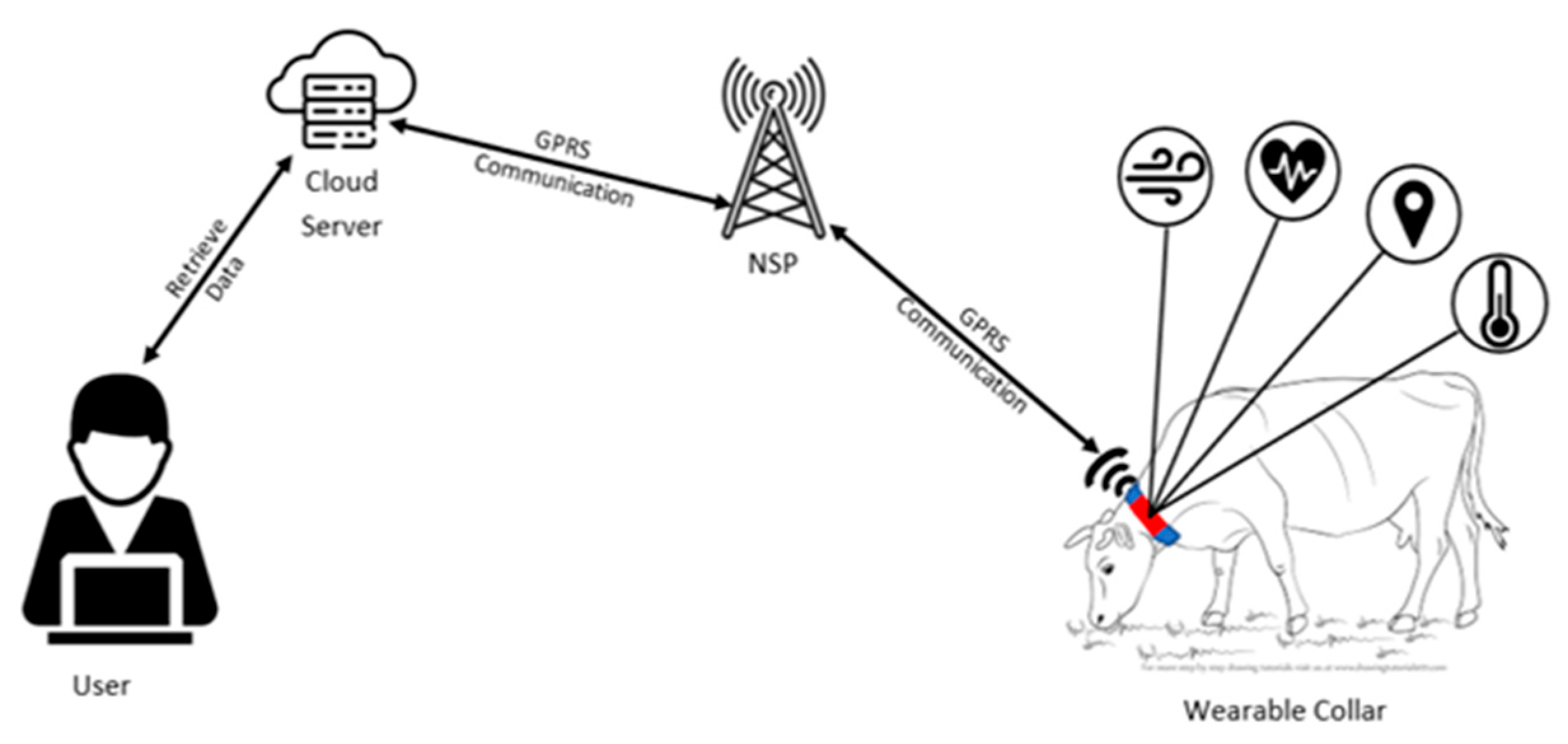
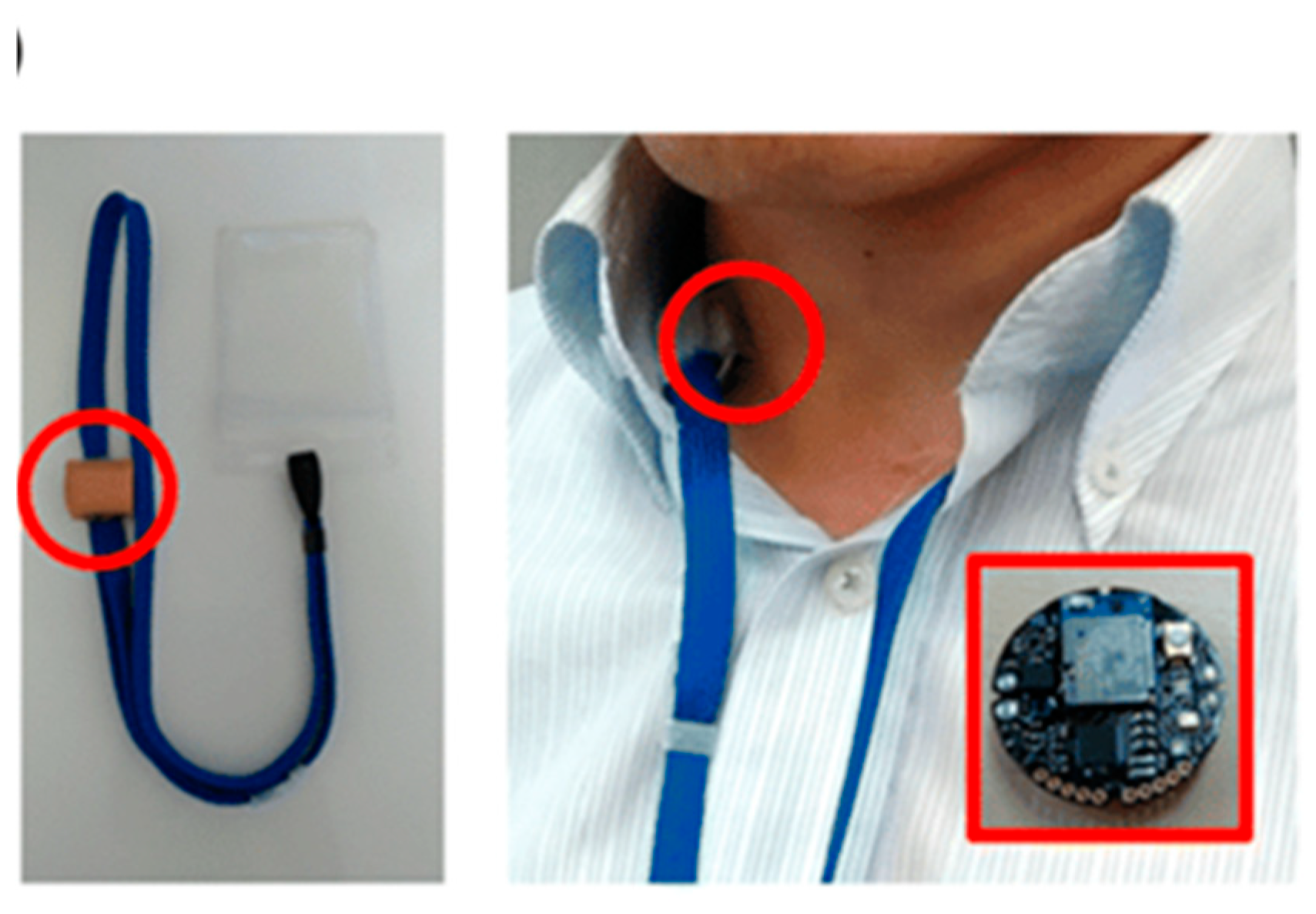
Nowadays, smart veterinary stethoscopes have found a great place in the field of cardiology and disease diagnosis due to their ability to increase the sound (up to 17 times). These stethoscopes have sensors that amplify the sounds received through the diaphragm and provide a clear sound to the listener. (
Figure 35)
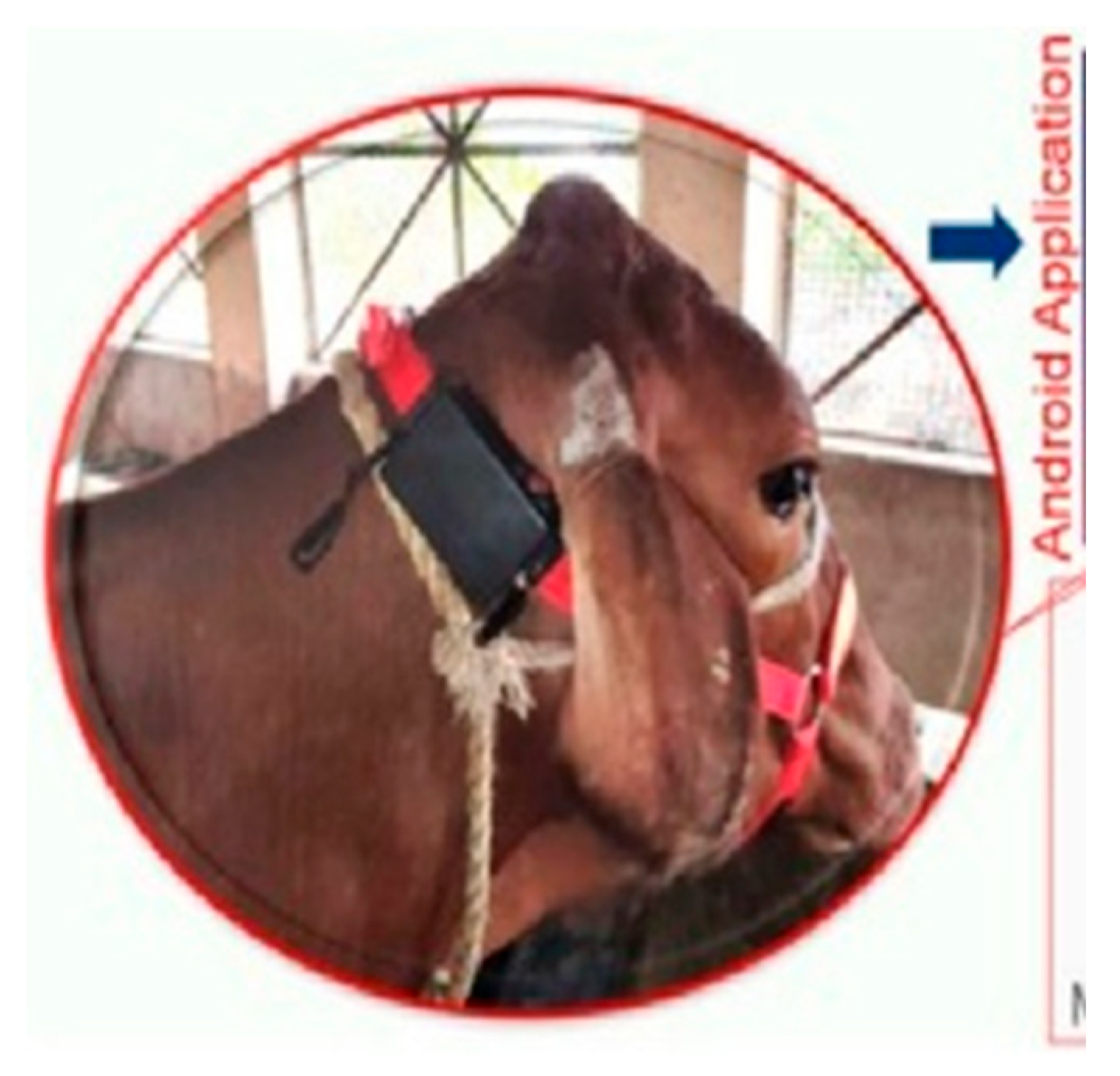
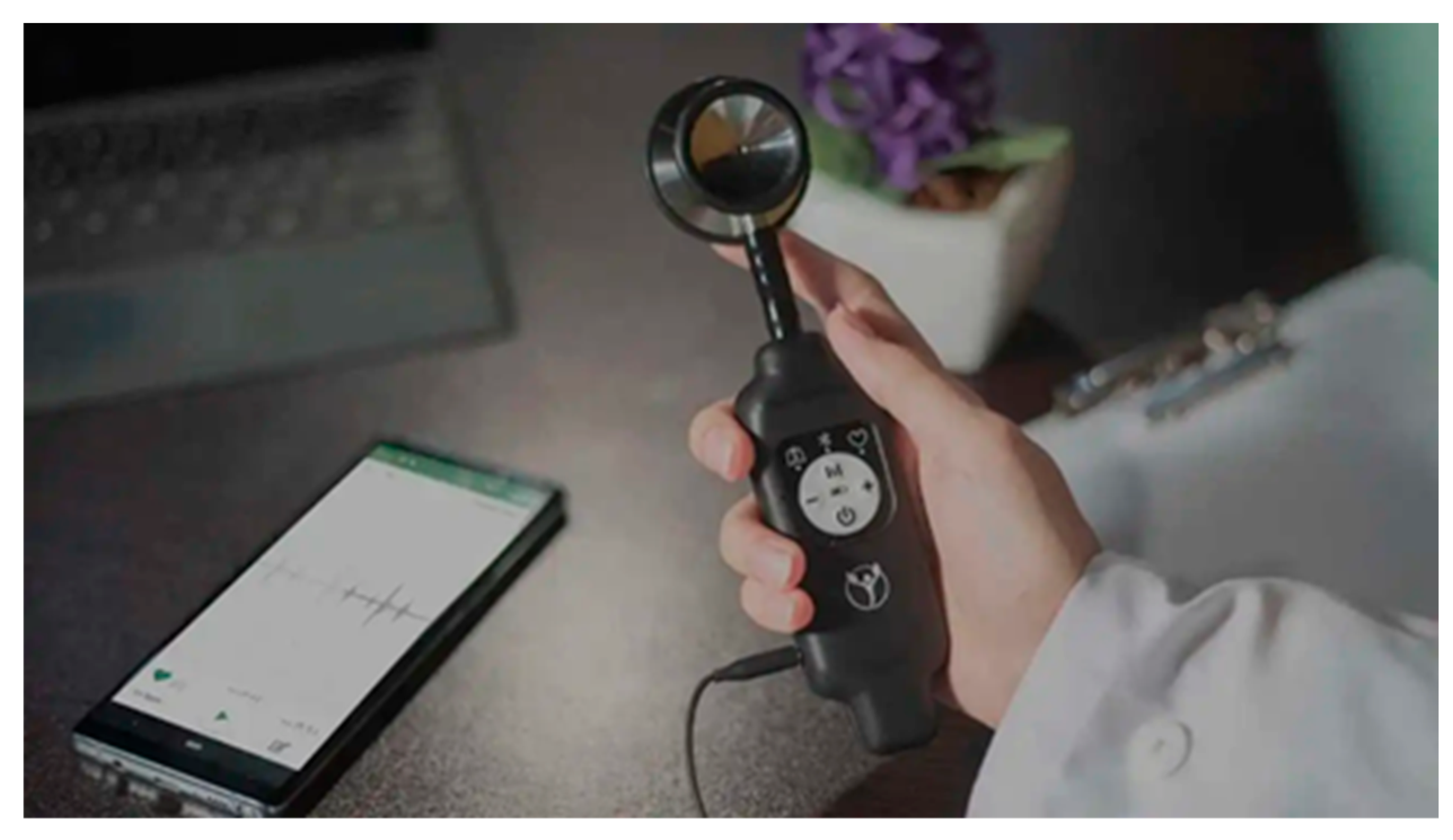
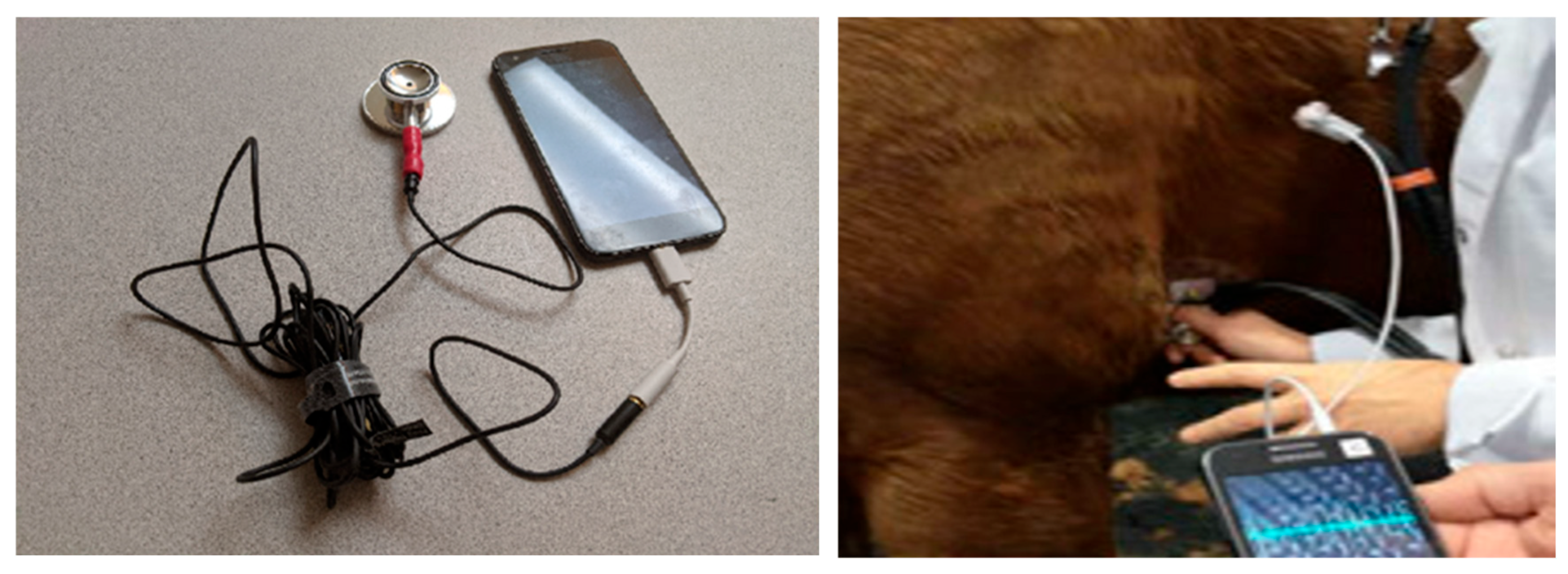
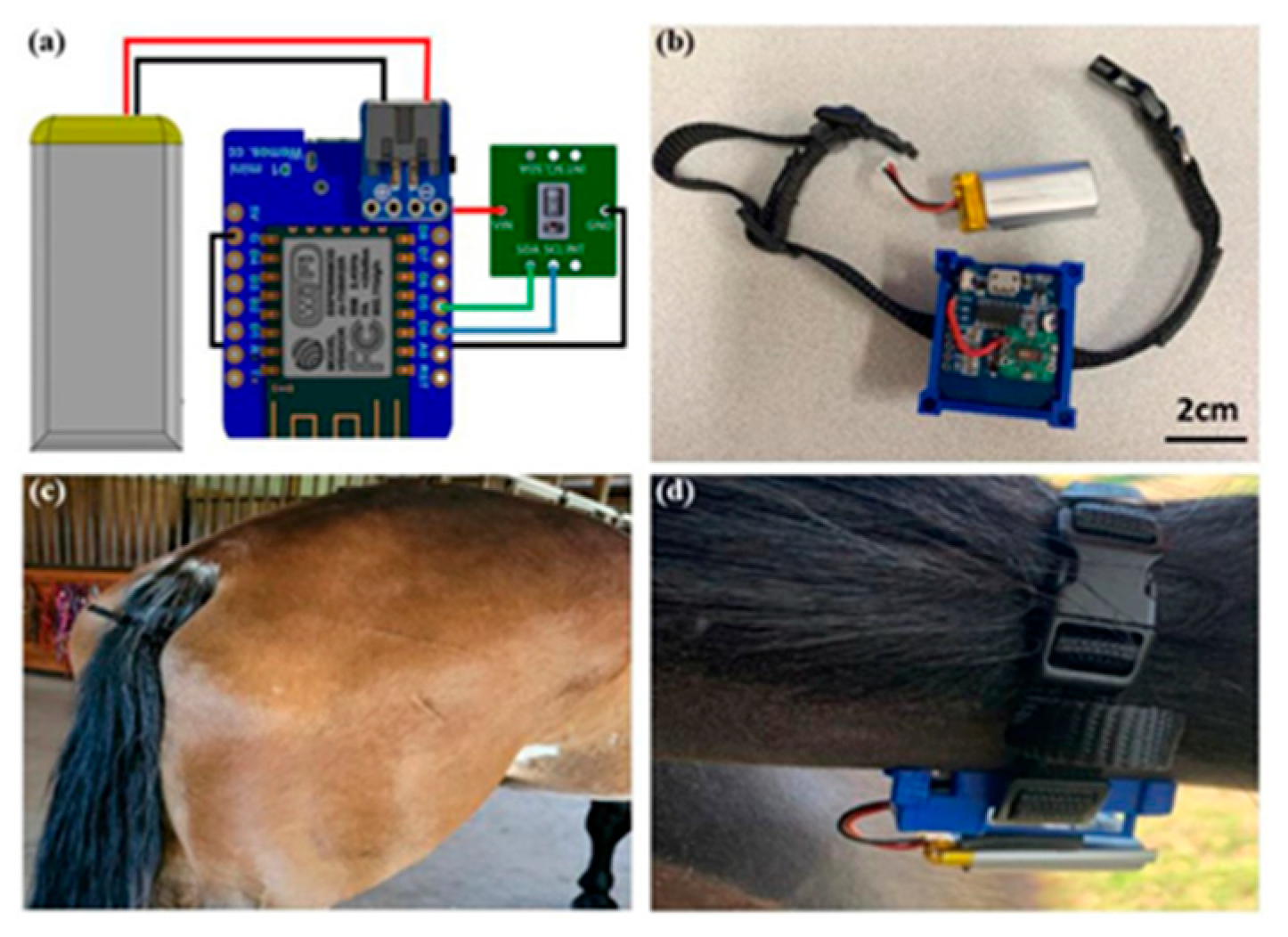
To obtain the best area of the animal's body for listening to the heartbeat and installing the device, as well as processing and ensuring the correctness of the proposed design, a simple test can be performed by phonocardiography. To do that, we only need a normal headset, a veterinary stethoscope, and a mobile phone. By connecting the diaphragm part of the stethoscope to the headset microphone, we can store the received sound in a mobile phone for processing and performing the necessary tests through machine learning and AI. (
Figure 36)
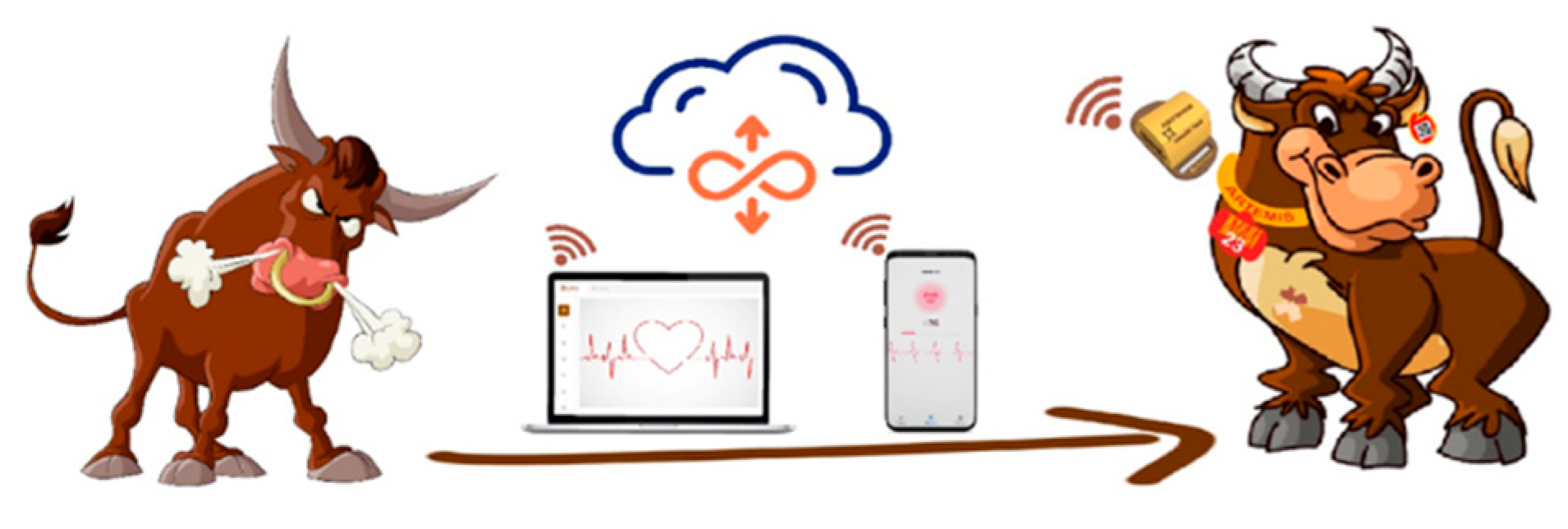
Furthermore, it is possible to personalize health information for each animal by using machine learning and processing and storing the received data from each animal in the initial minutes of connection and considering a specific data file for each animal, synchronized with that particular animal's moods and physical characteristics. From now on, we can compare the animal's information with the data stored for the same animal, and in case of any interference, quickly become aware of changes in the animal's condition. Of course, in case of stability, after comparing the above conditions with the stored data for all animals and system confirmation, if there is no discrepancy, the animal's health indicator will move to the stable phase.
For example: a cow's heart rate in a general state is 60, but perhaps a cow's normal heart rate in that specific cow is 58. In our initial connection, we observe the number 58. If the received number is not different from the general norm, we consider a heart rate of 58 as the health range for this animal. Based on this algorithm, other items such as temperature, respiration, etc., will also be manageable via machine learning.
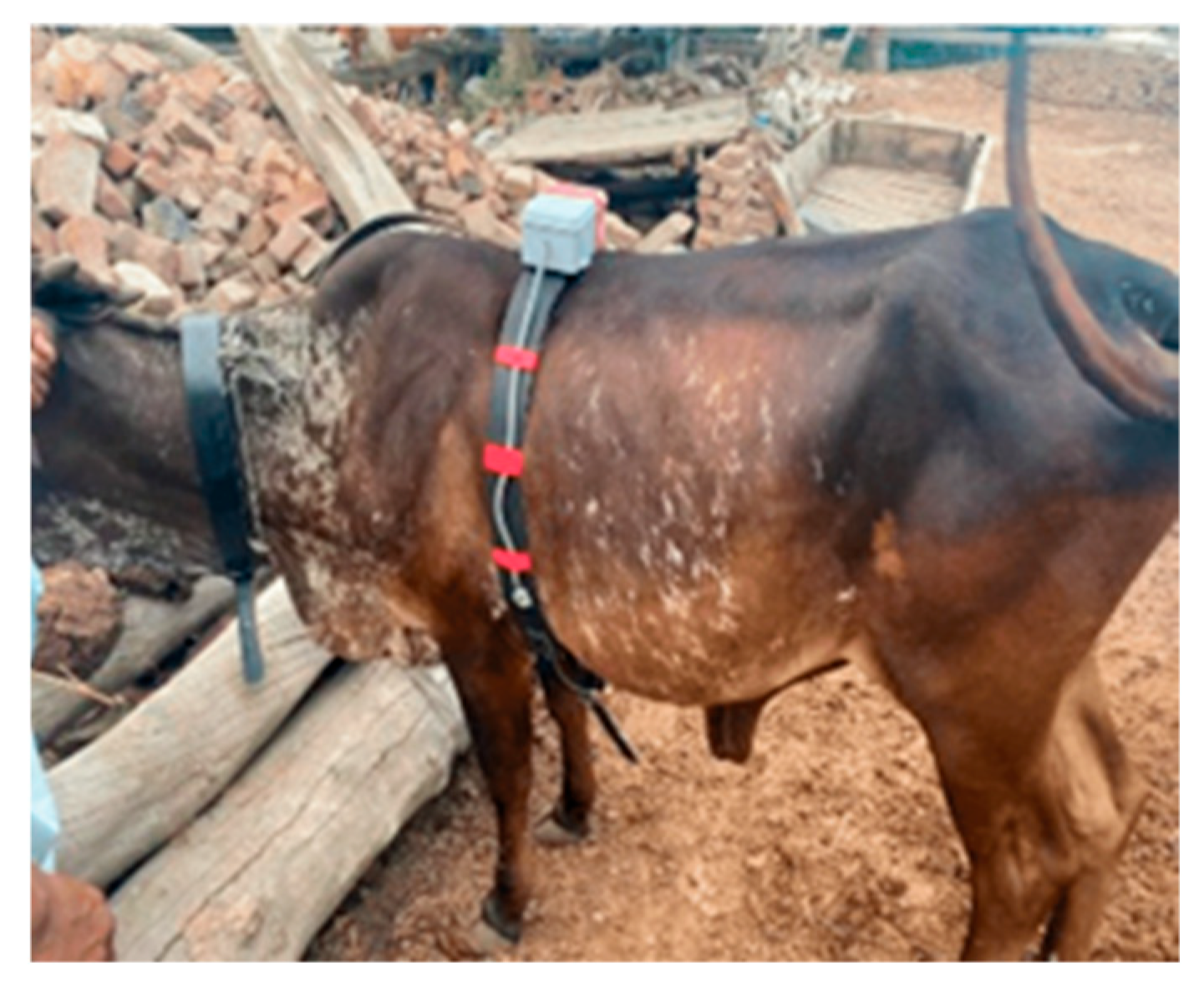
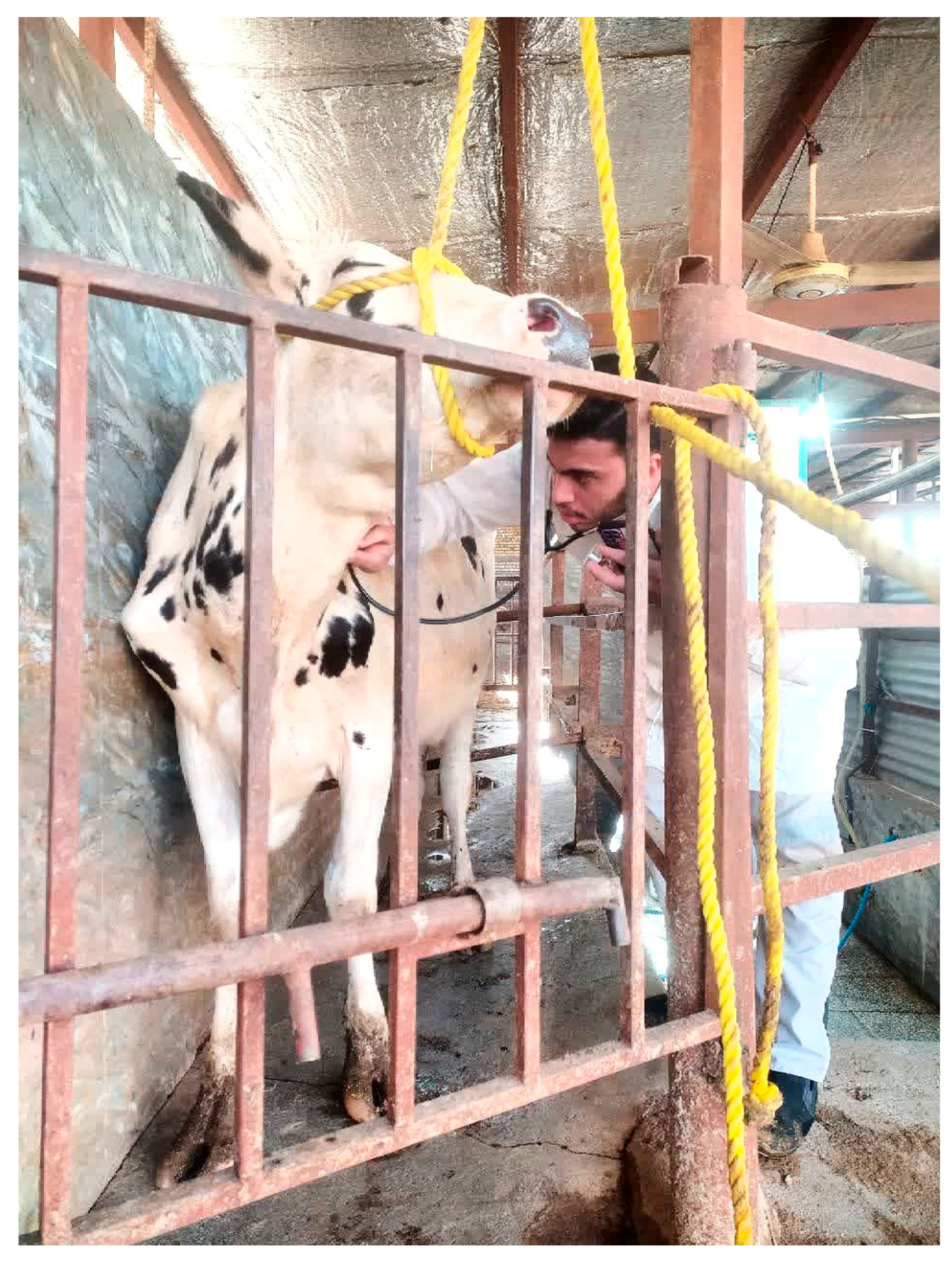
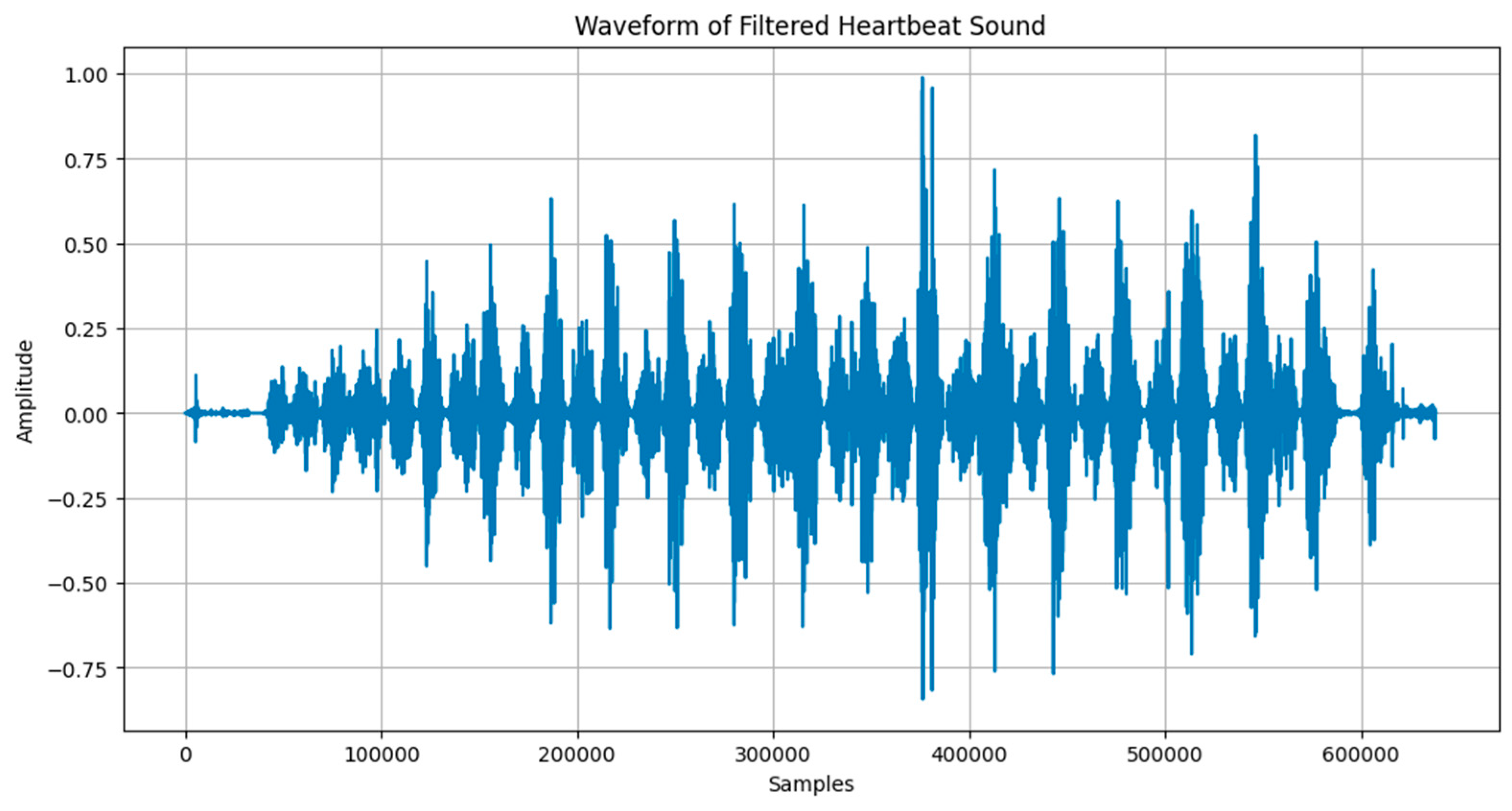
To evaluate the cardiac health of the subject cow, an audio recording of the heart sound was captured using a stethoscope and processed using digital signal processing techniques. (
Figure 37)
Raw recorded audio:
The raw signal was first filtered using a high-pass filter (cutoff: 40 Hz) to eliminate low-frequency background noise, followed by a low-pass filter (cutoff: 150 Hz) to remove high-frequency disturbances by software program and The resulting signal was then normalized to enhance the audibility of the heartbeat components via The code below:
# Download the output file
files.download(output_filename)
# Install necessary libraries
!pip install librosa matplotlib numpy scipy
# Import libraries
import numpy as np
import librosa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import spectrogram
# Load the filtered audio file
filtered_audio_path = “heartbeat_filtered.wav” # Name of the filtered file
y, sr = librosa.load(filtered_audio_path, sr=None)
# Plot the waveform
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(y)
plt.title(‘Waveform of Filtered Heartbeat Sound’)
plt.xlabel(‘Samples’)
plt.ylabel(‘Amplitude’)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Recorded sound processed by intelligent software:
Time-Domain Analysis
The following code displays the filtered and normalized heart sound waveform in the output:
# Calculate and plot the spectrogram
frequencies, times, Sxx = spectrogram(y, fs=sr)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.pcolormesh(times, frequencies, 10 * np.log10(Sxx), shading=’gouraud’)
plt.colorbar(label=’Intensity (dB)’)
plt.ylabel(‘Frequency (Hz)’)
plt.xlabel(‘Time (s)’)
plt.title(‘Spectrogram of Filtered Heartbeat Sound’)
plt.ylim(0, 500) # Limit frequency for better visibility (you can change this)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
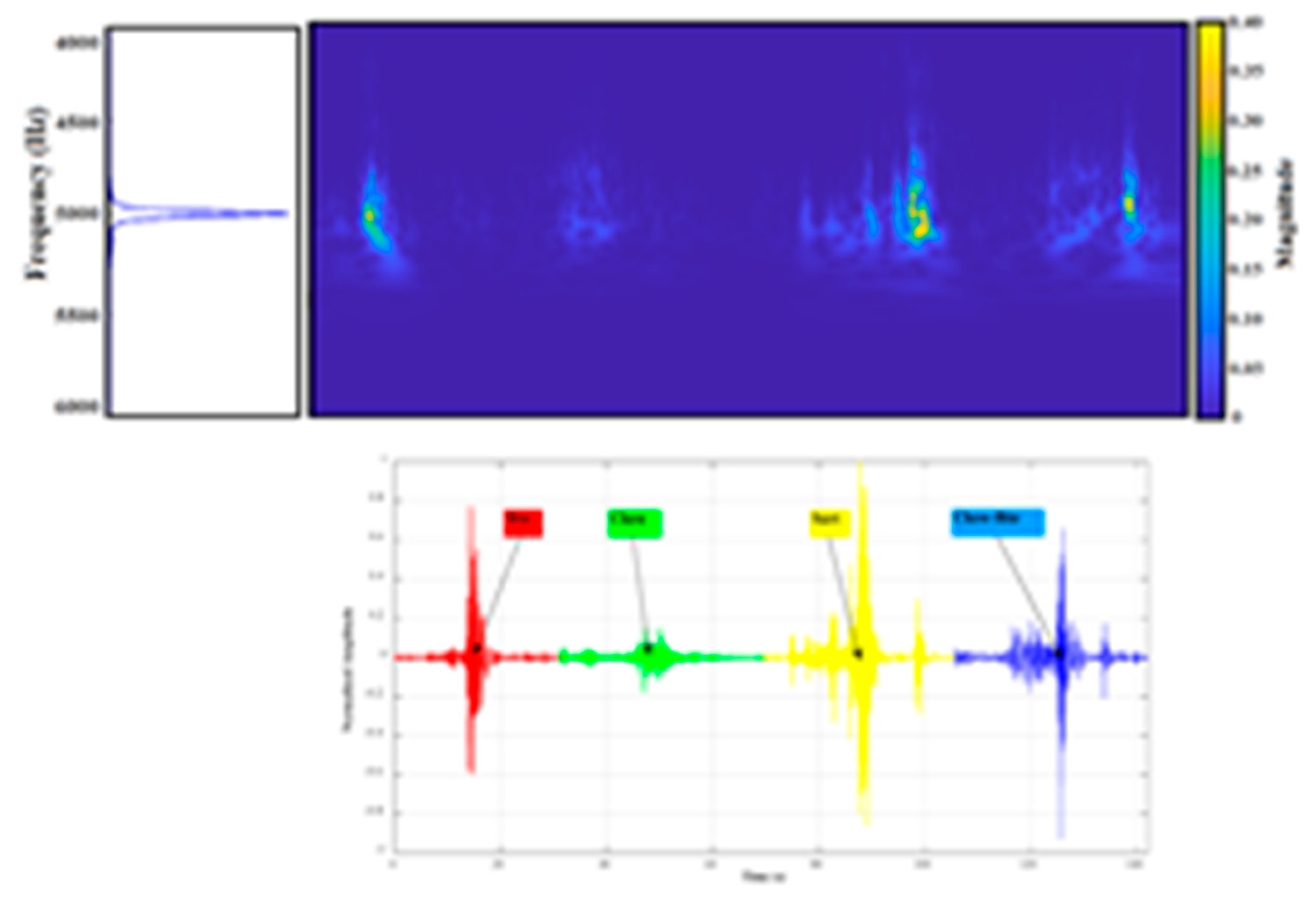
Each beat shows distinct peaks associated with the S1 (“lub”) and S2 (“dub”) components. The amplitude of these peaks suggests the presence of a relatively strong cardiac signal, further supported by the RMS value. (
Figure 38)
Frequency-Domain Analysis
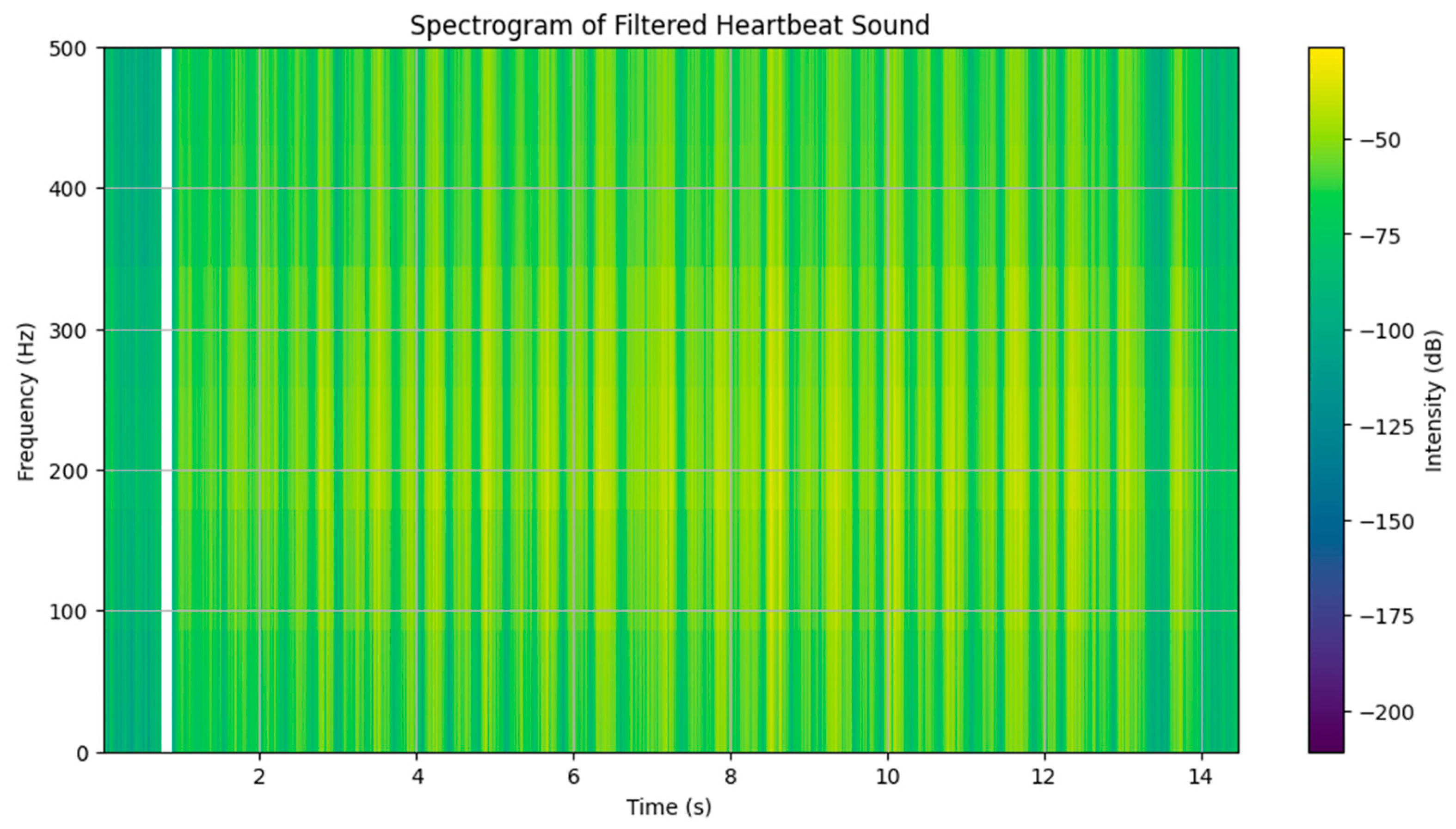
The spectrogram of the processed signal displays how the signal energy is distributed across frequencies and time. As expected, most of the signal power is concentrated in the 50–150 Hz range, where the mechanical sounds of heart valves typically reside. Guide lines have been added at 60 Hz and 120 Hz to emphasize the key frequency bands. (
Figure 39)
Feature Extraction and Quantitative Assessment
A set of audio features was extracted from the processed signal via this code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import librosa
# Load the filtered audio file
filtered_audio_path = “heartbeat_filtered.wav” # Name of the filtered file
y, sr = librosa.load(filtered_audio_path, sr=None)
# Calculate heart rate frequency
def calculate_heartbeat_frequency(y, sr):
onset_env = librosa.onset.onset_strength(y=y, sr=sr)
peaks = librosa.onset.onset_detect(onset_envelope=onset_env, sr=sr)
bpm_times = librosa.frames_to_time(peaks, sr=sr)
heart_rate = 60 / np.diff(bpm_times)
return heart_rate
# Calculate RMS
rms_value = np.sqrt(np.mean(y**2))
# Calculate heart rate frequency
heartbeat_frequencies = calculate_heartbeat_frequency(y, sr)
# s1: Mean heart rate frequency
s1 = np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies)
# s2: Standard deviation of heart rate frequency
s2 = np.std(heartbeat_frequencies)
# Prepare data for the table
data = {
‘Feature’: [‘Heart Rate (BPM)’, ‘RMS’, ‘s1 (Mean Heart Rate)’, ‘s2 (Standard Deviation)’],
‘Value’: [np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies), rms_value, s1, s2]
}
# Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Health analysis of the cow based on values
health_analysis = “”
heart_rate = np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies)
rms_threshold = 0.01 # Set RMS threshold (you can change this)
# Health analysis based on mean heart rate frequency
if heart_rate < 60:
health_analysis += “The cow has a low heart rate (below 60 BPM), which may indicate lethargy or underlying health issues.\n”
elif heart_rate > 80:
health_analysis += “The cow has a high heart rate (above 80 BPM), which could suggest stress or health concerns such as fever or dehydration.\n”
else:
health_analysis += “The heart rate is within the normal range (60-80 BPM), suggesting the cow is likely healthy.\n”
# Health analysis based on RMS
if rms_value < rms_threshold:
health_analysis += “The RMS value is low, indicating weak heart function or potential health challenges that need to be addressed.\n”
else:
health_analysis += “The RMS value is acceptable, suggesting good heart amplitude and functionality.\n”
# s1 and s2 analysis
if s2 > 10: # You can apply a new threshold value
health_analysis += “High variability in heart rate (s2) indicates possible stress or health issues that need monitoring.\n”
else:
health_analysis += “Low variability (s2) suggests stable heart rhythm, indicating better health status.\n”
# Add health analysis to DataFrame
health_analysis_df = pd.DataFrame({‘Feature’: [‘Health Analysis’], ‘Value’: [health_analysis]})
df = pd.concat([df, health_analysis_df], ignore_index=True)
# Display the table
print(“Tables and analysis of audio features:”)
print(df)
# Save the table as a CSV file
output_table = “heartbeat_analysis_results.csv”
df.to_csv(output_table, index=False)
print(f”\nThe analysis table has been saved as {output_table}.”)
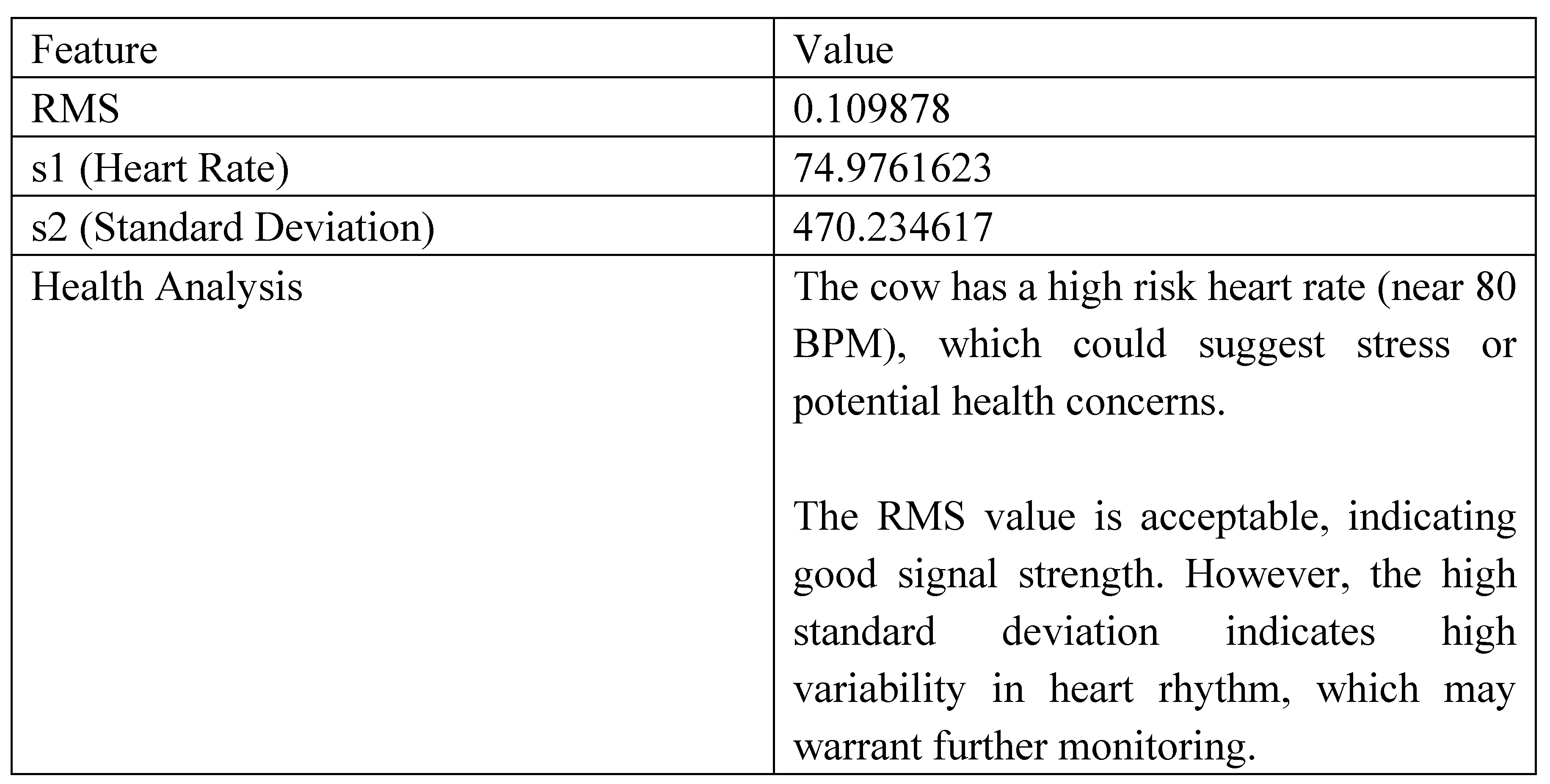
The average heart rate was calculated based on onset peak detection using the onset envelope. The RMS value represents the signal
’s energy, while the standard deviation (s2) reflects the variability of the detected beats. (
Figure 40)
Health Interpretation
Finally, a report text and interpretation of the animal's health will be sent to the farmer through the following code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import librosa
# Load the filtered audio file
filtered_audio_path = "heartbeat_filtered.wav" # Name of the filtered file
y, sr = librosa.load(filtered_audio_path, sr=None)
# Function to calculate heart rate frequency
def calculate_heartbeat_frequency(y, sr):
onset_env = librosa.onset.onset_strength(y=y, sr=sr) # Calculate onset strength
peaks = librosa.onset.onset_detect(onset_envelope=onset_env, sr=sr) # Detect peaks
bpm_times = librosa.frames_to_time(peaks, sr=sr) # Convert frames to time
heart_rate = 60 / np.diff(bpm_times) # Calculate heart rate in BPM
return heart_rate
# Calculate RMS value
rms_value = np.sqrt(np.mean(y**2))
# Calculate heart rate frequencies
heartbeat_frequencies = calculate_heartbeat_frequency(y, sr)
# s1: Mean heart rate
s1 = np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies)
# s2: Standard deviation of heart rate
s2 = np.std(heartbeat_frequencies)
# Prepare data for the table
data = {
'Feature': ['Heart Rate (BPM)', 'RMS', 's1 (Mean Heart Rate)', 's2 (Standard Deviation)'],
'Value': [np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies), rms_value, s1, s2]
}
# Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Health analysis based on values
health_analysis = ""
heart_rate = np.mean(heartbeat_frequencies)
rms_threshold = 0.01 # Set RMS threshold (can be adjusted)
# Health analysis based on mean heart rate
if heart_rate < 60:
health_analysis += "The cow has a low heart rate (below 60 BPM), indicating lethargy or underlying health issues. Immediate medical checkup is recommended.\n"
elif heart_rate > 80:
health_analysis += "The cow has a high heart rate (above 80 BPM), suggesting stress or health concerns such as fever or dehydration. Monitoring should be increased to identify the cause of this condition.\n"
else:
health_analysis += "The heart rate is within the normal range (60-80 BPM), suggesting the cow is likely healthy. Regular monitoring is still recommended to ensure continued health.\n"
# Health analysis based on RMS
if rms_value < rms_threshold:
health_analysis += "The RMS value is low, indicating weak heart function or potential health challenges. Veterinary advice is strongly suggested to investigate this condition further.\n"
else:
health_analysis += "The RMS value is acceptable, suggesting good heart amplitude and functionality. It indicates that the cow has a healthy heart at this moment.\n"
# s1 and s2 analysis
if s2 > 10: # You can apply a new threshold value
health_analysis += "High variability in heart rate (s2) indicates possible stress or health issues. Continuous monitoring and possible interventions may be required.\n"
else:
health_analysis += "Low variability (s2) suggests a stable heart rhythm, indicating better health status and lower stress levels in the cow.\n"
# Additional explanations on acceptable ranges
health_analysis += "\nAcceptable values and implications for cow health:\n"
health_analysis += "1. Heart Rate (BPM):\n"
health_analysis += " - Normal Range: 60-80 BPM (Healthy)\n"
health_analysis += " - Below 60 BPM: Possible lethargy or health issues.\n"
health_analysis += " - Above 80 BPM: Possible stress, fever, or dehydration.\n"
health_analysis += "\n2. RMS Value:\n"
health_analysis += " - Acceptable: Greater than 0.01 (Indicates good heart function)\n"
health_analysis += " - Low: Less than 0.01 (May indicate weak heart function)\n"
health_analysis += "\n3. Standard Deviation (s2):\n"
health_analysis += " - Low (<= 10): Indicates stable heart rhythm (Better health)\n"
health_analysis += " - High (> 10): Indicates variability (Possible stress or health issues)\n"
# Add health analysis to DataFrame
health_analysis_df = pd.DataFrame({'Feature': ['Health Analysis'], 'Value': [health_analysis]})
df = pd.concat([df, health_analysis_df], ignore_index=True)
# Display the table
print("Audio Feature Analysis and Health Assessment:")
print(df)
# Detailed health assessment explanation
detailed_explanation = """
Final report output:
Detailed Health Assessment:
The heart rate was near the above up range (60–80 BPM), which may suggest stress, fever, or dehydration.
The RMS value was sufficiently high (> 0.01), indicating strong signal amplitude and suggesting no immediate cardiac weakness.
However, the high variability (s2 > 10) in beat intervals points to potential irregularities in rhythm, which may require further investigation.
The analysis of the cow's heart rate and RMS values provides valuable insights into its health condition. Here’s a breakdown of the findings:
-
**Heart Rate (BPM)**: The average heart rate is a critical indicator of the cow's overall health.
- -
A heart rate within the normal range (60-80 BPM) suggests that the cow is healthy and does not exhibit signs of distress.
- -
A heart rate below 60 BPM may indicate lethargy, which could stem from various underlying health issues such as infections or anemia. If observed, a veterinary checkup is essential to rule out serious conditions.
- -
Conversely, a heart rate above 80 BPM can suggest stress, fever, or dehydration. This may require closer monitoring and possible intervention to address the underlying cause.
-
**RMS Value**: The Root Mean Square (RMS) value reflects the amplitude of the heart's electrical signal.
- -
An acceptable RMS value (greater than 0.01) indicates that the heart is functioning well, with strong contractions and efficient blood flow.
- -
A low RMS value could signal weak heart function, necessitating further veterinary assessment to identify potential health challenges.
-
**Standard Deviation (s2)**: This metric indicates the variability of the heart rate.
- -
A low standard deviation (≤ 10) suggests a stable heart rhythm, which is generally associated with good health and low stress levels.
- -
A high standard deviation (> 10) indicates significant variability in heart rate, which may be a sign of stress or health issues requiring ongoing observation and possibly medical intervention.
End of the test and report section.
The strategy of using artificial intelligence technologies, artificial neural networks, and machine learning to perform the above steps as well as how to use the Internet of Things to transfer information, and also the results of the tests will be gradually added to this part of the article.