Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
21 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Microbiome and ALL
3. Microbiota and Microbiome and Its Modulating Effects on Hematopoiesis in Health and Disease
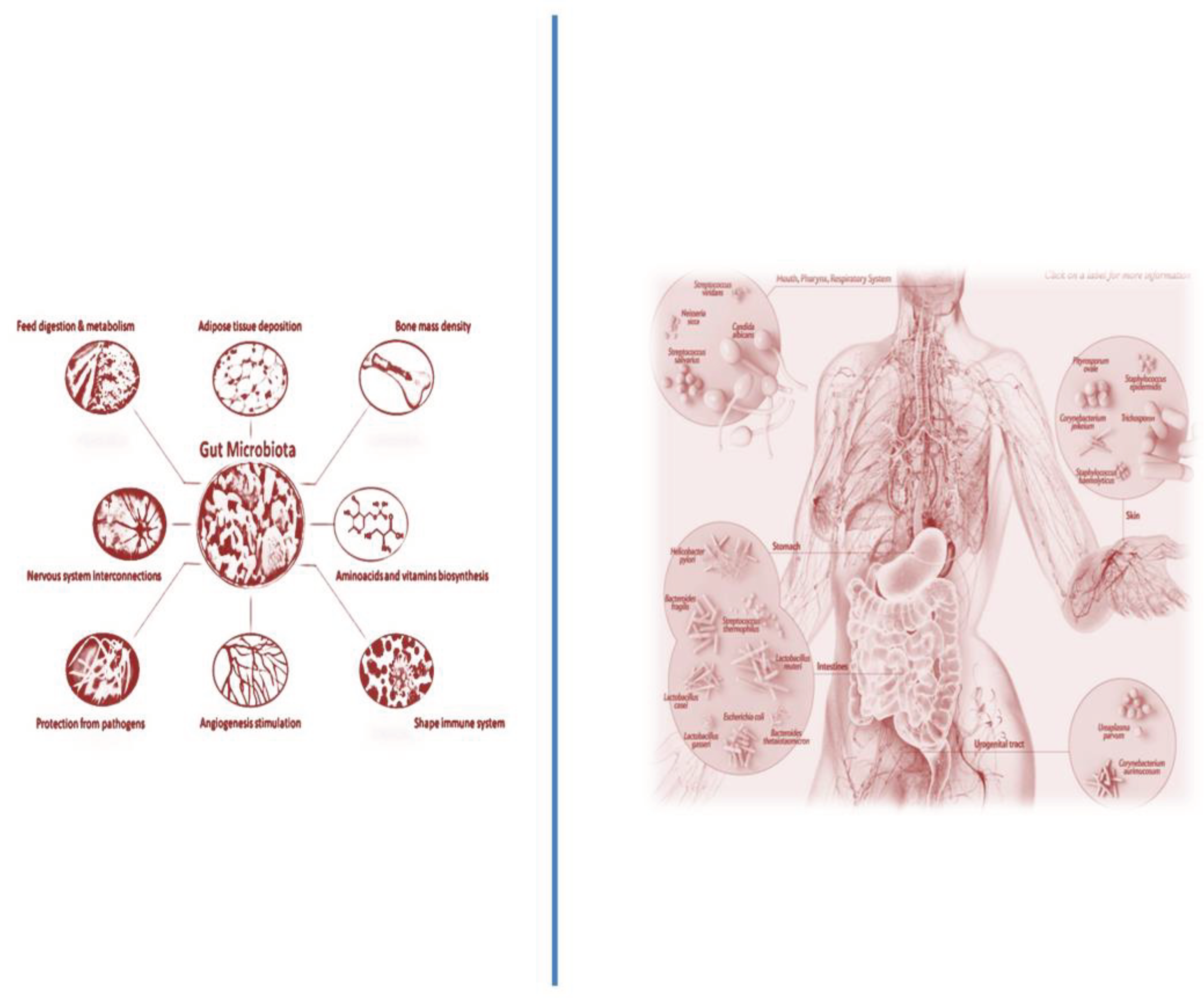
3.1. The GM Close Relationship with Hematopoiesis
3.2. Experimental Evidence for the Effects of Microbiota on Hematopoiesis
3.3. Developmental Programming of HS and the Susceptibility of Leukemia
4. Close Relationship between ALL and Microbiota
4.1. Gut Microbiota and Children Susceptibility for ALL Onset
4.2. Alterations in Microbiome at the Children ALL Diagnosis
4.3. Alterations in Microbiome during Children ALL Treatment with Chemotherapy
5. Diverse Levels of Strategies to Recovery Microbiome and Prevent All Onset
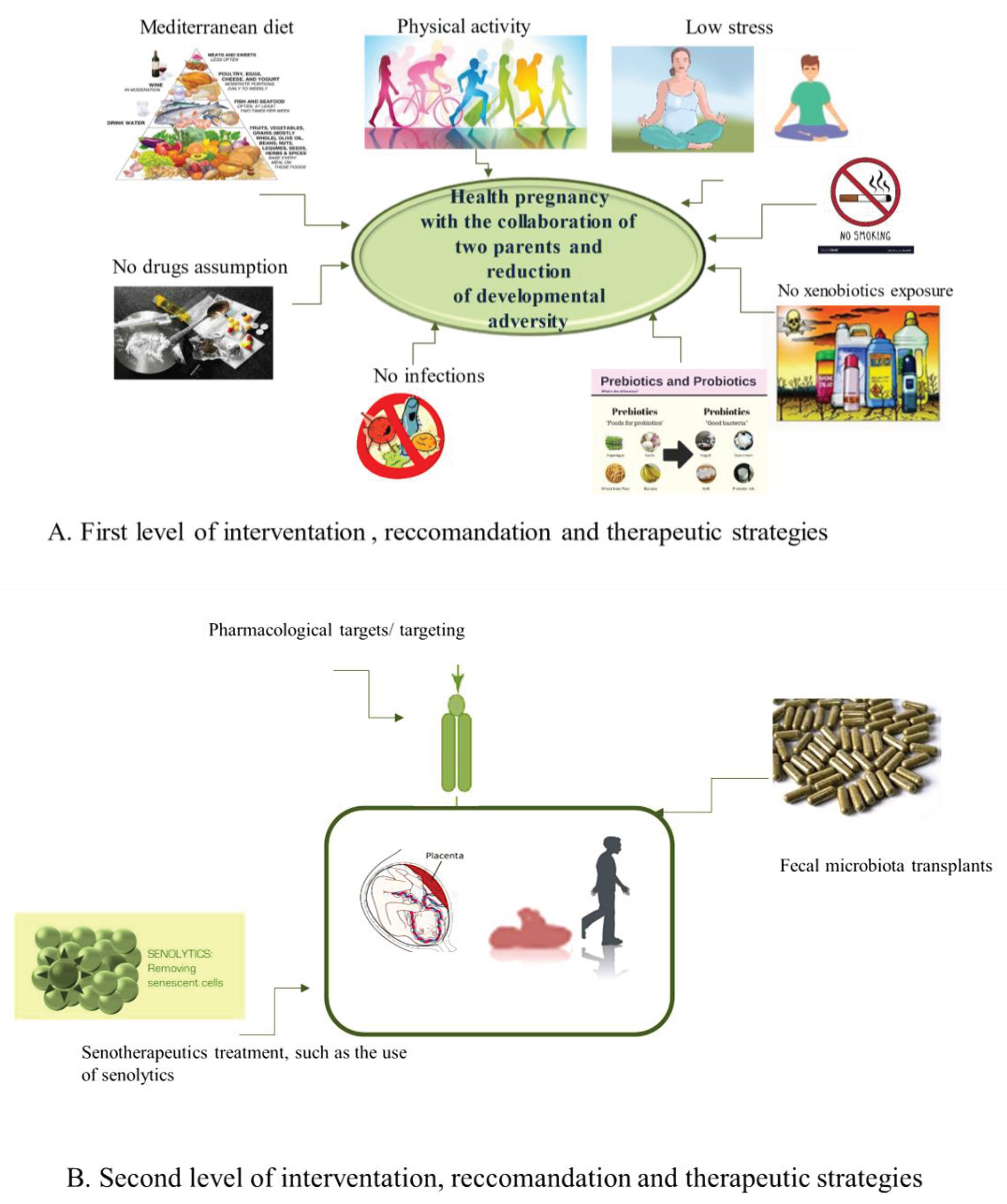
5.1. The First Level of Health-Promoting Strategies
5.2. Some Therapeutic Approaches of Second Level
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
References
- Greaves M. (2018). A causal mechanism for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature reviews. Cancer, 18(8), 471–484. [CrossRef]
- Rajagopala, S. V., Yooseph, S., Harkins, D. M., Moncera, K. J., Zabokrtsky, K. B., Torralba, M. G., Tovchigrechko, A., Highlander, S. K., Pieper, R., Sender, L., & Nelson, K. E. (2016). Gastrointestinal microbial populations can distinguish pediatric and adolescent Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) at the time of disease diagnosis. BMC genomics, 17(1), 635. [CrossRef]
- Ekpa, Q. L., Akahara, P. C., Anderson, A. M., Adekoya, O. O., Ajayi, O. O., Alabi, P. O., Okobi, O. E., Jaiyeola, O., & Ekanem, M. S. (2023). A Review of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) in the Pediatric Population: Evaluating Current Trends and Changes in Guidelines in the Past Decade. Cureus, 15(12), e49930. [CrossRef]
- Seth, R., & Singh, A. (2015). Leukemias in Children. Indian journal of pediatrics, 82(9), 817–824. [CrossRef]
- Tarlock, K.; Dahl, G.; Lacayo, N. Acute myeloid leukemia in children. In Wintrobe’s Clinical Hematology, 14th ed.; Lippincott Williams &Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 5016–5095.
- de Ville de Goyet, M., Kicinski, M., Suciu, S., Vandecruys, E., Uyttebroeck, A., Ferster, A., Freycon, C., Plat, G., Thomas, C., Barbati, M., Dresse, M. F., Paillard, C., Pluchart, C., Simon, P., Chantrain, C., Minckes, O., van der Werff Ten Bosch, J., Bertrand, Y., Rohrlich, P., Millot, F., European Organisation for Research, Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Children’s Leukemia Group (CLG) (2024). Long-term neurotoxicity among childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia survivors enrolled between 1971 and 1998 in EORTC Children Leukemia Group studies. Discover. Oncology, 15(1), 20. [CrossRef]
- Del Principe, M. I., Maurillo, L., Buccisano, F., Sconocchia, G., Cefalo, M., De Santis, G., Di Veroli, A., Ditto, C., Nasso, D., Postorino, M., Refrigeri, M., Attrotto, C., Del Poeta, G., Lo-Coco, F., Amadori, S., & Venditti, A. (2014). Central nervous system involvement in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: diagnostic tools, prophylaxis, and therapy. Mediterranean journal of hematology and infectious diseases, 6(1), e2014075. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D. L., Alonzo, T. A., Gerbing, R. B., Aplenc, R., Woods, W. G., Meshinchi, S., & Gamis, A. S. (2017). Central nervous system disease in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatric blood & cancer, 64(12), 10.1002/pbc.26612. [CrossRef]
- Van Delft, F. W., & Saha, V. (2004). Molecular techniques to improve outcome in childhood ALL. Methods in molecular medicine, 91, 111–122. [CrossRef]
- Cho, S. Y., Cheng, A. C., & Cheng, M. C. (2000). Oral care for children with leukaemia. Hong Kong medical journal = Xianggang yi xue za zhi, 6(2), 203–208.
- Fathi, A., Mirzarahimi, M., & Farajkhah, H. (2021). Réponse à un schéma chimiothérapeutique administré à des enfants atteints de LAL à cellules pré-B à risque élevé selon le protocole COG. Canadian oncology nursing journal = Revue canadienne de nursing oncologique, 31(3), 334–338. [CrossRef]
- Lim, H. C., & Kim, C. S. (2014). Oral signs of acute leukemia for early detection. Journal of periodontal & implant science, 44(6), 293–299. [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C. R., Garagnani, P., Madonna, R., Vaiserman, A., & Melino, G. (2019). Developmental programming of adult haematopoiesis system. Ageing research reviews, 54, 100918. [CrossRef]
- Tebbi C. K. (2021). Etiology of Acute Leukemia: A Review. Cancers, 13(9), 2256. [CrossRef]
- Pagani, I. S., Poudel, G., & Wardill, H. R. (2022). A Gut Instinct on Leukaemia: A New Mechanistic Hypothesis for Microbiota-Immune Crosstalk in Disease Progression and Relapse. Microorganisms, 10(4), 713. [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, M., Rüchel, N., Janssen, S., Borkhardt, A., & Gössling, K. L. (2021). The Microbiome in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 13(19), 4947. [CrossRef]
- Soares, S. C., Roux, L. J. D., Castro, A. R., Silva, C. C., Rodrigues, R., Macho, V. M. P., Silva, F., & Costa, C. (2023). Oral Manifestations: A Warning-Sign in Children with Hematological Disease Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hematology reports, 15(3), 491–502. [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C. R., & Monastero, R. (2023). Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases: How Much Do We Still Not Know?. Brain sciences, 14(1), 19. [CrossRef]
- Schirò, G., Iacono, S., & Balistreri, C. R. (2023). The Role of Human Microbiota in Myasthenia Gravis: A Narrative Review. Neurology international, 15(1), 392–404. [CrossRef]
- Scola, L., Giarratana, R. M., Torre, S., Argano, V., Lio, D., & Balistreri, C. R. (2019). On the Road to Accurate Biomarkers for Cardiometabolic Diseases by Integrating Precision and Gender Medicine Approaches. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(23), 6015. [CrossRef]
- Forte, A., Balistreri, C. R., De Feo, M., Della Corte, A., Hellstrand, P., Persson, L., & Nilsson, B. O. (2019). Polyamines and microbiota in bicuspid and tricuspid aortic valve aortopathy. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 129, 179–187. [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S., Razavi, S. H., Yadav, H., & Letizia Manca, M. (2024). New horizon to the world of gut microbiome: seeds germination. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 1–19. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Balistreri C. R. (2022). Promising Strategies for Preserving Adult Endothelium Health and Reversing Its Dysfunction: From Liquid Biopsy to New Omics Technologies and Noninvasive Circulating Biomarkers. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(14), 7548. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D., Liwinski, T., & Elinav, E. (2020). Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell research, 30(6), 492–506. [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y., Jin, R., & Chen, H. (2019). Interactions Between Gut Microbiota and Acute Childhood Leukemia. Frontiers in microbiology, 10, 1300. [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R. F., & Jobin, C. (2013). The microbiome and cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer, 13(11), 800–812. [CrossRef]
- Holler, E., Butzhammer, P., Schmid, K., Hundsrucker, C., Koestler, J., Peter, K., Zhu, W., Sporrer, D., Hehlgans, T., Kreutz, M., Holler, B., Wolff, D., Edinger, M., Andreesen, R., Levine, J. E., Ferrara, J. L., Gessner, A., Spang, R., & Oefner, P. J. (2014). Metagenomic analysis of the stool microbiome in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation: loss of diversity is associated with use of systemic antibiotics and more pronounced in gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, 20(5), 640–645. [CrossRef]
- Rajagopala, S. V., Yooseph, S., Harkins, D. M., Moncera, K. J., Zabokrtsky, K. B., Torralba, M. G., Tovchigrechko, A., Highlander, S. K., Pieper, R., Sender, L., & Nelson, K. E. (2016). Gastrointestinal microbial populations can distinguish pediatric and adolescent Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) at the time of disease diagnosis. BMC genomics, 17(1), 635. [CrossRef]
- Scola, L., Giarratana, R. M., Torre, S., Argano, V., Lio, D., & Balistreri, C. R. (2019). On the Road to Accurate Biomarkers for Cardiometabolic Diseases by Integrating Precision and Gender Medicine Approaches. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(23), 6015. [CrossRef]
- Balistreri C. R. (2022). Promising Strategies for Preserving Adult Endothelium Health and Reversing Its Dysfunction: From Liquid Biopsy to New Omics Technologies and Noninvasive Circulating Biomarkers. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(14), 7548. [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M., Cazzaniga, V., & Ford, A. (2021). Can we prevent childhood Leukaemia?. Leukemia, 35(5), 1258–1264. [CrossRef]
- Nycz, B. T., Dominguez, S. R., Friedman, D., Hilden, J. M., Ir, D., Robertson, C. E., & Frank, D. N. (2018). Evaluation of bloodstream infections, Clostridium difficile infections, and gut microbiota in pediatric oncology patients. PloS one, 13(1), e0191232. [CrossRef]
- Poore, G. D., Kopylova, E., Zhu, Q., Carpenter, C., Fraraccio, S., Wandro, S., Kosciolek, T., Janssen, S., Metcalf, J., Song, S. J., Kanbar, J., Miller-Montgomery, S., Heaton, R., Mckay, R., Patel, S. P., Swafford, A. D., & Knight, R. (2020). Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer diagnostic approach. Nature, 579(7800), 567–574. [CrossRef]
- Turpin, W., Espin-Garcia, O., Xu, W., Silverberg, M. S., Kevans, D., Smith, M. I., Guttman, D. S., Griffiths, A., Panaccione, R., Otley, A., Xu, L., Shestopaloff, K., Moreno-Hagelsieb, G., GEM Project Research Consortium, Paterson, A. D., & Croitoru, K. (2016). Association of host genome with intestinal microbial composition in a large healthy cohort. Nature genetics, 48(11), 1413–1417. [CrossRef]
- Beam, A., Clinger, E., & Hao, L. (2021). Effect of Diet and Dietary Components on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients, 13(8), 2795. [CrossRef]
- Ma, T., Chen, Y., Li, L. J., & Zhang, L. S. (2021). Opportunities and Challenges for Gut Microbiota in Acute Leukemia. Frontiers in oncology, 11, 692951. [CrossRef]
- https://www.poliambulatoriomodoetia.it/salute/microbiota-intestinale/.
- Adak, A., & Khan, M. R. (2019). An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 76(3), 473–493. [CrossRef]
- https://www.santagostino.it/it/santagostinopedia/microbiota-intestinale.
- Upadhyay Banskota, S., Skupa, S. A., El-Gamal, D., & D’Angelo, C. R. (2023). Defining the Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Lymphoid Malignancies. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(3), 2309. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S., Rhee, K. J., Albesiano, E., Rabizadeh, S., Wu, X., Yen, H. R., Huso, D. L., Brancati, F. L., Wick, E., McAllister, F., Housseau, F., Pardoll, D. M., & Sears, C. L. (2009). A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nature medicine, 15(9), 1016–1022. [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215.
- Balistreri, C. R., Garagnani, P., Madonna, R., Vaiserman, A., & Melino, G. (2019). Developmental programming of adult haematopoiesis system. Ageing research reviews, 54, 100918. [CrossRef]
- Groussin, M., Poyet, M., Sistiaga, A., Kearney, S. M., Moniz, K., Noel, M., Hooker, J., Gibbons, S. M., Segurel, L., Froment, A., Mohamed, R. S., Fezeu, A., Juimo, V. A., Lafosse, S., Tabe, F. E., Girard, C., Iqaluk, D., Nguyen, L. T. T., Shapiro, B. J., Lehtimäki, J., … Alm, E. J. (2021). Elevated rates of horizontal gene transfer in the industrialized human microbiome. Cell, 184(8), 2053–2067.e18. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J. L., Wilson, I. D., Teare, J., Marchesi, J. R., Nicholson, J. K., and Kinross, J. M. (2017). Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 356–365. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.20.
- Balmer, M. L., Schürch, C. M., Saito, Y., Geuking, M. B., Li, H., Cuenca, M., Kovtonyuk, L. V., McCoy, K. D., Hapfelmeier, S., Ochsenbein, A. F., Manz, M. G., Slack, E., & Macpherson, A. J. (2014). Microbiota-derived compounds drive steady-state granulopoiesis via MyD88/TICAM signaling. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 193(10), 5273–5283. [CrossRef]
- Taur, Y., Jenq, R. R., Perales, M. A., Littmann, E. R., Morjaria, S., Ling, L., No, D., Gobourne, A., Viale, A., Dahi, P. B., Ponce, D. M., Barker, J. N., Giralt, S., van den Brink, M., & Pamer, E. G. (2014). The effects of intestinal tract bacterial diversity on mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood, 124(7), 1174–1182. [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J. L., Elbadry, M. I., & Nakao, S. (2016). An altered gut microbiota may trigger autoimmune-mediated acquired bone marrow failure syndromes. Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 171, 62–64. [CrossRef]
- Trompette, A., Gollwitzer, E. S., Yadava, K., Sichelstiel, A. K., Sprenger, N., Ngom-Bru, C., Blanchard, C., Junt, T., Nicod, L. P., Harris, N. L., & Marsland, B. J. (2014). Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nature medicine, 20(2), 159–166. [CrossRef]
- Zapata, H. J., & Quagliarello, V. J. (2015). The microbiota and microbiome in aging: potential implications in health and age-related diseases. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 63(4), 776–781. [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A., Koliada, A., & Lushchak, O. (2018). Developmental programming of aging trajectory. Ageing research reviews, 47, 105–122. [CrossRef]
- Kozyrskyj, A. L., Kalu, R., Koleva, P. T., & Bridgman, S. L. (2016). Fetal programming of overweight through the microbiome: boys are disproportionately affected. Journal of developmental origins of health and disease, 7(1), 25–34. [CrossRef]
- Weissman I. L. (1994). Developmental switches in the immune system. Cell, 76(2), 207–218. [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A., Yáñez, A., Price, J. G., Chow, A., Merad, M., Goodridge, H. S., & Mazmanian, S. K. (2014). Gut microbiota promote hematopoiesis to control bacterial infection. Cell host & microbe, 15(3), 374–381. [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. E., Li, J., Garbett, K., Mirnics, K., & Patterson, P. H. (2007). Maternal immune activation alters fetal brain development through interleukin-6. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(40), 10695–10702. [CrossRef]
- Singh, N., Thangaraju, M., Prasad, P. D., Martin, P. M., Lambert, N. A., Boettger, T., Offermanns, S., & Ganapathy, V. (2010). Blockade of dendritic cell development by bacterial fermentation products butyrate and propionate through a transporter (Slc5a8)-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases. The Journal of biological chemistry, 285(36), 27601–27608. [CrossRef]
- Kurita-Ochiai, T., Fukushima, K., & Ochiai, K. (1995). Volatile fatty acids, metabolic by-products of periodontopathic bacteria, inhibit lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production. Journal of dental research, 74(7), 1367–1373. [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M. A., Singh, N., Martin, P. M., Thangaraju, M., Ganapathy, V., Waller, J. L., Shi, H., Robertson, K. D., Munn, D. H., & Liu, K. (2012). Butyrate suppresses colonic inflammation through HDAC1-dependent Fas upregulation and Fas-mediated apoptosis of T cells. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 302(12), G1405–G1415. [CrossRef]
- Josefsdottir, K. S., Baldridge, M. T., Kadmon, C. S., & King, K. Y. (2017). Antibiotics impair murine hematopoiesis by depleting the intestinal microbiota. Blood, 129(6), 729–739. [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, M. T., Nice, T. J., McCune, B. T., Yokoyama, C. C., Kambal, A., Wheadon, M., Diamond, M. S., Ivanova, Y., Artyomov, M., & Virgin, H. W. (2015). Commensal microbes and interferon-λ determine persistence of enteric murine norovirus infection. Science (New York, N.Y.), 347(6219), 266–269. [CrossRef]
- Chow, J., Lee, S. M., Shen, Y., Khosravi, A., & Mazmanian, S. K. (2010). Host-bacterial symbiosis in health and disease. Advances in immunology, 107, 243–274. [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E., Candela, M., Franceschi, C., & Brigidi, P. (2011). The aging gut microbiota: new perspectives. Ageing research reviews, 10(4), 428–429. [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C., Bonafè, M., Valensin, S., Olivieri, F., De Luca, M., Ottaviani, E., & De Benedictis, G. (2000). Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 908, 244–254. [CrossRef]
- Rampelli, S., Candela, M., Turroni, S., Biagi, E., Collino, S., Franceschi, C., O’Toole, P. W., & Brigidi, P. (2013). Functional metagenomic profiling of intestinal microbiome in extreme ageing. Aging, 5(12), 902–912. [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E., Franceschi, C., Rampelli, S., Severgnini, M., Ostan, R., Turroni, S., Consolandi, C., Quercia, S., Scurti, M., Monti, D., Capri, M., Brigidi, P., & Candela, M. (2016). Gut Microbiota and Extreme Longevity. Current biology : CB, 26(11), 1480–1485. [CrossRef]
- Grignolio, A., Mishto, M., Faria, A. M., Garagnani, P., Franceschi, C., & Tieri, P. (2014). Towards a liquid self: how time, geography, and life experiences reshape the biological identity. Frontiers in immunology, 5, 153. [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R. E., Steele, M., & Karrow, N. A. (2012). Fetal programming of the neuroendocrine-immune system and metabolic disease. Journal of pregnancy, 2012, 792934. [CrossRef]
- Bateson, P., Gluckman, P., & Hanson, M. (2014). The biology of developmental plasticity and the Predictive Adaptive Response hypothesis. The Journal of physiology, 592(11), 2357–2368. [CrossRef]
- Faa, G., Marcialis, M. A., Ravarino, A., Piras, M., Pintus, M. C., & Fanos, V. (2014). Fetal programming of the human brain: is there a link with insurgence of neurodegenerative disorders in adulthood?. Current medicinal chemistry, 21(33), 3854–3876. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B. T., Dasinger, J. H., & Intapad, S. (2015). Fetal programming and cardiovascular pathology. Comprehensive Physiology, 5(2), 997–1025. [CrossRef]
- Bateson P. (2015). Why are individuals so different from each other?. Heredity, 115(4), 285–292. [CrossRef]
- Projecto-Garcia, J., Biddle, J. F., & Ragsdale, E. J. (2017). Decoding the architecture and origins of mechanisms for developmental polyphenism. Current opinion in genetics & development, 47, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E. J., & Kim, Y. J. (2017). What is fetal programming?: a lifetime health is under the control of in utero health. Obstetrics & gynecology science, 60(6), 506–519. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J. O., Ramalho, C., Henriques-Coelho, T., & Areias, J. C. (2017). Fetal programming as a predictor of adult health or disease: the need to reevaluate fetal heart function. Heart failure reviews, 22(6), 861–877. [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P. O., & Matthews, S. G. (2018). Prenatal Stress, Glucocorticoids, and Developmental Programming of the Stress Response. Endocrinology, 159(1), 69–82. [CrossRef]
- Walker, D. J., & Spencer, K. A. (2018). Glucocorticoid programming of neuroimmune function. General and comparative endocrinology, 256, 80–88. [CrossRef]
- Wells J. C. (2017). Worldwide variability in growth and its association with health: Incorporating body composition, developmental plasticity, and intergenerational effects. American journal of human biology : the official journal of the Human Biology Council, 29(2), 10.1002/ajhb.22954. [CrossRef]
- Zohdi, V., Lim, K., Pearson, J. T., & Black, M. J. (2014). Developmental programming of cardiovascular disease following intrauterine growth restriction: findings utilising a rat model of maternal protein restriction. Nutrients, 7(1), 119–152. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R., Wiemels, J. L., Metayer, C., Morimoto, L., Francis, S. S., Kadan-Lottick, N., DeWan, A. T., Zhang, Y., & Ma, X. (2017). Cesarean Section and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Population-Based, Record-Linkage Study in California. American journal of epidemiology, 185(2), 96–105. [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, S., Sheiner, E., Wainstock, T., Segal, I., Ben-Harush, M., Sergienko, R., & Walfisch, A. (2018). Cesarean Delivery and Childhood Malignancies: A Single-Center, Population-Based Cohort Study. The Journal of pediatrics, 197, 292–296.e3. [CrossRef]
- Amitay, E. L., & Keinan-Boker, L. (2015). Breastfeeding and Childhood Leukemia Incidence: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. JAMA pediatrics, 169(6), e151025. [CrossRef]
- Penders, J., Thijs, C., Vink, C., Stelma, F. F., Snijders, B., Kummeling, I., van den Brandt, P. A., & Stobberingh, E. E. (2006). Factors influencing the composition of the intestinal microbiota in early infancy. Pediatrics, 118(2), 511–521. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Xue, J., Zhou, X., You, M., Du, Q., Yang, X., He, J., Zou, J., Cheng, L., Li, M., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, J., Shi, W., & Xu, X. (2014). Oral microbiota distinguishes acute lymphoblastic leukemia pediatric hosts from healthy populations. PloS one, 9(7), e102116. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Zou, Y., Ruan, M., Chang, L., Chen, X., Wang, S., Yang, W., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., He, H., Gan, Y., Wang, K., & Zhu, X. (2020). Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Exhibit Distinctive Alterations in the Gut Microbiota. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 10, 558799. [CrossRef]
- Bai, L., Zhou, P., Li, D., & Ju, X. (2017). Changes in the gastrointestinal microbiota of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and its association with antibiotics in the short term. Journal of medical microbiology, 66(9), 1297–1307. [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M., Celano, G., Calabrese, F. M., Portincasa, P., Gobbetti, M., & De Angelis, M. (2020). The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms, 8(4), 573. [CrossRef]
- Milani, C., Duranti, S., Bottacini, F., Casey, E., Turroni, F., Mahony, J., Belzer, C., Delgado Palacio, S., Arboleya Montes, S., Mancabelli, L., Lugli, G. A., Rodriguez, J. M., Bode, L., de Vos, W., Gueimonde, M., Margolles, A., van Sinderen, D., & Ventura, M. (2017). The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR, 81(4), e00036-17. [CrossRef]
- Hakim, H., Dallas, R., Wolf, J., Tang, L., Schultz-Cherry, S., Darling, V., Johnson, C., Karlsson, E. A., Chang, T. C., Jeha, S., Pui, C. H., Sun, Y., Pounds, S., Hayden, R. T., Tuomanen, E., & Rosch, J. W. (2018). Gut Microbiome Composition Predicts Infection Risk During Chemotherapy in Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 67(4), 541–548. [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. L., Rajasuriar, R., Azanan, M. S., Abdullah, N. K., Tang, M. S., Lee, S. C., Woo, Y. L., Lim, Y. A., Ariffin, H., & Loke, P. (2017). Reduced microbial diversity in adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and microbial associations with increased immune activation. Microbiome, 5(1), 35. [CrossRef]
- Henrick, B. M., Chew, S., Casaburi, G., Brown, H. K., Frese, S. A., Zhou, Y., Underwood, M. A., & Smilowitz, J. T. (2019). Colonization by B. infantis EVC001 modulates enteric inflammation in exclusively breastfed infants. Pediatric research, 86(6), 749–757. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R., Wong, W. S. W., Saadon, R., Vilboux, T., Deeken, J., Niederhuber, J., Hourigan, S. K., & Yang, E. (2020). Gut microbial composition difference between pediatric ALL survivors and siblings. Pediatric hematology and oncology, 37(6), 475–488. [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M. M., Ness, K. K., Gurney, J. G., Mulrooney, D. A., Chemaitilly, W., Krull, K. R., Green, D. M., Armstrong, G. T., Nottage, K. A., Jones, K. E., Sklar, C. A., Srivastava, D. K., & Robison, L. L. (2013). Clinical ascertainment of health outcomes among adults treated for childhood cancer. JAMA, 309(22), 2371–2381. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G. T., Kawashima, T., Leisenring, W., Stratton, K., Stovall, M., Hudson, M. M., Sklar, C. A., Robison, L. L., & Oeffinger, K. C. (2014). Aging and risk of severe, disabling, life-threatening, and fatal events in the childhood cancer survivor study. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 32(12), 1218–1227. [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman A. (2018). Developmental Tuning of Epigenetic Clock. Frontiers in genetics, 9, 584. [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S., & Frenette, P. S. (2019). Haematopoietic stem cell activity and interactions with the niche. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 20(5), 303–320. [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R. (Ed.), 2016. Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) in Ageing and Age-Related Diseases: from Their Physiological and Pathological Implications toTranslation in Personalized Medicine [Special Issue]. Mechanisms Ageing Devolopment, pp. 1–80 159.
- Balistrieri, C.R., 2017a. Endothelial Progenitor Cells: A New Real Hope or Only an Unrealizable Dream? Springer International Publishing, Dordrecht, pp. 1–80.
- Balistreri, C.R., 2017b. The current obsession of age-related diseases and the race in identifying effective treatments and preventive interventions. J. Pathobiol. Physiol. 1, 2.
- Hillier, S. E., & Olander, E. K. (2017). Women’s dietary changes before and during pregnancy: A systematic review. Midwifery, 49, 19–31. [CrossRef]
- Biagi, C., Nunzio, M. D., Bordoni, A., Gori, D., & Lanari, M. (2019). Effect of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet during Pregnancy on Children’s Health: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 11(5), 997. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E. L., Vamos, C. A., & Daley, E. M. (2017). Physical activity during pregnancy and the role of theory in promoting positive behavior change: A systematic review. Journal of sport and health science, 6(2), 198–206. [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q. X., Venkatanarayanan, N., Loke, W., Yeo, W. S., Lim, D. Y., Chan, H. W., & Sim, W. S. (2019). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of yoga-based interventions for maternal depression during pregnancy. Complementary therapies in clinical practice, 34, 8–12. [CrossRef]
- Hill, B., Kothe, E. J., Currie, S., Danby, M., Lang, A. Y., Bailey, C., Moran, L. J., Teede, H., North, M., Bruce, L. J., & Skouteris, H. (2019). A systematic mapping review of the associations between pregnancy intentions and health-related lifestyle behaviours or psychological wellbeing. Preventive medicine reports, 14, 100869. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. W., Kuo, C. H., Kuo, F. C., Wang, Y. K., Hsu, W. H., Yu, F. J., Hu, H. M., Hsu, P. I., Wang, J. Y., & Wu, D. C. (2019). Fecal microbiota transplantation: Review and update. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan yi zhi, 118 Suppl 1, S23–S31. [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, M., Leclerc, M., Tinsley, C. R., & Petit, M. A. (2014). Bacteriophages: an underestimated role in human and animal health?. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 4, 39. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D. J., & Preston, T. (2016). Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut microbes, 7(3), 189–200. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Wang, W., & Zhang, F. (2023). The Next Generation Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: To Transplant Bacteria or Virome. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 10(35), e2301097. [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A., Ebadi, M., Rehman, T. U., Elhusseini, H., Kazadi, D., Halaweish, H., Khan, M. H., Hoeschen, A., Cao, Q., Luo, X., Kabage, A. J., Lopez, S., Holtan, S. G., Weisdorf, D. J., Khoruts, A., & Staley, C. (2023). Randomized Double-Blind Phase II Trial of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Versus Placebo in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and AML. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 41(34), 5306–5319. [CrossRef]
- Baumann K. (2018). Rejuvenating senolytics. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 19(9), 543. [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F., Prattichizzo, F., Grillari, J., & Balistreri, C. R. (2018). Cellular Senescence and Inflammaging in Age-Related Diseases. Mediators of inflammation, 2018, 9076485. [CrossRef]
- Gurău, F., Baldoni, S., Prattichizzo, F., Espinosa, E., Amenta, F., Procopio, A. D., Albertini, M. C., Bonafè, M., & Olivieri, F. (2018). Anti-senescence compounds: A potential nutraceutical approach to healthy aging. Ageing research reviews, 46, 14–31. [CrossRef]
- Xu, M., Pirtskhalava, T., Farr, J. N., Weigand, B. M., Palmer, A. K., Weivoda, M. M., Inman, C. L., Ogrodnik, M. B., Hachfeld, C. M., Fraser, D. G., Onken, J. L., Johnson, K. O., Verzosa, G. C., Langhi, L. G. P., Weigl, M., Giorgadze, N., LeBrasseur, N. K., Miller, J. D., Jurk, D., Singh, R. J., … Kirkland, J. L. (2018). Senolytics improve physical function and increase lifespan in old age. Nature medicine, 24(8), 1246–1256. [CrossRef]
- Abdul, Q. A., Yu, B. P., Chung, H. Y., Jung, H. A., & Choi, J. S. (2017). Epigenetic modifications of gene expression by lifestyle and environment. Archives of pharmacal research, 40(11), 1219–1237. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R. G., Twomey, L. C., Custaud, M. A., Turner, J. D., Moyna, N., Cummins, P. M., & Murphy, R. P. (2018). The role of epigenetics in cardiovascular health and ageing: A focus on physical activity and nutrition. Mechanisms of ageing and development, 174, 76–85. [CrossRef]
- Ferioli, M., Zauli, G., Maiorano, P., Milani, D., Mirandola, P., & Neri, L. M. (2019). Role of physical exercise in the regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging process. Journal of cellular physiology, 234(9), 14852–14864. [CrossRef]
- Pasyukova, E. G., & Vaiserman, A. M. (2017). HDAC inhibitors: A new promising drug class in anti-aging research. Mechanisms of ageing and development, 166, 6–15. [CrossRef]
- Fransquet, P. D., Wrigglesworth, J., Woods, R. L., Ernst, M. E., & Ryan, J. (2019). The epigenetic clock as a predictor of disease and mortality risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical epigenetics, 11(1), 62. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. H., Wang, H. T., & Kong, Q. P. (2019). Dynamic DNA Methylation During Aging: A “Prophet” of Age-Related Outcomes. Frontiers in genetics, 10, 107. [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, V. E., Goswami, A., & Salihu, H. M. (2017). Telomere length and fetal programming: A review of recent scientific advances. American journal of reproductive immunology (New York, N.Y. : 1989), 77(5), 10.1111/aji.12661. [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S., & Raj, K. (2018). DNA methylation-based biomarkers and the epigenetic clock theory of ageing. Nature reviews. Genetics, 19(6), 371–384. [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, M., Salei, N., & Krishnamoorthy, G. (2023). High salt diet does not impact the development of acute myeloid leukemia in mice. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 72(1), 265–273. [CrossRef]
- Karalexi, M. A., Dessypris, N., Thomopoulos, T. P., Ntouvelis, E., Kantzanou, M., Diamantaras, A. A., Moschovi, M., Baka, M., Hatzipantelis, E., Kourti, M., Polychronopoulou, S., Stiakaki, E., Mora, A. M., Wunsch-Filho, V., Infante-Rivard, C., Loutradis, D., & Petridou, E. T. (2017). Parental alcohol consumption and risk of leukemia in the offspring: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European journal of cancer prevention : the official journal of the European Cancer Prevention Organisation (ECP), 26(5), 433–441. [CrossRef]
- Fenech M. (2001). The role of folic acid and Vitamin B12 in genomic stability of human cells. Mutation research, 475(1-2), 57–67. [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M. L., Jensen, C. D., Block, G., Hudes, M. L., Chu, L. W., & Buffler, P. A. (2009). Maternal diet and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Public health reports (Washington, D.C. : 1974), 124(4), 503–514. [CrossRef]
- Palmer A. C. (2011). Nutritionally mediated programming of the developing immune system. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 2(5), 377–395. [CrossRef]
- Devine, S. M., & Larson, R. A. (1994). Acute leukemia in adults: recent developments in diagnosis and treatment. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 44(6), 326–352. [CrossRef]
- Bonaventure, A., Rudant, J., Goujon-Bellec, S., Orsi, L., Leverger, G., Baruchel, A., Bertrand, Y., Nelken, B., Pasquet, M., Michel, G., Sirvent, N., Bordigoni, P., Ducassou, S., Rialland, X., Zelenika, D., Hémon, D., & Clavel, J. (2013). Childhood acute leukemia, maternal beverage intake during pregnancy, and metabolic polymorphisms. Cancer causes & control : CCC, 24(4), 783–793. [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Lopez, J., Iguacel, I., Pisanu, S., Almeida, C. C. B., Steliarova-Foucher, E., Sierens, C., Gunter, M. J., Ladas, E. J., Barr, R. D., Van Herck, K., & Huybrechts, I. (2023). Role of Maternal Diet in the Risk of Childhood Acute Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(7), 5428. [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A., Ahmad, Q. M., Javed, T., Hayat, M. Z., Farooq, M. A., Anwar, H. M. Z., & Khan, M. A. (2020). Evaluation of diet as a risk factor in the development of childhood leukaemia: a case control study. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 70(3), 404–409. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. K., Chang, H. W., Yan, D., Lee, K. M., Ucmak, D., Wong, K., Abrouk, M., Farahnik, B., Nakamura, M., Zhu, T. H., Bhutani, T., & Liao, W. (2017). Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. Journal of translational medicine, 15(1), 73. [CrossRef]
- Aman, P., Pettersson, D., Zhang, J. X., Tidehag, P., & Hallmans, G. (1995). Starch and dietary fiber components are excreted and degraded to variable extents in ileostomy subjects consuming mixed diets with wheat- or oat-bran bread. The Journal of nutrition, 125(9), 2341–2347. [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F., Pellegrini, N., Vannini, L., Jeffery, I. B., La Storia, A., Laghi, L., Serrazanetti, D. I., Di Cagno, R., Ferrocino, I., Lazzi, C., Turroni, S., Cocolin, L., Brigidi, P., Neviani, E., Gobbetti, M., O’Toole, P. W., & Ercolini, D. (2016). High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut, 65(11), 1812–1821. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mantrana, I., Selma-Royo, M., Alcantara, C., & Collado, M. C. (2018). Shifts on Gut Microbiota Associated to Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Specific Dietary Intakes on General Adult Population. Frontiers in microbiology, 9, 890. [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R., Shively, C. A., Appt, S. A., Register, T. C., Michalson, K. T., Vitolins, M. Z., & Yadav, H. (2018). Gut Microbiome Composition in Non-human Primates Consuming a Western or Mediterranean Diet. Frontiers in nutrition, 5, 28. [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F., Ley, R. E., Sonnenburg, J. L., Peterson, D. A., & Gordon, J. I. (2005). Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science (New York, N.Y.), 307(5717), 1915–1920. [CrossRef]
- Cotillard, A., Kennedy, S. P., Kong, L. C., Prifti, E., Pons, N., Le Chatelier, E., Almeida, M., Quinquis, B., Levenez, F., Galleron, N., Gougis, S., Rizkalla, S., Batto, J. M., Renault, P., ANR MicroObes consortium, Doré, J., Zucker, J. D., Clément, K., & Ehrlich, S. D. (2013). Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature, 500(7464), 585–588. [CrossRef]
- Romond, M. B., Ais, A., Guillemot, F., Bounouader, R., Cortot, A., & Romond, C. (1998). Cell-free whey from milk fermented with Bifidobacterium breve C50 used to modify the colonic microflora of healthy subjects. Journal of dairy science, 81(5), 1229–1235. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C. H., Park, J., & Kim, M. (2014). Gut microbiota-derived short-chain Fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune network, 14(6), 277–288. [CrossRef]
- Russell, W. R., Gratz, S. W., Duncan, S. H., Holtrop, G., Ince, J., Scobbie, L., Duncan, G., Johnstone, A. M., Lobley, G. E., Wallace, R. J., Duthie, G. G., & Flint, H. J. (2011). High-protein, reduced-carbohydrate weight-loss diets promote metabolite profiles likely to be detrimental to colonic health. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 93(5), 1062–1072. [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C., Cavalieri, D., Di Paola, M., Ramazzotti, M., Poullet, J. B., Massart, S., Collini, S., Pieraccini, G., & Lionetti, P. (2010). Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(33), 14691–14696. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T. S., Rampelli, S., Jeffery, I. B., Santoro, A., Neto, M., Capri, M., Giampieri, E., Jennings, A., Candela, M., Turroni, S., Zoetendal, E. G., Hermes, G. D. A., Elodie, C., Meunier, N., Brugere, C. M., Pujos-Guillot, E., Berendsen, A. M., De Groot, L. C. P. G. M., Feskins, E. J. M., Kaluza, J., … O’Toole, P. W. (2020). Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: the NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut, 69(7), 1218–1228. [CrossRef]
- Keim, N. L., & Martin, R. J. (2014). Dietary whole grain–microbiota interactions: insights into mechanisms for human health. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 5(5), 556–557. [CrossRef]
- West, N. P., Christophersen, C. T., Pyne, D. B., Cripps, A. W., Conlon, M. A., Topping, D. L., Kang, S., McSweeney, C. S., Fricker, P. A., Aguirre, D., & Clarke, J. M. (2013). Butyrylated starch increases colonic butyrate concentration but has limited effects on immunity in healthy physically active individuals. Exercise immunology review, 19, 102–119.
- Schley, P. D., & Field, C. J. (2002). The immune-enhancing effects of dietary fibres and prebiotics. The British journal of nutrition, 87 Suppl 2, S221–S230. [CrossRef]
- Ponzo, V., Fedele, D., Goitre, I., Leone, F., Lezo, A., Monzeglio, C., Finocchiaro, C., Ghigo, E., & Bo, S. (2019). Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM). Nutrients, 11(2), 330. [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, M. K., Garcia-So, J., Justice, N., Myers, J., Tyagi, S., Nemchek, M., McMurdie, P. J., Kolterman, O., & Eid, J. (2021). Butyrate-producing human gut symbiont, Clostridium butyricum, and its role in health and disease. Gut microbes, 13(1), 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Geng, H. W., Yin, F. Y., Zhang, Z. F., Gong, X., & Yang, Y. (2021). Butyrate Suppresses Glucose Metabolism of Colorectal Cancer Cells via GPR109a-AKT Signaling Pathway and Enhances Chemotherapy. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, 8, 634874. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




