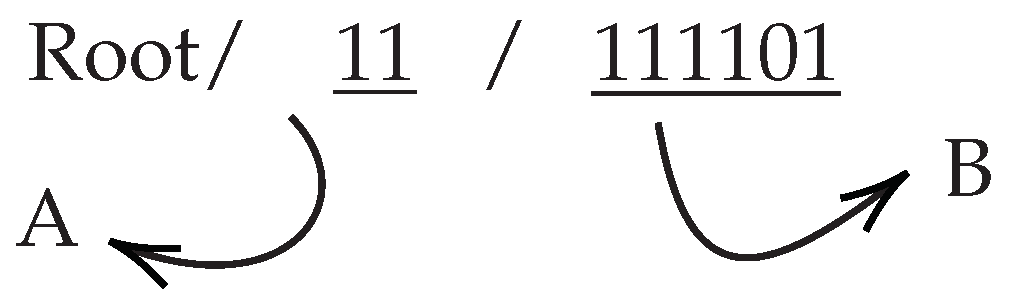1. Introduction
With the advancement of Internet-based services and sensors, such as the widespread adoption of GPS-based sensors, location-based services, improvements in computational data processing, and satellite imagery, a large amount of novel spatial information is produced daily [
1]. The widespread availability of tools to collect and share spatial data enables individuals and small communities to produce their own digital spatial content (e.g., Open Street Maps contributions have tripled between 2012 to 2017 [
2]). This enormous production of spatial data requires scalable data management systems [
3]. The data infrastructure technology supporting spatial data management and processing has changed from standalone relational database systems to spatial data warehouses that support a variety of data formats and analytical workloads [
4] and from centralized infrastructures to decentralized and Peer-to-peer (P2P) systems. New data structures have been proposed such as (e.g., HDF [
5], Data-Cubes [
6], Geoparquet [
7] ) and spatial data management and analytic frameworks (e.g., Apache iceberg [
8], Digital Earth [
9]) have emerged to manage and perform analysis on large-scale, high temporal and spatial resolutions.
Geospatial architectures are another area of technological change developed to handle spatial data management challenges. They have changed from clusters to cloud architectures and more parallel and distributed processing platforms (e.g., Spark [
10], Hadoop [
11]). Peer-to-peer (P2P) systems have been established in several application areas. In the past decade, P2P systems have been used widely in web3 [
12], blockchains [
13] and crypto-currencies [
14]. The combination of P2P file-sharing systems with blockchains provides scalability, security, immutability, and append-only attributes for sharing information amongst nodes on a network [
15]. These attributes make P2P networks suitable for content distribution and service discovery applications (see [
16,
17,
18,
19]). However, the main limitation of existing systems is they can only locate data on the network based on a key value using DHT [
20]. While DHTs have been used as a main building block for P2P applications, they are seriously deficient in one regard: they only directly support exact match queries [
21,
22,
23,
24]. The multi-dimensionality of spatio-temporal data is one of the big challenges in retrieving and querying these data in P2P networks. When querying spatio-temporal data, the ability to perform range queries is required, and it is not currently supported. The rapid increase in spatio-temporal data collection needs a new auxiliary indexing structure. These indexing structures are responsible for tracking the behaviour of moving objects through space [
25,
26]. These indexing methods allow P2P architectures to find and retrieve contents based on the user’s filters and address more complex data sharing needs, facilitating data management, query processing, and delivering data to the end-user.
While much work has been done towards expediting search in file-sharing P2P systems, issues concerning spatial indexing in P2P systems are significantly more complicated due to cases such as overlaps between spatial objects, avoidance of data scattering and the complexity of spatial queries [
27]. One-dimensional data mainly have been queried using DHTs in P2P networks [
28,
29,
30]. DHTs are not yet designed for complex spatial queries (e.g., range query, k-nearest neighbor query), and only support the location of data items based on a key value (i.e., equality lookups) [
20,
31]. For multi-dimensional data, there have been multiple approaches, including partitioning data into one-dimensional indexes using space-filling curves or kd-tree-based methods and indexing them using DHT methods (e.g. [
32,
33,
34]). These methods usually work best with static data, and dynamic content relocation (locality) is dependent on the accuracy of space-filling curves [
34].
The second approach is to use multiple DHT in the network (e.g. [
35,
36,
37] ). These methods need a higher level of network and node structure manipulation and are not commonly used in large-scale projects due to interoperability limitations of such approaches [
38]. A third approach is to construct traditional indexes that have been used in centralized environments and distribute these indexes on the P2P network (e.g., [
20,
21,
39,
40]). This approach can be done by constructing a tree and splitting it into parts and maintaining parts of semi-independent trees at each peer. Prefix Hash Tree (PHT) [
21] and similarly, P-Tree [
20] uses the same approach by storing a fraction of the overall tree on each peer. In PHT each node of the tree is labeled with a prefix which is defined recursively. Given a node with the label
l, its left and right children are labeled as
and
respectively. This pattern constructs a tree structure and enables range queries on a dataset [
21].
In this work, we propose a spatio-temporal indexing data structure that works in the data layer and uses a distributed InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) network. Our method is closer to the approach of Ranabhadran et. al. [
21] and does not require additional DHT to perform multi-dimensional range queries. The rest of this paper is divided into two main sections. First, we introduce the Distributed Spatio-Temporal Tree (DSTree) as a data structure to perform range spatio-temporal queries on a dataset and we check its features and performance by comparing it to other existing trees. Second, we will look at the integration of DSTree with distributed networks and propose a system architecture to perform queries on the IPFS using DSTree.
2. Spatio-Temporal Data Indexing Methods
P2P multidimensional query processing refers to the execution of advanced query operators over multidimensional data stored in a distributed system [
41]. The retrieved data from a query should be exact and complete. Exactness means the query result should not be approximate. The retrieved data should exactly belong to the query results set. This means that if we run a query on the same dataset on a centralized system the results should be exactly the same as when we run a query on the distributed system. A basic element of geospatial technology can be defined as three main components including location in space and time, and attribute of that location in space-time [
42]. In this work, our focus is to retrieve a geographic object based on space or time queries.
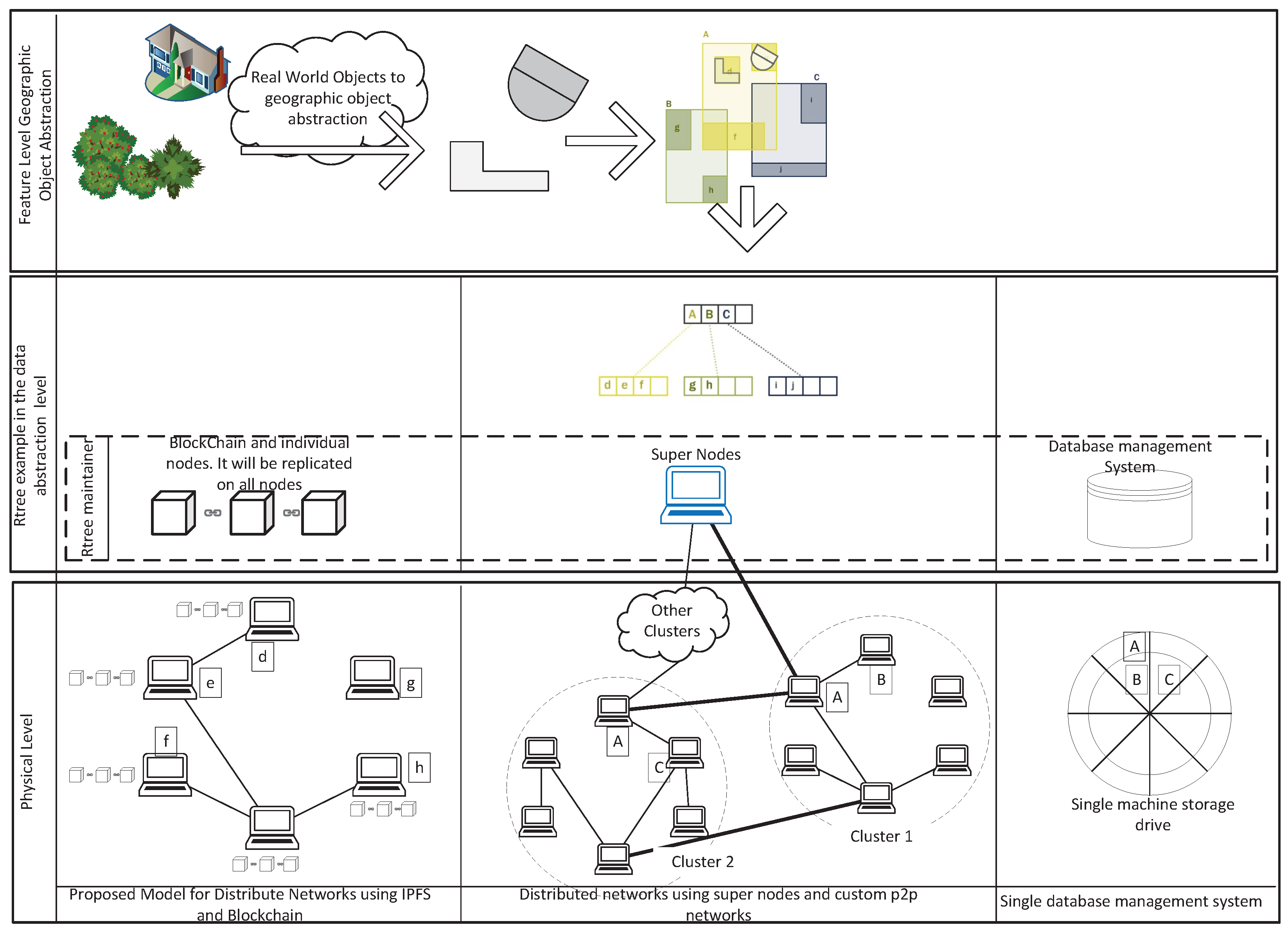
The spatio-temporal indexing methods in central systems are mainly performed at an abstract level (
Figure 1). They are used to improve query performance on the datasets. These indexes usually work as a separate layer on top of the data layer itself. Queries are usually performed against the indexes and then the actual reference to the geographic features are then retrieved from the index (See
Figure 1 right). In contrast, our method stores data on the nodes on the network using spatial indexing methods in both abstract and physical storage layers. For example, the purpose of indexing can also be to distribute data that are closer in space, on the nodes that are closer in the network (e.g. [
20], (See
Figure 1 middle)). Through the last couple of decades, many spatio-temporal access methods have been developed. There have been several approaches for spatio-temporal indexing so far (see [
25,
26,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48]). Handling temporal data in GIS ranges from time-stamping GIS layers (e.g. [
49] ) to more object-oriented approaches such as time-stamping events and processes (e.g. [
50] )[
44]. Another category of spatio-temporal models is trajectory-based access models which track the changes in the geographic object typologies over time (see [
47]). In central systems indexing models such as OCT-tree [
51] are sometimes used to process spatio-temporal queries (see [
47,
52,
53]). In using OctTrees for indexing spatial data each geographic object is considered as a cuboid. The spatial dimension of the data is considered as two dimensions of each cuboid. The third dimension of a cuboid is considered a time interval. There have been some newer approaches to the query process of spatio-temporal data using blockchains. For example, [
54] used a block-DAG-based index traversal algorithm, to handle spatio-temporal queries on a block-DAG. However, the main issue with the blockchain-based spatial-temporal indexes is the limited data storage capability on the blockchains [
55].
A decentralized spatial indexing technique must be scalable enough to be able to handle hundreds of thousands of peers and also dynamic enough to deal with peers joining/leaving the system anytime. Another feature of such structures is their ability to preserve the locality and the directionality of multidimensional information. Locality implies that neighboring multidimensional information is stored in neighboring nodes, while directionality implies that the index structure preserves orientation. The notions of locality and directionality are very important. If an index structure preserves these properties, then searching in the index corresponds to searching in the multidimensional space, which can highly improve query evaluation cost[
27]. R-tree-based indexes can efficiently answer various types of multidimensional queries, especially range queries [
57]. In addition, a spatio-temporal indexing method is required to support two types of topological relations. The first set of topological relations includes temporal typologies which are based on Allen’s temporal algebra covered in [
58,
59]. These relations include 7 typologies which are briefly explained in
Table 1. A time interval for Geographic Information (GI) can be defined as the duration in which a GI feature exists with a fixed state. This interval can be as small as a few milliseconds that it takes to collect a GI feature or can be a considerably longer time period such as geological land classifications or land cover. Defining time intervals and how a GI can be attached to a newer time interval depends on the context of the study. The second type of topological relations which needs to be addressed by a spatio-temporal indexing model is spatial topology.
Each indexing method is optimized for specific types of queries. Our proposed method is more suitable for the storage, query processing, and retrieval of log-based data. These data are produced over the time that different events happen. An example of such data is data that are being collected from a sensor over time or a VGI tool to share images from different locations by users or even open data which are being shared by different government departments such as crime data that are being shared by the police. Each of these datasets can have different access levels, and geoprivacy levels and are being collected over time.
3. DSTree: A Spatio-Temporal Index
A unit of geographic information (GI) in our model is defined as a spatio-temporal object which can be represented as the form of
where
is the identification of the object.
GI is spatial location
l, including longitude and latitude
along
x and
y dimensions in the interval
. Each
also has a set of attributes,
p, associated with it, and a Minimum Boundary Rectangular (MBR),
, in which is constructed based on its location,
l.
DSTree is a two-level tree structure. The approach of DSTree is closer to the work done by [
60,
61,
62]. They constructed a multilevel tree structure to improve the query process of trajectory data. In [
60]’s method they have formed a global space-time subdivision scheme. [
61] combined two trees, an R*-Tree, and a kd-Tree, to improve the query process in the centralized machines. Tao [
62] also used a series of temporal quad-Trees to handle interval queries in centralized systems. In a DSTree an Interval-Tree [
63,
64] is used as the top part of the tree, and a quad-Tree [
65] is used at the bottom part of the tree. The interval tree is responsible for temporal queries and the quad-Tree is responsible for performing the spatial part of the queries. We define a time-interval as a pair of real numbers
where
.
can be represented as
. The different variants of the interval-trees are capable of supporting open and half-open intervals. Interval trees are optimized for querying of the intervals which overlap with a given interval, but, can also be used for point queries. Having the ability to query overlapping intervals allows us to query based on the temporal topology in
Table 1. During each time-interval we assume that GI state does not change.
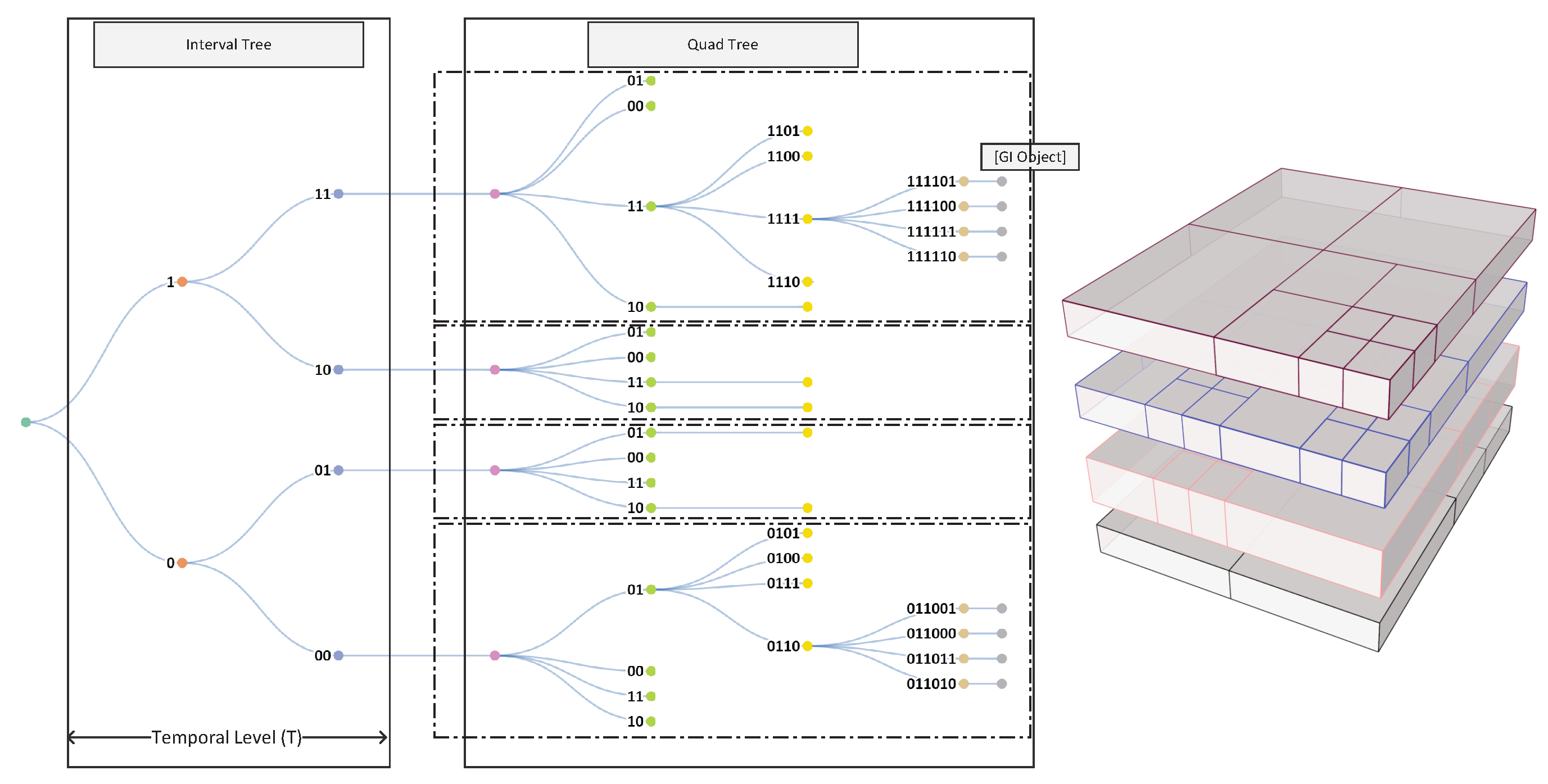
3.1. DSTree index
When constructing a DSTree it is possible to partition data into spatio-temporal chunks and assign a unique id to each portion of the data. The proposed DSTree indexes are composed of two parts (See
Figure 2). The first component (A) is called interval-tree index and the second component (B) is called the quad index. The interval-tree is a binary tree so each node can have only two children. By assigning 1 to the right child and 0 to the left child a series of IDs will be constructed. The length of digits in the interval-tree portion of the index equals
Temporal level (T). The second section of the DSTree index is a quad index. Each node in a quadtree consists of 4 children. Each child can be assigned an index from 00, 01, 10, and 11 and it can construct the quad index.
Figure 3 shows the DSTree index corresponding quad-tree indexes. More details about the parts adhere to the specification in
Figure 2.
The top part of the DSTree is a regular Interval-tree. However, the depth of this tree is controlled by a parameter called
Temporal level (T).
T is responsible for balancing between the top-level tree and the bottom-level tree. Once the top interval-tree is constructed the GI in the leaves (Each leaf includes
n GI) is used to construct a quad-tree. As a result, we will have one quad-tree at each leaf of the interval-tree at the level of
T. Regular quad-trees always have an extent equal to the minimum boundary box of the GI inserted into the tree. However, in a DSTree, all of the quad-trees should have the same extent, e.g., equal to
in geographic coordinates. Having the same spatial extent bottom part of DSTree allows us to query data across all of the interval-tree leaves.
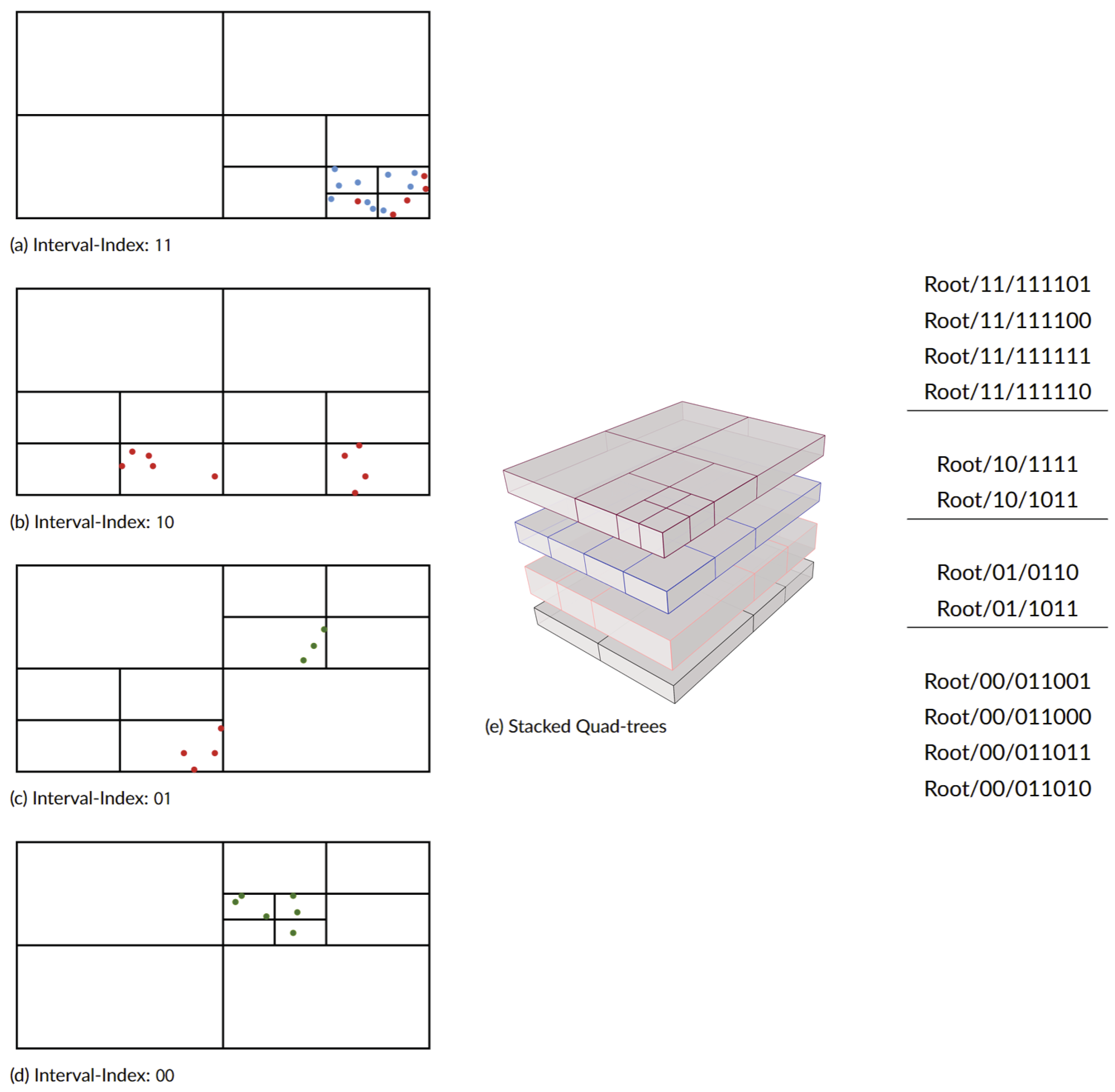
Figure 3 shows an example of constructed DStree.
Figure 4 shows the points which are used to construct that tree and their relative location and time-interval.
Figure 2 details an index entry.
Insert
In order to insert
into a DSTree, a two-step process is required. First, we need to find the proper node on the interval-tree part of the DSTree that
can to be added. Afterward, we will add the
to the proper quad-tree leaf using
. To do so we first get the low value of the interval at the root of DSTree. If the root’s low value is smaller than
’s low endpoint, then the new interval goes to the left sub-tree, otherwise, the new node goes to the right sub-tree. We continue the same process until the sub-tree level is equal to the
Temporal level (T) parameter of the DSTree. Once the node is selected if there is already a quad-tree in the node (node is spatial) we insert the
to the quad-tree using its
parameter. If the node is empty we generate a new quad-tree and proceed with adding it. Adding
to the quad-tree is similar to the regular quad-tree insert (e.g see [
65]). Once all the steps are done we update the max value of the ancestors of interval-tree portion if needed.
Delete
Deleting items from DSTree is a relatively complex process due to the complexities of removing intervals from a regular interval-tree. After deleting an
from the DSTree, if the node containing that
contains no more objects, that node may be deleted from the tree. This involves promoting a node further from the leaf to the position of the node being deleted which results in the reconstruction of the top part of the DSTree (For details about deleting items from interval-trees see [
64] pages 348-357).
Query
A spatio-temporal range search is a query of geographic objects that intersect with a boundary box,
, in two-dimensional space and also is in a temporal topological relation,
, with a time interval,
[
66]. There can be three main variations of queries a DSTree which include queries with both temporal interval and spatial extents, queries with only temporal interval, and queries with only spatial extent. Here we only cover the first variation. The approach to those two variations is similar and explained in more detail in
Figure 7. In order to perform a spatio-temporal range on a DSTree it is required to first query the interval-tree portion of the DSTree. If
I is in
relation with the root’s interval, we add the root’s interval to the candidate nodes list. If the left child of the root is not empty and the max value of the sub-tree in the left child is greater than
I’s low value, recur for the left child otherwise recur for the right child. Once the candidate nodes are selected, if the selected nodes have a quad-tree as their sub-tree, we perform a quad-tree search for
S, otherwise, we only check for the intersection of the selected node with the boundary box,
S.
DSTree construction from bulk data
Since DSTree is a two-level tree the performance of the insert, delete and construction of the tree depends on both the top level and bottom level of the trees. Construction of the DSTree from scratch for bulk data is a relatively straightforward process. First of all, an interval-tree is constructed based on the existing data. Once data are inserted into the hierarchical node structure, the algorithm traverses down from the root of the interval-tree until the tree level equals the Temporal level (T). Once the appropriate level is detected in the interval-tree all of the items under sub-trees (left and right branched) of the selected node are collected into one single node and a quad-tree is constructed in that node.
3.2. Performance metrics
The behaviour of the proposed tree structure is measured using a number of experiments with real data. These experiments are intended to reflect the conditions of the common tasks involved in spatial and temporal queries of the data. Results of multiple models compared to the method proposed. In the first set of the experiments data on the occurrence of crime from the Waterloo Regional Police Service
1 are used. This data details all the police-reported occurrences for the calendar year. The time frame of this data is from 2017 to 2022. The data includes occurrence data and time, response time, and geographic coordinates of the occurrence. In this experiment, only the location of each event and the response time of each event is used. In order to have a comparison between DSTree and the other existing models, we have used three other methods to process spatio-temporal queries. In choosing each method, the availability of source code to perform the tests were considered. OCT-tree is one of the methods which is used in the experiments similar to the work done by [
47,
52,
53] in which the third dimension of cuboid data is considered as the time-interval (source code available at [
67]). The second access method used is a regular quad-tree (source code available at [
68]). In this method, only a spatial query is performed and then to get the exact result set, all the results from the spatial query are tested to filtered based on the temporal parameters. The third method is an Interval-tree (source code available at [
69]). In this method, in contrast to the quad-tree method only a temporal query is performed, and once the results are extracted from the tree structure the spatial filter is applied to them to get the exact results. The above experiment is applied to the batches of
and
points. Each test was executed 5 times then repeated 10 times and the average time of the execution was measured. The spatio-temporal query was constant over the entire experiment.
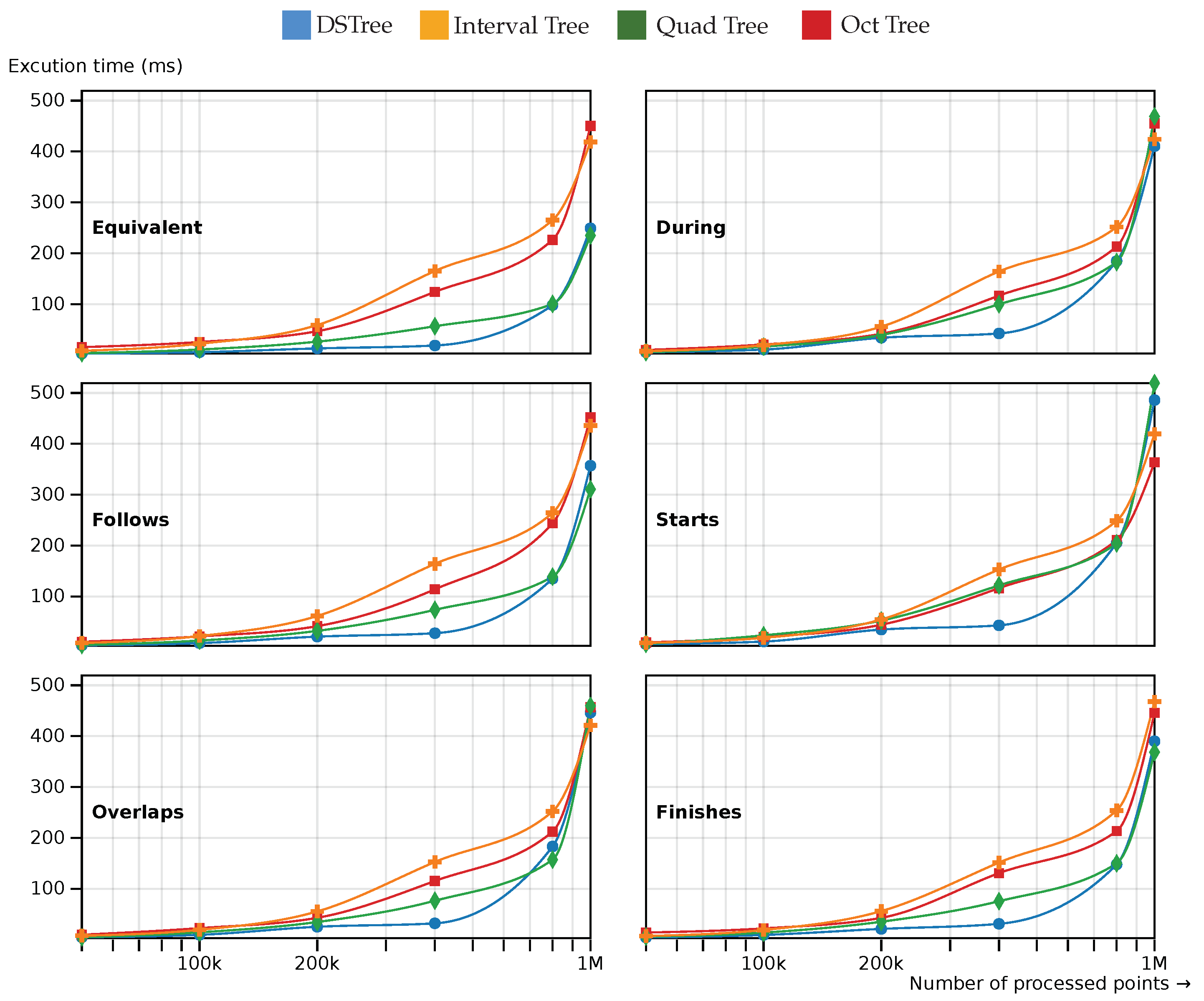
Figure 5 show the results of this comparison. The main query for these different models is defined as follows:
Find the events where their location has an topology relation with an extent equal to
and their response time has a topological relation T with a temporal extent of
where are the spatial extent of the entire dataset and are temporal extent of the data and T is the temporal topology from Table 1
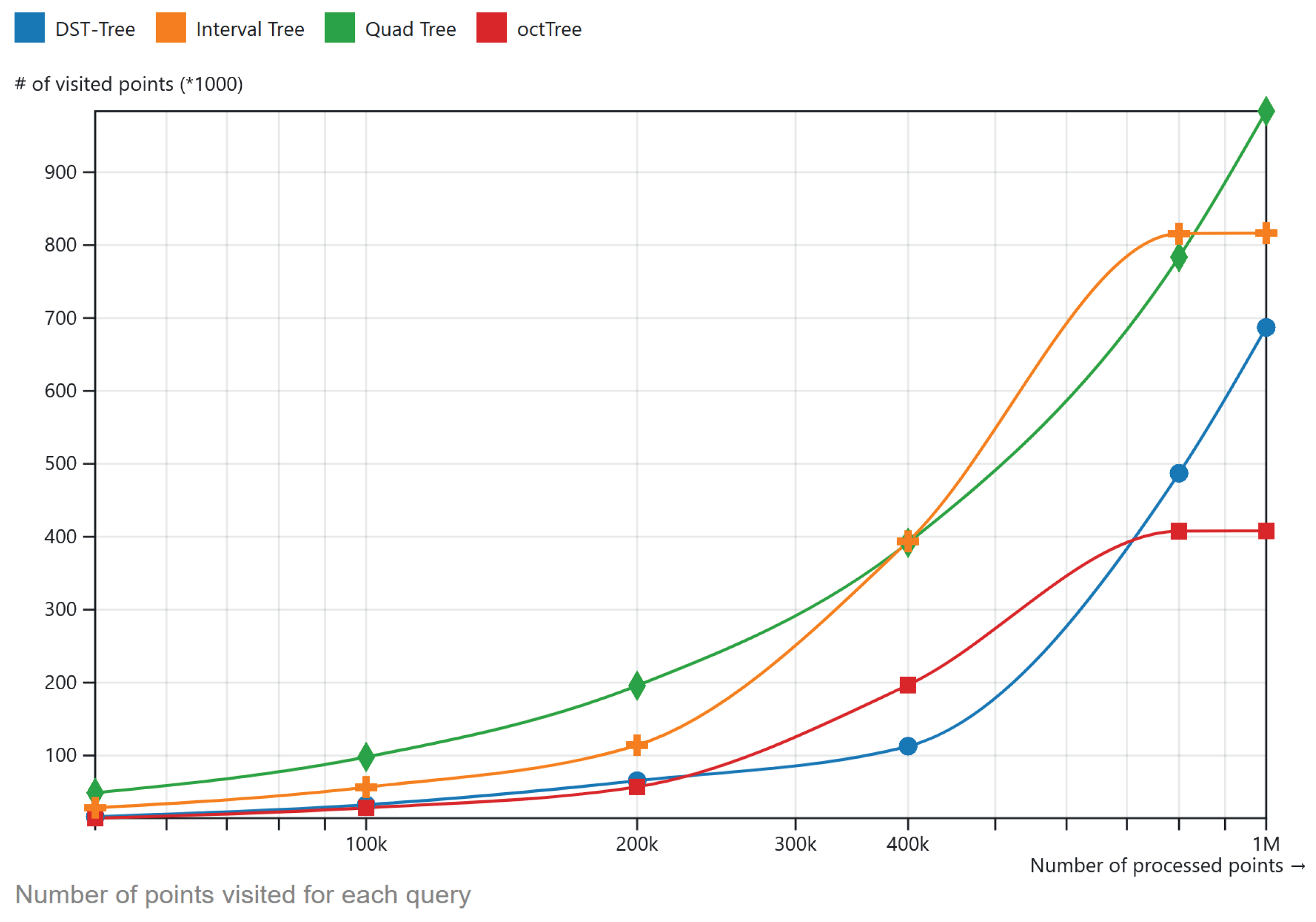
The second experiment is with the number of visited points in order to answer a constant spatio-temporal query. In the experiment only objects that the index traverses and are checked to answer each query are counted.
Figure 6 shows the results of this experiment.
Figure 6.
Number of the visited points in each model to answer a spatio-temporal query.
Figure 6.
Number of the visited points in each model to answer a spatio-temporal query.
Figure 7.
Three main scenarios to process queries using DSTree. Top: When a user requests only a spatial range in which we search all the quad-trees in the DSTree. Middle: When the user queries spatial and temporal ranges together, DSTree first queries interval-tree part of the graph and then searches quad-trees that exist at the bottom of those candidate nodes. Bottom: Cases user only provides a temporal range. As a result, we only search Interval-tree part of the DSTree and then simply query the root of the Quad-tree in each candidate node.
Figure 7.
Three main scenarios to process queries using DSTree. Top: When a user requests only a spatial range in which we search all the quad-trees in the DSTree. Middle: When the user queries spatial and temporal ranges together, DSTree first queries interval-tree part of the graph and then searches quad-trees that exist at the bottom of those candidate nodes. Bottom: Cases user only provides a temporal range. As a result, we only search Interval-tree part of the DSTree and then simply query the root of the Quad-tree in each candidate node.
As
Figure 5 shows DSTree shows a good performance for query processing in medium-sized datasets compared to other types of indexing methods. The metrics of the DSTree in all of the 6 temporal topologies are close to the Quadtree method. Oct tree and Interval tree also show close performance metrics. In
Figure 6 the number of the points which are visited during the queries is shown. In this figure, DStree has fewer visited points compared to QuadTree. The reason why they have close metrics is that the Quadtree is less computationally heavy compared to DSTree.
4. IPFS
The first generation of P2P systems, namely file-sharing applications such as BitTorrent, support only keyword lookups and mostly provide no load balancing. The second generation is mainly structured P2P systems supporting basic key-based routing [
31]. The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and a P2P network for storing and sharing data in a distributed file system. IPFS uses content-addressing to uniquely identify each file in a global namespace connecting all computing devices [
70]. Each file on the IPFS network has a unique hash address which is used as a reference to request it from the network. Any user in the network can serve a file by its content address, and other peers in the network can find and request that content from any node that has it using a distributed hash table (DHT)[
71].
At its core, IPFS is built on top of a data structure called The InterPlanetary Linked Data (IPLD) [
70]. The IPLD model is a set of specifications in support of decentralized data structures for the content-addressable web. Content IDs (CID) are hashes generated to allow the user to interact with IPFS in a trustless manner and recover their data. IPLD deals with decoding these hashes so that users can access their data. When new content is added to the IPFS network, that content is separated into several chunks and stored in different blocks. To reconstruct the whole file, a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) connects each bit of content together. In a DAG, we can only move from parent nodes to child nodes as each edge is oriented. Hierarchical data in particular is very naturally represented via DAGs.
IPLD creates a series of links to data internally but also allows users to create those links themselves through simple data structures that can be stored on IPFS. This capability allows us to store a DAG graph (in our case a DSTree) on IPFS. This capability allows users to request a portion of the data from the network without the need to download the entire dataset. For example, a user is able to store a graph shown in
Figure 3 as an IPLD object as shown in
Table 2. IPLD’s capability to store and retrieve DAG graphs allows us to store spatio-temporal data as a graph structure and as a result, we can request them based on the query parameters. DSTree only keeps a CID reference to the actual feature in each tree leaf. So depending on the query parameters we only need to retrieve a portion of the GI or specific subtree of the DSTree. For example, a DSTree leaf can be addressed as
where
DSTreeCID is the CID of the root of the DStree,
Interval-treeindex is the interval-tree portion and
quad-treeindex is the second portion of the DSTree index. Under each leaf, there will be a series of GI objects. Each GI can be stored separately on IPFS and its own CID,
GICID, can be used as a reference to the object itself. So to access a single feature we can use an IPFS Address similar to
DSTreeCID/Interval-treeindex/quad-treeindex/GICID. Note that
GICID is generated based on the content of the GI by IPFS and to have access to it we need to query it from DSTree.
5. Distributed Network Integration
In order to process queries on distributed networks (in our case IPFS) it is required to store data in a DAG format. We use DSTree to construct a DAG graph and once the tree structure is constructed an IPLD graph is formed from the DSTree graph. Then the IPLD object is stored on the IPFS network and a CID of the uploaded contents is used as a root gateway to access the entire tree structure. DSTree in this system acts as the main index structure to perform and answer spatio-temporal queries. Since DSTree is an indexing structure it does not store the actual GI. It only stores the CID of each individual GI as a reference to the object itself. This provides a lightweight graph that can be used by each client.
Data Management
As mentioned earlier the DSTree only stores a CID reference to the actual GI. The GI can be in any format (e.g., geojson, topojson, or other feature-level standards). In constructing the DSTree each GI first is uploaded on the IPFS as a regular file or IPLD object. Then for each GI, we will then have a set of . This Object is then inserted into a DSTree and the related DAG graph is then constructed. Once all the GI objects are added to the DSTree the graph structure is converted to an IPLD object and is uploaded on the IPFS and the pair of will be shared between users.
5.1. Architecture and Implementation
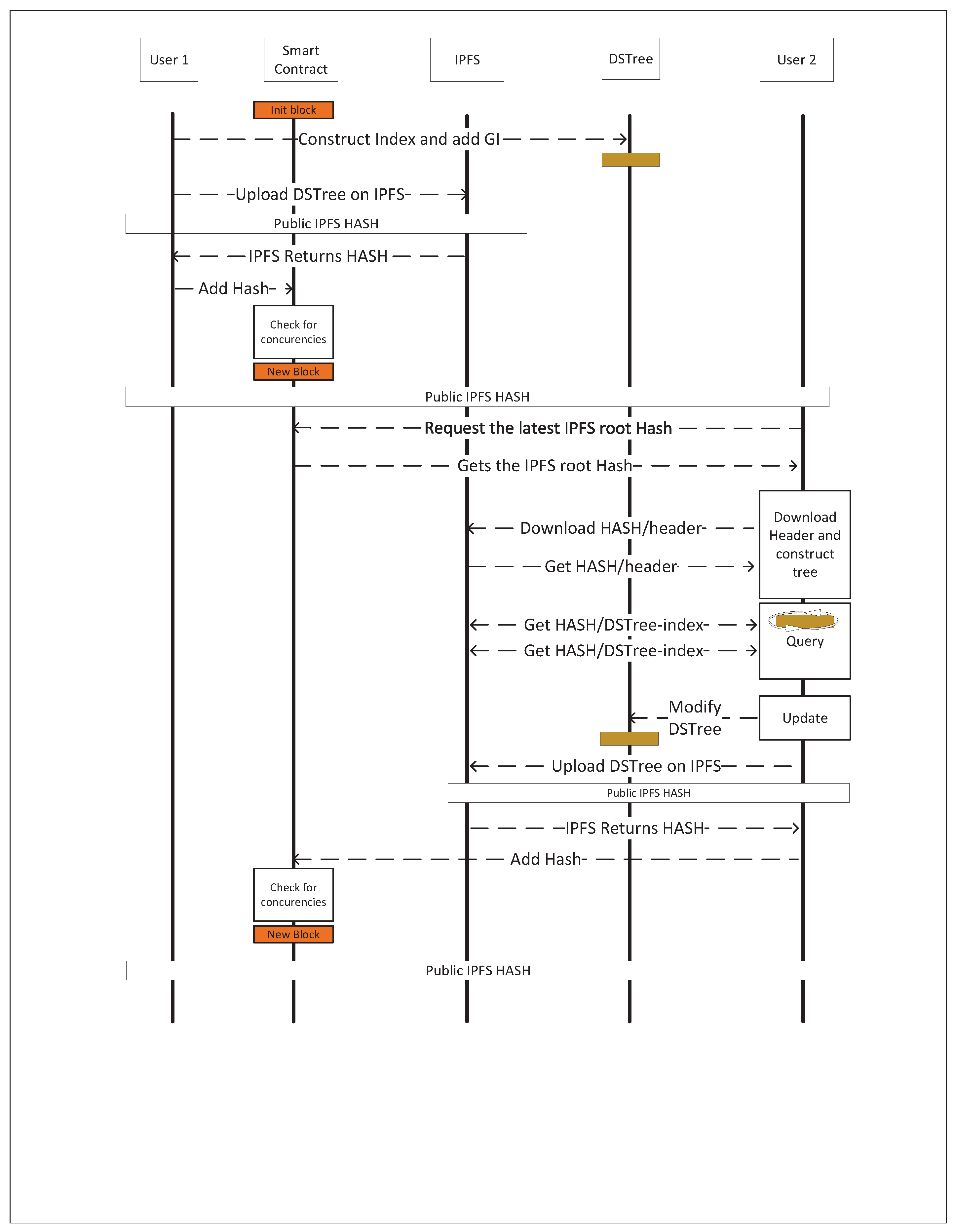
The proposed method to process queries on IPFS networks consists of four main components.
Figure 8 shows the flow of the communication between users on a distributed network in order to query, retrieve and store GI. The start of the data sharing process on IPFS is with a user,
, willing to share a GI,
, on the network. Once the user uploads the GI content on IPFS they use its CID, MBR, and time-interval associated to it,
, to construct a DSTree. In this step, the user is able to keep adding as many GI objects as they want to the DSTree. Once the construction of the DSTree is finished, the necessary metadata is also added to the data structure and an IPLD object,
, is constructed from DStree’s DAG graph. The
then is uploaded on the IPFS network and the related IPFS root hash,
, and its metadata,
, is retrieved from IPFS. Since the
is generated by IPFS based on the content of the DAG graph, we need to share this CID with other users to be able to access the index. In order to share the IPFS hash with other users a smart contract is used. This smart contract is responsible to keep a history of
hashes over time and provide the latest
hash to the users at any time. In our example, a simple smart contract using Solidity is developed and deployed on the Ethereum test network. This smart contract is used in a web application in order to provide access to the latest version of
hash and its metadata when a user visits the web application. Once the
hash is added to the smart contract it will be available to all the users who connect to this smart contract.
If a new user,
, accesses the smart contract then they will be able to fetch metadata and the IPLD DAG graph structure related to the DSTree. Then they will be able to replicate a version of DSTree on their own local environment and as a result, they are able to query data from that Index. The result of the query, an array of
s, then are requested from the IPFS through the query process explained in
Figure 7.
If the , wants to add a new GI, , to the dataset, they first add it to the DSTree and then construct a new IPLD graph and upload the data on IPFS. Since the content of the new DSTree is different from the previous one, a new IPFS hash is generated and the is returned to the user. In the next step , connects to the smart contract and adds as a new block to the underlying blockchain. At this point all the users will be able to access the updated data, , throughout the blockchain. The older version of the DSTree, , will also remain on the block history of the blockchain and will be accessible too.
Figure 8.
Query process and publishing spatio-temporal data on the IPFS. It shows the process of sharing the DSTree index between users using a blockchain, querying the content from the network by another user, and updating the data on the network
Figure 8.
Query process and publishing spatio-temporal data on the IPFS. It shows the process of sharing the DSTree index between users using a blockchain, querying the content from the network by another user, and updating the data on the network
6. Discussion
Unlike centralized systems, data storage in P2P networks is distributed across network nodes, providing scalability and no single point of failure. However, managing and processing queries on these networks has always been challenging. The proposed method to share and query spatio-temporal data on distributed networks tackles this issue by tracking and updating a spatio-temporal index between network users. In this approach, a blockchain is responsible for keeping a history of different versions of a DSTree index. Each user can replicate a version of DSTree on their node and run spatio-temporal queries on the index. Since each user performs the queries on their side, the indexing tree should check fewer items and support more topology out of the box. As shown in
Figure 6, the number of visited items in the DSTree is generally less than other indexing structures, providing less memory consumption on the client apps. While octree also visits fewer nodes/items during its query process, its tree construction is slower (
) compared to the other tree indexes. Also, it takes more time to answer the queries (see
Figure 5) since the internal intersection functions are 3-dimensional. They can also grow quickly if the time intervals are large [
47]. In a single Interval tree or quadtree approach, the results of the queries need to be checked for the spatial or temporal topologies accordingly during the post-processing stage. In addition, the DSTree can handle six main temporal topological relations (see
Table 1) during the query process without the need to post-process data. Time-wise, the DSTree also performs well on the small to average datasets (see
Figure 5). Update, insertion, and deletion of existing data is another requirement for the current data-sharing environments. Due to using an interval-tree as the top part of the tree, DSTree is not optimized for deleting the items. Inserting a new GI will only update a portion of the tree structure and not impact the entire DAG data graph. However, adding data with large intervals so that the GI temporal interval covers branches from the left to the right side of the interval-tree can cause a restructuring of the entire tree. For example, for time-series data such as sensor data or VGI, the DSTree performs better. In our police department example, the newly reported incidents can be added on top of the DStree, and it does not cause the restructuring of the entire tree.
Conflicts may appear during the update process of the DSTree and publishing the latest version of DSTree by users. To resolve such conflicts, there are several approaches. The conflict resolution between different versions of DSTree can be done either on the client side before pushing the latest version on the blockchain or on the smart contract before saving
. Both of these methods require a mechanism to detect and address conflicts. Because of the size limitations on the smart contracts, we are using a client-side conflict detection approach. In this approach, the DSTree graph is extracted from the latest version available on the blockchain and is compared with the version of the graph on the client side [
76]. Suppose the conflicts in the DSTree graph are detected (using tools like [
77]), the user will need to resolve the conflict and then publish it on the blockchain. However, this approach needs a trustful user interaction with the network.
The reason for using quad-trees is that since the root boundary box of all the quad-trees is constant, the quad index part of the DSTree index will always point to the same area in the geographic space over different time intervals. This provides a faster access method and the capability to exchange the quad-tree with a Discrete Global Grid System (DGGS). DGGS grid, similar to quad-tree, provides the same index value per each grid cell in the space. It also provides methods to aggregate data on multi-resolution levels [
78,
79,
80] and also provides built-in data locality and directionality of space [
81]. For instance, in sharing police department information over time, the reports can be censored using distributed k-anonymity methods on the P2P networks (e.g., [
82]) if the DGGS system is used as feature data storage.
Data locality in the IPFS with DSTree
Data locality is defined as
locality implies that neighboring multidimensional information is stored in neighboring nodes [31]. In an IPFS network, once each node downloads some particular content, it can be a data provider. Combining data partitioning using DSTree and sharing data on IPFS at the GI level allows users to request only a small portion of the entire dataset. As a result, they can also serve small chunks of a large dataset. This can provide a data locality in the P2P network based on the user activities in the VGI platforms. In our police data sharing example, once the dispatch teams share their location on the network, they have already become a data provider for that shared GI. Once the police officers visit that location, once again, they download that GI, and they will become another data provider for that specific GI on the IPFS network. This approach provides a level of data locality for the nodes close to each other since the nodes in a region usually tend to explore data related to their region. Other examples of use cases of such data locality include sharing geo-tagged information in small communities.
DSTree Limitations
The proposed DSTree model only supports the spatial topologies that the underlying spatial indexing method supports. In this paper, we only experimented with the intersection topology relation. However, it is possible to perform other topological relations such as overlay, within, and crosses and also perform KNN-based models. All of the temporal typologies are supported except disjoint. The focus of this paper was support for vector-based data structures. However, supporting raster data could be achieved by converting raster data into DGGS-based models or tiling the raster data instead of generating lower-level spatial index using the multi-resolution tiling structure.
Table 4 summarizes supported queries and future approaches to support other data models.
7. Conclusions
P2P has become very popular for storing and sharing information in a decentralized approach. The amount of daily spatial data being collected and shared in different sectors with different levels highlights the need for P2P data management, query, and processing. This paper proposes a new spatio-temporal multi-level tree structure, DSTree, which aims to address this problem. DSTree is capable of performing a range of spatio-temporal queries. To integrate this data structure on the IPFS distributed network, a framework that uses blockchain to share the IPFS CID of the index is proposed. Each user is capable of replicating DSTree and querying or updating it. However, this model is not optimized for deletion and is mainly suitable for append-only data over time. In this work, some of the challenges in sharing and querying spatio-temporal data on distributed networks are addressed. Despite the advantages of our proposed framework, challenges remain. We conclude that more significant research effort from GIScience and related fields in developing decentralized applications is needed. The need for the standardization of different feature types and feature Type Properties when sharing data on the IPFS network is one of the requirements. The possibility of using IPLD objects in sharing GI at the feature level can provide finer access to the information. In addition, it is necessary to address attribute-level query processing, which is not covered in the current work. The use of the smart contract to control access of the users to read and write data to the main chain can also be studied. This access control can even be at the feature level.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Majid Hojati. and Steven Roberts; methodology, Majid Hojati and Colin Robertson; software, Majid Hojati.; writing—original draft preparation, Majid Hojati.; writing—review and editing, Steven Roberts.; supervision, Steven Roberts and Colin Robertson.;
Funding
This research was funded by Global Water Future grant.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Global Water Futures research program for funding this work under the Developing Big Data and Decision Support Systems theme.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IPFS |
Interplanetary File System |
| DSTree |
Distributed Spatio-temporal Tree |
| DHT |
Distributed Hash Tree |
| P2P |
Peer-to-Peer |
| KNN |
K-nearest neighbour |
| DGGS |
Discrete global grid system |
| DAG |
Directed acyclic graph |
| IPLD |
InterPlanetary Linked Data |
| CID |
Content ID |
| GI |
Geographic information |
References
- Goodchild, M.F.; Fu, P.; Rich, P. Sharing Geographic Information: An Assessment of the Geospatial One-Stop. Annals of the Association of American Geographers 2007, 97, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J. OpenStreetMap Contributor LifeSpans - Revisiting and expanding on 2018 research paper. 2021.
- Doulkeridis, C.; Vlachou, A.; Nørvåg, K.; Kotidis, Y.; Vazirgiannis, M. Efficient search based on content similarity over self-organizing P2P networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications 2010, 3, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yadumi, S.; Xion, T.E.; Wei, S.G.W.; Boursier, P. Review on integrating geospatial big datasets and open research issues. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 10604–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, T.H. Hierarchical Data Format (HDF). 2023. Available online: https://www.hdfgroup.org/.
- Mahecha, M.D.; Gans, F.; Brandt, G.; Christiansen, R.; Cornell, S.E.; Fomferra, N.; Kraemer, G.; Peters, J.; Bodesheim, P.; Camps-Valls, G.; others. Earth system data cubes unravel global multivariate dynamics. Earth System Dynamics 2020, 11, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- github.com/opengeospatial. Geoparquet, 2022.
- iceberg, A. Apache iceberg, 2022.
- Goodchild, M.F. The future of digital earth. Ann. GIS 2012, 18, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Sarwat, M. Geospark: A cluster computing framework for processing large-scale spatial data. In Proceedings of the 23rd SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems; 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Eldawy, A.; Mokbel, M.F. Spatialhadoop: A mapreduce framework for spatial data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 31st international conference on Data Engineering; 2015; pp. 1352–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Bambacht, J.; Pouwelse, J. Web3: A Decentralized Societal Infrastructure for Identity, Trust, Money, and Data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.00398. [Google Scholar]
- Nofer, M.; Gomber, P.; Hinz, O.; Schiereck, D. Blockchain. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2017, 59, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decentralized Business Review 2008, 21260. [Google Scholar]
- Hojati, M.; Feick, R.; Roberts, S.; Farmer, C.; Robertson, C. Distributed spatial data sharing: a new model for data ownership and access control. Journal of Spatial Information Science under review. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djellabi, B.; Amad, M.; Baadache, A. Handfan: A flexible peer-to-peer service discovery system for internet of things applications. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Khan, A.I.; Kendall, E.A. Distributed network file storage for a serverless (P2P) network. The 11th IEEE International Conference on Networks, 2003. ICON2003. IEEE, 2004.
- Ehiagwina, F.O.; Iromini, N.A.; Olatinwo, I.S.; Raheem, K.; Mustapha, K. A State-of-the-Art Survey of Peer-to-Peer Networks: Research Directions, Applications and Challenges. management 2022, 14, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achir, M.; Abdelli, A.; Mokdad, L.; Benothman, J. Service discovery and selection in IoT: A survey and a taxonomy. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2022, 200, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainiceanu, A.; Linga, P.; Gehrke, J.; Shanmugasundaram, J. Querying Peer-to-Peer Networks Using P-Trees. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on the Web and Databases: Colocated with ACM SIGMOD/PODS 2004; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabhadran, S.; Ratnasamy, S.; Hellerstein, J.M. Prefix Hash Tree An Indexing Data Structure over Distributed Hash Tables. PODC 2004 conference, 2004.
- Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Y.; Taheri-Boshrooyeh, S.; Özkasap, Ö. DHT-based Edge and Fog Computing Systems: Infrastructures and Applications. Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS) 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Harren, M.; Hellerstein, J.M.; Huebsch, R.; Loo, B.T.; Shenker, S.; Stoica, I. Complex queries in DHT-based peer-to-peer networks. In Peer-to-Peer Systems; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002; pp. 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Triantafillou, P.; Pitoura, T. Towards a unifying framework for complex query processing over structured peer-to-peer data networks. In Databases, Information Systems, and Peer-to-Peer Computing; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2004; pp. 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Q. Building a spatiotemporal index for earth observation big data. International journal of applied earth observation and geoinformation 2018, 73, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokbel, M.F.; Ghanem, T.M.; Aref, W.G. Spatio-temporal access methods. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2003, 26, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, A.; Lifu, Y.; Kitsuregawa, M. P2PR-tree: An R-tree-based spatial index for peer-to-peer environments. In Current Trends in Database Technology - EDBT 2004 Workshops; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2004; pp. 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, G.M. A Computer Oriented Geodetic Data Base and a New Technique in File Sequencing. International Business Machines 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Stocia, I. Chord: A scalable peer-to-peer lookup service for internet applications. Proc. of ACM SIGCOMM, 2001, 2001.
- Sahin, O.D.; Antony, S.; Agrawal, D.; Abbadi, A.E. Probe: Multi-dimensional range queries in p2p networks. International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering. Springer, 2005, pp. 332–346.
- Liang, S.; others. A new peer-to-peer-based interoperable spatial sensor web architecture. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2008, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Wang, R.Y. Skipindex: Towards a scalable peer-to-peer index service for high dimensional data; Department of Computer Science, Princeton University: New Jersey, USA, 2004; pp. 703–704. [Google Scholar]
- Maymounkov, P.; Mazières, D. Kademlia: A Peer-to-Peer Information System Based on the XOR Metric. Peer-to-Peer Systems; Druschel, P.; Kaashoek, F.; Rowstron, A., Eds. Springer, 2002, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 53–65. [CrossRef]
- Kantere, V.; Skiadopoulos, S.; Sellis, T. Storing and indexing spatial data in P2P systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xu, Z.; Dwarkadas, S. Peer-to-peer information retrieval using self-organizing semantic overlay networks. Proceedings of the 2003 conference on Applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications, 2003, pp. 175–186. [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, M.; Ferhatosmanoglu, H. Peer-to-peer spatial queries in sensor networks. Proceedings Third International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing (P2P2003). IEEE, 2003, pp. 32–39. [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhou, S.; Qian, W.; Xu, L.; Tan, K.L.; Zhou, A. C2: a new overlay network based on can and chord. International Journal of High Performance Computing and Networking 2005, 3, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, A.; Lai, C. Range-capable Distributed Hash Tables. Gir, 2006.
- Jagadish, H.; Ooi, B.C.; Vu, Q.H.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, A. VBI-Tree: A Peer-to-Peer Framework for Supporting Multi-Dimensional Indexing Schemes. 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE’06), 2006, pp. 34–34. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Yang, B.; Garcia-Molina, H. One torus to rule them all: multi-dimensional queries in p2p systems. Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on the Web and Databases: colocated with ACM SIGMOD/PODS 2004, 2004, pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachou, A.; Doulkeridis, C.; Nørvåg, K.; Kotidis, Y. Peer-to-peer query processing over Multidimensional Data.
- Dangermond, J.; Goodchild, M.F. Building geospatial infrastructure. Geo-spatial Information Science 2019, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbert, S.; Pebesma, E. A temporal GIS for field based environmental modeling. Environmental Modelling & Software 2014, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M. Temporal GIS and spatio-temporal modeling. Proceedings of Third International Conference Workshop on Integrating GIS and Environment Modeling, Santa Fe, NM, 1996, Vol. 33.
- Pelekis, N.; Theodoulidis, B.; Kopanakis, I.; Theodoridis, Y. Literature review of spatio-temporal database models. The Knowledge Engineering Review 2004, 19, 235–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, Y.; Vazirgiannis, M.; Sellis, T. Spatio-temporal indexing for large multimedia applications. Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems. IEEE, 1996. [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.R.; Punni, S.; Aref, W.G. Spatio-temporal access methods: a survey (2010 - 2017). Geoinformatica 2019, 23, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Tian, Y. Decomposition Tree: A Spatio-Temporal Indexing Method for Movement Big Data. Cluster Computing 2015, 18, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.P. Temporality in spatial databases. GIS/LIS 88 Proceedings: Accessing the world 1988, pp. 880–889.
- Peuquet, D.J.; Duan, N. An event-based spatiotemporal data model (ESTDM) for temporal analysis of geographical data. International Journal of Geographical Information Systems 1995, 9, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackins, C.L.; Tanimoto, S.L. Oct-trees and their use in representing three-dimensional objects. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1980, 14, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Long, J.; Lin, S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W. A hybrid index model for efficient spatio-temporal search in HBase. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Lecture notes in computer science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, L.; Cong, G. Topic Exploration in Spatio-Temporal Document Collections. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Management of Data; Acm: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.; Nurgaliev, I.; Muzammal, M.; Jensen, C.S.; Fan, J. On spatio-temporal blockchain query processing. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 98, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xie, S.; Dai, H.N.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. Blockchain challenges and opportunities: A survey. International Journal of Web and Grid Services 2018, 14, 352–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PostGIS. PostGIS clustering data, 2022.
- Liu, B.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, D.L. Supporting complex multi-dimensional queries in P2P systems. 25th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS’05). IEEE, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.F. Maintaining knowledge about temporal intervals. In Readings in Qualitative Reasoning About Physical Systems; Elsevier, 1990; pp. 361–372.
- Gabbay, D.; Kurucz, A.; Wolter, F.; Zakharyaschev, M. Applied modal logic. In Many-Dimensional Modal Logics - Theory and Applications; Studies in logic and the foundations of mathematics, Elsevier, 2003; pp. 41–109.
- Qian, C.; Yi, C.; Cheng, C.; Pu, G.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H. Geosot-based spatiotemporal index of massive trajectory data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2019, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yoon, S.; Lee, Y. A Hybrid Approach Combining R⁎-Tree and k-d Trees to Improve Linked Open Data Query Performance. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Papadias, D. MV3R-Tree: A Spatio-Temporal Access Method for Timestamp and Interval Queries. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- de Berg, M.; Cheong, O.; van Kreveld, M.; Overmars, M. Computational geometry, 3 ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cormen, T.H.; Leiserson, C.E.; Rivest, R.L.; Stein, C. Introduction to Algorithms, Third Edition; The MIT Press, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Finkel, R.A.; Bentley, J.L. Quad trees a data structure for retrieval on composite keys. Acta Inform. 1974, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwig, M.; Schneider, M. Developments in spatio-temporal query languages. Proceedings. Tenth International Workshop on Database and Expert Systems Applications. DEXA 99. IEEE, 1999, pp. 441–449. [CrossRef]
- github.com/vasturiano. d3-octree, 2022.
- github.com/CorentinTh. quadtree-js, 2022.
- github.com/alexbol99. flatten-interval-tree, 2022.
- Benet, J. IPFS - Content Addressed, Versioned, P2P File System 2014. arXiv 2014, arXiv:cs.NI/1407.3561. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, R.; Ku, W.S.; Wang, H. Spatial data query support in peer-to-peer systems. Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, 2004. COMPSAC 2004., 2004, Vol. 2, pp. 82–85 vol.2. [CrossRef]
- Coulondre, S.; Libourel, T.; Spéry, L. Metadata And GIS: A Classification of Metadata for GIS. 1998.
- Brodeur.; Coetzee.; Danko.; Garcia.; Hjelmager. Geographic information metadata—an outlook from the international standardization perspective. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2019, 8, 280. [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J. Metadata for geo-spatial data sharing: A comparative analysis. Ann. Reg. Sci. 1999, 33, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossomaier, T.; Hope, B.A. Online GIS and Spatial Metadata, Second Edition, 2 ed.; CRC Press: London, England, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kleppmann, M.; Beresford, A.R. A Conflict-Free Replicated JSON Datatype. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2017, 28, 2733–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- github.com/automerge. automerge, 2022.
- Li, M.; Stefanakis, E. Geospatial operations of discrete global grid systems—a comparison with traditional GIS. J. geovisualization spat. anal. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.; Chaudhuri, C.; Hojati, M.; Roberts, S.A. An integrated environmental analytics system (IDEAS) based on a DGGS. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, M.; Robertson, C.; Roberts, S.; Chaudhuri, C. GIScience research challenges for realizing discrete global grid systems as a Digital Earth. Big earth data 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahr, K. Central place indexing: Hierarchical linear indexing systems for mixed-aperture hexagonal discrete global grid systems. Cartographica: The International Journal for Geographic Information and Geovisualization 2019, 54, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, M.; Farmer, C.; Feick, R.; Robertson, C. Decentralized geoprivacy: leveraging social trust on the distributed web. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2021, 35, 2540–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).