Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Design and Enrollment Criteria
Outcome Variables
Data Collection
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Demographic and Clinical Features of the Participants
Therapies Administered at Baseline
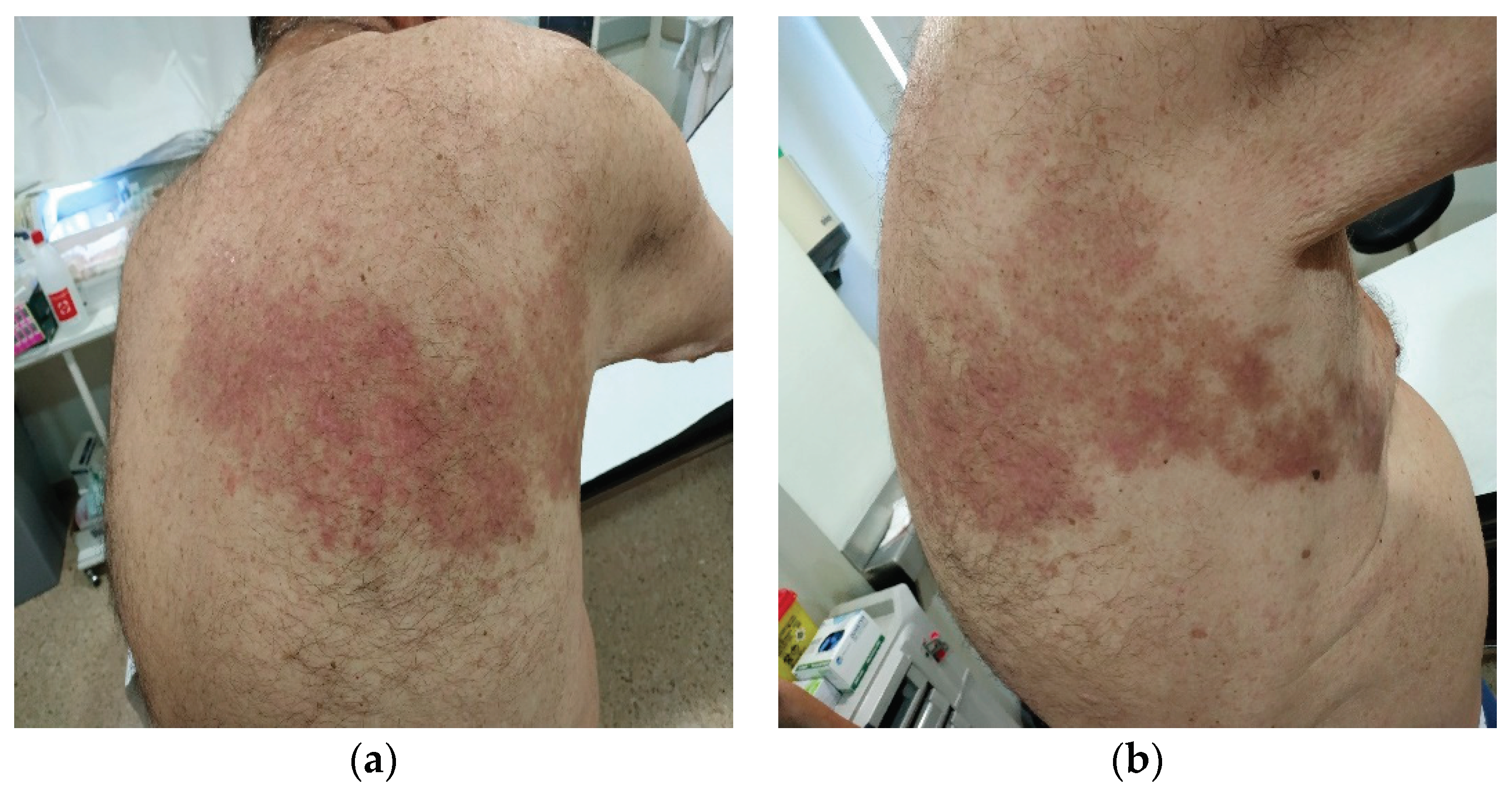
Herpes Zoster Infection Characteristic
RA Treatment in HZ Infection
Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
- -
- Lucía C. Domínguez-Casas has received research supports and participation in company-sponsored speaker’s bureau from Abbvie, Janssen, Lilly and Celgene.
- -
- S.Castañeda has received research supports from MSD and Pfizer and had consultation fees/participation in company-sponsored speaker’s bureau from BMS, Eli-Lilly, MSD, Roche and UCB.
- -
- R. Blanco received grants/research supports from Abbvie, MSD and Roche, and had consultation fees/participation in company sponsored speaker´s bureau from Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen and MSD.
- -
- Iván Ferraz-Amaro and Carmen Lasa-Teja have not conflicts of interest for this study
References
- Winthrop, K.L.; Tanaka, Y.; Lee, E.B.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Al Enizi, A.; Azevedo, V.F.; Curtis, J.R. Prevention and management of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis: a clinical review. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison L Smitten 1, Hyon K Choi, Marc C Hochberg, SamySuissa, Teresa A Simon, Marcia A Testa et al,; The risk of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the United States and the united kingdom. Arthritis& Rheumatism. 2007; Dec 15;57(8):1431–1438.
- Chen, S.-Y.; Suaya, J.A.; Li, Q.; Galindo, C.M.; Misurski, D.; Burstin, S.; Levin, M.J. Incidence of herpes zoster in patients with altered immune function. Infection 2013, 42, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winthrop, K.L.; Furst, D.E. Rheumatoid arthritis and herpes zoster: risk and prevention in those treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cho, S.; Lee, J.; Bae, S.; Sung, Y. Increased risk of opportunistic infection in early rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, V.; Rondaan, C.; Heijstek, M.; van Assen, S.; Bijl, M.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Breedveld, F.C.; D'Amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; et al. Incidence and prevalence of vaccine preventable infections in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIIRD): a systemic literature review informing the 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with AIIRD. RMD Open 2019, 5, e001041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchinat, S.; Cebrián-Cuenca, A.M.; Bricout, H.; Johnson, R.W. Similar herpes zoster incidence across Europe: results from a systematic literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 170–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerbrei, A. , Diagnosis, antiviral therapy, and prophylaxis of varicella-zoster virus infections. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2016 May;35(5):723-34.
- Amrita John, David H. Canaday, Herpes zoster in the older adult, Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 2017 Dec; 31(4): 811–826.
- Schmader, K. , Herpes zoster. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2018 Aug 7;169(3):ITC19-ITC31.
- Arvin, A.M. Humoral and Cellular Immunity to Varicella-Zoster Virus: An Overview. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, S58–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChristienRondaan, Aalzen de Haan, Gerda Horst, J. Cordelia Hempel, Coretta van Leer, Nicolaas A. Boset al., Altered cellular and humoral immunity to varicella-zoster virus in patients with autoimmune diseases, Arthritis& Rheumatology. 2014 Nov;66(11): 3122–3128.
- Lang, P.-O.; Aspinall, R. Vaccination for quality of life: herpes–zoster vaccines. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 33, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, R.R.; Peleg, R. Herpes zoster – typical and atypical presentations. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 129, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragya A., Nair; Bhupendra, C. Patel, Herpes Zoster,In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. 2022. Sep 5.
- Yamaguchi, R.; Tanaka, E.; Nakajima, A.; Inoue, E.; Abe, M.; Sugano, E.; Sugitani, N.; Saka, K.; Ochiai, M.; Higuchi, Y.; et al. Risk of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the biologics era from 2011 to 2015 and its association with methotrexate, biologics, and corticosteroids. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.A.; Hooper, M.M.; Kremer, J.M.; Reed, G.; Shan, Y.; Wenkert, D.; Greenberg, J.D.; Curtis, J.R. Herpes Zoster Reactivation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analysis of Disease Characteristics and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, T.R.; George, M.D. Risk for infections with glucocorticoids and DMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Boumpas, D.; Boki, K.; Vassilopoulos, D. Study of the natural course and specific immunity after herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving biologic DMARDs. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuke Kawai, Barbara P. Yawn,Risk Factors for Herpes Zoster: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings2017 Dec;92(12):1806-1821.
- Lecrenier, N.; Beukelaers, P.; Colindres, R.; Curran, D.; De Kesel, C.; De Saegher, J.-P.; Didierlaurent, A.M.; Ledent, E.Y.; Mols, J.F.; Mrkvan, T.; et al. Development of adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine and its implications for shingles prevention. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2018, 17, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theresa Mallick-Searle, Brett Snodgrass, Jeannine M Brant,Postherpetic neuralgia: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and pain management pharmacology. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare. 2016;9:447–454.
- Hata, A.; Kuniyoshi, M.; Ohkusa, Y. Risk of Herpes zoster in patients with underlying diseases: a retrospective hospital-based cohort study. Infection 2011, 39, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, W. Johnson, Marie-José Alvarez-Pasquin, Marc Bijl, Elisabetta Franco, Jacques Gaillat, João G. Clara et al., Herpes zoster epidemiology, management, and disease and economic burden in Europe: : a multidisciplinary perspective Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines2015 Jul; 3(4): 109–120.
- Calabrese, L.H.; Xie, F.; Yun, H.; Winthrop, K.L.; Baddley, J.W.; Calabrese, C.; Curtis, J.R. Herpes Zoster and the Risk of Stroke in Patients With Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 69, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, J.; Novosad, S.A.; Winthrop, K.L. Infection Risk and Safety of Corticosteroid Use. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2016, 42, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.R.; Zeringue, A.L.; Caplan, L.; Ranganathan, P.; Xian, H.; Burroughs, T.E.; Fraser, V.J.; Cunningham, F.; Eisen, S.A. Herpes Zoster Risk Factors in a National Cohort of Veterans with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangfeld, A.; Listing, J.; Herzer, P.; Liebhaber, A.; Rockwitz, K.; Richter, C.; Zink, A. Risk of Herpes Zoster in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated With Anti–TNF-α Agents. JAMA 2009, 301, 737–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, A.; Desai, R.J.; Solomon, D.H.; Ortiz, A.J.S.; Gale, S.; Bao, M.; Sarsour, K.; Schneeweiss, S.; Kim, S.C. Risk of serious infections in tocilizumab versus other biologic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multidatabase cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.; Xie, F.; Delzell, E.; Chen, L.; Levitan, E.B.; Lewis, J.D.; Saag, K.G.; Beukelman, T.; Winthrop, K.; Baddley, J.W.; et al. Risks of Herpes Zoster in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis According to Biologic Disease-Modifying Therapy. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 67, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.T.; Ducancelle, A.; Masson, C.; Lunel-Fabiani, F. Herpes zoster: Risk and prevention during immunomodulating therapy. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavia Sunzini, Iain McInnes, Stefan Siebert, Patient-reported outcomes from a randomised phase III study of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to biological agents (RA-BEACON). Annalsof Rheumatic Diseases. 2017 Apr;76(4):694-700.
- Roy Fleischmann, Eduardo Mysler, Stephen Hall, Alan J Kivitz, Robert J Moots, Zhen Luo et al., Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib monotherapy, tofacitinib with methotrexate, and adalimumab with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (ORAL Strategy): a Phase IIIb/IV, double-blind, head-to-head, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017 Jul 29;390 (10093): 457-468.
- Burmester, G.R.; Kremer, J.M.; Bosch, F.V.D.; Kivitz, A.; Bessette, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; A Othman, A.; Pangan, A.L.; Camp, H.S. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (SELECT-NEXT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Fleischmann, Aileen L. Pangan, In-Ho Song, Eduardo Mysler, Louis Bessette, Charles Peterfyet al., Upadacitinib versus placebo or adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: results of a phase 3, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2019 Nov;71(11):1788-1800.
- Chen, Y.-J.; Huang, W.-N.; Chen, H.-H.; Liao, T.-L.; Chen, J.-P.; Hsieh, T.-Y.M.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, D.-Y. Herpes Zoster in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, a single center experience from Taiwan. Medicine 2020, 99, e22504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechman, K.; Subesinghe, S.; Norton, S.; Atzeni, F.; Galli, M.; Cope, A.P.; Winthrop, K.L.; Galloway, J.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of infection risk with small molecule JAK inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, N.L.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Wieland, A.; A Vora, K.; Pulendran, B.; Ahmed, R. Understanding the immunology of the Zostavax shingles vaccine. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Shah, R.; Limmer, A.L.; E Nwannunu, C.; Patel, R.R.; Mui, U.N.; Tyring, S.K. Shingrix for Herpes Zoster: A Review. 2019, 24, 5–7.
- Furer, V.; Rondaan, C.; Heijstek, M.W.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Van Assen, S.; Bijl, M.; Breedveld, F.C.; D’Amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; et al. 2019 update of EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| RA patients (N=392) |
RA patients with HZ (N=30) |
RA patients without HZ (N=362) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean±SD) | 59±13 | 61±13 | 59±13 | 0.36 |
| Time of evolution of RA, (months)(mean±SD) | 136.9±109.8 | 158±118 | 135.3±109.2 | 0.33 |
| Women, n (%) | 309 (79) | 25 (83) | 284 (78) | 0.53 |
| Smokers, n (%) | 155 (40) | 11 (37) | 144 (40) | 0.74 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 165 (42) | 18 (60) | 147 (41) | 0.039 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 55 (14) | 6 (20) | 49 (14) | 0.33 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 148 (38) | 14 (47) | 134 (37) | 0.30 |
| Positive rheumatoid factor, n (%) | 223 (57) | 17 (57) | 206 (57) | 0.98 |
| Positive anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies, n (%) | 206 (53) | 13 (43) | 193 (53) | 0.29 |
| Erosive disease, n (%) | 145 (37) | 10 (33) | 135 (37) | 0.67 |
| Subcutaneous nodules, n (%) | 23 (6) | 1 (3) | 22 (6) | 0.57 |
| Interstitial lung disease, n (%) | 20 (5) | 3 (10) | 17 (5) | 0.21 |
| Sjögren´s syndrome, n (%) | 20 (5) | 1 (3) | 19 (5) | 0.65 |
| Vasculitis, n (%) | 23 (6) | 2 (7) | 21 (6) | 0.85 |
| Baseline use of therapies | ||||
| Prednisone | ||||
| N (%) | 228 (58) | 16 (55) | 212 (59) | 0.72 |
| Dose, mg/day | 5 (0-5) | 5 (0-5) | 3.75 (0-7.5) | 0.92 |
| Conventional synthetic DMARDs | ||||
| Methotrexate | 252 (64) | 20 (67) | 232 (64) | 0.78 |
| Leflunomide | 38 (10) | 2 (7) | 36 (10) | 0.56 |
| Sulfasalazine | 12 (3) | 1 (3) | 11 (3) | 0.61 |
| Azathioprine | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) | 0.99 |
| Biological DMARDs | ||||
| Any anti-TNFα | 92 (23) | 9 (30) | 83 (23) | 0.38 |
| Adalimumab | 35 (10) | 3 (10) | 32 (9) | 0.74 |
| Etanercept | 40 (10) | 5 (17) | 35 (10) | 0.23 |
| Infliximab | 7 (2) | 0 (0) | 7 (2) | 0.99 |
| Golimumab | 43 (11) | 4 (13) | 39 (11) | 0.56 |
| CertolizumabPegol | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) | 0.99 |
| Tocilizumab | 16 (4) | 1 (3) | 15 (4) | 0.99 |
| Rituximab | 11 (3) | 2 (7) | 9 (2) | 0.20 |
| Abatacept | 4 (1) | 0 (0) | 4 (1) | 0.99 |
| Cumulative treatment for RA | ||||
| Conventional DMARDs (not concomitant), n (%) | ||||
| Methotrexate | 351 (90) | 325 (90) | 26 (87) | 0.81 |
| Leflunomide | 126 (32) | 114 (31) | 12 (40) | 0.34 |
| Sulfasalazine | 90 (23) | 83 (23) | 7 (23) | 0.96 |
| Azathioprine | 22 (6) | 19 (5) | 3 (10) | 0.23 |
| Cyclosporine A | 11 (2) | 11 (3) | 0 (0) | 0.99 |
| Gold salts | 37 (9) | 34 (9) | 3 (10) | 0.75 |
| Penicillamine | 8 (2) | 7 (2) | 1 (3) | 0.47 |
| Biological DMARDs, n (%) | ||||
| Any anti-TNF | 260 (66) | 234 (65) | 26 (87) | 0.014 |
| Adalimumab | 145 (37) | 131 (36) | 14 (47) | 0.25 |
| Etanercept | 139 (35) | 123 (34) | 16 (53) | 0.033 |
| Infliximab | 40 (10) | 35 (10) | 5 (17) | 0.22 |
| Golimumab | 33 (8) | 30 (8) | 3 (10) | 0.73 |
| Certolizumab Pegol | 13 (3) | 12 (3) | 1 (3) | 0.99 |
| Tocilizumab | 134 (34) | 119 (33) | 15 (50) | 0.057 |
| Rituximab | 71 (18) | 62 (17) | 9 (30) | 0.079 |
| Abatacept | 53 (14) | 47 (13) | 6 (20) | 0.28 |
| Sarilimumab | 3 (1) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.093 |
| JAK inhibitors, n (%) | 42 (11) | 38 (11) | 4 (13) | 0.63 |
| Tofacitinib | 16 (4) | 14 (4) | 2 (1) | 0.46 |
| Baricitinib | 32 (8) | 30 (8) | 2 (7) | 0.99 |
| Upadacitinib | 4 (1) | 3 (1) | 1 (3) | 0.27 |
| Months of exposition to biological or targeted therapies, median (IQR) | ||||
| Any anti-TNF-α | 42 (12-82) | 43 (12-79) | 36 (13-101) | 0.69 |
| Adalimumab | 22 (9-56) | 23 (9-59) | 15 (9-31) | 0.43 |
| Etanercept | 26 (4-72) | 26 (4-64) | 25 (4-124) | 0.99 |
| Infliximab | 19 (7-40) | 19 (6-42) | 11 (9-38) | 0.82 |
| Golimumab | 22 (8-53) | 18 (6-53) | 34 (24-38) | 0.54 |
| Certolizumab | 21 (15-41) | 21 (12-40) | 58 (58-58) | 0.18 |
| Tocilizumab | 27 (7-65) | 28 (7-65) | 19 (6-41) | 0.22 |
| Rituximab | 24 (4-63) | 26 (5-68) | 9 (2-26) | 0.055 |
| Abatacept | 12 (6-33) | 11 (5-31) | 16 (16-33) | 0.26 |
| Sarilimumab | 3 (1-14) | 8 (1-14) | 3 (3-3) | 0.99 |
| JAK inhibitors (all) | 11 (6-18) | 11 (6-18) | 11 (2-19) | 0.81 |
| - Tofacitinib | 11 (2-19) | - | 11 (2-19) | - |
| - Baritinib | 9 (5-14) | 9 (5-14) | - | - |
| - Upadacitinib | 9 (1-28) | 1 (1-16) | 39 (39-39) | 0.16 |
| Case | Sex | Age at HZ | HZ location | HZ treatment | HZ antiviral treatment | Postherpetic Neuralgia | Concomitant RA treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 71 | Upper Extremity (left) | Unknown | - | No | Corticosteroids/MTX/TCZ |
| 2 | Female | 62 | Intercostal (right) | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | No | Corticosteroids/GLM |
| 3 | Male | 70 | Intercostal (right) | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | Yes | GLM |
| 4 | Female | 84 | Unknown | Topic | - | No | Corticosteroids/MTX |
| 5 | Female | 68 | Dorsal (right) | None | - | Yes | Corticosteroids/ABA |
| 6 | Female | 78 | Lumbar (left) | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | No | Corticosteroids/MTX |
| 7 | Male | 72 | Intercostal (left) | None | - | No | ETN |
| 8 | Female | 79 | Abdominal | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | Yes | Corticosteroids/MTX |
| 9 | Female | 36 | Unknown | Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/MTX |
| 10 | Female | 51 | Disseminated | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | Yes | Corticosteroids |
| 11 | Female | 66 | Dorsal (left) | None | - | No | Corticosteroids/MTX/ADA |
| 12 | Male | 82 | Ophthalmic(left) | Topic | - | No | Corticosteroids/ABA |
| 13 | Female | 45 | Abdominal | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | No | SARI |
| 14 | Female | 52 | Unknown | Topic/Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/TCZ |
| 15 | Female | 63 | Cervical | None | - | No | MTX |
| 16 | Female | 71 | Submammary fold (left) | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/MTX |
| 17 | Female | 68 | Intercostal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | Yes | None |
| 18 | Female | 53 | Intermammary fold | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | No | TOFA |
| 19 | Female | 75 | Lumbar | Systemic antiviral | Valaciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/MTX/UPA |
| 20 | Female | 58 | Unknown | Topic/Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | No | Corticosteroids |
| 21 | Male | 73 | Intercostal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | Yes | Corticosteroids/ABA |
| 22 | Female | 40 | Dorsal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/AZA/CZP |
| 23 | Female | 58 | Abdominal | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/TCZ |
| 24 | Female | 73 | Lumbar (right) | Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/LFN |
| 25 | Female | 66 | Unknown | Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | Yes | TOFA |
| 26 | Male | 57 | Intercostal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Brivudine | No | Corticosteroids/SSZ/ETN |
| 27 | Female | 61 | Dorsal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Aciclovir | No | LFN/ETN |
| 28 | Female | 63 | Facial (right) | Systemic antiviral | Famciclovir | No | MTX |
| 29 | Female | 67 | Gluteus (left) | Systemic antiviral | Valaciclovir | No | Corticosteroids/MTX/LFN |
| 30 | Female | 79 | Trigeminal (left) | Systemic antiviral | Valaciclovir | No | ETN |
| Age at the moment of HZ,mean±SD (years) | 64.7±11.8 |
| Time of evolution of RA, mean±SD (months) | 158.4±115.7 |
| Location, n(%) | |
| Trunk | 18 (60) |
| Head and neck | 4 (13) |
| Extremities | 2 (7) |
| Disseminated | 1 (3) |
| Unknown | 5 (17) |
| Antiviral treatment, n (%) | 23 (77) |
| Brivudine | 7 (30) |
| Famciclovir | 7 (30) |
| Aciclovir | 6 (126) |
| Valaciclovir | 3 (13) |
| Sequelae | |
| Postherpetic neuralgia | 7 (87) |
| Temporary visual alteration | 1 (13) |
| Current treatment when zoster infection occurred | |
| Prednisone, n (%) | 19 (63) |
| Prednisone dose, mg/day | 7.5 (5-10) |
| DMARDs, n (%) | 15 (50) |
| Metothrexate | 10 (67) |
| Leflunomide | 2 (13) |
| Metothrexate + leflunomide | 1 (7) |
| Azathioprine | 1 (7) |
| Sulfasalazine | 1 (7) |
| Biological therapy, n (%) | 15 (50) |
| Etanercept | 4 (27) |
| Abatacept | 3 (20) |
| Tocilizumab | 3 (20) |
| Golimumab | 2 (13) |
| Adalimumab | 1 (7) |
| Certolizumab | 1 (7) |
| Sarilumab | 1 (7) |
| JAK inhibitors, n (%) | 3 (10) |
| Tofacitinib | 2 (13) |
| Upadacitinib | 1 (33) |
| HR (95%CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean±SD) | 1.02 (0.99-1.05) | 0.21 |
| Time of evolution of RA (months) (mean±SD) | 1.002 (0.99-1.005) | 0.31 |
| Women, n (%) | 1.31 (0.50-3.42) | 0.58 |
| Active smokers, n (%) | 0.90 (0.43-1.90) | 0.79 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 2.25 (1.09-4.68) | 0.029 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 1.70 (0.70-4.17) | 0.24 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 1.50 (0.73-3.08) | 0.27 |
| Positive RF, n (%) | 0.96 (0.46-1.97) | 0.91 |
| Positive anti-CCP, n (%) | 0.67 (0.33-1.38) | 0.28 |
| Erosions, n (%) | 0.86 (0.40-1.85) | 0.71 |
| Subcutaneous nodules, n (%) | 0.53 (0.07-3.92) | 0.54 |
| Interstitial lung disease, n (%) | 2.10 (0.64-6.94) | 0.22 |
| Sjögren´s syndrome, n (%) | 0.62 (0.08-4.52) | 0.63 |
| Number of conventional DMARDs (not concomitant) | ||
| Methotrexate | 0.77 (0.29-2.06) | 0.60 |
| Leflunomide | 1.33 (0.67-2.66) | 0.42 |
| Sulfasalazine | 1.08 (0.46-2.51) | 0.87 |
| Azathioprine | 1.93 (0.59-6.38) | 0.28 |
| Gold salts | 1.04 (0.32.3.44) | 0.95 |
| Penicillamine | 1.58 (0.21-11.60) | 0.65 |
| Biological DMARDs, n (%) | ||
| Any anti-TNF | 1.12 (0.51-2.47) | 0.78 |
| Adalimumab | 1.21 (0.59-2.50) | 0.60 |
| Etanercept | 2.04 (0.99-4.18) | 0.05 |
| Infliximab | 1.88 (0.72-4.90) | 0.20 |
| Golimumab | 1.05 (0.32-3.48) | 0.93 |
| CertolizumabPegol | 0.98 (0.13-7.18) | 0.98 |
| Tocilizumab | 1.55 (0.75-3.17) | 0.23 |
| Rituximab | 1.94 (0.88-4.22) | 0.99 |
| Abatacept | 1.46 (0.59-3.57) | 0.41 |
| Sarilumab | 3.90 (0.53-28.62) | 0.18 |
| JAK inhibitors | 1.46 (0.56-3.82) | 0.44 |
| Tofacitinib | 1.34 (0.32-5.64) | 0.69 |
| Baricitinib | 0.73 (0.17-3.07) | 0.67 |
| Upadacitinib | 4.14 (0.56-30.59) | 0.16 |
| Design | Underlying disease | Number of RA patients | IR* of HZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfe et al (2006) | Observational | RA | 28852 | 7.70 |
| Smitten et al (2007) | Retrospective | RA RA |
122272 38621 |
9.83 3.71 |
| McDonald et al (2009) | Retrospective | RA and other MSK diseases | 20357 | 9.96 |
| Chen et al (2011) | Observational | Immune-mediated diseases | 11446 | 12.24 |
| Pappas et al (2015) | Observational | RA | 10614 | 13.20 |
| Harada et al (2017) | Prospective | RA | 1987 | 6.66 |
| Dominguez et al (2023) | Prospective | RA | 392 | 13.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





