1. Introduction
Diabetes is a complex chronic condition affecting millions globally. Successful management demands constant monitoring of blood glucose, diet, exercise, medication, and various other factors [
1]. The complexity of diabetes stems from its interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle influences. Effective interventions also require comprehensive knowledge about the patient, including genetics, demographics, health history, family history, lifestyle patterns, and real-time health data. However, existing approaches often struggle with personalization, preventing complications, ensuring patient awareness, and addressing adherence issues [
2]. A need exists for a comprehensive, patient-centered diabetes management system that adapts to individual needs, goals, and preferences, providing timely and accurate guidance.
Traditional research on diabetes management tends to adopt a piecemeal approach, focusing on isolated factors such as genomics, symptoms, or lab data alone. This fragmented view limits the effectiveness of interventions and hinders the development of truly personalized solutions [
3].
Digital twins represent an emerging technology with the potential to transform healthcare. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical entity capable of modeling and simulating its behavior and environmental interactions [
4]. Applied successfully in industries like aerospace and manufacturing [
5], digital twins now open new possibilities for personalized medicine and precision healthcare [
4].
This paper explores digital twins specifically for diabetes management, focusing on aspects of condition prediction and control. Our approach aims to be more holistic. We propose a digital twin framework facilitating the integration of diverse factors, empowering healthcare providers and patients to manage this complex disease comprehensively.
Our key contributions include:
Holistic Approach: Our framework promotes a holistic diabetes management approach by integrating diverse physiological, lifestyle, social, and environmental factors.
A patient-centric framework: We propose a framework built around Personal Health Knowledge Graphs (PHKGs) to capture the complex and evolving relationships among diverse data sources such as patient history, lifestyle, preferences, goals, and environmental factors.
Data Integration and Interoperability: Our framework incorporates HL7 standards [
6] to promote seamless interaction across devices, applications, programs, and institutional boundaries.
Extensibility and Adaptability: PHKGs offer a flexible structure, allowing them to expand as new knowledge about the patient becomes available.
Demonstrated Use Cases: We showcase the usage of the digital twin framework for real-world diabetes management applications like predicting glucose levels, optimizing insulin dosage, offering lifestyle recommendations, and health data visualization.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 provides a literature review on the diabetes management and existing applications of digital twins technology in healthcare.
Section 3 describes the design and implementation of our proposed framework and explains how it can create and assess digital twins for personalized diabetes care.
Section 4 presents use case study of our framework.
Section 5 concludes the paper and indicates future works.
2. Related works
2.1. Diabetes Management
While the multifaceted nature of diabetes is widely acknowledged, existing management approaches tend to adopt a fragmented view, focusing on isolated aspects of the disease. Numerous studies concentrate on identifying the genetic markers associated with an increased risk of diabetes [
7]. This research helps understand disease predisposition and may open doors to future personalized therapies. The powerful impact of lifestyle factors on diabetes risk and management is well documented [
8]. Interventions targeting diet, physical activity, and stress reduction are often essential components of diabetes care plans. Studies are increasingly examining the role of environmental factors as potential contributors to diabetes [
9]. Factors like air pollution, exposure to specific chemicals, and access to healthy foods are under scrutiny as these may significantly influence the risk of developing diabetes and the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Research into diabetes encompasses several key areas, each playing a crucial role in advancing our understanding and treatment of this complex disease. Risk prediction models seek to identify individuals at heightened risk based on genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, opening doors to proactive or preventative interventions [
10,
11]. Personalized treatment planning aims to tailor medication, diet, and exercise regimens to an individual’s unique biology and preferences, maximizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing side effects [
12,
13]. Preventive strategies focus on identifying modifiable factors like diet, physical activity, and exposure to environmental toxins, aiming to reduce the likelihood of diabetes developing or to slow disease progression in those already diagnosed [
14,
15]. While valuable independently, the greatest impact will likely come when these research areas are united within a holistic framework, allowing for truly personalized and dynamic risk assessments, treatment plans, and preventive measures.
2.2. Digital Twins in Healthcare
The concept of digital twins, virtual replicas of physical objects or systems, is revolutionizing the healthcare sector. Within this context, a digital twin aims to model a patient, organ, disease process, or even a whole healthcare system.
Digital twins offer unprecedented opportunities for personalized treatment. By integrating patient-specific data (genomic, medical history, lifestyle, real-time sensor data), these virtual replicas facilitate highly individualized care plans. Studies like Thamotharan et al. [
16] showcase how digital twins can optimize medication regimens (e.g., insulin administration), while others explore their use in surgery planning [
17] and tailored device development [
18,
19]. Beyond individual care, digital twins can inform larger-scale public health interventions. Researchers are investigating how they could model disease spread patterns, predict outbreaks [
20], and simulate the impact of public health policies in specific populations. Digital twins can accelerate drug discovery and streamline clinical trials [
21]. They offer the ability to test drug efficacy and safety profiles in a virtual environment, reducing time and risk while potentially tailoring therapies to specific populations [
22]. Digital twins serve as powerful tools for education and training. They allow medical professionals to practice complex procedures, visualize anatomical structures, and experiment with different treatment scenarios in a risk-free, simulated environment [
23,
24].
While promising, digital twin technology in healthcare is still developing. Seamless data flow across various systems and devices is crucial for robust digital twin creation. Efforts continue to standardize data exchange and ensure interoperability [
25,
26]. As with any patient data usage, privacy, security, and the potential for biases require careful attention within digital twin frameworks [
27,
28].
3. Constructing Patient-Centered Digital Twins for Diabetes Management
The core objective of this research is the development of digital twins for personalized diabetes management. This involves generating dynamic virtual representations of a patient’s health state that can simulate behavior, predict outcomes, and enable personalized insights.
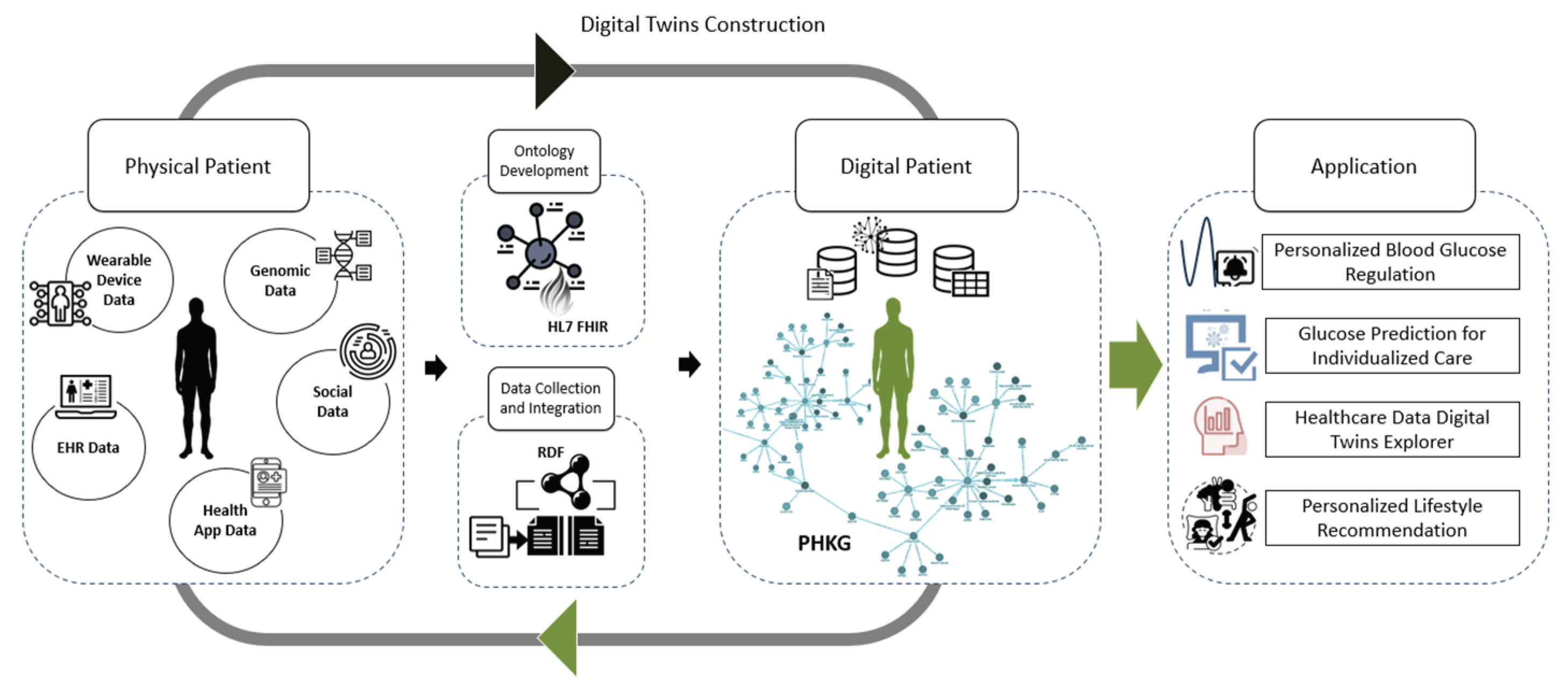
Figure 1 shows the framework of the proposed digital twin. Details of the framework is illustrated as follows:
3.1. Ontology Development
The cornerstone of our approach is the development of a robust and standardized ontology, meticulously aligned with HL7 FHIR standards [
29] to ensure interoperability and adherence to established industry practices. This health ontology is intricately designed to offer a comprehensive vocabulary and articulate the complex relationships inherent within the personal health domain, acting as the structural foundation upon which our digital twin models are constructed.
Our methodology for ontology development embraces a systematic, top-down approach, initiating with broad health-related categories such as “Medical Condition” and progressively dissecting these into more specific subcategories like “Diabetes”. This hierarchical structure allows for a nuanced categorization of health conditions. Each concept within the ontology is enriched with properties that detail its attributes and the relationships it shares with other concepts. These are divided into object properties, which connect different concepts within the ontology, and data properties, which link concepts to specific values, facilitating a detailed and relational representation of health data.
Given the dynamic nature of medical knowledge, our ontology is crafted with flexibility in mind, enabling it to evolve in response to new medical discoveries and shifts in healthcare practices. The process of ontology evolution is triggered by the emergence of new findings, initiating a multi-step maintenance protocol that begins with the identification of necessary updates. These updates may range from the introduction of novel concepts to alterations in existing relationships within the ontology. A critical reassessment of the updated ontology’s compatibility with existing data ensures seamless integration with the pre-established data framework, maintaining the coherence and functionality of the digital twin models.
Through this detailed and dynamic approach to ontology development, we ensure the creation of an adaptable and cutting-edge health ontology. This foundational framework not only underpins the accuracy and reliability of our digital twin models but also significantly enhances the personalization and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
3.2. Data Collection and Integration
Our approach to data collection and integration is both expansive and meticulous. We tap into a wide array of healthcare data sources, which include but are not limited to electronic health records (EHRs), inputs from wearable devices, mobile health applications, and direct patient-generated data. Each of these sources plays a pivotal role in painting a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health landscape, offering unique insights that are integral to the construction of a detailed and accurate digital twin.
To ensure the integrity and usability of the collected data, a rigorous quality control process is initiated. This critical phase addresses common data quality issues, such as missing values, inconsistencies, and outliers, which are inherent challenges in dealing with diverse healthcare data sets. Following the rectification of these issues, the data undergoes a transformation process. This crucial step involves mapping the raw data onto the predefined concepts and relationships within our health ontology. The aim here is to achieve a unified and standardized representation of the data, ensuring that it aligns seamlessly with the structured framework of our ontology, thereby facilitating accurate and effective data integration.
The cornerstone of our data integration strategy is the innovative use of the GLAV (Global-Local as View) framework [
30]. This advanced framework stands out from traditional data integration approaches, such as GAV (Global as View) and LAV (Local as View), by offering a more dynamic and flexible mapping capability. The essence of GLAV lies in its ability to support bidirectional mappings, which is particularly advantageous when dealing with the voluminous and intricate nature of healthcare data sets. This flexibility is crucial for accommodating the complex interrelations and the heterogeneity inherent in healthcare data, thereby ensuring a more cohesive and comprehensive integration process.
To further refine the data integration process and enhance the accuracy of mappings, we employ Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) [
31]. These advanced probabilistic graphical models are renowned for their proficiency in pattern recognition and their ability to learn complex patterns within data. By leveraging CRFs, we are able to discern and accurately map the intricate features of source data—such as column names and data types—to the relevant concepts within our ontology. This level of precision in mapping is pivotal for ensuring that the integrated data is not only accurate but also meaningful within the context of the digital twin, enabling a richer and more nuanced representation of the patient’s health status. Through this comprehensive and nuanced approach to data collection and integration, we ensure the assembly of a rich and coherent dataset. This dataset forms the backbone of our digital twins, providing the depth and breadth of information necessary for simulating realistic and detailed virtual representations of patients’ health conditions, thereby paving the way for personalized and precise healthcare interventions.
3.3. Personal Health Knowledge Graph (PHKG) Construction
The construction of the Personal Health Knowledge Graph (PHKG) is a critical phase that follows the integration and transformation of health data. This transformation marks the transition of raw health data into a structured format that is amenable to semantic querying and reasoning, laying the groundwork for the instantiation of the knowledge graph. The PHKG is sculpted based on the intricacies of the predefined ontology, serving as a dynamic representation of a patient’s health landscape.
The instantiation process within the PHKG begins with the identification and creation of specific instances for each ontological concept, derived from the integrated health data. For instance, an individual blood glucose measurement recorded in the health data is instantiated within the graph as a particular manifestation of the “Blood Glucose Level” concept. This step transforms abstract ontological concepts into concrete instances that reflect real-world data points related to the patient’s health status. Simultaneously, the relationships among these instances, as delineated by the ontology through a network of object and data properties, are materialized as edges within the graph. These edges serve as the connective tissue between concept instances, weaving a complex web of relationships that mirror the multifaceted nature of health data. For example, a “hasSymptom” relationship might be instantiated to connect a “Diabetes” concept instance with a “Frequent Urination” symptom instance, thereby encapsulating the symptomatology associated with the condition within the patient’s health profile.
The PHKG transcends its role as a mere data repository, emerging as a sophisticated knowledge representation framework capable of encapsulating a wide spectrum of health-related information. This includes, but is not limited to, diagnostic information, medication regimes, laboratory results, sensor-derived data, lifestyle parameters, and subjective patient experiences. The comprehensive nature of the PHKG makes it an invaluable resource for underpinning simulations and analyses within the digital twin framework, enabling a nuanced understanding of the patient’s health dynamics.
3.4. Digital Twin Generation
The generation of a digital twin for each patient is a sophisticated process that harnesses the depth and breadth of data encapsulated within the Personal Health Knowledge Graph (PHKG). This rich repository of semantically structured health data forms the bedrock upon which the digital twin is constructed, enabling a dynamic and personalized virtual representation of each patient’s health status.
The digital twin employs advanced simulation models that are meticulously calibrated using comprehensive data derived from the PHKG. These models are capable of simulating various physiological and metabolic processes relevant to the patient’s condition, providing a virtual environment in which the consequences of different interventions can be explored. The simulation models are designed to mimic the patient’s response to various treatments, lifestyle modifications, and potential disease progression pathways. This allows healthcare providers to visualize the potential outcomes of different therapeutic strategies, facilitating informed decision-making and personalized care planning. Moreover, the models can simulate the long-term implications of these interventions, aiding in the prevention and management of potential complications.
In parallel, the digital twin leverages machine learning algorithms that are trained on the heterogeneous and comprehensive dataset provided by the PHKG. These algorithms are adept at uncovering complex patterns within the data, including subtle correlations between various health indicators, treatment responses, and environmental or lifestyle factors. By analyzing these patterns, the algorithms can generate predictive insights into the patient’s future health trajectory, identify risk factors for disease progression, and suggest preemptive measures to mitigate these risks.
The machine learning component of the digital twin is not static; it continuously evolves as new data is incorporated into the PHKG, ensuring that the twin remains up-to-date with the patient’s current health status and the latest medical knowledge. This dynamic learning process enhances the precision of the digital twin’s predictions and recommendations, making them increasingly personalized and accurate over time.
4. Application of Digital Twins
Digital twins, with their rich data integration and simulation power, unlock diverse applications for diabetes management. Here, we explore key use cases, emphasizing how digital twin components drive their functionality.
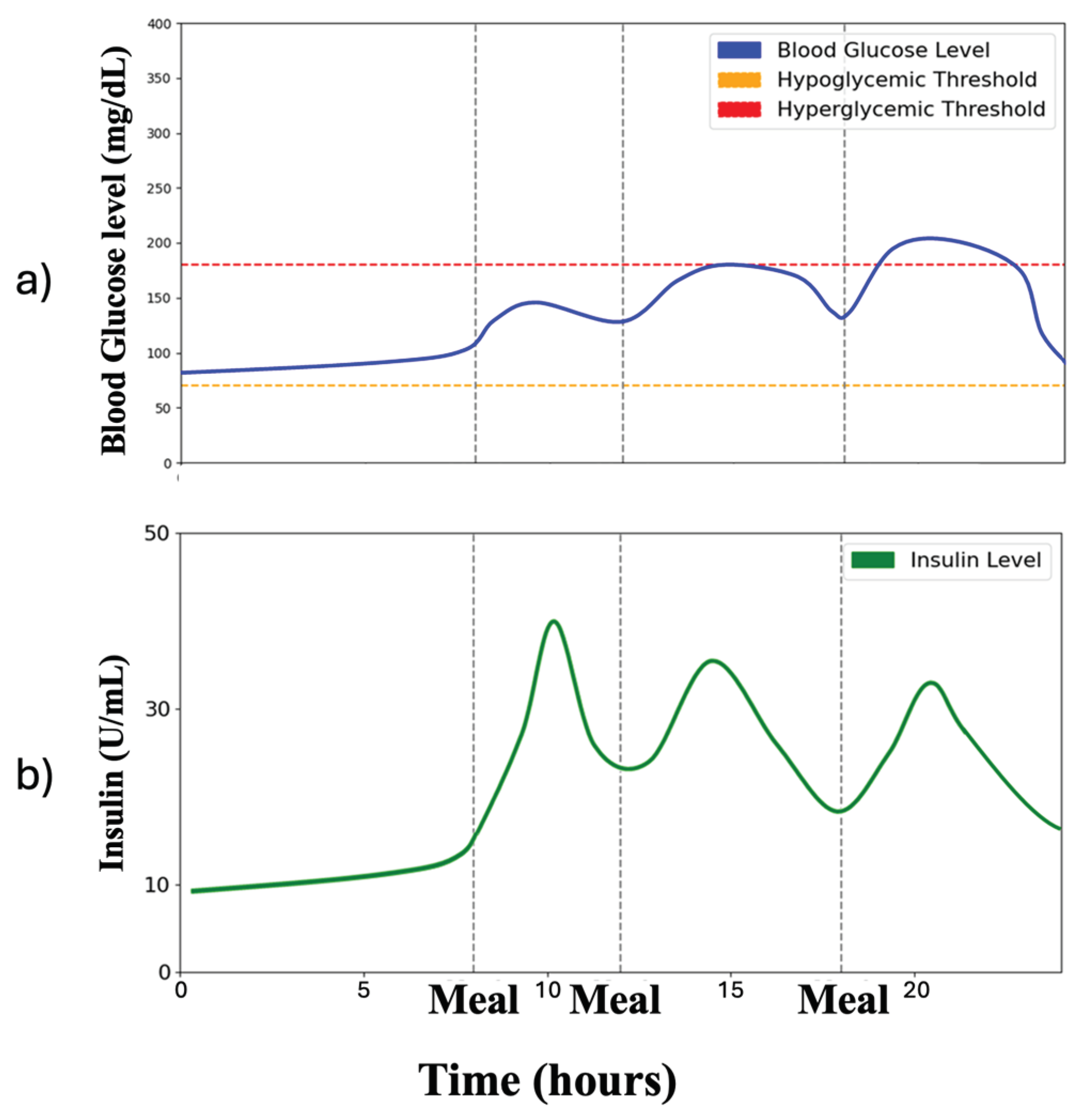
4.1. Personalized Blood Glucose Regulation[32]
Digital Twin’s Role: The digital twin provides historical patient data and a simulation environment to train and test insulin optimization strategies.
Algorithms: Reinforcement learning (RL), specifically the Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm, with its entropy-driven reward function, refines insulin dosages. The SAC algorithm balances precision with safe exploration to find optimal solutions for the individual.
Outcomes: The digital twin enables personalized, data-driven insulin optimization, enhancing blood glucose control while reducing risks like hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. This demonstrates the power of digital twins to drive individualized care.
Figure 2 demonstrates the application of Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) based Reinforcement Learning (RL) on a patient’s digital twin to enhance glucose level regulation, aiming to minimize the percentage of time that blood glucose level is in risk range and stabilize overall glucose levels.
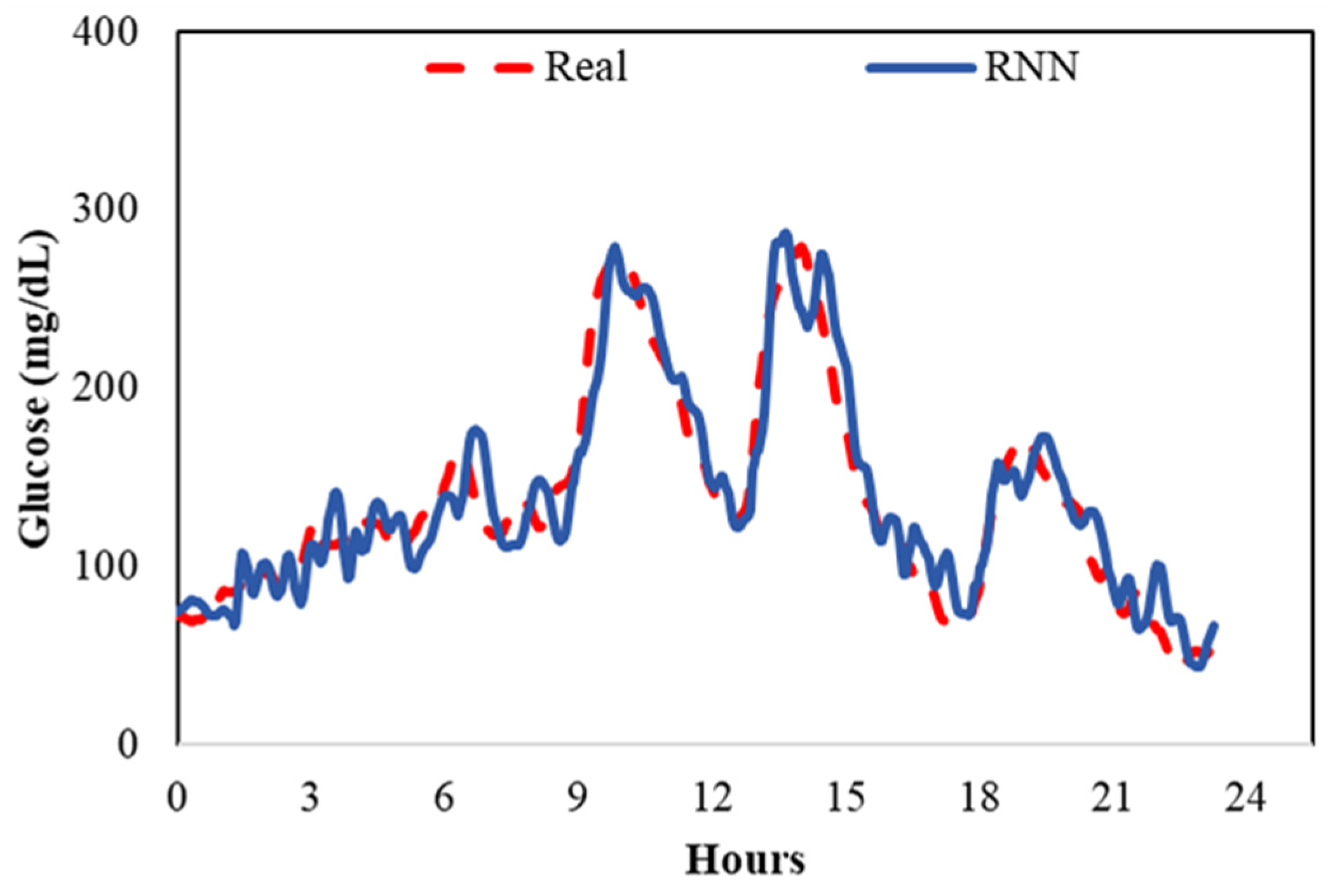
4.2. Glucose Prediction for Individualized Care [33]
Digital Twin’s Role: Provides a structured dataset integrating glucose trends, food intake, insulin use, and other patient-specific factors. This dataset is essential for training predictive models.
Algorithms: Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are ideal for analyzing time-series data within the digital twin. These networks identify complex patterns in individual glucose trajectories.
Outcomes: The digital twin-powered predictive models yield tailored glucose forecasts. This allows proactive care adjustments, helping patients and providers make informed decisions to maintain optimal blood glucose levels.
Figure 3 illustrates the process of incorporating RNN with our digital twins to predict glucose values, achieving an average RMSE of 19.83 mg/dL based on the digital twins’ data.
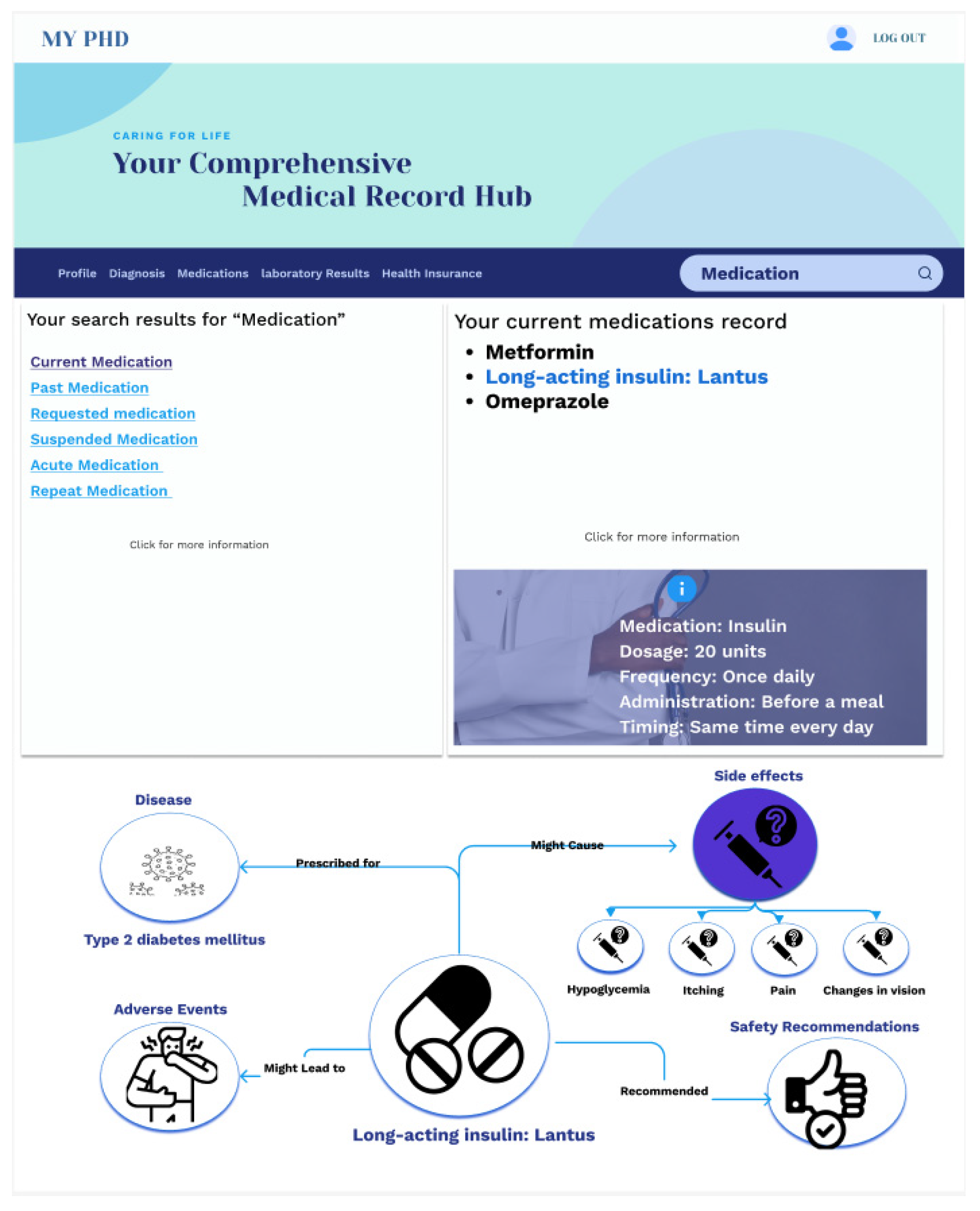
4.3. Healthcare Data Digital Twins Explorer [34]
Digital Twin’s Role: The structured PHKG and its rich relationships between health concepts form the core of this application.
-
Interaction Modes: As shown in
Figure 4, two interfaces provide flexibility:
Keyword Search: Natural language processing converts user queries into SPARQL for knowledge graph retrieval. Semantic links offer further exploration avenues.
Navigation Interface: Dropdown trees and graph visualizations allow users to explore the PHKG’s knowledge hierarchy.
Outcomes: The digital twin empowers patients to understand their health data at their own pace. This enhanced data literacy facilitates patient participation in collaborative care.
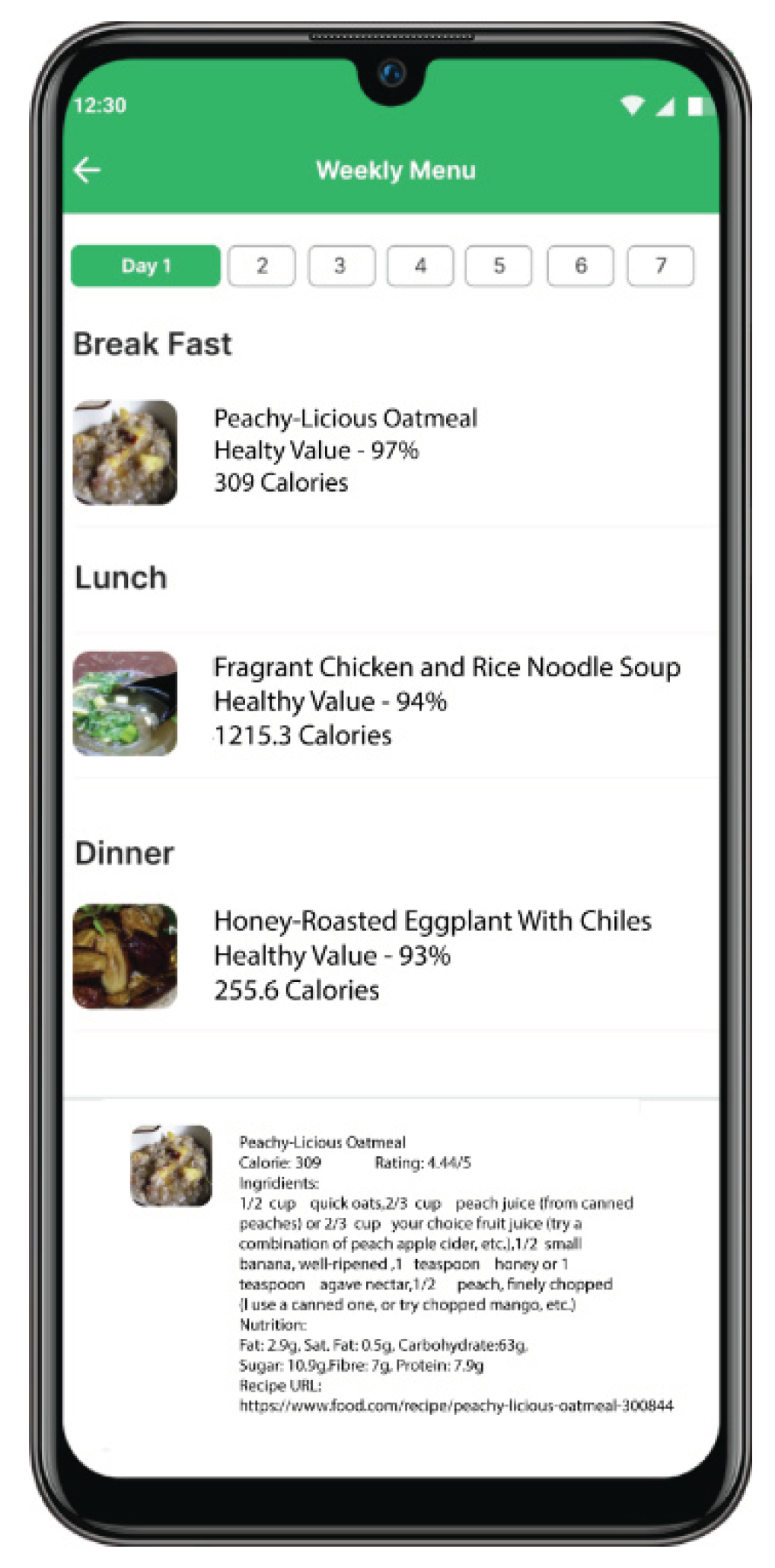
4.4. Personalzied Meal Recommendation [35]
Digital Twin’s Role: The PHKG integrates information about a patient’s health condition, diabetes management plan, dietary preferences, and allergies. This comprehensive data profile fuels the meal recommendation engine.
Logic Rules and Reasoning: Embedded within the knowledge graph are rules that reason about the patient’s health data and generate personalized meal suggestions. For example, rules might suggest meals that meet specific calorie goals, avoid allergens, and align with diabetes management guidelines.
Outcomes: The digital twin goes beyond simply providing data; it offers actionable recommendations tailored to the individual’s needs. This empowers patients to make informed dietary choices that support their blood sugar control and overall health.
Figure 5 shows an mobile application we developed for personalzied meal recommendations for patients with diabetes.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented a novel approach to personalized diabetes management using digital twins and patient-centric knowledge graphs (PHKGs). We emphasized the importance of including diverse healthcare data sources while ensuring interoperability through standardized ontologies. We outlined a comprehensive methodology for constructing digital twins for diabetes management, encompassing ontology development, data collection and integration, PHKG construction, and digital twin generation. We highlighted the strengths of our approach, including patient-centricity, knowledge sharing through standardized ontologies, and the adaptability of the PHKG to incorporate new data and knowledge.
We showcased the use of the digital twin in several applications critical for diabetes management: personalized blood glucose regulation, glucose prediction for individualized care, exploration of healthcare data through the PHKG user interface, and generation of personalized meal recommendations.
We plan to further explore advanced machine learning algorithms, particularly those suited for causal reasoning within the PHKG. This will enhance the digital twin’s ability to not only predict outcomes but also identify the underlying factors influencing those outcomes. Large-scale clinical trials will be crucial to validate the effectiveness of the digital twin approach in improving clinical outcomes for patients with diabetes. We envision the expansion of the digital twin framework beyond diabetes management to encompass other chronic conditions. The core functionalities and the patient-centric design principles can be adapted to other use cases within the broader healthcare domain. By continuously developing and refining the digital twin approach, we hold the potential to revolutionize personalized diabetes management, empowering patients to take an active role in their health and well-being.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S.R. and J.L.; methodology, F.S.R. and R.H; validation, F.S.R., J.L.; formal analysis, F.S.R., R.H., J.L., and X.Y; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.R.; writing—review and editing, F.S.R., R.H, J.L, and X.Y; supervision, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The National Science Foundation (NSF) supported this work with award numbers 1722913 and 2218046.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mommersteeg, P.M.; Herr, R.; Pouwer, F.; Holt, R.I.; Loerbroks, A. The association between diabetes and an episode of depressive symptoms in the 2002 World Health Survey: an analysis of 231 797 individuals from 47 countries. Diabetic Medicine 2013, 30, e208–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.; Ahlbom, A.; Carlsson, S. Diabetes prevalence in Sweden at present and projections for year 2050. PloS one 2015, 10, e0143084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.B.; Cheng, A.Y.; Davies, M.J.; Gerstein, H.C.; Green, J.B.; Skolnik, N. Person-centered, outcomes-driven treatment: a new paradigm for type 2 diabetes in primary care. 2020.
- Kamel Boulos, M.N.; Zhang, P. Digital twins: from personalised medicine to precision public health. Journal of personalized medicine 2021, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Wu, H. The potential of the Medical Digital Twin in diabetes management: a review. Frontiers in Medicine 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Level Seven International. (2023). HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). HL7. https://www.hl7.org/fhir/. Available online: (accessed on.
- Ortiz-Martínez, M.; González-González, M.; Martagón, A.J.; Hlavinka, V.; Willson, R.C.; Rito-Palomares, M. Recent Developments in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Screening of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Current Diabetes Reports 2022, 22, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.L.; Long, G.H.; Johansson, I.; Weinehall, L.; Fhärm, E.; Wennberg, P.; Norberg, M.; Griffin, S.J.; Rolandsson, O. Change in lifestyle behaviors and diabetes risk: evidence from a population-based cohort study with 10 year follow-up. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2017, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beulens, J.W.J.; Pinho, M.G.M.; Abreu, T.C.; den Braver, N.R.; Lam, T.M.; Huss, A.; Vlaanderen, J.; Sonnenschein, T.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Environmental risk factors of type 2 diabetes—an exposome approach. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fregoso-Aparicio, L.; Noguez, J.; Montesinos, L.; García-García, J.A. Machine learning and deep learning predictive models for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome 2021, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjaboue, R.; Farhat, I.; Ferlatte, C.-A.; Ngueta, G.; Guay, D.; Delorme, S.; Ivers, N.; Shah, B.R.; Straus, S.; Yu, C.; et al. Predictive models of diabetes complications: protocol for a scoping review. Systematic Reviews 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, S.W. Personalizing Type 2 Diabetes Management: Use of a Patient-Centered Approach to Individualizing A1C Goals and Pharmacological Regimens. Clinical Diabetes 2017, 35, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Hirsch, I.B. Personalized Diabetes Management: Moving from Algorithmic to Individualized Therapy. Diabetes Spectrum 2014, 27, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backholer, K.; Peeters, A.; Herman, W.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Liew, D.; Ademi, Z.; Magliano, D.J. Diabetes Prevention and Treatment Strategies: Are we doing enough? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2714–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie-Rosett, J.; Hu, F.B. Nutritional Strategies for Prevention and Management of Diabetes: Consensus and Uncertainties. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamotharan, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Kesavadev, J.; Krishnan, G.; Mohan, V.; Seshadhri, S.; Bekiroglu, K.; Toffanin, C. Human Digital Twin for Personalized Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2023, 12, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nye, L. Digital Twins for Patient Care via Knowledge Graphs and Closed-Form Continuous-Time Liquid Neural Networks. arXiv:2307.04772 2023.
- Croatti, A.; Gabellini, M.; Montagna, S.; Ricci, A. On the Integration of Agents and Digital Twins in Healthcare. Journal of Medical Systems 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Mumu, A.A.; Ali, M.W.; Sarker, S.; Muyeen, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Das, P.; Hasan, M.M.; Tasneem, Z.; Islam, M.M.; et al. Toward IoRT Collaborative Digital Twin Technology Enabled Future Surgical Sector: Technical Innovations, Opportunities and Challenges. Ieee Access 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesapane, F.; Rotili, A.; Penco, S.; Nicosia, L.; Cassano, E. Digital Twins in Radiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wang, C.; Y, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. P-2.15: Status Quo and Future Development of Digital Twins in Medical and Health Fields. Sid Symposium Digest of Technical Papers 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, R.; Surendran, S. A Digital Twin Approach for Deepened Classification of Patients With Hepatitis, Fibrosis and Cirrhosis. Journal of Physics Conference Series 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ser, J.D.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Xu, L.; Firmin, D.; Gatehouse, P.; Yang, G. HDL: Hybrid Deep Learning for the Synthesis of Myocardial Velocity Maps in Digital Twins for Cardiac Analysis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riascos, R.; Ostrosi, E.; Sagot, J.C.; Stjepandić, J. Conceptual Approach for a Digital Twin of Medical Devices. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; He, X.; Song, X.; Shu, L.; Li, Z. The Digital Twin in Medicine: A Key to the Future of Healthcare? Frontiers in Medicine 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turab, M.; Jamil, S. A Comprehensive Survey of Digital Twins in Healthcare in the Era of Metaverse. BioMedInformatics 2023, 3, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoltick, M.M.; Maisel, J.B. Societal Impacts: Legal, Regulatory and Ethical Considerations for the Digital Twin. In The Digital Twin, Crespi, N., Drobot, A.T., Minerva, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; pp. 1167–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H. Improving cloud storage and privacy security for digital twin based medical records. Journal of Cloud Computing 2023, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiourtis, A.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Menychtas, A.; Maglogiannis, I.; Kyriazis, D. Structurally Mapping Healthcare Data to HL7 FHIR through Ontology Alignment. Journal of Medical Systems 2019, 43, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Embley, D.W. Combining the best of global-as-view and local-as-view for data integration. In Proceedings of the Information systems technology and its applications, 2004., 3rd international conference ISTA’2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Fan, Z. A comprehensive review of conditional random fields: variants, hybrids and applications. Artificial Intelligence Review 2020, 53, 4289–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarani Rad, F.; Li, J. Optimizing Blood Glucose Control through Reward Shaping in Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services (HealthCom), Chongqing, China; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, J. Edge AI Empowered Personalized Privacy-Preserving Glucose Prediction with Federated Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services (HealthCom), Chongqing, China; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hendawi, R.; Li, J. Comprehensive Personal Health Knowledge Graph for Effective Management and Utilization of Personal Health Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, MEDICINE, HEALTH, and CARE; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.; Li, J.; Hasan, W. Personalized Flexible Meal Planning for Individuals With Diet-Related Health Concerns: System Design and Feasibility Validation Study. JMIR Form Res 2023, 7, e46434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).