1. Introduction
In selecting observatory sites for ground-based optical/infrared astronomy, some of considerations are seeing, number of clear nights, humidity, and the night-sky brightness [
1,
2]. Cloud coverage is one of the most important elements affecting observations. Thick cloud significantly reduces the observable stellar magnitude and efficiency of telescope observations. Moreover, precipitation might be carried by clouds, which may damage the optical surface, structure, and electronics of telescope. To solve these problems, most well-known astronomical observatories deploy all-sky cameras to monitor the sky conditions and identify the distribution of cloud coverage.
Real-time cloud coverage identification can improve the effectiveness and quality of telescopes observations. In addition, the total amount of observable time throughout the year can be calculated if we know the number of clear nights and the distribution of cloud coverage. The optical telescopes are normally conducted at night. However, nighttime cloud images present specific challenges compared to daytime images: (1) The color-based images identification techniques are difficult to apply because the nighttime images don't have distinguishable color information. (2) The identification process is more difficult because the nighttime images have low grayscale values and lack of cloud contours due to poor illumination condition. Therefore, one of the main goals of astronomical observation is to propose a precise and automatic identification method for cloud images identification throughout the night.
In the field of astronomy, cloud coverage analysis was usually conducted by manual observation. For instance, some outstanding telescopes and observation sites, such as Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) [
3], Large Optical/Infrared Telescope (LOT) [
4], and Dome A [
5], employed manual observation methods to estimate night cloud distribution. However, manual observation is to identify and interpret cloud images by visual analysis. It is still the semiquantitative method. The accuracy of manual observation is susceptible to subjective factors like observer experience, and this method is labor-intensive. Therefore, manual observation is primarily utilized for offline cloud coverage statistics. It is difficult to make real-time observation by manual observation method. Therefore, many researchers have investigated some other methods including pixel segmentation, photometry, and machine learning techniques for identification of nighttime cloud images. The pixel segmentation method assesses cloud distribution by comparing pixel variations between clouds and clear sky areas. Dev et al. [
6] employed superpixel techniques for binary segmentation of nighttime images. Azhar et al. [
7] classified the nighttime cloud images into clear and cloudy regions based on the peak value of the all-sky image histogram. Jadhav et al. [
8] utilized Gaussian fitting and threshold methods for binary cloud images segmentation. However, the pixel segmentation approach is primarily suitable for cloud images with significant grayscale contrasts between targets and background. The segmentation accuracy tends to be low under low illumination and minimal grayscale discrepancies in images. The photometry method involves analyzing cloud coverage distribution by measuring the brightness (or luminosity) of celestial objects. Yin et al. [
9] created a reference image of star magnitudes and distinguished moonless cloud images by comparing star brightness of the reference image with the target image. Mandat et al. [
10] segmented a night cloud image into 70 subregions, counted the number of stars in each subregion, and utilized the Yale Bright Star Catalog BSC5 to analyze cloud distribution. Nevertheless, the photometry method is not suitable for handling images with poor signal-to-noise ratios, and it is ineffective for images with bright moon that affect observable star magnitudes.
Due to the extraordinary development of computer processing power and pattern recognition technology, machine learning based automatic cloud images recognition has emerged as the hot research topic in recently. For instance, a novel deep convolutional neural network, named CloudU-Net [
11], has been proposed for binary segmentation of cloud images. Li et al. [
12] employ Support Vector Machines (SVM), K Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Decision Trees (DT), and Random Forests (RF) for automated cloud classification, and the input features include cloud weight, cloud area ratio, and cloud dispersion. Two machine learning models [
13], namely Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) and ResNet, have been utilized for binary classification of cloud images.
Traditional machine learning algorithms have some disadvantages, such as low computing efficiency, interpretability issues, and high dimensionality of model. To meet the requirements of real-time cloud identification at telescope sites, this study proposes a nighttime cloud images classification algorithm based on XGBoost[
14,
15]. In addition, the PSO algorithm is used to globally optimize the model's key hyperparameters. We propose a PSO+XGBoost model for classifying cloud images at night. This model achieves 96.91% overall accuracy and allows for real-time automatic classification of cloud images.
The main contributions of this paper are presented as follows:
(1) Considering the limitations of conventional manual observation methods and the constrained computer resources of observatories. A PSO+XGBoost model is proposed to identify the cloud coverage. We use the PSO algorithm to optimize the hyperparameters of XGBoost, which improves the generalization and precision of the proposed model.
(2) Considering no color features and poor illumination of nighttime images, the images are divided into 37 subregions and a set of 19 features are extracted from each subregion, which improves reliability and reduces complexity of cloud coverage identification.
(3) After analyzing the relative importance of all input features, we found that the most important feature is the elevation angle of moon, which provides a comprehensive
interpretation of the nighttime images identification.
This paper is organized in the following sections:
Section 2 provides a comprehensive introduction to instrument and data description, while
Section 3 provides a detailed explanation of the automated classification approach. The comprehensive experimental results are elaborated in
Section 4. Finally, we present the conclusion in
Section 5.
2. Instrument and Data Description
2.1. Instrument
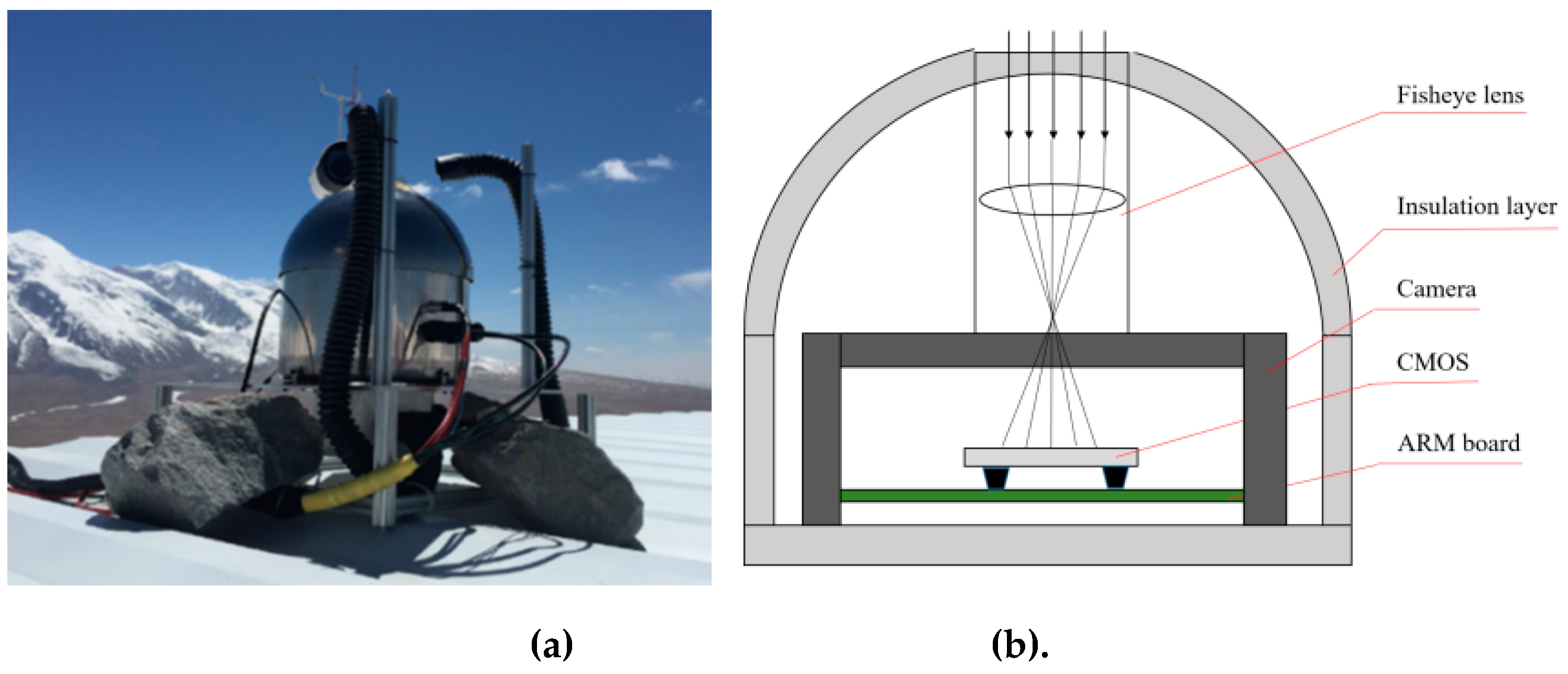
We use the nighttime cloud images collected from KLCAM (Kunlun Cloud and Aurora Monitor). The KLCAM was built by National Astronomical Observatories (NAO) and installed at the Muztagh Observatory (74°53 '48 "E, 38°19' 47" N) in April 2017. It operated until 2019 August and 48,870 images were obtained, with exposure time of 30 seconds. The KLCAM (see
Figure 1a) is equipped with a 3456*5184 Canon EOS 100D camera and a Sigma 5mm f/2.8 fisheye lens. KLCAM generated one image every 30 minutes.
Figure 1b shows the structural schematic of KLCAM. A customized ARM-based computer controls the images acquisition and storage [
16]. The format of raw images is RGGB. We used the two green channels as samples and merged the pixel values of the two green channels into a single channel.
To show the long-term trend within an entire year, we use nighttime images collected KLCAM in entire 2018 year to construct our training and testing data. All images are selected when the sun altitude angle lower than the horizon by 18° [
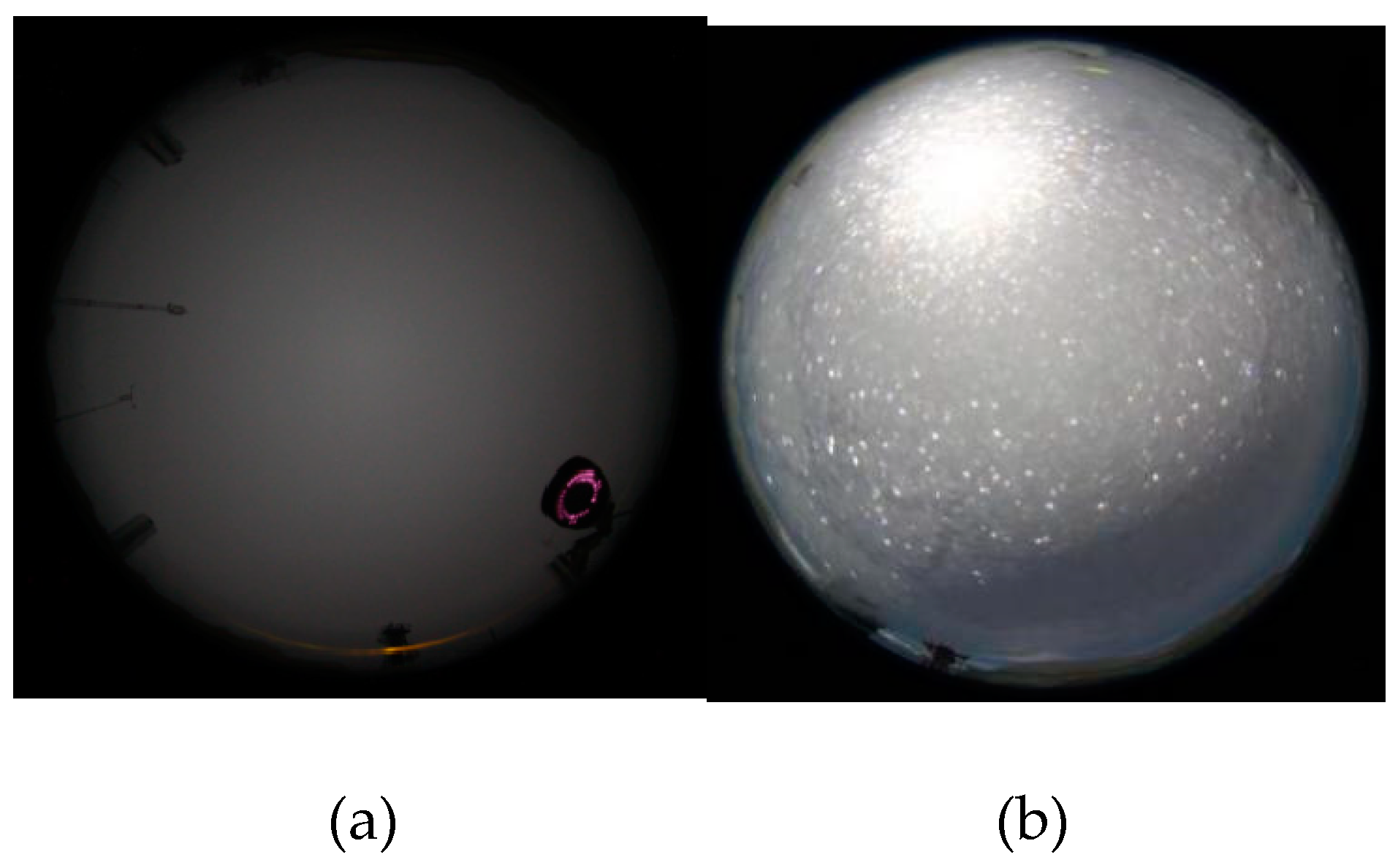
1]. The measurement using the KLCAM is limited by local weather conditions, such as snow, fog, and frost on the camera. Examples of fog and frost are shown in
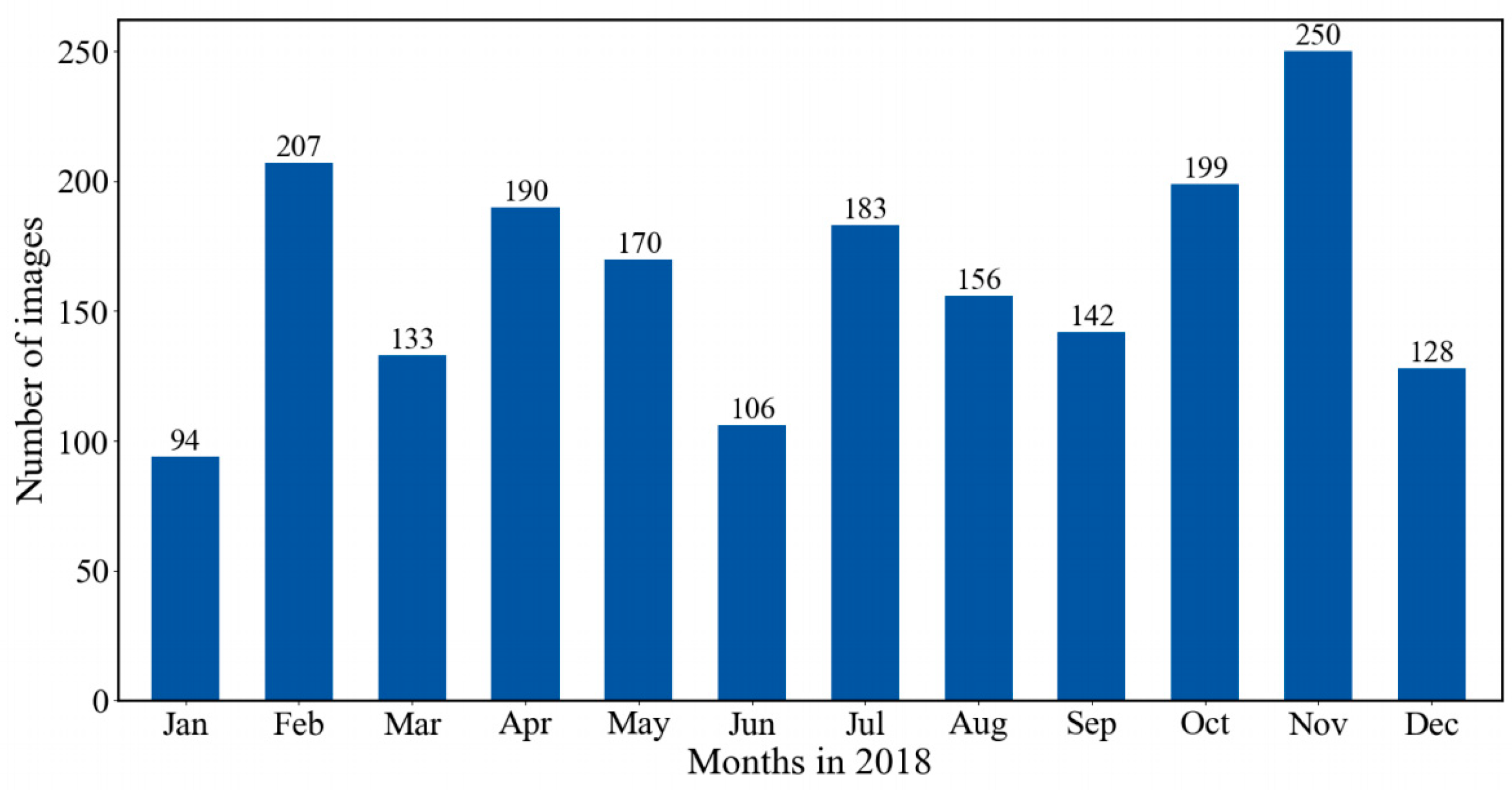
Figure 2. These defective images were removed. In total, we have 1958 nighttime images for training and testing. We compare the available nighttime images in different months in 2018 in
Figure 3. It can be seen that the monthly average of nighttime images in 2018 is 163, with the lowest number of 94 in January and the highest number of 250 in November.
2.2. Image Preprocessing
The images contain not only the sky but also ground buildings and topography because of the large field of view of KLCAM. These local background features seriously impact the accuracy of cloud image recognition. Hence, we crop the images by masking the local background objects. Furthermore, we divide the images into subregions in order to identify the distribution of cloud coverage.
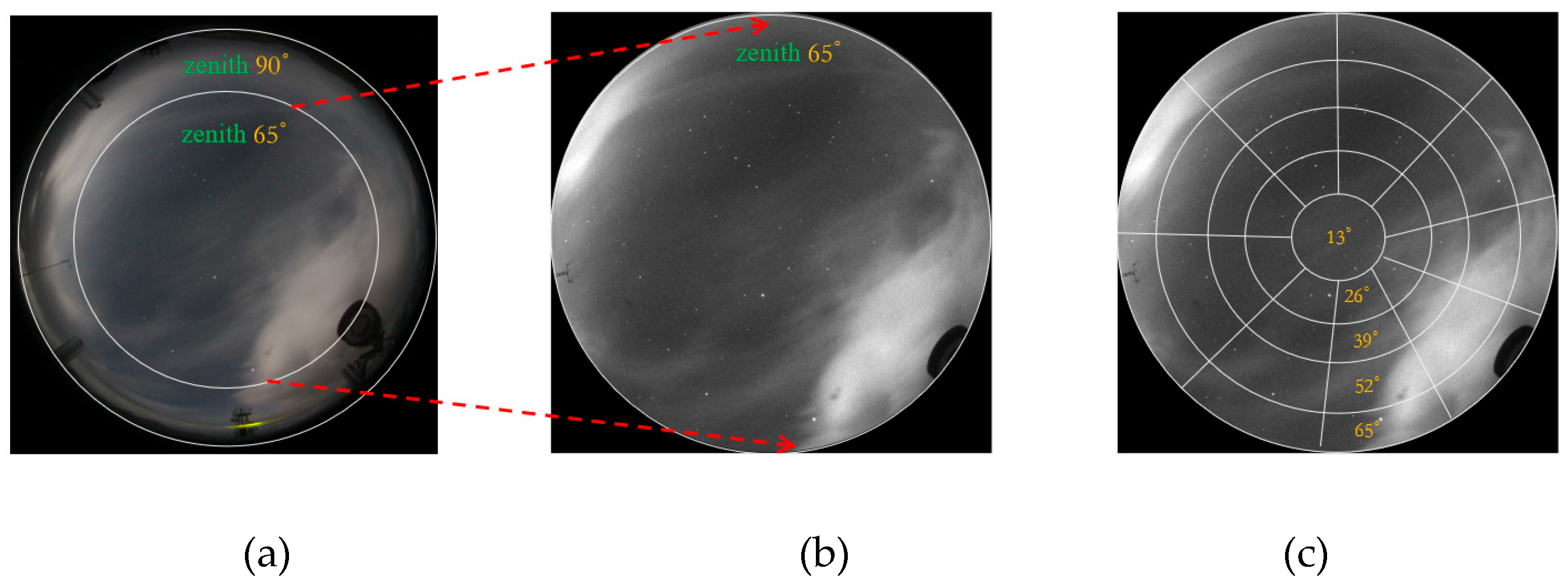
(1) Image cropping: The local background objects, such as buildings, telescopes, and topography elements, have similar characteristics (color or shape) to clouds. These objects may be misclassified as clouds. Furthermore, ground-based astronomical telescopes normally avoid observing objects near the horizon due to significant atmospheric interference and dispersion. Therefore, we mask the portions of the image where the zenith angle exceeds 65°. The size of the image after cropping is 1410*1430 pixels, and all images are saved in 16-bit FITS format. The cropped image is shown in
Figure 4b.
(2) Subregion division: We adopted a method similar to that for TMT site testing method [
3], which is a widely used method to classify the cloud in the field of astronomy. The TMT method divides each image into two rings centered on the local zenith. The outer ring is the area between the zenith angle of 44.7° and 65°. The inner ring is the area within the zenith angle of 44.7°. The advantage of this division is that the outer ring has the same area as the inner ring. The area outside the outer ring is simply ignored because of the observing limit of TMT. In our research, we divide each image into many subregions to get detailed spatial information. The borders of these subregions are defined in terms of zenith and azimuth. First, we divided each image into five rings centered at the zenith, each ring occupies the zenith angle 13°. Then, we divided each image into 37 subregions and the range of azimuth angle of each subregion is 40°. This subregion division has the advantage that segments on the same circle have the same elevation and the same airmass. The labeled subregions are shown in
Figure 4c.
2.3. Data Set Description
A total of 72,446 subregions were taken after the 1958 raw nighttime images are divided. Subsequently, each subregion is labeled manually based on the cloud distribution. Each subregion is classified into three different categories, as depicted in
Figure 4c.
1. Clear: No clouds are detected in subregions.
2. Moon: The presence of the moon distorts or obscures the edges and details of low-brightness clouds. Meanwhile, the moon significantly changes the background of the sky, making astronomical observations unimplementable. Therefore, the subregion with moon is labeled as a "moon" category.
3. Covered: All subregions that do not belong to the "clear" and "moon" categories are classified into this category.
To reduce the subjective assessment, the subregions are marked independently by three individuals. Then, we follow the principle of minority obeying majority if the labeling results are different. This approach increases the reliability of the manual labeling method.
3. Methodology
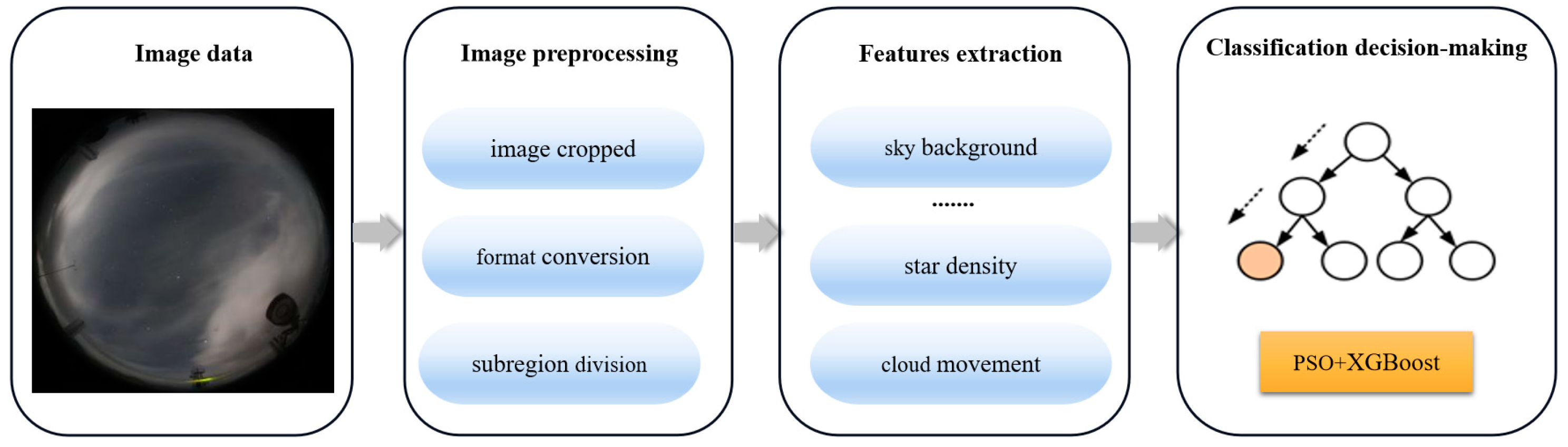
We adopted a PSO+XGBoost model to classify the nighttime cloud images automatically. The workflow of our framework is illustrated in
Figure 5. Our framework has three components: image preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification decision-making. More specifically, image preprocessing is the premise of cloud identification. We apply features extraction to each subregion to produce new features. These new features are fed into the PSO+XGBoost model for cloud identification. The image preprocessing is explained in the previous section. The details of the next two components are presented in the subsequent parts of this section.
3.1. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction generates manageable synoptic data structure from the original time series images, while preserving the characteristics of the original images as much as possible. Feature extraction can reduce the massive of images and use human experience for future processing. Cloud features include the visual features and the non-visual features related to cloud images. We extracted a total of 19 features from the images to train and test our proposed model.
(1) Sky background: The brightness of clouds depends on the sky illumination conditions. Then, clouds appear dark or bright patches against the clear sky. Furthermore, the brightness distribution of the sky background is usually uneven due to the solar or lunar elevation [
17]. We utilize the sky background estimation technique employed in SExtractor [
18,
19] to assess the gray level of the sky background of different subregions. The sky background estimation technique uses the mode value via σ-clipping, and its formula is:
(2) Star density: The number of stars in one subregion varies significantly at different times due to the Earth's rotation and the uneven distribution of stars. However, star density can reflect the clarity of the sky directly. For example, the presence of stars precludes the presence of thick clouds, and a high density of stars normally indicates a clear sky. Therefore, the star density is utilized as a characteristic in cloud image classification. We calculate the star density by dividing the number of stars by the total subregion pixels area. This method can eliminate the variability of subregion sizes.
(3) Cloud gray values: The sky and clouds have different light scattering and reflection characteristics. This induces the different gray values of sky and clouds. Therefore, in order to indirectly reflect the distribution of cloud coverage and cloud thickness, we first calculated the gray values of each subregion and background. Then, the gray values of background are subtracted from gray values of each subregion to obtain the gray values of residual image. The average, median, and standard deviation of grayscale are calculated from residual images as features. Moreover, the gray values of subregions are also highly influenced by the elevation and azimuth angles of moon and sun. Therefore, besides three grayscale features from residual images, we extract other four features for each subregion: solar elevation angle, solar azimuth, moon elevation angle, moon azimuth.
(4) Cloud movement: In addition to the image's visual characteristics, non-visual elements like the surrounding environment can influence cloud properties. Since clouds are seldom stationary, the wind blows the clouds and causes clouds movement at different speeds. The dynamic behavior of clouds influences the distribution within the same subregion. Seven features are derived from the nighttime images that were taken 30 minutes ago. The features include the star density, the median, mean, and standard deviation of gray values of sky background, and the median, mean, and standard deviation of gray values of residual images.
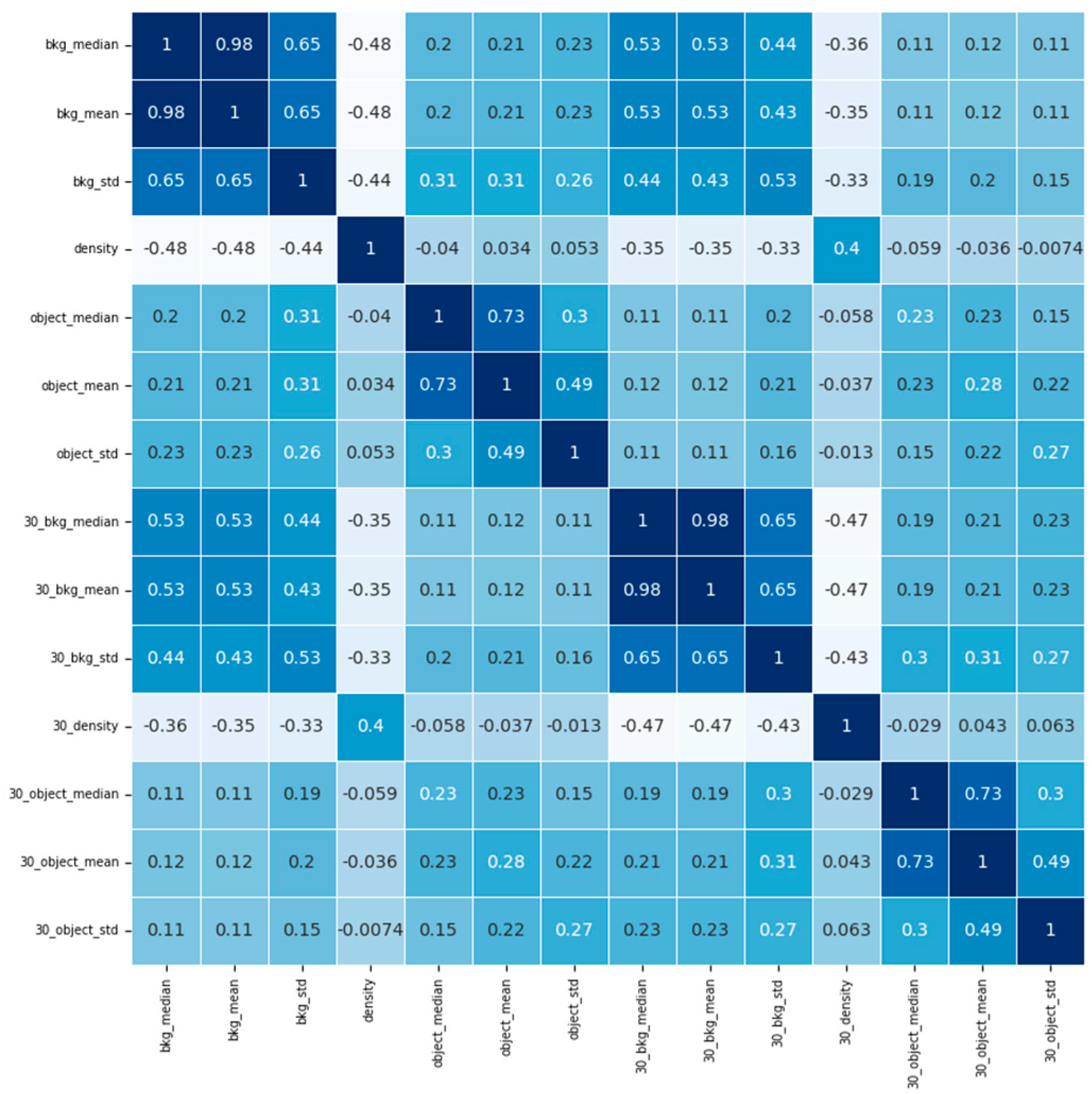
To examine the correlation between features from current images and images 30 minutes ago, we use Kendall coefficient [
20] to calculate the correlation coefficient between features. The Kendall coefficient between variables i and j can be calculated as:
where c is the number of element pairs with consistency in i and j, d is the number of inconsistent element pairs, n is the total number of samples. The value range of
is between −1 and 1. When
≤0.39, it indicates a low correlation. When 0.39≤
≤0.59, it indicates a moderate correlation. When
≥0.6, it indicates a high correlation.
We plotted the correlation matrix between features in
Figure 6, it can be seen that the maximum correlation coefficient between the seven features from the current images and the images 30 minutes ago is 0.53, which is the moderate correlation. The rest of the correlation coefficients are lower than 0.39. Hence, it can be concluded that the cloud movement will not introduce a high correlation in features.
(5) Subregion index: The subregion index of each subregion indicates the location on the local sky. Therefore, the subregion index is selected as a feature.
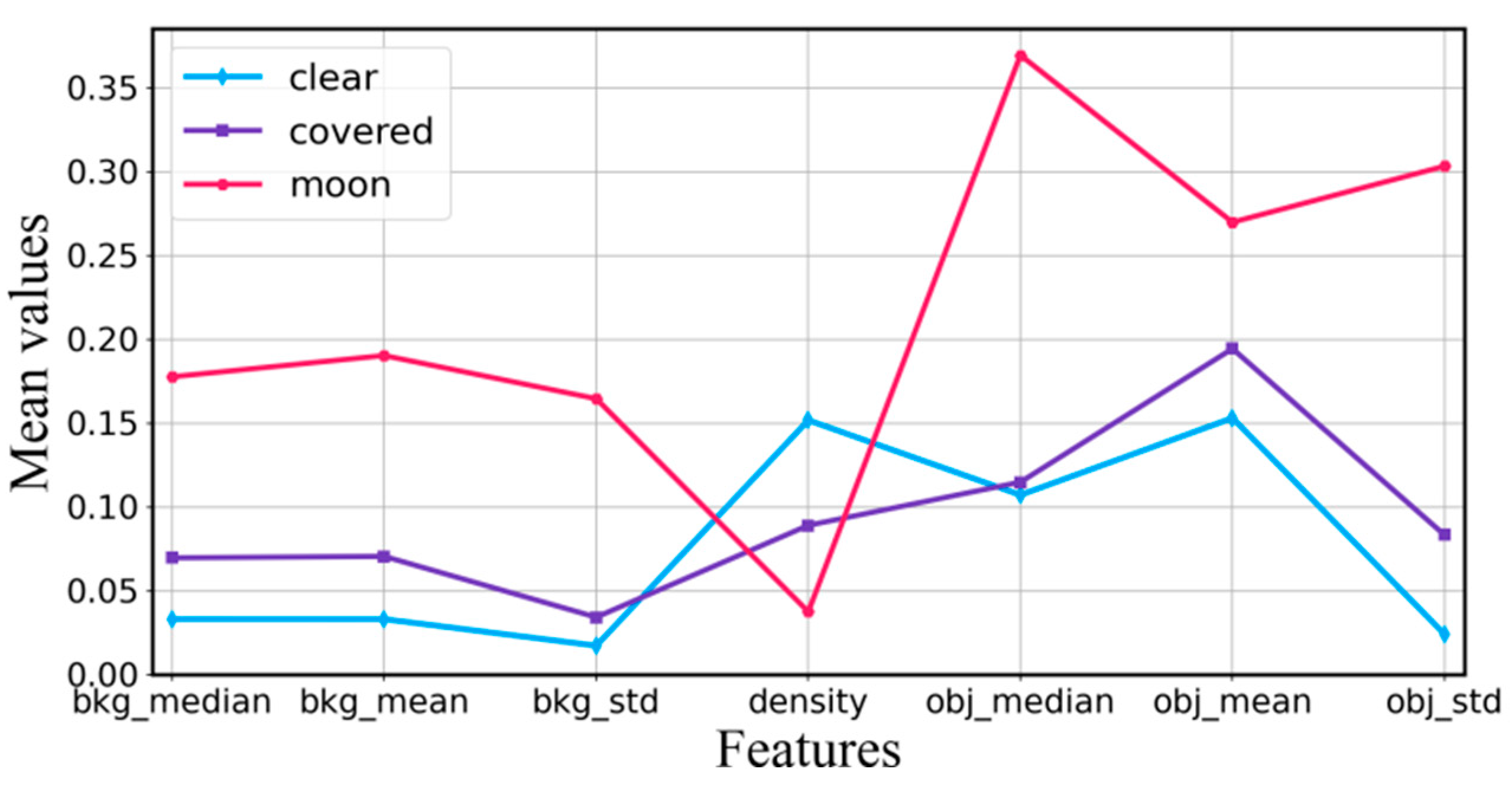
To visualize the relationships between extracted features, we plot three values curves of seven features in
Figure 7. The seven features include the median, mean, and standard deviation of the sky background, star density, and the median, mean, and standard deviation of residual images. These features are normalized, and their mean values are plotted in
Figure 7. From
Figure 7, we can see that the extracted seven features show significant distance differences when the cloud categories are different. It means that there is a high correlation between the features and the categories of clouds. When the moon exists in subregion, all feature values are at its highest position, except the star density. The “covered” feature curve is located between “clear” and “moon” feature curve. When the sky is clear, the value of star density is at its highest position, while all other features exhibit the lowest values.
3.2. PSO+XGBoost
XGBoost is a supervised algorithm based on decision trees. XGBoost utilizes ensemble learning to combine multiple decision trees to form a strong learner. This principle can solve the problem of the weak learning ability of a single decision tree. XGBoost explicitly adds a regular term to control the complexity of the model to prevent overfitting. It constructs multiple Classification and Regression Tree (CART) to make predictions. Each tree is constructed iteratively using the errors of all previous trees and gradually reducing the overall error. The final prediction is the sum of the outputs of all trees. The advantage of XGBoost is that it has outperformance over neural network models in processing uncorrelated tabular data. Moreover, XGBoost has few parameters, a simple structure, and fast training speed on CPU. At actual telescope sites, the computational capabilities is limited because most telescopes are located in remote places. Moreover, the correlation between images is not high. Therefore, XGBoost is suitable for images processing in these situations.
Let
represent the training set with n samples, where the true value for input sample
is denoted by
. In cumulative training, the prediction
at step (k) can be calculated as:
where,
is the predicted value of the first (K-1) trees, and
is the predicted model of the
th tree.
The objective function for regularization and optimization of the learning process is represented as:
where
is a differentiable loss function, which quantifies training error by measuring the difference between predicted classification value(
) and actual value(
). The
is a regularization term used to prevent from overfitting. The definition of the regularization term is as follows:
where
denotes the number of leaf nodes in a tree,
and
are the L1 and L2 regularization coefficients, respectively, and
denotes the weight of the
th leaf node of the tree. For an in-depth exploration of XGBoost, see reference [
14].
The XGBoost model includes essential hyperparameters such as the learning rate, maximum number of iterations, maximum depth, and L2 regularization term. The model performance deeply depends on the expert's experience and the model is prone to local optimization due to the huge number of hyperparameters. To address the issue, various stochastic techniques such as simulated annealin[
21], genetic algorithm[
22] and PSO[
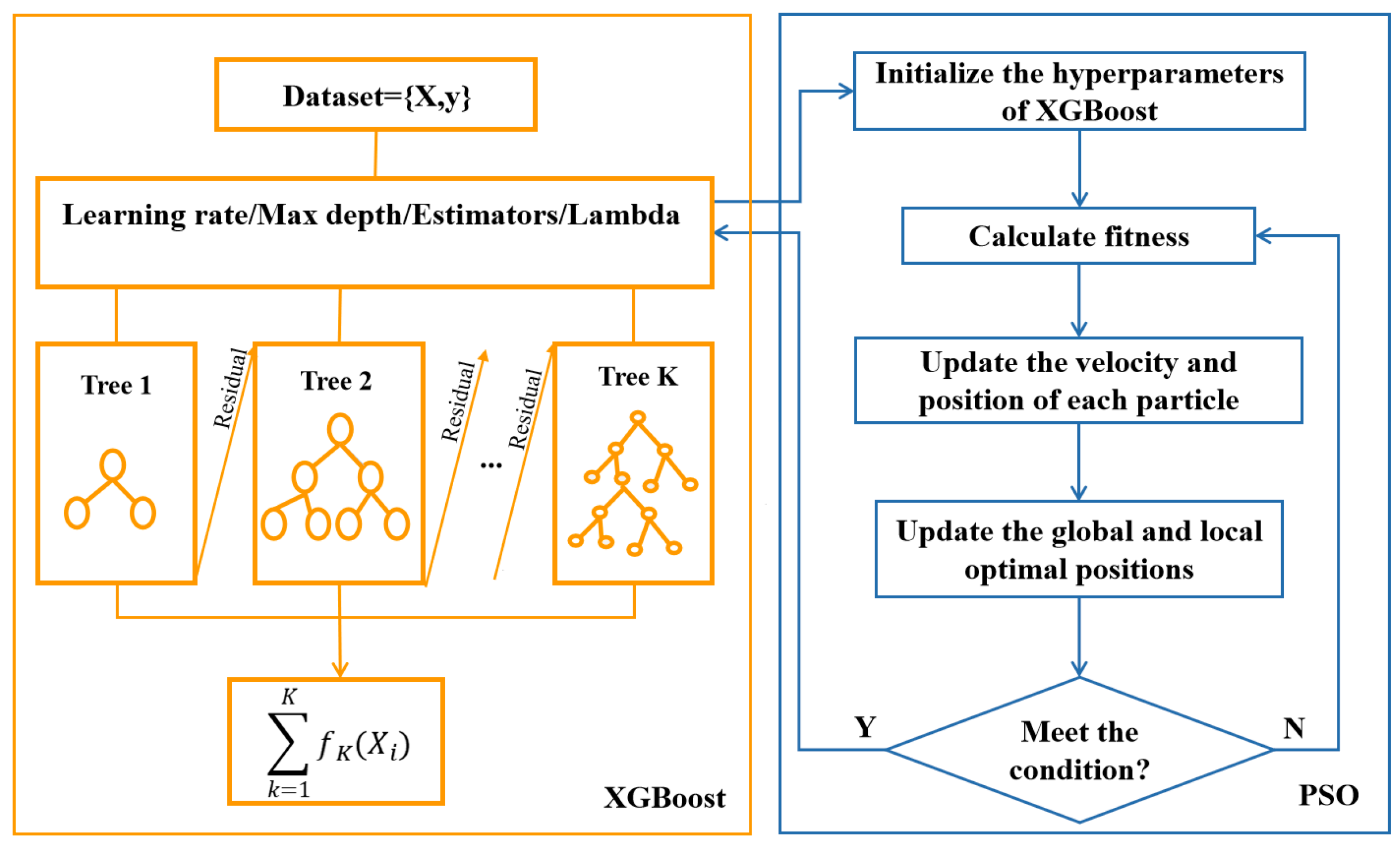
23] are employed. The PSO method possesses several benefits over other algorithms, including robust global search capability, parallel search capability, and straightforward programming implementation. Therefore, PSO is selected for optimizing hyperparameters of XGBoost. PSO algorithm is a heuristic methodology that draws inspiration from the collective foraging activities observed in birds. It continuously alters the movement of the whole group through sharing knowledge among group members. The target of PSO algorithm is to ultimately realize the global optimal solution to the problem. The flowchart of PSO+XGBoost is shown in
Figure 8.
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setup
The experiments were conducted on a customized workstations with an Intel Xeon E5-2683 v4 @ 2.10 GHz CPU, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU, 64GB RAM, and the Windows 10 operating system. The programming environment is Python 3.8, utilizing the integrated development environment PyCharm.
4.2. Model Parameters
We collected 72446 labeled subregions from our 1958 training data images. The detailed label categories are shown in
Table 1. We can see from
Table 1 that the number of “clear” samples is 47378, the number of “moon” samples is 2928, and the number of “covered” samples is 22140. The ratios of “clear”, “moon”, to “covered” samples are approximately 16:1:7. This means that the training sample has class imbalance, and the number of clear sky samples are in the majority compared to other categories. To achieve better performance of the XGBoost model, we set some key parameters of PSO algorithm that determine the physical capacity of the network, including the maximum number of iterations is 25, swarm’s population size is 20, learning factors c1 =1.6 and c2 = 0.4, and weight factor ω= 0.4. We tuned four key hyper-parameters of XGBoost by PSO, including the learning rate, the maximum tree depth, iterations, and L2 regularization. For each set of these hyper-parameters chosen, the model is recompiled, re-initialized, and retrained. Through PSO optimization algorithm, these four hyper-parameters of XGBoost are configured such that the learning rate is 0.16, the maximum tree depth is 8, iterations are 1200, and L2 regularization is 4.15. To evaluate the performance of our proposed model, we have compared our model with four models: SVM, KNN, RF, and LightGBM. The hyperparameters of all models are optimized to achieve the highest classification accuracy. All hyperparameters of five models are listed in
Table 2.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
To evaluate the performance of the model on the test data, we use four evaluation metrics: accuracy, precision, recall and F1
-score. The metrics are expressed as below:
where FP is the number of false-positive instances. TN is the number of true-negative instances. TP is the number of true-positive instances. FN is the number of false-negative instances.
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Comparison of Different Models
In this study, 72,446 samples are randomly allocated into training and testing sets in the ratio of 8:2.
Table 3 presents the classification results for various cloud categories and the classification time for one cloud image. The classification accuracy of the PSO+XGBoost model reached 96.91%, surpassing SVM, KNN, RF, and LightGBM by 29.46%, 11.17%, 1.90%, and 0.53% respectively. In addition, the PSO+XGBoost model exhibited superior precision, recall, and F1 score in the "clear," "moon," and "covered" categories. This results validated that our proposed model has remarkable performance in classification recognition in terms of accuracy and stability. Additionally, the classification time of our proposed model for one cloud image is 0.975 seconds. The classification time can meet the demand of real-time telescope scheduling.
Since the accuracy of PSO+XGBoost and LightGBM is similar, we use independent sample t-test to assess the statistical significance between these two models. The test significance level (α) is established as 0.05, and the original hypothesis (H0) posits that there is no substantial disparity in accuracy. If the p-value is less than 0.05, the two models are regarded to have significant differences. If the p-value is larger than or equal to 0.05, the two models are considered to be not statistically different. The independent sample t-test results between PSO+XGBoost and LightGBM are illustrated in
Table 4. As can be seen, the p-values is 0.006< 0.05, indicating a significant statistical difference.
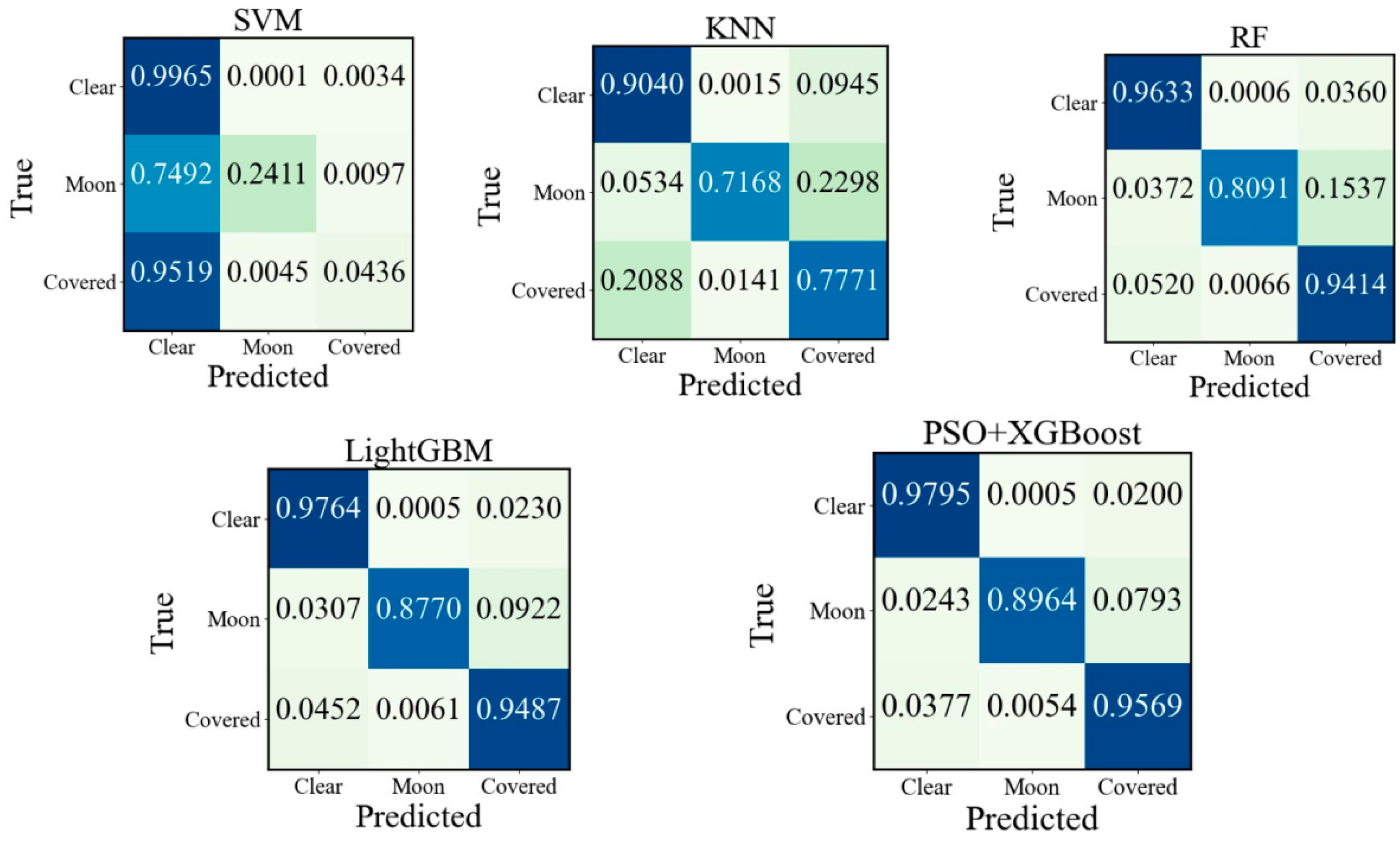
To evaluate the classification results more intuitively, a confusion matrix is used to express the relationship between the classification result and the true label. The corresponding result is depicted in
Figure 9. The horizontal axis of the confusion matrix represents the predicted labels of the cloud image samples, while the vertical axis represents the true labels. The main diagonal elements represent the correct classification results. As shown in
Figure 9, the classification accuracy of PSO+XGBoost for the “clear” class is 97.95%, which is higher than SVM, KNN and RF by 1.70%, 7.55% and 1.62%, respectively, and higher than LightGBM as reported in the paper [
13] by 0.31%. The classification accuracies for “moon” and “covered” samples are 89.64% and 95.69%, respectively. Therefore, PSO+XGBoost has the best performance among all models. In the PSO+XGBoost confusion matrix, the highest probability of misclassification is “moon” class, and the probability that “moon” class is misclassified to “covered” class accounted for 7.93%. The main reason is that the moon in some cloud images is small, which causes their grayscale values are similar to those of the “covered” class. Furthermore, the grayscale values of the brighter clouds at night are similar to grayscale values of moon. The ratio of misclassification from “covered” to “clear” is 3.77%. This misclassification is primarily attributed to poor illumination conditions in nighttime cloud images and the low gray value of the images. These factors result in similar grayscale values for both categories of image samples.
To analyze the relative importance of input feature, we calculated the number of times a feature appears in all decision tree and plotted them in
Figure 10. The more times a feature is used to construct a decision tree, the more important it is. As shown in
Figure 10, it is clear that the elevation angle of moon is the highest importance score in cloud distribution classification. The reason is that when the moon is present, the edges and details of low-luminosity clouds become blurred and difficult to observe. Furthermore, the brightness of the moon severely changes the background of the sky, reducing the observable magnitude and making astronomical observations unimplementable.
4.4.2. Comparative Results of the Manual Observation Technique
In order to evaluate the accuracy and generalization ability of our proposed model, we compared the results with the manual observation at Muztagh[
24]. The manual observation was used to analyze the nighttime cloud images from 2017 to 2021 to determine the number of observable time. The specific method divides the nighttime images into two regions within zenith angles 65°, with the outer one at a zenith angle of 65° and the inner one at 44.7°. The outer and inner circles without clouds are considered “clear”. The term “outer” indicates that clouds are only detected inside the outer ring (between 65° and 44.7° circles). The observable time is the sum of “clear” and “outer”. The percentage of observable time at Muztagh in 2018 is 66% based on manual observation.
To align the evaluation criteria with the manual observation as closely as possible, we segment the nighttime cloud images into an inner circle and an outer circle delineated by zenith angles 39°. The zenith angles for manual observation and our proposed method are 44.7° and 39°, respectively. The difference between zenith angles of inner circle of the two methods is 5.7°. To ensure the reliability of the comparison results, the definitions of cloud distribution and observable time are same for both methods.
Figure 11 displays example images of “clear” and “outer” cloud categories in this paper.
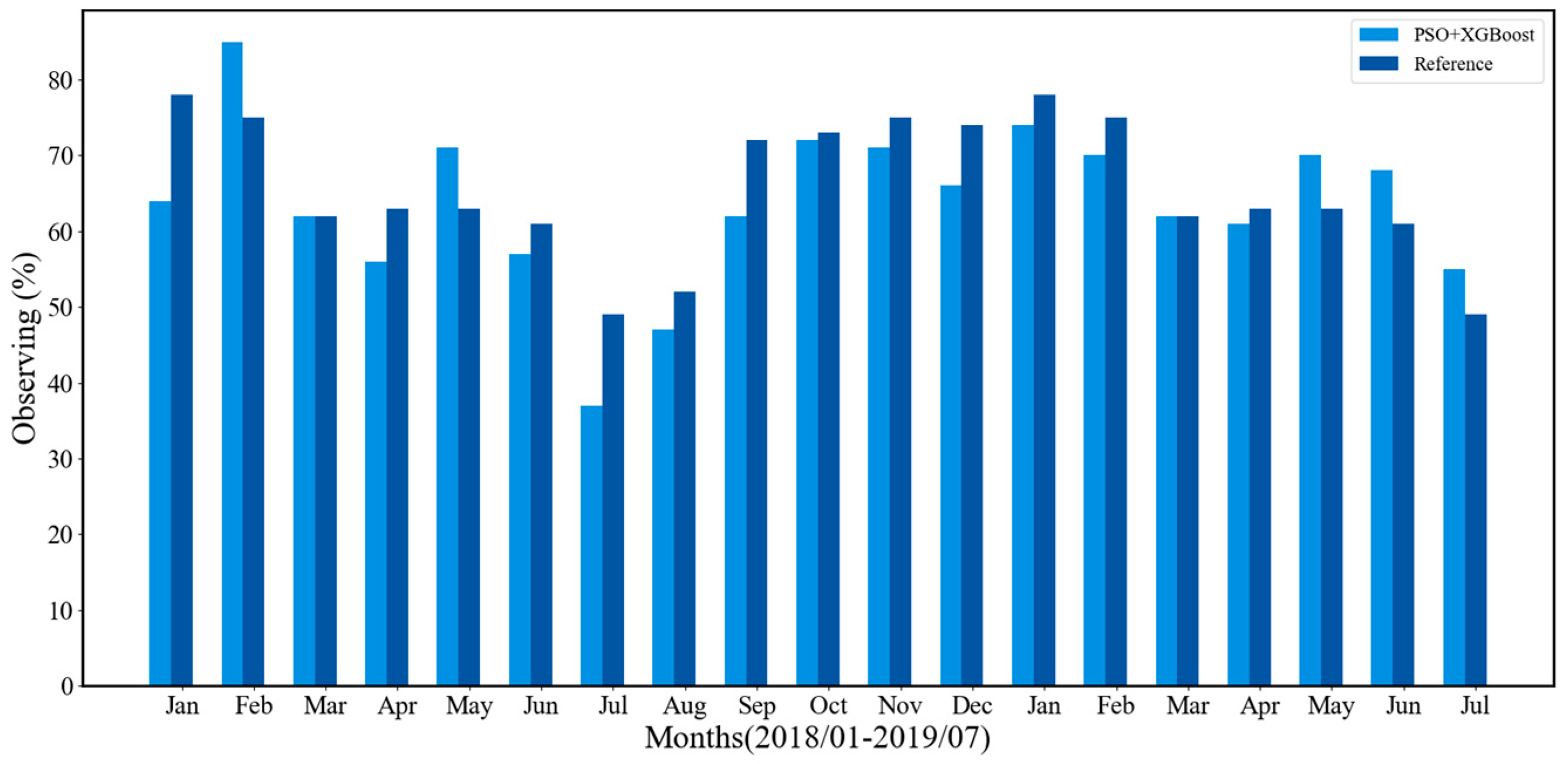
Figure 12 shows the monthly observable time of the manual observation method and the proposed method from January 2018 to July 2019. Comparison with manual observation method, the monthly average error of the proposed method is 7% in 2018, while it is 4.4% in 2019. The maximum error of the proposed method occurred in January 2018, with the error is 14%. The main reason is that the number of available images is small due to underexposed nighttime images. The proposed method achieves 63% of observable time throughout the entire year of 2018, which is less than 3% manual observation. The main reason for this error is that we use an all-sky camera with a 30-minute sampling period. This will lead to variations in cloud cover distribution between consecutive images and some of cloud cover distribution information is missing. In contrast, the sampling period in manual observation method is 5-minute, which can capture more detailed information on cloud distribution.
5. Conclusions
Cloud coverage directly impacts the quality and efficiency of telescope observations. Traditional manual cloud observation methods are subjective and labor-intensive. Therefore, this paper proposes an automatic cloud identification method using PSO+XGBoost. The method utilizes the all-sky camera nighttime cloud images in Muztagh in 2018. We divide nighttime cloud images into 37 subregions. Each subregion is labeled as “clear”, “moon” or “covered” based on the cloud distribution. The experimental results show that the overall classification accuracy of the PSO+XGBoost method reaches 96.91%. The precision, recall, and F1 score outperform other machine learning algorithms, such as SVM, KNN, RF, and LightGBM. To verify the accuracy and generalization ability of the model, the results are compared with manual observation method. The comparison results reveal that the average error in the monthly observable time in 2018 is 7%. These results indicate that the proposed method meets the observation requirements. The classification time of our proposed method for one cloud image is 0.975 seconds. This time meets the real-time requirement of the telescope scheduling program.
Most of the features extracted in this study, however, are based on the grayscale values of the images. In order to improve the classification accuracy and reliability of our proposed method, additional features may be considered in future studies to conduct a more comprehensive understanding of cloud characteristics. These features may include meteorological data, which can influence cloud movement and formation. Moreover, the spectrum can be included in features. The spectrum reflects the physical attributes of the cloud, such as brightness, whiteness, and temperature. In addition, we utilize the subregion division method to determine the celestial position in the sky. The accuracy of position is not high. In the future, we can calibrate the position of objects in images. This will allow us to accurately determine cloud distribution through projection and curve fitting. We can improve the positional accuracy of cloud identification and enable better to schedule of the telescope.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z., F.D. and Y.H.; methodology, X.Z., F.D. and Y.H.; software, X.Z. and F.D.; validation, X.Z. , F.D. , X.H. and K.H.; formal analysis, Z.Z., X.Z., Z.R. and Y.H.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, Y.H.; data curation, F.D. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., F.D. and X.H., K.H. and Y.H.; supervision, F.D. and Y.H.; project administration, F.D. and Y.H.; funding acquisition, F.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research project was supported by the program “the Operation, Maintenance, and Upgrading Fund for Astronomical Telescopes and Facility Instruments”, budgeted from the Ministry of Finance of China (MOF) and administrated by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study can be obtained upon request from the corresponding author. However, they are not accessible to the public as they are subject to laboratory regulations.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of National Astronomical Observatories for their effort in setting up the KLCAM instrument and serving the Muztagh Observatory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zou, H.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ashley, M.C.B.; Cui, X.; Feng, L.; Gong, X.; Hu, J.; Kulesa, C.A.; Lawrence, J.S. SKY BRIGHTNESS and TRANSPARENCY in THEi-BAND at DOME A, ANTARCTICA. The Astronomical Journal 2010, 140, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.S.; Ashley, M.C.B.; Tokovinin, A.; Travouillon, T. Exceptional Astronomical Seeing Conditions above Dome c in Antarctica. Nature 2004, 431, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidmore, W.; Matthias Schöck; Magnier, E.; Walker, D.; Feldman, D.; Riddle, R.; Els, S.; Travouillon, T.; Bustos, E.; Seguel, J. Using All Sky Cameras to Determine Cloud Statistics for the Thirty Meter Telescope Candidate Sites. Proceedings of SPIE 2008.
- Cao, Z.H.; Hao, J.X.; Feng, L.; Jones, H.R.A.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, L.Y.; Song, T.F.; Wang, J.F.; Chen, H.L. Data Processing and Data Products from 2017 to 2019 Campaign of Astronomical Site Testing at Ali, Daocheng and Muztagh-Ata. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics 2020, 20, 082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shang, Z.H.; Hu, K.L.; Hu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Cao, Z.H.; Ashley, M.C.B.; Wang, W. Cloud Cover and Aurora Contamination at Dome a in 2017 from KLCAM. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2020, 501, 3614–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.; Savoy, F.M.; Yee Hui Lee; Winkler, S. Nighttime Sky/Cloud Image Segmentation. arXiv (Cornell University) 2017.
- Afiq, M.; Hamid, A.; Mohd, W.; Mohamad, N.S. Urban Night Sky Conditions Determination Method Based on a Low Resolution All-Sky Images. IEEE Conference Proceedings 2019, 2019, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, T.; Aditi, K. Cloud Detection in All Sky ConCam Images by Gaussian Fitting and Valley Detection in Histogram. 2015.
- Yin, J.; Yao, Y.Q.; Liu, L.Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, H.S. Cloud Cover Measurement from All-Sky Nighttime Images. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2015, 595, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušan Mandát; Pech, M.; Ebr, J.; Miroslav Hrabovský; Prouza, M.; Bulik, T.; Ingomar, A. All Sky Cameras for the Characterization of the Cherenkov Telescope Array Candidate Sites. arXiv (Cornell University) 2013.
- Li, X.T.; Wang, B.Z.; Qiu, B.; Wu, C. An All-Sky Camera Image Classification Method Using Cloud Cover Features. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 2022, 15, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.J.; Zhou, Y.T.; Qiu, B.; Guo, D.J.; Li, M.C. CloudU-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Daytime and Nighttime Cloud Images’ Segmentation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2021, 18, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommert, M. Cloud Identification from All-Sky Camera Data with Machine Learning. The Astronomical Journal 2020, 159, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin. Q. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. CoRR 2016.
- Jin, Q.W.; Fan, X.T.; Liu, J.; Xue, Z.X.; Jian, H.D. Estimating Tropical Cyclone Intensity in the South China Sea Using the XGBoost Model and FengYun Satellite Images. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.H.; Hu, K.L.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, W. Kunlun Cloud and Aurora Monitor. Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Min, Q.L.; Lu, W.T.; Ma, Y.; Yao, W.; Lu, T.S.; Du, J.; Liu, G.Y. A Total Sky Cloud Detection Method Using Real Clear Sky Background. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 2016, 9, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, E.; Arnouts, S. SExtractor: Software for Source Extraction. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 1996, 117, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inside Catalogs: A Comparison of Source Extraction Software. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 2013, 125, 68–82. [CrossRef]
- Du, M.S.; Wei, Y.X.; Hu, Y.P.; Zheng, X.W.; Ji, C. Multivariate Time Series Classification Based on Fusion Features. Expert Systems with Applications 2024, 248, 123452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Luo, Y. Square-Based Black-Box Adversarial Attack on Time Series Classification Using Simulated Annealing and Post-Processing-Based Defense. Electronics 2024, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Darin, J. M.; Edwin, R.T. Optimization of Topological Reconfiguration in Electric Power Systems Using Genetic Algorithm and Nonlinear Programming with Discontinuous Derivatives. Electronics 2024, 13, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, K.J. Research on Carbon Asset Trading Strategy Based on PSO-VMD and Deep Reinforcement Learning. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 140322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, G.J.; Pu, G.X.; Wang, L.T.; Cao, Z.H.; Ren, L.Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, S.G.; Bai, C.H.; Esamdin, A. Site-Testing at the Muztagh-Ata Site v. Nighttime Cloud Amount during the Last Five Years. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics 2023, 23, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).