Introduction
The nanotechnology is the scientific field in which the nanoscale-materials is study between 1 and 100 nm. It is a research area that works at nanoscale and provides number of focal points for a variety of scientific disciplines, including pharmacology, dentistry, and bioengineering [
1]. The prospects for nanomaterials in the future is significantly impacted by green chemistry. The development of secure, environment friendly NPs should be the ultimate goal of this area and it should be widely accepted in the world of nanotechnology [
2]. The properties of the integrated particles, such as their physicochemical properties, shape and size is greatly affected by the solvents and reducing entities used for reduction of nanoparticles, and these properties have also affected the utilization of nanoparticles. For a long time, the traditional methods have been utilized, but studies have revealed that the green methods are widely important for the synthesis of nanoparticles because they are environment friendly, less expensive, simpler to characterize and have less failure risks [
3]. The chemical and physical methods of synthesizing nanoparticles have various consequences for the environment due to their hazardous metabolites. The synthesis process of NPs from plants can be done by using plant extract, a metal salt is created, and the reaction is completed in only a few minutes to a few hours at room temperature. The green synthesis is incredibly attractive due to their toxicity minimizing potential. Because of these consequences, using plant extracts, amino acids and vitamins is popular nowadays [
4].
Although the potential of the biological entities for the reduction of metal precursors has been widely known to scientists since the nineteenth century. Researchers become further interested in the biological processes because of development of the green synthesis which uses the natural capping, stabilizing and reducing agents instead of the hazardous, expensive, and the energy-intensive chemicals [
5]. A significant number of undesired and dangerous compounds are being released, and rapid urbanization, industrialization and growth of population are all responsible for the destruction of the atmosphere of earth. Additionally, there is an excessive need of developing the synthesis methods that not involve the harmful hazardous substances. Biological/Green synthesis of nanoparticles is thus a valid replacement for physical and chemical approaches. The biological entities have enormous potential for synthesis of the nanoparticles. Reduction of precursors of metal biogenically to corresponding nanoparticles is cost-effective, chemically-free, sustainable, and suitable for mass production [
5,
6]. Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) comprised to the group II-VI of the semiconductor nanoparticles. The distinctive optoelectronic capabilities nanoparticles, which are very different from those of the bulk material, are the result of quantum confinement. They are utilized as biological sensors, light emitting diodes, and the subject of substantial research in photocatalysis. They are also used to evaluate the alternative water purifying techniques which is as a result of the growth of industry and growing concern over the environmental effects of organic dyes in water bodies. For the photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under UV or visible illumination, semiconductor nanoparticles like CdS are excellent due to their distinctive photophysical and photochemical features [
7].
In recent years, various attempts to synthesized CdS nanoparticles with green synthesis approach have been made in an effort to meet the high demand for environment-friendly CdS nanoparticles. Wei et al. report the use of starch as capping agent in synthesis of the CdS nanoparticles (15–18 nm). Sanghi et al. reported the immobilized fungus Coriolus versicolor was used to synthesize spherical shaped CdS nanoparticles (100-200 nm) in ambient settings. According to Prasad et al., reproducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus sp. were used to synthesize CdS NPs with sizes of 4.93 and 3.75 nm, respectively. Immobilized Rhodobacter sphaeroides was employed by Bai et al. to synthesize CdS nanoparticles having an average size from 2.3 to 36.8 nm. Bacillus licheniformis bacterium was used to synthesize spherical CdS NPs with a size of less than ~5.1 nm. Lakshmipathy et al. employed the extract of watermelon rind as a stabilizing and capping agent to produce CdS nanoparticles (size ~ 90 nm). According to Srinivasa et al., the tea decoction served as a natural stabilizer in green synthesis of CdS nanoparticles have an average size of 9 nm [
8].
The semiconductor nanoparticles such as CdS, ZnS, and CdSe, among others, have gained more attention in the recent two decades due to their distinct size-dependent electrical and optical properties. CdS nanostructures are given significant precedence over other semiconducting materials due to their tunable band gap, superior chemical stability, and simple and affordable fabrication methods. Researchers have also reported the use of various techniques to synthesize CdS NPs, some of these are chemical precipitation, microwave heating, laser ablation, salvo thermal, hydro thermal, photochemical, and ultrasonic irradiation etc. [
9].
Although many other types of nanoparticles have been synthesized and are being used for various purposes, semiconductor nanoparticles are of particular importance. The interest of researchers in semiconductors in nanocrystalline forms and the processes for synthesizing those NPs has increased significantly over the past few years due to their unique and distinctive spectroscopic and optical features and their uses in environmental remediation. Semiconductor nanoparticles can be utilized to remediate polluted water in addition to sensing and inactivating environmentally harmful gasses. Several semiconductor nanoparticles, including CdS, CdSe, ZnO, ZnSe, and CuO, can be synthesized using various bottom-up manufacturing procedures, but CdS-NPs are the ones that have been the subject of the most research due to their unique physical and chemical characteristics. Since most optical-electronic devices use CdS semiconductor nanoparticles as the sample photoconductor, because they are extremely sensitive to the detection of visible light. CdS nanoparticles play a key role in water filtration as well as water splitting as an electrocatalyst for the analysis of O
2 and H
2 gases. Due to their improved fluorescence and optical qualities, they can be used to improve solar cells efficacy, detect and cure cancer, and for a variety of biological purposes [
10,
11].
Plant History
Fabaceae family Comprises of 257 genus one of them is
Lathyrus which is further comprises of 62 species one of them is
Lathyrus aphaca L. The
Lathyrus is a Neolithic plant genus whose species has spread across three continents and endured millennia of cultivation. It is a tough legume crop that is regarded as one of the most resistant to climate change and as a source of survival food during famines brought on by drought [
12]. Lathyrus maritimus L. (beach pea) seeds and parts of plant were examined for presence and concentration of the phytochemicals, including phenolics, trypsin inhibitor, various types of phosphorus, non-protein nitrogen, oligosaccharides, phytic acid, b-N-oxalylamino-l-alanine (BOAA) and condensed tannins [
13]. The
Lathyrus Aphaca L. specie is an annual herbaceous weed those flourishes in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), India’s fertile and wastelands. The plants have a lifespan of 4 to 5 months and are known to lower saffron and wheat yields. Flowers are little, papilionoid, cream-colored, flawless, odorless, and nectarless. These characteristics define the Fabaceae family, to which this species belongs. In December, the seeds of this plant begin to germinate, beginning its life cycle. After a two-month vegetative phase, the plants spend February and March in the reproductive period, which is when fruit development starts. The acetone extract of the
Lathyrus Aphaca L. stem shows highest radical scavenging activity so it may be used as antioxidant agent [
14]. The two novel triterpenoid saponins were isolated from0020methanolic extract of
Lathyrus Aphaca L. stem, the one compound is the 3-O-[β-D-galactopyranosyl-(14)]-β-D-xylopyranosyl-3β,11α,28-trihydroxy-olean-12-ene-28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside, while compound two is 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4) α-L-arabinofuranosyl 2α,3β,19α-trihydroxy-olean-12-ene which is characterized through spectral analysis, different colour reactions, and chemical degradations. Based on the results of the experiment, it was determined that both substances had an allelopathic effect on the development of shoots from Zea mays seeds. Alkaloids, triterpenes, glycosides, tannins, and the volatile bases have all been found in the leaves of
Lathyrus Aphaca L. specie [
15].
Materials and Methods
Materials:
Grinded powder of Lathyrus aphaca L., Na2S.H2O, (CH3-COO)2 Cd.2H2O, methanol, ethanol, and distilled water, were used as received. Bacterial species, Fungi species, Gentamicin sulphate (40µg/mL) and Fluconazole (20µg/mL) were all obtained from department of Zoology, Government Post Graduate College Mardan.
Extraction:
The preparation of
Lathyrus aphaca L. extract via Soxhlet apparatus was adopted from the literature procedures. 20 grams of the grinded powder of the
Lathyrus aphaca L. plant which was kept in the thimble prepared manually from porous paper, and then inserted in their chamber of the Soxhlet. Extraction was performed in the 200 ml ethanol filled in the flask of Soxhlet fitted at bottom. The upper part of the Soxhlet was fixed in a condenser by the water out and inflow. The evaporation of solvent occurs at the temperature 80 °C over a heat plate in a sand bath, the cycling of solvent occurs by vaporization and going back to chamber for extraction from sample in thimble, and emptied into the flask by reaching the level of liquid extract to siphon arm, this cycle take place again and again. The process was continued to occur until the solvent cannot leave the residue then the solvent was evaporated to get dried extract which is stored until further usage [
16].
Green synthesis of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles
Dissolve 1 g of
Lathyrus aphaca L. extract in 90 ml of distilled water then filtered the aquas extract to remove undissolved residue. Then 1.33 g of Cadmium Acetate was completely dissolved in 35 ml of aquas extract and stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes to form a homogeneous mixture. Then 0.4 g of Sodium Sulphide was completely dissolved in 10 ml of aquas extract and added dropwise to the homogeneous mixture of Cadmium Acetate, the resultant solution was stirred for 1 hour. The appearance of yellow coloration is the visual confirmation of CdS nanoparticles formation. After stirring the solution is then centrifuged and washed with plenty of distilled water 3 times and with ethanol 3 times. Then the obtained product is dried and then annealed at 100 °C to get the final CdS nanoparticles. The dried CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles were then collected and stored for further characterization and utilization for antimicrobial assay [
17].
Preparation of sample solution for antimicrobial assay
The dried nanoparticles were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) for a solution of the concentration 20 mg/mL. For mixing properly, the solution was sonicated for 25 minutes at ambient temperature.
Antibacterial Activity
The antibiotics gentamicin (40µg/discs) was used for comparison of the activity. The bacteria used was Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus species, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. The sensitivity test analysis for antibacterial, the Muller Hinton Agar (MHA) is utilized for preparation of bacterial media. Culture was prepared in media of 250ml distilled water by dissolving the 9.5 g of the MHA. Amber color solution obtained was mixed carefully and boiled with proper agitation for dissolving the agar powder and a clear to slight opalescent type gel was obtained. Then media was autoclave for the sterilization at 121°C temperature, for about 15 minutes. The sterilized media was then allowed to cool down at ambient temperature in the laminar flow hood, then pour 25ml of media in each petri plate and leave for some time for allowing media for solidification. Then spread the microbes’ culture on the media by using swab of cotton that the whole media was cover by turning 90° inclination to avoid leaving any space. About 6 bores was made in each petri plate which was separated from one another by about 2.5cm distance. 10 µl of each sample (125, 250, 500, and 1000 µg/mL concentration) was poured in first four bores, antibiotic in second last bore and the solvent in last bore. Beside this for the positive control, five petri plates are placed for all the microbes having no antibiotic sample was added, while for the sterility of the media negative control, a 1 petri plate is placed having no microbes. All the petri plates were stored in biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) incubator at about 37 °C for 24 hours.
Antifungal Activity
Antifungal activity of the samples was executed on a nutrient agar having fungus species Aspergillus flavus, Alternaria alternata, Collatotrichum dematium, Fusarium roseum, and Curvularia lunata. The culturing was done as the McFarland standard sterilized media which was prepared at the 121°C temperature for about 14 minutes in the autoclave. A well-diffusion method is applied as per requirement after steaking cultured for about 12 to 14 hours. The 10 µL of each sample (125, 250, 500, and 1000 µg/mL concentration) was utilized for activity analysis and 10 µL of Fluconazole (20 µg/mL) was used as the standard. For the positive control, five plates were placed for all the microbes having no antifungal sample, while for the sterility of the media a one petri plate was placed having no microbes as a negative control. Then all the petri plates were stored for the incubation period of about 72 hours at about 20 °C temperature.
Characterization
The characterization of synthesized CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles was performed according to the previous studies with minimal changes. The absorbance spectrum from 200 to 800 nm of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles is recorded by the UV-visible spectrophotometer. Morphology of nanoparticles was characterized by utilizing the SEM (scanning electron microscopy) technique. Elemental analysis was carried out to check the purity and the elemental content of the sample by using the EDX (Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy). The FTIR (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy) analysis was performed in infrared region of the 400 to 4000 cm
−1 for analyzing functional groups in the sample and presence of the phytochemicals on surface of nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried out for analyzing the crystallinity of the sample whose intensities were recorded from 10 to 80° at the 2 Theta angles [
11].
Results and Discussion
The plant powder in the water, or another solvent was used for extraction of chemical constituents or phytochemicals from plant. Here, the Soxhlet method was opted for extraction. The solution of extract prepared in the distilled water was directly utilized for further synthesis of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticle. This approach allowed the direct attachment of phytochemicals to the surface of nanoparticles. The studies of phytochemical of different plants have revealed that all plant extract containing some chemical constituents such as the flavonoids, alkaloids, glycosides, saponins, tannins, carbohydrates, proteins, and steroids. The phenolic metabolites (flavonoids, polyphenols, phenolic acid,) showed extensive potential due to their biological applications. These components protect the plants from the damaging oxidatively and act as good antioxidants for the animals. From historical point of view that the humans were using the medicinal plants by intaking in food for preventing and curing diseases. Since extraction of the plant is alcohol based, results in active phenolic compounds as compared to extracts based on water. The decomposition temperatures of active chemical components of plant are not same. Thus, some of active components are assumed for covering the surface of the nanoparticles. Synthesis of nanoparticles with the addition of plant extract may results in the growth of nuclei in manner that to achieve the lower surface energy to form the spherical nanoparticles. Hence method adopted for growth based on solution, lead to the aggregation of the nanoparticles and reduce high surface energy of the nanoparticles. Phytochemicals’ presence of plant extract can be controlled, which limits rate of growth. Finally, nuclei of the CdS or aggregated structure of CdS was expected to be capped/covered by phytochemicals of plant extract. The hybrid structures synthesized in this manner are protected against the attack of oxygen, and lead to synthesis of stable CdS-LA hybrid structure [
18].
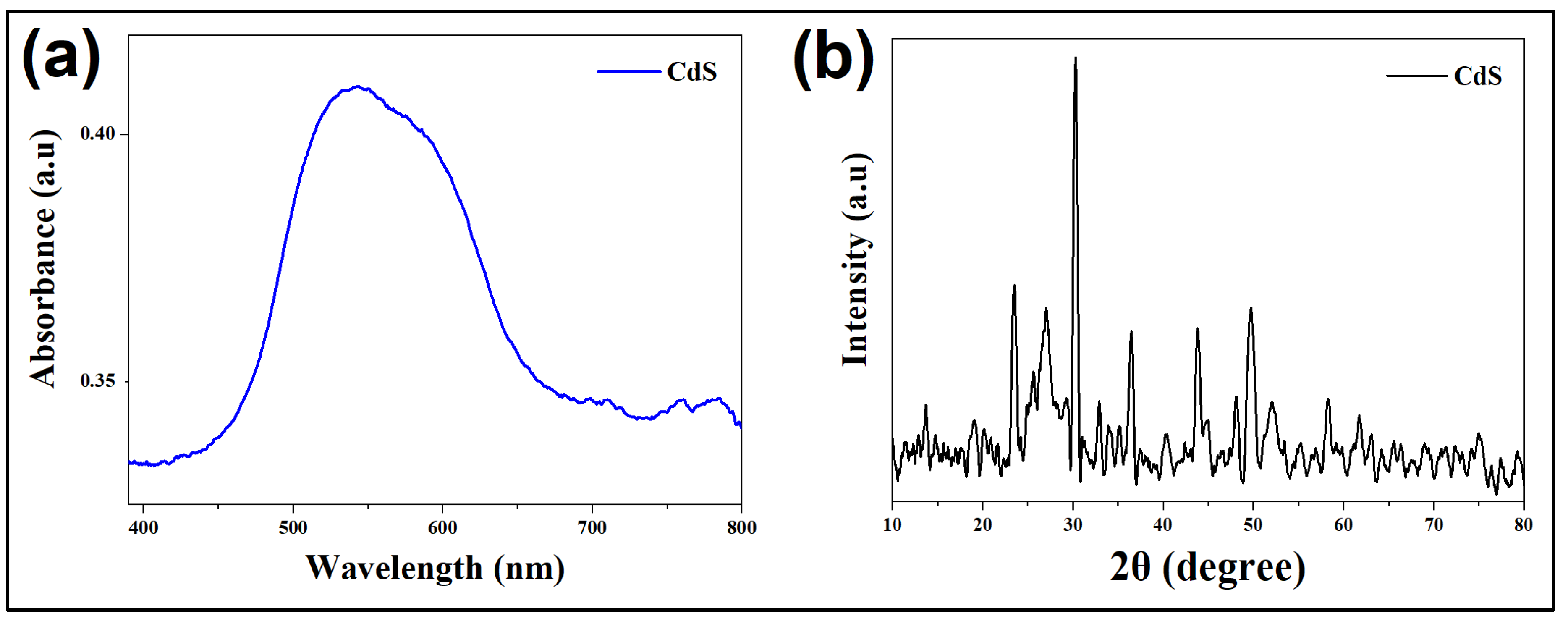
The synthesized CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles (
Lathyrus aphaca L. extract capped CdS nanoparticles) were analyzed structurally by XRD. The pattern recorded were given in
Figure 1. CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles showed a hexagonal crystal structure. The nanoparticles having a plant extract on their surface showed a broad hexagonal peak, which evidenced the presence of nanoparticles of smaller size in sample. The results interpreted are as follows: presence of phytochemicals limit the rate of fast growth of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles, and a slight variation in peak values arises due to the modification of surface induced by plant constituents. The studies reported that plant extract as a reducing/capping agent for the metal nanoparticle and act as a surfactant to lowering the growth rate of nanoparticles. Here plant extract as a source of different chemical constituents is expected to act as a surfactant by decreaseing the growth kinetics and might cover the surface of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles [
18].
The UV-visible spectroscopy was used to recorded the data of absorbance at different wavelengths (
Figure 1). The peak values of absorption of the sample are blue-shifted by addition of plant extract. This shift in peaks is caused due to effect of quantum confinement, that results due to nanoparticles of small size in sample of CdS-LA hybrid. The peak value is 543 nm for the sample CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles. Thus, the clearly confirm the presence of small size nanoparticles, and the result supported the X-ray diffraction analysis [
18].
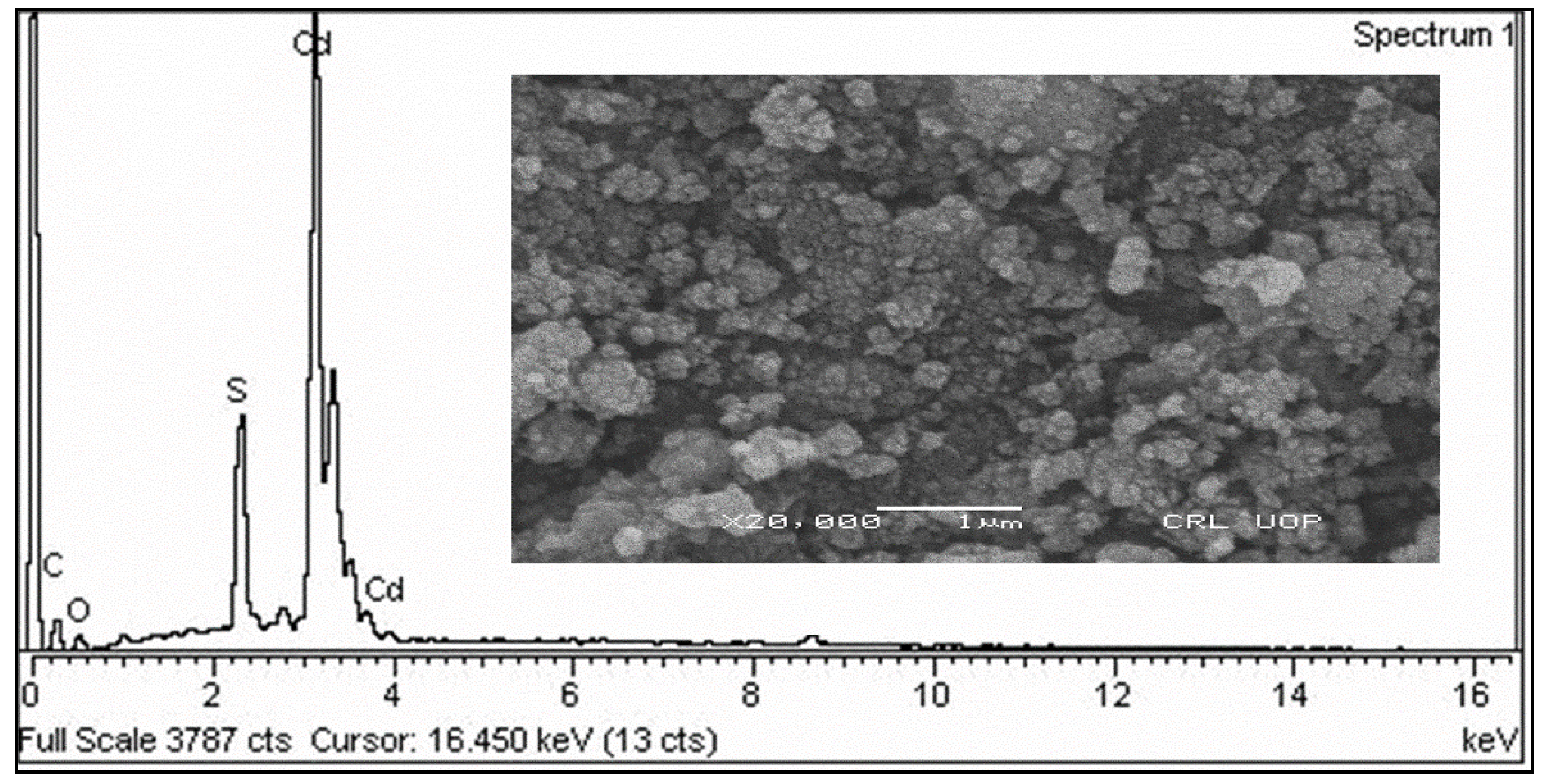
SEM analysis exposed that the surface appearance of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles was homogenous. The morphology of synthesized nanoparticles also showed that the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles have a spherical shape. Furthermore, our results were in compliance with previous previously reported studies [
19]. Hence the hexagonal geometry of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles made it a potent antibacterial agent due to the nanoparticle’s entry in microbial cells on the basis of their structural morphology [
20]. The scanning electron micrograph of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles is shown in
Figure 3.
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles.
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles.
Figure 3.
EDX spectrum and SEM image of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles.
Figure 3.
EDX spectrum and SEM image of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles.
EDX analysis was executed for verification of the CdS-LA hybrid formation. The spectrum of the selected area of the sample is shown in the
Figure 3. The elemental constituents identified in the EDX were Cd (cadmium), S (sulphur), C (carbon), and O (oxygen). The weight percentages of the element other than Cd and S confirmed presence of the phytochemicals of plant extract. Thus, EDX analysis confirmed attachment of the different chemical constituents of plant extract on surface of the CdS nanoparticles [
18].
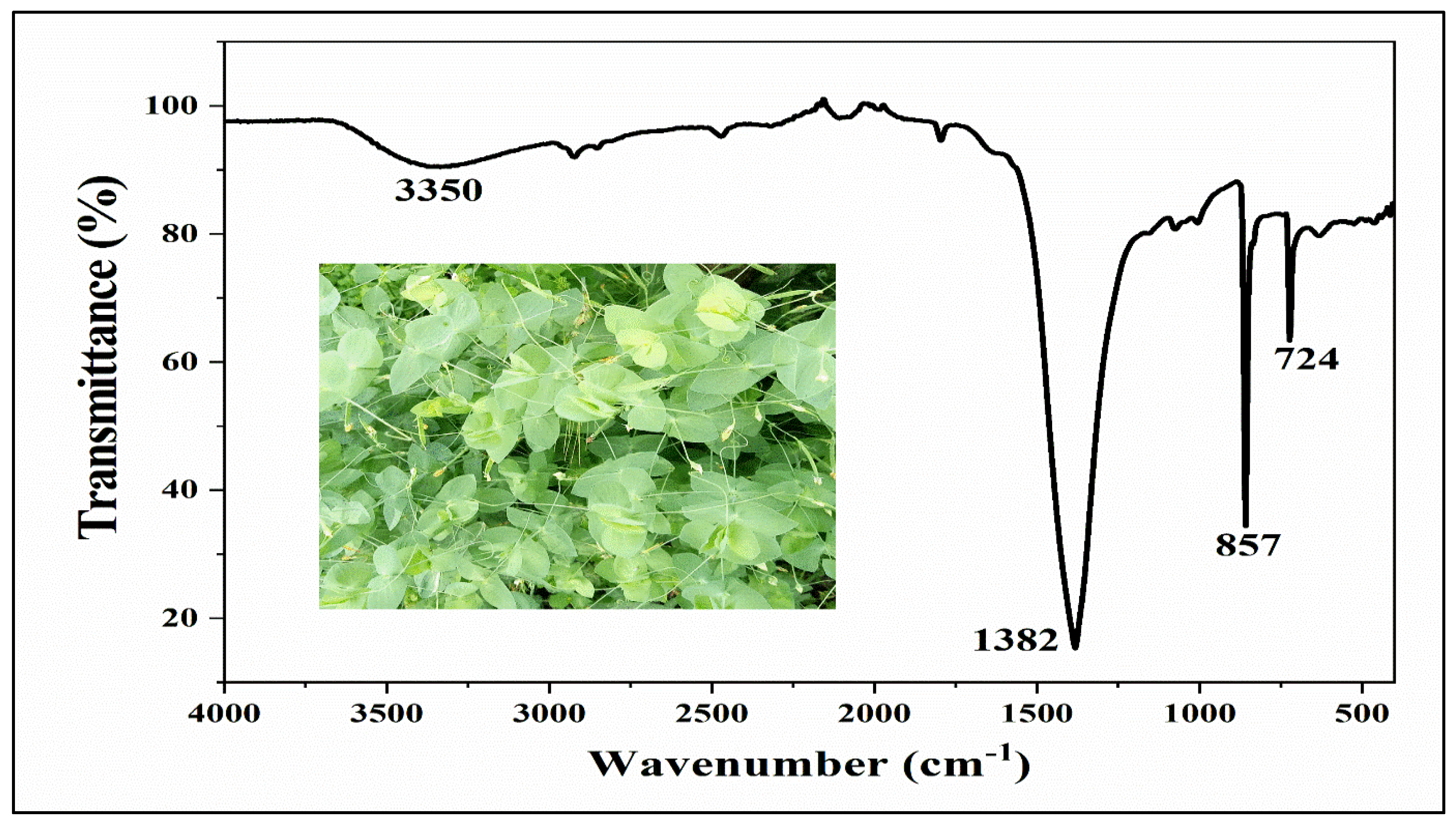
The FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) spectrum of CdS-LA hybrid was demonstrated in
Figure 2. The peaks at 3150-3350 cm
-1 are due to stretching of the -OH group, which indicate presence of the water content on surface of nanoparticles. The peak given at the 1382 cm
-1 was evolved from vibration of the C (carbon) with H (hydrogen). Phytochemicals of plant extract contain H, O, and C as the basic elements in its structure, hence, vibration of the H and C is indication of presence of the phytochemicals on the surface of the nanoparticles. The peaks obtained at 857, 724, 614, and 559 cm
-1 for vibrations of Cd-S bonds. Thus, the results of FTIR agreed with elemental analysis of sample and surface modification of CdS nanoparticle were confirmed by FTIR spectra of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles samples [
18].
Antibacterial Activity:
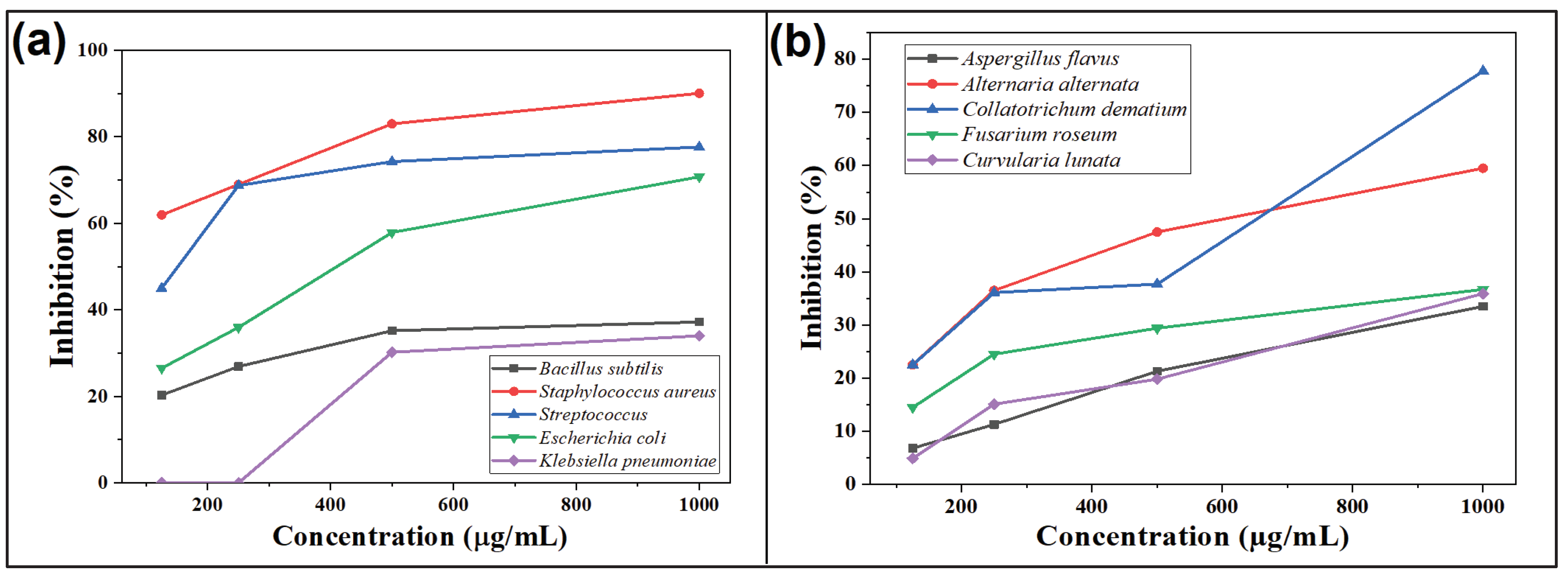
The antibacterial activity of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles was performed on five different species of bacteria. Comparison of the antibacterial activity of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles and standard Gentamicin sulphate against different species of bacteria was performed in which the inhibition zone of Gentamicin sulphate was taken as 100% as shown in
Figure 4. The antibacterial activity of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles recorded is increases with increase in their concentration. The antibacterial activity recorded by different concentration of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles against the five given species of bacteria as shown in
Table 1 but maximum antibacterial activity recorded was recorded against the
Staphylococcus aureus specie. The
Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae which has 13.02, 28.82, 31.06, 26.89, and 10.2mm of inhibition zone respectively by 1000µg/mL of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles as compared to the inhibition shown by standard Gentamicin sulphate (40µg/mL) (
Table 1). The activity was shown by CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles is due to the phytochemicals of the plant extract that are present on the surface of CdS nanoparticles as a reducing and capping agent, which is also responsible for the antifungal activity of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles which was confirmed by the previous study on the antifungal activity of
Lathyrus plant seeds [
21].
Antifungal Activity:
The antifungal activity was performed on the five human and plant pathogenic fungi by ‘Poison food technique. The comparison of the activity of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles and standard Fluconazole against five different species of fungi are given in
Figure 4. The inhibition potential of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles increases with increase in their concentration. The maximum inhibition was shown by 1000µg/mL of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles against the
Collatotrichum dematium fungi which was 77.8%. The
Aspergillus flavus, Alternaria alternata, Fusarium roseum, and
Curvularia lunata which was 33.5, 59.5, 36.7, 35.9% respectively by 1000µg/mL of CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles as compared to the standard Fluconazole (20 µg/mL) (
Table 2). The activity was shown by CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles is due to the phytochemicals of the plant extract that are present on the surface of CdS nanoparticles as a reducing and capping agent which was confirmed by the previous study on the antibacterial activity of extract of
Lathyrus specie [
22].
Conclusion
It was concluded that the green synthesis was employed for CdS nanoparticles synthesis via a simple wet chemical approach. The plant extract was employed for modification of surface of the CdS nanoparticles. The growth dynamics of the CdS nanoparticles could be controlled by using plant extract in synthesis of nanoparticles. The antibacterial and antifungal activity was performed for five different species of bacteria and fungi to evaluate the biological applications of the CdS-LA hybrid nanoparticles The EDX analysis of sample confirmed attachment of the phytochemicals of plant extract with the CdS surface as evident from the elemental analysis. The peak in visible region of absorption spectrum is in between 500-600 nm was attributed to the CdS nanoparticles. The results of the biological activity revealed that the CdS nanoparticles capped by Lathyrus Aphaca extract has inhibition potential against various species of bacteria and fungi which show the biological importance of the green synthesis of nanoparticles using different biological moieties.
References
- M. Rafique, I. Sadaf, M. S. Rafique, and M. B. Tahir, “A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications,” Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, vol. 45, no. 7, pp. 1272–1291, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. S. Varma, “Greener approach to nanomaterials and their sustainable applications,” Curr Opin Chem Eng, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 123–128, May 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. M. Abdelghany et al., “Recent Advances in Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Applications: About Future Directions. A Review,” Bionanoscience, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 5–16, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Gour and N. K. Jain, “Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles,” Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 844–851, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Jayaseelan et al., “Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi,” Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, vol. 90, pp. 78–84, May 2012. [CrossRef]
- I. Hussain, N. B. Singh, A. Singh, H. Singh, and S. C. Singh, “Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application,” Biotechnol Lett, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 545–560, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Rao and G. Pennathur, “Green synthesis and characterization of cadmium sulphide nanoparticles from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and their application as photocatalysts,” Mater Res Bull, vol. 85, pp. 64–73, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Tudu, M. Zubko, J. Kusz, and A. Bhattacharjee, “CdS nanoparticles (< 5 nm): green synthesized using Termitomyces heimii mushroom–structural, optical and morphological studies,” Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process, vol. 127, no. 2, pp. 1–9, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Rao and G. Pennathur, “Green synthesis and characterization of cadmium sulphide nanoparticles from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and their application as photocatalysts,” Mater Res Bull, vol. 85, pp. 64–73, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Ullah, S. Rasheed, I. Ali, and N. Ullah, “Plant Mediated Synthesis of CdS Nanoparticles, their characterization and application for photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic dye,” Chemical Review and Letters, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 98–107, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Shivashankarappa and K. R. Sanjay, “Escherichia coli-based synthesis of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity studies,” Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 939–948, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Lambein, S. Travella, Y. H. Kuo, M. Van Montagu, and M. Heijde, “Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.): orphan crop, nutraceutical or just plain food?,” Planta 2019 250:3, vol. 250, no. 3, pp. 821–838, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- U. D. Chavan, D. B. McKenzie, R. Amarowicz, and F. Shahidi, “Phytochemical components of beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L.),” Food Chem, vol. 81, no. 1, pp. 61–71, May 2003. [CrossRef]
- R. N. Yadava and N. Asati, “ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY OF EXTRACTS OF LATHYRUS APHACA LINN,” Yadava et al. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, vol. 7, p. 995, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Iqbal, M. I. A. Rehmani, S. Sagheer, N. Kaleem, and J. Muneer, “Herbicidal potential of some dry land plants against lathyrus aphaca (L.), winter season weed,” Planta Daninha, vol. 38, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Hassan, H. Ullah, and M. G. Bonomo, “Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of the Medicinal Plant Veronica biloba,” J Chem, vol. 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- “Photocatalytic Activity of Heavy Metal Doped CdS Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using Ocimum sanctum Leaf Extract,” Biointerface Res Appl Chem, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 12547–12559, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Naranthatta, P. Janardhanan, R. Pilankatta, and S. S. Nair, “Green Synthesis of Engineered CdS Nanoparticles with Reduced Cytotoxicity for Enhanced Bioimaging Application,” ACS Omega, vol. 6, no. 12, pp. 8646–8655, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Kumar, R. K. Sharma, N. Goyal, and S. Gautam, “Synthesis, characterization & study of Ni-doped CdS nanoparticle for high voltage application,” Vacuum, vol. 160, pp. 75–80, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Azam et al., “Microbial synthesized cadmium oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and protein leakage in bacterial cells,” Microb Pathog, vol. 144, p. 104188, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Khan, “Two antifungal active triterpenoid saponins from the seeds of Lathyrus plants,” Nat Prod Res, vol. 25, no. 18, pp. 1687–1694, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- N. Khan, S. Quereshi, … A. P.-T. J. of, and undefined 2009, “Antibacterial activity of seed extracts of commercial and wild Lathyrus Species,” journals.tubitak.gov.trNA Khan, S Quereshi, A Pandey, A SrivastavaTurkish Journal of Biology, 2009•journals.tubitak.gov.tr, vol. 33, no. 2, 2009. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).