Submitted:
02 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias within Studies
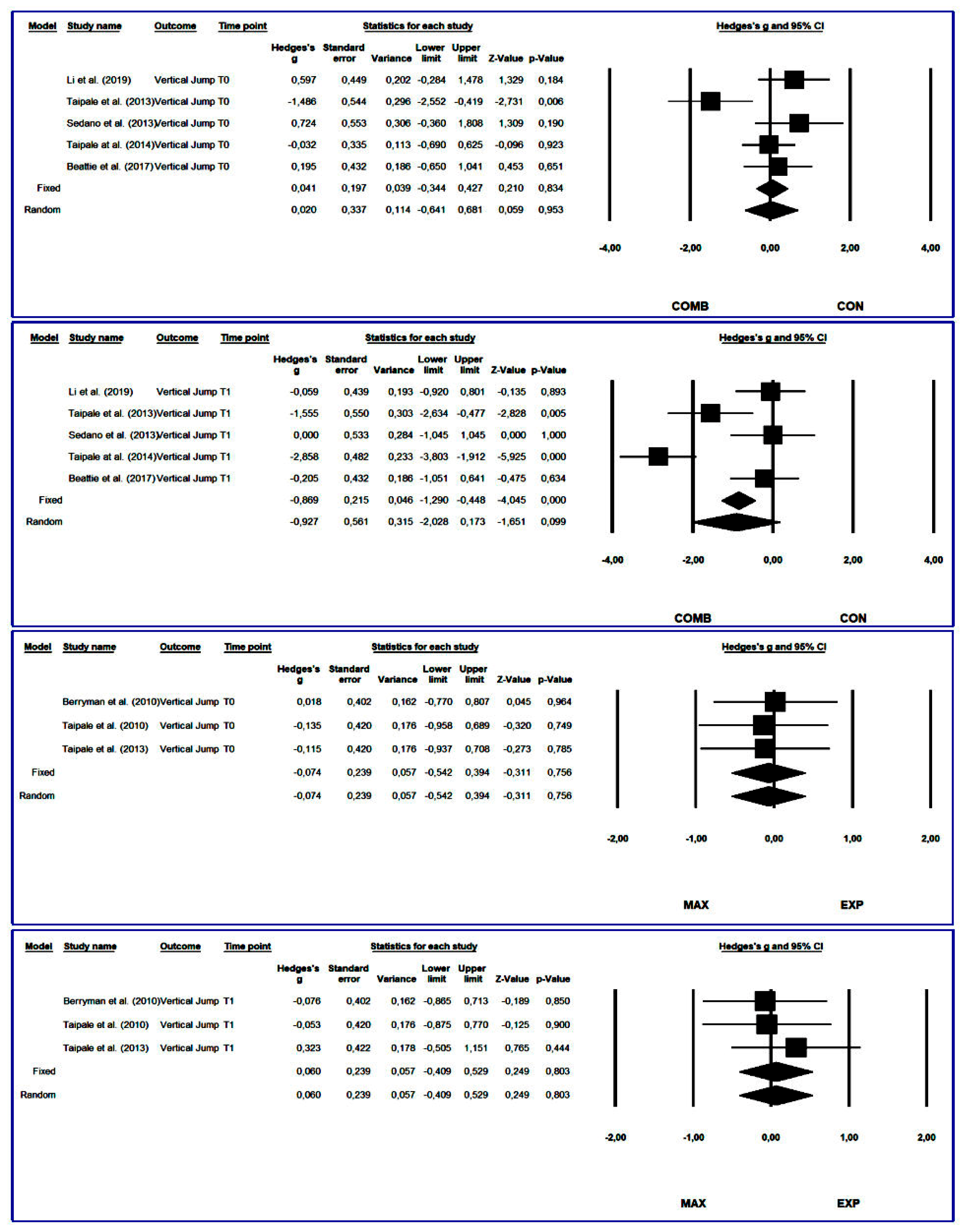
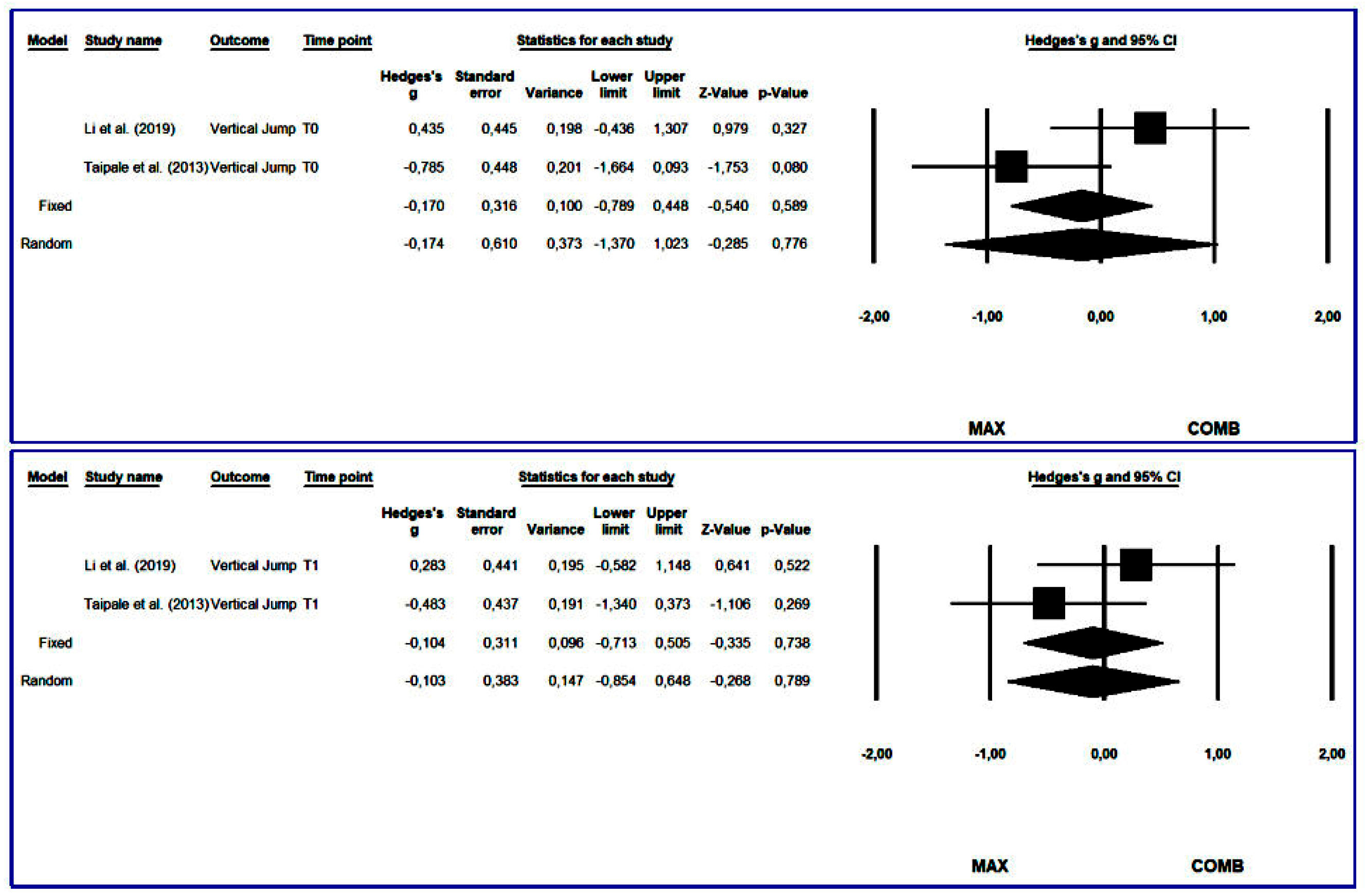
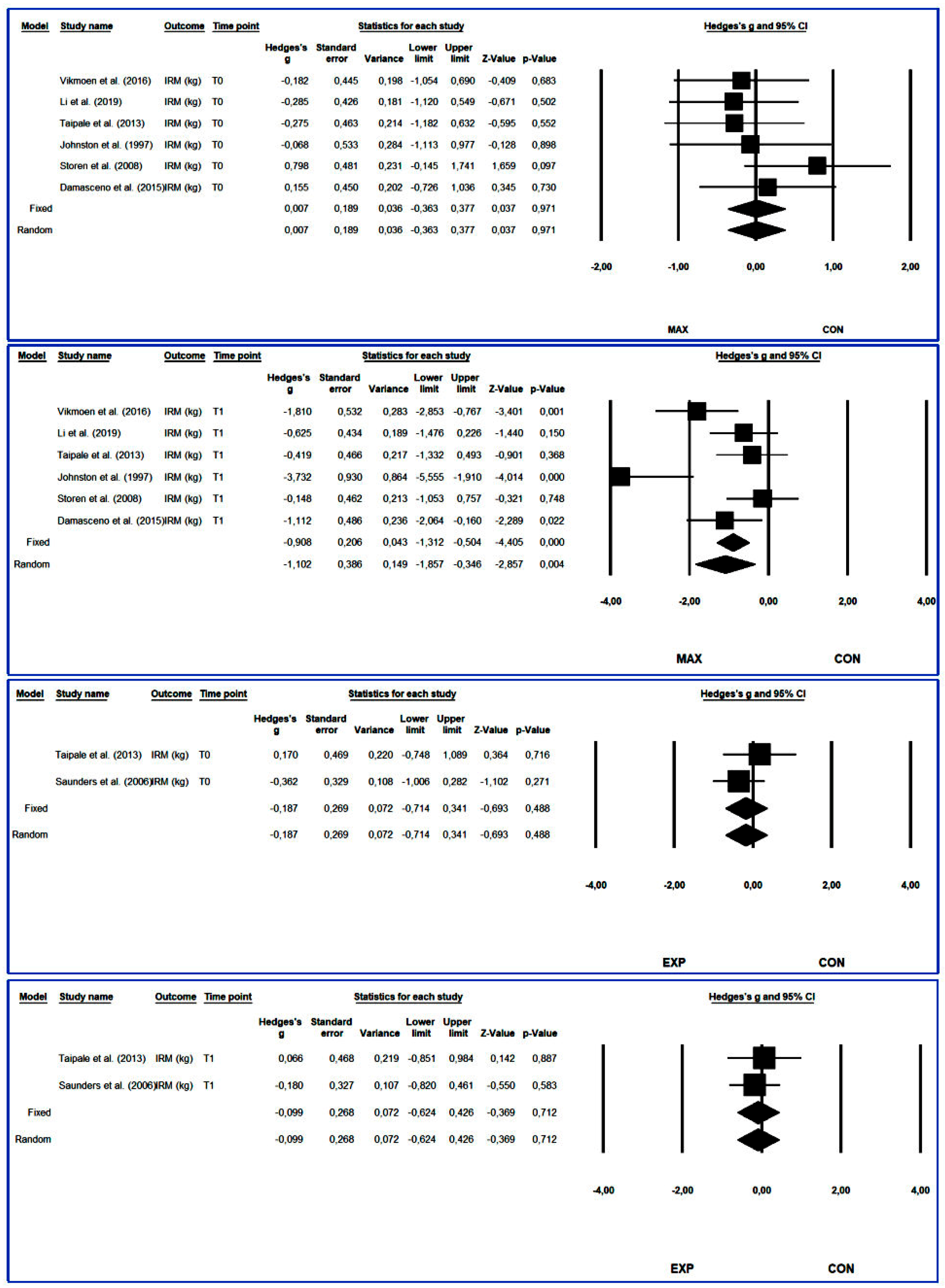
3.4. Synthesis of Results
3.4.1. Vertical Jump
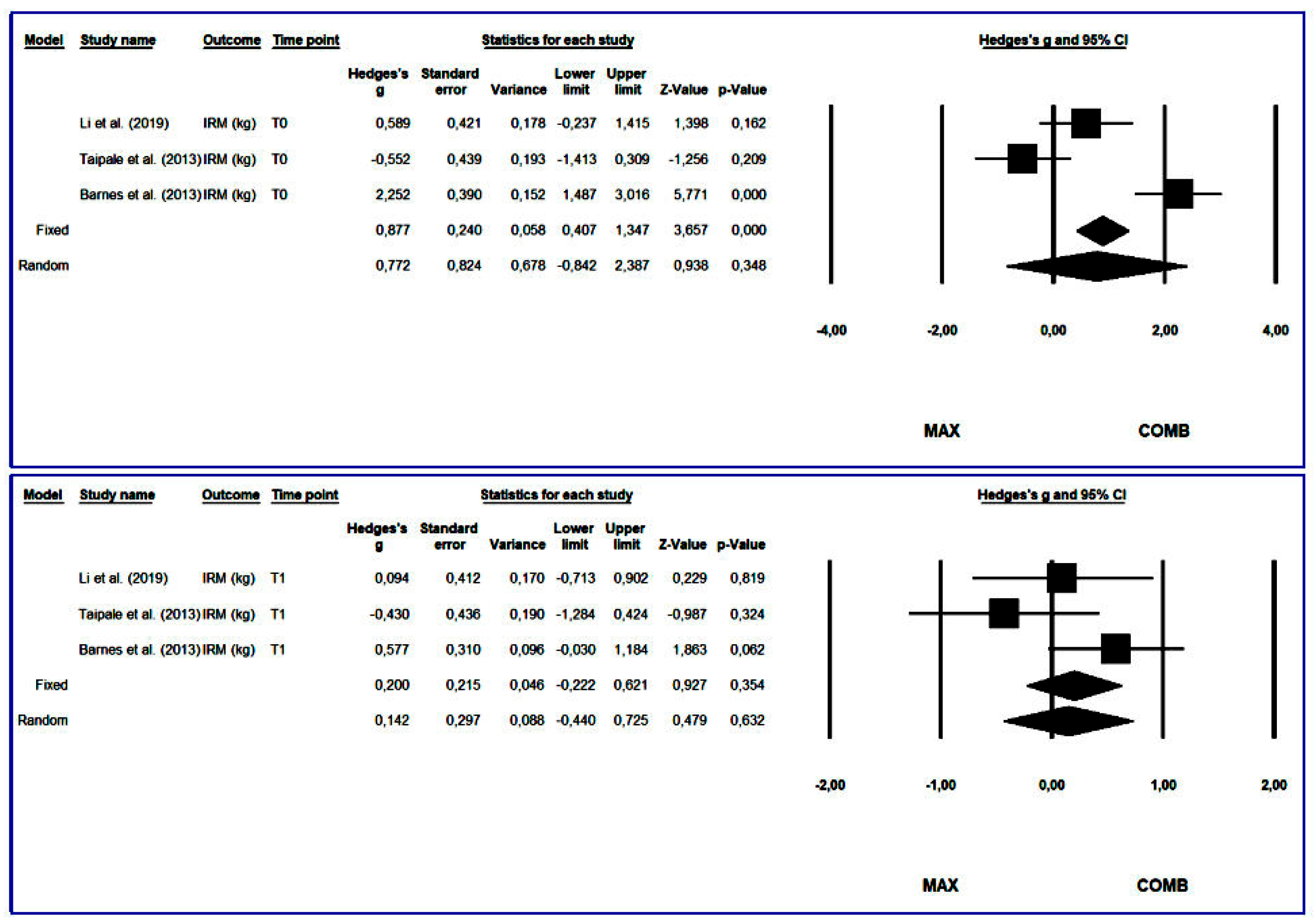
3.4.2. One-Repetition Maximum Squat
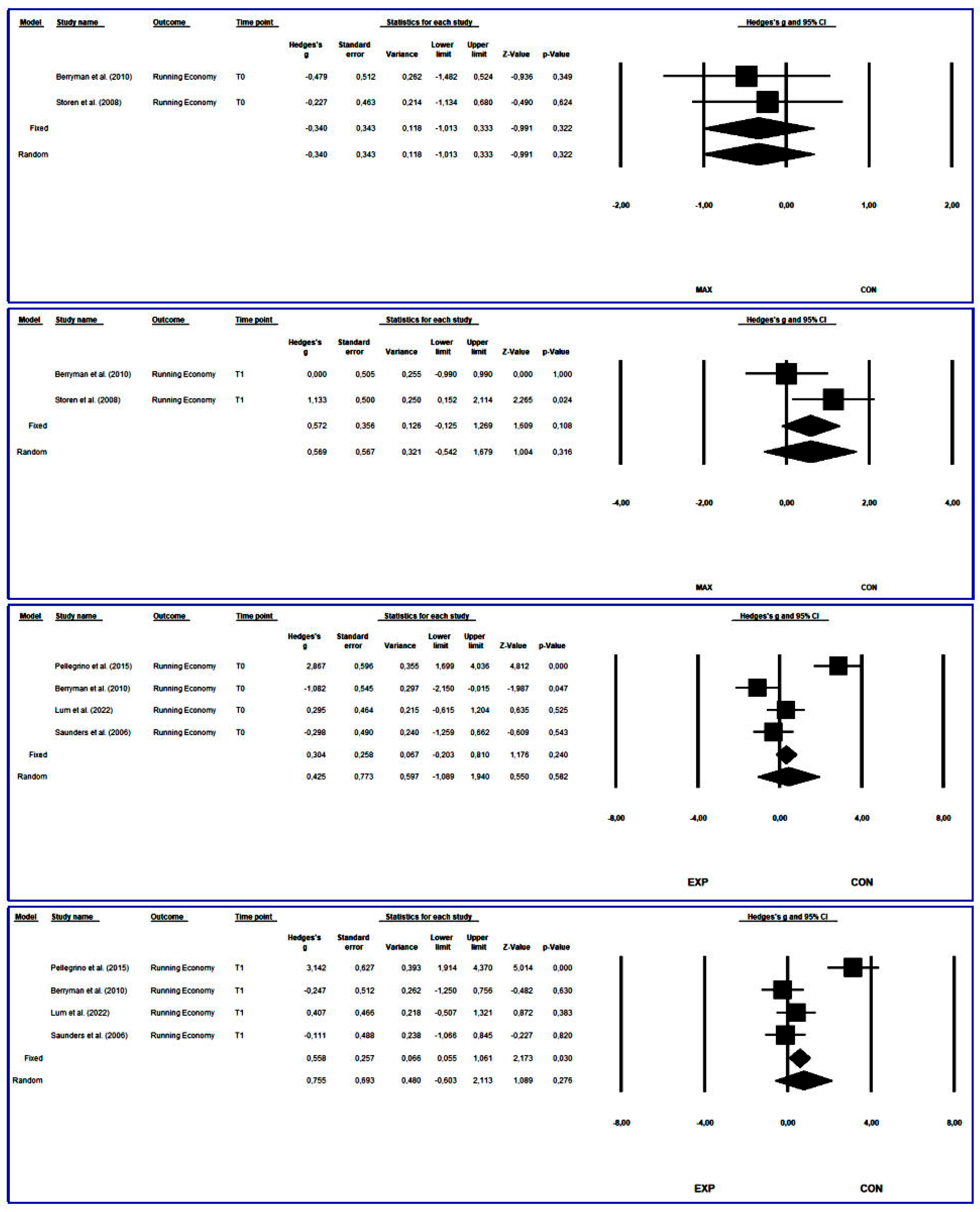
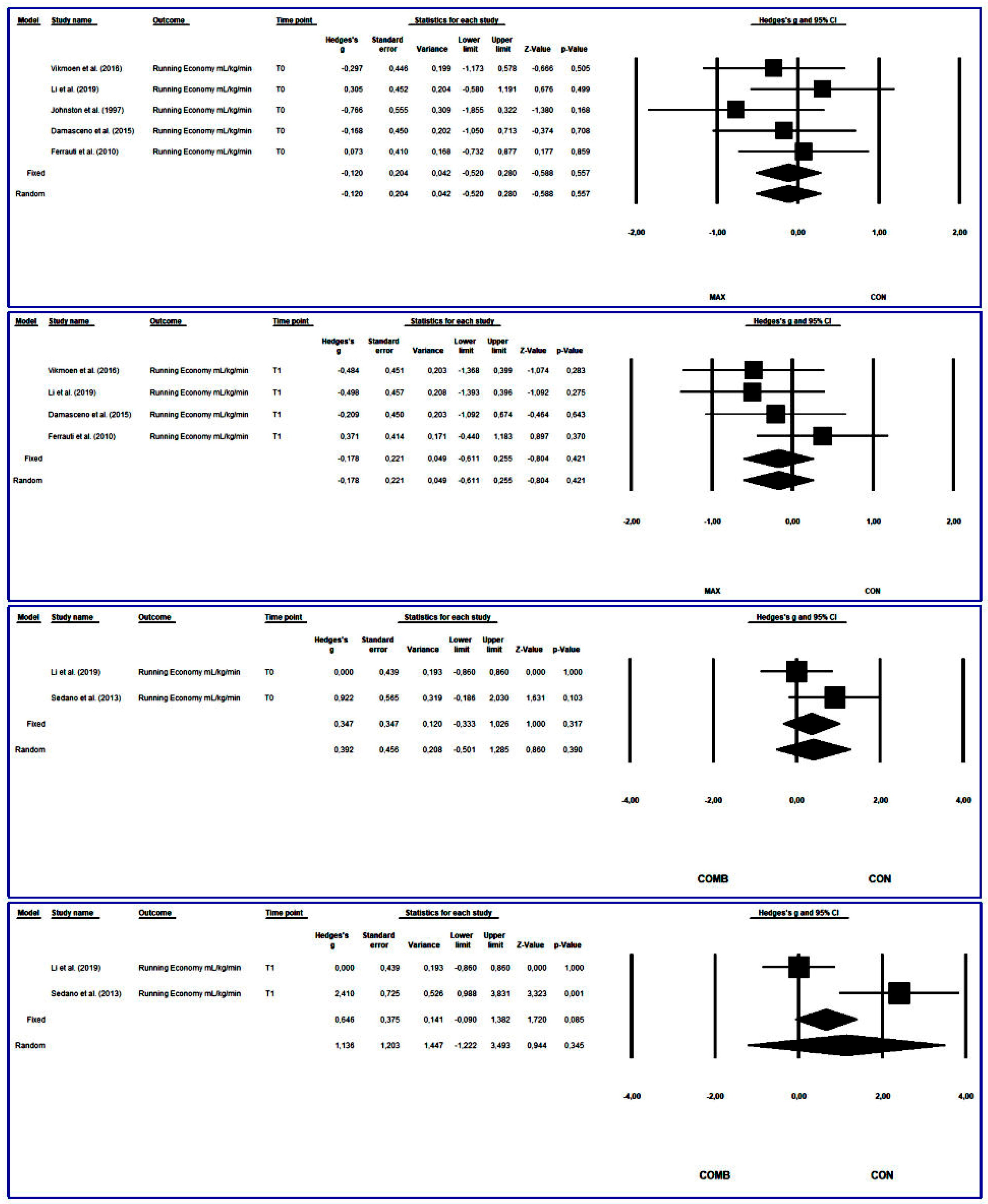
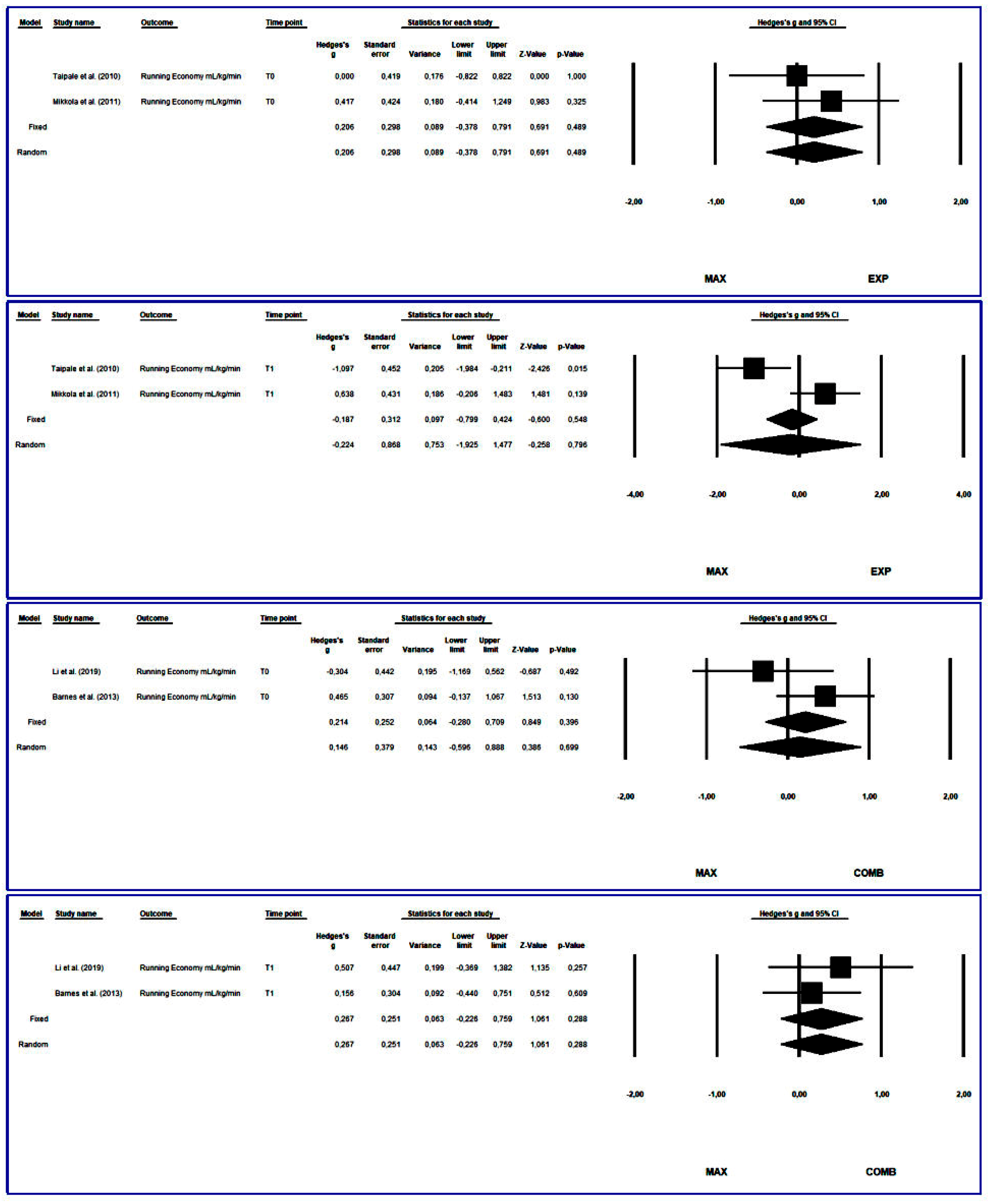
3.4.3. Running Economy
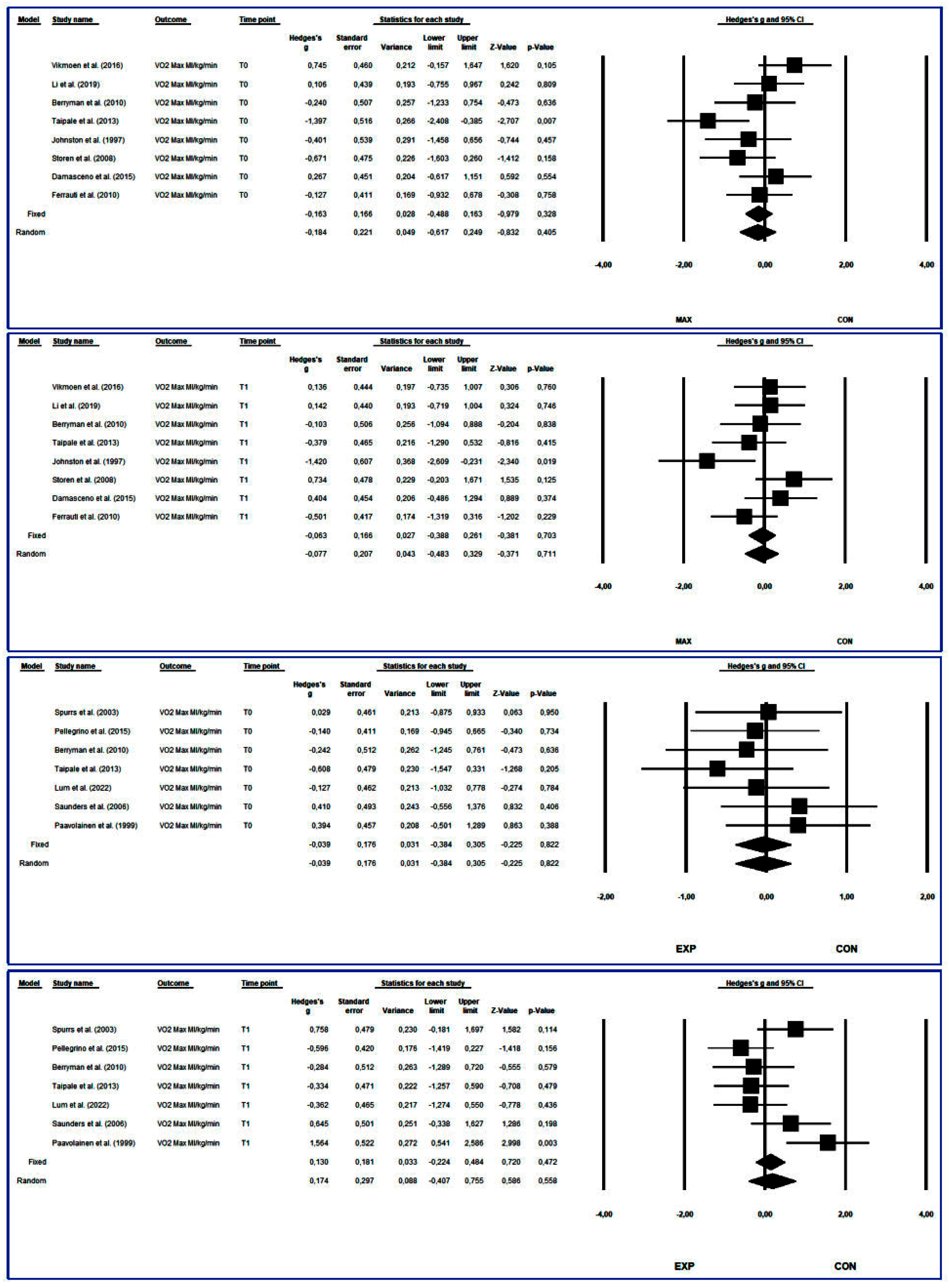
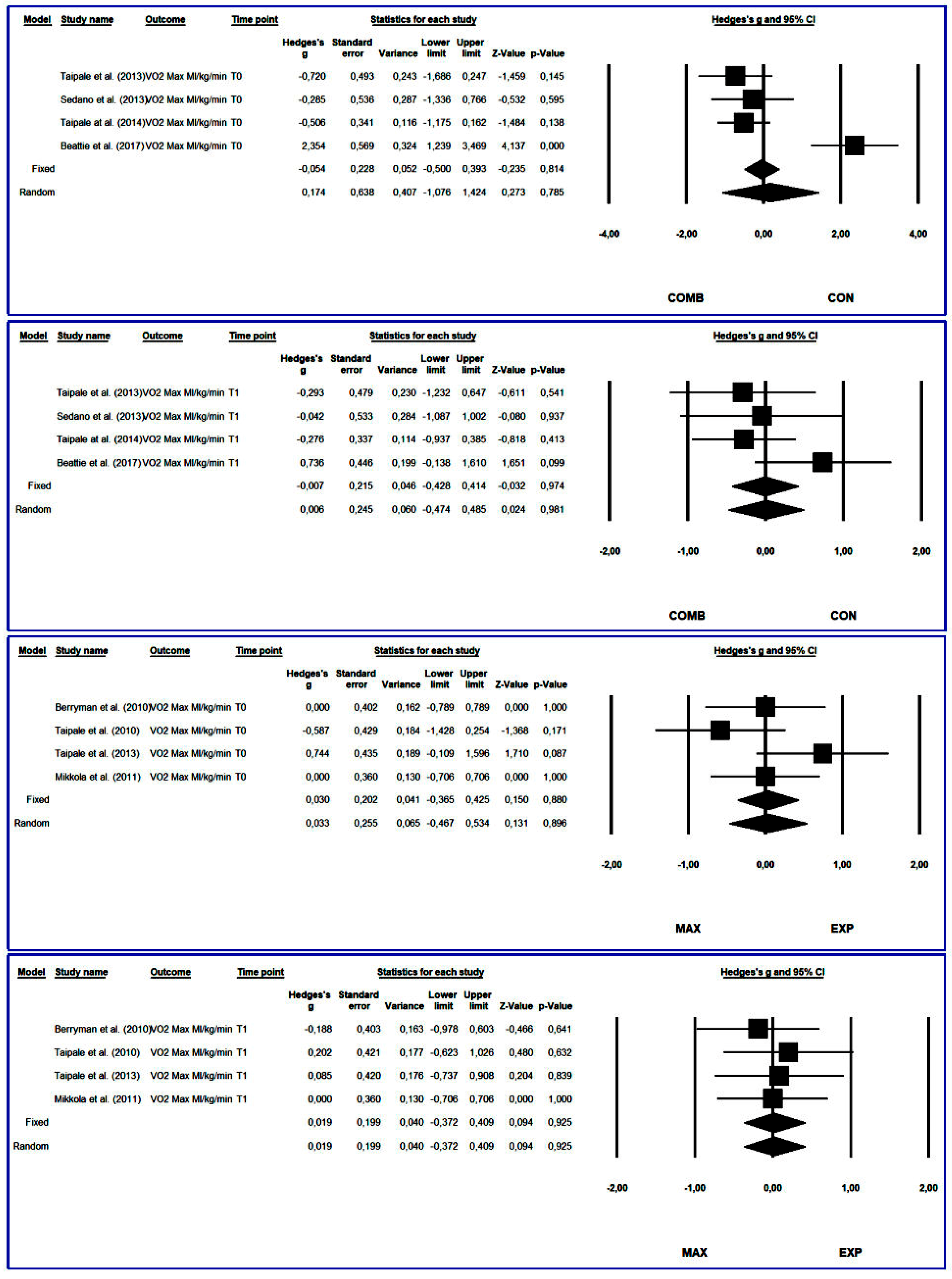
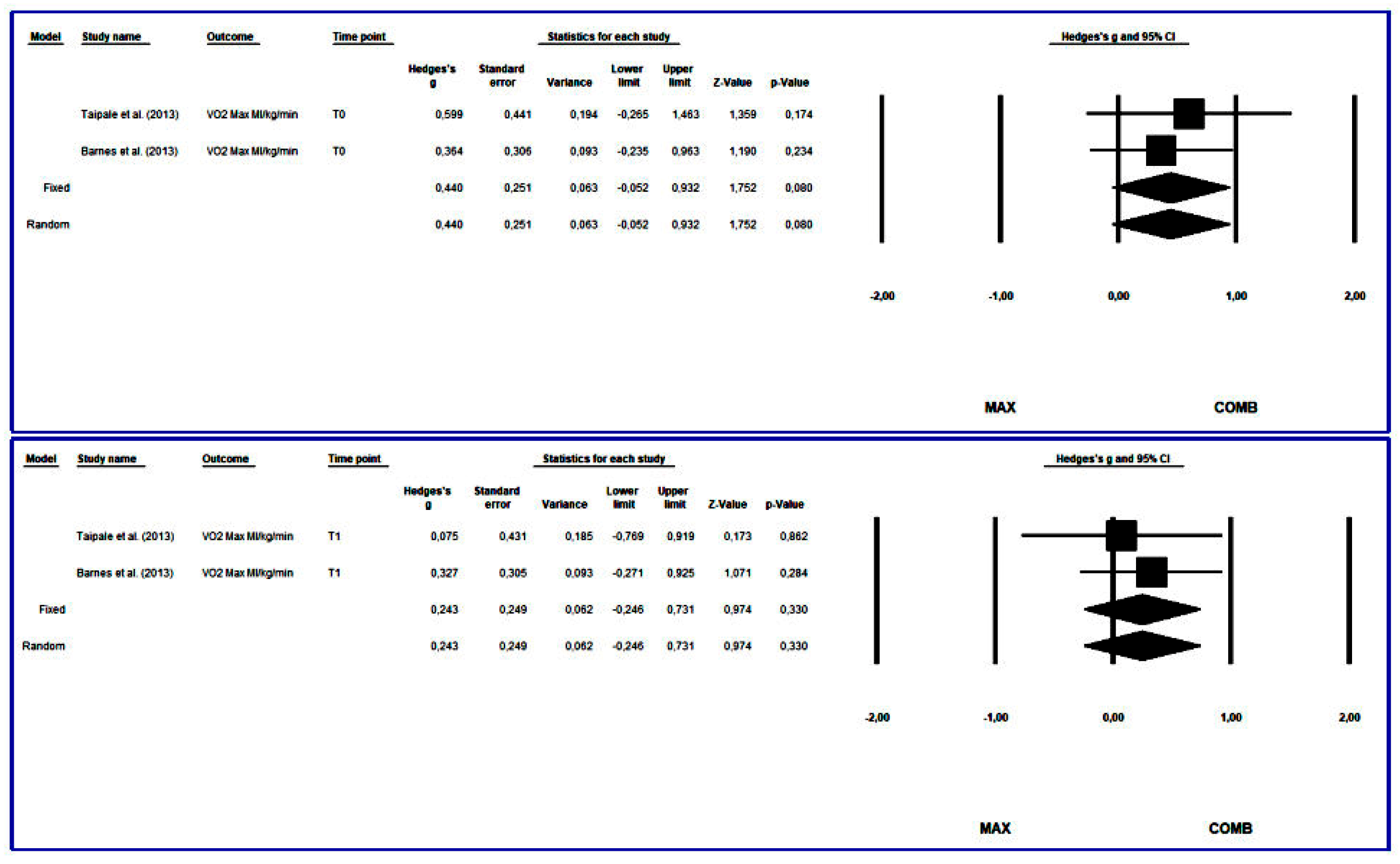
3.4.4. Maximum Oxygen Consumption
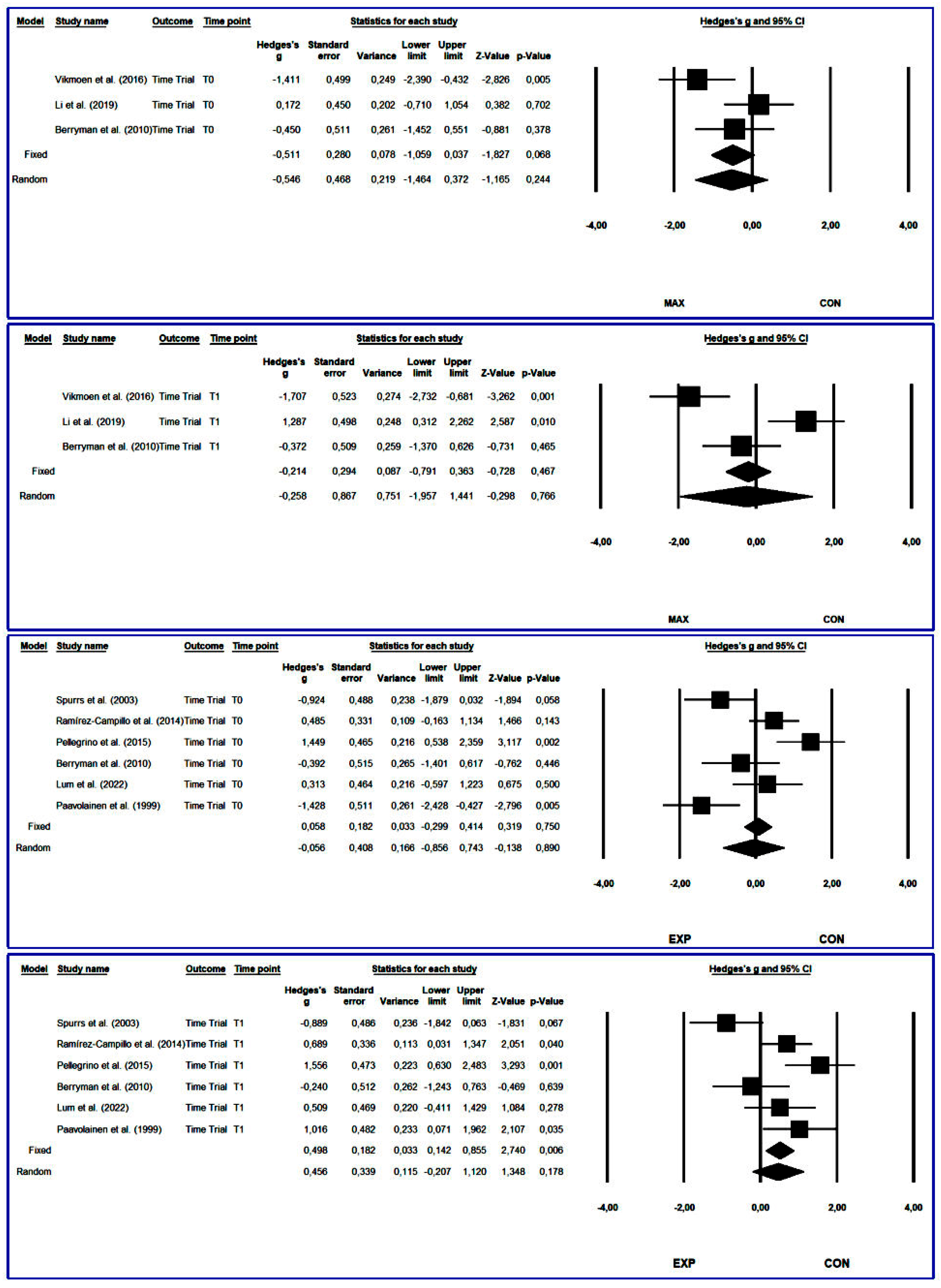
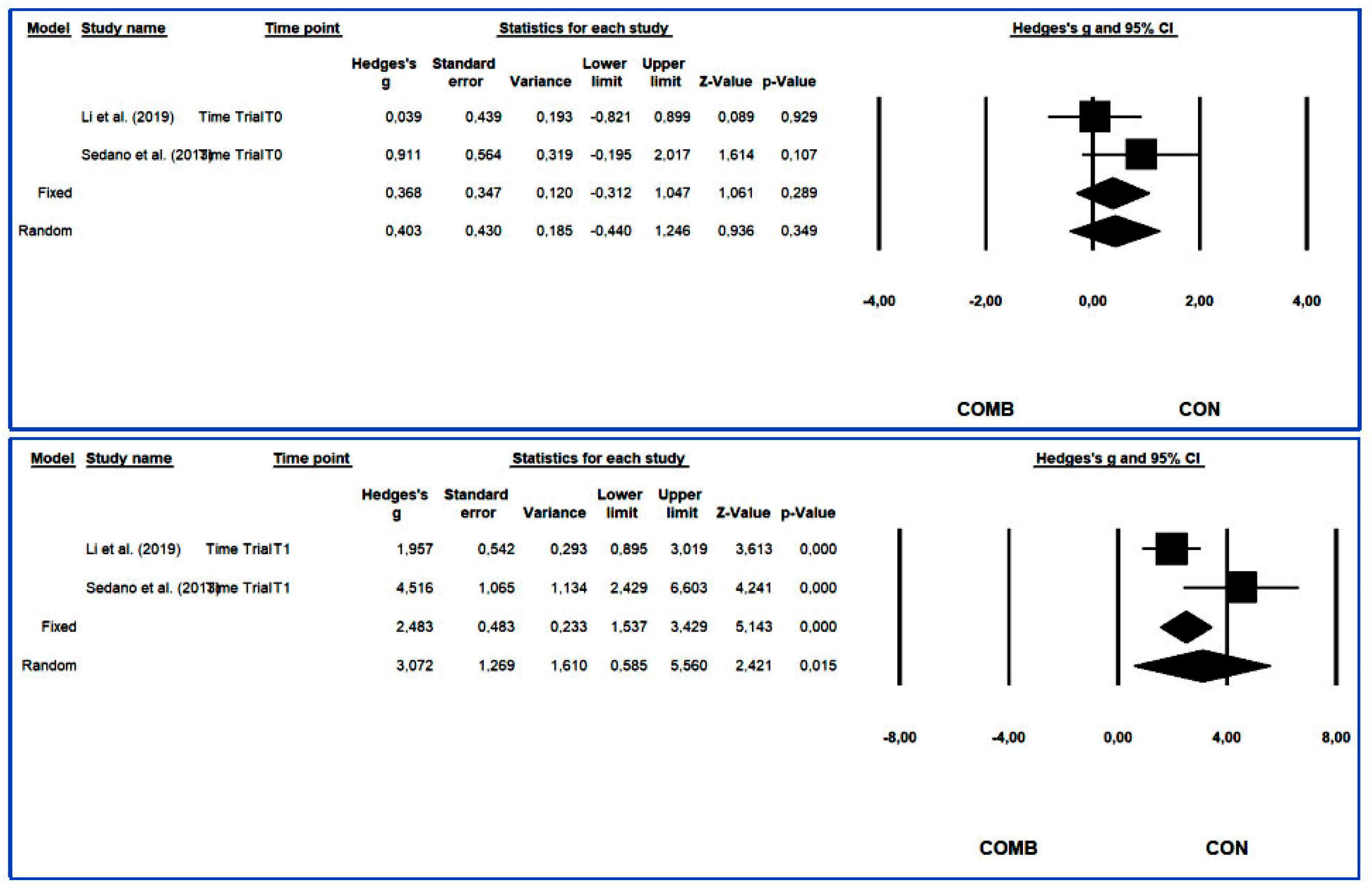
3.4.5. Time Trial
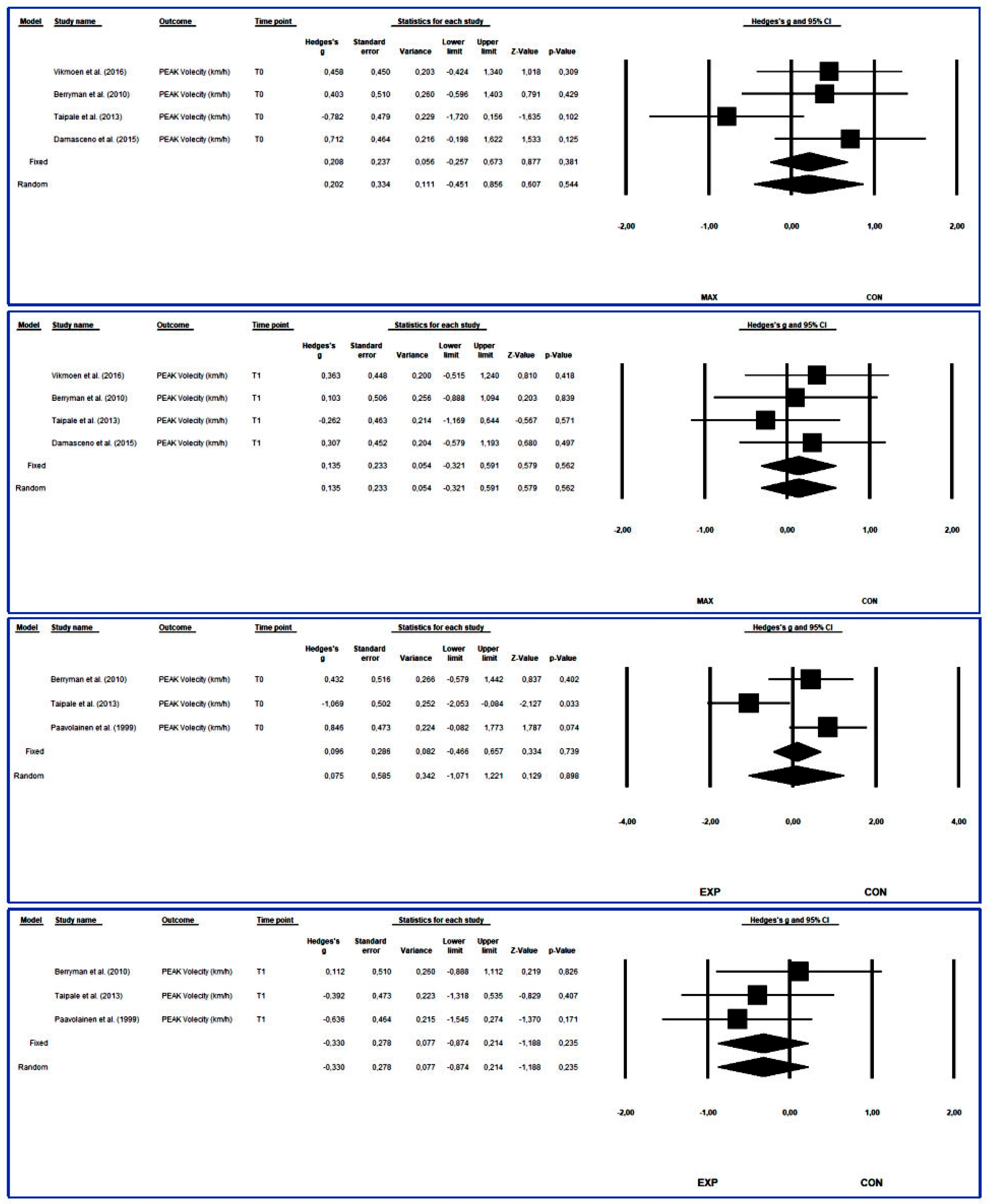
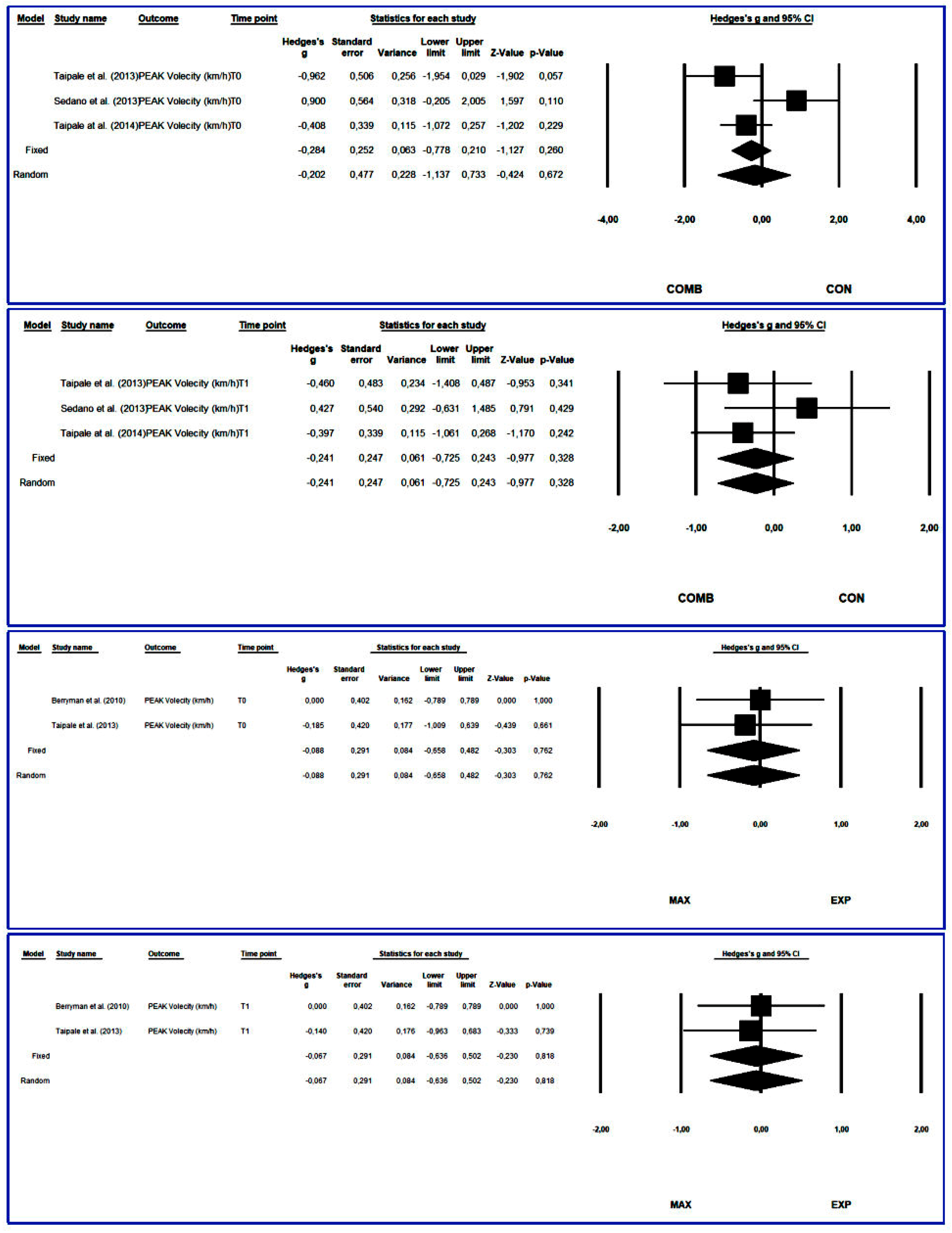
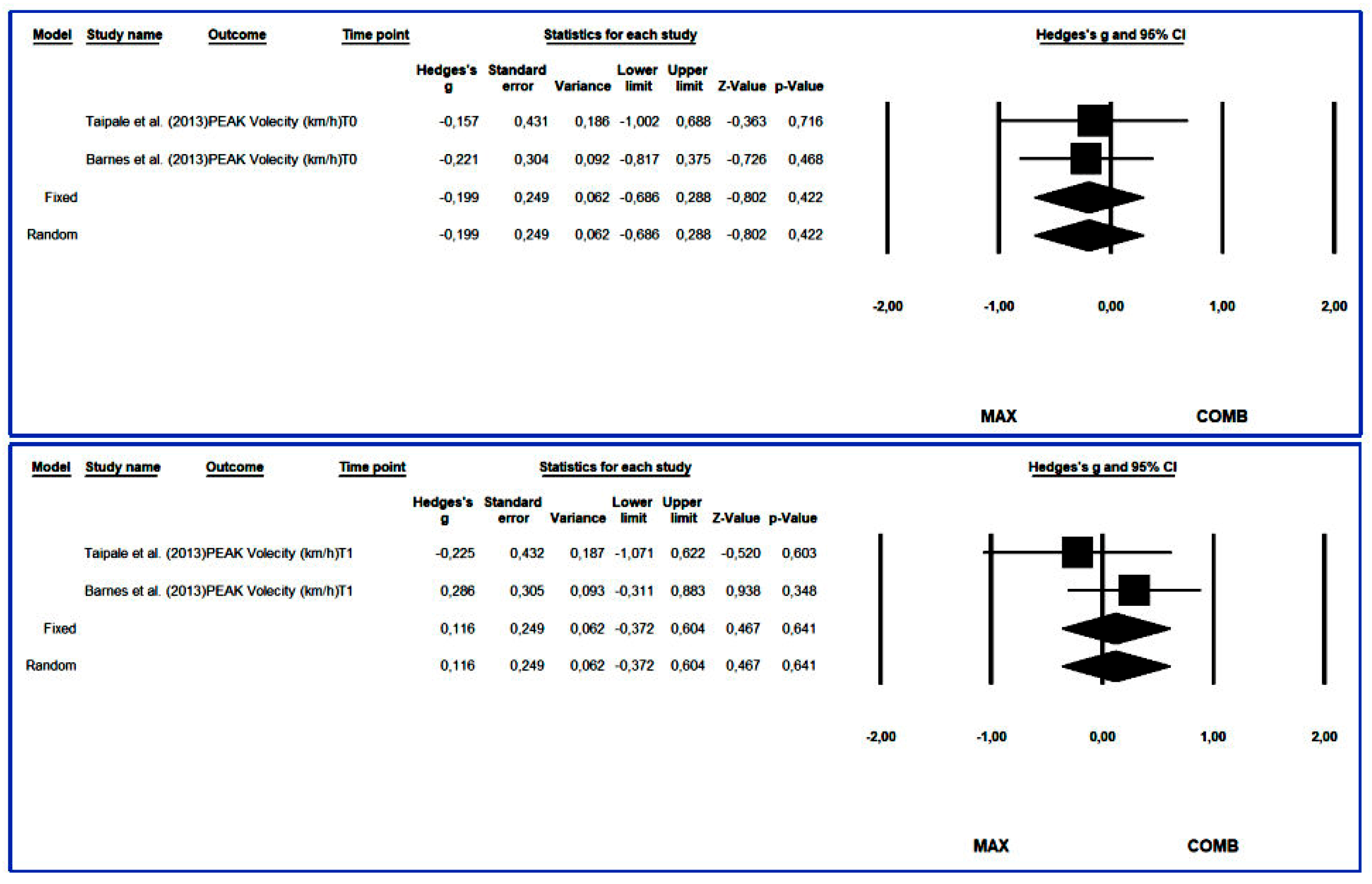
3.4.6. Peak Velocity
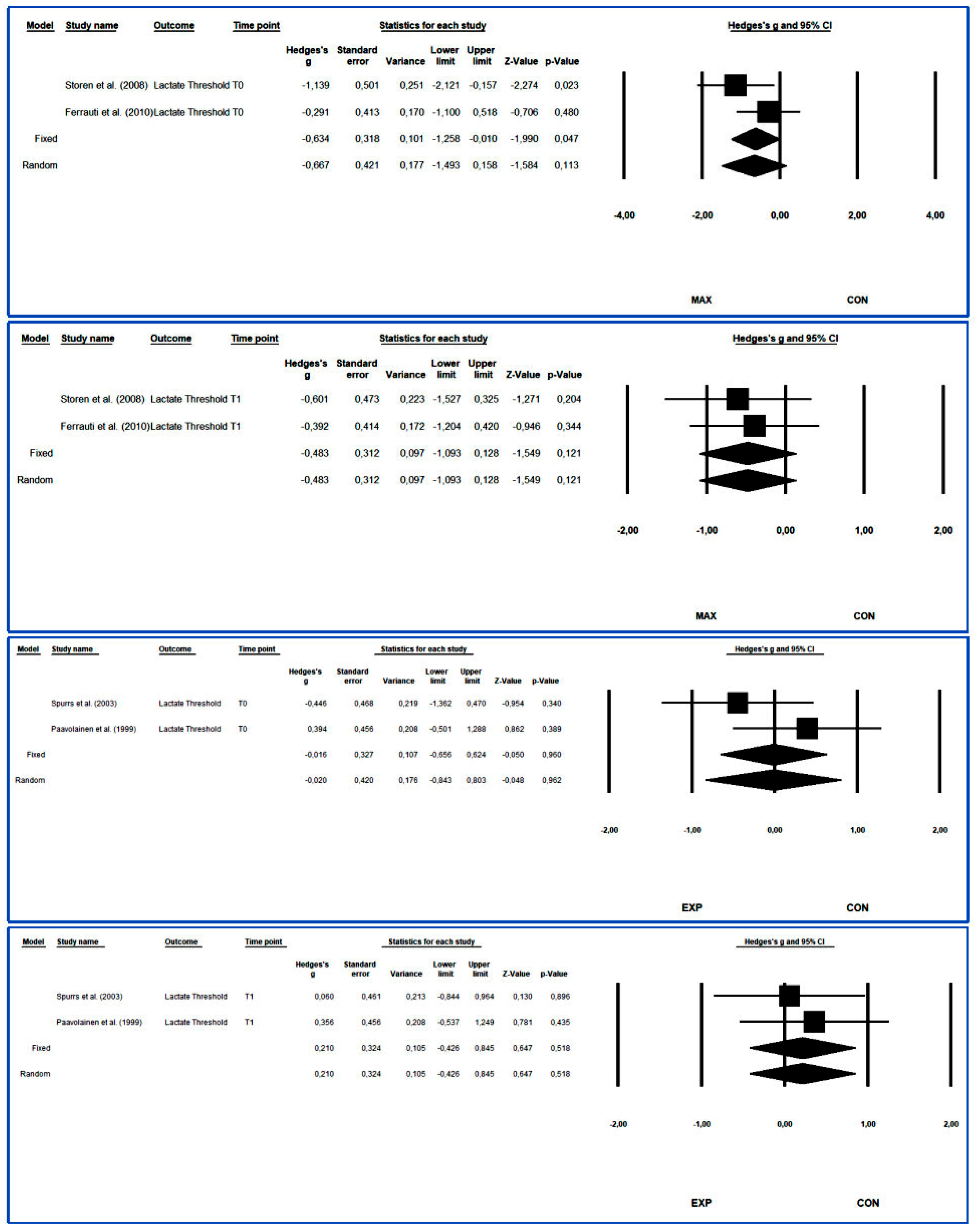
3.4.7. Lactate Threshold
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. List of Abbreviations
- 1RM: one-repetition maximum squat
- IC: confidence interval
- COMB: combined maximum and explosive strength
- COMBG: experimental group that underwent concurrent training of maximum
- and explosive strength and endurance
- CON: control group
- ES: effect size
- END: endurance
- ET: endurance training
- EXP: explosive strength
- EXPG: experimental group that underwent concurrent training of explosive strength and endurance
- F: female
- HRmax: maximum heart rate
- I: intervention group
- IRR: inter-rater reliability
- LT: lactate threshold
- MAX: maximum strength
- MAXG: experimental group that underwent a concurrent training of maximum strength and endurance
- M: male
- n: sample size
- PICOS: Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcomes
- PV: peak velocity
- PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- RE: running economy
- VJ: vertical jump
- VO2max: maximum oxygen consumption
- vVO2max: Velocity at VO2max
- Wk: week
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mikkola, J.; Vesterinen, V.; Taipale, R.; Capostagno, B.; Häkkinen, K.; Nummela, A. Effect of Resistance Training Regimens on Treadmill Running and Neuromuscular Performance in Recreational Endurance Runners. J Sports Sci 2011, 29, 1359–1371. [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, R.; Newton, R. U.; Sutton, D.; Shi, Y.; Ding, H. Effects of Complex Training versus Heavy Resistance Training on Neuromuscular Adaptation, Running Economy and 5-Km Performance in Well-Trained Distance Runners. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6787. [CrossRef]
- Zamora, A.C.F.; Cedeño, E.M.R.; Blanco, Y. R. Adaptaciones fisiológicas al entrenamiento concurrente de la resistencia con la fuerza muscular (revisión). Revista científica Olimpia 2017, 14, 119–129.
- Beattie, K.; Carson, B.P.; Lyons, M.; Rossiter, A.; Kenny, I.C. The Effect of Strength Training on Performance Indicators in Distance Runners. J Strength Cond Res 2017, 31, 9–23. [CrossRef]
- Beattie, K.; Kenny, I.C.; Lyons, M.; Carson, B.P. The Effect of Strength Training on Performance in Endurance Athletes. Sports Med 2014, 44, 845–865. [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Kirby, B.S.; Clark, I.E.; Rice, H.M.; Fulkerson, E.; Wylie, L.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Wilkins, B.W. Physiological demands of running at 2-hour marathon race pace. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2021, 130, 369–379. [CrossRef]
- Minetti, A.E.; Ardigò, L.P.; Saibene, F. Mechanical determinants of the minimum energy cost of gradient running in humans. J Exp Biol 1994, 195, 211–25. [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, M.V.; Lima-Silva, A.E.; Pasqua, L.A.; Tricoli, V.; Duarte, M.; Bishop, D.J.; Bertuzzi, R. Effects of Resistance Training on Neuromuscular Characteristics and Pacing during 10-Km Running Time Trial. Eur J Appl Physiol 2015, 115, 1513–1522. [CrossRef]
- Duffield, R.; Dawson, B.; Goodman, C. Energy System Contribution to 1500- and 3000-Metre Track Running. J Sports Sci 2005, 23, 993–1002. [CrossRef]
- Coffey, V.G.; Hawley, J.A. Concurrent Exercise Training: Do Opposites Distract? J Physiol 2017, 595, 2883–2896. [CrossRef]
- Blagrove, R.C.; Howatson, G.; Hayes, P.R. Effects of Strength Training on the Physiological Determinants of Middle- and Long-Distance Running Performance: A Systematic Review. Sports Med 2017, 48, 1117–1149. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, L.M.; Lopez, R.M.; Klau, J.F.; Casa, D.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Maresh, C.M. The Effects of Resistance Training on Endurance Distance Running Performance Among Highly Trained Runners: A Systematic Review. J Strength Cond Res 2008, 22, 2036–2044. [CrossRef]
- Trowell, D.; Vicenzino, B.; Saunders, N.; Fox, A.; Bonacci, J. Effect of Strength Training on Biomechanical and Neuromuscular Variables in Distance Runners: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med 2020, 50, 133–150. [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, M.; Prieske, O.; Hortobágyi, T.; Granacher, U. The Effects of Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training on Physical Fitness and Athletic Performance in Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1057. [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, B.R.; Mujika, I. Optimizing Strength Training for Running and Cycling Endurance Performance: A Review. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2014, 24, 603–612. [CrossRef]
- Blagrove, R.C.; Howe, L.P.; Cushion, E.J.; Spence, A.; Howatson, G.; Pedlar, C.R.; Hayes, P.R. Effects of Strength Training on Postpubertal Adolescent Distance Runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2018, 50, 1224–1232. [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.; Lanferdini, F.J.; da Silva, E.S.; Geremia, J.M.; Sonda, F.C.; Fletcher, J.R.; Vaz, M.A.; Peyré-Tartaruga, L.A. Triceps Surae Muscle-Tendon Properties as Determinants of the Metabolic Cost in Trained Long-Distance Runners. Front Physiol 2022, 12, 767445. [CrossRef]
- Billat, L.V.; Koralsztein, J.P. Significance of the Velocity at &OV0312;O2max and Time to Exhaustion at This Velocity. Sports Med 1996, 22, 90–108. [CrossRef]
- Berryman, N.; Mujika, I.; Arvisais, D.; Roubeix, M.; Binet, C.; Bosquet, L. Strength Training for Middle- and Long-Distance Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2018, 13, 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Taipale, R.S.; Mikkola, J.; Salo, T.; Hokka, L.; Vesterinen, V.; Kraemer, W.J.; Nummela, A.; Häkkinen, K. Mixed Maximal and Explosive Strength Training in Recreational Endurance Runners. J Strength Cond Res 2014, 28, 689–699. [CrossRef]
- Hendrickse, P.W.; Venckunas, T.; Platkevicius, J.; Kairaitis, R.; Kamandulis, S.; Snieckus, A.; Stasiulis, A.; Vitkiene, J.; Subocius, A.; Degens, H. Endurance Training-Induced Increase in Muscle Oxidative Capacity without Loss of Muscle Mass in Younger and Older Resistance-Trained Men. Eur J Appl Physiol 2021, 121, 3161–3172. [CrossRef]
- Blagrove, R.C.; Howe, L.P.; Howatson, G.; Hayes, P.R. Strength and Conditioning for Adolescent Endurance Runners. Strength Cond J 2020, 42, 2–11. [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, P.; Andersen, J. L. Effects of Strength Training on Endurance Capacity in Top-Level Endurance Athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2010, 20, 39–47. [CrossRef]
- Ferrauti, A.; Bergermann, M.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J. Effects of a Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training on Running Performance and Running Economy in Recreational Marathon Runners. J Strength Cond Res 2010, 24, 2770–2778. [CrossRef]
- García-Manso, J.M.; Arriaza-Ardiles, E.; Valverde, T.; Moya-Vergara, F.; Mardones-Tare, C. Efectos de un entrenamiento concurrente de fuerza y resistencia sobre carreras de media distancia. Cultura, Ciencia y Deporte 2017, 12, 221–227.
- Vikmoen, O.; Raastad, T.; Seynnes, O.; Bergstrøm, K.; Ellefsen, S.; Rønnestad, B.R. Effects of Heavy Strength Training on Running Performance and Determinants of Running Performance in Female Endurance Athletes. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0150799. [CrossRef]
- Berryman, N.; Mujika, I.; Arvisais, D.; Roubeix, M.; Binet, C.; Bosquet, L. Strength Training for Middle- and Long-Distance Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2018, 13, 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Leveritt, M.; Abernethy, P.J.; Barry, B.K.; Logan, P.A. Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training. Sports Med 1999, 28, 413–427. [CrossRef]
- Støren, O.; Helgerud, J.; Støa, E.M.; Hoff, J. Maximal Strength Training Improves Running Economy in Distance Runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2008, 40, 1087–1092. [CrossRef]
- Lum, D.; Barbosa, T.M.; Aziz, A.R.; Balasekaran, G. Effects of Isometric Strength and Plyometric Training on Running Performance: A Randomized Controlled Study. Res Q Exerc Sport 2023, 94, 263–271. [CrossRef]
- González-Badillo, J.J; Ribas, J. Bases de la programación del entrenamiento de fuerza. Inde: Barcelona, Spain, 2002.
- Ambrosini, L.; Presta, V.; Goldoni, M.; Galli, D.; Mirandola, P.; Vitale, M.; Gobbi, G. Are We Able to Match Non Sport-Specific Strength Training with Endurance Sports? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Plan the Best Training Programs for Endurance Athletes. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7280. [CrossRef]
- Eihara, Y.; Takao, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Maeo, S.; Terada, M.; Kanehisa, H.; Isaka, T. Heavy Resistance Training Versus Plyometric Training for Improving Running Economy and Running Time Trial Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med Open 2022, 8, 138. [CrossRef]
- Berryman, N.; Maurel, D.B.; Bosquet, L. Effect of plyometric vs. dynamic weight training on the energy cost of running. J Strength Cond Res 2010, 24, 1818–1825. [CrossRef]
- Denadai, B.S.; de Aguiar, R.A.; de Lima, L.C.R.; Greco, C.C.; Caputo, F. Explosive Training and Heavy Weight Training Are Effective for Improving Running Economy in Endurance Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med 2017, 47, 545–554. [CrossRef]
- Mian; O.S.; Thom, J.M.; Ardigò, L.P.; Narici, M.V.; Minetti, A.E. Metabolic cost, mechanical work, and efficiency during walking in young and older men. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2006, 186, 127–139. [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.R.; Hopkins, W.G.; Mcguigan, M.R.; Northuis, M.E.; Kilding, A.E. Effects of Resistance Training on Running Economy and Cross-Country Performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2013, 45, 2322–2331. [CrossRef]
- Latash, M.L. Muscle Coactivation: Definitions, Mechanisms, and Functions. J Neurophysiol 2018, 120, 88–104. [CrossRef]
- Spurrs, R.W.; Murphy, A.J.; Watsford, M.L. The Effect of Plyometric Training on Distance Running Performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 2003, 89, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Greenwood, M. Complex Training Reexamined. Strength Cond J 2014, 36, 11–19. [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) Design as a Framework to Formulate Eligibility Criteria in Systematic Reviews. Emerg Med J 2020, 37, 387–387. [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro Scale for Rating Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys Ther 2003, 83, 713–721. [CrossRef]
- Cashin, A.G.; McAuley, J.H. Clinimetrics: Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) Scale. J Physiother 2020, 66, 59. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S. Psychosocial Models of the Role of Social Support in the Etiology of Physical Disease. Health Psychol, 1988, 7, 269–297. [CrossRef]
- Vassos, E.; Collier, D.A.; Fazel, S. Systematic Meta-Analyses and Field Synopsis of Genetic Association Studies of Violence and Aggression. Mol Psychiatry 2014, 19, 471–477. [CrossRef]
- Taipale, R.S.; Mikkola, J.; Vesterinen, V.; Nummela, A.; Häkkinen, K. Neuromuscular Adaptations during Combined Strength and Endurance Training in Endurance Runners: Maximal versus Explosive Strength Training or a Mix of Both. Eur J Appl Physiol 2013, 113, 325–335. [CrossRef]
- 47 DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials. Control Clin Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.E.; Quinn, T.J.; Kertzer, R.; Vroman, N.B. Strength Training in Female Distance Runners: Impact on Running Economy. J Strength Cond Res 1997, 11, 224–229. [CrossRef]
- Taipale, R.S.; Mikkola, J.; Nummela, A.; Vesterinen, V.; Capostagno, B.; Walker, S.; Gitonga, D.; Kraemer, W.J.; Häkkinen, K. Strength Training in Endurance Runners. Int J Sports Med 2010, 31, 468–476. [CrossRef]
- Paavolainen, L.; Häkkinen, K.; Hämäläinen, I.; Nummela, A.; Rusko, H. Explosive-Strength Training Improves 5-Km Running Time by Improving Running Economy and Muscle Power. J Appl Physiol 1999, 86, 1527–1533. [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.U.; Telford, R.D.; Pyne, D.B.; Peltola, E.M.; Cunningham, R.B.; Gore, C.J.; Hawley, J.A. Short-term plyometric training improves running economy in highly trained middle and long distance runners. J Strength Cond Res 2006, 20, 947–954. [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Álvarez, C.; Henríquez-Olguín, C.; Baez, E.B.; Martínez, C.; Andrade, D.C.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of Plyometric Training on Endurance and Explosive Strength Performance in Competitive Middle- and Long-Distance Runners. J Strength Cond Res 2014, 28, 97–104. [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, J.; Ruby, B.C.; Dumke, C.L. Effect of Plyometrics on the Energy Cost of Running and MHC and Titin Isoforms. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2016, 48, 49–56. [CrossRef]
- Sedano, S.; Marín, P.J.; Cuadrado, G.; Redondo, J.C. Concurrent Training in Elite Male Runners: The Influence of Strength versus Muscular Endurance Training on Performance Outcomes. J Strength Cond Res 2013, 27, 2433–2443. [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, S.; Bartolomei, S. The Effects of Two Different Explosive Strength Training Programs on Vertical Jump Performance in Basketball. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2018, 58. 1375–1382. [CrossRef]
- Pattison, K.J.; Drinkwater, E.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Stepto, N.K.; Fyfe, J.J. Modulation of Countermovement Jump–Derived Markers of Neuromuscular Function With Concurrent vs. Single-Mode Resistance Training. J Strength Cond Res 2020, 34, 1497–1502. [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, M.; Prieske, O.; Hortobágyi, T.; Granacher, U. The Effects of Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training on Physical Fitness and Athletic Performance in Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1057. [CrossRef]
- Vikmoen, O.; Raastad, T.; Ellefsen, S.; Rønnestad, B.R. Adaptations to Strength Training Differ between Endurance-Trained and Untrained Women. Eur J Appl Physiol 2020, 120, 1541–1549. [CrossRef]
- García-Orea, G.P.; Elvar, J.R.H.; Campillos, J.A.; Grigoletto, M.E.D.S.; Del Rosso, S. Entrenamiento concurrente de fuerza y resistencia: una revisión narrativa. Int J Phys Exerc Heal Sci Trainers 2016, 1.
- Wilson, J.M.; Marin, P.J.; Rhea, M.R.; Wilson, S.M.C.; Loenneke, J.P.; Anderson, J.C. Concurrent Training. J Strength Cond Res 2012, 26, 2293–2307. [CrossRef]
- Karp, J.R. Training Characteristics of Qualifiers for the U.S. Olympic Marathon Trials. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2007, 2, 72–92. [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, J.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Stepto, N.K. Interference between Concurrent Resistance and Endurance Exercise: Molecular Bases and the Role of Individual Training Variables. Sports Med 2014, 44, 743–762. [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Williams, M.G.; Eynon, N.; Ashton, K.J.; Little, J.P.; Wisloff, U.; Coombes, J.S. Genes to Predict VO2max Trainability: A Systematic Review. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 831. [CrossRef]
- Helgerud, J.; Høydal, K.; Wang, E.; Karlsen, T.; Berg, P.; Bjerkaas, M.; Simonsen, T.; Helgesen, C.; Hjorth, N.; Bach, R.; Hoff, J. Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve VO2max more than moderate training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2007, 39, 665–671. [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, J.J.; Loenneke, J.P. Interpreting Adaptation to Concurrent Compared with Single-Mode Exercise Training: Some Methodological Considerations. Sports Med 2018, 48, 289–297. [CrossRef]
- Boullosa, D.; Del Rosso, S.; Behm, D.G.; Foster, C. Post-Activation Potentiation (PAP) in Endurance Sports: A Review. Eur J Sport Sci 2018, 18, 595–610. [CrossRef]
- Shamim, B.; Devlin, B.L.; Timmins, R.G.; Tofari, P.; Lee Dow, C.; Coffey, V.G.; Hawley, J.A.; Camera, D.M. Adaptations to Concurrent Training in Combination with High Protein Availability: A Comparative Trial in Healthy, Recreationally Active Men. Sports Med 2018, 48, 2869–2883. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K. Anaerobic Threshold: Its Concept and Role in Endurance Sport. Malays J Med Sci 2004, 11, 24–36.
- Edge, J.; Bishop, D.; Goodman, C. The Effects of Training Intensity on Muscle Buffer Capacity in Females. Eur J Appl Physiol 2006, 96, 97–105. [CrossRef]
- Theofilidis, G.; Bogdanis, G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Karatzaferi, C. Monitoring Exercise-Induced Muscle Fatigue and Adaptations: Making Sense of Popular or Emerging Indices and Biomarkers. Sports (Basel) 2018, 6, 153. [CrossRef]
- Juel, C.; Halestrap, A.P. Lactate Transport in Skeletal Muscle — Role and Regulation of the Monocarboxylate Transporter. J Physiol 1999, 517, 633–642. [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Lanao, J.; Rhea, M.R.; Fleck, S.J.; Lucia, A. Running-Specific, Periodized Strength Training Attenuates Loss of Stride Length During Intense Endurance Running. J Strength Cond Res 2008, 22, 1176–1183. [CrossRef]
- Prieto-González, P.; Sedlacek, J. Effects of Running-Specific Strength Training, Endurance Training, and Concurrent Training on Recreational Endurance Athletes’ Performance and Selected Anthropometric Parameters. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 10773. [CrossRef]
- Mujika, I.; Rønnestad, B.R.; Martin, D.T. Effects of Increased Muscle Strength and Muscle Mass on Endurance-Cycling Performance. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2016, 11, 283–289. [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Fernández, C.; Santos-Concejero, J.; Grivas, G.V. Effects of Strength Training on Running Economy in Highly Trained Runners: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials. J Strength Cond Res 2016, 30, 2361–2368. [CrossRef]
- Petré, H.; Löfving, P.; Psilander, N. The Effect of Two Different Concurrent Training Programs on Strength and Power Gains in Highly-Trained Individuals. J Sports Sci Med 2018, 17, 167–173.
- Patoz, A.; Breine, B.; Thouvenot, A.; Mourot, L.; Gindre, C.; Lussiana, T. Does Characterizing Global Running Pattern Help to Prescribe Individualized Strength Training in Recreational Runners? Front Physiol 2021, 12, 631637. [CrossRef]
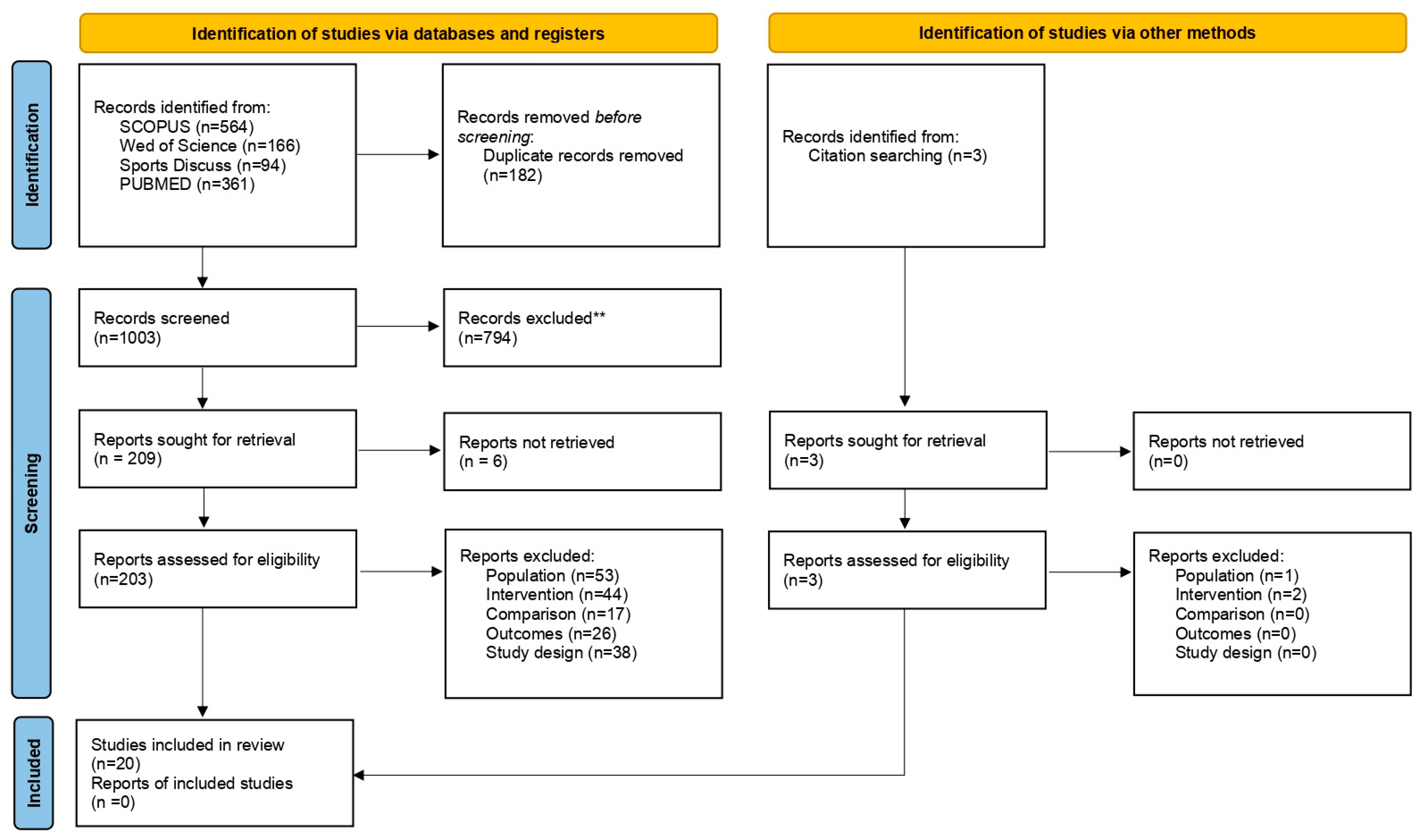


| Category | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
| Population | Recreational and professional endurance runners of both sexes aged between 18 and 45. | Recreational or professional athletes under the age of 18 or above 45. Non-runners. Individuals suffering from injuries or medical conditions. |
| Intervention | Concurrent strength training (MAX, EXP, or COMB) combined with endurance training. Training protocols of at least five weeks. | Concurrent training protocols or cohorts that underwent muscular endurance, body weight, or isometric training sessions. Strength interventions performed using electrical muscle stimulation or vibratory plates. Training protocols of less than five weeks. |
| Comparison | Research involving a minimum of two groups, either one experimental and one control group, or two experimental groups. | Absence of a minimum of two groups, either one experimental and one control group, or two experimental groups. Studies where different experimental groups perform the same concurrent training at different times or days. Studies using ergogenic aids. |
| Outcomes | Studies wherein at least one performance parameter (i.e., VO2max, running economy, lactate threshold) was reported. | Studies that did not report any performance parameter, and it was not possible to obtain such data after contacting their authors. |
| Study design | Randomized and nonrandomized controlled studies. | Cross-sectional studies. Interventions published in sources classified as grey literature, such as reports, conference proceedings not subjected to peer review, or publications not issued by commercial publishers. |
| Authors | n | Age (years) | Level | Intervention | Randomized | Duration (weeks) |
PEDro score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johnston et al. (1997) | 12F | 30.30 | Endurance runners | I: MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 10 | 6 |
| Støren et al. (2008) [29] | 17(9M,8F) | 29.18 | Well-trained endurance runners | I: MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Ferrauti et al. (2010) | 22(16M,6F) | 40 | Recreational runners | I: MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Damasceno et al. (2015) | 19M | 33.50 | Recreational endurance runners | I: MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Vikmoen et al. (2016) | 19F | 32.93 | Well-training endurance athletes | I: MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 11 | 6 |
| Li et al. (2019) | 28M | 20.71 | Well-trained endurance runners | I1: MAX+END I2:COMB+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Paavolainen et al. (1999) | 18M | 23.44 | Elite cross-country runners | I: EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 9 | 6 |
| Spurrs et al. (2003) | 17M | 25 | Endurance runners | I: EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 6 | 6 |
| Saunders et al. (2006) | 15M | 24.20 | Highly-trained endurance runners | I: EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 9 | 6 |
| Ramírez-Campillo et al. (2014) | 36(22M,14F) | 22.10 | Highly competitive endurance runners | I: EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 6 | 6 |
| Pellegrino et al. (2016) | 22(14M,8F) | 33.35 | Experienced endurance runners | I: EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 6 | 6 |
| Berryman et al. (2010) | 28M | 29.85 | Moderately to well-trained endurance runners | I1:EXP+END I2:MAX+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Taipale et al. (2010) | 28M | 35.37 | Recreational endurance runners | I1:EXP+END I2:MAX +END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Mikkola et al. (2011) | 27M | 35.55 | Recreational endurance runners | I1:EXP+END I2:MAX +END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Barnes et al. (2013) | 42(23M,19F) | 19.72 | Cross-country runners | I1: MAX+END I2: COMB+END |
Yes | 10 | 6 |
| Taipale et al. (2013) | 30M | 34.57 | Recreational endurance runners | I1: MAX+END I2: EXP+END I3: COMB+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Lum et al. (2022) | 26(18M,8F) | 26 | Endurance runners | I1:EXP+END CON: END |
Yes | 6 | 6 |
| Sedano et al. (2013) | 18M | 23.70 | Well-training runners | I1:COMB+END CON: END |
Yes | 12 | 6 |
| Taipale at al. (2014) | 34(16M,18F) | 32.14 | Recreational endurance runners | I: COMB+END CON: END |
Yes | 8 | 6 |
| Beattie et al. (2017) | 20M | 28.55 | Competitive distance runners | I: COMB+END CON: END |
No | 40 | 5 |
| Study | Duration// Frequency |
Training parameters | Exercises |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johnston et al. (1997) | 10 weeks// ST:3/wk; E:4-5/wk | ST: (MAXG) 2x20/2´ (bent-leg heel raise); 2x12/2´ (straight-leg heel raise); 2x15/2´ (sit-up, abdominal curl); 3x8/2´ (Leg extension, leg curl, seated row, lat pulldown; 3x6/2´ (squat, lunge, bench press, seated press, hammer curl) ET:20-30km/week at steady pace |
Squat, knee flexion, knee extension, seated press, lat pulldown, hummer curl, sit-up, lunge, heel raise, bench press |
| Støren et al. (2008) | 8 weeks// ST:3/wk | ST: (MAXG) 4x4RM/3´ ET: Continue with their normal endurance training (60-95%HRmax) |
Half-squat |
| Ferrauti et al. (2010) | 8 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST: (MAXG) 4x3-5RM/3´ (leg press, leg extension, leg curl, ankle extension, hip extension); 3x20-25RM/90´´ (bench press, lateral flexion, trunk flexion, trunk extension, trunk rotation, reverse fly). ET: 240(121) min/wk |
Leg press, leg extension, leg curl, hip extension, ankle extension, reverse fly bench press, trunk flexion, trunk extension, lateral flexion, trunk rotation |
| Damasceno et al. (2015) | 8 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST: (MAXG) Wks 1–2: 3x8–10RM/3´; wks 3–4: 3x6–8 RM/3´; wks 5–6: 3x4–6 RM/3´; wks 7–8: 2x3–5 RM/3´ ET: Maintained their endurance training program on different days than ST |
Half-squat, leg-press, plantar flexion, and knee extension |
| Vikmoen et al. (2016) | 11 weeks// ST:3/wk; ET: 6/wk |
ST: (MAXG) Wks 1–3: 3x10RM and 6RM; wks 4–6: 3x8RM and 5RM; wks 7–11: 3x6RM and 4RM ET: Weekly training: 1:3.7(1.6) h at 60%-82% HRmax; 1.1(0.5) h at 83%-87%, 3:0.8(0.5) h; 88%-100% of maximal HR |
Half squat, leg press, standing one-legged hip flexion, ankle plantar flexion |
| Li et al. (2019) | 8 weeks// ST:3/wk | ST: MAXG: 5x5(80-85%1RM)/3´; COMBG: 3x5(80-85%1RM)/4´ (Back squat, Bulgarian squat, Romanian deadlift); 3x6/4’ (drop jump, single leg hop, double leg hurdle hop) ET: Continuous training (70-85%HRmax), and interval training (90-95% HRmax). Total distance: 77.25(2.33) km/wk |
MAXG: Back squat, Bulgarian squat, Romanian deadlift COMBG: Back squat, drop jump, Bulgarian squat, single leg hop, Romanian deadlift, double leg hurdle hop |
| Paavolainen et al. (1999) | 9 weeks | ST: (EXPG) Alternative jumps, bilateral countermovement, drop and hurdle jumps, and 1-legged 5-jump, leg-press, leg extension, leg curl without additional weight or with the barbell on the shoulders. Leg-press, leg extension, leg curl: 5-20reps(0-40%1RM) ET: 30-120´ at <84%HRmax |
Alternative jumps, bilateral countermovement, drop and hurdle jumps, and 1-legged 5-jump, leg-press, leg extension, leg curl |
| Spurrs et al. (2003) | 6 weeks// ST:2/wk the first 3 wks, and 3/wk the last 3 wks | ST: (EXPG) 2x10 (Squat jump); 2x10-12 (split scissor jump); 2-3x10-12 (double leg bound); 2-3x10-15 (alternate leg bound, single leg forward hop); 2-3x6-10 (depth jump); 2-3x10 (double leg hurdle jump, single leg hurdle hop) ET: 60-80km/wk |
Squat jump, split scissor jump, double leg bound, alternate leg bound, single leg forward hop, depth jump, double leg hurdle jump, single leg hurdle hop |
| Saunders et al. (2006) | 9 weeks// ST:3/wk | ST: (EXPG) 1-2x15 (back extension); 2-5x6-8 (leg press); 1-3x6 (countermovement jumps); 1-3x20 (knee lifts); 1-3x10 (ankle jumps); 1-3x10 (hamstring curls); 4-6x10m (alternate-leg bounds); 1-5x20-30m (skip for height); 1-4x20 (single-leg ankle jumps); 5x5 (continuous hurdle jumps); 5x8 (scissor jumps for height) ET: 107(43) km/wk including continuous training and interval training |
Back extension, leg press, countermovement jumps, knee lifts, ankle jumps, hamstring curls, alternate-leg bounds, skip for height, single-leg ankle jumps, continuous hurdle jumps, scissor jumps for height |
| Ramírez-Campillo et al. (2014) | 6 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST: (EXPG) 2x10/2´ from a 20cm box; 2x10/2´ from a 40cm box; 2x10/2´ from a 60 cm box ET: 67.2(18.9) km/wk |
Bounce drop jumps |
| Pellegrino et al. (2016) | 6 weeks// ST:15sessions/6wks | ST: (EXPG) 60-228 jumps/session | Deep and box jumps |
| Berryman et al. (2010) | 8 weeks// ST:1/wk; ET:3/wk | ST: MAXG: 3x8/3´; EXPG: Drop jumps from 20, 40, or 60 cm boxes ET: Session 1: 10-6x200-800m at 96-105% of peak treadmill speed; session: 6-1x5-30min at 70-80% of peak treadmill speed; session 3: 30-60min at 70% peak treadmill speed |
MAXG: Concentric half-squat; EXPG: drop jumps |
| Taipale et al. (2010) | 8 weeks// ST:2/wk; ET: in non-strength training days | ST: MAXG: 3x4-6 (80-85%1RM) (squat and leg press) and 2x12-15 (50-60%1RM) (calf exercise); EXPG group: 3x6 (30-40%1RM) (explosive squats and leg press); 2-3x10 (20kg) (scissor jump); 2-3x5 (maximal individual squat jumps); 2-3x5 (20kg between wks 4-8) (maximal squat jumps) ET: Wks 0-4: 20(5)-26(4.6) km/wk; wks 4-8: 29.8(7.8)-38.3(4.8) km/wk |
MAXG: squat, leg press, calf exercise; EXPG: explosive squats, scissor jump, maximal individual squat jumps, maximal squat jumps |
| Mikkola et al. (2011) | 8 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST: MAXG: Wks 1-4: 3x6/2-3´; wks 5-8: 3x4/2-3´. EXPG group: 3x6/2-3´ (squat and leg press); 2x5/2-3´ (squat jumps (singles and non-stop)); 2x10/2-3´ (scissor jumps) ET: Most of the endurance training (>95%) was of low intensity and was performed below the lactate aerobic threshold |
MAXG: Squat and leg press; EXPG: squat, leg press, squat jumps (singles and non-stop), scissor jumps |
| Barnes et al. (2013) | 10 weeks// ST:1-2/wk; ET: 6/wk | ST: MAXG: 2-4x6-20; COMBG: 1-4x6-20 | MAXG: Back squat, calf raise, dumb bell military press, glute/hamstring raise, lateral pull down, box step-up, dead lift, calf raise, dumb bell incline bench press, resisted monster walk, pull-up, Bulgarian split squat. COMBG: Same exercises as MAXG plus: forward hop, countermovement jump, alternate leg bound, tuck jump, box jump, side shuffle, scissor jump |
| Taipale et al. (2013) | 8 weeks// ST:1-2/wk; ET: On non-strength training days | ST: MAXG: 3x4–6(80–85%1RM)/2´ (squat and leg press); 2x12–15(50–60%1RM)/2´ (calf exercise); 3x20-30(body weight)/2´ (Sit-ups, back-extension); EXP+END: 3x6(30-40%1RM)/2´ (squat and leg press); 2–3x10sec (20kg) (scissor jump); 2-3x5 (body weight)/2´ (maximal squat jump); 3x20-30 (body weight)/2´ (Sit-ups, back-extension); COMBG: wks 0-4: 2x6RM/2´ (squat and leg press); wks 4-8: 3x4RM/2´ (squat/leg press); 2-3x8-10/2´ (box jumps, vertical jumps); 3x20-30 (body weight)/2´ (Sit-ups, back-extension) ET: 5:38(0:56) h per week below lactate threshold |
MAXG: Squat, leg press, calf exercise, sit-ups, back-extension. EXPG: Leg press, scissor jump, maximal squat jump, single body weight, maximal squat jump, sit-ups, back-extension. COMBG: Squat and leg press, box jumps, vertical jumps, sit-ups, back-extension |
| Lum et al. (2022) | 6 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST (EXPG): 2-4x5/3´ |
Depth jump, single leg bounding, side split jump |
| Sedano et al. (2013) | 12 weeks// ST: 2/wk; ET: 6/wk | ST (COMBG): 3x7 reps (70 %1RM) + 10 reps/5´ ET: cross-country or road running (0.5-1.5h), fartlek (0.5-1.5h), and interval training. |
Barbell squat + Vertical jumps over hurdles (40 cm); Lying leg curl + Horizontal jumps; Seated calf raises + Vertical jumps over hurdles (40cm); leg extension + horizontal jumps |
| Taipale at al. (2014) | 8 weeks// ST:1-2/wk; ET:2-4/wk | ST (COMBG): Wks 1-4: 2x6RM/3´ (squat and leg press); 2X8/2-3´ (box jumps, vertical jumps), 3x20-30/2´ (sit-ups and back extension). Wks 5-8: 2x4RM/3´ (squat and leg press); 2X10/2-3´ (box jumps, vertical jumps), 3x20-30/2´ (sit-ups and back extension) ET: M: 18(11) km/wk; F: 23(13) km/wk |
Squat, leg press, box jumps, vertical jumps, sit-ups, back extension |
| Beattie et al. (2017) | 40 weeks// ST:2/wk | ST (COMBG): Wks 1-12: 2-3x3-6 (pogo jumps); 2-3x3-8 (back squat); 2-3x6-12 (romanian deadlift); 1-3x6-12 (split squat). Wks 13-20: 3x5-6 (drop jump); 2-3x3-8 (back squat); 1-3x5-12 (romanian deadlift); 1-3x5-10 (split squat). Wks 21-32: 1-5x4-5 (drop jump); 1-3x3 (jump squat); 1-3x3-5 (back squat); 1-3x5-8 (single leg Romanian deadlift); 1x8 (single leg squat). Wks 33-40: 1-3x4-5 (drop jump); 1-3x3 (jump squat); 1-3x3-5 (back squat); 1-3x5-8 (single leg Romanian deadlift); 1x8 (single leg squat) | Pogo jumps, back squat, Romanian deadlift, split squat, drop jump, countermovement jump, reverse lunge, skater squat, jump squat, |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





