Submitted:
24 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Implications of Expropriation: Displacement and Opposition
2.1. Compensation Principles and Legal Framework in Ethiopia
2.2. Total Economic Value and Willingness to Accept in Compensation Estimation
3. Research Methods
3.1. Study Area
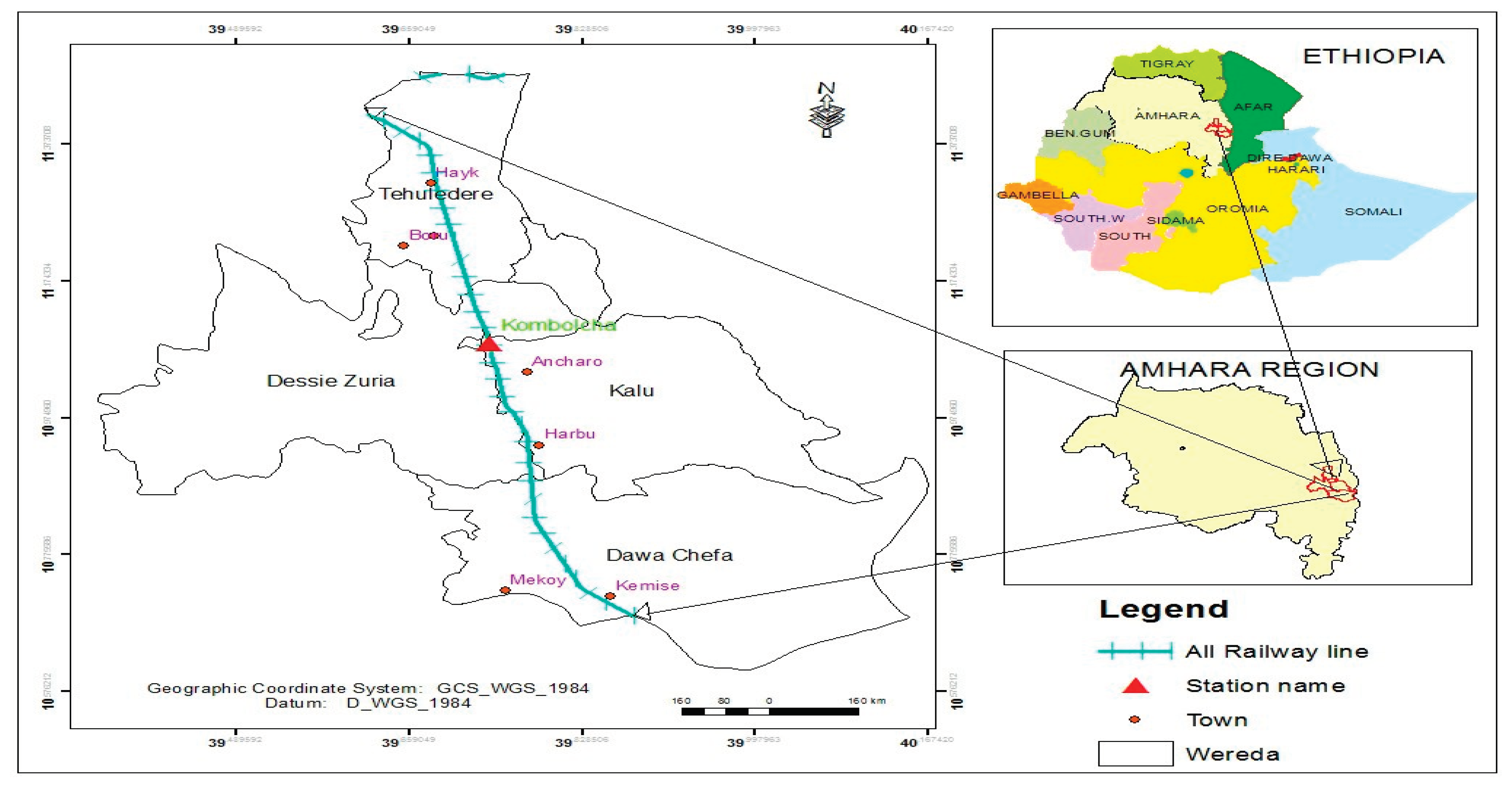
3.2. Description of the Applied Model
3.3. Sampling and Data Collection
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Analysis WTA Compensation
| Variables | Descriptions |
| age | Age of the respondent |
| comamt | Amount of paid compensation |
| comform | Compensation form (cash, kind & both) |
| compaid | Compensation paid (Dummy, 1 if yes, 0 if no ) |
| disp | Displaced households (Dummy, 1 if yes, 0 if no ) |
| edu | Level of education (1 = no formal education) |
| empy | Employment status of the respondent |
| exp | Expenses of the respondent |
| fam | Family size of the respondent (1 = Below 3) |
| incom | Income level of the respondent |
| lcomamt | Log forms of amount of given compensation |
| lincom | Log forms of respondent’s income |
| lsatcom | log forms of expected amounts of fair compensation by the respondent |
| marl | Marital status of the respondent |
| relg | Religion of the respondent |
| repl | Forms of kind compensation for replaced land |
| satcom | Compensation that would satisfy the respondent |
| satis | Compensation Satisfaction level of the respondent (Dummy, 1 if yes, 0 if no ) |
| sex | Sex of household head (Dummy, 1 if male, 0 if female ) |
4.1.1. Demographic Information of the Respondents
| Types of the Variable | Frequency | Percentage (%) | ||
| Sex | Male | 126 | 81.82% | |
| Female | 28 | 18.18% | ||
| Marital status | Single | 30 | 19.48% | |
| Married | 124 | 80.52% | ||
| Widowed | 0 | 0.0% | ||
| Divorced | 0 | 0.0% | ||
| Religion | Muslim | 146 | 94.81% | |
| Orthodox | 8 | 5.19% | ||
| Employment status | Farmer | 76 | 49.35% | |
| Private organization employee | 11 | 7.14% | ||
| Government employee | 14 | 9.09% | ||
| Own business | 10 | 6.49% | ||
| No job | 43 | 27.92% | ||
| Education | No formal education | 22 | 14.29% | |
| Primary education | 83 | 53.90% | ||
| Secondary education | 39 | 25.32% | ||
| Diploma | 10 | 6.49% | ||
| Family Size | Below 3 | 19 | 12.34% | |
| 4-7 | 116 | 75.33% | ||
| Above 7 | 19 | 12.34% | ||
4.2. Compensation Measures and Adequacy for Displaced Households
| Frequency | Percentage (%) | ||
| Got replacement land | Yes | 99 | 64.3% |
| No | 55 | 35.7% | |
| Get compensation due to involuntary resettlement | Yes | 154 | 100.0% |
| No | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Satisfaction with compensation | Satisfied | 27 | 17.6% |
| unsatisfied | 126 | 82.4% | |
| Compensation form | In cash only | 23 | 14.9% |
| In Kind only | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Both | 131 | 85.1% | |
4.3. Inferential Analysis of WTA Compensation
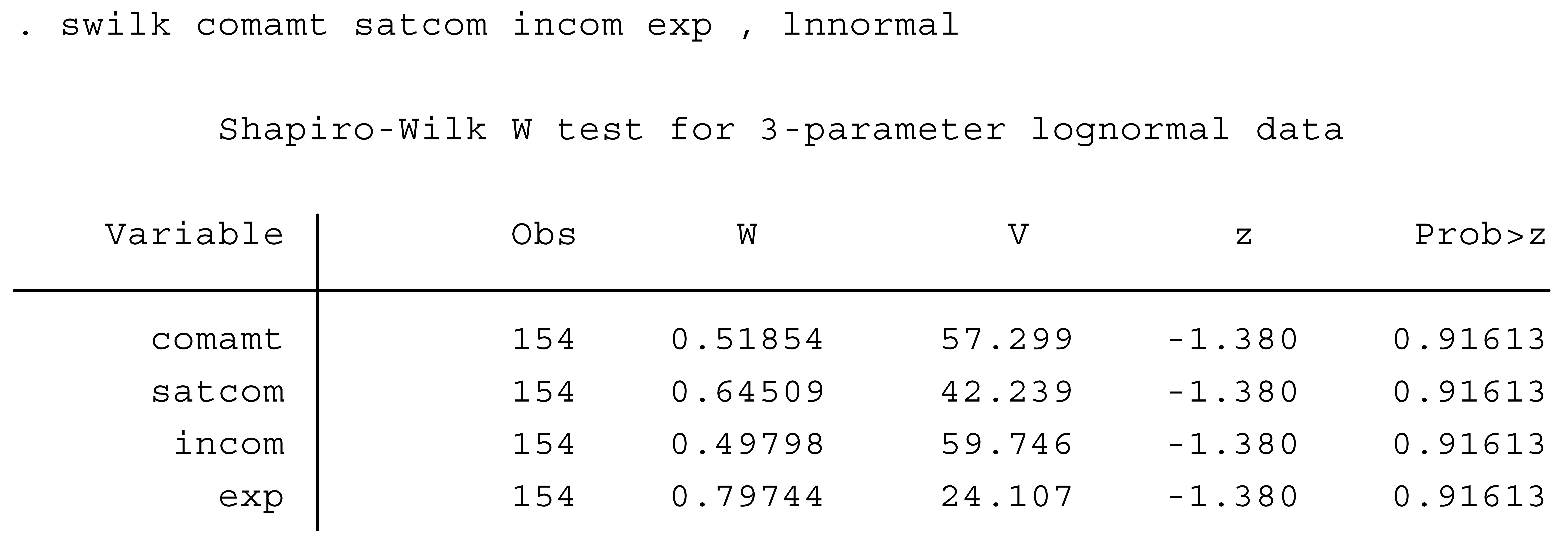
4.3.1. Normality Test for Continuous Data
| Variable | Obs | W | V | z | Prob>z |
| satcom | 154 | 0.645 | 42.239 | -1.380 | 0.916 |
| comamt | 154 | 0.519 | 57.299 | -1.380 | 0.916 |
4.3.2. Significant Predictors of Compensation Acceptance
| satis | Coef. | St.Err. | t-value | p-value | [95% Conf | Interval] | Sig |
| lcomamt | 2.854 | .628 | 4.55 | 0 | 1.624 | 4.085 | *** |
| lsatcom | -2.818 | .651 | -4.33 | 0 | -4.094 | -1.543 | *** |
| sex | -.905 | .582 | -1.55 | .12 | -2.046 | .236 | |
| marl | 2.334 | .846 | 2.76 | .006 | .676 | 3.993 | *** |
| relg | 2.326 | .829 | 2.81 | .005 | .701 | 3.951 | *** |
| empy | .084 | .512 | 0.16 | .869 | -.92 | 1.089 | |
| age | .002 | .021 | 0.08 | .938 | -.04 | .044 | |
| edu | .791 | .304 | 2.61 | .009 | .196 | 1.386 | *** |
| fam | -.013 | .193 | -0.07 | .947 | -.392 | .366 | |
| lincom | .003 | .137 | 0.02 | .981 | -.265 | .271 | |
| repl | .893 | .567 | 1.58 | .115 | -.218 | 2.005 | |
| Constant | -8.889 | 4.4 | -2.02 | .043 | -17.512 | -.265 | ** |
| Mean dependent var | 0.182 | SD dependent var | 0.387 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.635 | Number of obs | 154 | ||||
| Chi-square | 92.798 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 77.237 | Bayesian crit.(BIC) | 113.680 | ||||
| *** p<.01, ** p<.05, * p<.1 | |||||||
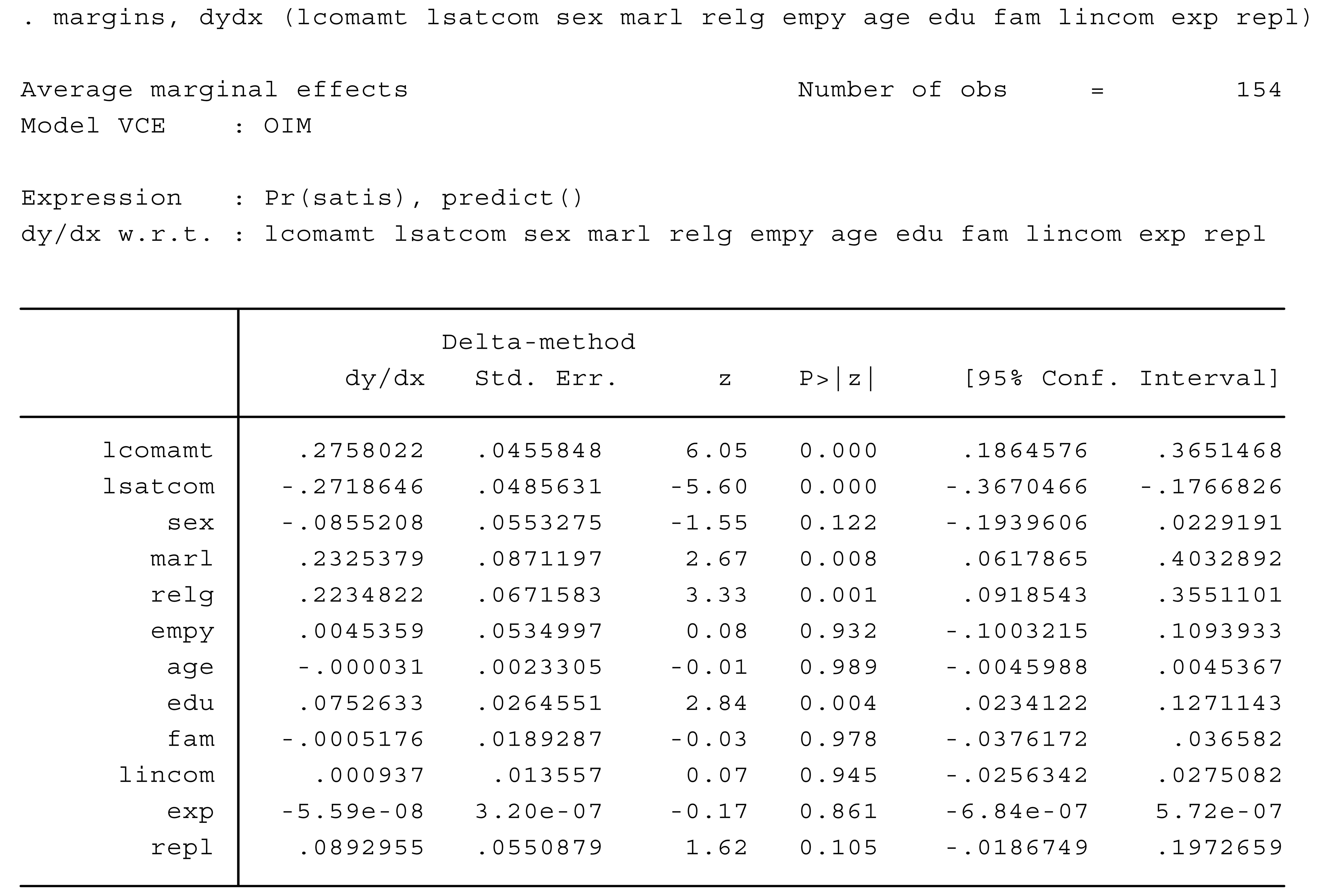
4.3.3. Impact of Compensation Amount on Satisfaction Likelihood
| Average marginal effects Number of obs = 154 Model VCE : OIM Expression : Pr (satis), predict () dy/dx w.r.t.: lcomamt lsatcom sex marl relg empy age edu fam lincom exp repl | ||||||
| Delta-method | ||||||
| dy/dx | Std.Err. | z | P>z | [95%Conf. | Interval] | |
| lcomamt | 0.276 | 0.046 | 6.050 | 0.000 | 0.186 | 0.365 |
| lsatcom | -0.272 | 0.049 | -5.600 | 0.000 | -0.367 | -0.177 |
| sex | -0.086 | 0.055 | -1.550 | 0.122 | -0.194 | 0.023 |
| marl | 0.233 | 0.087 | 2.670 | 0.008 | 0.062 | 0.403 |
| relg | 0.223 | 0.067 | 3.330 | 0.001 | 0.092 | 0.355 |
| empy | 0.005 | 0.053 | 0.080 | 0.932 | -0.100 | 0.109 |
| age | -0.000 | 0.002 | -0.010 | 0.989 | -0.005 | 0.005 |
| edu | 0.075 | 0.026 | 2.840 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.127 |
| fam | -0.001 | 0.019 | -0.030 | 0.978 | -0.038 | 0.037 |
| lincom | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.070 | 0.945 | -0.026 | 0.028 |
| exp | -0.000 | 0.000 | -0.170 | 0.861 | -0.000 | 0.000 |
| repl | 0.089 | 0.055 | 1.620 | 0.105 | -0.019 | 0.197 |
4.4. Minimum Acceptable Compensation
5. Conclusions
Reference
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflict of Interest
Appendix
- 1.
-
Normality test
- 2.
-
Probit Regression

- 3.
-
Marginal Effects
References
- Sangha, K.K.; Gordon, I.J.; Costanza, R. Ecosystem Services and Human Wellbeing-Based Approaches Can Help Transform Our Economies. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 2022, 10, 841215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutandwa, E.; Grala, R.K.; Petrolia, D.R. Estimates of willingness to accept compensation to manage pine stands for ecosystem services. Forest Policy and Economics 2019, 102, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayas JM, R.; Newton, A.C.; Diaz, A.; Bullock, J.M. Enhancement of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services by Ecological Restoration: A Meta-Analysis. Science 2009, 325(5944), 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, J.D.; Mazzotta, M.J.; Spies, T.A.; Harmon, M.E. Applying the Ecosystem Services Concept to Public Land Management. Agricultural and Resource Economics Review 2013, 42(1), 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calow, P. The importance of money as a common currency in ecosystem service valuation—A comment on the Roskilde Workshop recommendations for risk assessment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2017, 36(4), 866–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebner, D.L.; Bettinger, P.; Siry, J.P. Introduction to forestry and natural resources (First edition); Elsevier; Academic Press, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wright WC, C.; Eppink, F.V.; Greenhalgh, S. Are ecosystem service studies presenting the right information for decision making? Ecosystem Services 2017, 25, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galik, C.S.; Grala, R.K. Conservation program delivery in the southern U.S.: Preferences and interactions. Journal of Environmental Management 2017, 198, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkonen, M.; Huttunen, S.; Primmer, E.; Repo, A.; Hildén, M. Policy coherence in climate change mitigation: An ecosystem service approach to forests as carbon sinks and bioenergy sources. Forest Policy and Economics 2015, 50, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, S.; Pagiola, S.; Wunder, S. Designing payments for environmental services in theory and practice: An overview of the issues. Ecological Economics 2008, 65(4), 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corte, K.; Cairns, J.; Grieve, R. Stated versus revealed preferences: An approach to reduce bias. Health Economics 2021, 30(5), 1095–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.-L.; Huang, C.J.; Shaw, D. A general model of starting point bias in double-bounded dichotomous contingent valuation surveys. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 2005, 50(2), 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.C.; Hanemann, M.; Signorello, G. One-and-One-Half-Bound Dichotomous Choice Contingent Valuation. Review of Economics and Statistics 2002, 84(4), 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, J. Contingent Valuation: From Dubious to Hopeless. Journal of Economic Perspectives 2012, 26(4), 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, F.; Martinsson, P. Do Hypothetical and Actual Marginal Willingness to Pay Differ in Choice Experiments? Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 2001, 41(2), 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, M. Reforming Ethiopia’s Expropriation Law. Mizan Law Review 2016, 9(2), 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, M.M. Compensation and benefit sharing: Why resettlement policies and practices must be reformed. Water Science and Engineering 2008, 1(1), 89–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D. Impact of Development-induced displacement on the Tribal community, with special reference to the women in Odisha. ASEAN Journal of Community Engagement 2020, 4(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.; Torre, A.; Magsi, H. Land-use conflict and socio-economic impacts of infrastructure projects: The case of Diamer Bhasha Dam in Pakistan. Area Development and Policy 2017, 2(1), 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaoro, D. Developing against Development: Resistance as Participation in Development Induced Displacement in Kenya. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Oppio, A.; Corsi, S.; Mattia, S.; Tosini, A. Exploring the relationship among local conflicts and territorial vulnerability: The case study of Lombardy Region. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.G. Land readjustment as an alternative land development tool for peri-urban areas of Ethiopia. Property Management 2015, 33(1), 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Zhu, L.; Lo, K. Livelihood adaptation and life satisfaction among land-lost farmers: Critiquing China’s urbanisation-driven land appropriation. Bulletin of Geography. Socio-Economic Series 2019, 46(46), 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, G.T. Land Expropriation and Compensation Payment in Ethiopia: Review. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Adelaja, A. Forced Displacement and Agriculture: Implications for Host Communities. Sustainability 2021, 13(10), 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constitution. Constitution of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, A.; Gerbaud, V.; Boix, M.; Montastruc, L. A Meta-ontology to Design Sustainable Project in a Competitive Stakeholder’s Context. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier, 2017; Volume 40, pp. 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hong, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, Q.; Meng, X. Assessing willingness to accept compensation for polluted farmlands: A contingent valuation method case study in northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences 2016, 75(3), 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civil Code Proclamation No. 165/1960., Pub. L. No. Proclamation No. 165/1960, Civil Code. 1960.
- Gashaw, T.A. Land Expropriation and Compensation Payment in Ethiopia: Review. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development 2015, 6(13). Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234647125.pdf.
- Ambaye, D. Conceptualizing Expropriation. 2015; 93–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dires, T.; Fentie, D.; Hunie, Y.; Nega, W.; Tenaw, M.; Agegnehu, S.K.; Mansberger, R. Assessing the Impacts of Expropriation and Compensation on Livelihood of Farmers: The Case of Peri-Urban Debre Markos, Ethiopia. Land 2021, 10(6), 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanclay, F. Project-induced displacement and resettlement: From impoverishment risks to an opportunity for development? Impact Assessment and Project Appraisal 2017, 35(1), 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singto, C.; Fleskens, L.; Vos, J. Compensation for displacement caused by dam building: Representation, recognition, and outcomes in Thailand. Impact Assessment and Project Appraisal 2022, 40(5), 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, B.; Webber, M.; Yuefang, D. Involuntary Resettlement as an Opportunity for Development: The Case of Urban Resettlers of the Three Gorges Project, China. Journal of Refugee Studies 2008, 21(1), 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, L.J.; Wet C de Mander, H.; Nagraj, V.K. Displacement, Resettlement, Rehabilitation, Reparation, and Development. Secretariat of the World Commission on Dams. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Phonepraseuth, V. From Resettlement To Sustainable Livelihood Development: The Potential Of Resettlement And Livelihood Restoration Arrangement To Achieve Livelihood Sustainability. Massey University. 2012. Available online: https://mro.massey.ac.nz/handle/10179/3594.
- Egze, A.; Zeleke, T.; Seyoum, A. The impact of involuntary resettlement on households’ livelihood: A case study of railway infrastructure induced resettlement in South Wello zone of Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 138402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanzima, J. Large dams: Long term impacts on riverine communities and free flowing rivers: by Thayer Scudder, Springer Nature Singapore Pvt Ltd, 2019, 284 pp., €135.19 (hardback), €107.09 (paperback), ISBN 978-981-13-2550-2 (e-book). Water International 2020, 45(7–8), 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhao, M. Rural Households’ Willingness to Accept Compensation Standards for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution: A Case Study of the Qinba Water Source Area in Northwest China. Water 2019, 11(6), 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, H.A.; Almaleeh, T.A.; Elshareef, I.M.M. Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services Provided by Dellanj Forest Using Contingent Valuation Methods. Journal of Economics and Public Finance 2022, 8(4), p58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan-Basri, B.; Bakar, N.; Bakar, N. Willingness to Pay (WTP) and Willingness to Accept (WTA): Why Bother? 2015. Available online: https://www.ukm.my/fep/perkem/pdf/perkem2015/PERKEM_2015_3C2.pdf.
- Ginsburgh, V. Contingent Valuation, Willingness to Pay, and Willingness to Accept. In Economic Ideas You Should Forget; Frey, B.S., Iselin, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing, 2017; pp. 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariel, P.; Hoyos, D.; Meyerhoff, J.; Czajkowski, M.; Dekker, T.; Glenk, K.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Liebe, U.; Olsen, S.B.; Sagebiel, J.; Thiene, M. Environmental Valuation with Discrete Choice Experiments: Guidance on Design, Implementation and Data Analysis; Springer International Publishing, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA, C. S. A. of E. Population and Housing Census, central statistical agency of Ethiopia (CSA (2007)). 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abegaz, W.B. Temperature and Rainfall Trends in North Eastern Ethiopia. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources 2020, 25(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, K.G.; Bereket, M.T.; Abebaw, G.; Yimam, E. Assessment of public knowledge, attitude and practices towards rabies in the community of Kombolcha, Southern Wollo, Amhara Reginal State, Ethiopia. Journal of Public Health and Epidemiology 2019, 11(1), 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, P.; Ramadani, A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Bornstein, M.M. A Systematic Review of WTA-WTP Disparity for Dental Interventions and Implications for Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Healthcare 2020, 8(3), 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, A. Valuing Households’ Willingness to Pay for Water Transfers from the Irrigation Sector: A Case Study of the City of Seville (Southern Spain). Sustainability 2019, 11(24), 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T.; Berhane, T.; Mulatu, D.W.; Rannestad, M.M. Willingness to accept compensation for afromontane forest ecosystems conservation. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyongesa, J.M.; Bett, H.K.; Lagat, J.K.; Ayuya, O.I. Estimating farmers’ stated willingness to accept pay for ecosystem services: Case of Lake Naivasha watershed Payment for Ecosystem Services scheme-Kenya. Ecological Processes 2016, 5(1), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemann, M.; Bateman, I.J.; Carson, R.T.; Day, B.; Hanley, N.; Hett, T.; Jones-Lee, M.; Loomes, G. Economic Valuation with Stated Preference Techniques: A Manual; Edward Elgar Publishing, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereket, G.K. Socio-cultural and economic impacts of development induced displacement on resettled people: The case of Welkayt Sugar Factory in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. International Journal of Sociology and Anthropology 2020, 12(4), 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboda, C.; Vedeld, P.O.; Musali, P.; Nabanoga, G.; Mugagga, F. Vulnerability of households to resettlement and compensation measures for an oil refinery project in the Albertine region of Uganda. Geo-Journal 2022, 888(3), 3121–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.; Saharan, T. Urban development-induced displacement and quality of life in Kolkata. Environment and Urbanization 2019, 31(2), 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia 2019, 22(1), 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y. Rural households’ willingness to accept compensation for energy utilization of crop straw in China. Energy 2018, 165, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiale, E.D.; Balcombe, K.; Srinivasan, C. Determinants of Farm Households’ Willingness to Accept (WTA) Compensation for Conservation Technologies in Northern Ghana. Bio-Based and Applied Economics 2020, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.H.; Cherry, T.L.; Kallbekken, S.; Torvanger, A. Willingness to accept local wind energy development: Does the compensation mechanism matter? Energy Policy 2016, 99, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Kong, F. The Analysis of Farmers’ Willingness to Accept and Its Influencing Factors for Ecological Compensation of Poyang Lake Wetland. Procedia Engineering 2017, 174, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postelnicu, T. Probit Analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkapitux, C.; Neef, A.; Polkongkaew, W.; Pramoon, N.; Nonkiti, S.; Nanthasen, K. Willingness of upstream and downstream resource managers to engage in compensation schemes for environmental services. 2009. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




