Submitted:
23 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Goal #1: To quantify data factors in the data set and separate into events, outcomes, and points of interest.
- Goal #2: To showcase visualization of the results derived from Goal #1
- Goal #3: To help explain how to build knowledge and data using visualization.
- Goal #4: To leverage ML models to showcase the utility in the educational data.
- Goal #5: To understand the intent of usage of the data and impact.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
3.1. Dataset
| Type | Grade Level | % of Students Did Not Meet | % of Students Approaches | % of Students Meets | % of Students Masters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 3 | 22.39 | 77.18 | 49.80 | 28.23 |
| Sd | 0 | 13.48 | 14.34 | 16.18 | 12.9 |
| Min | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25% | 3 | 13 | 70 | 40 | 20 |
| 50% | 3 | 21 | 79 | 50 | 27 |
| 75% | 3 | 30 | 87 | 60 | 35 |
| Max | 3 | 90 | 100 | 100 | 77 |
3.2. Extraction, Transformation and Loading
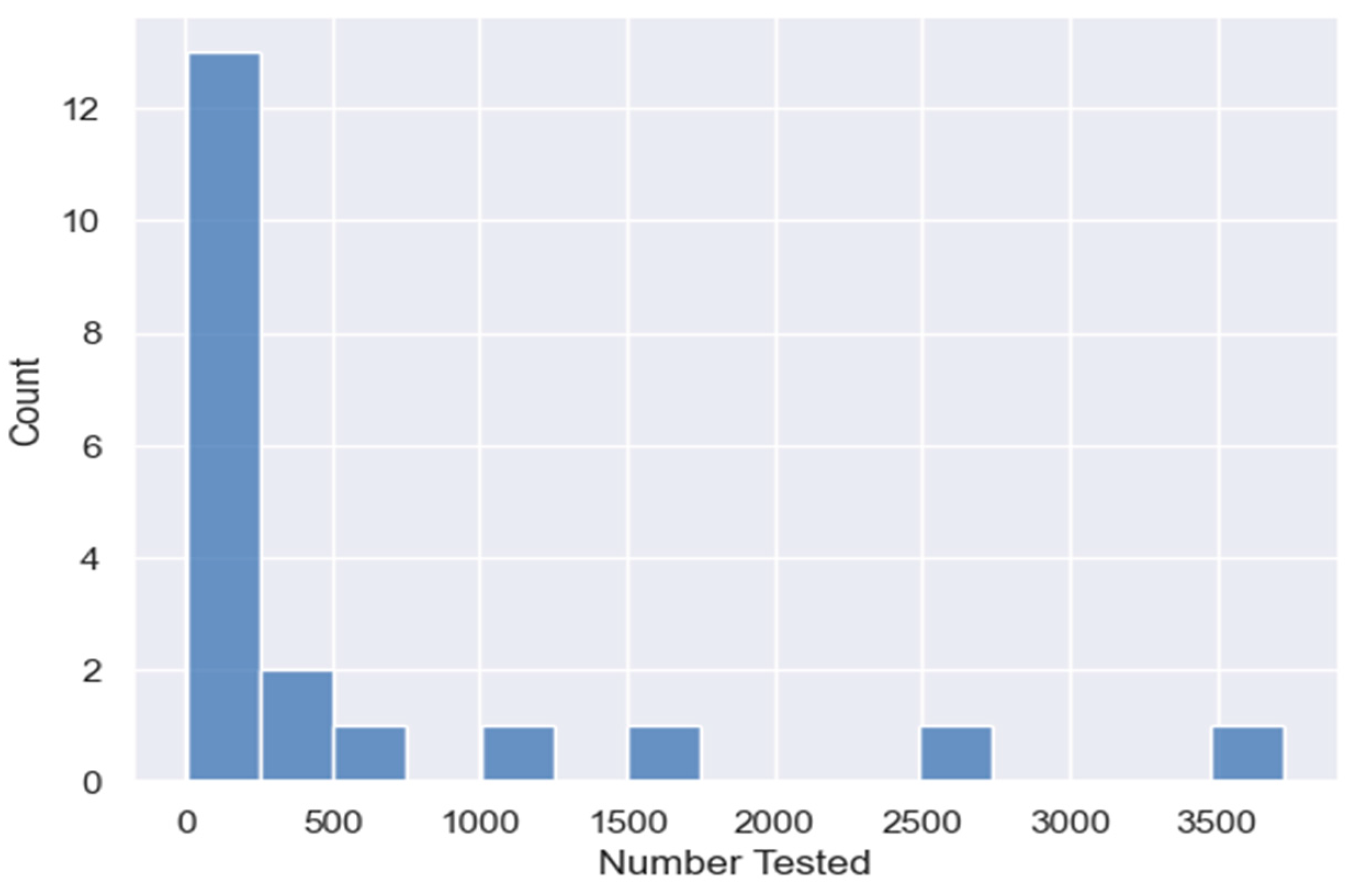
- Number of students tested
- Percent of students at proficiency
- Dates of assessment
- Location
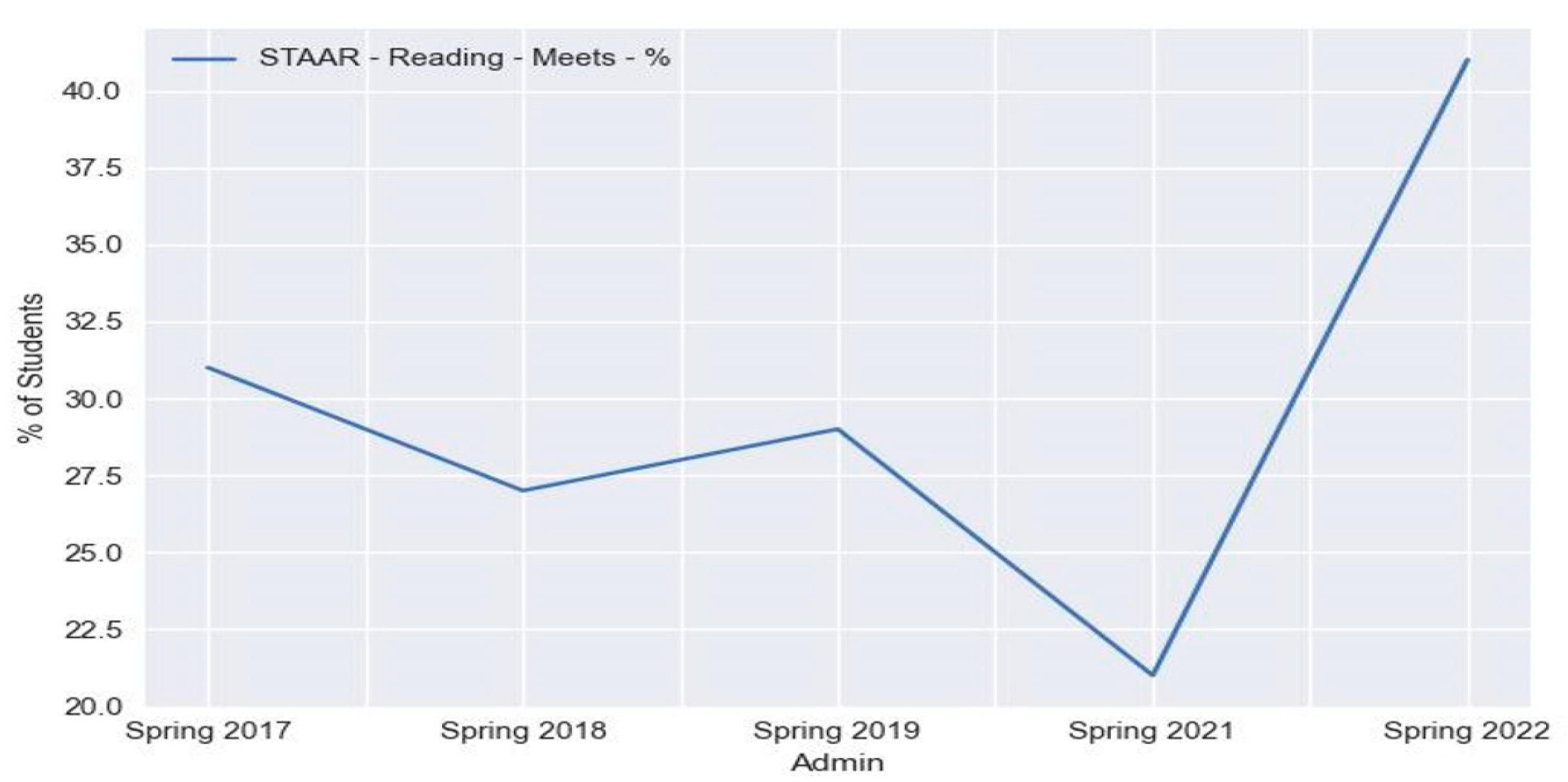
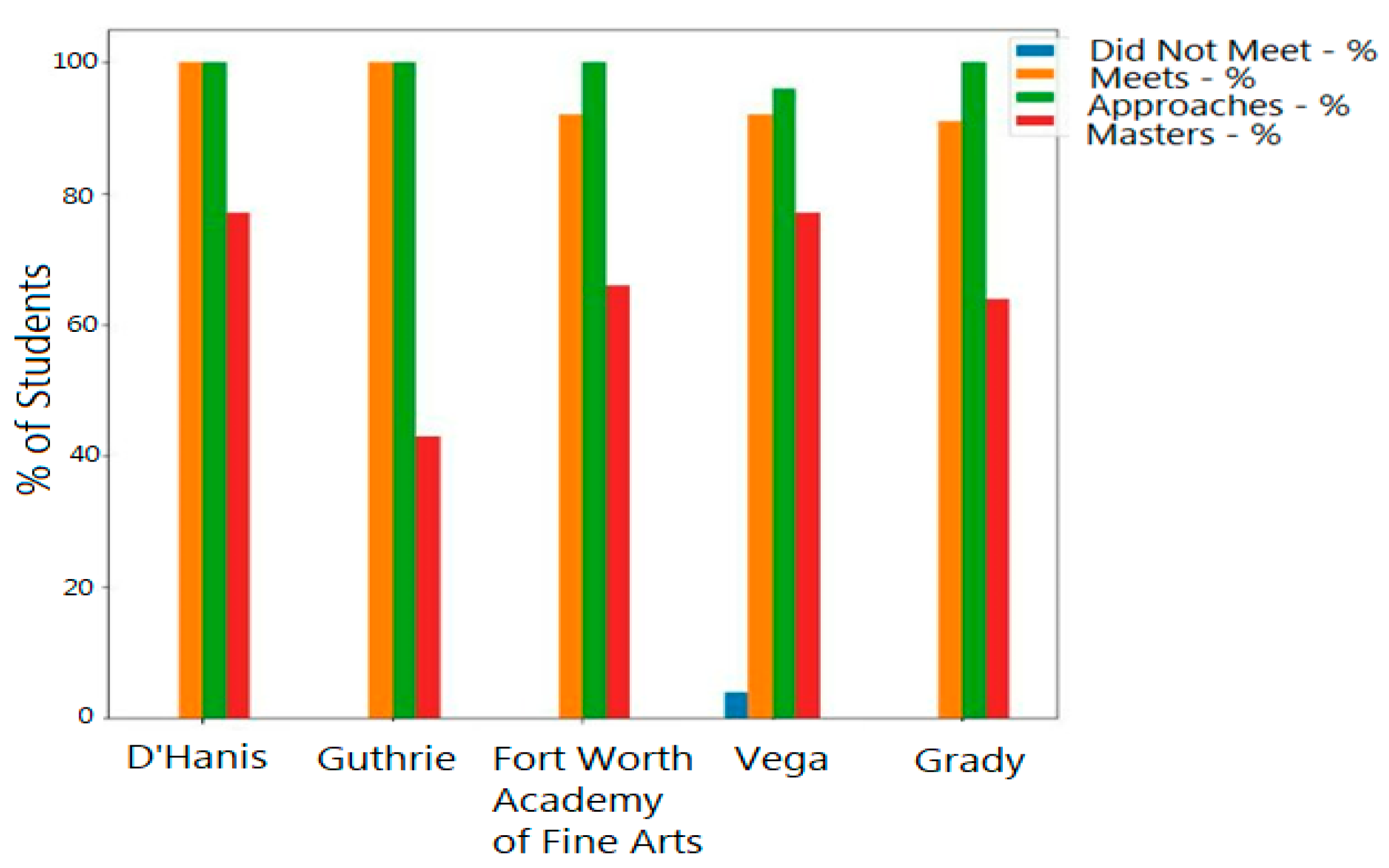
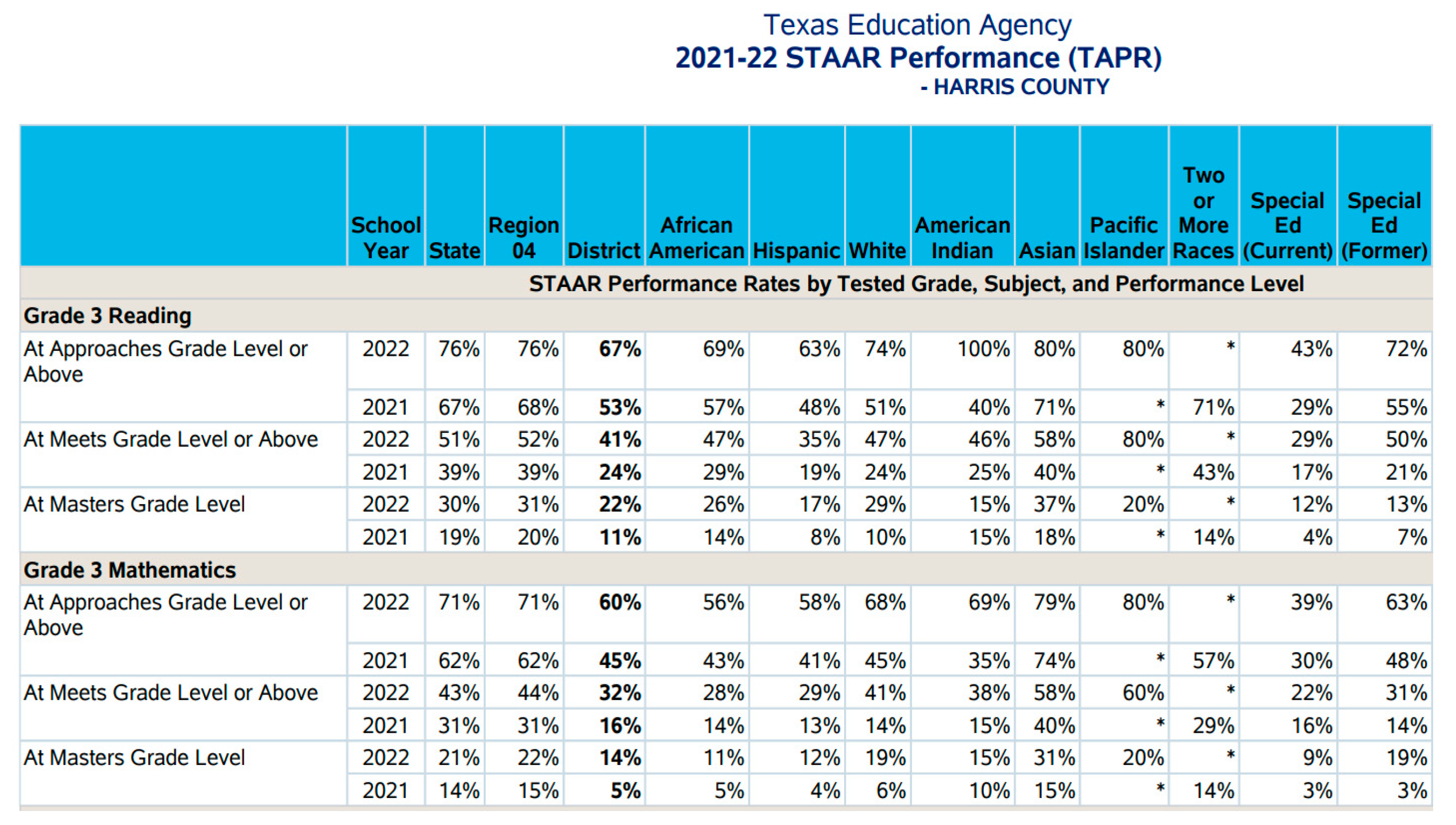
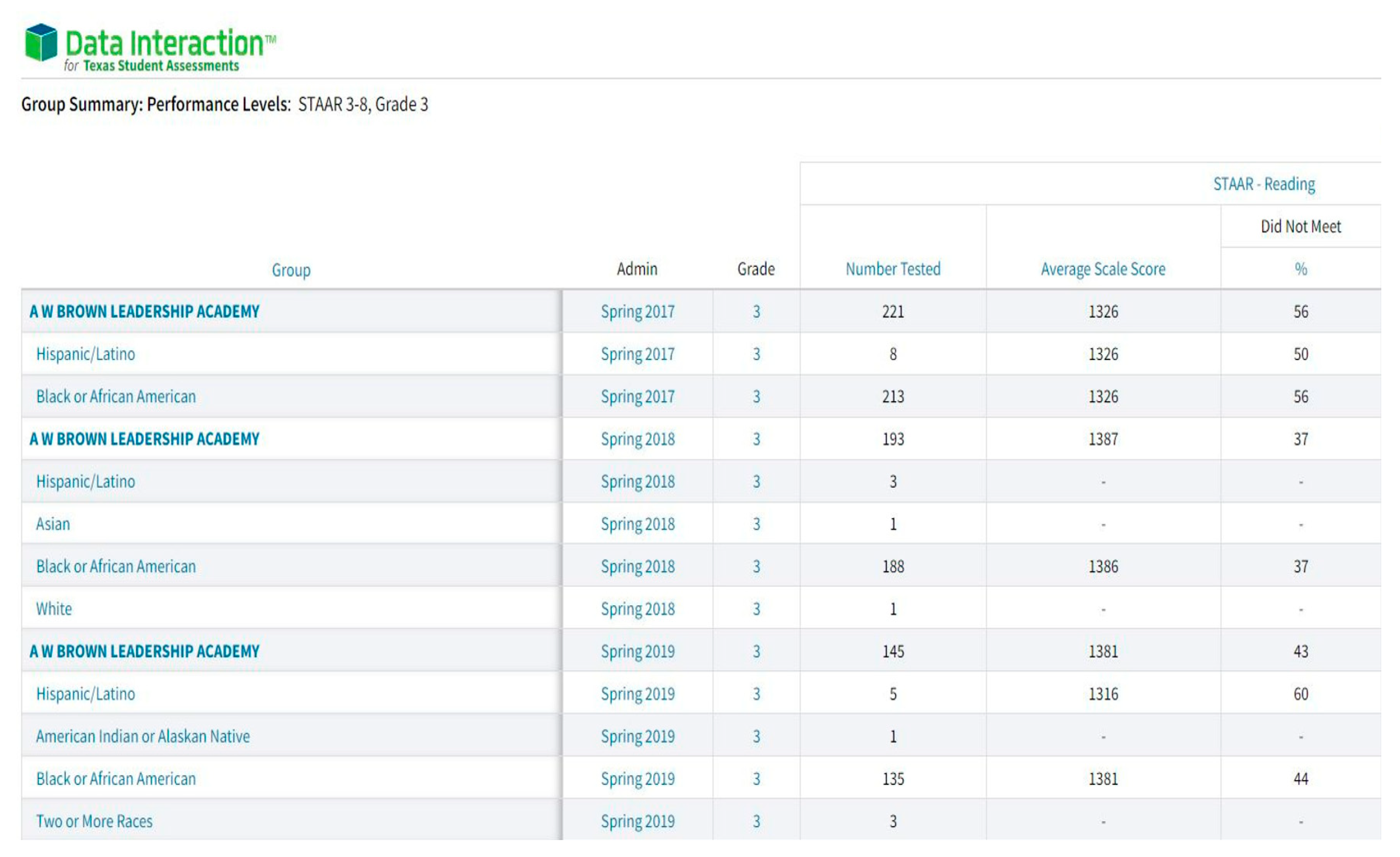
3.3. Learning Models
3.3.1. Expected Results
-
Financial Benefits
- Result #1: Reduce expenditure of funds on resources to generate products
- Result #2: Inexpensive data evaluation to interested entities
-
Technical Benefits
- Result #1: Computerized model of data and correlations
- Result #2: Additional hands-on usage of data visualization
- Result #3: Evidentiary support/background research used as preliminary to future work
-
Other BenefitsThese benefits are those that are specific to the stakeholders:
- Result #1: Increased stakeholder investment and satisfaction
- Result #2: Opportunity to be used in conferences and research presentations
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
| Steps | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Step 1: | Determine the data used in the implementation |
| Step 2: | Create the Python code to generate the desired data analysis |
| Step 3: | Save the Python code in a specified location and make note of the file path |
| Step 4: | Create a batch script file to execute the data to the web browser of choice through StreamLit. Use the file path of the saved Python file for the run command |
| Step 5: | Save the batch script preferably in an easy to manage location for instant access or deployment |
| Step 6: | Assign an image icon to the batch script |
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
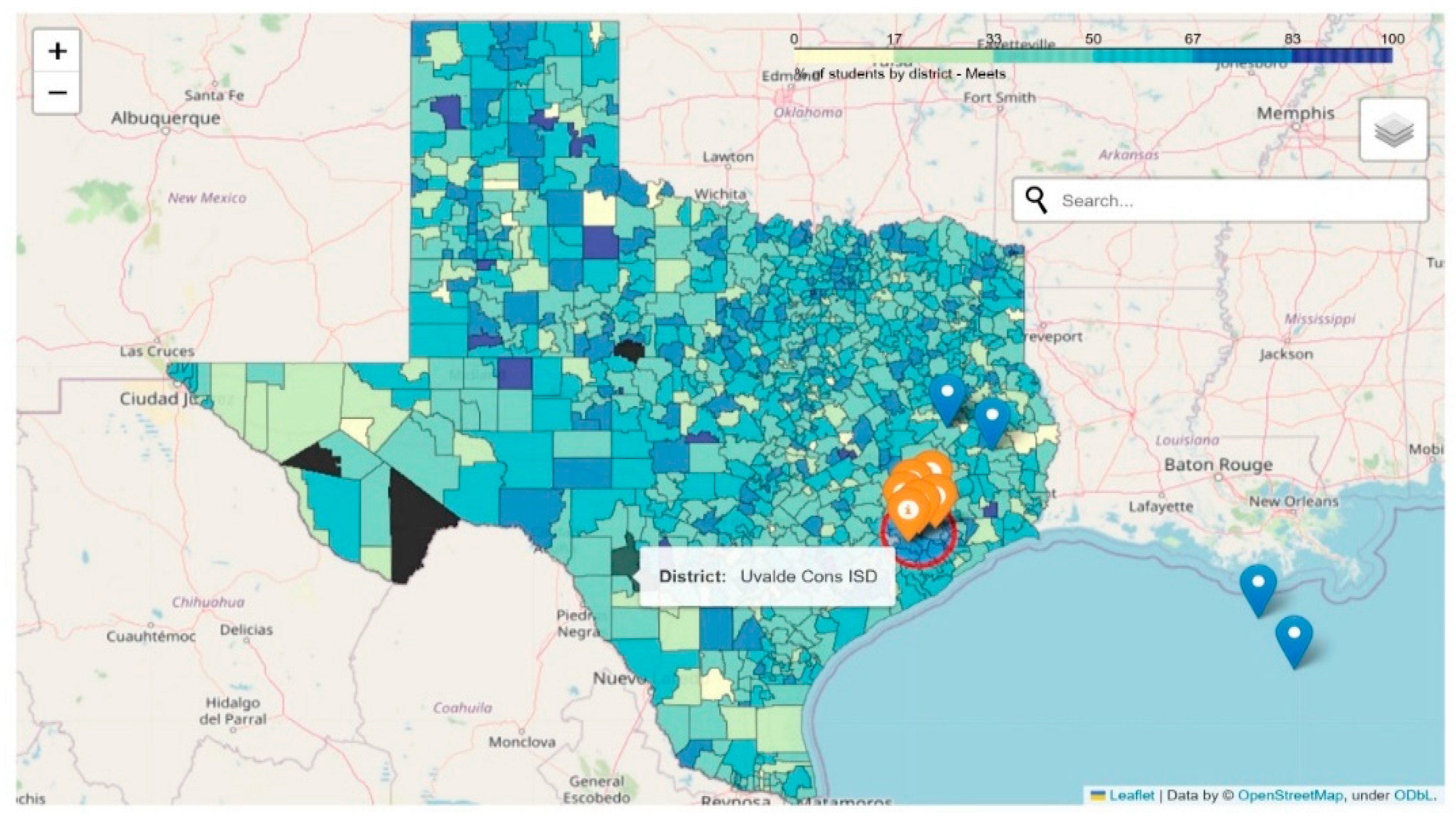
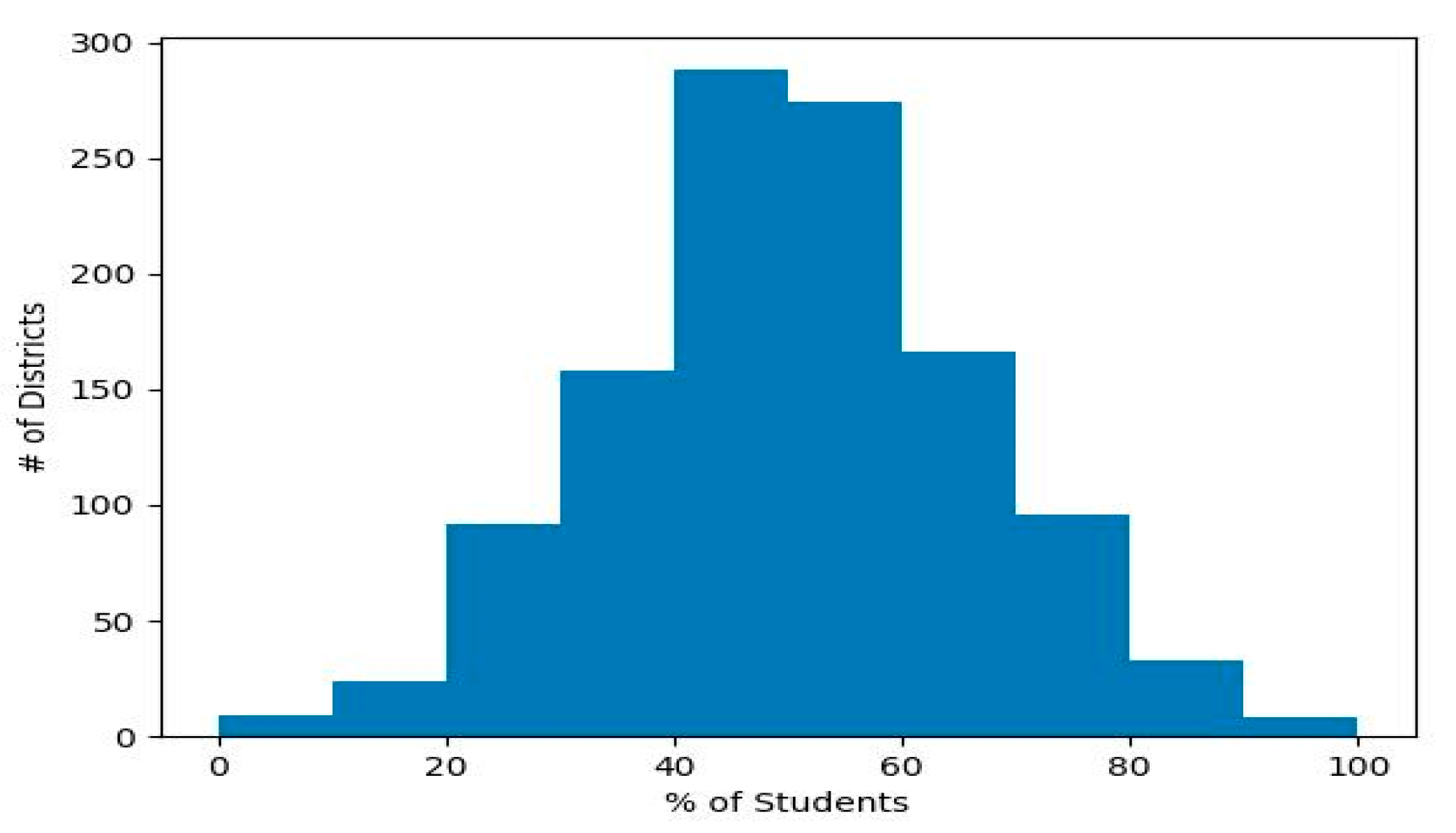
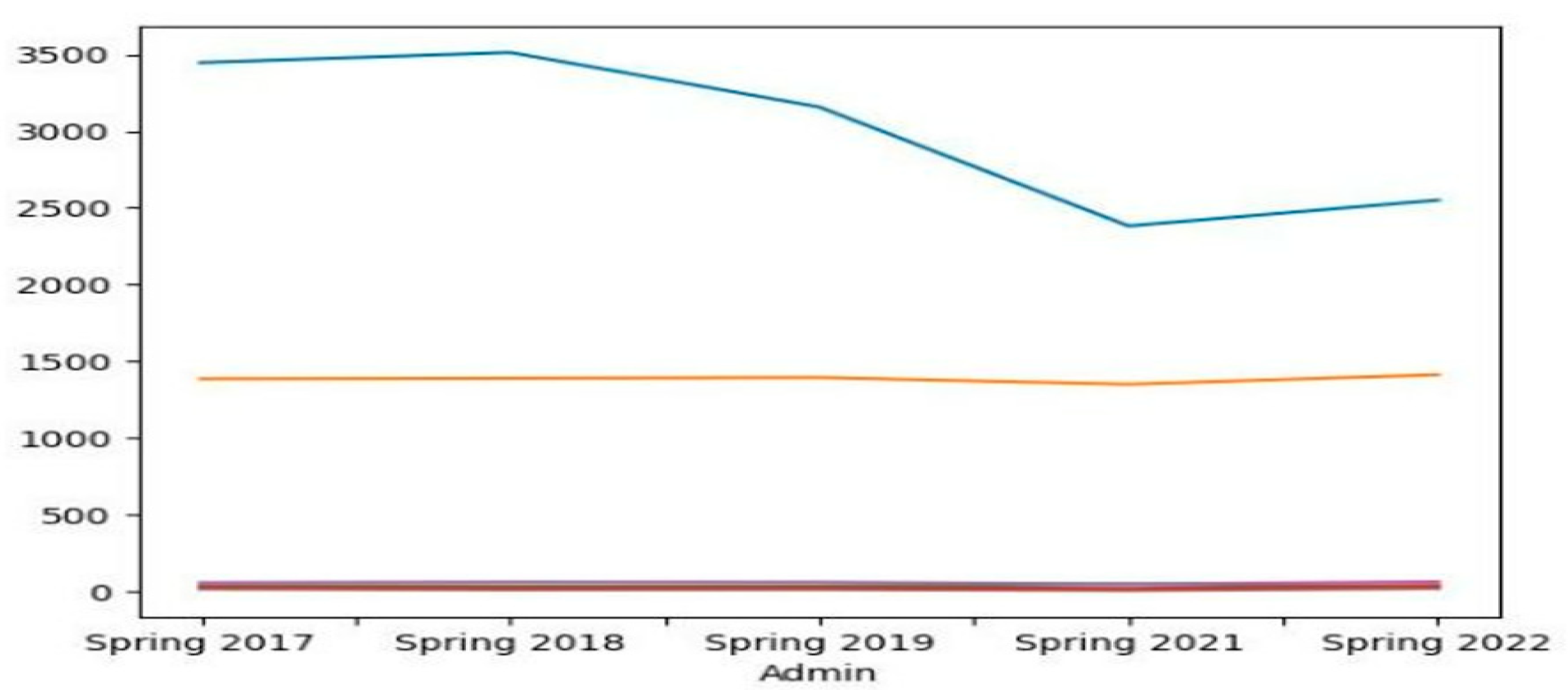
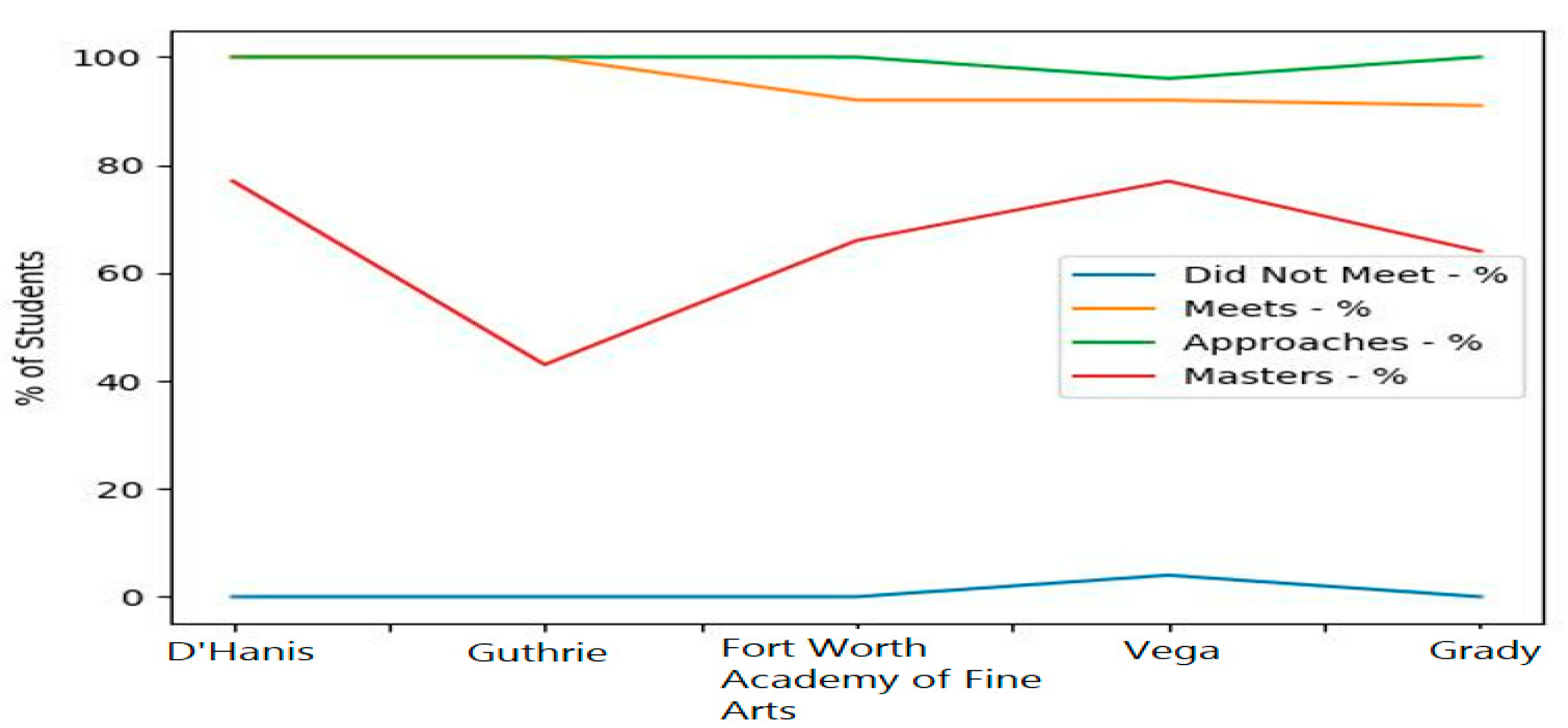
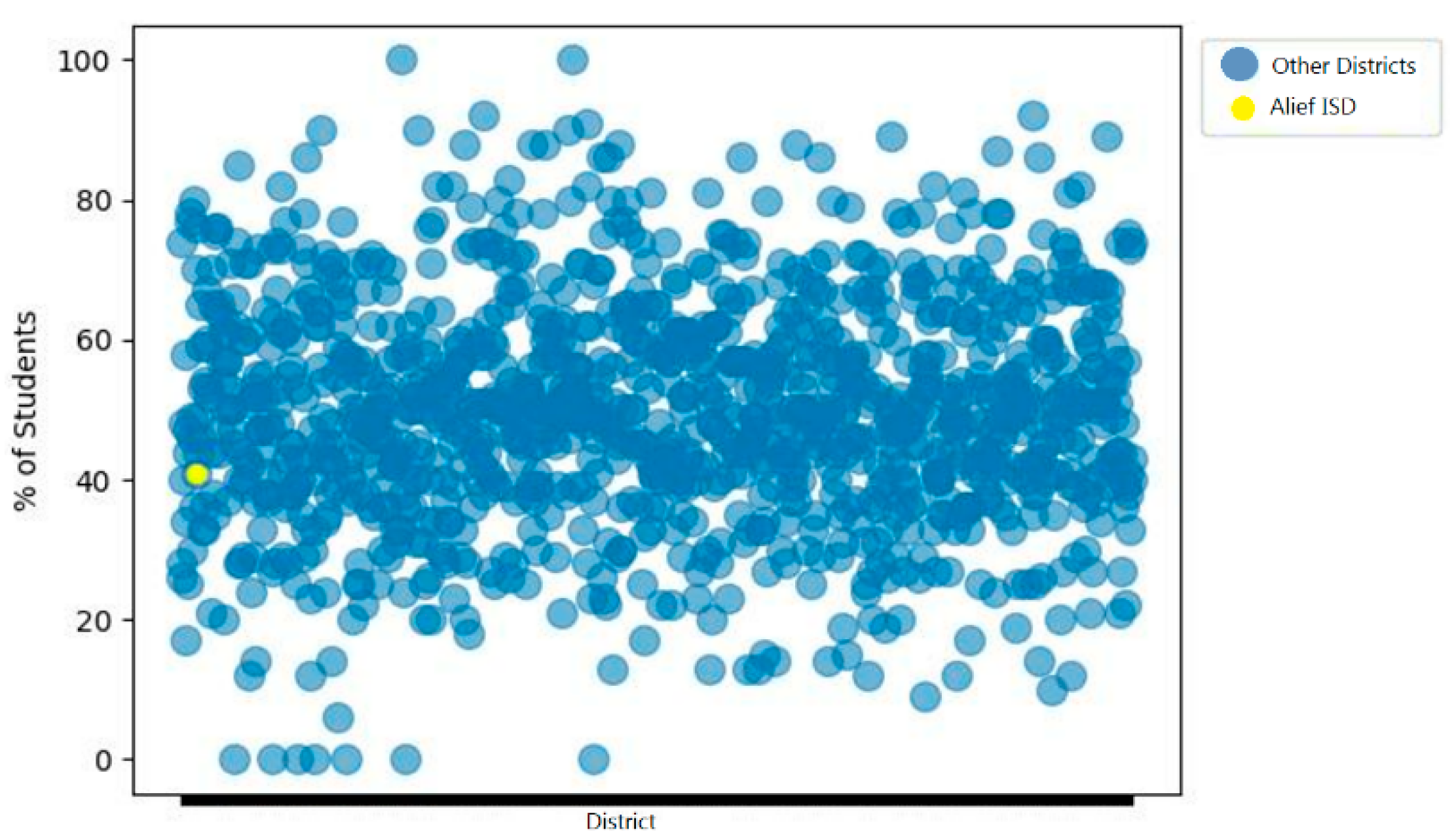
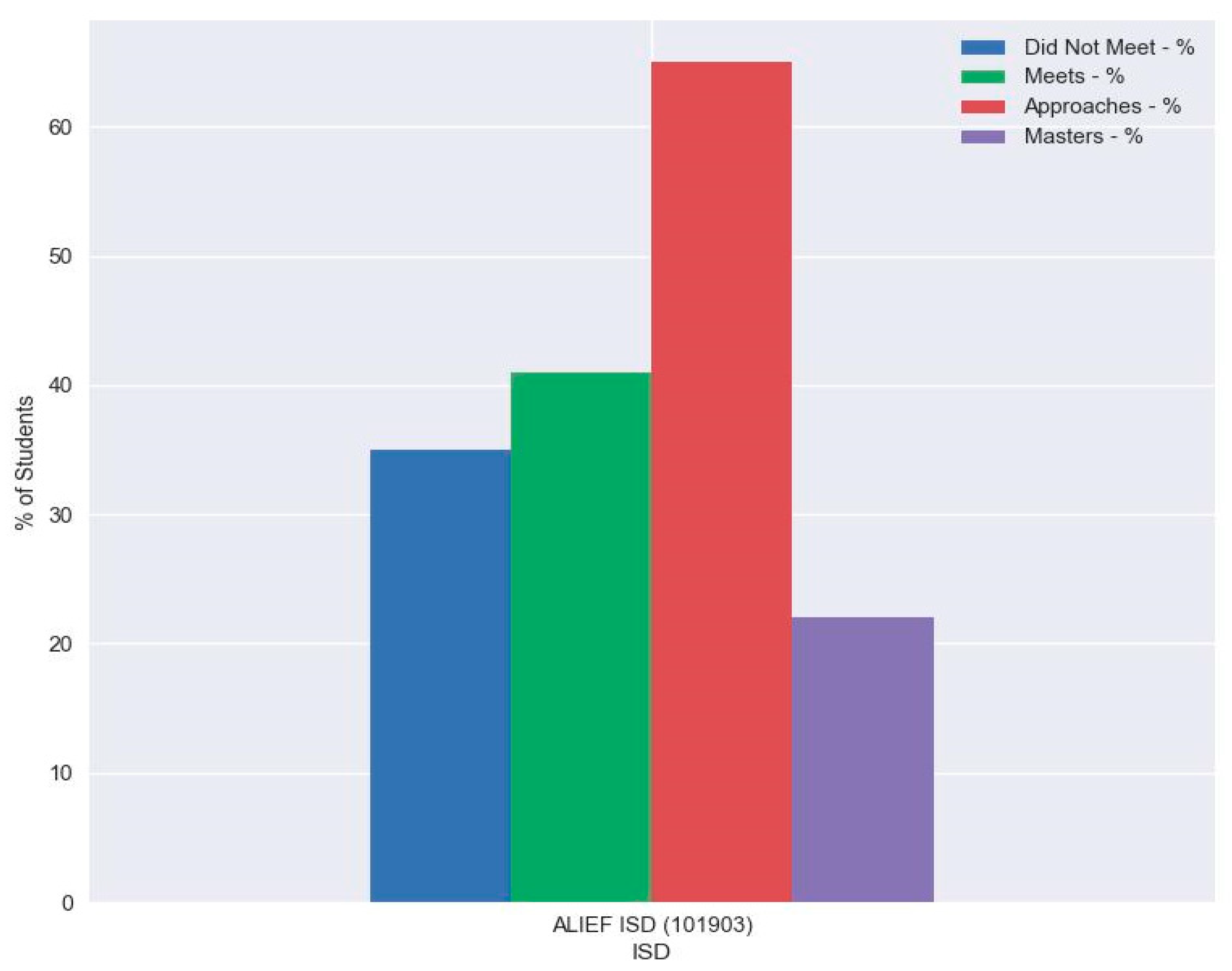
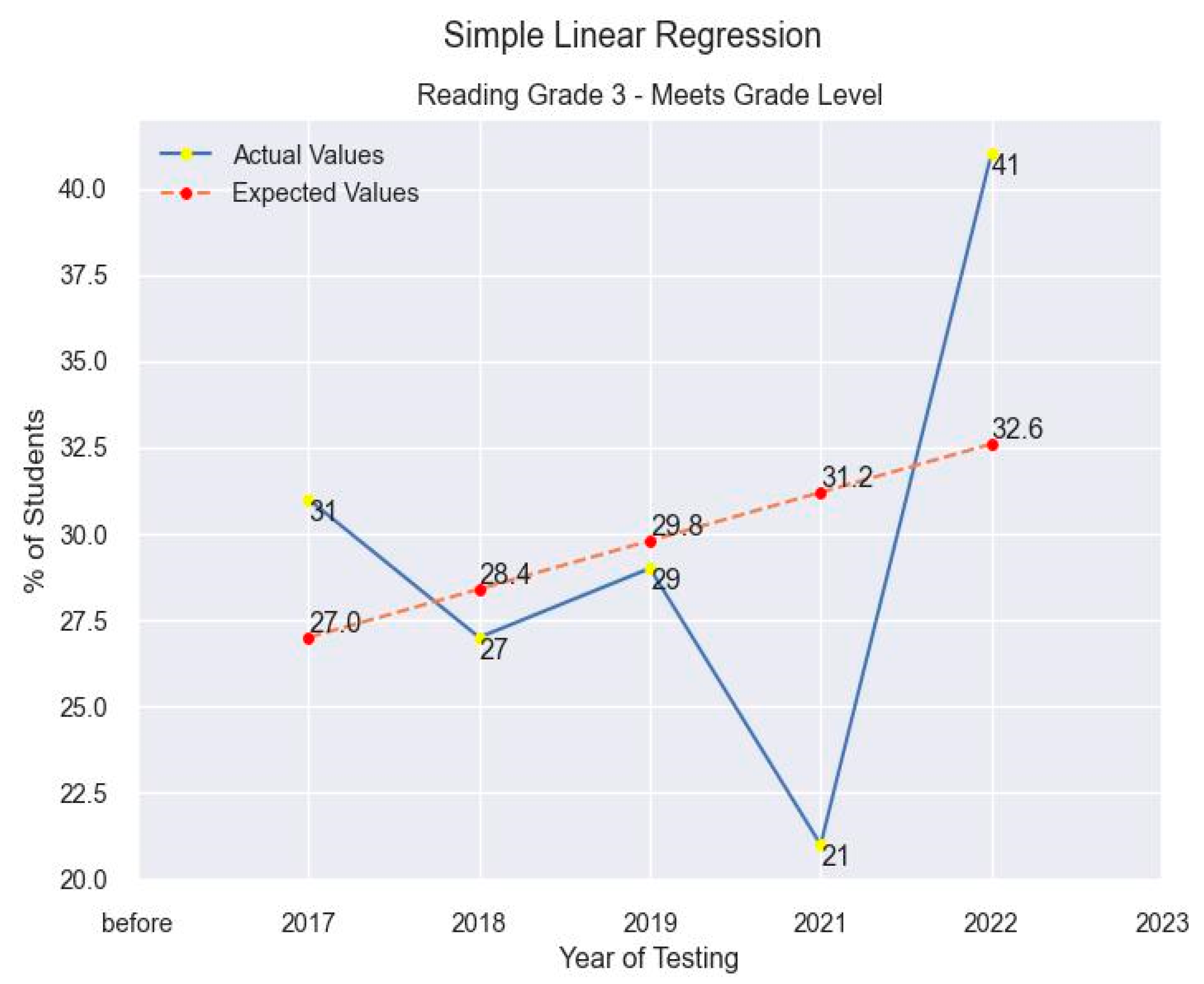
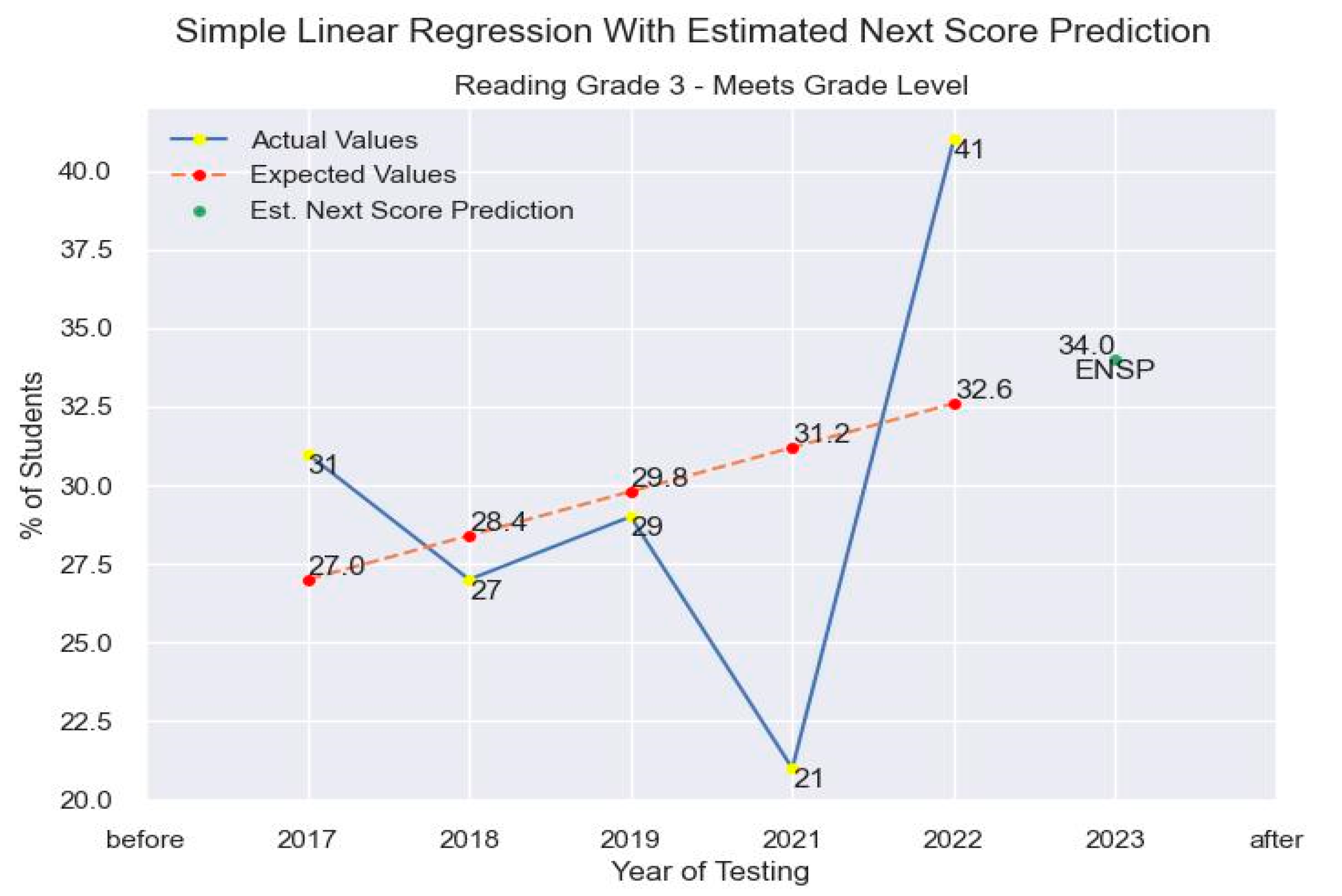
4.3. Results
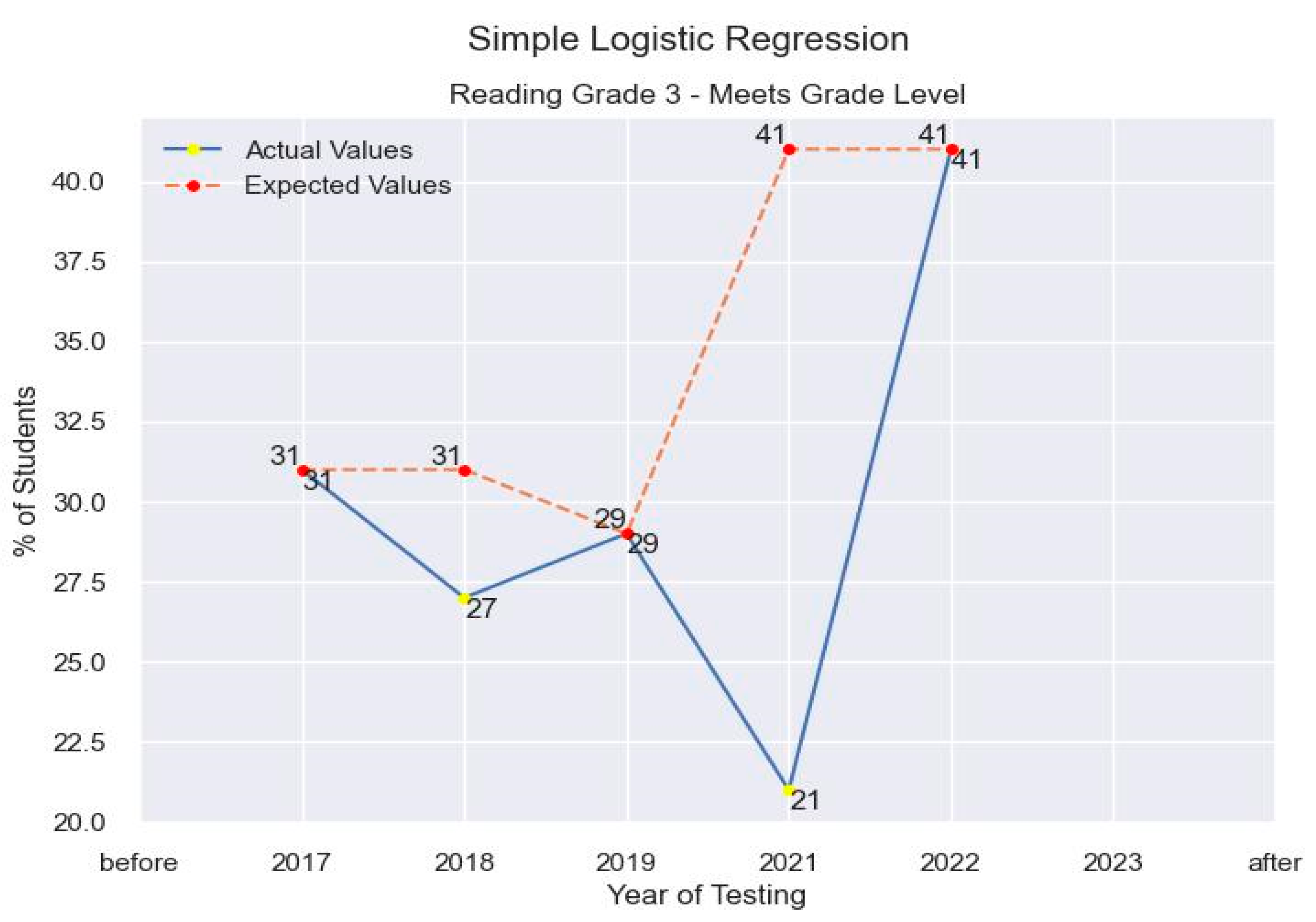
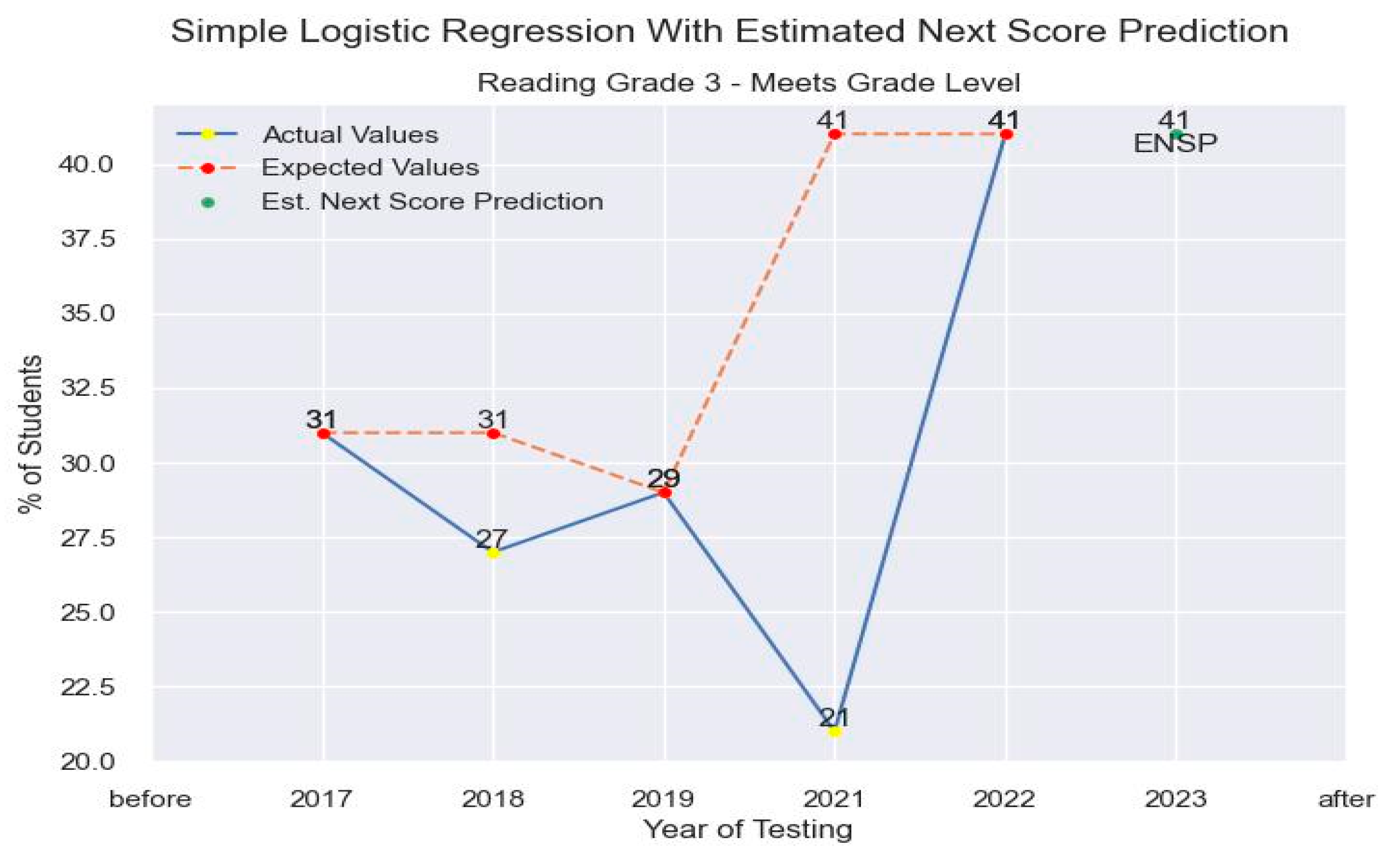
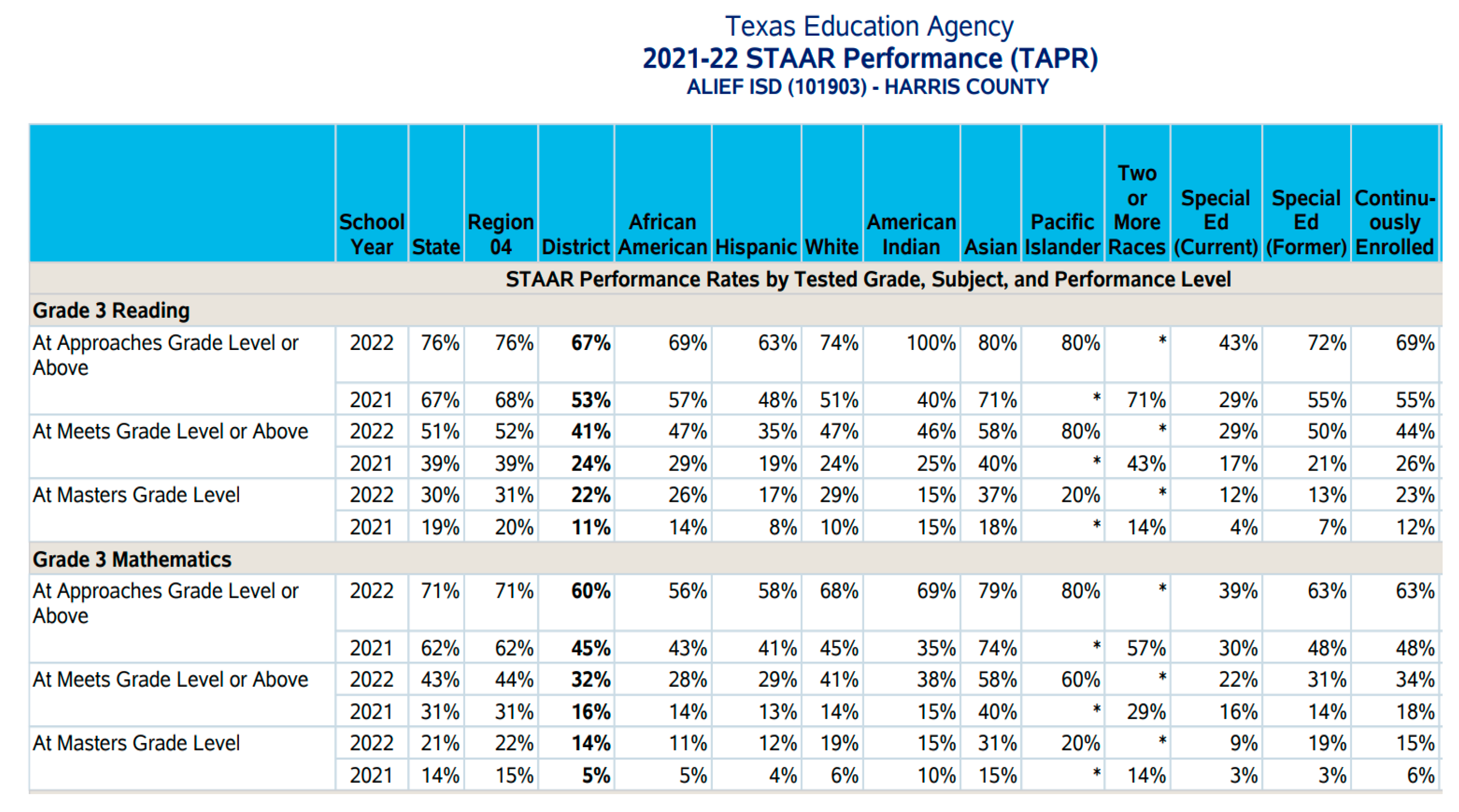
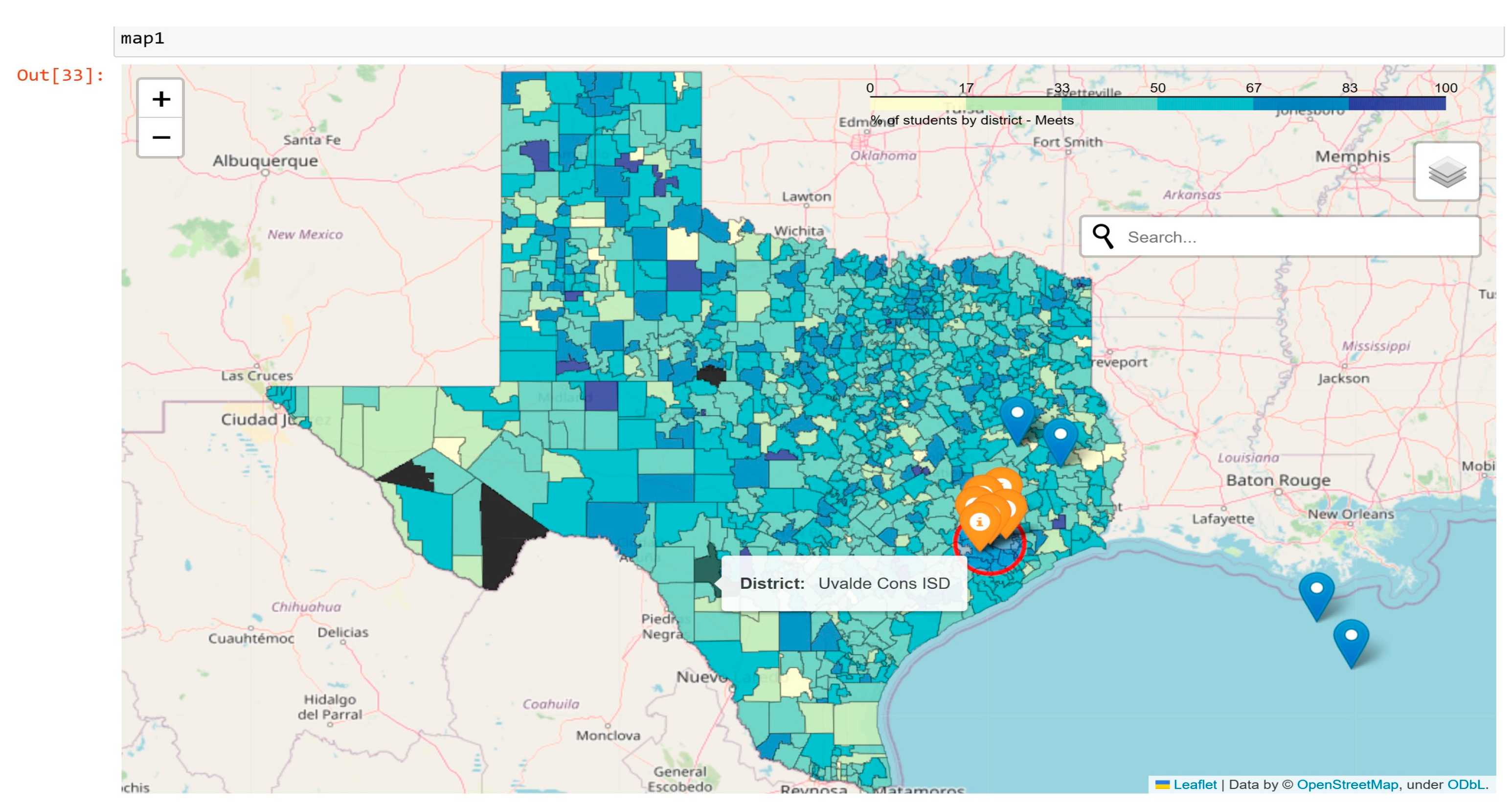
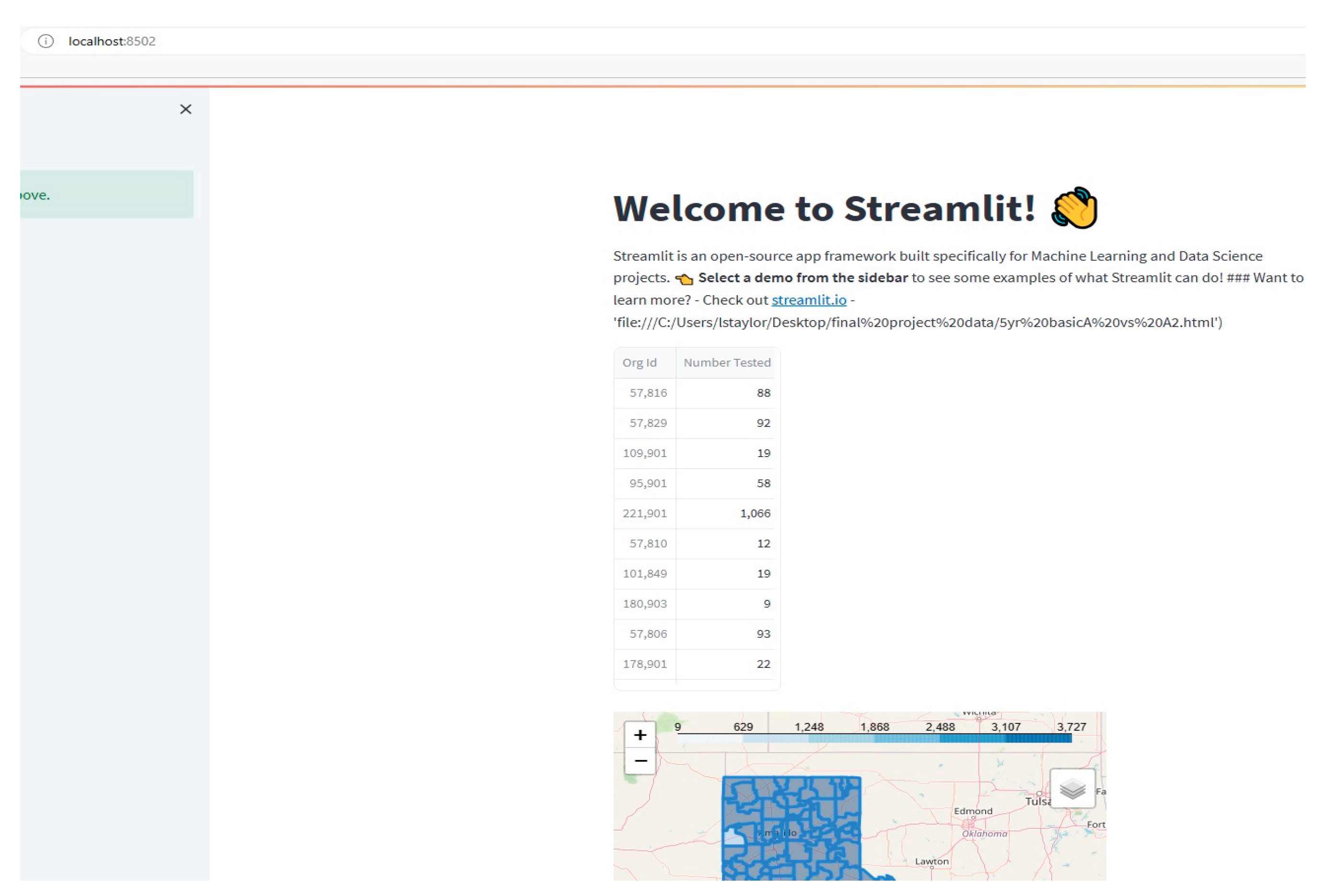
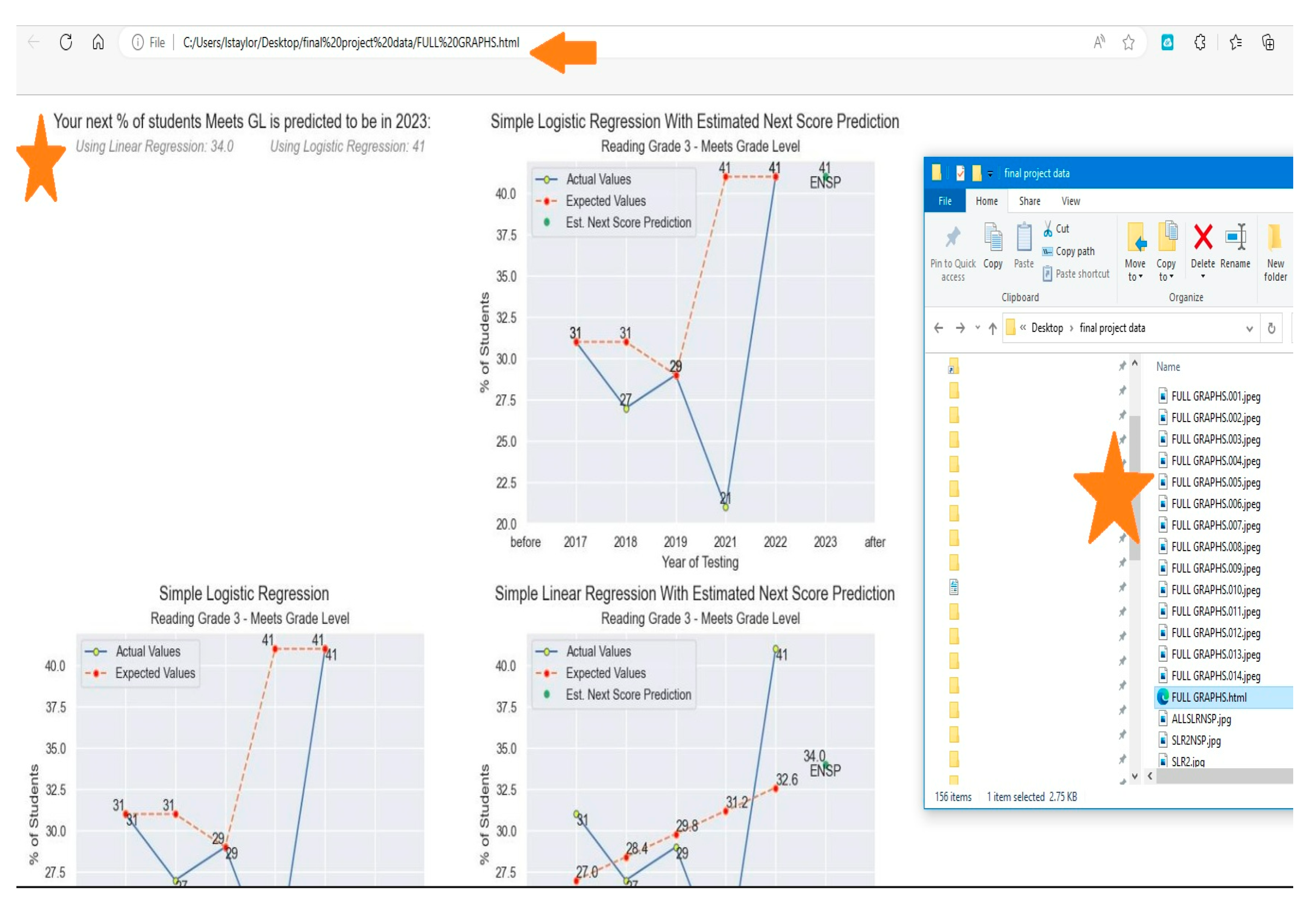
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, N., Wu, E., Li, G. 2019. Towards Democratizing Relational Data Visualization. In 2019 International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD ’19), June 30–July 5, 2019, Amsterdam, Netherlands. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 6 pages. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Education, Office of Educational Technology, Artificial Intelligence and Future of Teaching and Learning: Insights and Recommendations, Washington, DC, 2023.
- Ocheja, P., Flanagan, B., Oyelere, S., Ogata, H. (2022). Visualization of education blockchain data: trends and challenges. Interactive Learning Environments. [CrossRef]
- Pella, S. (2012). What should count as data for data driven instruction? Toward contextualized data-inquiry models for teacher education and professional development. Middle Grades Research Journal, 7. 57-75.
- Marshall, K. (2009). What Data-Driven Instruction Should Really Look Like. Available online: URL: https://www.teachermagazine.org (accessed on 28 Jan 2024).
- Results Driven Accountability Data and Reports. Available online: URL: https://tea.texas.gov/reports-and-data/school-performance/results-driven-accountability-data-and-reports (accessed on 28 Jan 2024).
- Dayana, B. D., Samanta, A., Ranganathan, N., Venkatachalam, K., & Jain, N. (2019). A comprehensive approach to visualize industrial data set to meet business intelligence requirements using statistical models and big data analytics. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 7(6), 1437–1443.
- Moss, G. (2014). The Rise of Data in Education Systems: Collection, visualization and use. London Review of Education. 12. 154-155. [CrossRef]
- Yafeng, Z., Yaning, Z., Xue, B., Qian, F. (2021). Survey of Big Data Visualization in Education. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2009014. [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.P. (2020) The Importance of Data Cleaning: Three Visualization Examples, CHANCE, 33:1, 4-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X., Chu, X., Sing Chai, C., Siu Yung Jong, M., Istenic, A., Spector, M., Liu, J., Yuan, J., Li, Y. "A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education from 2010 to 2020", Complexity, vol. 2021, Article ID 8812542, 18 pages, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Uyan Dur, B. (2014). Data Visualization and Infographics in Visual Communication Design Education at the Age of Information. Journal of Arts and Humanities (JAH), Volume -3, No.-5, May, 2014.
- Rui, Z., Badarch, T. (2022). Research on Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Education. American Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 5(2), 72-79. [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. 1985. Applications of Artificial Intelligence Within Education. DOI: 10.1016/0898-1221(85)90054-9. [CrossRef]
- Beck, J., Stern, M., Haugsjaa, E. (1996). Applications of AI in education. XRDS 3, 1 (September 1996), 11–15. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., Zhao, P., Li, Y., Tai Chui, K. 2022. Design of Education Information Platform on Education Big Data Visualization. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Llaha, O., Aliu, A. (2023). Application of Data Visualization and Machine Learning Algorithms for Better Decision Making.
- Williamson, B. (2016). Digital education governance: data visualization, predictive analytics, and ‘real-time’ policy instruments, Journal of Education Policy, 31:2, 123-141. [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, J., Howard, A. (2020). Emerging challenges in AI and the need for AI ethics education. [CrossRef]
- Akgun, S., Greenhow, C. Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. AI Ethics 2, 431–440 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Data Interaction for Texas Student Assessments. (2023). Group Summary: Performance Levels: STAAR 3-8, Grade 3. Available online: URL: https://txreports.emetric.net/ (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- Louisiana Department of Education. (2023). STATEWIDE RESULTS. Available online: URL: https://www.louisianabelieves.com/resources/library/data-center/Statewide-Results (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- Louisiana Department of Education. (2023). ELEMENTARY & MIDDLE SCHOOL PERFORMANCE. Available online: URL: https://www.louisianabelieves.com/resources/library/elementary-and-middle-school-performance (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- National Center for Education Statistics. (2023). Data & Tools. Available online: URL: https://nces.ed.gov/ (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- Texas Academic Performance Reports. (2023). Available online: URL: https://tea.texas.gov/texas-schools/accountability/academic-accountability/performance-reporting/texas-academic-performance-reports (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- Texas Assessment Research Portal. (2023). Available online: URL: https://txresearchportal.com/ (accessed on 10 Dec 2023).
- Linear Regression. Available online URL: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rgrosse/courses/csc321_2018/readings/L02%20Linear%20Regression.pdf/ (accessed on 10 Jan 2024).
- Logistic Regression. Available online URL: https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/5.pdf (accessed on 10 Jan 2024).
- Neuman, S.B. (2016). Code Red: The Danger of Data-Driven Instruction. Educational Leadership, 74, 24-29.
- Seo, K., Tang, J., Roll, I. et al. The impact of artificial intelligence on learner–instructor interaction in online learning. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 18, 54 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, C., Selwyn, N. (2019): Deep learning goes to school: toward a relational understanding of AI in education, Learning, Media and Technology. [CrossRef]
- Van der Vorst, T., Jelicic, N. (2019). Artificial Intelligence in Education: Can AI bring the full potential of personalized learning to education?, 30th European Conference of the International Telecommunications Society (ITS): "Towards a Connected and Automated Society", Helsinki, Finland, 16th-19th June, 2019, International Telecommunications Society (ITS), Calgary. http://hdl.handle.net/10419/205222.
- Hershkovitz, A. (2015). Towards data-driven instruction. Teaching, Instruction, Cognition and Learning.
- Williamson, B. 2014. New centers of data visualization in education. DMLcentral.net, 26 June 2014.
- 35. Vincent-Lancrin, S. and R. van der Vlies (2020), "Trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI) in education: Promises and challenges", OECD Education Working Papers, No. 218, OECD Publishing, Paris. [CrossRef]
- Firat, Elif E., Laramee, R. (2018). Towards a Survey of Interactive Visualization for Education.
- Ojha, S., Narendra, A., Mohapatra, S., & Misra, I. (2023). From Robots to Books: An Introduction to Smart Applications of AI in Education (AIEd). arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10026.
- Sharma, R. (2021). Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Education. 1-4.
- Xu, Z., Wei, Y., Zhang, J. (2021). AI Applications in Education. In: Shi, S., Ye, L., Zhang, Y. (eds) Artificial Intelligence for Communications and Networks. AICON 2020. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 356. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, P. Chen and Z. Lin, "Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 75264-75278, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J. P., & Mourad, T. (2018). The growing importance of data literacy in life science education. American journal of botany, 105(12), 1953–1956. [CrossRef]
- Davis Bianco, S. (2010). Improving Student Outcomes: Data-driven Instruction and Fidelity of Implementation in a Response to Intervention (RTI) Model. TEACHING Exceptional Children Plus, 6(5) Article 1. Retrieved [date] from http://escholarship.bc.edu/education/tecplus/vol6/iss5/art1.
- Halverson, R., Grigg, J., Prichett, R., Thomas, C. (2006). The new instruction leadership: Creating data-driven instructional systems in schools. Journal of School Leadership. 25. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).