Submitted:
20 February 2024
Posted:
20 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
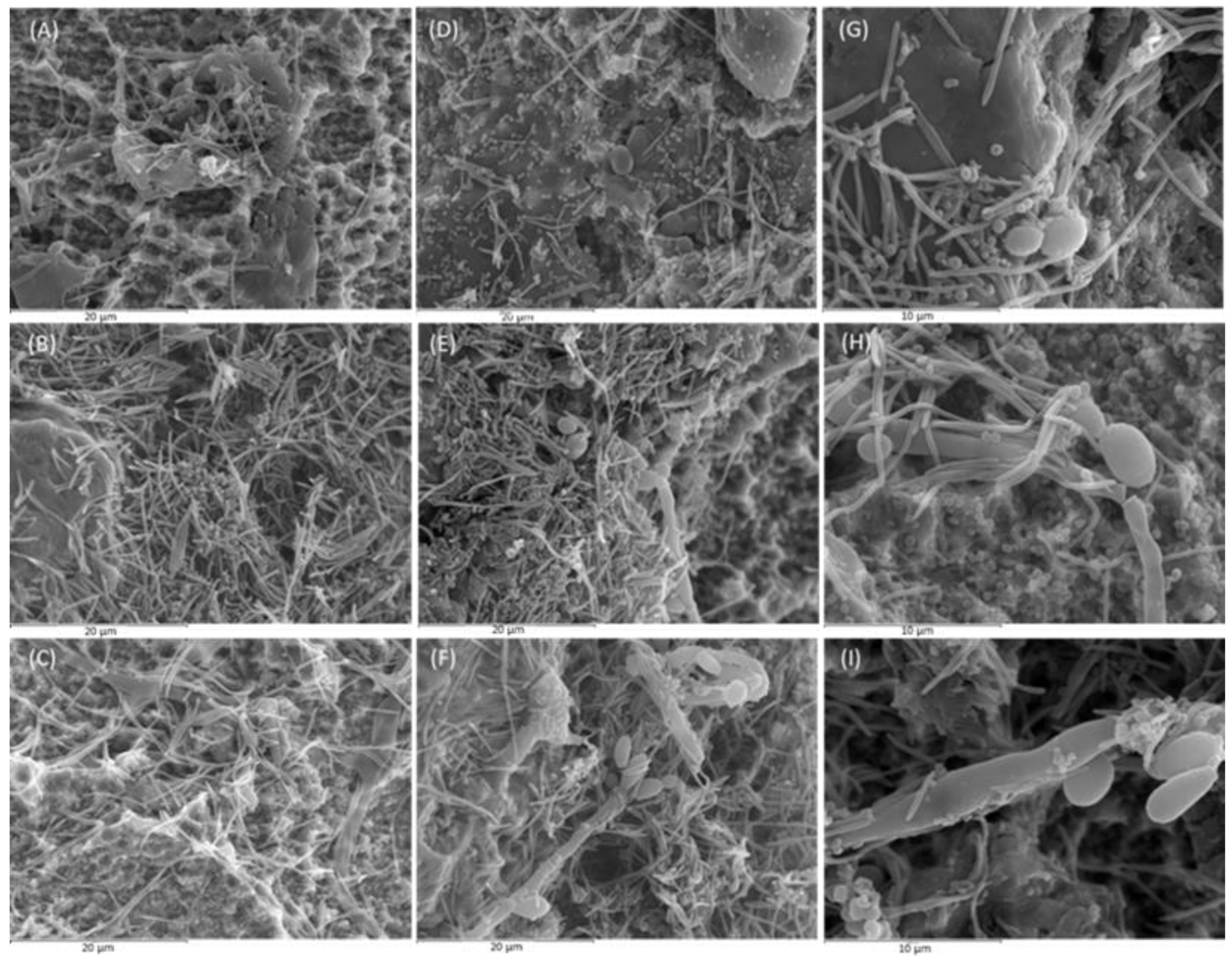
2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis
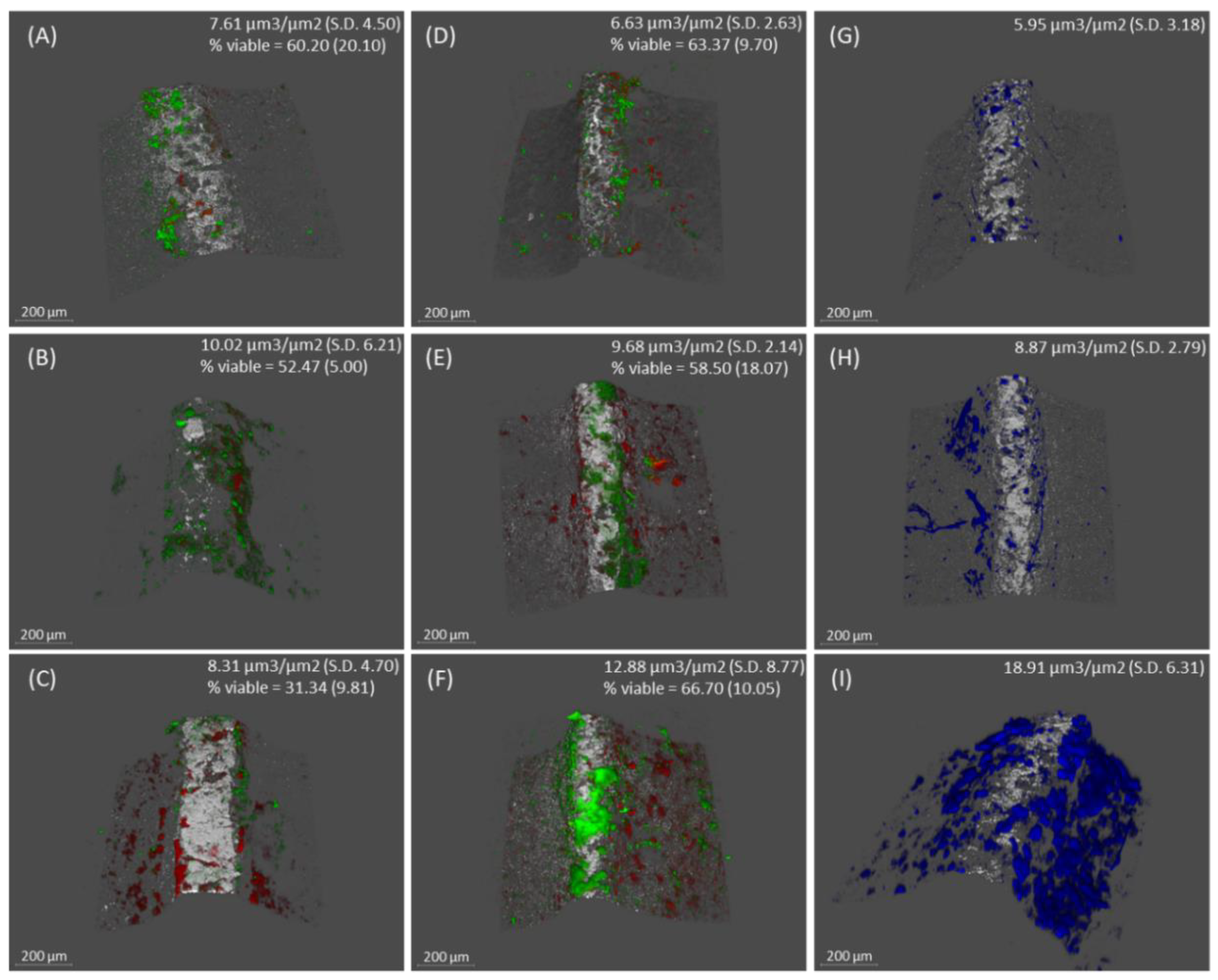
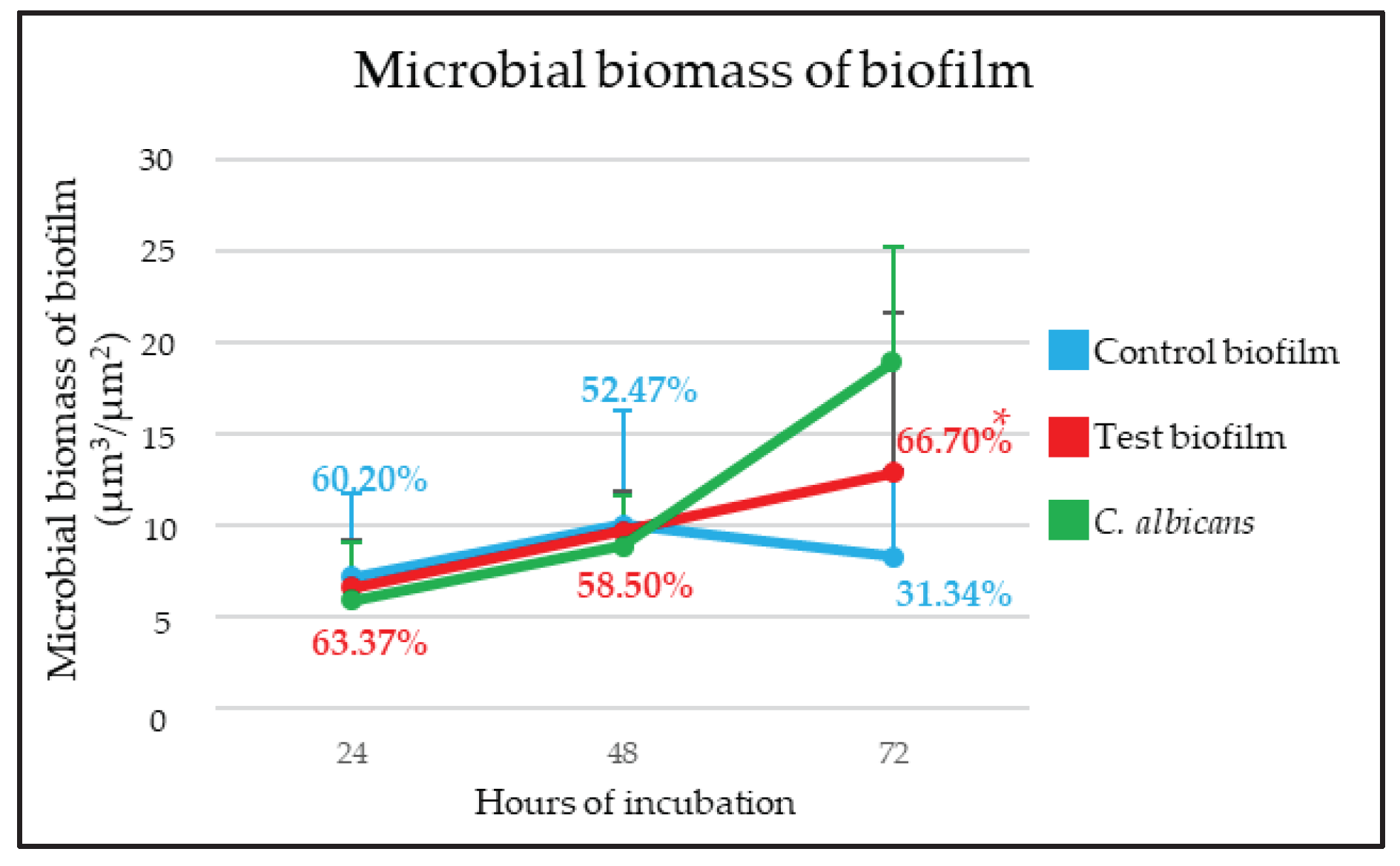
2.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) analysis
2.3. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbial strains and culture conditions
4.2. In vitro dynamic multispecies biofilm model
4.3. Experimental groups
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CSLM)
4.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.7. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buser, D.; Janner, S.F.; Wittneben, J.G.; Bragger, U.; Ramseier, C.A.; Salvi, G.E. 10-year survival and success rates of 511 titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: a retrospective study in 303 partially edentulous patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2012, 14, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Sennerby, L.; De Bruyn, H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol 2000 2017, 73, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfredsen, K. A 10-year prospective study of single tooth implants placed in the anterior maxilla. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2012, 14, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Periodontol 2018, 89 Suppl 1, S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Berglundh, T.; Schwarz, F.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N.; Tonetti, M.S.; Sanz, M.; et al. Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases-The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J Clin Periodontol 2023, 50 Suppl 26, 4–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin Periodontol 2015, 42 Suppl 16, S158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, A.; Renvert, S.; Dahlen, G. Microbial findings at failing implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1999, 10, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, R.; Gerlach, T.; Hahnel, S.; Schwarz, F.; Handel, G.; Gosau, M. In vivo and in vitro biofilm formation on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res 2010, 21, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Ribeiro, C.; Cogo-Muller, K.; Franco, G.C.; Silva-Concilio, L.R.; Sampaio Campos, M.; de Mello Rode, S.; Claro Neves, A.C. Initial oral biofilm formation on titanium implants with different surface treatments: An in vivo study. Arch Oral Biol 2016, 69, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J Bacteriol 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Imai, K.; Sato, H.; Ogata, Y. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and Porphyromonas gingivalis in Japanese peri-implantitis patients. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelongo-Jauregui, D.; Srinivasan, A.; Ramasubramanian, A.K.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. An In Vitro Model for Candida albicans(-)Streptococcus gordonii Biofilms on Titanium Surfaces. J Fungi (Basel) 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Gilli, F.; Wiedemeier, D.B.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Karygianni, L. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Jurevic, R.J.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Cui, F.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Gillevet, P.M. Characterization of the oral fungal microbiome (mycobiome) in healthy individuals. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1000713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.W.L.; Pang, L.M.; Wang, Y. From Jekyll to Hyde: The Yeast-Hyphal Transition of Candida albicans. Pathogens 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canabarro, A.; Valle, C.; Farias, M.R.; Santos, F.B.; Lazera, M.; Wanke, B. Association of subgingival colonization of Candida albicans and other yeasts with severity of chronic periodontitis. J Periodontal Res 2013, 48, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urzua, B.; Hermosilla, G.; Gamonal, J.; Morales-Bozo, I.; Canals, M.; Barahona, S.; Coccola, C.; Cifuentes, V. Yeast diversity in the oral microbiota of subjects with periodontitis: Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis colonize the periodontal pockets. Med Mycol 2008, 46, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Iyer, S.S. A Comparative Evaluation of Subgingival Occurrence of Candida Species in Chronic Periodontitis and Peri-implantitis: A Clinical and Microbiological Study. International Journal of Clinical Implant Dentistry With Dvd 2015, 1, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, G.E.; Cosgarea, R.; Sculean, A. Prevalence and Mechanisms of Peri-implant Diseases. J Dent Res 2017, 96, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Becker, K.; Rahn, S.; Hegewald, A.; Pfeffer, K.; Henrich, B. Real-time PCR analysis of fungal organisms and bacterial species at peri-implantitis sites. Int J Implant Dent 2015, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrabiah, M.; Alshagroud, R.S.; Alsahhaf, A.; Almojaly, S.A.; Abduljabbar, T.; Javed, F. Presence of Candida species in the subgingival oral biofilm of patients with peri-implantitis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2019, 21, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahhaf, A.; Al-Aali, K.A.; Alshagroud, R.S.; Alshiddi, I.F.; Alrahlah, A.; Abduljabbar, T.; Javed, F.; Vohra, F. Comparison of yeast species in the subgingival oral biofilm of individuals with type 2 diabetes and peri-implantitis and individuals with peri-implantitis without diabetes. J Periodontol 2019, 90, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranayake, L.P.; McCourtie, J.; MacFarlane, T.W. Factors affecting th in-vitro adherence of Candida albicans to acrylic surfaces. Arch Oral Biol 1980, 25, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, J.; Sudbery, P.E. Candida Albicans: a molecular revolution built on lessons from budding yeast. Nat Rev Genet 2002, 3, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, F.L.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence 2013, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-La-Torre, J.; Quindos, G.; Marcos-Arias, C.; Marichalar-Mendia, X.; Gainza, M.L.; Eraso, E.; Acha-Sagredo, A.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M. Oral Candida colonization in patients with chronic periodontitis. Is there any relationship? Rev Iberoam Micol 2018, 35, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamster, I.B.; Grbic, J.T.; Mitchell-Lewis, D.A.; Begg, M.D.; Mitchell, A. New concepts regarding the pathogenesis of periodontal disease in HIV infection. Ann Periodontol 1998, 3, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Wachtler, B.; Schaller, M.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Host-pathogen interactions and virulence-associated genes during Candida albicans oral infections. Int J Med Microbiol 2011, 301, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A.; Kashleva, H.; Villar, C.C. Bioactive interleukin-1alpha is cytolytically released from Candida albicans-infected oral epithelial cells. Med Mycol 2004, 42, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, Y.W.; Wilson, M.; Lewis, M.; Del-Bel-Cury, A.A.; da Silva, W.J.; Williams, D.W. Modulation of Candida albicans virulence by bacterial biofilms on titanium surfaces. Biofouling 2016, 32, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, D.J.; Wilson, M.J.; Wei, X.; Bradshaw, D.J.; Lewis, M.A.O.; Williams, D.W. Modulation of Candida albicans virulence in in vitro biofilms by oral bacteria. Lett Appl Microbiol 2019, 68, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtiar, E.W.; Bachtiar, B.M.; Jarosz, L.M.; Amir, L.R.; Sunarto, H.; Ganin, H.; Meijler, M.M.; Krom, B.P. AI-2 of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans inhibits Candida albicans biofilm formation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartnicka, D.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Zawrotniak, M.; Satala, D.; Michalik, K.; Zielinska, G.; Bochenska, O.; Kozik, A.; Ciaston, I.; Koziel, J.; et al. Adhesive protein-mediated cross-talk between Candida albicans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in dual species biofilm protects the anaerobic bacterium in unfavorable oxic environment. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, C.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Sun, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, H. Inhibitory effects of oral Actinomyces on the proliferation, virulence and biofilm formation of Candida albicans. Arch Oral Biol 2015, 60, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnheer, T.; Karygianni, L.; Flury, M.; Belibasakis, G.N. Fusobacterium Species and Subspecies Differentially Affect the Composition and Architecture of Supra- and Subgingival Biofilms Models. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, J.S.; Mitchell, A.P. Genetic control of Candida albicans biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 2011, 9, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.; Borelli, C.; Korting, H.C.; Hube, B. Hydrolytic enzymes as virulence factors of Candida albicans. Mycoses 2005, 48, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztukowska, M.N.; Dutton, L.C.; Delaney, C.; Ramsdale, M.; Ramage, G.; Jenkinson, H.F.; Nobbs, A.H.; Lamont, R.J. Community Development between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Candida albicans Mediated by InlJ and Als3. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, R.; Sugamata, M.; Kiyoura, Y. Candida albicans enhances invasion of human gingival epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Microb Pathog 2011, 51, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Bartnicka, D.; Zawrotniak, M.; Zielinska, G.; Kieronska, A.; Bochenska, O.; Ciaston, I.; Koziel, J.; Potempa, J.; Baster, Z.; et al. The activity of bacterial peptidylarginine deiminase is important during formation of dual-species biofilm by periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis and opportunistic fungus Candida albicans. Pathog Dis 2018, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C. Heme Competition Triggers an Increase in the Pathogenic Potential of Porphyromonas gingivalis in Porphyromonas gingivalis-Candida albicans Mixed Biofilm. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 596459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzmi, M.H.; Dashper, S.; Catmull, D.; Cirillo, N.; Reynolds, E.C.; McCullough, M. Coaggregation of Candida albicans, Actinomyces naeslundii and Streptococcus mutans is Candida albicans strain dependent. FEMS Yeast Res 2015, 15, fov038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Cen, L.; Kaplan, C.; Zhou, X.; Lux, R.; Shi, W.; He, X. Cellular Components Mediating Coadherence of Candida albicans and Fusobacterium nucleatum. J Dent Res 2015, 94, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bor, B.; Cen, L.; Agnello, M.; Shi, W.; He, X. Morphological and physiological changes induced by contact-dependent interaction between Candida albicans and Fusobacterium nucleatum. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 27956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Bertolini, M.; Thompson, A.; Mansfield, J.M.; Grassmann, A.A.; Maas, K.; Caimano, M.J.; Barao, V.A.R.; Vickerman, M.M.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Role of glucosyltransferase R in biofilm interactions between Streptococcus oralis and Candida albicans. ISME J 2020, 14, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sobue, T.; Bertolini, M.; Thompson, A.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Streptococcus oralis and Candida albicans Synergistically Activate mu-Calpain to Degrade E-cadherin From Oral Epithelial Junctions. J Infect Dis 2016, 214, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, M.M.; Xu, H.; Sobue, T.; Nobile, C.J.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Candida-streptococcal mucosal biofilms display distinct structural and virulence characteristics depending on growth conditions and hyphal morphotypes. Mol Oral Microbiol 2015, 30, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, E.A.R.; Rached, R.N.; Ignacio, S.A.; Rosa, R.T.; Jose da Silva, W.; Yau, J.Y.Y.; Samaranayake, L.P. Phenotypic evaluation of the effect of anaerobiosis on some virulence attributes of Candida albicans. J Med Microbiol 2008, 57, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, A.H.; Nygaard-Østby, B.; Bøygard, G.K.; Eribe, E.R.; Olsen, I.; Gjermo, P. Yeasts in periodontal pockets. J Clin Periodontol 2001, 28, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J Periodontol 2018, 89 Suppl 1, S267–s290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.F.; Tsui, C.; Kucharikova, S.; Andes, D.; Van Dijck, P.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Commensal Protection of Staphylococcus aureus against Antimicrobials by Candida albicans Biofilm Matrix. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, V.; Isabal, S.; Sanchez, M.C.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M.; Leon, R. Characterization and application of a flow system for in vitro multispecies oral biofilm formation. J Periodontal Res 2014, 49, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.C.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Fernandez, E.; Figuero, E.; Marin, M.J.; Leon, R.; Blanc, V.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. An in vitro biofilm model associated to dental implants: structural and quantitative analysis of in vitro biofilm formation on different dental implant surfaces. Dent Mater 2014, 30, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.C.; Alonso-Espanol, A.; Ribeiro-Vidal, H.; Alonso, B.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. Relevance of Biofilm Models in Periodontal Research: From Static to Dynamic Systems. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Espanol, A.; Bravo, E.; Ribeiro-Vidal, H.; Virto, L.; Herrera, D.; Alonso, B.; Sanz, M. The Antimicrobial Activity of Curcumin and Xanthohumol on Bacterial Biofilms Developed over Dental Implant Surfaces. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.X.; Zhao, H.H.; Wang, F.K. PCR-detectable Candida DNA exists a short period in the blood of systemic candidiasis murine model. Open Life Sci 2020, 15, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements. opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas. methods. instructions or products referred to in the content. |
| Species | Incubation time (hours) | Analysis | Condition | Microbial counts (CFU/ml) | % Viability | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 95% CI | ||||||||
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Mean | (SD) | ||||||
| Streptococcus oralis | 24 | Total | Control | 1.13x107 | 6.71x106 | 4.04x105 | 1.87x107 | ||
| Test | 1.16x107 | 4.69x106 | 6.52x106 | 1.80x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 5.85x106 | 3.76x106 | 1.31x106 | 1.10x107 | 51.78 | 14.69 | ||
| Test | 5.76x106 | 3.45x106 | 1.23x106 | 1.08x107 | 46.45 | 14.67 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 1.22x107 | 4.87x106 | 5.41x106 | 1.82x107 | |||
| Test | 1.65x107 | 6.86x106 | 7.20x106 | 2.59x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 6.51x106 | 2.71x106 | 3.51x106 | 1.08x107 | 56.54 | 19.16 | ||
| Test | 8.69x106 | 2.63x106 | 5.02x106 | 1.15x107 | 58.79 | 23.24 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 9.43x106 | 3.43x106 | 4.17x106 | 1.35x107 | |||
| Test | 1.24x107 | 7.25x106 | 7.06x106 | 2.98x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 3.95x106 | 1.54x106 | 2.21x106 | 6.26x106 | 45.24 | 18.15 | ||
| Test | 8.30x106* | 3.80x106 | 3.08x106 | 1.48x107 | 70.92* | 25.05 | |||
| Species | Incubation time (hours) | Analysis | Condition | Microbial counts (CFU/ml) | % Viability | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 95% Confidence interval for mean | ||||||||
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Mean | (SD) | ||||||
|
Actinomyces naeslundii |
24 | Total | Control | 7.58x105 | 4.95x105 | 1.14x105 | 1.31x106 | ||
| Test | 1.01x106 | 8.02x105 | 9.75x104 | 2.18x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 4.20x105 | 3.48x105 | 2.58x104 | 1.03x106 | 66.91 | 30.38 | ||
| Test | 5.65x105 | 3.90x105 | 1.01x105 | 1.03x106 | 68.79 | 20.82 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 5.51x105 | 3.48x105 | 1.10x105 | 1.09x106 | |||
| Test | 9.00x105 | 7.45x105 | 9.02x104 | 2.38x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 3.33x105 | 2.13x105 | 1.10x105 | 6.61x105 | 74.22 | 37.58 | ||
| Test | 5.72x105 | 3.96x105 | 9.98x104 | 1.31x106 | 83.24 | 38.63 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 4.43x105 | 2.93x105 | 7.39x104 | 8.09x105 | |||
| Test | 1.21x106 | 9.92x105 | 4.18x104 | 2.65x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.98x105 | 1.21x105 | 7.39x104 | 4.15x105 | 57.1 | 26.76 | ||
| Test | 4.11x105 | 3.05x105 | 5.14x104 | 9.60x105 | 58.47 | 39.11 | |||
|
Veillonella parvula |
24 | Total | Control | 5.18x107 | 4.45x107 | 6.70x106 | 1.49x108 | ||
| Test | 3.48x107 | 2.11x107 | 6.62x106 | 5.61x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 3.31x107 | 2.14x107 | 6.99x106 | 6.49x107 | 79.09 | 28.19 | ||
| Test | 2.31x107 | 1.34x107 | 4.97x106 | 4.38x107 | 76.76 | 30.06 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 4.58x107 | 3.08x107 | 6.79x106 | 9.32x107 | |||
| Test | 5.77x107 | 4.51x107 | 8.90x106 | 1.31x108 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 2.45x107 | 1.35x107 | 6.68x106 | 4.25x107 | 67.78 | 26.03 | ||
| Test | 3.57x107 | 2.79x107 | 5.63x106 | 8.43x107 | 67.2 | 17.34 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 3.04x107 | 2.26x107 | 5.15x106 | 6.81x107 | |||
| Test | 2.31x107 | 1.30x107 | 5.45x106 | 4.44x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.23x107 | 1.09x107 | 3.49x106 | 3.73x107 | 50.44 | 25.03 | ||
| Test | 1.05x107 | 5.73x106 | 3.41x106 | 1.78x107 | 51.21 | 21.46 | |||
|
Fusobacterium nucleatum |
24 | Total | Control | 1.95x106 | 1.04x106 | 3.64x105 | 3.27x106 | ||
| Test | 2.05x106 | 8.77x105 | 1.32x106 | 4.17x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 5.96x105 | 4.57x105 | 4.30x104 | 2.45x105 | 29.12 | 13.21 | ||
| Test | 9.39x105 | 6.15x105 | 1.16x106 | 1.77x106 | 46.1 | 18.89 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 2.85x106 | 2.08x106 | 1.70x105 | 5.09x106 | |||
| Test | 1.10x107* | 5.45x106 | 4.19x106 | 2.02x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.52x106 | 1.24x106 | 7.17x104 | 3.64x106 | 47.42 | 14.9 | ||
| Test | 5.15x106* | 3.04x106 | 1.20x106 | 8.35x106 | 48.25 | 12.38 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 4.15x106 | 3.45x106 | 6.15x104 | 9.60x106 | |||
| Test | 1.35x107* | 5.86x106 | 3.64x106 | 2.12x107 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.31x106 | 1.07x106 | 8.92x103 | 2.63x106 | 27.42 | 9.711 | ||
| Test | 7.53x106* | 5.74x106 | 4.54x105 | 1.86x107 | 54.36* | 26.21 | |||
| Species | Incubation time (hours) | Analysis | Condition | Microbial counts (CFU/ml) | % Viability | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 95% Confidence interval for mean | ||||||||
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Mean | (SD) | ||||||
|
Porphyromonas gingivalis |
24 | Total | Control | 3.31x104 | 1.50x104 | 5.20x103 | 4.79x104 | ||
| Test | 3.83x104 | 2.18x104 | 1.13x104 | 6.20x104 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.43x104 | 8.24x103 | 6.25x103 | 2.56x104 | 40.27 | 14.91 | ||
| Test | 2.21x104 | 1.27x104 | 6.41x103 | 3.87x104 | 57.3 | 19.82 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 2.02x105 | 1.03x105 | 7.29x104 | 3.44x105 | |||
| Test | 4.14x105* | 1.86x105 | 1.57x105 | 6.11x105 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 6.51x104 | 3.21x104 | 2.84x104 | 1.15x105 | 37.67 | 17.43 | ||
| Test | 2.25x105* | 1.13x105 | 7.34x104 | 4.07x105 | 54.38* | 9.468 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 3.65x105 | 1.97x105 | 1.10x105 | 5.81x105 | |||
| Test | 1.13x106* | 5.51x105 | 6.98x105 | 2.44x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.24x105 | 5.57x104 | 4.93x104 | 2.05x105 | 37.91 | 9.136 | ||
| Test | 6.78x105* | 1.84x105 | 4.75x105 | 9.28x105 | 65.29* | 18.16 | |||
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans | 24 | Total | Control | 2.82x106 | 1.03x106 | 1.35x106 | 3.75x106 | ||
| Test | 2.72x106 | 8.14x105 | 1.68x106 | 4.07x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.10x106 | 4.24x105 | 1.27x105 | 1.52x106 | 44.34 | 23.92 | ||
| Test | 1.49x106 | 3.53x105 | 9.54x105 | 1.99x106 | 56.01 | 7.191 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | 4.04x106 | 1.44x106 | 2.15x106 | 6.34x106 | |||
| Test | 3.79x106 | 1.24x106 | 1.45x106 | 5.41x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.38x106 | 2.43x105 | 9.64x105 | 1.76x106 | 38.36 | 15.88 | ||
| Test | 2.11x106* | 7.45x105 | 5.47x105 | 3.06x106 | 55.28* | 10.77 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | 5.01x106 | 1.37x106 | 3.47x106 | 7.29x106 | |||
| Test | 4.90x106 | 1.65x106 | 2.52x106 | 6.60x106 | |||||
| Viable | Control | 1.56x106 | 3.28x105 | 1.21x106 | 2.16x106 | 32.17 | 6.379 | ||
| Test | 3.15x106* | 3.63x105 | 2.53x106 | 3.70x106 | 71.99* | 29.11 | |||
| Candida albicans | 24 | Total | Control | ||||||
| Test | 2.37x104 | 7.86x103 | 1.74x104 | 4.05x104 | |||||
| Viable | Control | ||||||||
| Test | 3.21x103 | 7.51x102 | 2.30x103 | 4.72x103 | 14.02 | 2.734 | |||
| 48 | Total | Control | |||||||
| Test | 7.65x104 | 2.72x104 | 3.87x104 | 1.13x105 | |||||
| Viable | Control | ||||||||
| Test | 3.02x104 | 1.04x104 | 1.62x104 | 4.36x104 | 45.37 | 23.73 | |||
| 72 | Total | Control | |||||||
| Test | 2.35x105 | 7.75x104 | 1.26x105 | 3.17x105 | |||||
| Viable | Control | ||||||||
| Test | 9.12x104 | 1.90x104 | 6.54x104 | 1.14x105 | 43.84 | 20.06 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





