Submitted:
18 February 2024
Posted:
21 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Matrices and Their Determinants
| Determinant of A | |
| Adjoint matrix of A | |
| Identity matrix |
1.2. Semi-Structured Complex Numbers: Enabling Division by Zero
A semi-structured complex number is a three-dimensional number of the general form h = x + yi + zp; that is a linear combination of real (1), imaginary (i) and unstructured (p) units whose coefficients, x, y, z are real numbers.
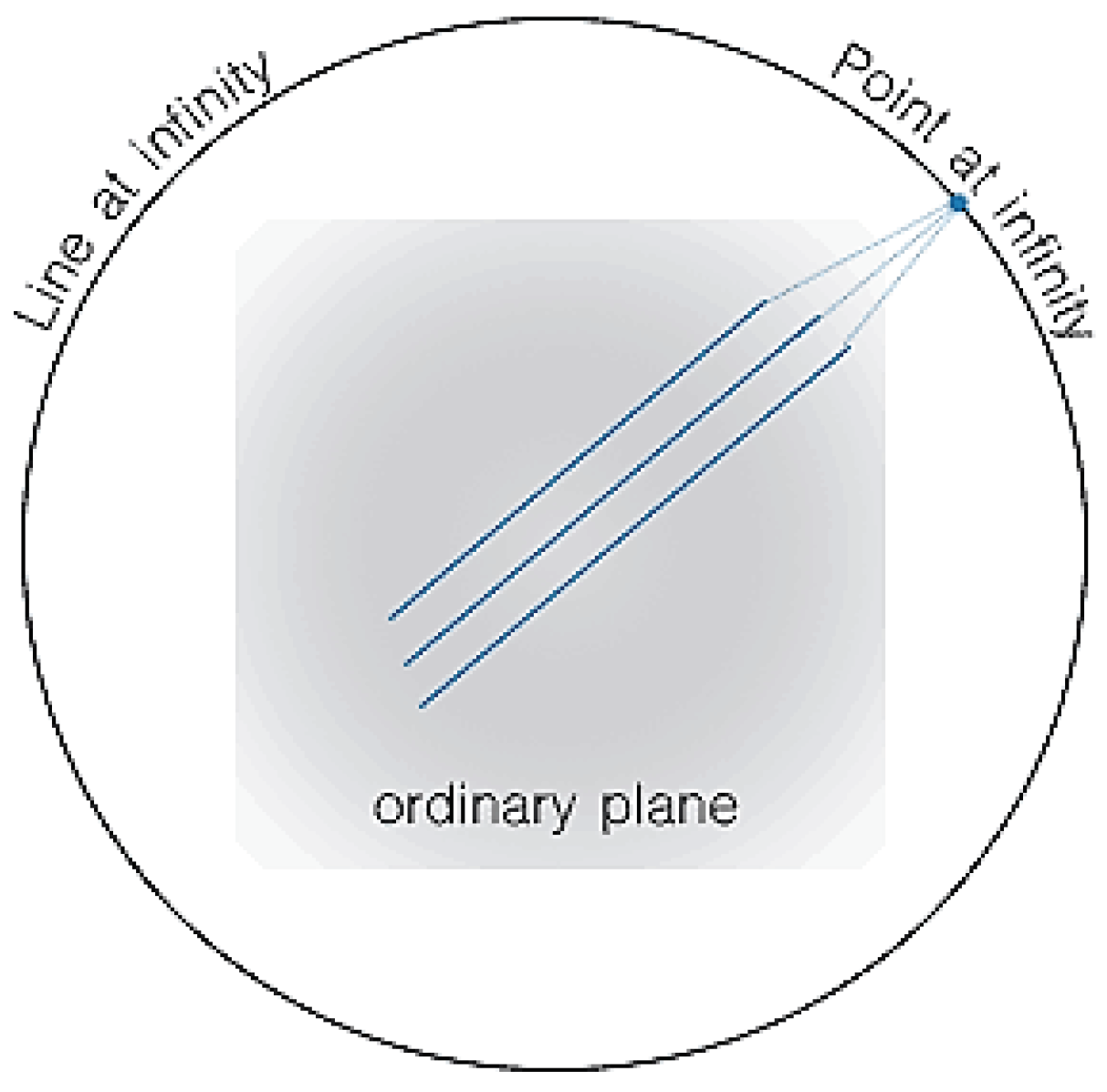
1.3. Projective Geometry
1.4. Major Contributions
Use semi-structured complex numbers and projective geometry to find the inverse of a general singular 2 × 2 matrix, give its geometric interpretation and its potential applications.
- The inverse of a 2 ×2 matrix is given by the equation:where is the unstructured unit.
- Singular matrices and their inverses can be used to find a unique solution to a pair of simultaneous equations that appear to have infinitely many solutions and a pair of simultaneous equations that appear to have no solution. This unique solution is called the principle inverse solution.
- Singular matrices map coordinates in projective space to coordinates in Euclidean space and their inverse maps coordinates in Euclidean space to coordinates in projective space.
- The inverse of a singular matrix proves that parallel lines in Euclidean space do not intersect but in projective space intersect at a “point at infinity”.
- The inverse of a singular matrix proves that collinear lines that intersect at infinitely many points in Euclidean space only intersect at one point in projective space.
2. Inverse of a Singular Matrix
3. Solving Simultaneous Equations Represented by a Singular Matrix
3.1. Solving Simultaneous Equations Which Appear to Have Infinitely Many Solutions
3.2. Solving Simultaneous Equations Which Appear to Have No Solutions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Appendix A. Other Important Properties of the Determinant of a Square Matrix
- If is the identity matrix of the order , then the
- If the matrix is the transpose of matrix M, then
- If the matrix is the inverse of matrix M, then
- If two square matrices M and N have the same size, then
- If matrix M has a size and C is a constant, then
- If X, Y and Z are three positive semidefinite matrices of equal size, then the following holds true along with the corollary for . Additionally,
- In a triangular matrix, the determinant is equal to the product of the diagonal elements.
- The determinant of a matrix is zero if all the elements of the matrix are zero.
- The determinant of a matrix can be calculated using the Laplace formula for Determinant of a matrix A with dimensions . This formula is given below:where 𝑎𝑖𝑗 is the entry of the 𝑖 𝑡ℎ row and 𝑗 𝑡ℎ column of A, and 𝑀𝑖𝑗 is the determinant of the submatrix 𝑀 obtained by removing the 𝑖 𝑡ℎ row and the 𝑗 𝑡ℎ column of A.
Appendix B. Research Conducted on Division by Zero
| Research | Research Aim |
|---|---|
| [3,4,5] | Explores the application of division by zero in calculus and differentiation |
| [6] | Uses classical logic and Boolean algebra to show the problem of division by zero can be solved using today’s mathematics |
| [7] | Develops an analogue to Pappus Chain theorem with Division by Zero |
| [8] | This paper proposes that the quantum computation being performed by the cancer cell at its most fundamental level is the division by zero. This is the reason for the insane multiplication of cancer cells at its most fundamental scale. |
| [9] | Explores evidence to suggest zero does divide zero |
| [10] | Considered using division by zero to compare incomparable abstract objects taken from two distinct algebraic spaces |
| [11] | Show recent attempts to divide by zero |
| [12] | Generalize a problem involving four circles and a triangle and consider some limiting cases of the problem by division by zero. |
| [13] | Paper considers computing probabilities from zero divided by itself |
| [14,15] | Considers how division by zero is taught on an elementary level |
| [16] | Develops a method to avoid division by zero in Newton’s Method |
| [17] | This work attempts to solve division by zero using a new form of optimization called Different-level quadratic minimization (DLQM) |
Appendix C. Major Results of Semi-Structured Complex Numbers from Paper [2]
| Result 1 | Semi-structured complex number set can be defined as follows:
The number h is called semi-structured complex because it contains a structured complex part and an unstructured part . |
| Result 2 | The unstructured number was redefined as:
Integer powers of yield the following cyclic results: |
| Result 3 | does not belong to the set of complex numbers (that is, ), but belongs to a higher order number set called the set of semi-structured complex numbers such that the set of complex numbers is a subset of (that is, ). |
| Result 4 | The field of semi-structured complex numbers was defined, and proof was given that this field obeys the field axioms. This implies (1) the number set can easily be used in everyday algebraic expressions and can be used to solve algebraic problems, (2) the number set can be used to form more complicated structures such as vector spaces and hence solve more complex problems that may involve “division by zero”. |
| Result 5 | Semi-structured complex number set does not form an ordered field. For the objects in a field to have an order, operations such as greater than or less than can be applied to these objects. This is because in an ordered field the square of any non-zero number is greater than 0; this is not the case with semi-structured complex numbers. |
| Result 6 | Semi-structured complex numbers can be represented by points in a 3-dimensional Euclidean -space. The xyz-space consist of three perpendicular axes: the real -axis, the imaginary y-axis, and the unstructured -axis. These axes form three perpendicular planes: the real-imaginary -plane, the real-unstructured -plane, and the imaginary-unstructured -plane. |
| Result 7 | The unit was used to find a viable solution to the logarithm of zero. The logarithm of zero was found to be:
|
| Result 8 | The new definition of provided an unambiguous understanding that simply represents clockwise rotation of the vector from the positive unstructured z-axis to on the positive real x-axis along the real-unstructured -plane. Note that is any real number. |
| Result 9 | Semi-structured complex numbers have both a 3D and 4D representation in the form: (3D form) (4D form) where: are real numbered scalars and are semi-structured basis units. |
| Result 10 | Two new Euler formulas were developed. 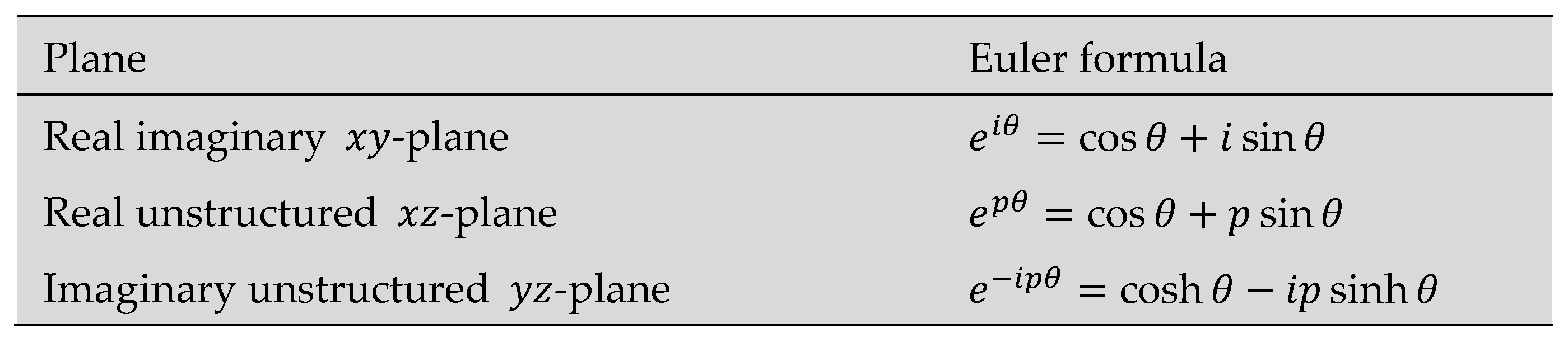 When combined with the original Euler formula describes the relationship between trigonometric, hyperbolic, and exponential functions for the entire semi-structured complex Euclidean |
| Result 11 | Semi-structured complex numbers can be used to resolve singularities that may arise in engineering and science equations (because of division by zero) to develop reasonable conclusions in the absence of experimental data. |
| Result 12 | From Result 10 semi-structured complex numbers can present in four forms as given below:

|
| Result 13 | The zeroth root of a number h can be found using the equation |
| Result 14 | Since this implies that which further implies that |
| Result 15 | Any real number with the semi-structured unit attached to it is not a physically measurable quantity. That is, where is a real number is not physically measurable (however, can be calculated given enough information) |
| Result 16 | If and measure different (but quantitatively related) aspects of the same object, where is physically measurable but is not, then and can be combined into one equation in the form |
Appendix D. Proof of Inverse of Singular Matrix
Appendix E. Numerical Examples of Solving Simultaneous Equations That Can Be Represented by Singular Matrices
References
- P. Jean Paul and S. Wahid, "Unstructured and Semi-structured Complex Numbers: A Solution to Division by Zero.," Pure and Applied Mathematics Journal,, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 49-61, 2021.
- Paul, P. J., & Wahid, S. (2022). Reformulating and Strengthening the theory of Semi-strucutred Complex Numbers. International Journal of Applied Physics and Mathematics, 12(4), 34-58.
- S. Pinelas and S. Saitoh, "Division by Zero Calculus and Differential Equations," in Differential and Difference Equations with Applications: ICDDEA, Amadora, Portugal, 2018.
- S. Saitoh, "Introduction to the division by zero calculus," in Scientific Research Publishing, Inc, USA, 2021.
- H. Okumura, "The arbelos in Wasan geometry: Atsumi’s problem with division by zero calculus," Sangaku Journal of Mathematics, vol. 5, pp. 32-38, 2021.
- Barukčić, "Classical logic and the division by zero," International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology IJMTT, vol. 65, no. 7, pp. 31-73, 2019.
- H. Okumura, "An Analogue to Pappus Chain theorem with Division by Zero," In Forum Geom, vol. 18, pp. 409-412, 2018.
- M. P. Lobo, "Cancer: Division by Zero," Open Journal of Mathematics and Physics, vol. 2, no. 73, p. 5, 2020.
- M. P. Lobo, "Does zero divide zero," Open Journal of Mathematics and Physics, vol. 2, no. 69, p. 3, 2020.
- J. Czajko, "On unconventional division by zero," World Scientific News, vol. 99, pp. 133-147, 2018.
- H. Okumura, "Is It Really Impossible To Divide By Zero," J Appl Math, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 191-198, 2018.
- H. Okumura, "A four circle problem and division by zero," Sangaku Journal of Mathematics, vol. 4, pp. 1-8, 2020.
- W. Mwangi, "Definite Probabilities from Division of Zero by Itself Perspective," Asian Journal of Probability and Statistics, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 1-26, 2020.
- J. Dimmel and E. Pandiscio, "When it’s on zero, the lines become parallel: Preservice elementary teachers’ diagrammatic encounters with division by zero," The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, vol. 58, pp. 1-27, 2020.
- F. Karakus and B. Aydin, "Elementary Mathematics Teachers’specialized Content Knowledge Related To Division By Zero," Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Sciences, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 25-40, 2019.
- Abdulrahman, "A Method to Avoid the Division-by-Zero or Near-Zero in Newton-Raphson Method," Feburary 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358857049_A_Method_to_Avoid_the_Division-by-Zero_or_Near-Zero_in_Newton-Raphson_Method (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Y. Zhang, Y. Ling, M. Yang and M. Mao, "Exemplar Different-Level Quadratic Minimization,," in The 2018 5th International Conference on Systems and Informatics, 2018.
- Hasoun, R. K., Khlebus, S. F., & Tayyeh, H. K., "A new approach of classical Hill Cipher in public key cryptography.," International Journal of Nonlinear Analysis and Applications, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1071-1082, 2021.
- Paragas, J. R., Sison, A. M., & Medina, R. P., "Hill cipher modification: A simplified approach.," 2019 IEEE 11th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks (ICCSN), pp. pp. 821-825, 2019.
- Hraoui, S., Gmira, F., Abbou, M. F., Oulidi, A. J., "A new cryptosystem of color image using a dynamic-chaos hill cipher algorithm," Procedia computer science, vol. 148, pp. 399-408, 2019.
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Non-existence of inverse | Singular matrices do not have an inverse. The inverse of a matrix is essential for various mathematical operations, such as solving linear systems of equations or performing certain transformations. Without an inverse, these operations become impossible or highly constrained. In practical terms this would mean that singular matrices cannot be used to represent processes and in cases where they do end up representing practical processes expensive workarounds are often employed to avoid or overcome them. This results in wasted time and money. |
| Limited applicability in solving equations | Singular matrices cannot be used to uniquely solve systems of linear equations. In a non-singular matrix, each equation in the system corresponds to a unique solution. However, in the case of a singular matrix, the system of equations may have either no solution or infinitely many solutions. This limitation restricts their use in many practical applications represented by a system of linear equations. |
| Numerical instability | The lack of an inverse can introduce significant errors or inaccuracies, especially when solving equations or performing matrix operations. Small changes in the matrix elements can result in large changes in the computed solutions, making the results unreliable. |
| Ambiguity in interpretation | Singular matrices can lead to ambiguity in interpreting the data or model they represent. In some cases, a singular matrix may indicate redundancy or collinearity in the data, where certain variables or observations are perfectly correlated. This can make it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions or make accurate predictions based on the matrix representation alone. |
| Limitations in matrix factorization techniques | Many matrix factorization techniques, such as lower–upper (LU) decomposition or Eigen decomposition, rely on the existence of an inverse matrix. Singular matrices may not be amenable to these factorization methods, limiting their applicability in various computational algorithms and numerical techniques. |
| Reduced rank and dimensionality | Singular matrices have a reduced rank compared to non-singular matrices. The rank of a matrix represents the maximum number of linearly independent rows or columns. A singular matrix has at least one row or column that can be expressed as a linear combination of the other rows or columns, which reduces the effective dimensionality of the matrix. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




