Submitted:
19 February 2024
Posted:
20 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Our contributions
- Considering the Industrial metaverse architecture we elucidate the concept of the industrial metaverse and various enabling technologies used to build and experience the industrial metaverse.
- Explore new and upcoming prevalent use cases of the Industrial Metaverse and deployments.
- Exploration of the impact of the technologies underpinning the industrial metaverse such as data centers and network infrastructure on the environment.
- Address novel security and privacy risks as well as outlining open research challenges, keeping in mind that the industrial metaverse is based on a strong data fabric.
1.3. Paper organization
2. Methodological Approach
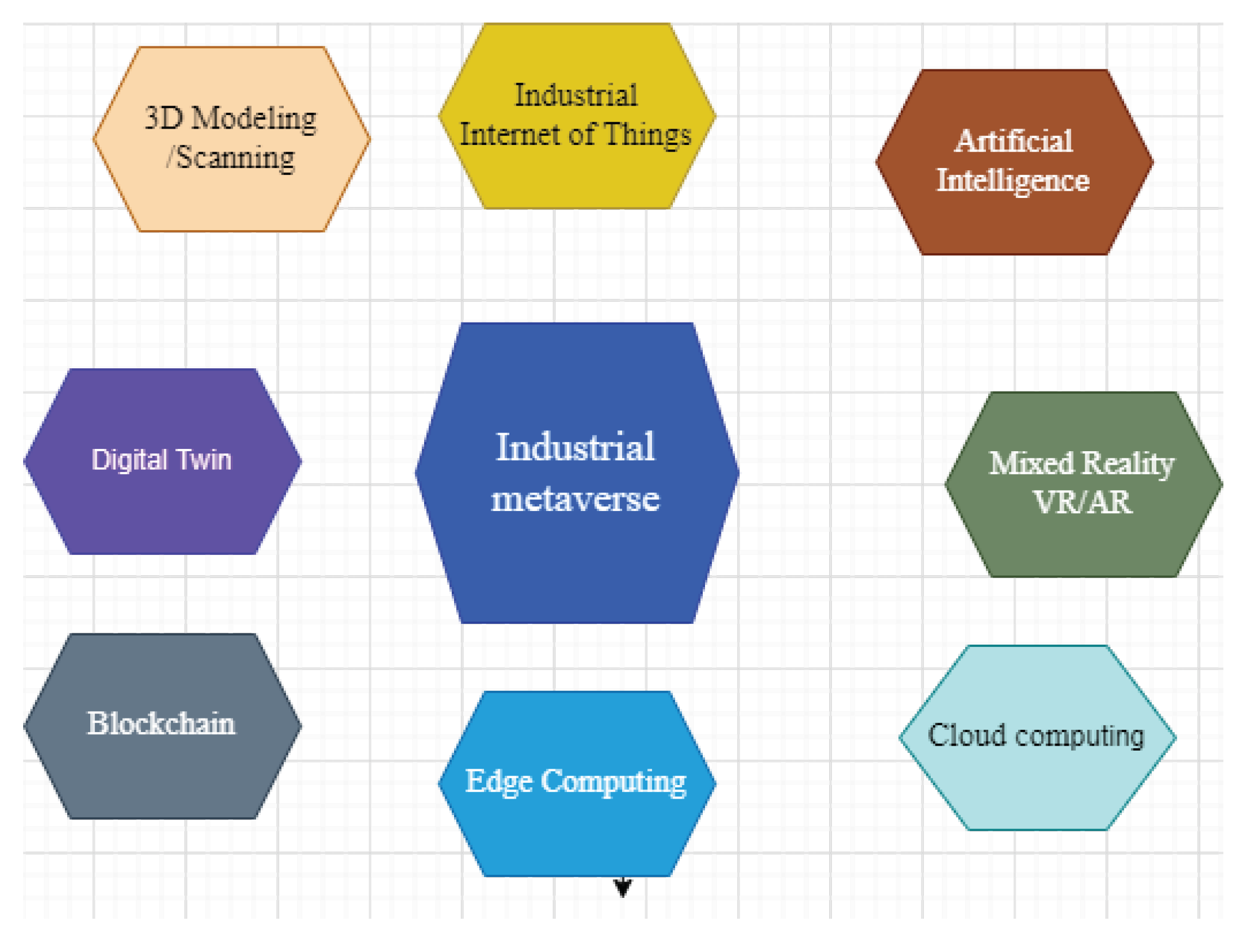
3. Industrial Metaverse Architecture, Roadmap and Core Technologies Overview
3.1. Industrial Internet of Things
3.2. Artificial Intelligence
- Security: The Metaverse poses various security challenges, such as identity theft, fraud, and cyber-attacks. AI can be used to monitor user behaviour and detect any suspicious activity, such as stealing personal information or engaging in malicious behaviour.
- Personalisation: AI algorithms can analyse user data to create a personalised experience for each user. For example, an AI system can learn a user’s preferences for virtual clothing, virtual accessories, and virtual activities, and suggest personalised options.
- Creating and managing digital entities: In the Metaverse, AI is used to create and manage various digital entities such as non-player characters (NPCs), virtual assistants, and chatbots. These entities can interact with users and provide them with personalised experiences based on their preferences and behaviour.
- Immersion: AI can help create more immersive virtual environments by enabling realistic physics, lighting, and sound effects. For example, AI algorithms can simulate the behaviour of water, fire, and other natural elements, making the virtual environment more realistic.
- Real-time translation: AI can enable real-time translation of languages spoken in the Metaverse, making it easier for people from different countries to communicate and collaborate. This could lead to the creation of a truly global virtual community.
- Intelligent NPCs: Non-Player Characters (NPCs) are characters controlled by the game’s AI, which can interact with users in the virtual environment. AI algorithms can enable NPCs to understand natural language and respond appropriately, making the interactions more realistic and engaging [18].
3.3. Cross, Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality
3.4. Cloud Computing
- Increased adoption of Metaverse and Cloud Computing in various industries: The Metaverse is expected to have a significant impact on various industries, including gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, and retail. Cloud Computing will be essential in providing the necessary infrastructure to support these virtual experiences. As a result, we can expect to see increased adoption of Metaverse and Cloud Computing in these industries in the coming years.
- Advancements in VR/AR technology: VR/AR technology is a crucial component of the Metaverse, and we can expect to see continued advancements in this area, leading to more realistic and immersive virtual experiences. These advancements will require a robust and scalable cloud infrastructure to support the high computing requirements of VR/AR.
- The growth of the creator economy: The Metaverse has the potential to create new opportunities for creators to monetize their skills and talents. Cloud Computing will be essential in providing the necessary infrastructure for creators to develop and distribute their content on a global scale.
- Improved remote collaboration and work: The Metaverse and Cloud Computing are expected to improve remote collaboration and work, enabling teams to work together seamlessly in virtual environments. This development could lead to increased productivity and a more flexible and efficient workforce.
- Ethical and privacy concerns: The use of Metaverse and Cloud Computing raises ethical and privacy concerns, such as data privacy, ownership, and security. As the Metaverse and Cloud Computing continue to evolve, it will be essential to address these concerns to ensure that they are used responsibly and ethically.
3.5. Edge-Computing
3.6. Blockchain
3.7. 3D modelling/Scanning
- Faro Technologies: Faro is a leading 3D scanning company Faro. It provides a vast array of software, laser scanners, and 3D measuring, imaging, and realization technology.
- Artec 3D: Artec 3D, which is well-known for its portable, handheld 3D scanners, offers solutions for businesses in the automotive, aerospace, and entertainment sectors as well as for independent producers.
- Hexagon: Hexagon provides high-precision 3D scanning and metrology solutions for sectors including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, with a strong emphasis on industrial applications.
- Leica Geosystems: Leica, a member of the Hexagon group, is well known for its precise, high-quality 3D scanning solutions for a range of markets, including building, surveying, and mapping sectors. They have cutting-edge laser scanning technology, such as the Leica BLK series, which makes it possible to seamlessly incorporate places and items from the real world into the metaverse.
3.8. Digital Twin
- Speed prototyping as well as product re-designing:
- Cost-effective: In classical prototyping the redesign of a product is often expensive owing to the use of costly physical raw materials. In addition, a destructive test signifies the end of that costly prototype. Contrary to the classical approach, DT allows the testing of products under different operating scenarios, including destructive scenarios, without any additional costs. practically this translates to reduced costs on the par of DT deployment.
- Predicting Problems/System Planning: A digital twin enables the identification and forecasting of issues and failures at different stages of the product life cycle. This is particularly helpful for products with numerous parts, complex structures, and various materials because it gets harder to predict component failures using standard approaches as a product’s complexity increases. Fault rectification is much simpler, less expensive, and quicker in the digital world than in the physical one. Before the product goes into production, a digital twin makes it possible to identify and virtually eliminate all potential output dangers, assuring that the physical twin will work as intended [32].
- Optimizing Solutions and Improved Maintenance:
- Accessibility:
- Safer than the Physical Counterpart:
- Waste Reduction:
- Documentation and Communication:
-
- (I)
- High Fidelity
- (II)
- Dynamic
- (III)
- Self Evolving
- (IV)
- Identifiable
- (V)
- multi-physical
- (VI)
- multi-scale
- (VII)
- multidisciplinary
4. Use Cases and Deployment
- Industrial design and engineering: The Metaverse is a meta-design space, where Metaverse designers create various interconnected design spaces, each of which creates a unique experience [38]. The macro and micro levels of real-world design are both improved by metaverse design. At the macro level, designing in the metaverse may entail working together in real-time inside a virtual representation of the inside of large-scale items like airplanes. At the micro level parts might be tested, changed, and iterated in a matter of seconds as opposed to investing money and effort in constructing or printing a 3D model or prototype. Practically, design engineers can construct detailed industrial designs owing to the metaverse. To view the product in a real-world environment, interact with it, and alter the design, they employ virtual reality. This method allows you to innovate more quickly and cost-effectively because it saves time and lowers the cost of physical prototypes. In addition, the metaverse offers designers and engineers fresh viewpoints and inspiration, enabling them to produce more original and useful creations. Industrial metaverse apps can speed up design and engineering processes and help you launch better goods more quickly.
- Supply chain management and logistics: The supply chain’s transparency and insight into how goods are produced, stored, distributed, and sold will expand thanks to the metaverse. Additionally, the metaverse encourages collaboration up and down the supply chain, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of the entire chain [39]. Examples of industrial metaverse use cases include VeChain and TradeLens. They demonstrate how supply chain processes can be streamlined and optimized using this technology. The TradeLens technology automates and digitizes supply chain activities, minimizing paper-based documentation and manual processes, using smart contracts and digital signatures. VeChain simulates every stage of the supply chain, from raw materials to finished goods, using blockchain technology and the metaverse. Blockchain technology is used to track each transaction and movement.
-
Manufacturing operations and maintenance: Industrial big data, operational data management, artificial intelligence, robotic process automation and autonomous systems, digital twins, and cloud computing are just a few of the cutting-edge technologies that make up the industrial metaverse. In the manufacturing industry, the metaverse enhances efficiency through product design, production, and maintenance. The metaverse improves productivity in the industrial sector through product design, production, and maintenance.
- In product design: Product design is the process of making physical or digital products. The metaverse enables designers to have the full autonomy to create products that never existed previously. For instance, fashion companies like Nike and Balenciaga have created items that, even if they were available to consumers, they might not necessarily choose to wear in real life, but which helps them create or define their virtual personas on this platform. Given the nearly endless amount of innovation, designers have never-before-seen chances to push the limits of design [40].
- Improve the manufacturing and production process: Metaverse simulations provide the capability to test several factory scenarios and gain insights from scaling up or reducing production. A provision of optimization opportunities within the facilities through these simulations without affecting the manufacturing that is already taking place. Practically, in a smart factory, operators can use Microsoft Dynamics 365 Guides for real-time instructions overlaid on equipment, while IoT sensors collect data on machine performance, quality metrics, and inventory levels. This renders it possible for operators to quickly spot and fix problems, optimize production settings, and enhance the general effectiveness and quality of manufacturing.
- Improve quality control: IoT sensors are deployed for the collection of data in manufacturing processes. This facilitates the collection of real-time data from the various equipment and machinery. Subsequently, analyzing data from its manufacturing processes and identifying defects or issues that need to be addressed [41]. Manufacturing companies can streamline processes and boost efficiency by using metaverse applications and technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). For example, Dynamics 365 Guides and Remote Assist, can be leveraged for 3D drawing in a real-world environment. Moreover, front-line workers wearing HoloLens can also annotate their physical space with digital ink, creating an interactive and immersive experience. In the automotive manufacturing industry, BMW workers wear headsets that overlay digital information onto real-world objects. This allows them to visually inspect and identify defects in the components in real-time, reducing the risk of defective products reaching the assembly line or being shipped to customers.
- Better warehouse and logistics management: AR can be leveraged to streamline logistics and warehousing procedures by utilizing metaverse technology. A case in point is that of DHL, a global logistics company that is using augmented reality (AR) headsets to provide their workers with real-time information, such as order details, inventory locations, and picking instructions, overlaid onto their field of vision. This allows their workers to work hands-free and efficiently navigate the warehouse, reducing errors and improving order accuracy.
- Training: The adoption of "immersive training environments," more often known as the Industrial Metaverse, is necessary to train workers, both seasoned and novice ones, in Industry 5.0 working settings and from the Operator 5.0 point of view. The need for more efficient and effective practical training (either local or remote) is what drives the market demand for these types of advanced cyber-physical training environments. This is so that workers, both experienced and novice, can safely experience and learn from their operational mistakes and poor decisions. Even though mistakes can be the best teachers in some industrial situations, it may not be practical or safe to use them as a learning tool. The significant costs, hazards, and time-consuming activities that traditional physical or virtual training settings entail for businesses can thus be reduced with the use of contemporary industrial Metaverse-based training environments. However, to provide "safe" immersive industrial environments where employees can experiment with novel and creative methods of doing things, even using trial-and-error techniques, which may result in process improvements. A better user experience is one of the most significant advantages of using "Metaverse-based solutions" while educating employees. Complete immersion offers a more complete cognitive and sensory perception of the entire environment and the issues, as well as a richer user experience [42]. As an example, complex machinery can be practised by being operated by trainees, who can also receive safety instructions, learn how to perform maintenance and repairs, conduct remote training, and acquire critical soft skills. This encourages a staff that is more effective and knowledgeable. Employees and trainees can now take advantage of Dynamics 365 Guides’ more sophisticated features, which include pre-join settings for HoloLens users joining Teams calls that lets them turn on or off their audio and video before joining the session. During the meeting, users can also change these settings. This permits frontline staff to use the HoloLens as their primary calling device in settings where secrecy is crucial without jeopardizing securites. Dynamics 365 Guides simplify document navigation. Through action steps, this also offers the additional capability of linking straight from one guide to another. As with clicking on hyperlinks to get to different online pages, this enables easy switching between various training materials or manuals. These cutting-edge training techniques provide a secure and monitored environment for practical learning, which boosts productivity, lowers costs, and improves safety in industrial settings.
- Marketing and sales for manufacturing products Metaverse enables you to create virtual product experiences that allow customers to visualize and interact with products in a virtual environment. Metaverse has created numerous possibilities for industries to market their products by organizing Virtual product launches using the metaverse to launch brand-new products. Companies can create virtual launch events where users can virtually experience the new products, learn about their features, and even pre-order them. This creates buzz and anticipation among their customer bases. Virtual factory tours help customers connect with your brand. This allows them to experience the manufacturing process and get an inside look at your facilities without physically visiting the factories. Virtual booths at trade shows to showcase your products to a global audience. These booths can engage visitors and demonstrate your products using virtual presentations, videos, or interactive demos. Virtual trade shows offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to market your products and reach potential customers globally.
- Research and development: With its immersive and collaborative features, industrial metaverse apps have changed the way that industries undertake research and development (R & D). In the end, this results in previously unheard-of levels of invention, effectiveness, and inventiveness. classically, physical prototypes were used to conduct (R & D) on products which was not only time-consuming but costly as well. The industrial metaverse simulates the design of a product or service at a very early stage as a cost-effective design approach. It enables the design team to quickly pivot and make the best and most appropriate design choices. Early-stage product creation using the metaverse would be a good, "low-hanging fruit" use case for industries [43]. The Ford Motor Company is a typical example, It has been investigating how to leverage the metaverse for research and development in fields like car design, safety testing, and manufacturing efficiency. They have built virtual prototypes of their vehicles and tested them virtually for performance and safety using virtual reality (VR) simulations.
| Use case scenario | Summary | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Design and Engineering | Industrial metaverse apps can help you streamline design, and engineering processes and bring better products to market faster | [44,45] |
| Supply Chain and Logistics | optimize the flow of goods, identify potential bottlenecks, and reduce waste. | [39,46] |
| Manufacturing operations and maintenance | Enhance product design, production, manufacturing process, quality control, warehouse, and logistics management | [47,48,49] |
| Training | remote training, virtual environments, multi-user interaction and automated supervision | [50,51,52] |
| Marketing and sales for manufacturing products | Virtual product launches, factory tours, and Virtual booths at trade shows | [53,54] |
| Research and development | design, safety testing, and manufacturing optimization | [55,56,57] |
4.1. Deployment
- Coca-Cola HBC: Coca-Cola HBC, a partner of the beverage giant, leveraged the IM to enhance the sustainability and resilience of its supply chain. The collaborative effort between Microsoft and Coca-Cola HBC created an immersive digital replica of its bottling facility in Edelstal, Austria, consequently minimizing waste and increasing sustainability while boosting operational efficiency. Further reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation, Coca-Cola HBC implemented automated yard management and vision picking which improved resources and availability checks, as well as guiding trucks into loading docks, and minimizing errors. Coca-Cola HBC’s ultimate goal is to have zero carbon emissions by 2040. This supply chain is enhanced by the IM, Coca-Cola HBC has achieved greater operational efficiency, sustainability, and profitability while simultaneously meeting the evolving demands and expectations of its clients and stakeholders.
-
General Motors (GM): General Motors (GM) has been using Process Simulate from Siemens to create an ergonomically efficient production line in a short period. GM must update its production line regularly to accommodate for design changes of existing vehicles and the production of new cars. For efficiency, engineers work remotely with a virtual reality device to immerse themselves in the designs. It helps understand manual assembly, hand clearances, operator movements, and the operator’s line of sight. With this information, engineers can identify a problem at an early stage and solve it before the issue occurs in real life. The team at GM is leveraging the motion capture possibility with Process Simulate where a line design engineer wears a suit and performs the activity that an operator will do in real life. The captured motions help the engineer understand what the awkward positions are and for how long an operator needs to be in that position. Engineers can ergonomically optimize the production line and reduce work-related health problems. To this end, GM advances in other areas with IM as follows:
- All the motions captured will be combined with biomechanics (study of how the bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments work together and have an impact on the fatigue of the operator). Future software will simulate the biomechanics of a specific operator performing tasks over a long period of time. Based on the simulation health issues can be identified accurately and solutions like customized Exosuits or tailored Personal Protective Equipment can be created for the operator.
- All these 3D models of operators can be converted into a Digital Twin and used to simulate realistic factories. GM has a large production workforce and a high number of robots in the line, making it important to check that operator movements are not be hindered by the robots. GM can make sure that operators and robots work in perfect synergy before commissioning the production line.
- Simulate and track the operator tasks in real time. By tracking biomechanics live, precautionary measures can be taken before any work-related disease or accident occurs. The IM will help companies secure the health and happiness of their most important resource: HUMANS.
- Automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): his industry has been using virtual reality and other digital technologies to optimize manufacturing and improve designs for some time. The Digital Twin of Planning comes into play because it can simulate an entire production line accurately and will Ultimately, help virtually plan entire factories before a single brick has been laid. One OEM set its sights on creating an environment where the Digital Twin of Planning is neither based on trial and error nor on manual calculation or human experience but rather based on real-life, real-time, and accurate measurements from the factory shopfloor. The data from virtual simulations and the real production data run in parallel with all nonconformities being captured and assessed. To support this, an IM architecture was developed ensuring that all authoring tools (as data sources) were connected to layers that allow for joint and connected simulation and visualization. The heart of these connections is a data layer and the management thereof in between authoring tools, simulation and visualization layers. With the capability of simulating entire productions before any real undertakings, the OEM reduces the risk of new technology introductions, has stricter adherence to ramp-up curves, earlier concept validations, and overall, a more stable production process and a better understanding of the behavioural model of a full factory. The Digital Twin of Planning and IM architecture also support lower levels of energy consumption, thus supporting sustainability, and drive a more flexible, modular production where it becomes feasible to automatically, at the click of a button, select the optimal plant to produce a certain part or model. The automotive OEM may likely further grow and create the Digital Twin of Operations which has the potential to improve simulations, including predictive maintenance and real-life digital control functionalities.
-
Renault Industrial Metaverse: The Renault industrial metaverse consists of four dimensions, which constitute a complete, persistent, and real-time industrial Metaverse. These dimensions are mass data collection, digital twins of processes, connecting the Supply Chain ecosystem, and a set of advanced technologies. The metaverse is envisaged to generate savings of €320 million, an additional €260 million in inventory savings, a 60% reduction in vehicle delivery time, a 50% reduction in the carbon footprint of vehicle manufacturing, and a contribution to the 60% reduction in warranty costs targeted by the Group. Renault Group is accelerating its digitalization with the first industrial Metaverse. Today, 100% of production lines are connected (8,500 pieces of equipment), 90% of supply flows are constantly monitored and 100% of Supply Chain data is hosted in the Renault Group Metaverse, a true replica of the physical world controlled in real-time. Engaged in Industry 4.0 since 2016, digital technology has already led to savings of €780 million. By 2025, it will enable €320m in various savings, to which will be added €260m in savings on inventories, a 60% reduction in vehicle delivery time, and a 50% reduction in the carbon footprint of its vehicle manufacturing, as well as a significant reduction in innovation cycles and a contribution to the 60% reduction in warranty costs targeted by the Group.
- Mass Data Collection: In the process of collecting data from all its industrial sites, Renault Group has developed a unique data capture and standardization solution, a platform for collecting mass data to feed the industrial Metaverse, and subsequently facilitates the levers for the performance of the production process in real-time. Mass data collection will benefit from dynamic spectrum technologies works in [61,62,63] and this may perhaps be extended to smart farming [64].
- Digital Twins of Processes: The use of digital twins is enriched with supplier data, sales forecasts, quality information, but also exogenous information such as the weather or road traffic, etc., as well as Artificial Intelligence allowing the development of predictive scenarios.
- Connecting the Supply Chain ecosystem: The utilization of digital twins is enhanced by supplier data, sales predictions, quality information, but also external information like the weather or traffic, etc., as well as artificial intelligence allowing the formulation of predictive scenarios.
- Set of advanced technologies: Advanced technologies (Cloud, real-time, 3D, big data...) are converging to speed up this digital transition. For the convergence of the technologies required to manage the digital twins and their ecosystems in a resilient manner, the Renault Group has created a special platform [65].
5. Environmental impact and sustainable development
- Energy Consumption: It is anticipated that the servers and data centres needed to support the development of the industrial metaverse will consume a substantial amount of energy. This might result in a considerable rise in energy usage, especially if the metaverse gains the widespread acclaim that many have predicted [68] Although the metaverse can reduce carbon emissions associated with travel, building, and maintaining infrastructure, the servers and data centres that power the metaverse can also consume significant energy. Clearly, given the IM’s infancy stages, energy consumption is still sketchy. However, cloud computing and data centres are the main tools of the IM data centres are large groups of connected enterprise servers frequently used to store, process, or transmit large quantities of data. This means data centres use a large amount of electricity which leads to several environmental issues. In one of the few major cases, the amount of energy consumed over the years was examined using the TRUBA dataset. The dataset includes the daily energy consumption of supercomputers, storage, and networking devices. TRUBA’s forecast results point to a reduction in energy consumption in the future. Furthermore, the same study also shows that the energy consumption of TRUBA is decreasing, but it must be noted that the usage of cloud servers for deep learning tasks is increasing [69]. Ensuring the underlying infrastructure supporting your metaverse is powered by renewable energy sources is key to achieving overall net zero.
- E-Waste: Electronic waste (E-waste) has significantly increased because of the growing desire for the newest technology, posing an environmental threat. A case in point is the Innovation in cellular phones which shifts almost completely to the digital part of the IM. Innovation is a costly endeavor, involving lots of trials and errors that generate waste of many kinds. By shifting the innovation process to the IM digital part industry can cut on this waste, save resources, and speed up the innovation cycles. However, these faster innovations lead to shorter product lifetimes and henceforth to increased obsolescence and waste. Take as an example the cellphone market that showed a sale of 1.7+ billion cellphones in 2021. Since this is now a (almost) mature market most of these cellphone went to replace existing ones leading to e-waste of 1.5+ billion cell phones. A significant portion of that replacement was motivated by innovation, as new captivating models hit the market. Stopping innovation is not good for business, and eventually not good for any of us who ultimately benefit from innovation, but it must go hand in hand with recycling and reusing. The IM, extending to all layers, as discussed previously, can become an essential force in making this happen [70]. The threats posed by e-waste are real, and they are made worse by the unorganized sector, which frequently strips e-waste of its most beneficial components. Lethal substances like lead, cadmium, beryllium, mercury, and brominated flame retardants are present in all electronic garbage. The likelihood of these hazardous compounds, contaminating the land, poisoning the air, and leaking into water bodies increases when gadgets and devices are disposed of illegally. The amount of worn and abandoned electronics is increasing along with the global demand for electronic devices. Every year, around 50 million tonnes of e-waste are produced, which more than the combined weight of all commercial aircraft is ever built. Instead with these things in mind, one can conclude that the Metaverse will be more detrimental to the environment than beneficial [71]. However, according to [72] only 17.4 % of electronic waste is recycled globally, leading to heightened environmental and health issues, particularly in economically developing countries. Electronic waste is leading to a loss of at least US $57 billion annually through the disposal of key raw materials, such as iron, copper, gold, and others. Adopting circular models can help companies access untapped opportunities and lower environmental impact to address critical e-waste challenges.
- Virtual Economies and Blockchain: Virtual economies within the Metaverse, often backed by blockchain technologies like NFTs and cryptocurrencies, have substantial energy requirements. The energy consumption of blockchain networks, especially those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, is a significant concern. Bitcoin mining has been found to consume as much energy as small countries, which translates into a significant carbon footprint. Whereas miners initially used central processing units (CPUs) to find PoWs, they quickly realized that graphic processing units (GPUs) were better equipped for the task. However, because blockchain mining uses a lot of energy and emits carbon dioxide, the environmental effects of blockchain technology on gaming must be taken into consideration. GameFi platforms should investigate environmentally friendly solutions, like proof-of-stake consensus algorithms, to reduce their carbon footprint and support the gaming industry’s sustainable growth [73].
- Elimination of pollution-generating activities: Increasingly, with the adoption of the industrial metaverse, numerous pollution-generating activities are being eliminated. These activities range from commuting, face-to-face meetings, offsite work events, and transport. Already virtual meeting space gather. town a virtual space platform that offers a new way of conducting online meetings, events, and conferences have attracted more than 4 million users. The platform provides a 2D environment where users can interact with each other in real-time, almost as if they were in the same physical location [74] and [75].
- Reduction in pollution generated by activities: The metaverse can be used to create different scenarios for an entity such as a city, and a factory in other to assess their impact on energy consumption. To evaluate the effects of various scenarios on energy usage, an entity like a factory can be created using the industrial metaverse. For instance, the industrial metaverse’s digital twins can be used to inexpensively and safely replicate real-world performance conditions. A case in point is that of microsoft’s deployment of industrial metaverse capabilities for Hellenic, which is among the largest Coca-Cola bottlers. Hellenic has more than 55 facilities across Europe and serves 29 markets in the region. Just one Hellenic production line produces 90, 000 bottles of Coca-Cola products per hour. Microsoft created digital twins utilizing data from sensors, which made it possible for factory workers to become immersed in the twins. It was reported that, in 12 weeks, the factory cut energy consumption by over 9 %.
- Reduction in the consumption of physical objects: It is important to consider the potential consequences of virtual consumption and how it may impact the environment. While virtual environments can be designed to be more sustainable than physical environments, it is not yet clear how they will affect energy use and carbon emissions [76]. Realizing the possibility of much less materialistic consumption can be facilitated by the industrial metaverse. It is stated that 21% of the consumers expressed their willingness to engage in digital activities in the future which is expected to reduce buying physical items [77].
- Precise assessment of pollution generated and improvement in reward and enforcement: Ascertaining the level of pollution generated by an entity can assist reward and enforcement processes to be improved as well as carbon-friendly habits to be incentivized. While tracing carbon across the real world is complex, it is possible to trace it in the metaverse by creating fungible digital assets on the blockchain. Tokenization facilitates the transaction of carbon credits and creates a carbon market, where voluntary carbon credits can be freely traded. The credits may represent emissions that have been mitigated due to activities such as forestry conservation and engagement in ways to sequestrate carbon such as soil improvement and changes in land use management. This is exemplified by Reseed company’s platform which utilizes blockchain technology to ensure the validity of carbon stock management, from registration through validation and verification, enabling farmers to receive additional income while providing a potential return to investors [78]. All in all, to get ready for sustainability within the industrial metaverse, enterprises may consider utilizing renewable energy sources and cloud services. Furthermore, developing a culture of examining the effects of products on the environment as well as creating a circular economy.
6. Innovative Security and privacy threats
- Data Security and Cybersecurity Risks: With the increased reliance on interconnected systems and data sharing, the Industrial Metaverse raises concerns about data security and cybersecurity risks. To this end, more and more devices as well as platforms are increasingly becoming interconnected. Practically, this increases the risk of cyber threats and data breaches. Safeguarding sensitive data is thus imperative to protect enterprises, governments, and individuals.
- Privacy Implications and Regulatory Compliance: The Industrial Metaverse also brings to the fore challenges with regulatory compliance and privacy issues. Thus, with companies collecting and analyzing huge amounts of data, there is a need to ensure that the privacy of individuals is respected and protected. Striking a balance between innovation and privacy rights is a challenge that needs to be addressed.
- Avatar Authentication Issue: Increasingly, digital avatars such as faces, videos, and voices are employed in the virtual world, which is a metaverse, user authentication and verification are common chores in comparison to the real world. Realistically, attackers can simply make identical sounds and movies by mimicking the appearance of the real user using sophisticated AR and VR tools and devices, together with AI bots. Consequently, the security and privacy of avatars remain a major concern.
7. Future Research challenges
- Security by design: The robust data sets linked to digital twins are useful for both businesses and criminals. Digital twins are vulnerable to manipulation by criminals who could use them to steal identities, encrypt data, extort businesses, or spy on corporate [81] secrets. A case in point is the deployment of fake digital twins which enable criminals to use stolen data to create virtual representations of people or entire environments for criminal intents. A deep flake scenario could, for example, be the deceptive imitation of a company’s executive member in a virtual conference room in the metaverse, enticing the victim to disclose sensitive information. Data Poisoning is another aspect wherein data from the underlying AI and ML learning systems may be intentionally altered. This taints the insights businesses derive from their simulations and, in the worst instance, may result in disastrous business decisions based on inaccurate data. Companies run the danger of allocating funds to unproductive channels in the belief that they are acting based on reliable projections from their digital twins if, for instance, demographic data or action profiles of the modeled target groups are fabricated. Consequently, user privacy and security must be foundational design elements while designing any metaverse applications, rather than being included as add-ons at a later stage [82].
- Communications and Protocol design: Immersive IM experiences will require high download speeds, low-latency, and large capacity to facilitate heterogeneous interconnected devices to communicate with the virtual model at the requisite level. In industrial settings, this will require 5G and possibly also 6G networks [80]. To this end, a paradigm shift in communication protocol will be required that should be goal-oriented and semantic aware. Communication protocol design will need to consider the vision of a seamless IM experience. Ultimately, a model design will be required to standardize the communication protocols for the IM that can be flexibly accessed from heterogeneous communication systems in different virtual worlds.
- Energy-Efficient and Green Industrial Metaverse: The Industrial Metaverse market is now projected to be worth between $100 and $150 billion US dollars, with a conservative 2030 forecast of about $400 billion but with a potential upside of more than $1 trillion [41]. The industrial metaverse is creating more opportunities for companies and workers alike and increasing the adoption of greener practices and renewable energy [83].
8. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- vttresearch. A Human-Driven Industrial Metaverse. https://www.vttresearch.com/sites/default/files/2022-11/Human-Driven%20Industrial%20Metaverse%20A4%20(1).pdf, November 2022. 20 August 2023.
- Siemens. Industrial metaverse. https://assets.new.siemens.com/siemens/assets/api/uuid:cb896aa3-9e72-4574-b512-01f41eff489a/Factsheet-What-is-the-Industrial-Metaverse.pdf, 2022. 16 August 2023.
- Howard. Industrial Metaverse: How It’s Transforming the Future of Industry. https://community.fs.com/article/industrial-metaverse-how-its-transforming-the-future-of-industry.html, 2023. 13 October 2023.
- Xian, W.; Yu, K.; Han, F.; Fang, L.; He, D.; Han, Q.L. Advanced Manufacturing in Industry 5.0: A Survey of Key Enabling Technologies and Future Trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Lin, D.; Ramadoss, R.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Z.; Luo, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, B.; Wei, L.; Ma, R. White Paper-The Industrial Metaverse Report. The Industrial Metaverse Report 2023, pp. 1–20.
- Wang, F. What are the characteristics of the industrial metaverse?. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-characteristics-industrial-metaverse-/. Accessed: 2024-01-23.
- GRAHAM, S. Beyond the Hype: Understanding the Industrial Metaverse. https://blog.hexagonmi.com/beyond-the-hype-understanding-the-industrial-metaverse/. Accessed: 2024-01-23.
- GRAHAM, S. Exploring the Industrial Metaverse: A Roadmap to the Future. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Exploring_the_Industrial_Metaverse_2023.pdf. Accessed: 2024-01-22.
- Benze, M. Harness the Potential of the Industrial Metaverse. https://medium.com/@mathewbenze/harness-the-potential-of-the-industrial-metaverse-5a0a43ae8150. Accessed: 2024-01-23.
- Yao, X.; Ma, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, E.; Faccio, M. Enhancing wisdom manufacturing as industrial metaverse for industry and society 5.0. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 2022, 35, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRAHAM, S. Gartner Unveils Top Predictions for IT Organizations and Users in 2023 and Beyond. https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2022-10-18-gartner-unveils-top-predictions-for-it-organizations-and-users-in-2023-and-beyond#:~:text=By%202025%2C%20without%20sustainable%20artificial,data%2C%20compute%20resources%20and%20power. Accessed: 2024-01-22.
- Minella, M.T.; Minella, M.T. Batch and Spring. The Definitive Guide to Spring Batch: Modern Finite Batch Processing in the Cloud 2019, pp. 1–12.
- Wenzheng, L. ConceptĶ Technology Features and System Architecture of Industrial Metaverse. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC). IEEE, 2023, pp. 13–16.
- Hwang, G.J.; Chien, S.Y. Definition, roles, and potential research issues of the metaverse in education: An artificial intelligence perspective. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 2022, 3, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.Z.; Rehman, M.; Zangoti, H.M.; Afzal, M.K.; Armi, N.; Salah, K. Industrial internet of things: Recent advances, enabling technologies and open challenges. Computers & electrical engineering 2020, 81, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, H.; Hallaq, B.; Cunningham, J.; Watson, T. The industrial internet of things (IIoT): An analysis framework. Computers in industry 2018, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Pham, Q.V.; Pham, X.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Han, Z.; Kim, D.S. Artificial intelligence for the metaverse: A survey. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 117, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRAHAM, S. Role of AI in metaverse, from content creation to cybersecurity. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/small-biz/security-tech/technology/role-of-ai-in-metaverse-from-content-creation-to-cybersecurity/articleshow/99256925.cms?from=mdr. Accessed: 2024-01-22.
- Mystakidis, S. Metaverse. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Wang, D.; Ren, J.; Lyu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Shen, X. Distributed artificial intelligence empowered by end-edge-cloud computing: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2022, 25, 591–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musamih, A.; Yaqoob, I.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Al-Hammadi, Y.; Omar, M.; Ellahham, S. Metaverse in healthcare: Applications, challenges, and future directions. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine 2022, 12, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Gillani, S.; Ahmed, E.; Yaqoob, I.; Imran, M. The role of edge computing in internet of things. IEEE communications magazine 2018, 56, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheer, P. Metaverse and Cloud Computing: Future of Technology. https://www.testpreptraining.com/blog/metaverse-and-cloud-computing-future-of-technology/, 2020. 07 August 2023.
- Khan, W.Z.; Ahmed, E.; Hakak, S.; Yaqoob, I.; Ahmed, A. Edge computing: A survey. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 97, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S. Multi-access edge computing architecture, data security and privacy: A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 18706–18721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ng, W.C.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Kang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Yang, Q.; Shen, X.S.; Miao, C. A full dive into realizing the edge-enabled metaverse: Visions, enabling technologies, and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2022, 25, 656–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekallu, T.R.; Huynh-The, T.; Wang, W.; Yenduri, G.; Ranaweera, P.; Pham, Q.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Liyanage, M. Blockchain for the metaverse: A review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.09738. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Feng, Z.; Gong, Q.; Huang, Y.; Huang, D. Privacy-preserving scheme in the blockchain based on group signature with multiple managers. Security and Communication Networks 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- arrival3d.com. 3D LASER SCANNING SERVICES: INTRODUCING THE INDUSTRIAL METAVERSE. https://arrival3d.com/3d-laser-scanning-services-industrial-metaverse/, 2023. 10/09/2023.
- Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, A.; Nee, A.Y. Digital twin in industry: State-of-the-art. IEEE Transactions on industrial informatics 2018, 15, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Fuenmayor, E.; Hinchy, E.P.; Qiao, Y.; Murray, N.; Devine, D. Digital twin: Origin to future. Applied System Innovation 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćosović, M.; Mirjana, M. Application of the digital twin concept in cultural heritage, 2022. 13 October 2023.
- Barricelli, B.R.; Casiraghi, E.; Fogli, D. A survey on digital twin: Definitions, characteristics, applications, and design implications. IEEE access 2019, 7, 167653–167671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Snider, C.; Nassehi, A.; Yon, J.; Hicks, B. Characterising the Digital Twin: A systematic literature review. CIRP journal of manufacturing science and technology 2020, 29, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doston, k. Industrial use cases hint of a future for metaverse. https://futureiot.tech/industrial-use-cases-hint-of-a-future-for-metaverse/. Accessed: 2023-09-30.
- FutureIoT, E. How the industrial metaverse will transform manufacturing. https://siliconangle.com/2022/12/24/industrial-metaverse-will-transform-manufacturing/. Accessed: 2023-09-30.
- Vincent Douin, Alex Bayz, A.M.H.R.N.H.S.K.M.C.J.F.L.L. The metaverse at work. https://onestore.nokia.com/asset/213304?mkt_tok=OTM3LVdSWi02MTgAAAGO_3rQJCUTw9eelzERw7epRbJEODM0PkXJhjzOUpExlUXa9SmTITGmxZvS2QikHit7zUvuPe1FIpIOJetHuuXuFNX1zbz19iuXEsxVv7SKOEaMv4o. Accessed: 2023-10-03.
- Seidel, S.; Berente, N.; Nickerson, J.; Yepes, G. Designing the metaverse. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 55th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. IEEE, 2022, pp. 13–16.
- Büyüközkan, G. Metaverse and Supply Chain Management Applications. In Metaverse: Technologies, Opportunities and Threats; Springer, 2023; pp. 383–395.
- Habr, N. How is the Metaverse changing product design? https://www.designhubz.com/blog/how-is-the-metaverse-changing-product-design. Accessed: 2023-08-30.
- Albert Meige, R.E. The Industrial Metaverse. https://www.adlittle.com/sites/default/files/reports/ADL_BLUE%20SHIFT_Industrial_metaverse_2023_0.pdf, 2023. Accessed: 03/10/2023.
- Zambiasi, L.P.; Rabelo, R.J.; Zambiasi, S.P.; Romero, D. Metaverse-Based Softbot Tutors for Inclusive Industrial Workplaces: Supporting Impaired Operators 5.0. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems. Springer, 2023, pp. 662–677.
- Panel, E. 16 Innovative Potential (And Current) Applications For The Metaverse. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/07/24/16-innovative-potential-and-current-applications-for-the-metaverse/?sh=339612f68f4a, 2023. Accessed: 03/10/2023.
- Hu, Y.; Chen, H. The Trend of Industrial Design from the Perspective of Metaverse. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction. Springer, 2022, pp. 397–406.
- Bellalouna, F.; Puljiz, D. Use case for the Application of the Industrial Metaverse Approach for Engineering Design Review. Procedia CIRP 2023, 119, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.; Negi, S.; et al. The Metaverse in Supply Chain Management: Application and Benefits. International Journal of Advanced Virtual Reality 2023, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, Z. AR-Driven Industrial Metaverse for the Auxiliary Maintenance of Machine Tools in IoT-Enabled Manufacturing Workshop. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 19th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–6.
- Bordegoni, M.; Ferrise, F. Exploring the intersection of metaverse, digital twins, and artificial intelligence in training and maintenance. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2023, 23, 060806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.C.; Magalhães, L.C.; Ramos, J.B.; Moura, L.R.; de Moraes, R.E.; Gonçalves, J.B.; Hisatugu, W.H.; Souza, M.T.; de Lacalle, L.N.; Ferreira, J.C. Conceiving a Digital Twin for a Flexible Manufacturing System. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.G.; Vasconcelos, N.V.d.; Winkler, I.; Catapan, M.F. Innovating Industrial Training with Immersive Metaverses: A Method for Developing Cross-Platform Virtual Reality Environments. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, M.M.; Jelinek, T.; Nübel, K. Training and preparing tomorrow’s workforce for the fourth industrial revolution. Education Sciences 2022, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; O’farrell, E.; Clarke, P. Examining the training and education potential of the metaverse: Results from an empirical study of next generation SAFe training. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process 2023, 35, e2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroroh, D.K.; Pan, J.K.; Chen, S.M.; Chu, C.H. Industrial Product Demonstration in Metaverse using XR Technologies.
- Rach, M. The Future of Marketing and Sales Automation. Marketing and Sales Automation: Basics, Implementation, and Applications 2023, p. 431.
- Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, X. QoE enhancement of the industrial metaverse based on Mixed Reality application optimization. Displays 2023, 79, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, S.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lau, V.K. Toward Industrial Metaverse: Age of Information, Latency and Reliability of Short-Packet Transmission in 6G. IEEE Wireless Communications 2023, 30, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Kubala, P.; Tucmeanu, E.R.; Corpodean, H. Virtual Clones of Cyber-Physical Production Systems, Workspace Digital Twins, and Multi-Sensor Fusion Technologies in the Interactive Industrial Metaverse. Economics, Management and Financial Markets 2022, 17, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Merklinger, C. Ethical and social challenges posed by the future metaverse. https://digitalfuturesociety.com/app/uploads/2023/07/Ethical-and-social-challenges-posed-by-the-future-metaverse_ENG.pdf. Accessed: 2023-09-23.
- Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Ye, P.; Duan, H.; Wang, F.Y. A novel scenarios engineering methodology for foundation models in metaverse. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 2022, 53, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, H. Remember Your Digital Twins When You Enter the Metaverse. https://www.siemens-advanta.com/blog/digital-twins-industrial-metaverse, 2023. Accessed: 03/10/2023.
- Nleya, S.M. Design and optimisation of a low cost Cognitive Mesh Network 2016.
- Nleya, S.M.; Bagula, A.; Zennaro, M.; Pietrosemoli, E. A TV white space broadband market model for rural entrepreneurs. In Proceedings of the Global Information Infrastructure Symposium-GIIS 2013. IEEE, 2013, pp. 1–6.
- Peng, H.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, P.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Hsia, C.C.; Wang, L.C. 6G toward Metaverse: Technologies, Applications, and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE VTS Asia Pacific Wireless Communications Symposium (APWCS), 2022, pp. 6–10.
- Nleya, S.M.; Ndlovu, S. Smart dairy farming overview: innovation, algorithms and challenges. Smart Agriculture Automation Using Advanced Technologies: Data Analytics and Machine Learning, Cloud Architecture, Automation and IoT 2021, pp. 35–59.
- Boulogne-Billancourt. Renault Group launches the first industrial Metaverse. https://media.renaultgroup.com/renault-group-launches-the-first-industrial-metaverse/#:~:text=Renault%20Group%20then%20modelled%20its,time%20by%20a%20control%20tower., November 14, 2022. Accessed: 03/10/2023.
- Hoshino Neta, C.S.; da Cal Seixas, S.R. Environmental Impacts and Sustainable Development. In Encyclopedia of Sustainability in Higher Education; Springer, 2019; pp. 596–601.
- Kshetri, N.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Pollution-reducing and pollution-generating effects of the metaverse, 2023.
- Solutions, B.S. The Metaverse and the Environment: How It Could Change the Way We Interact with the Natural World. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/metaverse-environment-how-could-change-way-we/. Accessed: 2024-01-25.
- Eviren, B.; Bozkurt, D.; Yozgatlıgil, C. Sustainability of metaverse (sustainverse). In Proceedings of the METU Culture and Convention Center, 2022.
- Metaverse, I. Exploring Ideas tO Foster the Metaverse. https://metaversereality.ieee.org/images/files/pdf/exploring-ideas-to-foster-the-metaverse.pdf. Accessed: 2023-12-23.
- Palak.; Sangeeta.; Gulia, P.; Gill, N.S.; Chatterjee, J.M. Metaverse and Its Impact on Climate Change. In The Future of Metaverse in the Virtual Era and Physical World; Springer, 2023; pp. 211–222.
- Weick, M.; Ray, N. How companies can leverage the circular economy to address global e-waste. https://www.ey.com/en_us/climate-change-sustainability-services/how-circular-economy-models-can-address-global-e-waste. Accessed: 2023-01-24.
- Far, S.B.; Rad, A.I.; Asaar, M.R. Blockchain and its derived technologies shape the future generation of digital businesses: a focus on decentralized finance and the Metaverse. Data Science and Management 2023, 6, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limano, F. New Digital Culture Metaverse Preparation Digital Society for Virtual Ecosystem. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences, 2023, Vol. 388.
- Merklinger, C. GATHER TOWN: IS IT WORTH THE HYPE? https://www.teamazing.com/gather-town-worth-the-hype/#:~:text=In%20short-,Gather.,in%20the%20same%20physical%20location. Accessed: 2024-01-23.
- Pellegrino, A.; Stasi, A.; Wang, R. Exploring the Intersection of Sustainable Consumption and the Metaverse: A Review of current literature and future Research Directions. Heliyon 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukhanov, Y.; Berggren, A. Exploring the Potential of the Metaverse in Operations Management: Towards Sustainable Practices, 2023.
- Derivry, T. GREENING DIGITAL SOVEREIGNTY: UNCOVERING THE LINKS BETWEEN GREEN AND DIGITAL POLICIES IN THE EU. https://www.sciencespo.fr/public/chaire-numerique/en/2023/01/24/greening-digital-sovereignty-uncovering-the-links-between-green-and-digital-policies-in-the-eu/. Accessed: 2024-01-23.
- Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, N.; Xing, R.; Liu, D.; Luan, T.H.; Shen, X. A survey on metaverse: Fundamentals, security, and privacy. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2022, 25, 319–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FutureIoT, E. The Industrial Metaverse: alive and kicking. https://www.simmons-simmons.com/en/publications/clj7b6e43008uthbsi8joa8dp/the-industrial-metaverse-alive-and-kicking. Accessed: 2023-09-30.
- Merklinger, C. Cyber Security in the Metaverse. https://blog.seeburger.com/cyber-security-in-the-metaverse/. Accessed: 2023-09-23.
- Gupta, A.; Khan, H.U.; Nazir, S.; Shafiq, M.; Shabaz, M. Metaverse Security: Issues, Challenges and a Viable ZTA Model. Electronics 2023, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, D. Discover how Microsoft is innovating in the metaverse for a sustainable, clean energy future. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/industry/blog/energy-and-resources/2023/01/12/discover-how-microsoft-is-innovating-in-the-metaverse-for-a-sustainable-clean-energy-future/. Accessed: 2023-09-23.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





