1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with vascular complications[
1], however, an increased incidence of cancer can also be observed. A pooled analysis of risks reported an association between diabetes mellitus (DM) and cancer, suggesting a risk of cancer in patients with DM versus non-DM subjects of 0.97 (95 % confidence interval [CI], 0.75–1.22) in men and 1.29 in women (95 % CI, 1.16–1.44)[
2]. Patients with T2DM underly an enhanced risk for liver, pancreas, endometrium, colon, rectum, breast and bladder cancer, and are at a decreased risk for prostate cancer[
2,
3].
The burden cancer seems to show an increased rate worldwide, however, the different geographical regions are not equally influenced[
4]. An annual decrease of the incidence of cancer was estimated in Hungary within the range of 0 to -0.9%[
4], but measured data are not available neither related to T2DM patients nor for the non-diabetic population.
Cancer and T2DM share a lot of risk factors [
3]. Glucotoxicity, hyperinsulinemia, inflammation and oxidative stress[
5] are major contributors of the development of long-term complications in T2DM. Moreover, obesity further contributes to the development of both T2DM and cancer. Alterations of leptin[
6,
7] and adiponectin[
8,
9] in T2DM may also play a role in the development of cancer. The reverse causality may also be supposed in pancreas and liver cancer patients, assuming that cancer in itself is responsible for the appearance of T2DM[
10].
Most data regarding T2DM and cancer are available for prevalent T2DM, with a longer duration of DM[
11]. Data on the risk of cancer in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM are scarcer[
12,
13]. The available data suggest that immediately after diagnosis, the incidence of cancer is high, sharply decreases during the first year, reaches a nadir, and then it reaches a plateau, or it increases again for several types of cancer[
10,
14].
Temporal analysis of the incidence of cancer in recently discovered T2DM may provide insight into many inherent properties of these diseases. Early onset of cancer after diagnosis of DM may be the consequence of the unknown onset of T2DM, since the onset of the disease may precede the diagnosis by months or years[
15]. Moreover, the abovementioned processes promoting cancer may be initiated already during prediabetes, as indicated by data showing an increased incidence of cancer in prediabetes[
16].
Our primary aim was to assess the overall and site-specific annual incidence of cancer in patients diagnosed with incident T2DM in Hungary between 2015 and 2018, stratified by age and gender. We also want to analyze in incident T2DM patients and non-diabetic controls the average annual percent change (AAPC) and after the manifestation of T2DM the lag time of the incidence of cancer.
2. Materials and Methods
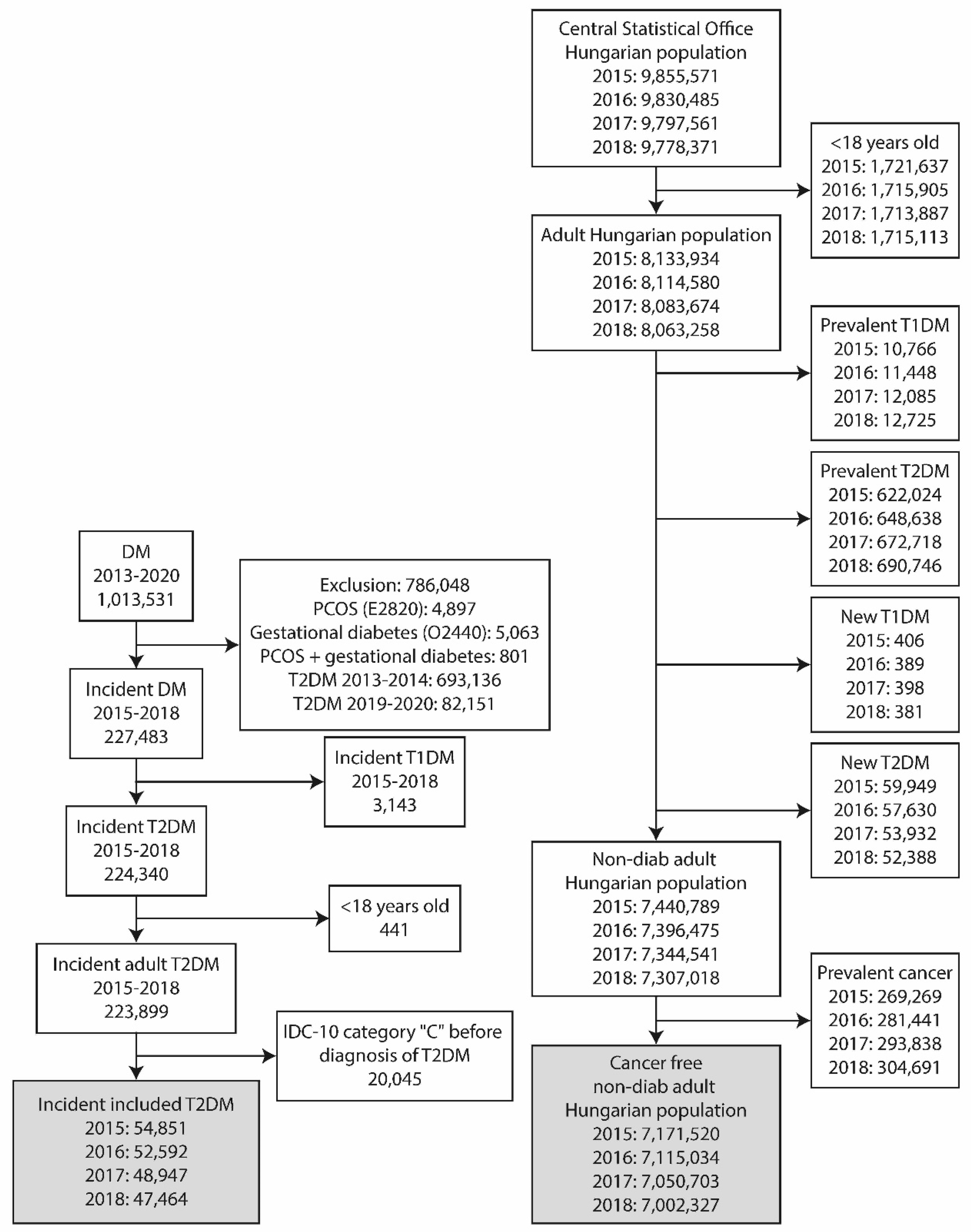
A nationwide, retrospective, longitudinal study was performed using the data from two different sources. The epidemiological data of adult T2DM patients were obtained from the National Institute of Health Insurance Fund database (NHIF). Similar data of the non-diabetic population was gathered from the database of the Hungarian Central Statistical Office (HCSO). Aiming to identify new cancer patients among incident T2DM patients and non-diabetic adult Hungarian population, a screening algorithm was developed (
Figure 1.).
Incident T2DM in the adult population
The nationwide insurance system covers the health care data of nearly 100% of the Hungarian population and collects information of ICD-10 code in the in- and out-patient visits. The data were anonymized. The index period covered all patients older than 18 years and diagnosed with T2DM between 2015 and 2018. The presence of ICD-10 code C was searched during the index period, from 1st of January 2009 and one year after the date of diagnosis of T2DM. Patients with any cancer prior to the index date were excluded from the analysis. Only incident T2DM patients were included in the study (Fig 1.). The NHIF has only provided aggregate data for subgroups with a number of cases more than 10 and the results of analysis models, in line with data protection rules.
Non-diabetic adult Hungarian population
The HCSO collects all health-related data from the entire Hungarian population. Patients younger than 18 years, diagnosed with prevalent or recent onset T2DM or T1DM, were excluded from the database in each year between 2015 and 2018 (
Figure 1). The remaining part of the population represented the non-diabetic adult population of Hungary. The presence of ICD-10 code C was searched to identify incident cancers. In the present analysis, the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) codes between C00 and C99 have been used. The details of this are given in the supplement.
Statistical analysis
R version 4.0.4 was used for a binomial logistic regression involving each year the population without cancer and T2DM on 1st of January. The index date was the diagnosis of T2DM (incident cases) and 1st of January for the others. The dependent variable was the incidence of cancer, while the independent variables were the presence of T2DM, the age group, the gender and all their interactions. The follow-up period was 365 days for everyone.
Odds ratio (OR) and AAPC were calculated by bootstrap with one billion repetitions and are shown together with their 95% confidence intervals. An adjustment for age and gender was made in statistical analyses, using a mean number of the underlying population from each subgroup throughout the study period.
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Board of the University of Pécs (9326-PTE 2022), by the National Institute of Pharmacy and Nutrition (KRID: 641936355) and by Medical Research Council (BMEÜ/95-3/2022/EKU).
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Patients
A total of 1.013.531 patients with incident DM were found between 2013 and 2020 (
Figure 1.). A population of 786.048 patients were excluded due to the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome or gestational diabetes or both, or diagnosis of DM between 2013-2014 or 2019-2020. Further 441 were excluded because of an age below 18 years, while 3.143 had T1DM. Patients with a diagnosis of cancer before the diagnosis of T2DM (n=20 045) were also excluded. Finally, 54.851, 52.592, 48.947, 47.464 patients with incident T2DM remained to fulfill inclusion criteria in the years 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, respectively.
The population of Hungary was 9.855.571, 9.830.485, 9.797.561, 9.778.371 in the years of 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018, respectively. After the exclusion of persons with an age below 18 years, finally 7.440.789, 7.396.475, 7.344.541, 7.307.018 patients free of diabetes were identified. Among these people, 48.008, 47.684, 46.370 and 45.074 patients were identified having cancer.
3.2. The Incidence of Cancer
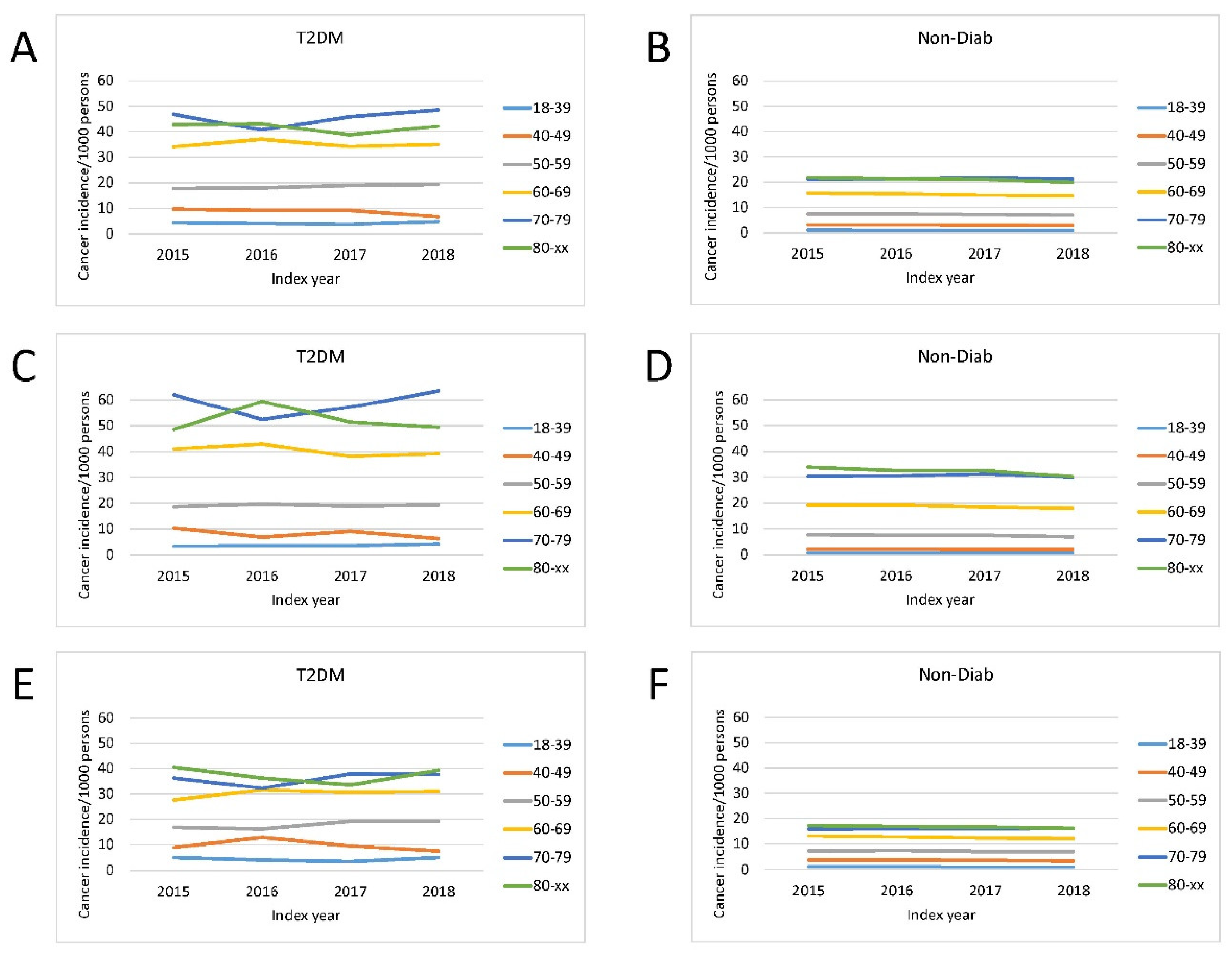
The overall incidence of a new cancer was markedly higher in patients with T2DM than in Non-Diab persons (
Figure 2.). The incidence of cancer was age-dependent, being the lowest in 18-39 years and the highest in 70-79 and 80+ age groups in both genders (
Figure 2.).
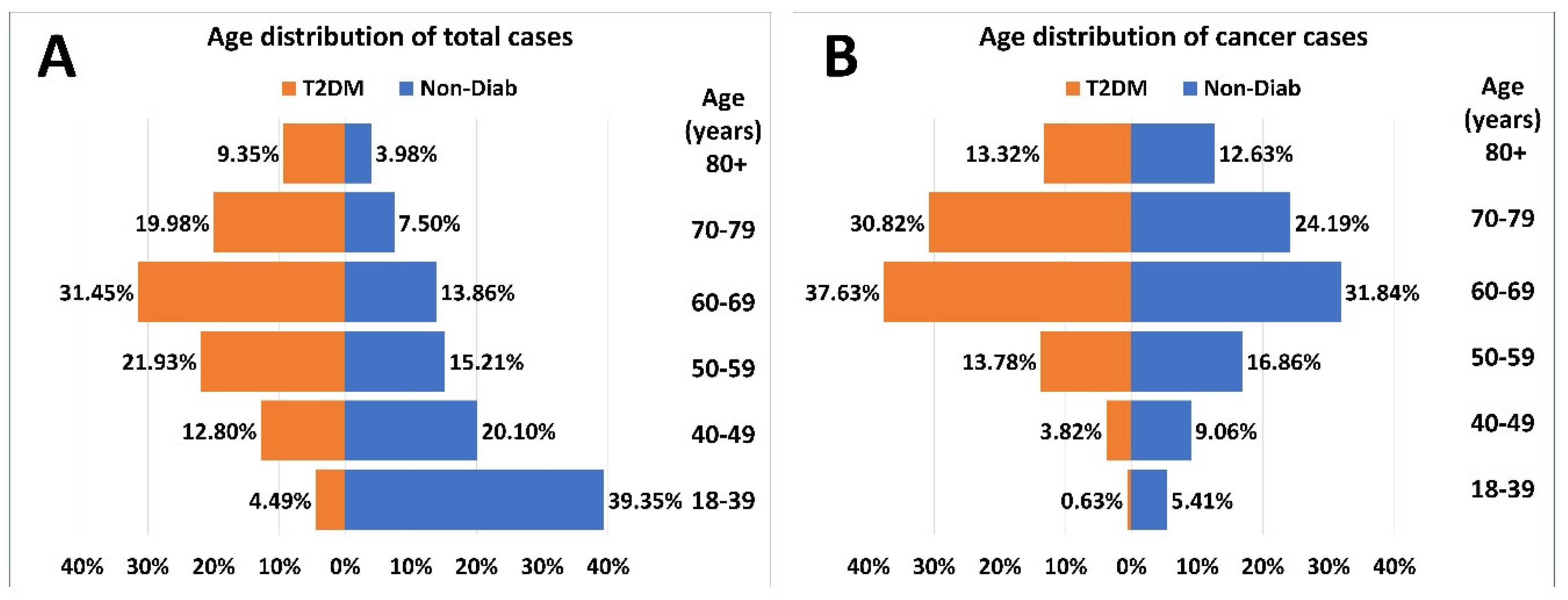
The age-distribution of patients at risk and cases with incident cancer had a different pattern in patients with T2DM and the Non-Diab group (
Figure 3.A). The proportion of the 18–39-year-old-group was the highest in the Non-Diab group. However, among patients with T2DM but without cancer, the 60–69-year-old-group dominated (
Figure 3.A). As opposed to that, within patients with cancer, the 60-69-year-old group dominated both in patients with or without T2DM (
Figure 3.B).
3.3. The risk of Cancer
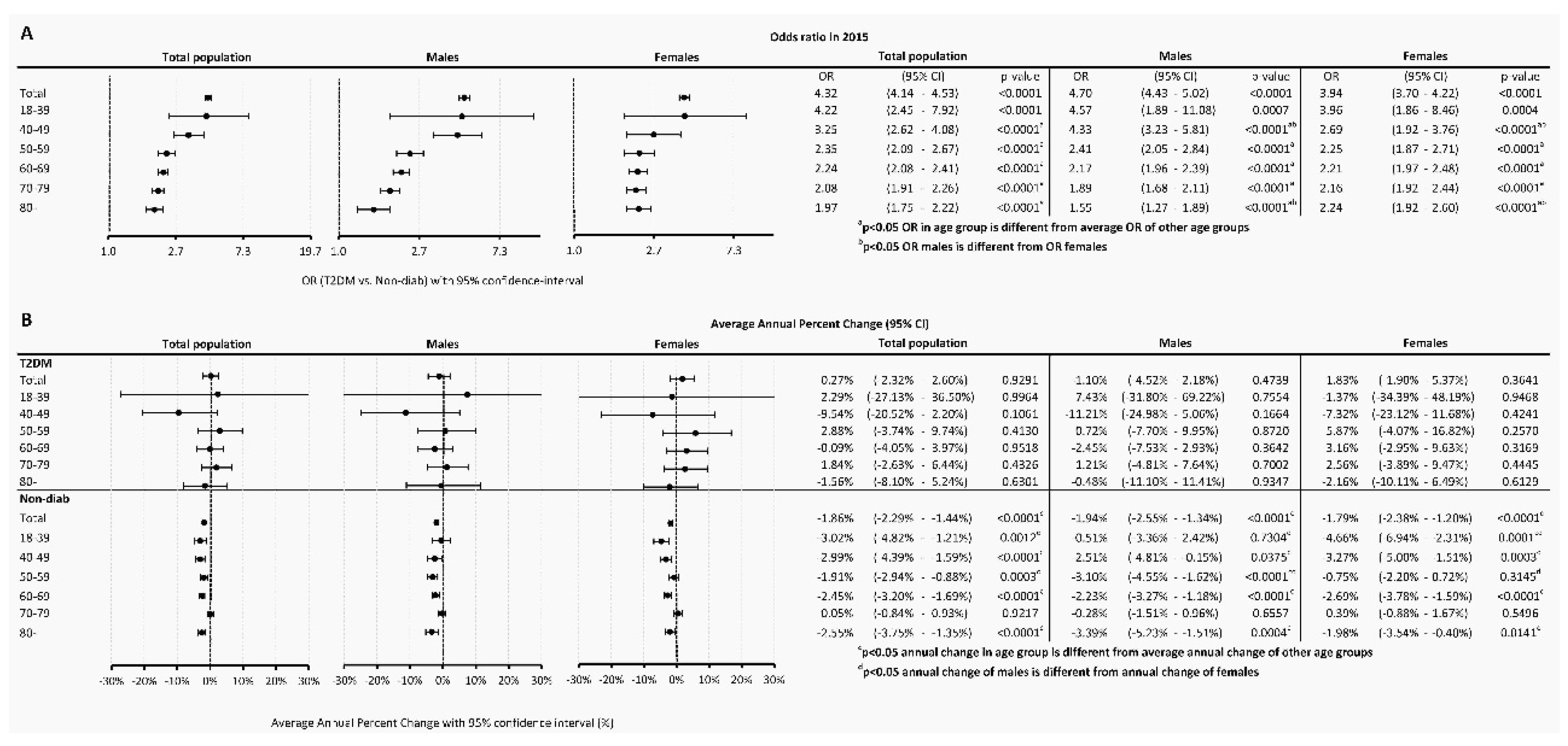
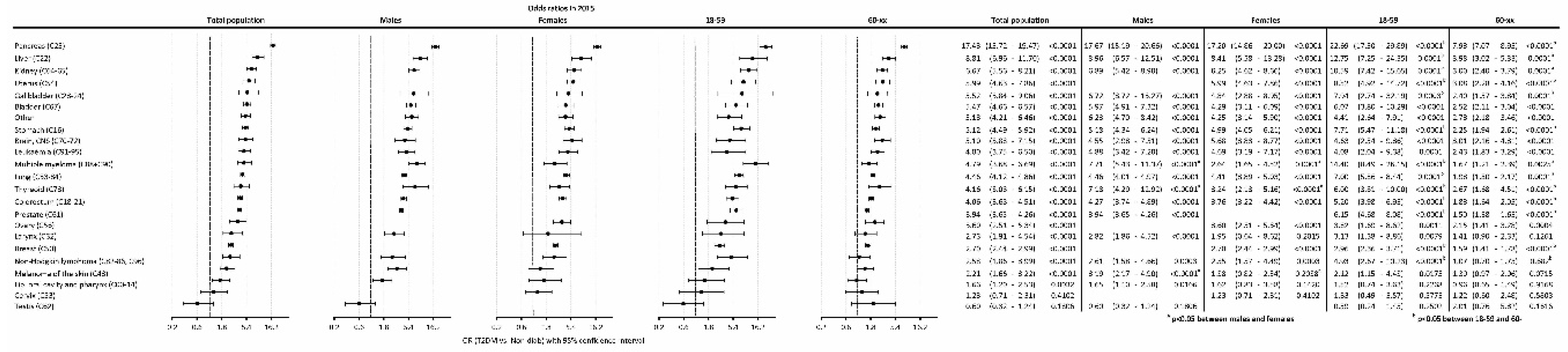
The odds ratio (OR) of having cancer in T2DM as compared to the Non-Diab group was 4.32 (4.14-4.53), P<0.0001) in the total population, while it was 4.70 (4.43-5.02), P<0.0001) and 3.94 (3.70-4.22), P<0.0001) in males and females, respectively (
Figure 4A).
When investigating different age groups, we found that, the odds were highest in the 18-39-year-old subgroup in the T2DM population, both in males and females. On the contrary, the lowest OR was present in the 80+ age group in the overall population, both in males and females. Male compared to female persons had a higher odd for a cancer between 40-49 years. Females had a higher odd to have an incident cancer in the age group 80+ as compared to males (
Figure 4A).
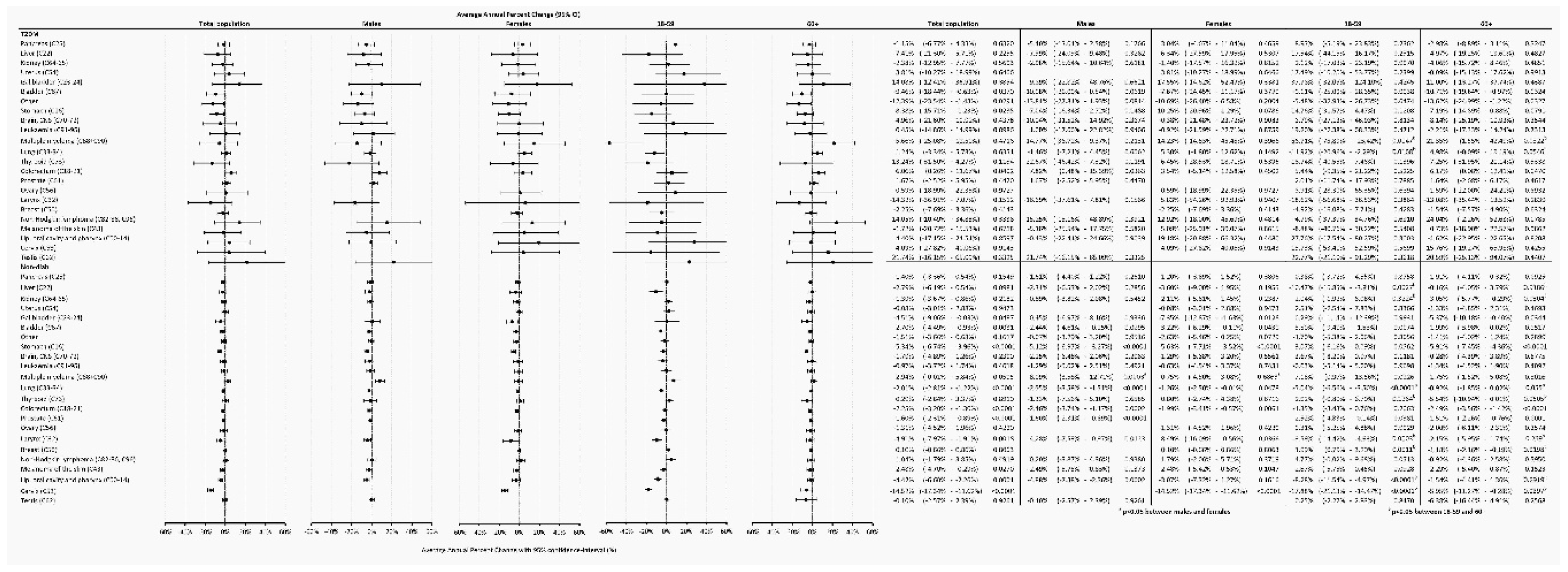
Temporary trends were also analyzed and found that in the Non-Diab group, between 2015-2018, overall AAPC decreased by -1.86% (-2.29 - -1.44%, P<0.0001) annually, as opposed to cancer incidence in the T2DM group, which was practically unchanged (AAPC, 0.27 [-2.32 – +2.60, P=0.9291]) (
Figure 4B). Similar AAPC difference was found between the T2DM and Non-Diab groups in males and females (
Figure 4B).
3.4. Risk of the Incidence of Cancer According to Specific Sites
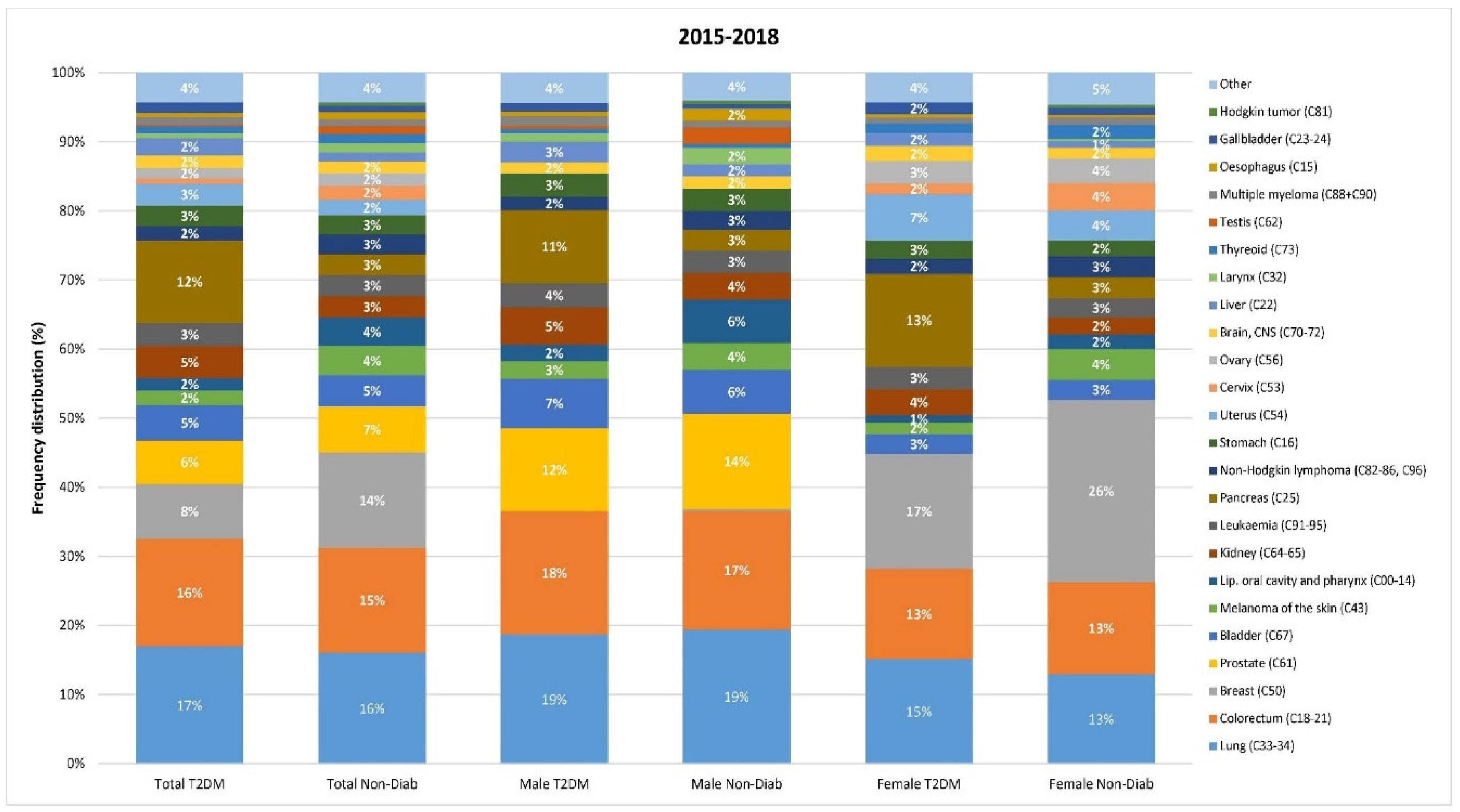
We also analyzed the risk of individual cancer sites. The most common manifestations of cancer were lung, colorectal, breast, prostate and bladder cancers in both groups. Cancers of the kidney, pancreas, uterine corpus seemed to account for a larger proportion in the T2DM as opposed to the Non-Diab group (
Figure 5.).
The highest odds of cancer were found for pancreas, liver, kidney, uterus, gallbladder, bladder, stomach, brain/CNS, leukemia, multiple myeloma, lung, thyroid, colorectum, prostate, ovary, larynx, breast, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, melanoma of the skin in T2DM patients compared to the non-diabetic population (
Figure 6.). Pancreas cancer had the highest odd (OR: 17.43). Cancer odds, in general, showed similar trends in male and female patients, whereas multiple myeloma, thyroid cancer and melanoma had a stronger association with T2DM in males than in females. Several types of cancer showed a higher risk in the 18-59 vs. the 60+ age groups, including pancreas, liver, kidney, uterus, lung, colorectal, prostate, and ovarian cancers.
3.5. Annual Average Percentage Changes (AAPC)
In the Non-Diab population, the overall incidence of gallbladder, bladder, stomach, colorectal, prostate, larynx, oropharyngeal and cervix cancer declined between 2015-2018, whereas in the T2DM group, the incidence decreased only in cases of bladder and stomach. Interestingly, in the T2DM group, the incidence of colorectal cancer significantly increased. Female and male patients showed similar trends in both groups, except for multiple myeloma, which showed an increase in males but not in females. We could find a significant difference between the 18-59 and 60+ age groups for several cancers. In some cases, the direction of change was also opposite, for instance for breast cancer in the Non-Diab group, where the frequency increased in the younger but decreased in the older subjects (
Figure 7.).
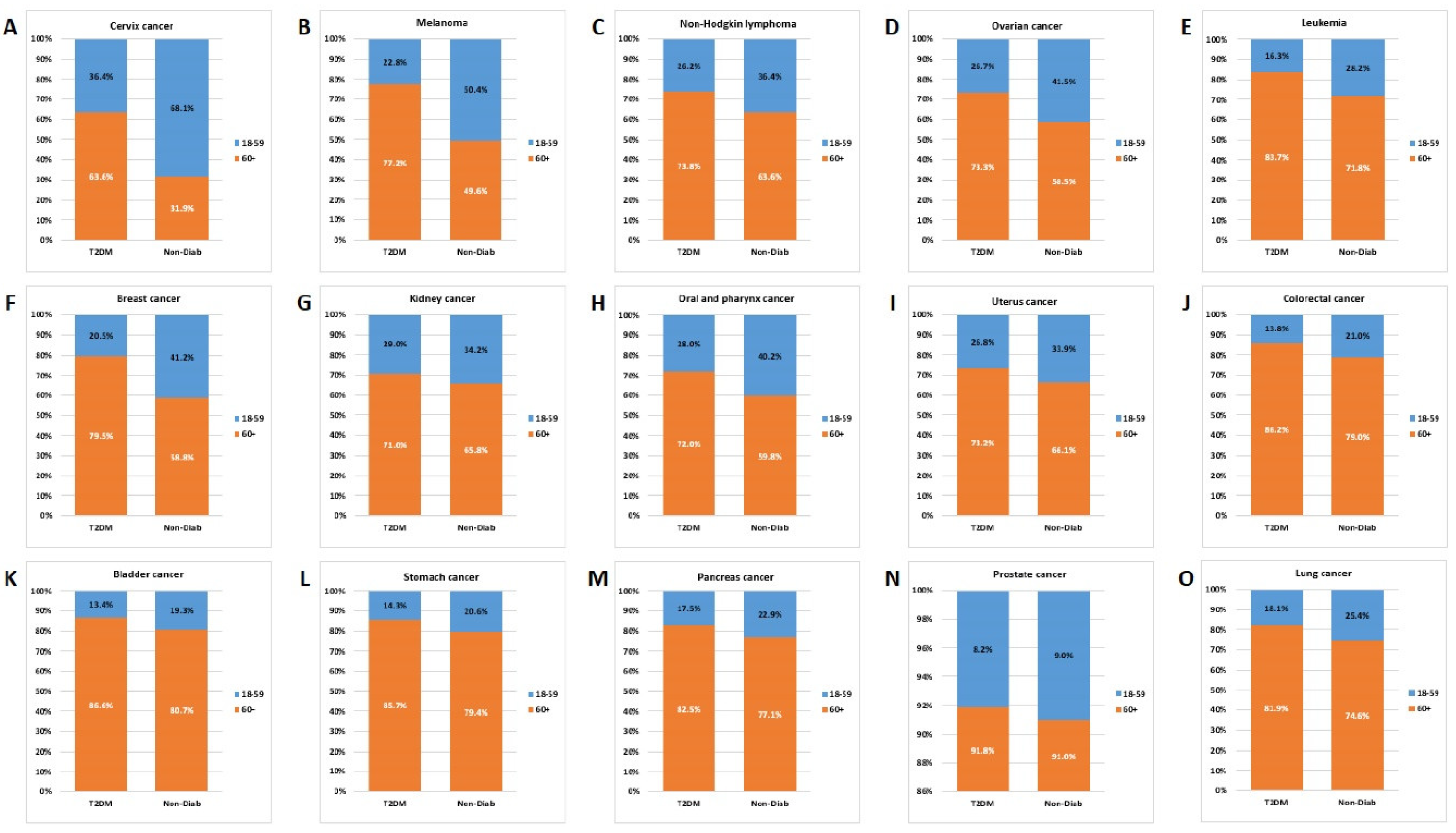
3.6. Age Distribution
Comparing the age distribution for individual cancer types, we found that the contribution of the 60+ age group was similar for lung, pancreas, stomach, bladder, colorectal, uterine corpus and kidney cancer, but with a dominance of the T2DM group. Opposed to that, in the case of cervix, melanoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, ovarian and breast cancers the contribution of the 18-59-year-old group was higher in the Non-Diab group than in the T2DM group (
Figure 8.).
3.7. Time of Detection
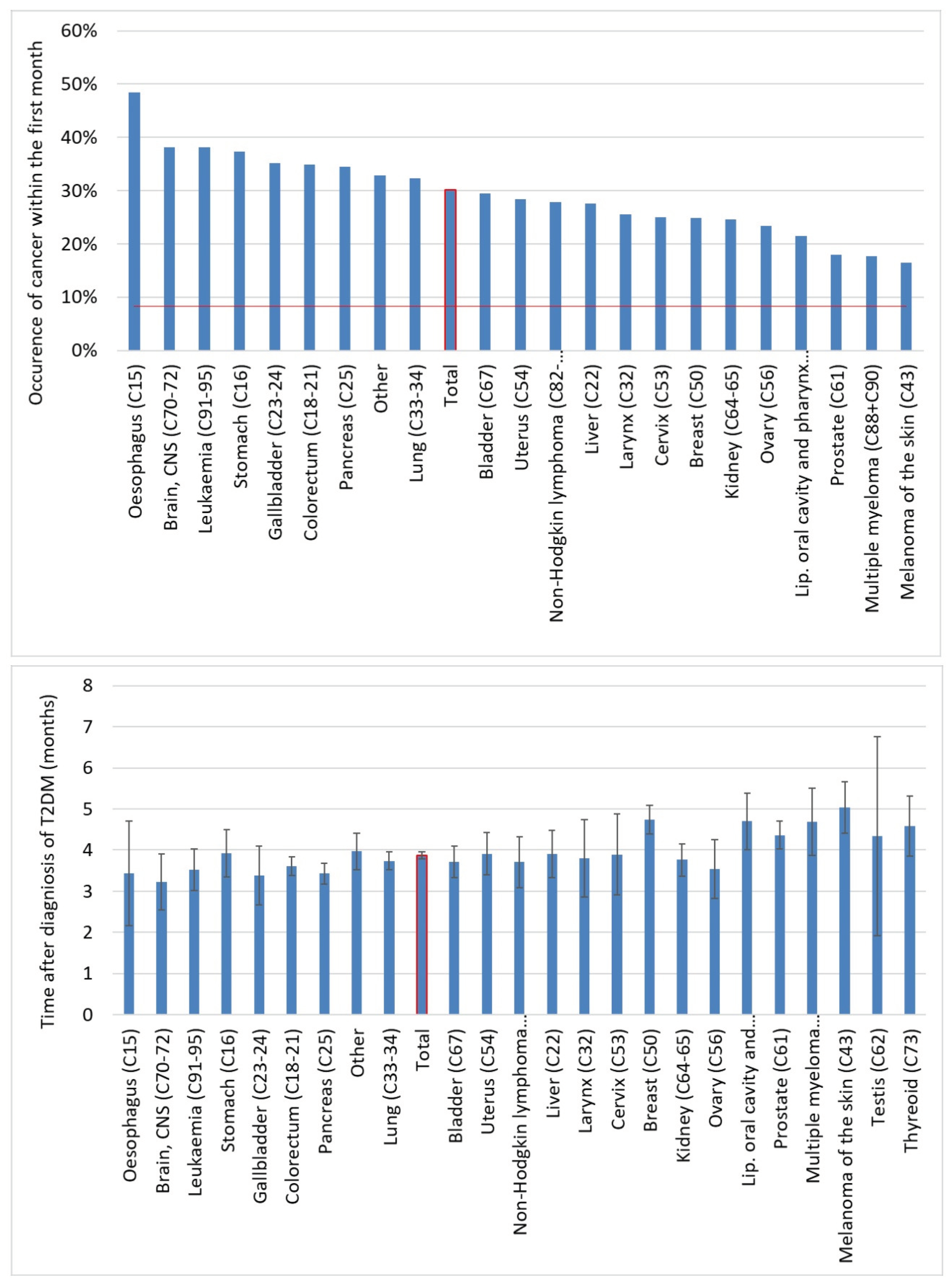
We further analyzed cancer onset within the first year. Overall, 30% of all cancers occurred in the first month after the diagnosis of T2DM. For the individual cancer types, the percentage varied between 16.5-48.5%, and the highest proportion was observed in the case of esophagus, brain, leukemia, stomach, gallbladder, colorectal and pancreas cancers. The average lag time between diagnosis of T2DM and diagnosis of overall cancer was 3.86 months, and the average lag time was below the expected 6 months for all of the cancer types investigated (
Figure 9.).
4. Discussion
The overall and site-specific incidence and AAPC of incident cancer within a year after the diagnosis of T2DM was analyzed in our study between 2015 and 2018. The analysis was stratified by gender and age, while the whole non-diabetic Hungarian population served as control. To our knowledge, this is the first analysis performed on the change of cancer incidence in recently diagnosed T2DM in four consecutive years.
In our study, the overall incidence of any cancer was much higher among patients with incident T2DM vs. Non-Diab persons (32.11 vs. 6.75/1 000 persons). The overall odds to develop a cancer was 4.32-times higher in T2DM compared to the Non-Diab controls.
The association between the development of cancer and T2DM has already been confirmed in numerous epidemiological observations (reviewed in [
17]), however mainly for prevalent DM. Several links[
18] have been described between T2DM and cancer such as obesity, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, inflammation and hyperinsulinemia[
17]. Much more poorly understood is the association between the incidence of cancer and recent-onset T2DM, however, some evidence also exists concerning this association[
13].
With regard to temporal trends of incident cancers, the highest incidence of cancer was found at the time of diagnosis of T2DM, and a decrease was detected within the first year after diagnosis of DM in two studies[
10,
14]. In both papers, the incidence of cancer was the lowest between 2 and 3 years after the diagnosis if DM, and it increased again thereafter.
According to another observation, the risk of cancer was highest within the first six months after diagnosis of DM (HR: 2.03 [1.99-2.03]), which decreased in the time interval of 6 months-3 years (HR: 1.19 [1.18-1.21]. The risk was significantly elevated for all 17 sites of cancer, but it became non-significant after 6 months for esophagus, larynx, breast, cervical and ovarian cancer[
12].
A further study compared the periods of 0-3 months, and 3 months – 10 years after diagnosis of DM, and a significant, approx. 2-3 times higher risk was found for colorectal, lung, cervical, endometrial, ovarian and prostate cancer, but not for breast or thyroid cancers within the first 3 months. In the period after 3 months, the significance diminished for lung, cervical and ovarian cancers[
13].
Another paper presented similar workup, but they found an increased risk of cancers of the pancreas, colorectum, lung, endometrium, prostate, thyroid and bladder but not for the cervix or ovaries in the first 3 months. The highest HR was present for cancer of the pancreas (8.13 [5.42-12.20])[
19]. We found an increased risk for nearly all types of cancer, except for cervical and testicular cancer. We have also found that the risk was highest for cancer of the pancreas.
One striking finding of our study was the high occurrence of cancer immediately after the diagnosis of T2DM. Some data indicate that the development of cancer may in fact even precede the diagnosis of DM[
19]. Therefore, in our study, cases with cancer diagnosed before the index date were excluded. However, hyperglycemia-related metabolic changes that promote carcinogenesis may be initiated already in prediabetic conditions and this notion is supported by ample evidence of the literature[
15,
16,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27].
However, reverse causality in the background cannot be excluded, mainly in the case of cancer of the pancreas, which may directly damage insulin-secreting beta-cells and impair their function or induce peripheral insulin resistance, thereby causing DM[
10]. The latter mechanism cannot be excluded even in the case of extrapancreatic cancers[
28].
On the other hand, the high incidence of cancer in the months just following the diagnosis of T2DM might also be in part the consequence of a detection bias or ascertainment bias according to the literature[
29]. This term means that at the time of diagnosing T2DM, more diagnostic tests are being carried out as a part of routine diagnostic schemes, and cancer is diagnosed by chance during such routine tests. While this approach may appear problematic in epidemiological studies, we believe that this might be an important practical consideration. Namely, at the diagnosis of T2DM, or within a 6 months-period after, it might be worth carrying out at least basic diagnostic procedures in terms of cancer screening (such as abdominal ultrasound, chest X-ray or low-dose CT, fecal occult blood tests, mammography, gynecological testing or PSA screening).
A 2010 consensus statement suggests that “patients with diabetes should … undergo appropriate cancer screenings as recommended for all people in their age and sex”[
3]. However, our data might also support the opinion of Suh et al., who suggest that in order to enable early diagnosis and primary prevention, “cancer should be screened in routine diabetes assessment”[
3].
Concerning the relation of colorectal cancer and new-onset T2DM, a study found that the HR of cancer was numerically higher in patients aged < 55 years as compared to the total population (1.8 [1.1-2.9] vs. 1.4 [1.3-1.6], respectively)[
30]. In our study, an important observation was the very high OR of cancer of the 18-39-year-old group with incident T2DM. This high risk in young individuals with T2DM becomes extremely important in the light of observations, where the incidence of T2DM in young adults and adolescents increased in the US in the total population but showed an even more steep rise in the American Indian and non-Hispanic black population[
31]. Also, according to a German study, the incidence of T2DM increased significantly in the 20-39-year-old population[
32]. Similar trends for younger patients were found in other studies as well[
33,
34]. This might draw attention to these – according to the results of our paper – high risk individuals.
This pattern of high risk in young individuals is very similar to the incidence of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in T2DM patients, being higher in young-onset diabetes[
35,
36]. The close association among the incidence of T2DM, cancer and cardiovascular risk in the young population may refer to a common pathogenetic background.
The incidence of cancer did not change among diabetic patients between 2015-2018, but slightly declined in the non-diabetic population. The latter is in line with the estimated annualized rate change of age-standardized incidence rate of cancers excluding non-melanoma skin cancer, which was globally 0 to -0.2 % (95% UI,−0.9% to 0.5%) and between 0 to -0.9 % in Hungary between 2010-2019[
4]. In contrast, the unchanged rate of incident cancer among recently diagnosed T2DM patients suggests that diabetes itself may contribute to the sustained cancer incidence.
The major strength of our study is the very high coverage of the Hungarian population by the database of NHIF and HCSO. The report of the date and histological diagnosis of a cancer is mandatory in this collection of data. The first report of T2DM may also be recovered. This fact makes the database of our analysis valid and accurate.
The weakness of data collection is that due to data protection regulations of NHIF provides only aggregated data, i.e., there is no available data for subgroups including less than ten patients. A further weakness is that cancer subclasses, and other laboratory data regarding T2DM follow-up and medical treatment were not available for analysis.
5. Conclusions
In summary, incident T2DM associates with an enhanced risk for incident cancer, the overall risk being as high as 4.45. There are 18 cancer sites where risk of cancer is higher in diabetic patients, pancreas, liver and kidney bearing the highest risk to develop cancer. The risk is substantially higher in younger ages, where the cardiovascular risk is also enhanced. The incidence of cancer is slowly declining in the non-diabetic population but not among diabetic patients. The age, gender and site-specific differences among different cancer sites need further exploration. We might need to re-evaluate the current screening strategies in terms of cancer in (young) individuals with newly registered T2DM.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Supplementary methods.
Author Contributions
G.A.M. and G.S. contributed equally. Conceptualization, I.W., Z.K., G.R., G.J., P.K., C.L.; methodology, I.W., Z.K., G.R.; software, Z.A-T., I.F., G.A.M.; validation, Z.A-T., I.F.; formal analysis, Z. A-T, I.F., G.A.M., G.S.; investigation, Z. A-T, I.F., G.A.M., G.S., I.W.; resources, I.W., P.K., C.L.; data curation, Z. A-T., I.F., G.R,; writing—original draft preparation, Z.A-T., G.A.M., G.S., I.W.; writing—review and editing, I.W., Z.K.; visualization, Z.A-T, I.F., G.A.M., G.S.; supervision, I.W., Z.K, G.R., G.J., P.K., C.L.; project administration, X.X. Z.A-T., I.F., G.A.M., G.S.; funding acquisition, I.W., P.K., C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Hungarian Diabetes Association provided funding for data collection and research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Board of the University of Pécs (9326-PTE 2022), by the National Institute of Pharmacy and Nutrition (KRID: 641936355) and by Medical Research Council (BMEÜ/95-3/2022/EKU).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data generated during the study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author. Individual, patient-level data are not available due to data protection rules of the NHIF.
Acknowledgments
Enikő Bodor is acknowledged for preparation and submission of the manuscript, and we would like to thank Professor Dr József Andor for language related stylistic help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Authors Zsolt Abonyi-Tóth, György Rokszin and Ibolya Fábián are employed by RxTarget Ltd., Szolnok, Hungary. Dr. Kiss is also employed by MSD Pharma Hungary Ltd., but this provides no relevant conflict of interest for the current research. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lotfy, M.; Kalasz, H.; Singh, J. Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: A Mini Review. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Engel, J.M.; Glurich, I.; Stankowski, R. V.; Williams, G.M.; Doi, S.A. Diabetes and Cancer I: Risk, Survival, and Implications for Screening. Cancer Causes Control 2012, 23, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.A.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Yee, D. Diabetes and Cancer: A Consensus Report. In Proceedings of the Diabetes Care; 2010; Vol. 33; pp. 1674–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Kocarnik, J.M.; Compton, K.; Dean, F.E.; Fu, W.; Gaw, B.L.; Harvey, J.D.; Henrikson, H.J.; Lu, D.; Pennini, A.; Xu, R.; et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019 A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohás-Cseh, J.; Molnár, G.A.; Pap, M.; Laczy, B.; Vas, T.; Kertész, M.; Németh, K.; Hetényi, C.; Csikós, O.; Tóth, G.K.; et al. Incorporation of Oxidized Phenylalanine Derivatives into Insulin Signaling Relevant Proteins May Link Oxidative Stress to Signaling Conditions Underlying Chronic Insulin Resistance. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Hsiao, M. Leptin and Cancer: Updated Functional Roles in Carcinogenesis, Therapeutic Niches, and Developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, N. Role of Leptin in Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 18, 13226–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumminia, A.; Vinciguerra, F.; Parisi, M.; Graziano, M.; Sciacca, L.; Baratta, R.; Frittitta, L. Adipose Tissue, Obesity and Adiponectin: Role in Endocrine Cancer Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, B.; Witte, D.R.; Friis, S. Cancer Occurrence in Danish Diabetic Patients: Duration and Insulin Effects. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Yeh, H.C.; Johnson, J.A.; Wild, S.H.; Gale, E.A.M.; Møller, H. Diabetes and Cancer (2): Evaluating the Impact of Diabetes on Mortality In Patients with Cancer. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, D.L.; Rhyu, Y.A.; Lee, S.E.; Ko, S.H.; Han, K.; Song, K.H. Site-Specific Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Bowker, S.L.; Richardson, K.; Marra, C.A. Time-Varying Incidence of Cancer after the Onset of Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence of Potential Detection Bias. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccardi, F.; Ling, S.; Brown, K.; Davies, M.; Khunti, K. Response to Comment on Zaccardi et Al. Duration of Type 2 Diabetes and Incidence of Cancer: An Observational Study in England. Diabetes Care 2023;46:1923-1930. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, J.P.; Allen, N.B.; Bancks, M.P.; Carr, J.J.; Lewis, C.E.; Lima, J.A.; Rana, J.S.; Gidding, S.S.; Schreiner, P.J. Duration of Diabetes and Prediabetes during Adulthood and Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Cardiac Dysfunction Inmiddle Age: The CARDIA Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Qiu, M.; Chen, P.; Tang, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Prediabetes and the Risk of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.L.; Rojna, M. Diabetes and Risk of Cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Reñones, C.; Baena-Díez, J.M.; Aguilar-Palacio, I.; Miquel, C.; Grau, M. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer: Epidemiology, Physiopathology and Prevention. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lega, I.C.; Wilton, A.S.; Austin, P.C.; Fischer, H.D.; Johnson, J.A.; Lipscombe, L.L. The Temporal Relationship between Diabetes and Cancer: A Population-Based Study. Cancer 2016, 122, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Rutegård, M.; Santoni, G.; Wallner, B.; Johansson, I.; Sund, M.; Xie, S.H.; Lagergren, J. Prediabetes and Diabetes in Relation to Risk of Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tu, R.; Lu, Z. Prediabetes and the Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Martínez, A.M.; Flores-Cortés, L.I.; Cardona-Chavarría, J.M.; Hernández-Gutiérrez, B.; Abundis, A.; Vázquez-Lara, J.; González-Guajardo, E.E. Prediabetes, Diabetes, and Risk of Breast Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.; Chen, X. Prediabetes and the Risk of Lung Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, Y.S.; Kang, G.; Han, K.; Park, J.O. Association of Prediabetes, Diabetes, and Diabetes Duration with Biliary Tract Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Metabolism. 2021, 123, 154848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Stankowski, R. V.; Berg, R.L.; Engel, J.M.; Glurich, I.; Williams, G.M.; Doi, S.A.R. Breast Cancer Incidence before and after Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Women: Increased Risk in the Prediabetes Phase. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 23, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Wu, K.; Ruan, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Qiu, H.; Tan, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Glucose Intolerance and Cancer Risk: A Community-Based Prospective Cohort Study in Shanghai, China. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Berg, R.L.; Engel, J.M.; Glurich, I.; Stankowski, R. V.; Williams, G.; Doi, S.A. Increased Risk of Colon Cancer in Men in the Pre-Diabetes Phase. PLoS One 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Màrmol, J.M.; Carlsson, M.; Raun, S.H.; Grand, M.K.; Lehrskov, L.L.; Richter, E.A.; Norgaard, O.; Sylow, L.; Màrmol, J.M.; Carlsson, M.; et al. Insulin Resistance in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Oncol. (Madr). 2023, 62, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Carstensen, B.; Witte, D.; Bowker, S.L.; Lipscombe, L.; Renehan, A.G. Diabetes and Cancer (1): Evaluating the Temporal Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer Incidence. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kort, S.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Sanduleanu, S.; Weijenberg, M.P.; Van Herk-Sukel, M.P.P.; Oldenhof, N.J.J.; Van Den Bergh, J.P.W.; Haak, H.R.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L. Higher Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus before the Age of Colorectal Cancer Screening Initiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenknecht, L.E.; Lawrence, J.M.; Isom, S.; Jensen, E.T.; Dabelea, D.; Liese, A.D.; Dolan, L.M.; Shah, A.S.; Bellatorre, A.; Sauder, K.; et al. Trends in Incidence of Youth-Onset Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in the USA, 2002–18: Results from the Population-Based SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönnies, T.; Hoyer, A.; Brinks, R.; Kuss, O.; Hering, R.; Schulz, M. Spatio-Temporal Trends in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Germany. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2023, 120, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, B.; Rønn, P.F.; Jørgensen, M.E. Prevalence, Incidence and Mortality of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Denmark 1996-2016. BMJ open diabetes Res. care 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliano, D.J.; Islam, R.M.; Barr, E.L.M.; Gregg, E.W.; Pavkov, M.E.; Harding, J.L.; Tabesh, M.; Koye, D.N.; Shaw, J.E. Trends in Incidence of Total or Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review. BMJ 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Qi, H.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Huo, Y.; et al. Association Between Age at Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Nationwide, Population-Based, Cohort Study. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Song, L.; Sun, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Yao, S.; Li, Y.; Yun, C.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; et al. Associations of Type 2 Diabetes Onset Age with Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: The Kailuan Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).