Submitted:
15 February 2024
Posted:
16 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study area
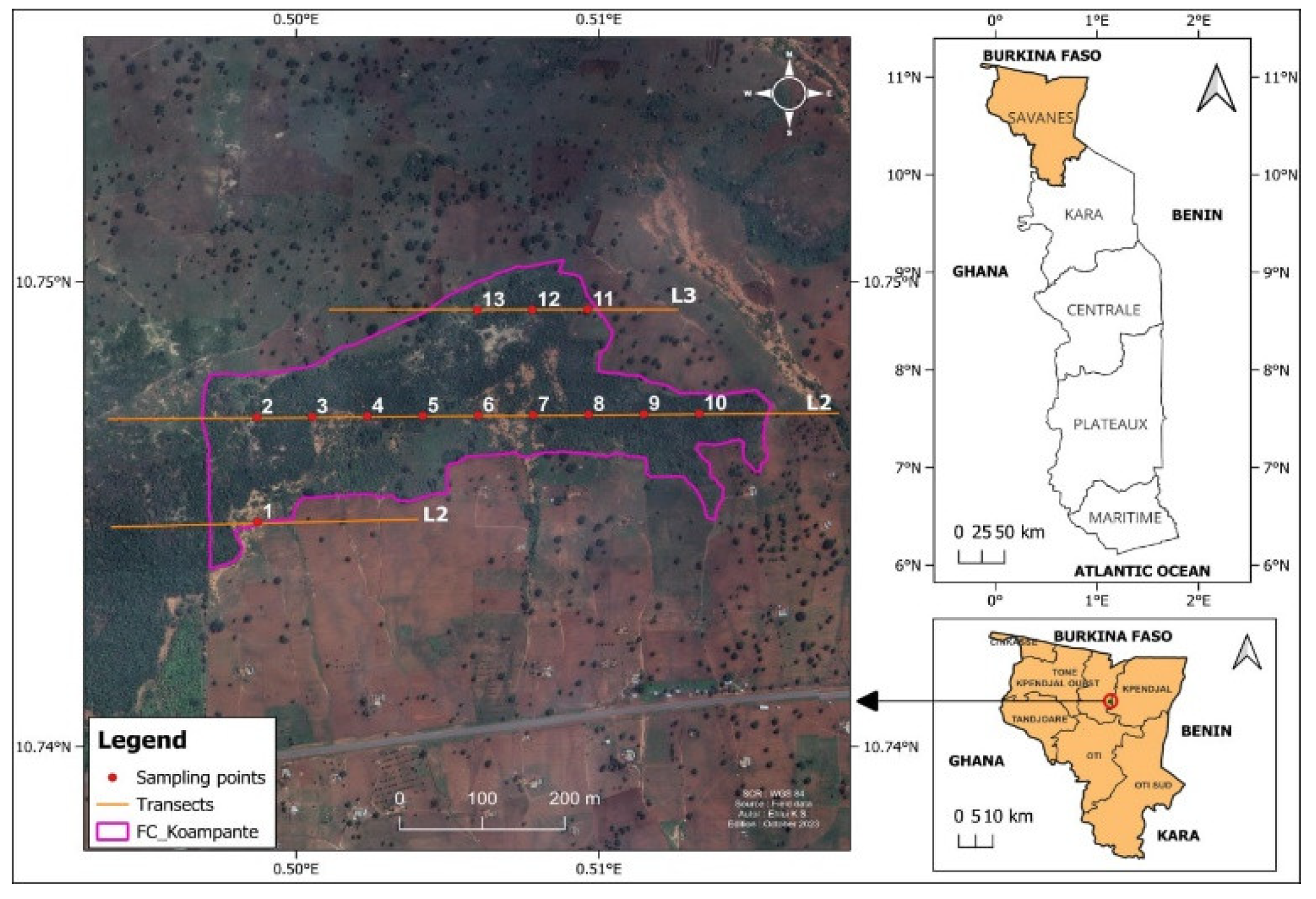
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Satelite image acquisition
2.2.2. Sampling design
2.2.3. Inventories
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Land Use Unit Mapping
2.3.2. Assessment Of The Floristic Diversity
2.3.3. Forest Characteriscics Analysis
3. Results
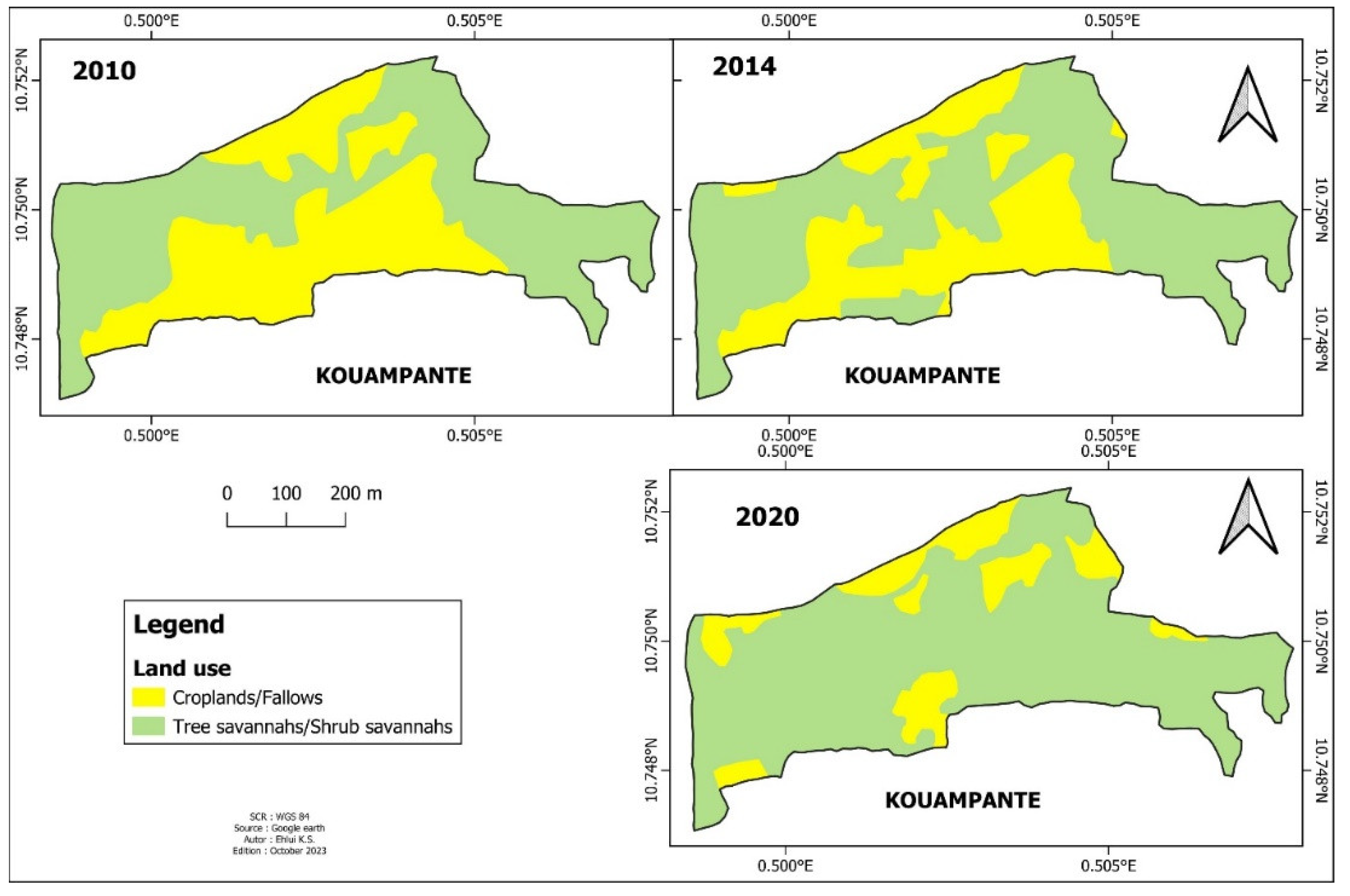
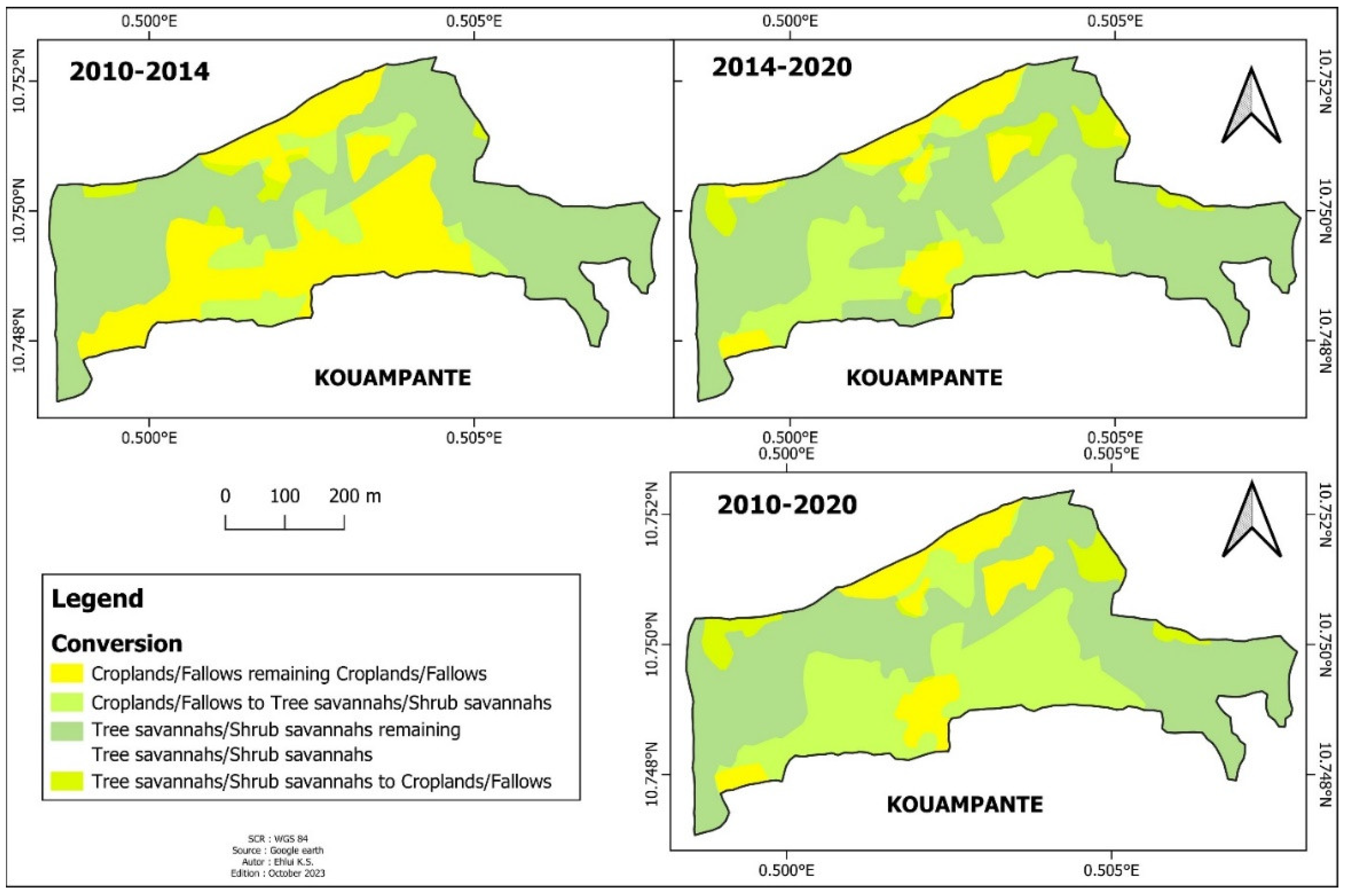
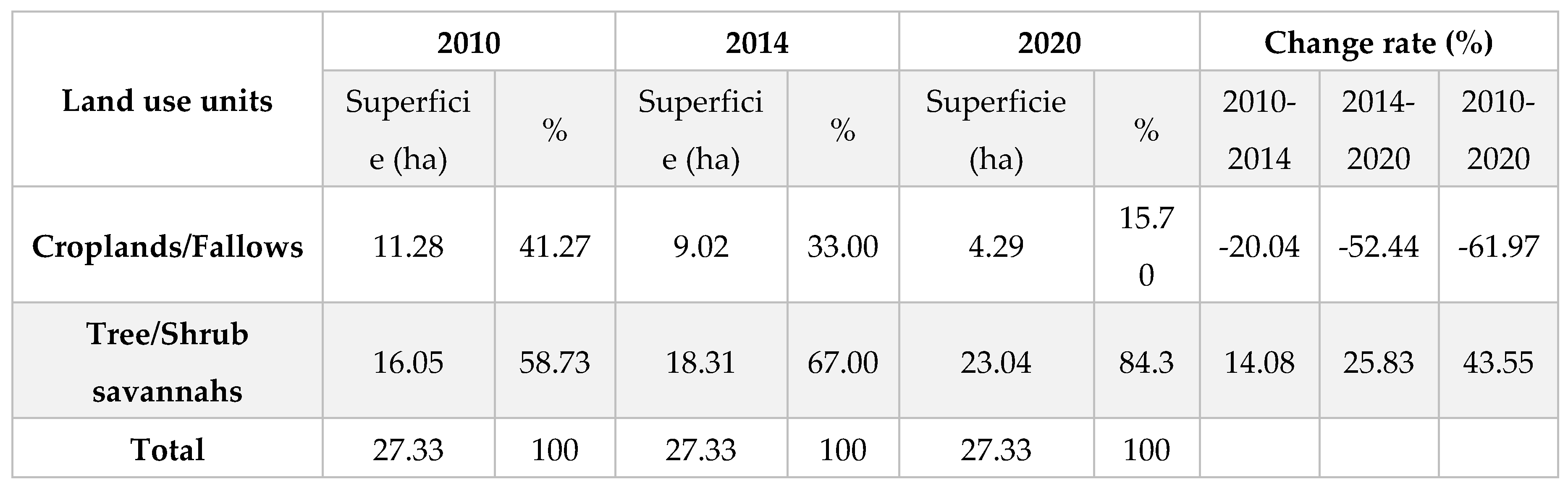
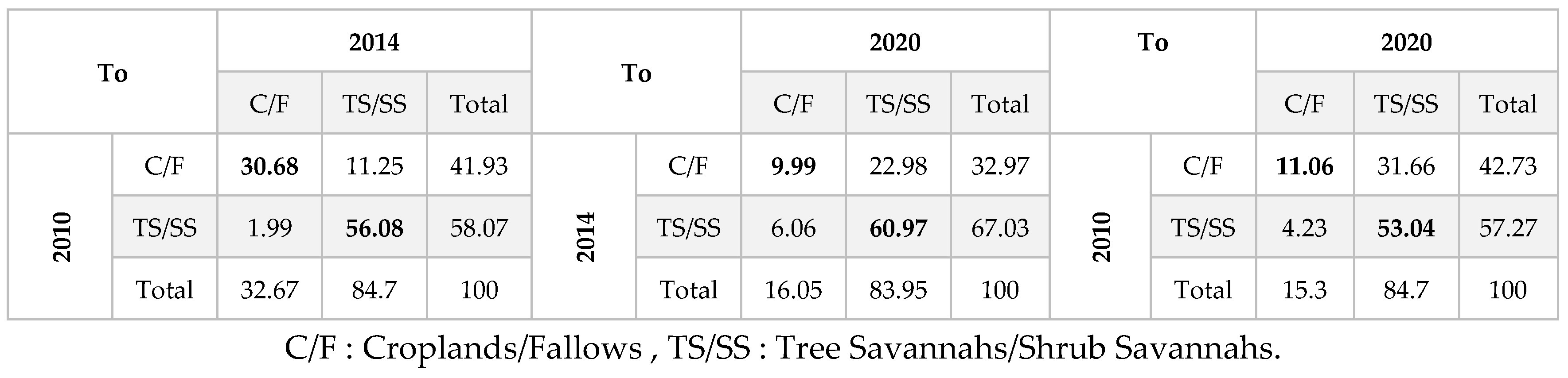
3.1. Land Use Units Dynamic
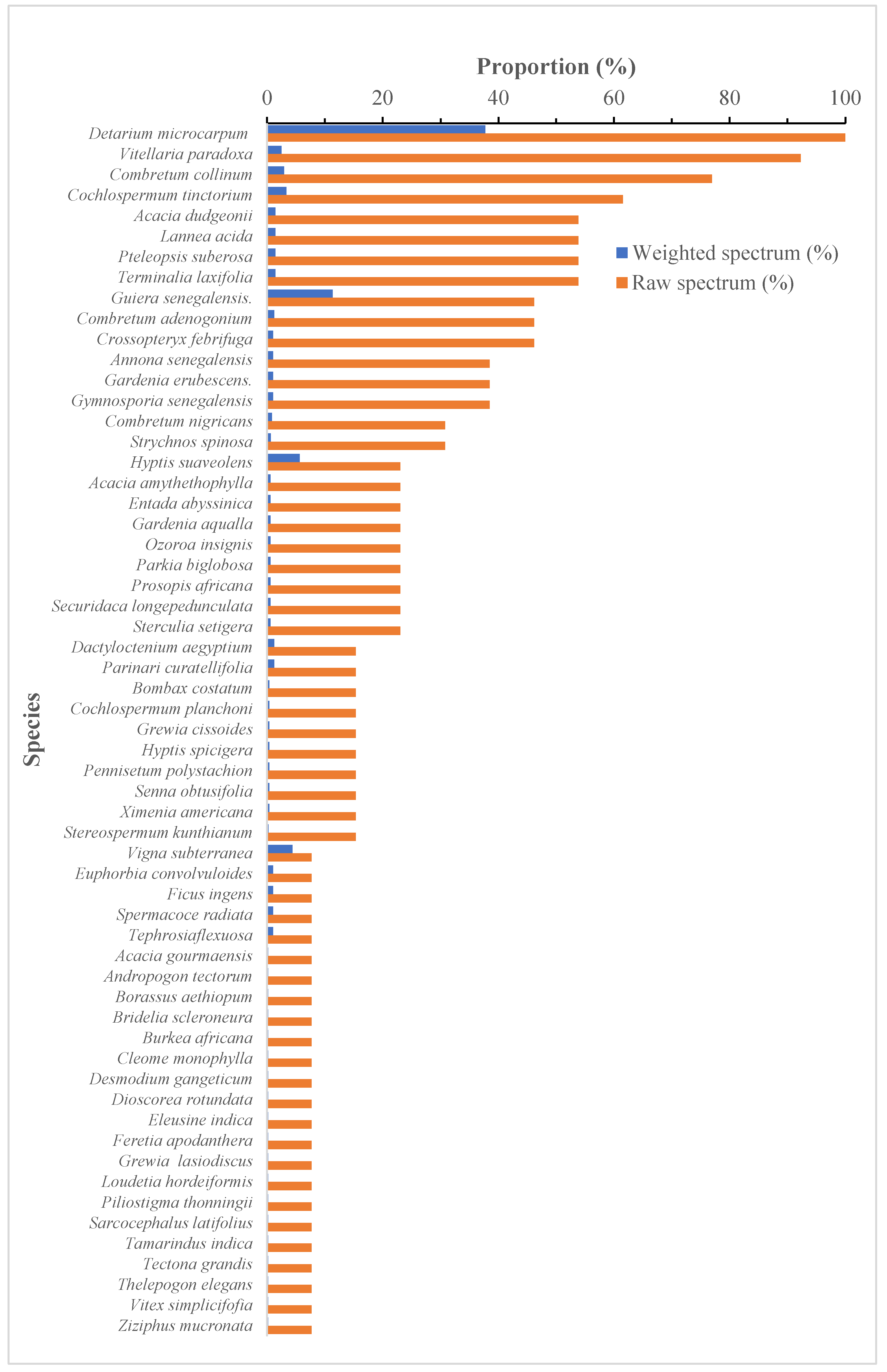
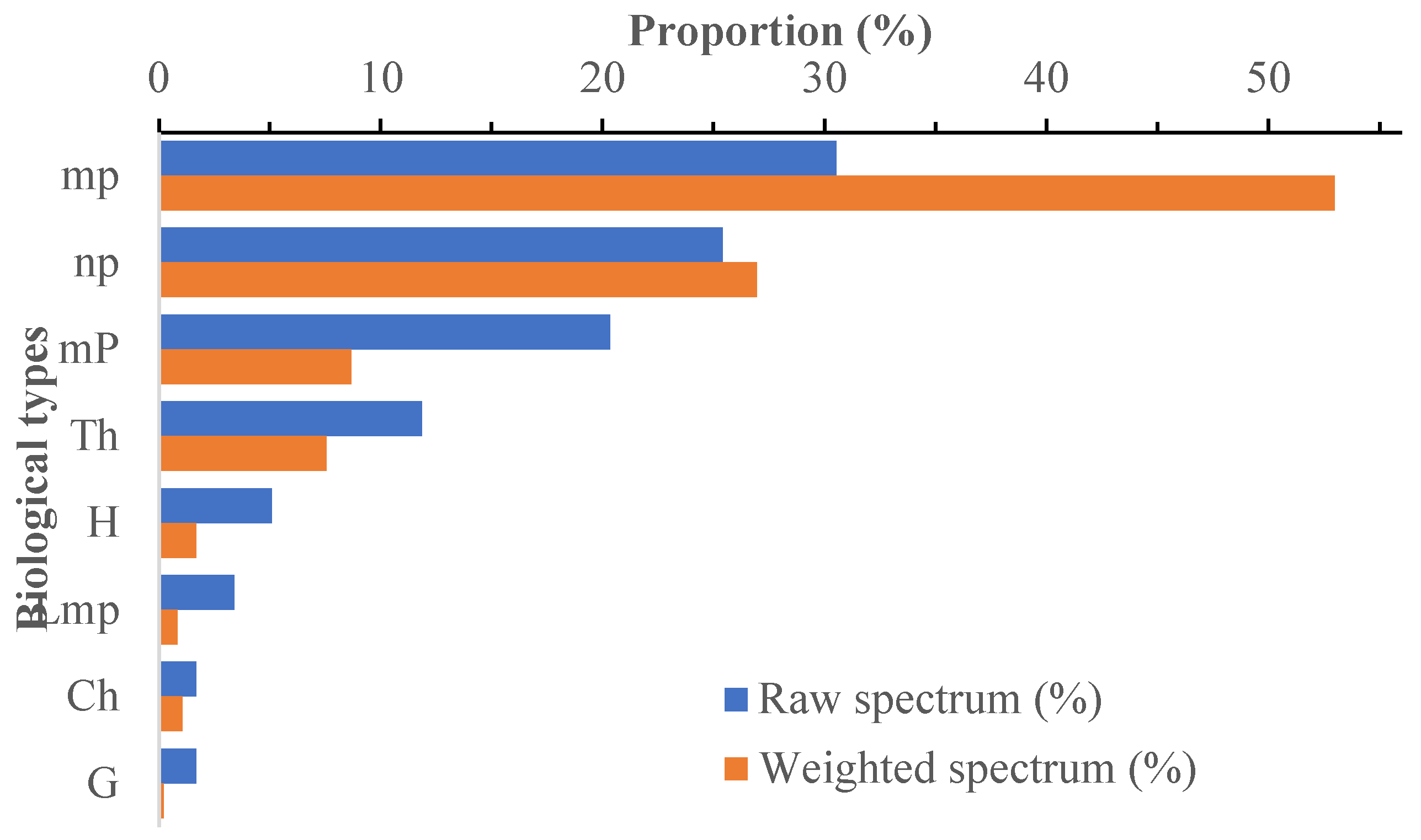
3.2. Floristic Diversity of Kouampante Community Forest (KCF)
3.3. Descriptrion of woody plant communities
3.4. Demographic structure
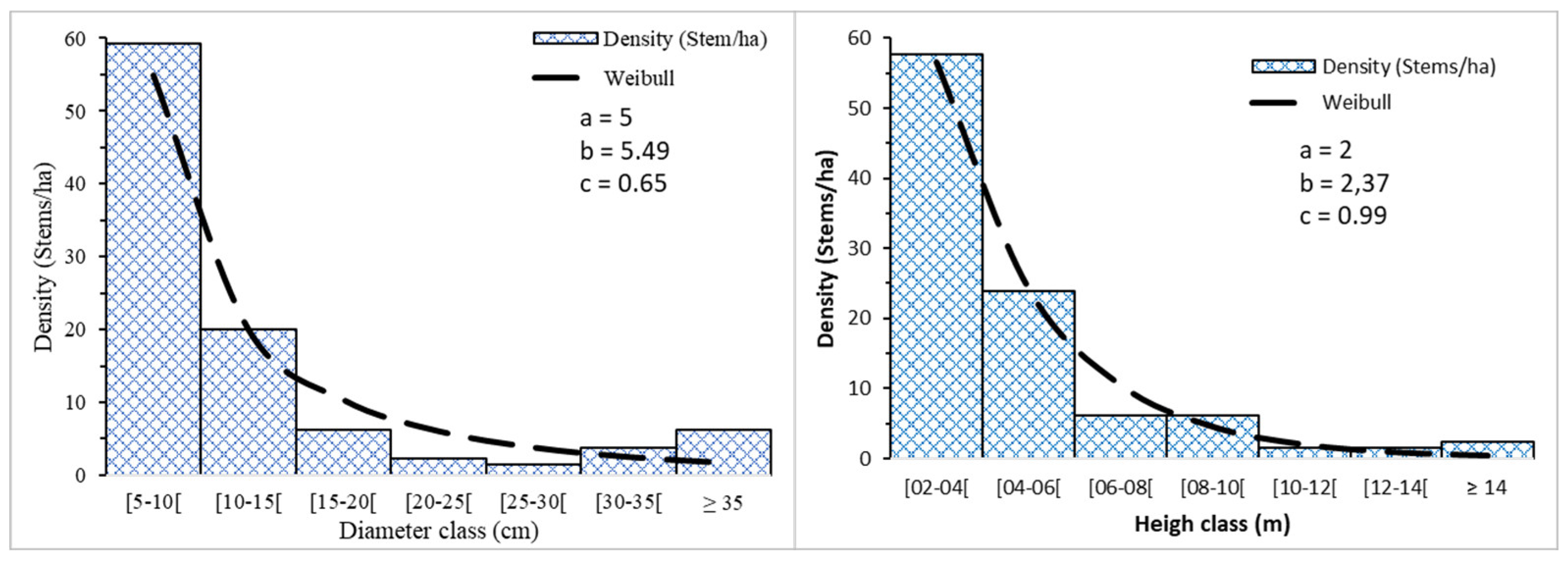
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of plant species within Kouampante Community Forest (NCF)
| Species | Families | TP | TB |
| Acacia amythethophylla Steud. ex A. Rich. | Fabaceae | SZ | mP |
| Acacia dudgeonii Craib ex Holland | Fabaceae | SZ | mp |
| Acacia gourmaensis A.Chev. | Fabaceae | SZ | mp |
| Andropogon tectorum Schumach. & Thonn. | Poaceae | GC-SZ | H |
| Annona senegalensis Pers. | Anonanceaae | GC-SZ | np |
| Bombax costatum Pellegr. & Vuillet | Malvaceae | SZ | mP |
| Borassus aethiopum Mart. | Arecaceae | GC-SZ | mP |
| Bridelia scleroneura Müll.Arg. | Phyllanthaceae | SZ | np |
| Burkea africana Hook. | Fabaceae | SZ | mp |
| Cleome monophylla L. | Cleomaceae | GC-SZ | Th |
| Cochlospermum planchonii Hook.f. | Bixaceae | SZ | np |
| Cochlospermum tinctorium A.Rich. | Bixaceae | SZ | np |
| Combretum adenogonium Steud. ex A.Rich. | Combretaceae | SZ | mp |
| Combretum collinum Fresen. | Combretaceae | SZ | mp |
| Combretum nigricans Lepr. ex var. elliotii (Engl. & Diels) Aubrev. | Combretaceae | GC-SZ | mP |
| Crossopteryx febrifuga (G.Don) Benth. | Rubiaceae | GC-SZ | mp |
| Dactyloctenium aegyptium (L.) WilId., | Poaceae | GC-SZ | H |
| Desmodium gangeticum (L.) nc. var. gangeticum | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Detarium microcarpum Guill. & Perr. | Fabaceae | SZ | mp |
| Dioscorea rotundata Poir. | Dioscoreaceae | GC-SZ | G |
| Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. | Poaceae | GC-SZ | H |
| Entada abyssinica Steud. ex A.Rich. | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | Lmp |
| Euphorbia convolvuloides Hochst. ex Benth. | Euphorbiaceae | SZ | Ch |
| Feretia apodanthera Delile ssp. apodanthera | Rubiaceae | SZ | mp |
| Ficus ingens (Miq.) Miq. | Moraceae | SZ | mp |
| Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Huteh. | Rubiaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Gardenia erubescens Stapf & Huteh. | Rubiaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Grewia lasiodiscus K. Schum. | Malvaceae | SZ | mp |
| Grewia cissoides Hutch. & DalzieI | Malvaceae | SZ | mp |
| Guiera senegalensis J.F.Gmel. | Combretaceae | SZ | np |
| Gymnosporia senegalensis (Lam.) Loes. | Celastraceae | SZ | np |
| Hyptis spicigera Lam. | Lamiaceae | SZ | np |
| Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit. | Lamiaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Lannea acida A.Rich. s.l. | Anacardiaceae | GC-SZ | mP |
| Loudetia hordeiformis (Stapf) C.E.Hubbard | Poaceae | GC-SZ | Th |
| Ozoroa insignis Delile | Anacardiaceae | SZ | np |
| Parinari curatellifolia Planch. ex Benth. | Chrysobalanaceae | SZ | mp |
| Parkia biglobosa (Jacq.) R.Br. ex Benth. | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | mP |
| Pennisetum polystachion (L.) Sehult. polystachion | Poaceae | GC-SZ | Th |
| Piliostigma thonningii (Schumach.) Milne-Redh. | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Prosopis africana (GuilI. & Perr.) Taub. | Fabaceae | SZ | mP |
| Pteleopsis suberosa Engl. & Diels | Combretaceae | SZ | mp |
| Sarcocephalus latifolius (Sm.) E.A.Bruce | Rubiaceae | GC-SZ | Lmp |
| Securidaca longepedunculata Fresen. | Polygalaceae | SZ | mp |
| Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | np |
| Spermacoce radiata (DC.) Hiem | Rubiaceae | GC-SZ | Th |
| Sterculia setigera Delile | Malvaceae | SZ | mP |
| Stereospermum kunthianum Cham. | Bignoniaceae | SZ | mP |
| Strychnos spinosa Lam. | Loganiaceae | SZ | mP |
| Tamarindus indica L. | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | mP |
| Tectona grandis L.f. | Verbenaceae | I | mP |
| Tephrosiaflexuosa G.Don | Fabaceae | GC-SZ | Th |
| Terminalia laxifolia Engl. | Combretaceae | SZ | mp |
| Thelepogon elegans Roth ex Roem. | Poaceae | SZ | Th |
| Vigna subterranea (L.) Verde. | Fabaceae | I | Th |
| Vitellaria paradoxa C.F.Gaertner subsp. i | Sapotaceae | SZ | mP |
| Vitex simplicifolia Oliv. | Verbenaceae | SZ | np |
| Ximenia americana L. | Olacaceae | GC-SZ | mp |
| Ziziphus mucronata Willd. | Rhamnaceae | SZ | mp |
References
- K. Adjonou, M. Kpeli Poukpezi, K. N. Segla, and K. Kokou, “Impacts of traditional practices on biodiversity and structural characteristics of sacred groves in northern Togo, West Africa,” Acta Oecologica, vol. 110, no. October 2020, p. 103680, 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, B. Badjare, Y. A. Woegan, F. komi G. Amouzou, M. Kpadjao, and K. Akpagana, “Ecologie des bosquets sacrés de la préfecture de Tone dans la Région des Savanes au Togo,” Rev. Espac. Geogr. Soc. Marocaine, vol. 56, no. January, p. 23, 2022.
- K. S. Ehlui et al., “Anthropogenic Threats to Degraded Forest Land in the Savannahs ’ Region of Togo from 1984 to 2020 , West Africa,” J. Geosci. Environ. Prot., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 164–179, 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. Bhusal, N. S. Paudel, A. Adhikary, J. Karki, and K. Bhandari, “Halting Forest Encroachment in Terai: What Role for Community Forestry?,” J. For. Livelihood, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 15–34, 2018.
- B. Kombate et al., “Structure et modélisation du carbone de la Forêt Classée de Missahohoé au Togo.,” African J. L. Policy Geospatial Sci. 6(1) 42-61., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 42–61, 2023.
- P. B. Giri, M. Yucharoen, S. Gyawali, and P. Gentle, “Implementing SDG-15 Through Community Forestry Management A Case of Tarpakha Community Forest, Gorkha, Nepal,” EnvironmentAsia, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 1–11, 2023.
- C. Wulandari, P. Budiono, and D. Iswandaru, “Importance of social characteristic of community to support restoration program in protection forest,” Indones. J. For. Res., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 173–186, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Baynes, J. Herbohn, C. Smith, R. Fisher, and D. Bray, “Key factors which influence the success of community forestry in developing countries,” Glob. Environ. Chang., vol. 35, pp. 226–238, 2015. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, H. Egbelou, M. Samarou, and F. Fousseni, “La foresterie communautaire au Togo: Où en sommes-nous?,” Rev. Marocaine des Sci. Agron. Vétérinaires, vol. 11, no. December, pp. 532–543, 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, H. Egbelou, B. Kombate, S. Biaou, and K. Batawila, “Diversité et structure des formations végétales de la forêt communautaire d ’ Alibi -1 au Togo,” Rev. Sci. Technol., Synthèse, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 06–20, 2023.
- M. Moayeri, A. Abedi, S. Mohammadreza, and A. Mastouri, “Detection of social forestry approaches and its impact on managing forestry plans in Golestan province,” J. Wood For. Sci. Technol., vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1–28, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. J. . Beukeboom, C. Van der Laan, A. Van Kreveld, and G. Akwah, “Can community forestry contribute to livelihood improvement and biodiversity?,” 2010.
- K. S. Ehlui et al., “Mapping and Floristic Diversity of the Nakpadjouak Community Forest , Tami Canton , Togo ( West Africa ),” Nat. Resour., 2024. [CrossRef]
- F. Folega et al., “Caractérisation écologique de la Foret Communautaire d’Edouwossi-Cope (région des Plateaux-Togo),” J. Rech. Sci. Univ. Lomé, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 47–61, 2017.
- W. Atakpama, H. Egbelou, F. Folega, C. Afo, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “Diversité floristique des forêts communautaires de la préfecture de Dankpen au Togo,” Rev. Marocaine des Sci. Agron. Vétérinaires, vol. 10 (4), no. December, pp. 548–557, 2022.
- D. M. Bawa, K. Wala, F. Folega, and K. Akpagana, “Caractéristiques floristiques et structurales de la forêt communautaire d ’ Agbandi au centre du Togo ( Afrique de l ’ ouest ) Floristic and structural characteristics of Agbandi communi ...,” Rev Écosystèmes Paysages, vol. 02, no. july, pp. 55–74, 2022.
- M. Kossi et al., “État et dynamique spatio- temporelle de la forêt communautaire d ’ Edouwossi - Copé , Région des Plateaux-Togo Spatio-temporal dynamics of the Edouwossi-Copé community forest , region of,” Rev Écosystèmes Paysages, vol. 02, no. 01, pp. 12–26, 2022.
- F. Folega et al., “Land Use Change and the Structural Diversity of Affem Boussou Community Forest in the Tchamba 1 Commune (Tchamba Prefecture, Togo),” Conservation, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 346–362, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Koumoi, “Cartographie et caractérisation floristique de la forêt communautaire Edzi Hado dans la préfecture de l’Avé, Région Maritime (Togo),” Rev. Ecosystèmes Paysages ( Togo ), vol. 3, no. 1, 2023.
- W. Atakpama, F. Folega, M.-E. Kpadjao, and F. komi G. Amouzou, “Problématique de gestion durable de la biodiversité des bosquets sacrés de la Région des Savanes au Togo Challenge of sustainable management of biodiversity of sacred groves of the Region of Savannahs in Togo,” Rev. Sci. Technol., Synthèse, vol. 27, no. January 2022, pp. 22–32, 2021.
- Y. Konko, J. P. Rudant, G. K. Akpamou, K. D. Noumonvi, and K. Kokou, “Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Southeastern Community Forests in Togo (West Africa),” J. Geosci. Environ. Prot., vol. 06, no. 07, pp. 51–65, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. K. Musyoki, J. Mugwe, K. Mutundu, and M. Muchiri, “Factors influencing level of participation of community forest associations in management forests in Kenya,” J. Sustain. For., vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 205–216, 2016. [CrossRef]
- F. Folega, W. Atakpama, M. Kanda, K. Wala, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “Agroforestry parklands and carbon sequestration in tropical Sudanese region of Togo,” Rev. Mar. Sci. Agron. Vét., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 563–570, 2019.
- F. Folega et al., “Assessment and impact of anthropogenic disturbances in protected areas of northern Togo,” For. Stud. China, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 216–223, 2012.
- K. Dimobe, K. Wala, K. Batawila, M. Dourma, Y. A. Woegan, and K. Akpagana, “Analyse spatiale des différentes formes de pressions anthropiques dans la réserve de faune de l’Oti-Mandouri (Togo),” VertigO, no. Hors-série 14, 2012.
- Polo-Akpisso et al., “Habitat biophysical and spatial patterns assessment within Oti-Keran-Mandouri protected area network in Togo,” Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 214–229, 2018. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, B. Badjare, E. Yawo, K. Aladji, and K. Batawila, “fosse de Doungh au Togo Alarming degradation of forest resources in the classified forest of Doungh pit in Togo,” African J. L. Policy Geospatial Sci., vol. 6, no. May, pp. 2657–2664, 2023.
- Folega, F. Folega, Y. Woegan, K. Wala, and K. Akpagana, “Dynamique des émissions de gaz à effet de serre liées au secteur foresterie et autres affectations des terres (FAT) dans le paysage du socle Eburnéen au Togo.,” Rev Écosystèmes Paysages (Togo), vol. 01(01): 58, no. December, 2021.
- H. Ern, “Die Vegetation Togos. Gliederung, Gefährdung, Erhaltung Author(s): Hartmut Ern Source:,” Willdenowi, vol. 9, pp. 295–312, 1979.
- J. F. Brunel, P. Hiepko, and H. Scholz, “Flore analytique du Togo: Phanerogames,” Englera, no. 4, pp. 3–751, 1984. [CrossRef]
- K. Akpagana and P. Bouehet, “Etat actuel des connaissances sur la flore et la végétation du Togo,” Acta Bot. Gall., vol. 141, no. 3, pp. 367–372, 1994.
- B. Kebenzikato et al., “Distribution et structure des parcs à Adansonia digitata L.(baobab) au Togo (Afrique de l’Ouest),” Afrique Sci., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 434–449, 2014.
- M. Samarou et al., “Caractérisation écologique et structurale des parcs à tamarinier ( Tamarindus indica L ., Fabaceae ) dans la zone soudanienne du Togo ( Afrique de l ’ Ouest ),” Rev Écosystèmes Paysages, vol. 02, no. July, pp. 109–125, 2022.
- E. Padakale et al., “Woody Species Diversity and Structure of Parkia biglobosa Jacq. Dong Parklands in the Sudanian Zone of Togo (West Africa),” Annu. Res. Rev. Biol., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 103–114, 2015.
- M. Samarou, N. Lekeriba, W. Atakpama, and B. Komlan, “Diversité et importance économique des plants forestiers utilisés dans la restauration des paysages dans la région Maritime au Togo Diversity and economic importance of woody plants used for forest landscape restoration in the Maritime region of Togo,” Rev. Ecosystèmes Paysages, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 149–166, 2023.
- B. Kebenzikato, W. Atakpama, M. Samarou, K. Wala, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “Importance socio-économique du baobab ( Adansonia digitata ) au Togo,” Rev. Mar. Sci. Agron. Vét., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 294–302, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Ibrahim-naim, W. Atakpama, A. K. Bessan, and N. Liyabin, “Diversité floristique et biomasse fourragère des parcours potentiels de pastoralisme du socle éburnéen au Togo Floristic diversity and fodder biomass of potential grazing land of the Eburnean basement in Togo Résumé,” Écosystèmes et Paysages (Togo), vol. 01, no. 1, pp. 12–29, 2021.
- Polo-Akpisso et al., “Habitat biophysical and spatial patterns assessment within Oti-Keran-Mandouri protected area network in Togo,” Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 214–229, 2018.
- Badjare, Y. A. Woegan, F. Folega, and W. Atakpama, “VULNÉRABILITÉ DES RESSOURCES LIGNEUSES EN LIEN AVEC LES DIFFÉRENTES FORMES D ’ USAGES AU TOGO : CAS DU PAYSAGE DES AIRES PROTÉGÉES DOUNGH-FOSSE AUX LIONS ( RÉGION DES SAVANES ) VULNERABILITY OF WOODY RESOURCES IN RELATION TO DIFFERENT FORMS OF USE IN TOGO,” Rev. Agrobiol., vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 2552–2565, 2021.
- H. Egbelou, W. Atakpama, M. Dourma, and K. Akpagana, “Dynamique spatio-temporelle et flore de la forêt d ’ Aboudjokopé au Togo,” Rev. Sci. Technol., Synth., vol. 27, no. December, pp. 37–50, 2021.
- F. Folega et al., “Potentialites ecologiques et socio-economiques de la foret communautaire d’agbedougbe (region des Plateaux-Togo),” J. la Rech. Sci. l’Université Lomé, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 31–50, 2017.
- Polo-Akpisso et al., “Plant Species Characteristics and Woody Plant Community Types within the Historical Range of Savannah Elephant, Loxodonta africana Blumenbach 1797 in Northern Togo (West Africa),” Annu. Res. Rev. Biol., vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 283–299, 2015. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, K. M. W. Agbetanu, L. L. Atara, S. Biaou, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “Biodiversité et gestion des feux de végétation dans la réserve de faune d ’ Abdoulaye au Togo Biodiversity and management of burn fire within Abdoulaye Wildlife Forest in Togo,” Rev. Sci. Technol., Synthèse, vol. 27, no. December, pp. 51–64, 2021.
- Thiombiano, R. Glèlè-Kakai, P. Bayen, J. I. Boussim, and A. Mahamane, “Méthodes et dispositifs d’inventaires forestiers en Afrique de l’Ouest : état des lieux et propositions pour une harmonisation,” Ann. des Sci. Agron., vol. 19, no. April, pp. 15–31, 2015.
- F. Folega and R. Ekoungoulou, “paysage du socle éburnéen au Togo Diversité structurale des ligneux en lien avec l ’ utilisa- tion des terres en paysage du socle éburnéen au Togo,” Ann. Rech. For. Alge rie, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 7–25, 2022.
- K. B. Kokou, W. Atakpama, B. Kombate, H. Egbelou, and N. A. Koffi, “Dynamique et modélisation du stock de carbone de la Forêt Classée d’Amou-Mono au Togo,” Rev. Ecosystèmes Paysages, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 1–16, 2023.
- L. Assi-Ake, “Reviews and Announcements,” Taxon, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 739–753, 1985.
- F. White, La vegetation de l’Afrique. Paris: ORSTOM-UNESCO, 1986.
- P. W. West, Tree and Forest Measurement, no. May. 2004.
- B. Kombate et al., “Dynamique de l’occupation de sol et modélisation du carbone de la Forêt Communautaire d’Alibi 1,” Ann. la Rech. For. en Algérie, vol. 12, no. 2, p. Sous presse, 2023.
- W. Atakpama, E. Asseki, E. Kpemissi Amana, C. Koudegnan, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “mportance socio-économique de la forêt communautaire d’Edouwossi-copé dans la préfecture d’Amou au Togo.,” Rev. Marocaine des Sci. Agron. Vétérinaires, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 55–63, 2018.
- Polo-Akpisso, K. Wala, O. Soulemane, F. Folega, K. Akpagana, and Y. Tano, “Assessment of Habitat Change Processes within the Oti-Keran-Mandouri Network of Protected Areas in Togo (West Africa) from 1987 to 2013 Using Decision Tree Analysis,” Sci, vol. 2, no. 1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama et al., “Vulnérabilité de la flore de la Forêt Classée de Missahohoé au feu de végétation,” Ann. Rech. For. Alger., vol. 13, no. 01, pp. 37–53, 2023.
- K. Dimobe et al., “Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Land Use and Habitat Fragmentation within a Protected Area Dedicated to Tourism in a Sudanian Savanna of West Africa,” J. Landsc. Ecol. Republic), vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 75–95, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Biaou et al., “Dynamique spatio-temporelle de l ’ occupation du sol de la forêt classée de Ouénou-Bénou au Nord Bénin To cite this version : HAL Id : hal-02189367 Dynamique spatio-temporelle d e l ’ occupation du sol de la forêt classée de Ouénou-Bénou au Nord Bénin,” in Hal-02189367, 2019, no. 2, pp. 1–20.
- W. Atakpama, K. Akpagana, and H. Pereki, “Cartographie , diversité et structure démographique de la forêt communautaire d ’ Amavénou dans la préfecture d ’ Agou au Togo Université Ouaga I Pr Joseph KI-ZERBO Revue de Géographie de l ’ Université de Ouagadougou,” Rev. Géographie l’Université Ouagadougou, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 59–82, 2017.
- F. Folega et al., “Land use patterns and tree species diversity in the Volta Geological Unit, Togo,” J. Mt. Sci., vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 1869–1882, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Atakpama, K. B. Amegnaglo, B. Afelu, F. Folega, K. Batawila, and K. Akpagana, “Biodiversité et biomasse pyrophyte au Togo,” VertigO, vol. 19, no. 3, p. 21, 2019.
- B. R. Tsoumou, K. J. Lumandé, J. P. Kampé, and J. D. Nzila, “Estimation de la quantité de carbone séquestré par la Forêt Modèle de Dimonika (Sud-ouest de la République du Congo),” Rev. Sci. Tech. Forêt &Environnement du Bassin du Congo, vol. 6, no. Avril, pp. 39–45, 2016.

| Scientific name | DENR | DOM | FR | IVI |
| Detarium microcarpum Guill. & Perr. | 37.50 | 6.56 | 84.62 | 128.68 |
| Vitellaria paradoxa C.F.Gaertner subsp. paradoxa | 12.50 | 4.80 | 69.23 | 86.54 |
| Combretum collinum Fresen. | 9.38 | 1.73 | 53.85 | 64.95 |
| Parkia biglobosa (Jacq.) R.Br. ex Benth. | 7.81 | 20.74 | 30.77 | 59.32 |
| Lannea acida A.Rich. s.l. | 7.03 | 3.92 | 46.15 | 57.11 |
| Entada abyssinica Steud. ex A.Rich. | 4.69 | 33.46 | 15.38 | 53.53 |
| Sterculia setigera Delile | 4.69 | 5.84 | 30.77 | 41.30 |
| Terminalia laxifolia Engl. | 5.47 | 1.17 | 30.77 | 37.41 |
| Acacia dudgeonii Craib ex Holland | 4.69 | 1.66 | 23.08 | 29.42 |
| Bombax costatum Pellegr. & Vuillet | 1.56 | 5.41 | 15.38 | 22.35 |
| Tamarindus indica L. | 1.56 | 8.67 | 7.69 | 17.92 |
| Prosopis africana (GuilI. & Perr.) Taub. | 0.78 | 2.92 | 7.69 | 11.39 |
| Ficus ingens (Miq.) Miq. | 0.78 | 2.76 | 7.69 | 11.23 |
| Parinari curatellifolia Planch. ex Benth. | 0.78 | 0.24 | 7.69 | 8.71 |
| Lannea microcarpa Engl. & K. Krause | 0.78 | 0.12 | 7.69 | 8.59 |
| Families | DENR | DOM | DIV | FIV |
| Fabaceae | 57.03 | 74.01 | 37.5 | 168.54 |
| Combretaceae | 14.84 | 2.91 | 18.75 | 36.50 |
| Anacardiaceae | 6.25 | 11.25 | 12.5 | 30.00 |
| Malvaceae | 7.81 | 4.04 | 12.5 | 24.35 |
| Chrysobalanaceae | 12.50 | 4.80 | 6.25 | 23.55 |
| Moraceae | 0.78 | 2.76 | 6.25 | 9.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




